#Agricultural Fumigants
Text
Agriculture Fumigants Market Size, Share and Growth Analysis
0 notes
Text
EFT Drone Official Store September Golden Autumn Sale
Offer 1: All original drone frame spare parts are 20% off.
Offer 2: Enjoy 20% off on all drone frames, buy 10 sets of drone frames and get one free.
Optional drone frame models: four-axis, six-axis, 0-30kg multiple loads and multiple models are available.
EP series: EFT E410P, EFT E416P, EFT E420P, EFT E610P, EFT E616P, EFT E620P
G series: EFT G06, EFT G20, EFT G20Q, EFT G410, EFT G610, EFT G616, EFT G420, EFT G620, EFT G630
X series: EFT X6100, EFT X6120
Offer 3: Enjoy 20% off on spreaders and spreader sets, buy 10 sets and get one free.
Optional spreader models: EPS200pro, EPS220, EPS240, EPS250, EPS270
EFT official manufacturer, the biggest discount of the year, all products are guaranteed to be authentic and original, and they are in stock and shipped quickly~ Come and buy now:https://www.store.effort-tech.com

#drone news#drone offer#eft drone official store#drone factory#agriculture drone#Pest Control Tools#spraying drone#Fumigation drone#Pesticide spraying drone#agricultural drone eft#farming drone#drones agricola puvirisador#대형 농업용드론#EFT Drone Discounts#drone spare parts
0 notes
Text
"Protect Your Crops: Latest Trends in Fumigation and Pest Control"
Protect your crops and ensure food safety with cutting-edge fumigation products. Discover the latest trends and innovations in pest control.
For More Details Click Here

0 notes
Text

The global agricultural fumigants market was valued at US$ 2.4 billion in 2023. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 3.6% between 2024 and 2032, reaching an estimated US$ 3.3 billion by 2032.
0 notes
Text

#Agricultural Fumigants Market#Agricultural Fumigants Market Size#Agricultural Fumigants Market Share#Agricultural Fumigants Market Trends
0 notes
Text
Agricultural Fumigants Market Expected to Witness Growth from Innovation in Fumigant Products and Farmland Expansion

Innovation in fumigant products and expansion of farmlands into pest-prone areas is expected to drive the Global Agricultural Fumigants Market growth in the forecast period, 2024-2028.
According to TechSci Research report, “Agricultural Fumigants Market – Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Competition Forecast & Opportunities, 2028”, the Global Agricultural Fumigants Market stood at USD 2.45 Billion in 2022 and is anticipated to grow with a CAGR of 4.81% in the forecast period, 2024-2028. The Global Agricultural Fumigants Market is driven by growing demand for higher agricultural yield due to the increasing population globally. Additionally, the rising instances of pest attacks on crops necessitate the use of fumigants, further driving the market. Government initiatives to promote agricultural practices and advancements in technology in the field of pest control also contribute to the market growth. However, stringent regulations regarding fumigant usage and growing environmental concerns may restrict the growth of the market.
The global agricultural fumigants market is experiencing substantial growth driven by increasing agricultural production and rising food security concerns. Fumigants, which are chemical substances used for pest control, soil disinfection, and post-harvest applications, play a crucial role in combating a wide range of pests such as insects, nematodes, and pathogens. By effectively eliminating these pests, fumigants contribute to preserving crop yields and ensuring food safety.
In addition to their pest control properties, fumigants are also gaining recognition for their ability to enhance the shelf-life of stored agricultural products. This is particularly important in reducing post-harvest losses and improving the overall quality of produce. As consumer demand for fresh and high-quality food continues to rise, the use of fumigants becomes increasingly essential in maintaining product integrity and extending the shelf-life of perishable goods.
Furthermore, the agricultural industry is witnessing advancements in eco-friendly fumigants and integrated pest management practices. These innovations aim to minimize the environmental impact of fumigants while maximizing their efficacy in pest control. By adopting sustainable and integrated approaches, farmers and agricultural practitioners can effectively manage pests while minimizing harm to the environment and promoting long-term agricultural sustainability.
Browse over XX market data Figures spread through XX Pages and an in-depth TOC on "Global Agricultural Fumigants Market.”
https://www.techsciresearch.com/report/global-agricultural-fumigants-market/1616.html
Overall, the future of the global agricultural fumigants market looks promising, driven by the increasing adoption of eco-friendly solutions and the growing emphasis on integrated pest management practices. As the world continues to face challenges in food security and sustainable agriculture, the role of fumigants in ensuring crop protection and post-harvest preservation will remain crucial for the agricultural industry's growth and development. As technology advancements continue, new and innovative fumigant formulations are expected to emerge, further enhancing the effectiveness and environmental sustainability of pest control practices in agriculture. With continuous research and development, the field of fumigants is poised to evolve and contribute significantly to the global agricultural landscape.
The Global Agricultural Fumigants Market is segmented into product type, crop type, form, function, application, pest control method, regional distribution, and company.
Based on form, in the global agricultural fumigants market, the liquid form of fumigants dominates the industry. This dominance can be attributed to various factors that make liquid fumigants highly preferred by farmers and agricultural businesses. One key advantage of liquid fumigants is their convenience of application. Farmers find it easier to apply liquid fumigants, which saves time and effort during the pest control process. Moreover, liquid fumigants offer effective pest control, ensuring the comprehensive extermination of pests and diseases. Their ability to infiltrate the soil more thoroughly enables them to reach pest hiding places, thereby safeguarding crop health and maximizing yield.
In addition to their convenience and effectiveness, liquid fumigants are known for their ease of handling and storage. Farmers appreciate the simplicity of the application process, as it minimizes the risk of mishandling or accidents. The ease of storage also contributes to the popularity of liquid fumigants, as farmers can manage their inventory more efficiently. Overall, liquid fumigants have a proven track record in pest management and play a crucial role in ensuring the productivity and sustainability of agricultural practices worldwide. Their dominance in the market is a testament to their effectiveness and the trust placed in them by farmers. Based on region, North America stands at the forefront of the Global Agricultural Fumigants Market for several compelling reasons.
This region boasts highly advanced farming practices, leveraging cutting-edge technologies and innovative techniques to optimize crop production. With a well-established agricultural industry, North America benefits from a robust infrastructure, extensive research and development capabilities, and a skilled workforce dedicated to agricultural excellence. Moreover, the government in North America provides steadfast support for crop protection, offering comprehensive policies and initiatives that safeguard agricultural yields. This unwavering commitment to crop protection ensures the resilience and sustainability of the agricultural sector in the face of pests and diseases, which are prevalent in the region.
Furthermore, the increasing global demand for high-quality agricultural products further reinforces the significance of agricultural fumigants in North America. By effectively mitigating the risks posed by pests and diseases, agricultural fumigants enable farmers to deliver premium-quality crops that meet the stringent requirements of discerning consumers worldwide. In recent years, North America has also witnessed a significant shift towards sustainable farming practices.
The adoption of modern, environmentally-friendly farming methods further enhances the region's dominance in the agricultural fumigants market. By prioritizing sustainability and embracing eco-friendly alternatives, North American farmers uphold their commitment to responsible agriculture while continuing to meet the growing demand for food and agricultural products.
Major companies operating in Global Agricultural Fumigants Market are:
BASF SE
ADAMA Ltd.
Dow Inc.
FMC Corporation
UPL Limited
Degesch GmbH
Nufarm Ltd.
American Vanguard Corporation
Nippon Chemical Industrial Co., Ltd.
Arkema SA
Download Free Sample Report
https://www.techsciresearch.com/sample-report.aspx?cid=1616
Customers can also request for 10% free customization on this report.
“The future of the global agricultural fumigants market appears extremely promising, reflecting the ever-increasing need for high-quality agricultural produce and the growing concerns over post-harvest losses worldwide. As modern farming practices continue to gain traction and awareness about soilborne diseases rises, the demand for efficient fumigants is expected to witness a significant surge. Moreover, with ongoing advancements in fumigant technology and the implementation of stringent food safety regulations, the agricultural fumigants market is poised for even greater growth in the foreseeable future.
These factors, combined with the continuous efforts to enhance crop protection and minimize yield losses, are expected to solidify the market's position and drive its expansion to new heights.,” said Mr. Karan Chechi, Research Director with TechSci Research, a research-based management consulting firm.
“Agricultural Fumigants Market - Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, 2018-2028 Segmented By Product Type (Methyl Bromide, Phosphine, Chloropicrin, Metam Sodium, 1, 3- Dichloropropene and Others), By Crop Type (Cereals & Grains, Oilseeds & Pulses, Fruits & Vegetables and Others), By Form (Solid, Liquid and Gaseous), By Function (Nematicides, Insecticides, Fungicides, Herbicides), By Application (Soil and Warehouse), By Pest Control Method (Tarpaulin Fumigation, Non-Tarpaulin Fumigation by Injection, Structural Fumigation, Vacuum Chamber Fumigation and Others), By Region and Competition”, has evaluated the future growth potential of Global Agricultural Fumigants Market and provides statistics & information on market size, structure and future market growth. The report intends to provide cutting-edge market intelligence and help decision makers take sound investment decisions. Besides, the report also identifies and analyzes the emerging trends along with essential drivers, challenges, and opportunities in Global Agricultural Fumigants Market.
Browse Related Research
Aquafeed Market
https://www.techsciresearch.com/report/aquafeed-market/5004.html
Poultry Processing Equipment Market
https://www.techsciresearch.com/report/poultry-processing-equipment-market/2420.html
Alfalfa Market
https://www.techsciresearch.com/report/global-alfalfa-market/1299.html
Contact
Techsci Research LLC
420 Lexington Avenue, Suite 300,
New York, United States- 10170
Tel: +13322586602
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.techsciresearch.com
#Agricultural Fumigants Market#Agricultural Fumigants Market Size#Agricultural Fumigants Market Share#Agricultural Fumigants Market Trends#Agricultural Fumigants Market Growth
0 notes
Text
Types Of Soil And The Best Soil For Gardening.
https://www.instagram.com/theplanting_season
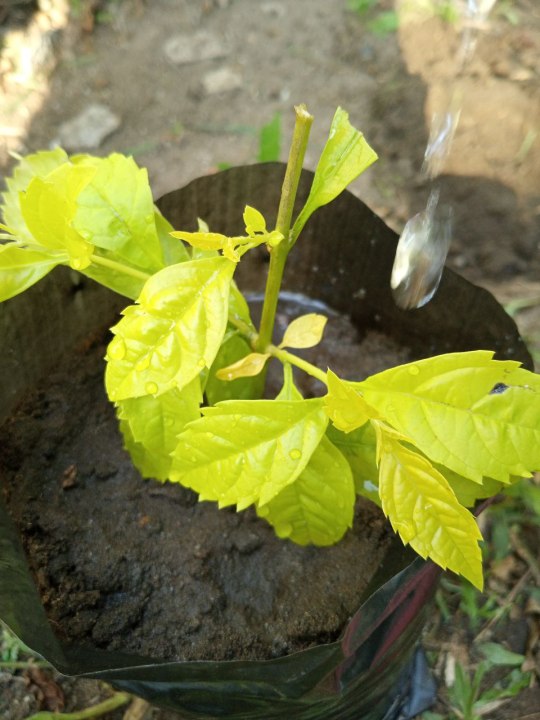



In general, the most desirable soil for gardening is one that is fertile, well-draining, and has good aeration. A soil that is rich in organic matter, such as compost or manure, is ideal for most plants. This type of soil will provide nutrients that plants need to grow strong and healthy, and it will also help to retain moisture. Soils that have excessive amounts of sand or clay can be poor for growing plants. Sandy soils are often too free-draining and lack nutrients, while clay soils may be too dense and retain too much water, leading to root rot and other problems.
On the other hand,Loamy soil is a type of soil that is considered ideal for gardening and plant growth. It is a mixture of sand, silt, clay, and organic matter, with roughly equal portions of each. Loamy soil is easy to work and provides good drainage, while also retaining moisture and nutrients. It is nutrient-rich, well-draining soil that offers the ideal balance of air and water for most plants. It can be found in many regions across the world and is often considered the best soil for gardening.
If you have good soil, you have solved 90% of the planting puzzle.
#trending#popular#gardening#plants#tumblrgirl#landscaping#photography#agriculture#farming#environment#horticulture#viralposts#viral on internet#nigeria#foodporn#agricultural fumigants market
0 notes
Link
Agricultural Fumigants Market Latest Trends, Demands, Overview and Analysis
0 notes
Text
Note that the studies that were released by companies affiliated with polluters happened in 2019, during the trump administration.
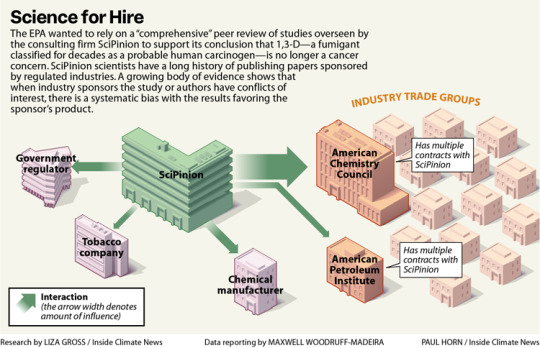
Excerpt from this story from Inside Climate News:
On a Southern California spring morning in 1973, a tanker truck driver jackknifed his rig and dumped the agricultural fumigant he was transporting onto a city street. A Los Angeles Fire Department emergency response team spent four hours cleaning up the chemical, 1,3-dichloropropene, or 1,3-D, a fumigant sold as Telone that farmers use to kill nematodes and other soil-dwelling organisms before planting.
Seven years after the spill, two emergency responders developed the same rare, aggressive blood cancer—histiocytic lymphoma—and died within two months of each other. In 1975, a farmer who’d accidentally exposed himself to 1,3-D repeatedly through a broken hose was diagnosed with another blood cancer, leukemia, and died the next year.
Within a decade of the men’s deaths, described as case studies in JAMA Internal Medicine, the National Toxicology Program, or NTP, reported “clear evidence” that 1,3-D causes cancer in both rats and mice. The finding led the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency to classify the chemical as “likely to be carcinogenic to humans” the same year, 1985. So it wasn’t a surprise when researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles reported in 2003 that Californians who’d lived at least two decades in areas with the highest applications of 1,3-D faced a heightened risk of dying from pancreatic cancer.
Yet EPA’s Office of Pesticide Programs’ Cancer Assessment Review Committee, or CARC, concluded in 2019 that 1,3-D—originally embraced by tobacco companies for its unparalleled ability to kill anything in soil that might harm their plants—isn’t likely to cause cancer after all.
In doing so, EPA, whose mission is to protect human health and the environment, rejected the human evidence, calling the UCLA study “low quality.” It also dismissed the authoritative NTP study and studies in lab animals that documented 1,3-D’s ability to damage DNA, a quintessential hallmark of cancer.
Instead, EPA’s CARC relied on studies provided by Dow AgroSciences (now called Corteva), the primary manufacturer of 1,3-D, and proposed a review of evidence linking the fumigant to cancer by SciPinion, a consulting firm hired by Dow, as an external peer review of its work. The decision to entrust external review to a Dow contractor has drawn repeated criticism, including from the agency’s watchdog, the Office of Inspector General, or OIG.
“During EPA’s search of the open literature, a comprehensive third-party peer review of the cancer weight-of-evidence assessment that considered toxicokinetics, genotoxicity and carcinogenicity data for 1,3-D was conducted and published in 2020 by SciPinion,” said agency spokesperson Timothy Carroll. EPA argued that the SciPinion review satisfied the criteria for an external review, Carroll said, and that another panel would have arrived at the same conclusion, given the specialized expertise required.
The OIG had recommended EPA conduct an external peer review of its 1,3-D cancer risk assessment in a 2022 report that outlined several problems with the agency’s process. An external review, the OIG said, requires “independence from the regulated business,” again noting the deficiency in a new report released in early August.
The scientists who run SciPinion have long consulted for manufacturers of harmful products, often publishing studies that deploy computer models to question the need for more protective health standards.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
EFT G630 agriculture drone frame
EFT Brand Exclusive G630/Multi-purpose Agricultural Drone Frame 30L Large Payload Sprayer for Pesticide Spraying 40kg Spreader Set for Seed and Fertilizer Spreading!
Technology helps farmers, efficient operations!
#eftdrone#spraying drone#effort tech#drone factory#agriculture drone#drone news#drone parts#eft g620#eft drone frame#Fumigation drone#drone farm sprayer#drone pulverizador agricola
0 notes
Text
As social and architectural constructs (re)produced through daily practices, environmental landscapes are a medium through which relations of power are solidified. Here environmental law enforcement and warfare—practices that compel the conditions of the terrain or agriculture to collude with the conditions of security and surveillance—are mobilized by colonial and imperial states to reconfigure biopolitical landscapes according to violent political logics and projects of exclusion. For example, from 2009 to 2011, US military operations in the Arghandab River Valley in Afghanistan razed and flattened "mudbrick walls, homes, and dense foliage" to establish lines of sight against insurgent cover so as to support durable lines of force. As part of their counterinsurgency practices, the military trained Arghandab farmers in "pruning practices for the overgrown pomegranate trees that hindered military patrol mobility," and pushed forward the planting of alternative crops with 'straight' and 'rational' layouts to enable more effective military patrolling in the area. Similar environmental practices are used by sovereign powers to organize and regulate the movement of criminalized bodies and racialized communities as part of their internal border-control measures. For instance, in the case of the migrant camp known as the Calais 'Jungle,' forced socio-spatial transformations of the landscape weaponized the terrain on which the camp sat. With changes to the discourse on migration, from a "moralistic humanitarian imperative to help refugees," to the portrayal of "migration as a threat against an imagined ethno-nationalist base," the camp was demolished by the French government with the argument that its terrain be 're-naturalized' and re-integrated with the surrounding natural environment. Here, the landscape itself was mobilized and militarized by the state as an instrument of power to legitimize displacement and reproduce racial hierarchies.
Complementing practices of environmental law enforcement and warfare, the use of herbicides in aerial fumigation first entered the repertoire of counterinsurgency tactics of imperial powers after World War II. The deployment of Agent Orange over Vietnam by the US Air Force is possibly the most known example where, from 1961 to 1971, the US military dropped around 19 million gallons of defoliants over large areas of South Vietnam. Aimed at operationalizing a sovereign cartographic gaze, the use of Agent Orange as an experimental form of chemical and biological warfare stripped foliage to improve visibility and to deprive communities of food supplies. Responding to these forced biopolitical modifications of the landscape, broad-based resistance movements in rural areas interrupted the colonial and imperial gaze by compelling these powers to recognize the inextricable role of the environment in modern warfare.
In 1971, the agrochemical corporation Monsanto invented glyphosate, a broad-spectrum herbicide meant to dissipate in the soil. Used in places like Colombia in the context of a decades-long War on Drugs, glyphosate was aerially sprayed with the declared aim to eradicate plants that fueled the drug trade. Indeed, as recently as April 2019, herbicide spraying was approved as a practice of border control by the Texas Senate, to battle 'illegal' immigration from Mexico. Seeking to align the lines of sight with the lines of force, herbicide spraying campaigns by colonial and imperial powers aimed at modifying environmental and political landscapes therefore surfaces as a tool for modern law enforcement and warfare.
Since 2014, the settler-colonial modification of Gaza's environment through the clearing and bulldozing of agricultural and residential land along its eastern perimeter has been complemented by the unannounced aerial spraying of crop-killing herbicides. This practice targets not only the health and livelihoods of Palestinian farmers along the border, but also the landscape itself, leaving its traces deep within the soil of Gaza as the infrastructure of life.
The IOF first began spraying herbicides by air to raze Palestinian fields in Gaza along its imposed buffer zone from 11–13 October 2014. This practice has since been continuously applied in key harvest periods resulting in the destruction of entire swaths of formerly arable land and the loss of livelihoods for Gazan farmers. The spring and winter of 2019 were the first two seasons during which the military has not conducted aerial spraying in the past four years. However, the Israeli Ministry of Defence (MOD) has yet to officially declare ceasing this devastating practice altogether. As part of the continuum of Israeli settler-colonial practices, aimed at the territorial, demographic, and political control of Israeli-Jews over indigenous Arab-Palestinians, herbicide spraying serves as an additional modification tool of the lived and natural environment in Gaza.
Shourideh C. Molavi, Environmental Warfare in Gaza: Colonial Violence and New Landscapes of Resistance
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
In pesticide-heavy Brazil, could crop dusting be killed off?

The use of crop dusting in Brazil—the world's biggest consumer of pesticides—has helped fuel the giant agricultural industry that props up Latin America's largest economy. But as public health concerns mount, the future of the practice is increasingly in doubt.
As fields of produce and local communities expand until they nearly collide, residents are exposed to the harsh chemicals sprayed down onto the plants from the air.
"When the planes fly around our houses, we feel the effects on our health: eye irritation, skin allergies, cough," said Diogenes Rabello, the leader of a Sao Paulo chapter of the Rural Workers Without Land Movement, an agricultural reform organization.
Critics of the method—officially known as aerial fumigation—won a victory in May, when the Brazilian Supreme Court ruled in favor of a 2019 ban in the northeastern state of Ceara. Other states are considering following suit.
But the decision sent shockwaves through the giant agribusiness sector in Brazil, which consumed nearly 720,000 metric tons of pesticides in 2021, or 20 percent of the global total, according to the United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization.
Continue reading.
#brazil#politics#brazilian politics#environmentalism#farming#mod nise da silveira#image description in alt
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
AIM Control I AIM Group is third party inspection company and 3rd marine surveying in providing the services of fumigation services
See more:
Best Regards
Dr Capt. Nguyen Te Nhan / G.D
Agriculture Industry Marine Control Inspection Group of Companies®
E-mail: [email protected]
MSN : [email protected]
#Tally #Survey #Inspection #Certification #Investigation #Expertise #Witness
#Diving #Underwater #Warranty #Approval #Asia #American #Africa #EU #Middleeast #Global .
#Surveyors #Inspectors #Consultant #Tallymen #Divers #Experts #investigator #controller #auditor #testing #laboratory #certificate #certification
#aimcontrol #aimgroup #thirdpartyinspection #marinesurvey #cargoinspection #qualitycontrol
1 note
·
View note
Text
Effective Pest Control Solutions for Every Home
The term "滅蟲" (mièchóng), which translates to "pest control" in English, refers to the process of eliminating or controlling the population of pests that may be harmful to human health, property, and the environment. Pest control is a crucial aspect of maintaining hygiene, protecting agricultural productivity, and ensuring a safe living environment. In this article, we will explore various pest control methods, the importance of controlling pests, and modern approaches to managing pest problems.
The Importance of Pest Control (滅蟲的重要性)
Pests such as insects, rodents, and other vermin can cause significant damage to homes, businesses, and agricultural fields. The following are some key reasons why pest control is essential:
Health Risks: Many pests carry diseases that can affect humans and animals. For instance, mosquitoes can transmit malaria and dengue, while rodents can spread diseases like hantavirus and leptospirosis.
Property Damage: Pests such as termites can cause severe damage to wooden structures, leading to expensive repairs. Rodents can chew through wires, insulation, and even cause electrical fires.
Agricultural Impact: Crop pests can destroy vast amounts of agricultural produce, leading to economic losses and food scarcity. Insects like aphids, caterpillars, and beetles can reduce crop yields and affect food quality.
Contaminated Food: Household pests such as cockroaches, ants, and rats can contaminate food supplies, posing serious health risks when ingested by humans.
Types of Pests Commonly Targeted in Pest Control (常見的滅蟲對象)
Different regions and environments attract specific types of pests. Here are some of the most common pests that are controlled using various techniques:
Insects: Cockroaches, mosquitoes, termites, ants, flies, bed bugs
Rodents: Rats, mice
Birds: Pigeons (in urban areas)
Other Vermin: Snakes, lizards, spiders
Traditional Pest Control Methods (傳統的滅蟲方法)
Historically, pest control has involved a variety of manual and chemical techniques aimed at eradicating or reducing the population of unwanted creatures. Some traditional methods include:
Chemical Pesticides: These are substances used to kill pests. They are available in different forms such as sprays, baits, and fumigants. While effective, overuse can lead to environmental harm and the development of pesticide resistance.
Trapping: Traps are commonly used for rodents, insects, and other pests. These may include glue traps, mechanical traps, and bait stations.
Physical Barriers: Nets, screens, and fences can prevent pests from entering an area. These are especially useful in protecting crops and stored food.
Sanitation: Maintaining a clean environment reduces the likelihood of pest infestations. Removing food sources, sealing cracks, and eliminating stagnant water can keep pests at bay.
Modern Approaches to Pest Control (現代的滅蟲方法)
With growing environmental concerns and advancements in technology, modern pest control methods are evolving. Some contemporary approaches include:
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): This is an eco-friendly approach that combines different pest control methods, such as biological control, habitat manipulation, and chemical management, to minimize harm to the environment while effectively controlling pest populations.
Biological Control: This method involves using natural predators or parasites to control pest populations. For example, ladybugs are introduced to control aphid populations in agriculture.
Ultrasonic Devices: These devices emit high-frequency sound waves that are uncomfortable for pests like rodents and insects, driving them away without harming the environment.
Genetic Modification: Some modern agricultural practices involve genetically modifying crops to make them resistant to pests or diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
Smart Traps: Advances in technology have led to the development of smart traps equipped with sensors and cameras. These traps can monitor pest activity and alert property owners to infestations in real time.
Challenges in Pest Control (滅蟲面臨的挑戰)
Despite the availability of advanced pest control methods, several challenges persist:
Pesticide Resistance: Over time, pests can develop resistance to chemical pesticides, rendering traditional methods ineffective. This has led to increased research into alternative pest control techniques.
Environmental Concerns: The use of pesticides can negatively impact non-target species and contribute to environmental pollution. There is a growing need for sustainable and eco-friendly solutions.
Cost: Some modern pest control methods, such as biological control and smart traps, can be more expensive than traditional approaches, making them less accessible for small-scale farmers or low-income households.
Public Awareness: Lack of awareness about the importance of pest control and proper methods can exacerbate pest problems, especially in urban areas.
Conclusion
Effective pest control (滅蟲) is essential for protecting public health, preserving property, and ensuring the sustainability of agriculture. With the right combination of traditional and modern techniques, we can minimize the negative impact of pests while maintaining environmental balance. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more efficient, eco-friendly, and affordable solutions for pest control in the future.
0 notes
