#AutoHotkey autoit
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
DarkGate Malware Replaces AutoIt with AutoHotkey in Latest Cyber Attacks
http://i.securitythinkingcap.com/T7pFw6
0 notes
Text
AutoHotkey vs AutoIt: why AutoHotkey is the better choice for automating Windows programs
AutoHotkey vs AutoIt: why AutoHotkey is the better choice for automating Windows programs
AutoHotkey vs AutoIt: why AutoHotkey is the better choice for automating Windows programs Are you tired of struggling to automate repetitive tasks on your Windows computer? Look no further than AutoHotkey! In this article, we’ll explain why AutoHotkey is the superior choice over AutoIt for automating Windows programs. One of the biggest advantages of AutoHotkey is its simplicity and ease of use.…

View On WordPress
#AutoHotkey autoit#AutoHotkey vs autoit#how is AutoHotkey better than AutoHotkey#why AutoHotkey over autoit
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Install Virtualbox Without Admin Privileges On Pc

Let’s consider an easier way to force any program to run without administrator privileges (without entering the admin password) and with UAC enabled (Level 4, 3 or 2 of the UAC slider). Let’s take the Registry Editor as an example — regedit.exe (it is located in the C: Windows folder). Notice the UAC shield next to the app icon.
Installing VirtualBox Without Administrator Rights. Google Chrome installs without admin privileges, but it's only available for the user. STEP 2 Press “F8” three times at the first screen after the computer begins rebooting. Then select “Safe Mode” from the “Boot Options” menu that appears. STEP 3 Select the.
Set COMPATLAYER=RunAsInvokerstart SteamSetup.
Install Virtualbox Without Admin Privileges On Pc Xprog 5.3 Download Zig Powermaster Manual Adobe Top Spin 4 Pc Emulator Psp Easyworship K-lite Codec Pack Pro Tools Edirol Ua 25 Cubase Primus Acca Software Crack Works Test Drive Unlimited 2 Highly Compressed Download Game Java Resident Evil 4 Tampilan Ps2 240x320.
Portable software as a general rule is written in poor languages. AutoHotkey, AutoIt and NSIS are the three main languages in use, because they allow people to moderately easily produce not enormous binaries and have a surprisingly low initial learning curve (though later on you hit plenty of walls with them; none of them is suited as a general purpose programming language).
Install Virtualbox Without Admin Privileges On Pci
I speak this as the developer of the PortableApps.com Launcher, which I did in NSIS as the launchers already in use were NSIS, and as size matters a lot (that killed things like Python outright, though using the RPython parts of PyPy with the garbage collector ripped out would have worked---I checked it out and was able to successfully compile <100KB executables; D was disqualified for some reason I do not recall, Go for its heavy runtime even after ripping out the Unicode tables, &c.), and as I was not at all comfortable in C or C++ at the time.

I rather suspect that a large part of the reason for the apparently poor language choice is that the people that develop and use such things are strongly predominantly young people who are having to rove from computer to computer; as they get older, they tend to end up with a machine of their own and so no longer need portable apps. I don't any more, for example (and I don't use Windows any more either). The developers of these things are in consequence similarly young and have not yet learned good sense in programming (I include myself in that category, though I reckon the PortableApps.com Launcher to contain best-of-class engineer in the portable software space---five years later, at age 22, I am surprisingly unashamed of it, though now I would write it in Rust; I should try that one of these years).
Install Virtualbox Without Admin Privileges On Pc Windows 10
I don't have administrator account on my mac. Ask Question Asked 5 years. I can't install the new OS without resolving this. Danganronpa v1 game. There are several ways to regain/recreate administrator privileges on a Mac. The administrator account exists, but the password is forgotten. Jun 11, 2010 Actually, VirtualBox requires admin privileges because it loads a driver. I don't think there's any way around it. All I can suggest is QEMU. It's portable and can run with standard privileges. How to install logitech ffb for mac.

1 note
·
View note
Text
plugin-prismjs (A README Experience)
A plugin for Micro.blog that injects Prism Javascript and CSS stylesheets to enable syntax highlighting for a sh$t ton of grammars within inline <code> tags and <pre><code> combination code blocks. Its code lives here.
Prism looks for <code class="language-xxx"> tags for inline syntax highlighting and for <pre><code class="language-xxx"> tags for syntax highlighting blocks of code.
For example, the opening tags for the following would be <pre><code class="language-ebnf">:

The configuration for the Javascript that lives at static/assets/js/prism.js is captured by its monster opening comment block:
/* PrismJS 1.25.0 https://prismjs.com/download.html#themes=prism&languages=markup+css+clike+javascript+abap+abnf+actionscript+ada+agda+al+antlr4+apacheconf+apex+apl+applescript+aql+arduino+arff+asciidoc+aspnet+asm6502+asmatmel+autohotkey+autoit+avisynth+avro-idl+bash+basic+batch+bbcode+bicep+birb+bison+bnf+brainfuck+brightscript+bro+bsl+c+csharp+cpp+cfscript+chaiscript+cil+clojure+cmake+cobol+coffeescript+concurnas+csp+coq+crystal+css-extras+csv+cypher+d+dart+dataweave+dax+dhall+diff+django+dns-zone-file+docker+dot+ebnf+editorconfig+eiffel+ejs+elixir+elm+etlua+erb+erlang+excel-formula+fsharp+factor+false+firestore-security-rules+flow+fortran+ftl+gml+gap+gcode+gdscript+gedcom+gherkin+git+glsl+gn+go+graphql+groovy+haml+handlebars+haskell+haxe+hcl+hlsl+hoon+http+hpkp+hsts+ichigojam+icon+icu-message-format+idris+ignore+inform7+ini+io+j+java+javadoc+javadoclike+javastacktrace+jexl+jolie+jq+jsdoc+js-extras+json+json5+jsonp+jsstacktrace+js-templates+julia+keepalived+keyman+kotlin+kumir+kusto+latex+latte+less+lilypond+liquid+lisp+livescript+llvm+log+lolcode+lua+magma+makefile+markdown+markup-templating+matlab+maxscript+mel+mermaid+mizar+mongodb+monkey+moonscript+n1ql+n4js+nand2tetris-hdl+naniscript+nasm+neon+nevod+nginx+nim+nix+nsis+objectivec+ocaml+opencl+openqasm+oz+parigp+parser+pascal+pascaligo+psl+pcaxis+peoplecode+perl+php+phpdoc+php-extras+plsql+powerquery+powershell+processing+prolog+promql+properties+protobuf+pug+puppet+pure+purebasic+purescript+python+qsharp+q+qml+qore+r+racket+cshtml+jsx+tsx+reason+regex+rego+renpy+rest+rip+roboconf+robotframework+ruby+rust+sas+sass+scss+scala+scheme+shell-session+smali+smalltalk+smarty+sml+solidity+solution-file+soy+sparql+splunk-spl+sqf+sql+squirrel+stan+iecst+stylus+swift+systemd+t4-templating+t4-cs+t4-vb+tap+tcl+tt2+textile+toml+tremor+turtle+twig+typescript+typoscript+unrealscript+uri+v+vala+vbnet+velocity+verilog+vhdl+vim+visual-basic+warpscript+wasm+web-idl+wiki+wolfram+wren+xeora+xml-doc+xojo+xquery+yaml+yang+zig&plugins=line-numbers+toolbar+copy-to-clipboard */
The functionality of the page was spotty, but the following link oughta load that monster configuration up there into the Prism Download Page .
I threw in the copy to clipboard plugin (which is dependent on the toolbar plugin) for that little copy button:
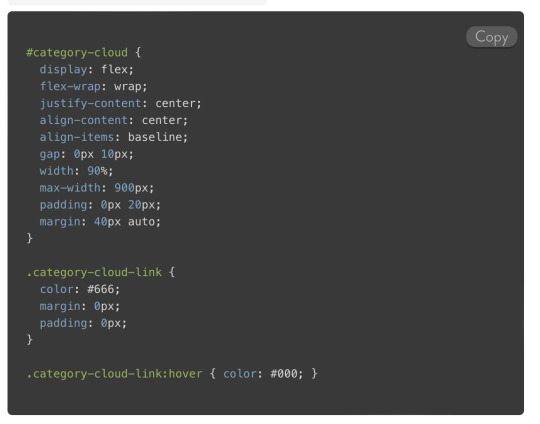
I also include the line numbers plugin. It looks for tags that include a line-numbers class.
For example, the opening tags for this code might be <pre><code class="language-json">:

Or, you could toss in the line-numbers class, kinda like <pre class="line-numbers"><code class="language-json">:

I have noticed that the line number appearance can be kinda spotty as far as alignment. The problem seems to lie somewhere in the CSS. The HTML DOM contains the correct number of generated <span> tags to represent the lines.
Let’s check out the plugin parameters, shall we?
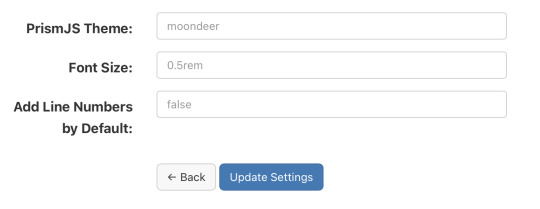
Alrighty, first up is the theme. I rolled my own darcula-esque them and named it moondeer. This what you see above and get by default. I included the stylesheets for all the themes that were available on the download page as well. All the stylesheets live at static/assets/css/prism-STYLE.css. So the out of the box theme lives at static/assets/css/prism-moondeer.css.
If you want to play around with the themes, these would be the supported parameter values: moondeer, default, dark, coy, funky, okaidia, solarized-light, twilight, tomorrow-night.
The stylesheet living at static/assets/css/prism.css addresses a line-number spacing issue I ran into.
So, the Font Size parameter gets inserted into the partial injected into the page <head>. Rather than maintain a bunch of stylesheets (and in order to parameterize it), I chose to set the size here and slap on !important.
I also chose to inject the Javascript here, figuring it would cut down on repainting highlighted text over the original input.
{{ $theme := site.Params.prismjs_theme | default "moondeer" }} <link rel="stylesheet" href="/assets/css/prism-{{ $theme }}.css"> <script src="/assets/js/prism.js"></script> {{ $font_size := site.Params.prismjs_font_size | default "0.5rem" }} <style>code[class*=language-],pre[class*=language-] { font-size: {{ $font_size }} !important; }</style>
Lastly, the Line Numbers parameter. This parameter only makes since for one reason … the cool f$&king shortcode I layed in there. It lives at layouts/shortcodes/language.html.
{{- $language := false -}} {{- if (and (and .IsNamedParams (.Get "language")) .Inner) -}} {{- $language = .Get "language" -}} {{- else if (and (.Get 0) .Inner) -}} {{- $language = .Get 0 -}} {{- end -}} {{ if $language }} {{- $code := .Inner | markdownify | chomp -}} {{- if hasPrefix $code "<pre><code>" -}} {{- $code = strings.TrimPrefix "<pre><code>" $code | strings.TrimSuffix "</code></pre>" -}} {{- $code = htmlUnescape $code -}} {{- $code = replaceRE "<" "<" $code -}} {{- $code = replaceRE "&" "&" $code -}} {{- $pre_class := "code-block" -}} {{- if (and .IsNamedParams (.Get "line-numbers")) -}} {{- $pre_class = printf "%s line-numbers" $pre_class -}} {{ else if (and (not .IsNamedParams) (and site.Params.prismjs_line_numbers (eq "true" site.Params.prismjs_line_numbers))) }} {{- $pre_class = printf "%s line-numbers" $pre_class -}} {{- end -}} <pre class="{{ $pre_class }}"><code class="language-{{ $language }}"> {{ printf "%s" $code | htmlUnescape | safeHTML }} </code></pre> {{ else if hasPrefix $code "<code>" }} {{ $code = strings.TrimPrefix "<code>" $code | strings.TrimSuffix "</code>" }} {{ $code = htmlUnescape $code }} {{ $code = replaceRE "<" "<" $code }} {{ $code = replaceRE "&" "&" $code }} <code class="language-{{ $language }}"> {{ printf "%s" $code | htmlUnescape | safeHTML }} </code> {{ end }} {{ end }}
The paired shortcode works with either a single, unnamed parameter specifying the language … kinda like…
{{< language json >}} { "currentlyreading": "*Books I am somewhat in the process of reading*", "finishedreading": "*Books I've managed to get myself to read*", "wanttoread": "*Books that gaze at me judingly from beneath the television, where they currently live, for having yet to crack their spine (f$&kers).*", "didwanttoread": "*Books whose gaze of judgement I've kinda become okay with as my interest in reading them has waned.*" } {{< /language >}}
or with named parameters … one mandatory and one optional. The mandatory named parameter is language and the optional parameter is line-numbers. This might look something like…
{{< language language="json " line-numbers="true" >}} { "currentlyreading": "*Books I am somewhat in the process of reading*", "finishedreading": "*Books I've managed to get myself to read*", "wanttoread": "*Books that gaze at me judingly from beneath the television, where they currently live, for having yet to crack their spine (f$&kers).*", "didwanttoread": "*Books whose gaze of judgement I've kinda become okay with as my interest in reading them has waned.*" } {{< /language >}}
The Line Numbers plugin parameter contols shortcode behaviour when left unspecified. This value defaults to false. If you set it to "true", than invoking the unnamed parameter shortcode would result in a code block decorated with line numbers. The value set (or not set) for Line Numbers also controls the inclusion of line numbers when the named parameter language is used without supplying a line-numbers parameter to the shortcode. Supplying the value "true" for line-numbers oughta enable line numbers for a block of code being sent through the shortcode. And with that, the over-explanation of the Line Numbers parameter is complete.
Like nearly all my shortcodes these days, I created it as bridge between Ulysses and my Micro.blog content. So, I can be all working up a sheet in Ulysses, and be all:

and then it comes out the other side all:

It’s worth noting that I believe I have found a mobile Safari bug that affects the font-size of the highlighted text on an iPhone when in portrait. Your mileage may vary; but, this was my experience.
0 notes
Text
AutoHotkey 1.1.32.0 2019 Download
AutoHotkey 1.1.32.0 2019 Download

AutoHotkey 1.1.32.0 Code File Download Cracked Working 100%
Other features include remap keys, change soundcard settings (like volume or mute), use a joystick or keyboard as a mouse; make any window transparent, always-on-top, or alter its shape; manipulate the clipboard, customize the tray menu’s icon and menu items, run existing AutoIt v2 scripts, and convert any script into an EXE file that…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Original Post from Security Affairs Author: Pierluigi Paganini
The French police force, National Gendarmerie, announced to have neutralized the Retadup malware on over 850,000 computers taking over its C2 server.
The French police force, National Gendarmerie, announced the successful takedown of a huge RETADUP botnet after it has taken the control of its command and control (C2) server. The operation allowed the France law enforcement agency to remotely disinfect more than 850,000 computers worldwide with the help of Avast malware researchers.
#BellesAffaires #Cybercriminalité La #gendarmerie démantèle l’un des plus gros réseaux d’ordinateurs piratés au monde ! En lien avec le #FBI, les #cybergendarmes parviennent à ��désinfecter” à distance plus de 850 000 ordinateurs. Une #PremièreMondiale !
— Gendarmerie nationale (@Gendarmerie) August 28, 2019
Most of the infected systems were located in Latin America, more than 85% of victims did not have any security software installed. The highest number of infection was in Peru, followed by Venezuela, Bolivia, Mexico and Ecuador.
The Retadup bot has been around since at least 2015, it was involved in several malicious campaigns aimed at delivering malware such as information stealers, ransomware and miners.
In recent campaigns, the Retadup worm was observed delivering Monero cryptocurrency miners in Latin America.
Earlier this year, malware researchers from Avast antivirus firm discovered a design flaw in the C&C protocol of the botnet that could have been exploited to remove the malware from infected computers.
The exploitation of the flaw required the control of the command and control server that was hosted with a hosting provider located in France.
Then Avast contacted the Cybercrime Fighting Center (C3N) of the French National Gendarmerie in March this year and requested its support to dismantle the botnet.
The French authorities took control over the RETADUP C2 server in July and replaced it with a C2 server designed to disinfect the machines by abusing the design flaw in its protocol. The server instructed the bot to remove itself from infected machines.
“In accordance with our recommendations, C3N dismantled a malicious command and control (C&C) server and replaced it with a disinfection server.” reads a blog post published by Avast. “The disinfection server responded to incoming bot requests with a specific response that caused connected pieces of the malware to self-destruct. At the time of publishing this article, the collaboration has neutralized over 850,000 unique infections of Retadup.”
The National Criminal Intelligence Service at Gendarmerie Nationale will keep the disinfection server online for a few more months to remove the malware from the largest number of computers. Experts noticed that some infected computers still haven’t contacted the disinfection server, some have been offline since July.
“We managed to clean more than 850,000 machines that were infected by the Retadup virus.This fleet of computers made it possible to make global attacks of very, very great magnitude.You can imagine our satisfaction to have succeeded to remove the viruses from the computers of the victims, who at first did not even know that their machines were infected.” explained Jean-Dominique Nollet, head of the National Criminal Intelligence Service at Gendarmerie Nationale.
“Basically, we managed to detect where was the command server, the control tower of the network of infected computers, the ‘botnet‘. It was copied, replicated with a server of ours, and made to do things that allow the virus to be idle on the victims’ computers.”
The French authorities also shared with the FBI its findings on the botnet, the experts, in fact, discovered that part of the C2 infrastructure was in the United States. The FBI quickly took down this C2 server on July 8.
“Some parts of the C&C infrastructure were also located in the US. The Gendarmerie alerted the FBI who took them down, and on July 8 the malware authors no longer had any control over the malware bots. Since it was the C&C server’s responsibility to give mining jobs to the bots, none of the bots received any new mining jobs to execute after this takedown.” continues Avast. “This meant that they could no longer drain the computing power of their victims and that the malware authors no longer received any monetary gain from mining.”
Experts explained that Retadup has been under active development for years now, for this reason, there are many different variants in the wild. These variants are quite similar and only differ in how the implementation of the functionality, while the core is written in either AutoIt or AutoHotkey.
The analysis of the C&C server allowed the experts to discover that it also contained a .NET controller for an AutoIt RAT called HoudRat. Researchers believe it is just a more and less prevalent variant of Retadup.
Technical details on the Retadup bot are included in the analysis published by Avast.
window._mNHandle = window._mNHandle || {}; window._mNHandle.queue = window._mNHandle.queue || []; medianet_versionId = "3121199";
try { window._mNHandle.queue.push(function () { window._mNDetails.loadTag("762221962", "300x250", "762221962"); }); } catch (error) {}
Pierluigi Paganini
(SecurityAffairs – Retadup botnet, hacking)
The post French Police remotely disinfected 850,000 PCs from RETADUP bot appeared first on Security Affairs.
#gallery-0-6 { margin: auto; } #gallery-0-6 .gallery-item { float: left; margin-top: 10px; text-align: center; width: 33%; } #gallery-0-6 img { border: 2px solid #cfcfcf; } #gallery-0-6 .gallery-caption { margin-left: 0; } /* see gallery_shortcode() in wp-includes/media.php */
Go to Source Author: Pierluigi Paganini French Police remotely disinfected 850,000 PCs from RETADUP bot Original Post from Security Affairs Author: Pierluigi Paganini The French police force, National Gendarmerie, announced to have neutralized the Retadup malware on over 850,000 computers taking over its C2 server.
0 notes
Text
Polymorphic Monero-Mining RETADUP Worm keeps threat detection on its toes
http://cryptobully.com/polymorphic-monero-mining-retadup-worm-keeps-threat-detection-on-its-toes/
Polymorphic Monero-Mining RETADUP Worm keeps threat detection on its toes
Polymorphic Monero-Mining RETADUP Worm gets an AutoHotKey Variant
A cryptocurrency mining worm written in the same open-source scripting language used for creating Windows hotkeys and using polymorphism is giving conventional threat detection techniques a run for their money.
Trend Micro researchers identified the malware via the endpoint of public sector organization as an AutoHotKey variant of the Monero-Mining RETADUP worm.
“AutoHotKey is relatively similar to the script automation utility AutoIt, from which RETADUP’s earlier variants were based on and used for both cybercrime and cyberespionage,” researchers said in the April 23 blog post.
Despite the malware operator’s history of deploying malware in targeted attacks, the observed sample only focused on cryptomining.
Reacher’s said the RETADUP’s AutoHotKey version and AutoIt variant both have similar endgames of mining Monero and both use the same techniques to propagate, evade detection, and install the malicious Monero miner.
The shift in programming languages was attributed to AutoHotKey being a novelty as a scripting language meaning that several security tools aren’t actively detecting and analyzing malware written in the language.
Researchers also noted the malware polymorphic behavior makes it more difficult to detect by IT teams without the time or resources to actively seek out similar or unique threats and thwart them down the line.
The stealth techniques used by the malware underscores the importance of having insight into an organization’s online perimeter from endpoints and networks to servers. The malware also highlights the need for organizations to have 24/7 monitoring and in-depth research and correlation on similar incidents to enable threat analysts to provide further insight on a case-to-case basis.
This will help catch attacks like RETADUP and help determine is threats are one-off, part of a coordinated, targeted attack, or part of an opportunistic cybercriminal campaign.
Monero
0 notes
Text
AutoHotkey 1.1.32.0 File 2019 Download
AutoHotkey 1.1.32.0 File 2019 Download

AutoHotkey Latest Activation Is Here Full Torrent Free
Other features include remap keys, change soundcard settings (like volume or mute), use a joystick or keyboard as a mouse; make any window transparent, always-on-top, or alter its shape; manipulate the clipboard, customize the tray menu’s icon and menu items, run existing AutoIt v2 scripts, and convert any script into an EXE file that can be…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Original Post from Trend Micro Author: Trend Micro
For a piece of malware to be able to do its intended malicious activity, it has to be able to sneak inside a machine’s system without being flagged by cybersecurity defenses. It camouflages and packages itself to look like a benign piece of code and, when it has cleared past security filters, unleashes its payload. When malware is difficult to discover — and has limited samples for analysis — we propose a machine learning model that uses adversarial autoencoder and semantic hashing to find what bad actors try to hide. We, along with researchers from the Federation University Australia, discussed this model in our study titled “Generative Malware Outbreak Detection.”
Seeing the Stealthy: Obfuscated Malware
Malware authors know that malware is only as good as its ability to remain undetected for it to compromise a device or network. Hence, they use different tools and techniques to keep attacks under the radar. And malware authors have been hard at work at making malware even harder to detect, using various techniques such as sandbox evasion, anti-disassembly, anti-debugging, antivirus evasion, and metamorphism or polymorphism. Take for example the RETADUP worm, which was previously used for targeted attacks and cyberespionage, which turned polymorphic. Its new variant is coded in AutoHotKey and, like one of its AutoIt variants, is geared towards cybercriminal cryptocurrency mining.
When malware is obfuscated, it is hard for traditional antivirus systems to detect. We discussed in a previous article how to address this issue: by identifying an important feature in malware samples that remains relatively unchanged no matter how morphed the samples become, i.e., the program instruction sequence. This follow-up blog will give a deeper insight into how adversarial autoencoder deals with the program instruction sequence, and what semantic hashing does in our proposed model.
A Deeper Learning: Adversarial Autoencoder and Semantic Hashing
Our machine learning model, which we call aae-sh, is composed of two independent modules. The first one uses adversarial autoencoder to acquire the latent representation for the program instruction sequence, a feature that is resistant to obfuscation techniques. The second deals with the class number for the latent representation, which is computed via HDBSCAN, a clustering algorithm, with a predefined threshold.
Adversarial autoencoder
For malware outbreaks with only a limited number of samples, adversarial autoencoder is effective as it enables the production of smooth approximated nearby distributions of even a small number of training samples. In fact, our proposed machine learning model uses a single malware sample for each malware class for training with adversarial autoencoder.
The core architecture for malware outbreak detection in the study is taken from the original adversarial autoencoder.
Figure 1. Adversarial autoencoder architecture used for malware outbreak detection
Note: The input, x, and the reconstructed input, p(x), have the instruction sequence feature.
What adversarial autoencoder does is it combines an arbitrary autoencoder with generative adversarial network (GAN). GAN is responsible for training the generator and the discriminator in a tight competitive loop. For an autoencoder to work in this model, it must have the following properties:
The stacked weights are symmetric and shared between encoder and decoder.
It must have all of GAN’s generator properties. An encoder functions dually, hence, it needs to have the training techniques used for the generator while maintaining its autoencoder property.
The ability to identify relocated functions is a preferred malware outbreak detection property. And a stacked convolutional autoencoder aims to take advantage of the translation invariant property of the architecture,[1] allowing the machine learning model to determine the program instruction sequence despite code transposition and integration metamorphism.[2]
Alireza Makhzani et al introduced the need for both the adversarial network and the autoencoder to be mutually trained with stochastic gradient descent in two phases — the reconstruction phase and the regularization phase — after which they are executed on each mini-batch of samples.
There are a number of hyperparameters that can be tuned in the network architecture, including how much of diverse malware clusters should be detected or the batch size. For training malware samples under this model, batch normalization within the GAN generator is necessary to help generate a consistent latent representation for each cluster. To make sure that this happens, the Adam optimizer, an auxiliary optimization algorithm for stochastic gradient descent, was used for both the reconstruction and regularization phases. Meanwhile, for consensus optimization — which mitigates the instability caused by standard adversarial autoencoder training — RMSProp was used. RMSProp is an optimization algorithm for deep neural networks. The hyperparameters of the model were then determined.
Once training is done, the encoder output is taken as a latent vector that represents the input sample. The input sample is then used for semantic hashing.
Semantic hashing
Semantic hashing transforms the latent representation acquired via adversarial autoencoder into a class number for prediction. To get the class number, the latent vector represented by real valued numbers are binarized using the bitwise mean value of the training samples. Then, the hamming distance — which is the number of positions at which parallel symbols between two strings of equal lengths are not the same — is used to calculate the distance for the two given latent vectors.[3] A test sample is assigned a class with the closest training sample.
Analysis: Flashback Variants
In our research, using the aae-sh model, we accurately identified malware variants whose major feature mass is identical across all samples in the cluster despite having been morphed or modified. Visual analysis of the families detected by aae-sh showed similar instruction sequences even with variations within the family. We discovered that certain malware families, like Flashback, reuse the same piece of code repetitively across their variants — which the aae-sh model is able to catch and identify effectively. The study detected a cluster which contains many Flashback variants (cluster 49). Note that aae-sh detected the samples of different lengths as long as the instruction sequences are similar.
Figure 2. Visualization of the instruction sequences of malware samples within cluster 49 identified by aae-sh
Note: The X-axis represents the feature while the Y-axis represents the sample number.
And because aae-sh identifies malware variants based on the instruction sequence pattern, we noted around 447 samples of the Flashback variant that were not named according to its malware family, as VirusTotal analysts tag detection names based on analyst-specific heuristics.
Figure 3. VirusTotal detection names for the samples in cluster 49 that are visualized in Figure 2
Our study also showed that, aside from accurately detecting malicious samples, the aae-sh model also records 91 percent accuracy over benign samples compared to the traditional classification models’ 100 percent false positives.
Our research paper “Generative Malware Outbreak Detection” gives a comprehensive discussion on the methods, results, and analysis of our proposed machine learning model for detecting malware outbreaks with limited samples.
[1] Jonathan Masci, Ueli Meier, Dan Cireşan, Jürgen Schmidhuber. “Stacked Convolutional Auto-encoders for Hierarchical Feature
Extraction.” In Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning–ICANN 2011, pages 52-59, September 2014.
[2] Ilsun You and Kangbin Yim. “Malware Obfuscation Techniques: A Brief Survey.” In 2010 International Conference on Broadband, Wireless Computing, Communication and Application, pages 297-300, 4 November 2010.
[3] Ruslan Salakhutdinov and Geoffrey Hinton. “Semantic Hashing.” In International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, pages 969-978, 7 July, 2009.
The post A Machine Learning Model to Detect Malware Variants appeared first on .
#gallery-0-5 { margin: auto; } #gallery-0-5 .gallery-item { float: left; margin-top: 10px; text-align: center; width: 33%; } #gallery-0-5 img { border: 2px solid #cfcfcf; } #gallery-0-5 .gallery-caption { margin-left: 0; } /* see gallery_shortcode() in wp-includes/media.php */
Go to Source Author: Trend Micro A Machine Learning Model to Detect Malware Variants Original Post from Trend Micro Author: Trend Micro For a piece of malware to be able to do its intended malicious activity, it has to be able to sneak inside a machine’s system without being flagged by cybersecurity defenses. 1,208 more words
0 notes