#Barcode Decoding Software Market
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The barcode decoding software market size was valued at $329.8 million in 2022, and is estimated to reach $612.1 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2023 to 2032.
Download Sample Report: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/request-sample/A304290
#Barcode Decoding Software Market#Barcode Decoding Software Industry#Barcode Decoding Software#Barcode Decoding Software Market Size#Barcode Decoding Software Market Growth
0 notes
Text
Barcode Definitions 101 | Uses & Guide | AIDC INDIA – 2025
Barcodes play a vital role in today’s business environment. From retail checkout systems to inventory tracking, they have transformed the way data is collected and managed. As we step into 2025, it becomes more important to understand barcode definitions and their role in modern operations. This guide from AIDC Technologies India is designed to simplify everything you need to know about barcodes and their practical uses.
2. What Is a Barcode? A Simple Definition Explained
A barcode is a machine-readable code represented as numbers and parallel lines or squares. Barcode definitions explain how this code is structured and what type of data it holds. Barcodes typically encode product information like SKU, batch number, or manufacturing details. They are scanned using barcode readers, which instantly convert visual patterns into digital data.
3. Types of Barcodes Used in 2025
There are various types of barcodes in use, each with its own format and function. Barcode definitions help identify which format suits a particular industry or task:
1D Barcodes: These are linear barcodes like UPC, EAN, and Code 128, often used in retail and inventory.
2D Barcodes: These include QR codes and Data Matrix codes, used for storing more complex data.
PDF417: A stacked linear barcode used on IDs and transport documents.
Each format has a specific barcode definition and is designed to meet unique requirements based on space, readability, and data needs.
4. How Barcodes Work: From Scanning to Data Collection
The basic process begins with printing a barcode on a label or product. A barcode scanner reads the lines or squares, and decoding software extracts the stored information. Barcode definitions help determine what type of scanner and software are needed to read the code accurately. This simple process eliminates manual entry and ensures fast, reliable data capture across operations.
5. Key Uses of Barcodes in Modern Industries
Barcode definitions are foundational in a wide range of sectors. In retail, barcodes are used for pricing and checkout. In warehouses, they track stock movement and inventory levels. Healthcare uses barcodes for labeling medicine and managing patient records. Logistics companies depend on barcodes for real-time tracking of shipments. The correct use of barcode definitions ensures that the data captured is accurate and usable.
6. AIDC India’s Role in Barcode Solutions
AIDC Technologies India provides complete barcode systems—from labels and scanners to printers and integration software. Our deep understanding of barcode definitions allows us to recommend the right type of barcode solution for your specific industry. We support clients in retail, manufacturing, healthcare, education, and logistics with customized systems that improve data tracking and minimize errors.
7. Benefits of Using Barcodes in Business
Barcodes offer several benefits that go beyond just automation. Proper use of barcode definitions brings improvements in many business areas:
Speed: Barcodes speed up scanning and reduce checkout time.
Accuracy: Minimizes manual errors in data entry.
Inventory Control: Keeps track of stock movement in real time.
Cost Savings: Reduces labor and improves efficiency.
By applying the right barcode definitions, businesses can unlock these advantages more effectively.
8. Barcode Definitions vs QR Codes vs RFID
Understanding how barcode definitions compare to other technologies helps in selecting the best system. Barcodes are simpler and more cost-effective for small to medium-sized operations. QR codes, which are 2D barcodes, can store more data and are often used in mobile marketing or payment systems. RFID, which uses radio waves, allows item tracking without line-of-sight scanning. However, barcode systems remain more accessible and easier to implement.
9. Smart Barcode Scanning Solutions by AIDC India
AIDC India offers barcode scanning devices that are optimized to read all standard barcode definitions. Whether it’s a handheld scanner for retail or an industrial-grade scanner for warehouses, our devices ensure fast, accurate, and error-free data collection. We also provide software tools that integrate these scanners with your inventory or billing systems for seamless workflows.
10. Choosing the Right Barcode System for Your Business
Barcode definitions help businesses choose the right format, printing method, and scanning tools. AIDC India helps you evaluate your operational needs, the volume of data you need to encode, and the environment where scanning takes place. Based on these factors, we recommend and implement barcode systems that align with your goals.
11. Future of Barcodes: Trends to Watch in 2025
As we look ahead, barcode definitions are evolving with technology. Mobile barcode scanning is becoming more popular, especially in e-commerce and delivery services. Smart inventory systems are using AI to analyze barcode data for forecasting and planning. Environment-friendly printing solutions are also emerging. AIDC India stays updated with these trends to provide future-ready barcode solutions for businesses of all sizes.
12. Get Started with Barcode Solutions from AIDC India
Barcodes are a small but powerful part of your business infrastructure. With the right barcode definitions and tools, you can automate operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. AIDC Technologies India offers everything you need—from barcode labels and printers to scanners and integration support.
Call to Action: Ready to streamline your operations with smart barcode solutions? Contact AIDC Technologies India today for a free consultation, customized recommendations, and reliable tools that match your business goals.
#BarcodeDefinitions2025#BarcodeGuide#BarcodeUses#AIDCIndiaBarcode#BarcodeTechnology#SmartTrackingSolutions#BarcodeBasics#InventoryManagement#BarcodeScanning#RetailTech2025
0 notes
Text
Global Fixed Industrial Scanning Software Industry Insights 2025
On 2025-3-17 Global Info Research released【Global Fixed Industrial Scanning Software Market 2025 by Manufacturers, Regions, Type and Application, Forecast to 2031】. This report includes an overview of the development of the Fixed Industrial Scanning Software industry chain, the market status of Consumer Electronics (Nickel-Zinc Ferrite Core, Mn-Zn Ferrite Core), Household Appliances (Nickel-Zinc Ferrite Core, Mn-Zn Ferrite Core), and key enterprises in developed and developing market, and analysed the cutting-edge technology, patent, hot applications and market trends of Fixed Industrial Scanning Software. According to our (Global Info Research) latest study, the global Fixed Industrial Scanning Software market size was valued at US$ 243 million in 2024 and is forecast to a readjusted size of USD 345 million by 2031 with a CAGR of 5.2% during review period. Fixed industrial scanning software is a specialized solution designed to optimize the operation of stationary industrial scanners used in applications like logistics, manufacturing, and retail. This software enables the seamless integration of scanners into workflows, allowing for real-time decoding of barcodes, QR codes, and other symbologies with high accuracy and speed. It often features advanced image processing, data analytics, and connectivity options, including IoT and cloud integration, to provide actionable insights and ensure efficient data flow. With customizable configurations, fixed industrial scanning software can adapt to various environments, such as conveyor systems or assembly lines, enhancing productivity, traceability, and operational efficiency. This report is a detailed and comprehensive analysis for global Fixed Industrial Scanning Software market. Both quantitative and qualitative analyses are presented by company, by region & country, by Type and by Application. As the market is constantly changing, this report explores the competition, supply and demand trends, as well as key factors that contribute to its changing demands across many markets. Company profiles and product examples of selected competitors, along with market share estimates of some of the selected leaders for the year 2025, are provided.
Market segment by Type: On-premise、Cloud-based Market segment by Application:Automotive、Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals、Electronics & Semiconductor、Postal & Logistics、Packaging & Bottling、Othes Major players covered: COGNEX、Adaptive Vision、Omron Microscan Systems、STEMMER IMAGING、Opto Engineering、RoboRealm、Euresys、National Instruments、Janta (Novanta)、Matrox Imaging、Zebra Aurora
Market segment by region, regional analysis covers: North America (United States, Canada and Mexico), Europe (Germany, France, United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, and Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, Korea, India, Southeast Asia, and Australia),South America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, and Rest of South America),Middle East & Africa (Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, South Africa, and Rest of Middle East & Africa). The content of the study subjects, includes a total of 15 chapters: Chapter 1, to describe Fixed Industrial Scanning Software product scope, market overview, market estimation caveats and base year. Chapter 2, to profile the top manufacturers of Fixed Industrial Scanning Software, with price, sales, revenue and global market share of Fixed Industrial Scanning Software from 2020 to 2025. Chapter 3, the Fixed Industrial Scanning Software competitive situation, sales quantity, revenue and global market share of top manufacturers are analyzed emphatically by landscape contrast. Chapter 4, the Fixed Industrial Scanning Software breakdown data are shown at the regional level, to show the sales quantity, consumption value and growth by regions, from 2020 to 2031. Chapter 5 and 6, to segment the sales by Type and application, with sales market share and growth rate by type, application, from 2020 to 2031. Chapter 7, 8, 9, 10 and 11, to break the sales data at the country level, with sales quantity, consumption value and market share for key countries in the world, from 2020 to 2024.and Fixed Industrial Scanning Software market forecast, by regions, type and application, with sales and revenue, from 2025 to 2031. Chapter 12, market dynamics, drivers, restraints, trends and Porters Five Forces analysis. Chapter 13, the key raw materials and key suppliers, and industry chain of Fixed Industrial Scanning Software. Chapter 14 and 15, to describe Fixed Industrial Scanning Software sales channel, distributors, customers, research findings and conclusion.
Data Sources: Via authorized organizations:customs statistics, industrial associations, relevant international societies, and academic publications etc. Via trusted Internet sources.Such as industry news, publications on this industry, annual reports of public companies, Bloomberg Business, Wind Info, Hoovers, Factiva (Dow Jones & Company), Trading Economics, News Network, Statista, Federal Reserve Economic Data, BIS Statistics, ICIS, Companies House Documentsm, investor presentations, SEC filings of companies, etc. Via interviews. Our interviewees includes manufacturers, related companies, industry experts, distributors, business (sales) staff, directors, CEO, marketing executives, executives from related industries/organizations, customers and raw material suppliers to obtain the latest information on the primary market; Via data exchange. We have been consulting in this industry for 16 years and have collaborations with the players in this field. Thus, we get access to (part of) their unpublished data, by exchanging with them the data we have.
From our partners.We have information agencies as partners and they are located worldwide, thus we get (or purchase) the latest data from them. Via our long-term tracking and gathering of data from this industry.We have a database that contains history data regarding the market.
Global Info Research is a company that digs deep into global industry information to support enterprises with market strategies and in-depth market development analysis reports. We provides market information consulting services in the global region to support enterprise strategic planning and official information reporting, and focuses on customized research, management consulting, IPO consulting, industry chain research, database and top industry services. At the same time, Global Info Research is also a report publisher, a customer and an interest-based suppliers, and is trusted by more than 30,000 companies around the world. We will always carry out all aspects of our business with excellent expertise and experience.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
gs1 barcode
A GS1 barcode is a barcode that follows the global standards established by GS1, an international organization responsible for developing and maintaining standards for business communication, particularly in product identification and supply chain management. GS1 barcodes are used worldwide to uniquely identify products, services, or assets in various industries, such as retail, healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing.
What is a GS1 Barcode?
A GS1 barcode is a graphical representation of data that encodes information in a machine-readable format. This data can be used to identify products, track shipments, and manage inventory. The most common type of GS1 barcode is the UPC (Universal Product Code) in the retail industry, but GS1 also covers a wide range of other barcode types used in different applications.
Components of a GS1 Barcode
GS1 Company Prefix: The GS1 Company Prefix is a unique identifier assigned to a company by GS1. It is the starting point for generating a GS1 barcode. This prefix allows businesses to identify their products uniquely in the global marketplace.
Product Identifier (GTIN): A Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) is used to uniquely identify a product. It could be a 12-digit UPC code, a 13-digit EAN code, or a 14-digit GTIN-14 code, depending on the type of barcode being used.
Check Digit: The final digit in a GS1 barcode is a check digit. It is calculated using a mathematical formula and is used to validate the barcode’s accuracy when it is scanned.
Additional Information: Depending on the application, additional information, such as batch numbers, expiration dates, or serial numbers, can be encoded into the barcode.
Types of GS1 Barcodes
There are several different types of GS1 barcodes, each designed for specific applications:
UPC (Universal Product Code):
Used primarily in the United States and Canada for retail products.
The UPC-A is a 12-digit barcode that encodes a GS1 Company Prefix, product identifier, and a check digit.
EAN (European Article Number):
A 13-digit barcode commonly used outside of North America.
It is very similar to the UPC, but it has a 13-digit format to accommodate international product identification.
GTIN-14 (Global Trade Item Number):
A 14-digit barcode used for identifying trade items at various levels in the supply chain, such as cartons or pallets.
GS1 DataBar:
A compact barcode that can encode more information than traditional UPC or EAN barcodes.
Used for small or variable data products, such as fresh produce or small items that cannot accommodate a larger barcode.
GS1-128:
A 1D barcode that can encode multiple types of data, including batch numbers, expiration dates, and serial numbers.
It is commonly used in logistics, healthcare, and shipping.
QR Codes (Quick Response Codes):
A type of 2D barcode that can store large amounts of information and is commonly used in marketing, product information sharing, and digital transactions.
QR codes are widely used on packaging, advertisements, and websites to link users to additional product information or promotions.
How GS1 Barcodes Work
Barcode Creation: To create a GS1 barcode, you first need to obtain a GS1 Company Prefix by registering with GS1. This prefix is used to create unique product identifiers (GTINs), which form the base of your barcode.
Barcode Generation: Once you have your GTIN, you can use barcode generation software or services to create the visual barcode. This barcode will be in the form of black bars and spaces that represent the encoded product data.
Scanning: When a GS1 barcode is scanned by a barcode scanner, the scanner reads the pattern of bars and spaces, decodes the GTIN, and retrieves the corresponding product information from a database.
Data Retrieval: The system retrieves the product details (name, price, description, etc.) from the product database or inventory management system. This streamlines the process of checking out, stocking, or tracking items in the supply chain.
Benefits of GS1 Barcodes
Global Standardization: GS1 barcodes are universally recognized and accepted in retail, logistics, and supply chain industries worldwide. They ensure that products are identifiable across different regions and businesses, making international trade easier.
Faster and More Accurate Transactions: Scanning GS1 barcodes eliminates the need for manual data entry, which speeds up transactions and reduces errors at the point of sale (POS).
Improved Inventory Management: By using GS1 barcodes, businesses can track inventory more efficiently. This helps reduce stockouts, minimize overstocking, and ensure accurate stock levels across different locations.
Enhanced Traceability: GS1 barcodes provide a way to track products throughout the entire supply chain, from manufacturing to distribution to retail. This is especially important in industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare, where product traceability and recalls are essential.
Compliance: Many industries and retailers require GS1 barcodes for product listings, packaging, and sales. Using GS1 barcodes helps businesses comply with regulatory requirements and retailer specifications.
How to Get a GS1 Barcode
To get a GS1 barcode for your products, follow these steps:
Register with GS1: First, visit the official GS1 website in your region (such as GS1 US, GS1 UK, or GS1 International) to create an account and register your business. You will be assigned a GS1 Company Prefix.
Assign GTINs to Your Products: Using the GS1 Company Prefix, assign a unique GTIN to each of your products. The GTIN will form the base of your barcode and will uniquely identify each item.
Generate the Barcode: Once you have your GTIN, you can use barcode creation software or services to generate the GS1 barcode. Some barcode printers and software are available through GS1 or third-party providers.
Print the Barcode: After generating your GS1 barcode, print it on your product packaging, labels, or tags. Ensure that the barcode is printed clearly and is scannable.
Test the Barcode: It’s important to test your GS1 barcode using a barcode scanner to verify that it’s readable and correctly links to the product data.
Conclusion
A GS1 barcode is an essential tool for businesses, enabling efficient product identification, inventory management, and supply chain tracking. By adhering to GS1 standards, businesses ensure that their products are identifiable globally and are compliant with industry regulations. Whether you're a small business or a large corporation, implementing GS1 barcodes can streamline your operations, improve accuracy, and provide the traceability required in today's fast-paced business world.
0 notes
Text
Enhance Your Security with QR Code Technology: A Guide to Safe Scanning
Enhance Your Security with QR Code Technology: A Guide to Safe Scanning
In today’s tech-driven world, QR codes have become a part of everyday life. Whether you're scanning a code to access a website, share contact information, or make a payment, these quick response codes make life more convenient. But, with great convenience comes the need for security, especially when scanning QR codes online. In this post, we’ll explore QR scanners, QR code readers, and the best ways to scan QR codes online while ensuring your security.
What is a QR Code?
A QR (Quick Response) code is a type of barcode that can store various forms of data, such as website links, product details, contact information, and more. These codes are widely used for marketing, payments, and sharing important information due to their ease of access and versatility.
What is a QR Scanner?
A QR scanner is a tool, typically found on smartphones or dedicated apps, that reads QR codes. When you scan a QR code, the scanner interprets the data embedded in the code and performs an action, such as opening a website or saving a contact.
What is a QR Code Reader?
A QR code reader is the software or feature that decodes the data stored in a QR code. It can be integrated into your phone’s camera, downloaded as a standalone app, or built into certain services like browsers or payment platforms. This reader is responsible for converting the data from the QR code into a usable form, such as a link or text.
How to Safely Scan QR Codes Online
With the rise in QR code usage comes the need for awareness about the security risks involved. QR codes can be exploited by cybercriminals to trick users into accessing harmful sites or downloading malware. Here’s how you can protect yourself while scanning QR codes online:
Use Trusted QR Code Scanners: Stick to using reliable apps or built-in smartphone scanners from trusted sources like Google Play or the Apple App Store. These apps often come with security features to help you avoid potential risks.
Check the Source of the QR Code: Be cautious when scanning QR codes from unfamiliar sources. If you don’t know where the code came from, there’s a chance it could direct you to a malicious site or prompt unwanted downloads.
Verify the URL: After scanning the QR code, take a moment to verify the link. Check if the website is secure (look for “https” in the URL) and ensure it leads to the intended destination before clicking on it.
Avoid Automatic Actions: Some QR scanners perform actions like opening links or downloading files automatically after a scan. Make sure these features are disabled, giving you control over what happens after scanning the QR code.
Keep Your Software Updated: Regularly update your QR code reader apps and device software to ensure you are protected against security vulnerabilities.
The Role of QR Codes in Security
QR codes are incredibly convenient, but they can also be used by cybercriminals for malicious purposes. For example, a hacker could replace a legitimate QR code with one that directs users to a phishing site or a page designed to install malware on their devices. This is why it’s important to practice caution when scanning QR codes, especially those that come from unknown or suspicious sources.
Kavach QR: A Safe and Secure QR Code Solution
At Kavach QR, we understand the importance of both security and convenience. Our solution provides a safe way to share essential information, especially in emergencies. Kavach QR allows users to store crucial details like emergency contacts, health information, and personal details in a QR code. This ensures that important information is accessible quickly and securely when needed—without compromising your security.
By using Kavach QR, you can rest assured that your data is protected and easily accessible in critical situations. Our technology is designed to safeguard your personal information while making it available to those who need it in an emergency.
Conclusion
QR codes are a powerful tool, offering ease of use and quick access to a wealth of information. However, with this power comes the need for caution. By using trusted QR code scanners, verifying URLs, and keeping your devices updated, you can enjoy the benefits of QR code technology without worrying about security risks.
At Kavach QR, we are committed to providing a secure and reliable solution for accessing and sharing vital information through QR codes. Visit Kavach QR to learn more about how our technology can enhance your security and peace of mind in the digital age.
Stay secure, stay informed, and make the most of QR code technology with confidence.
0 notes
Text
Enhance Your Security with QR Code Technology: A Guide to Safe Scanning
Enhance Your Security with QR Code Technology: A Guide to Safe Scanning
In today’s tech-driven world, QR codes have become a part of everyday life. Whether you're scanning a code to access a website, share contact information, or make a payment, these quick response codes make life more convenient. But, with great convenience comes the need for security, especially when scanning QR codes online. In this post, we’ll explore QR scanners, QR code readers, and the best ways to scan QR codes online while ensuring your security.
What is a QR Code?
A QR (Quick Response) code is a type of barcode that can store various forms of data, such as website links, product details, contact information, and more. These codes are widely used for marketing, payments, and sharing important information due to their ease of access and versatility.
What is a QR Scanner?
A QR scanner is a tool, typically found on smartphones or dedicated apps, that reads QR codes. When you scan a QR code, the scanner interprets the data embedded in the code and performs an action, such as opening a website or saving a contact.
What is a QR Code Reader?
A QR code reader is the software or feature that decodes the data stored in a QR code. It can be integrated into your phone’s camera, downloaded as a standalone app, or built into certain services like browsers or payment platforms. This reader is responsible for converting the data from the QR code into a usable form, such as a link or text.
How to Safely Scan QR Codes Online
With the rise in QR code usage comes the need for awareness about the security risks involved. QR codes can be exploited by cybercriminals to trick users into accessing harmful sites or downloading malware. Here’s how you can protect yourself while scanning QR codes online:
Use Trusted QR Code Scanners: Stick to using reliable apps or built-in smartphone scanners from trusted sources like Google Play or the Apple App Store. These apps often come with security features to help you avoid potential risks.
Check the Source of the QR Code: Be cautious when scanning QR codes from unfamiliar sources. If you don’t know where the code came from, there’s a chance it could direct you to a malicious site or prompt unwanted downloads.
Verify the URL: After scanning the QR code, take a moment to verify the link. Check if the website is secure (look for “https” in the URL) and ensure it leads to the intended destination before clicking on it.
Avoid Automatic Actions: Some QR scanners perform actions like opening links or downloading files automatically after a scan. Make sure these features are disabled, giving you control over what happens after scanning the QR code.
Keep Your Software Updated: Regularly update your QR code reader apps and device software to ensure you are protected against security vulnerabilities.
The Role of QR Codes in Security
QR codes are incredibly convenient, but they can also be used by cybercriminals for malicious purposes. For example, a hacker could replace a legitimate QR code with one that directs users to a phishing site or a page designed to install malware on their devices. This is why it’s important to practice caution when scanning QR codes, especially those that come from unknown or suspicious sources.
Kavach QR: A Safe and Secure QR Code Solution
At Kavach QR, we understand the importance of both security and convenience. Our solution provides a safe way to share essential information, especially in emergencies. Kavach QR allows users to store crucial details like emergency contacts, health information, and personal details in a QR code. This ensures that important information is accessible quickly and securely when needed—without compromising your security.
By using Kavach QR, you can rest assured that your data is protected and easily accessible in critical situations. Our technology is designed to safeguard your personal information while making it available to those who need it in an emergency.
Conclusion
QR codes are a powerful tool, offering ease of use and quick access to a wealth of information. However, with this power comes the need for caution. By using trusted QR code scanners, verifying URLs, and keeping your devices updated, you can enjoy the benefits of QR code technology without worrying about security risks.
At Kavach QR, we are committed to providing a secure and reliable solution for accessing and sharing vital information through QR codes. Visit Kavach QR to learn more about how our technology can enhance your security and peace of mind in the digital age.
Stay secure, stay informed, and make the most of QR code technology with confidence.
0 notes
Text
Understanding Barcodes: Creation, Functionality and Impact

Barcodes are ubiquitous in modern commerce and industry, streamlining everything from inventory management to checkout processes. These compact, visually distinctive symbols encode information in a machine-readable format, revolutionizing the way data is stored, accessed, and processed. This article delves into the concept of barcodes, their creation, and their significant role in various sectors.
What is a Barcode? A barcode is a visual, machine-readable representation of data. It consists of a series of parallel lines (bars) and spaces of varying widths that together represent encoded information. Barcodes can be scanned and interpreted by optical scanners or cameras, converting the visual data into a digital format that computers can process.
There are several types of barcodes, broadly categorized into: Linear Barcodes: The traditional format, consisting of a series of parallel lines. Examples include the Universal Product Code (UPC) and the European Article Number (EAN). 2D Barcodes: These barcodes can encode more information in a smaller space using patterns of squares, dots, or other shapes. Examples include QR codes and Data Matrix codes.
How is a Barcode Made? Creating a barcode involves several steps, from data encoding to physical printing. Here’s a detailed look at the process:
Data Encoding:
The first step in creating a barcode is determining the data to be encoded. This data could be a product number, serial number, or any other piece of information that needs to be quickly and accurately retrieved. The chosen data is then converted into a format suitable for the type of barcode being used. Different barcode symbologies (standards) dictate how data is encoded. For example, UPC codes use a specific pattern of bars and spaces to represent numbers.
Choosing the Symbology:
The type of barcode symbology depends on the application. UPC and EAN are common for retail products, while Code 39 and Code 128 are used in logistics and manufacturing. QR codes and Data Matrix codes are popular for marketing and information storage due to their high data capacity.
Generating the Barcode:
Specialized software or online tools generate the barcode image based on the encoded data and selected symbology. This software converts the data into the appropriate series of bars and spaces (or dots and squares for 2D barcodes).
Printing the Barcode:
The generated barcode image is then printed on labels, packaging, or directly onto products. This can be done using various printing technologies, such as inkjet, laser, or thermal printers. The key is ensuring that the barcode is printed clearly and accurately to ensure reliable scanning.
How Do Barcodes Work? Once a barcode is created and applied to an item, it can be read by a barcode scanner. Here’s how the scanning process works:
Scanning:
A barcode scanner emits a beam of light (usually a laser or LED) that sweeps across the barcode. The scanner detects the reflected light from the barcode’s bars and spaces. Different parts of the barcode reflect light differently: the bars absorb light, and the spaces reflect it. The scanner’s sensor detects these variations in light reflection.
Decoding:
The scanner converts the reflected light into an electrical signal, which is then processed to interpret the pattern of bars and spaces. This pattern is converted back into the original data encoded in the barcode. For example, in a retail setting, a UPC code is converted into a product number that the computer system recognizes.
Data Processing:
Once the barcode data is decoded, it is transmitted to a computer or point-of-sale system. The system uses this data to perform a specific action, such as retrieving product information, updating inventory levels, or processing a sale.
Applications of Barcodes:
Retail: Barcodes streamline the checkout process, reduce errors, and manage inventory. UPC and EAN codes are ubiquitous in retail environments, allowing for quick and accurate scanning of products at checkout.
Healthcare: Barcodes are used for patient identification, medication tracking, and inventory management in hospitals and pharmacies, ensuring patient safety and operational efficiency.
Logistics and Supply Chain: Barcodes facilitate tracking and managing goods throughout the supply chain, from manufacturing to distribution to delivery. They enhance accuracy, efficiency, and visibility in logistics operations.
Manufacturing: Barcodes help manage parts, track production processes, and ensure quality control in manufacturing settings.
Libraries and Asset Management: Barcodes simplify the tracking of books, equipment, and other assets, ensuring efficient check-in/check-out processes and accurate inventory management.
The Future of Barcodes
The evolution of barcode technology continues with advancements like Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and Near Field Communication (NFC). These technologies offer additional benefits, such as longer range scanning and the ability to store more information. However, traditional barcodes remain indispensable due to their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and widespread adoption.
Barcodes are a cornerstone of modern data management and logistics, offering a simple yet powerful way to encode, store, and retrieve information. From their creation to their myriad applications, barcodes have revolutionized industries by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and convenience. As technology advances, barcodes will continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of data processing and management.
#point of sale#retail software#barcodescanners#retail billing software#retailsoftware#software#barcode printer
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to QR Code Generators: Creating Customized QR Codes with Ease
In today's digital age, QR codes have become an integral part of our lives. These pixelated squares store a wealth of information, from website links to contact details, and are easily scanned by smartphones, making them a versatile tool for businesses and individuals alike. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of QR codes, how to generate them, and how to make the most of their potential.
Chapter 1: Understanding QR Codes
Before diving into the world of QR code generators, it's essential to understand what QR codes are and their various applications.
What Is a QR Code? A QR code, short for Quick Response code, is a two-dimensional barcode that stores data both horizontally and vertically. Developed in Japan in the 1990s, QR codes have evolved from inventory tracking tools to a versatile marketing and information-sharing tool.
How Do QR Codes Work? Learn the inner workings of QR codes, including how they store data and how smartphones decode them. This knowledge will help you appreciate the magic behind these pixelated squares.
Applications of QR Codes Discover the diverse range of applications for QR codes, from marketing campaigns to contactless payments and everything in between.
Chapter 2: The Need for QR Code Generators
With the increasing demand for QR codes, manual generation can be tedious and error-prone. This chapter delves into the importance of QR code generators and how they simplify the process.
Why Use a QR Code Generator? Explore the benefits of using a QR code generator, such as saving time, reducing errors, and customizing codes to suit your needs.
Types of QR Code Generators Get an overview of the various QR code generator tools available, including online generators, desktop software, and mobile apps.
Chapter 3: How to Make a QR Code
In this chapter, we will walk you through the step-by-step process of creating your very own QR codes.
Choosing the Right QR Code Generator Find out how to select the best QR code generator tool based on your specific needs, whether it's for business, personal use, or a one-time project.
Creating a QR Code for a Link Learn how to generate a QR code that links to a website, a video, or any other online resource. We'll provide detailed instructions for popular QR code generators.
Customizing Your QR Code Explore the world of customized QR codes, where you can personalize colors, add logos, and enhance the visual appeal of your codes.
Chapter 4: QR Code Best Practices
To maximize the effectiveness of your QR codes, it's essential to follow best practices. This chapter outlines tips and tricks for creating QR codes that work seamlessly.
Designing User-Friendly QR Codes Discover how to ensure that your QR codes are easy to scan for everyone, including users with older smartphones or disabilities.
Tracking QR Code Performance Learn how to monitor the performance of your QR codes by using tracking and analytics tools. This enables you to assess the success of your campaigns and make improvements.
Chapter 5: Dynamic QR Codes
Dynamic QR codes offer a level of flexibility and convenience that static QR codes can't match. In this chapter, we explore the concept of dynamic QR codes and their advantages.
What Are Dynamic QR Codes? Understand the key differences between static and dynamic QR codes and why you might prefer dynamic codes for certain applications.
Creating and Managing Dynamic QR Codes Step into the world of dynamic QR code generation and management, including the ability to update the linked content even after distribution.
Chapter 6: The Best QR Code Generators in 2023
With numerous QR code generator options available, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one. In this chapter, we present a curated list of the best QR code generator tools for 2023.
QR Code Generator Reviews Get an in-depth look at the features, pricing, and user-friendliness of the top QR code generators, including QR Code Maker, QR Code Generator Pro, and QR Code Studio.
Chapter 7: Real-World Examples
To inspire your QR code usage, we provide real-world examples of how businesses and individuals leverage QR codes for various purposes.
Marketing Campaigns Explore how businesses use QR codes to drive marketing campaigns, engage customers, and gather valuable data.
Contactless Transactions Discover how QR codes are revolutionizing the way we make payments and streamline transactions in a post-pandemic world.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we've covered everything you need to know about QR code generators, from their origins to advanced customization and tracking. QR codes have evolved beyond their initial purpose and have become a powerful tool for businesses and individuals to connect with their audience, share information, and simplify everyday tasks. Whether you're a marketer, business owner, or tech enthusiast, this guide equips you with the knowledge and tools to harness the full potential of QR codes in 2023 and beyond. Start creating and sharing QR codes that make a difference today!
0 notes
Text
Barcode Definition 2025: How They Work in Modern Times

Barcodes have been a part of global commerce and logistics for decades—but in 2025, they’ve evolved far beyond basic black-and-white stripes on a product package. Today’s barcodes are smarter, faster, and more integrated into digital systems than ever before, playing a key role in supply chain automation, inventory management, retail checkouts, healthcare, and even customer engagement.
In this article, we’ll define what barcodes are in the context of 2025, explore how they function today, and discuss their growing importance in modern business and technology.
What is a Barcode in 2025?
A barcode is a machine-readable representation of data that encodes information into a visual pattern. Traditionally, barcodes used vertical lines (1D codes), but in 2025, 2D barcodes like QR codes, Data Matrix, and PDF417 have become standard in many industries.
Barcodes now serve as digital identifiers that connect physical objects to cloud-based data systems in real time. They're used for product tracking, authentication, traceability, marketing, and more.
How Barcodes Work in 2025
The basic principle remains the same: a barcode scanner reads the visual pattern and decodes it into usable data. However, in modern times, several advancements have transformed how barcodes are created, scanned, and used.
1. Modern Barcode Scanners
Devices now include smartphones, AI-enabled scanners, and IoT sensors.
Cameras and software can instantly scan multiple barcodes in one go.
Cloud integration means data is processed in real-time and accessible from anywhere.
2. Mobile and Cloud Integration
Scanned data is instantly uploaded to cloud-based inventory or ERP systems.
Businesses use barcode apps for real-time tracking, analytics, and automation.
APIs allow barcodes to interact with customer apps, POS systems, and logistics software.
3. 2D Barcode Expansion
QR codes and Data Matrix codes can store more data in less space.
They can encode URLs, product details, tracking IDs, and even dynamic content.
Often used in digital menus, vaccine passports, shipping labels, and smart packaging.
4. AI & Machine Learning Integration
AI enhances barcode recognition under poor lighting, angle distortion, or damaged labels.
Machine learning algorithms predict inventory needs based on barcode scan history.
5. Augmented Reality (AR) & Barcodes
Some systems allow workers to scan barcodes through AR glasses, showing item details instantly.
This improves picking speed and accuracy in large warehouses.
Types of Barcodes in 2025
TypeDescriptionCommon Use CasesUPC (1D)Basic linear barcodeRetail products, groceriesCode 128 (1D)High-density, alphanumericShipping, logisticsQR Code (2D)Square code, stores more dataMarketing, payments, authenticationData MatrixCompact 2D codePharmaceuticals, electronicsPDF417Stacked linear barcodeIDs, boarding passes, documents
Benefits of Modern Barcodes
✅ Real-Time Data Access
Scanned data is synced across platforms instantly, improving visibility and decision-making.
✅ High-Speed Scanning
Advanced scanners can read dozens of barcodes simultaneously, even from a distance or on moving packages.
✅ Enhanced Traceability
Used extensively in food, pharma, and logistics industries to track items from origin to delivery.
✅ Improved Customer Experience
QR codes connect products to rich media, reviews, promotions, or authentication tools.
✅ Cost-Effective & Scalable
Barcodes are low-cost to print or display and scale easily across large inventories or product lines.
Barcode Use Cases in 2025
● Retail & eCommerce
Dynamic pricing via barcode-linked software
Self-checkout systems using smartphone barcode scans
● Healthcare
Barcode wristbands for patients
Tracking medication, lab samples, and medical equipment
● Manufacturing
Parts traceability throughout production lines
Quality control through scan-and-check systems
● Logistics & Supply Chain
Real-time shipment tracking
Warehouse automation using barcode-based inventory robots
● Education & Events
Digital student IDs with QR codes
Entry passes and attendance via barcode scans
The Evolution of Barcodes: 2025 and Beyond
Barcodes are now a bridge between physical objects and digital ecosystems. As IoT, blockchain, and AI continue to grow, barcodes will serve as gateways for secure, real-time data exchange. In fact, smart barcodes embedded in sustainable packaging or NFC-enabled tags are already being tested to go beyond basic scanning.
Some emerging innovations include:
Dynamic barcodes that change after each scan to prevent fraud.
Biometric-linked barcodes for secure identity verification.
Voice-activated barcode scanning integrated with smart assistants.
Conclusion
Barcodes in 2025 are smarter, faster, and more connected than ever before. From retail shelves to hospital rooms, they continue to drive efficiency, accuracy, and innovation across industries. As businesses adapt to an increasingly digital and automated world, barcodes remain a simple yet powerful tool to bridge the physical and virtual realms.
Looking to upgrade your inventory or product tracking with advanced barcode solutions? Contact us today to get started with modern barcode systems built for 2025 and beyond.
#rfid solutions#asset management#real time tracking#barcode#aidc technologies india#aidc#electronic devices#technology#qr code#barcode printers
0 notes
Text
Barcode Readers Market Detailed Strategies, Competitive Landscaping and Developments for next 5 years
Barcode Readers Market Comprehensive Study is an expert and top to bottom investigation on the momentum condition of the Global Barcode Readers industry with an attention on the Global market. The report gives key insights available status of the Global Barcode Readers producers and is an important wellspring of direction and course for organizations and people keen on the business. By and large, the report gives an inside and out understanding of 2021-2027 worldwide Barcode Readers Market covering extremely significant parameters. Some key Players in This Report Include Honeywell International Inc.(United States),DATALOGIC SpA (Italy),System ID Barcode Solutions.(United States),Newland EMEA (Netherlands),Cognex Corporation (United States),Denso Wave Incorporated (Japan),OMRON Corporation (Japan),Socket Mobile (United States),Zebex Industries Inc.(Taiwan),TouchStar Technologies (United Kingdom),Opticon Sensors Europe B.V.(Netherlands) A barcode reader, also known as a barcode scanner is an electronic device that captures and read information from a barcode and transfer output printed barcodes to the connected computer. A barcode reader includes of a scanner, a decoder, and a cable that is connected to the computer. The connected computer decodes the data taken with the help of a software. Like a flatbed scanner, it contains of a light source, a lens and a light sensor translating optical impulses into electrical ones. Its decoder circuitry analyze the bar code's image data provided by the sensor & sending the barcode's content to the scanner's output port. In retail and manufacturing industries, barcode technology is rapidly adopted. Barcode scanners are one of the best solutions for recording product information without any major manual effort. With the technological advantages coupled with cutting-edge features of barcode scanners, the popularity is also increasing in healthcare industry. Market Trends: Increasing Application in Supply Chain Tracking
Emergence of Industry 4.0
Market Drivers: Growing Acceptance of Barcodes Readers across Various Industry Verticals
High Adoption of Automatic Data Capture (ADC) Devices in the Retail Industry
Market Challenges: High Competition among the Market Players
Increasing Effectiveness of portable barcode Scanner for Working with Complex Shapes and Designs
Market Opportunities: Growing Retail Industry Worldwide
Increasing Demand from the Developing Economies
The Global Barcode Readers Market segments and Market Data Break Down by Type (Laser Barcode Readers, Handheld Barcode Readers, Stationary Barcode Readers, Mobile Computer Readers, Others), Application (Retail, Transportation and Logistics, Manufacturing, Healthcare, Government, Entertainment, Others (Education, Travel, Hospitality)), Industry Vertical (Retail, Transportation and Logistics, Manufacturing, Healthcare, Government, Entertainment, Others (Education, Travel, Hospitality)), Component (Solution, Service)
Presented By
AMA Research & Media LLP
0 notes
Text
It was all downhill after the Cuecat
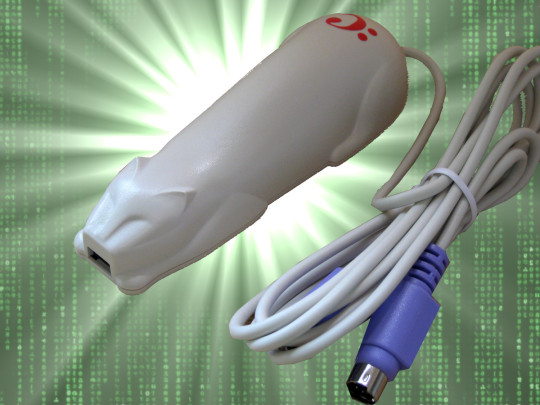

Sometime in 2001, I walked into a Radio Shack on San Francisco’s Market Street and asked for a Cuecat: a handheld barcode scanner that looked a bit like a cat and a bit like a sex toy. The clerk handed one over to me and I left, feeling a little giddy. I didn’t have to pay a cent.
The Cuecat was a good idea and a terrible idea. The good idea was to widely distribute barcode scanners to computer owners, along with software that could read and decode barcodes; the company’s marketing plan called for magazines and newspapers to print barcodes alongside ads and articles, so readers could scan them and be taken to the digital edition. To get the Cuecat into widespread use, the company raised millions in the capital markets, then mass-manufactured these things and gave them away for free at Radio Shacks around the country. Every Wired and Forbes subscriber got one in the mail!
That was the good idea (it’s basically a prototype for today’s QR-codes). The terrible idea was that this gadget would spy on you. Also, it would only work with special barcodes that had to be licensed from the manufacturer. Also, it would only work on Windows.
https://web.archive.org/web/20001017162623/http://www.businessweek.com/bwdaily/dnflash/sep2000/nf20000928_029.htm
But the manufacturer didn’t have the last word! Not at all. A couple of enterprising hardware hackers — Pierre-Philippe Coupard and Michael Rothwell — tore down a Cuecat, dumped its ROM, and produced their own driver for it — a surveillance-free driver that worked with any barcode. You could use it to scan the UPCs on your books or CDs or DVDs to create a catalog of your media; you could use it to scan UPCs on your groceries to make a shopping list. You could do any and every one of these things, because the Cuecat was yours.
Cuecat’s manufacturer, Digital Convergence, did not like this at all. They sent out legal demand letters and even shut down some of the repositories that were hosting alternative Cuecat firmware. They changed the license agreement that came with the Cuecat software CD to prohibit reverse-engineering.
http://www.cexx.org/cuecat.htm
It didn’t matter, both as a practical matter and as a matter of law. As a practical matter, the (ahem) cat was out of the bag: there were so many web-hosting companies back then, and people mirrored the code to so many of them, the company would have its hands full chasing them all down and intimidating them into removing the code.
Then there was the law: how could you impose license terms on a gift? How could someone be bound by license terms on a CD that they simply threw away without ever opening it, much less putting it in their computer?
https://slashdot.org/story/00/09/18/1129226/digital-convergence-changes-eula-and-gets-cracked
In the end, Cuecat folded and sold off its remaining inventory. The early 2000s were not a good time to be a tech company, much less a tech company whose business model required millions of people to meekly accept a bad bargain.
Back then, tech users didn’t feel any obligation to please tech companies’ shareholders: if they backed a stupid business, that was their problem, not ours. Venture capitalists were capitalists — if they wanted us give to them according to their need and take from them according to their ability, they should be venture communists.
Last August, philosopher and Centre for Technomoral Futures director Shannon Vallor tweeted, “The saddest thing for me about modern tech’s long spiral into user manipulation and surveillance is how it has just slowly killed off the joy that people like me used to feel about new tech. Every product Meta or Amazon announces makes the future seem bleaker and grayer.”
https://twitter.com/ShannonVallor/status/1559659655097376768
She went on: “I don’t think it’s just my nostalgia, is it? There’s no longer anything being promised to us by tech companies that we actually need or asked for. Just more monitoring, more nudging, more draining of our data, our time, our joy.”
https://twitter.com/ShannonVallor/status/1559663985821106177
Today on Tumblr, @wilwheaton responded: “[T]here is very much no longer a feeling of ‘How can this change/improve my life?’ and a constant dread of ‘How will this complicate things as I try to maintain privacy and sanity in a world that demands I have this thing to operate.’”
https://wilwheaton.tumblr.com/post/698603648058556416/cory-doctorow-if-you-see-this-and-have-thoughts
Wil finished with, “Cory Doctorow, if you see this and have thoughts, I would LOVE to hear them.”
I’ve got thoughts. I think this all comes back to the Cuecat.
When the Cuecat launched, it was a mixed bag. That’s generally true of technology — or, indeed, any product or service. No matter how many variations a corporation offers, they can never anticipate all the ways that you will want or need to use their technology. This is especially true for the users the company values the least — poor people, people in the global south, women, sex workers, etc.
That’s what makes the phrase “So easy your mom can use it” particularly awful “Moms” are the kinds of people whose priorities and difficulties are absent from the room when tech designers gather to plan their next product. The needs of “moms” are mostly met by mastering, configuring and adapting technology, because tech doesn’t work out of the box for them:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/05/19/the-weakest-link/#moms-are-ninjas
(As an alternative, I advocate for “so easy your boss can use it,” because your boss gets to call up the IT department and shout, “I don’t care what it takes, just make it work!” Your boss can solve problems through raw exercise of authority, without recourse to ingenuity.)
Technology can’t be understood separately from technology users. This is the key insight in Donald Norman’s 2004 book Emotional Design, which argued that the ground state of all technology is broken, and the overarching task of tech users is to troubleshoot the things they use:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/04/29/banjo-nazis/#cuckoos-egg
Troubleshooting is both an art and a science: it requires both a methodical approach and creative leaps. The great crisis of troubleshooting is that the more frustrated and angry you are, the harder it is to be methodical or creative. Anger turns attention into a narrow tunnel of brittle movements and thinking.
In Emotional Design, Norman argues that technology should be beautiful and charming, because when you like a technology that has stopped working, you are able to troubleshoot it in an expansive, creative, way. Emotional Design was not merely remarkable for what it said, but for who said it.
Donald Norman, after all, was the author of the hugely influential 1998 classic The Design of Everyday Things, which counseled engineers and designers to put function over form — to design things that work well, even if that meant stripping away ornament and sidelining aesthetics.
https://www.basicbooks.com/titles/don-norman/the-design-of-everyday-things/9780465050659/
With Emotional Design, Norman argued that aesthetics were functional, because aesthetics primed users to fix the oversights and errors and blind spots of designers. It was a manifesto for competence and humility.
And yet, as digital technology has permeated deeper into our lives, it has grown less configurable, not more. Companies today succeed where Cuecat failed. Consolidation in the online world means that if you remove a link from one search engine and four social media sites, the material in question vanishes for 99% of internet users.
It’s even worse for apps: anyone who succeeds in removing an app from two app stores essentially banishes it from the world. One mobile platform uses technological and legal countermeasures to make it virtually impossible to sideload an app; the other one relies on strong-arm tactics and deceptive warnings to do so.
That means that when a modern Coupard and Rothwell decides to unfuck some piece of technology — to excise the surveillance and proprietary media requirements, leaving behind the welcome functionality — they can only do so with the sufferance of the manufacturer. If the manufacturer doesn’t like an add-on, mod, plug-in or overlay, they can use copyright takedowns, anticircumvention law, patent threats, trademark threats, cybersecurity law, contract law and other “IP” to simply banish the offending code:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
Many of these laws carry dire penalties. For example, distributing a tool that bypasses an “access control” so that you can change the software on a gadget (say, to make your printer accept third-party ink) is a felony under Section 1201 of the DMCA, punishable by a $500k fine and a 5-year prison sentence.
If Cuecat’s manufacturers had simply skinned their firmware with a thin scrim of DRM, they could have threatened Coupard and Rothwell with prison sentences. The developments in “IP” over the two decades since the Cuecat have conjured up a new body of de facto law that Jay Freeman calls “felony contempt of business model.”
Once we gave companies the power to literally criminalize the reconfiguration of their products, everything changed. In the Cuecat era, a corporate meeting to plan a product that acted against its users’ interests had to ask, “How will we sweeten the pot and/or obfuscate our code so that our users don’t remove the anti-features we’re planning to harm them with?”
But in a world of Felony Contempt of Business Model, that discussion changes to “Given that we can literally imprison anyone who helps our users get more out of this product, how can we punish users who are disloyal enough to simply quit our service or switch away from our product?”
That is, “how can we raise the switching costs of our products so that users who are angry at us keep using our products?” When Facebook was planning its photos product, they deliberately designed it to tempt users into making it the sole repository of their family photos, in order to hold those photos ransom to keep Facebook users from quitting for G+:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2021/08/facebooks-secret-war-switching-costs
Companies claim that their lock-in strategies are about protecting their users: “Move into our walled garden, for it is a fortress, whose battlements bristle with fearsome warriors who will defend you from the bandits who roam the countryside”:
https://locusmag.com/2021/01/cory-doctorow-neofeudalism-and-the-digital-manor/
But this “feudal security” offers a terrible temptation to the lords of these fortresses, because once you are inside those walls, the fortress can easily be converted to a prison: these companies can abuse you with impunity, for so long as the cost of the abuse is less than the cost of the things you must give up when you leave.
The tale that companies block you from overriding their decisions is for your own good was always dubious, because companies simply can’t anticipate all the ways their products will fail you. No design team knows as much about your moment-to-moment struggles as you do.
But even where companies are sincere in their desire to be the most benevolent of dictators, the gun on the mantelpiece in Act I is destined to go off by Act III: eventually, the temptation to profit by hurting you will overpower whatever “corporate ethics” once stayed the hand of the techno-feudalist who rules over your fortress. Under feudal security, you are one lapse in corporate leadership from your protector turning into your tormentor.
When Apple launched the Ipad 12 years ago, I published an editorial entitled “Why I won’t buy an iPad (and think you shouldn’t, either),” in which I predicted that app stores would inevitable be turned against users:
https://memex.craphound.com/2010/04/01/why-i-wont-buy-an-ipad-and-think-you-shouldnt-either/
Today, Apple bans apps if they “use…a third-party service” unless they “are specifically permitted to do so under the service’s terms of use.” In other words, Apple specifically prohibits developers from offering tools that displease other companies’ shareholders, no matter whether this pleases Apple customers:
https://developer.apple.com/app-store/review/guidelines/#intellectual-property
Note that clause 5.2.2 of Apple’s developer agreement doesn’t say “You mustn’t violate a legally enforceable term of service.” It just says, “Thou shalt not violate a EULA.” EULAs are garbage-novellas of impenetrable legalese, larded with unenforceable and unconscionable terms.
Apple sometimes will displease other companies on your behalf. For example, it instituted a one-click anti-tracking setting for Ios that cost Facebook $10 billion in a matter of months:
https://www.cnbc.com/2022/02/02/facebook-says-apple-ios-privacy-change-will-cost-10-billion-this-year.html
But Apple also has big plans to expand its margins by growing its own advertising network. When Apple customers choose ad-blockers that block Apple’s ads, will Apple permit it?
https://www.wired.com/story/apple-is-an-ad-company-now/
The problem with app stores isn’t whether your computing experience is “curated” — that is, whether entities you trust can produce collections of software they vouch for. The problem is when you can’t choose someone else — when leaving a platform involves high switching costs, whether that’s having to replace hardware, buy new media, or say goodbye to your friends, customers, community or family.
When a company can leverage its claims to protecting you to protect itself from you — from choices you might make that ultimately undermine its shareholders interests, even if they protect your own interests — it would be pretty goddamned naive to expect it to do otherwise.
More and more of our tools are now digital tools, whether we’re talking about social media or cars, tractors or games consoles, toothbrushes or ovens:
https://www.hln.be/economie/gentse-foodboxleverancier-mealhero-failliet-klanten-weten-van-niets~a3139f52/
And more and more, those digital tools look more like apps than Cuecats, with companies leveraging “IP” to let them control who can compete with them — and how. Indeed, browsers are becoming more app-like, rather than the other way around.
Back in 2017, the W3C took the unprecedented step of publishing a DRM standard despite this standard not having anything like the consensus that is the norm for W3C publications, and the W3C rejected a proposal to protect people who reverse-engineered that standard to add accessibility features or correct privacy defects:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2017/09/open-letter-w3c-director-ceo-team-and-membership
And while we’re seeing remarkable progress on Right to Repair and other policies that allow the users of technology to override the choices of vendors, there’s another strong regulatory current that embraces companies’ ability to control their users, in the hopes that these big companies will police their users to prevent bad stuff, from controversial measures like filtering for copyright infringement to more widely supported ideas like blocking child sex abuse material (CSAM, AKA “child porn”).
There are two problems with this. First, if we tell companies they must control their users (that is, block them from running plugins, mods, skins, filters, etc) then we can’t tell them that they must not control their users. It comes down to whether you want to make Mark Zuckerberg better at his job, or whether you want to abolish the job of “Mark Zuckerberg.”
https://doctorow.medium.com/unspeakable-8c7bbd4974bc
Then there’s the other problem — the gun on the mantelpiece problem. If we give big companies the power to control their users, they will face enormous internal pressure to abuse that power. This isn’t a hypothetical risk: Facebook’s top executives stand accused of accepting bribes from Onlyfans in exchange for adding performers who left Onlyfans to a terrorist watchlist, which meant they couldn’t use other platforms:
https://gizmodo.com/clegg-meta-executives-identified-in-onlyfans-bribery-su-1849649270
I’m not a fan of terrorist watchlists, for obvious reasons. But letting Facebook manage the terrorist watchlist was clearly a mistake. But Facebook’s status as a “trusted reporter” grows directly out of Facebook’s good work on moderation. The lesson is the same as the one with Apple and the ads — just because the company sometimes acts in our interests, it doesn’t follow that we should always trust them to do so.
Back to Shannon Vallor’s question about the origins of “modern tech’s long spiral into user manipulation and surveillance” and how that “killed off the joy that people like me used to feel about new tech”; and Wil Wheaton’s “constant dread of ‘How will this complicate things as I try to maintain privacy and sanity.”
Tech leaders didn’t get stupider or crueler since those halcyon days. The tech industry was and is filled with people who made their bones building weapons of mass destruction for the military-industrial complex; IBM, the company that gave us the PC, built the tabulating machines for Nazi concentration camps:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IBM_and_the_Holocaust
We didn’t replace tech investors and leaders with worse people — we have the same kinds of people but we let them get away with more. We let them buy up all their competitors. We let them use the law to lock out competitors they couldn’t buy, including those who would offer their customers tools to lower their switching costs and block abusive anti-features.
We decided to create “Felony Contempt of Business Model,” and let the creators of the next Cuecat reach beyond the walls of their corporate headquarters and into the homes of their customers, the offices of their competitors, and the handful of giant tech sites that control our online discourse, to reach into those places and strangle anything that interfered with their commercial desires.
That’s why plans to impose interoperability on tech giants are so exciting — because the problem with Facebook isn’t “the people I want to speak to are all gathered in one convenient place,” no more than the problem with app stores isn’t “these companies generally have good judgment about which apps I want to use.”
The problem is that when those companies don’t have your back, you have to pay a blisteringly high price to leave their walled gardens. That’s where interop comes in. Think of how an interoperable Facebook could let you leave behind Zuckerberg’s dominion without forswearing access to the people who matter to you:
https://www.eff.org/interoperablefacebook
Cuecats were cool. The people who made them were assholes. Interop meant that you could get the cool gadget and tell the assholes to fuck off. We have lost the ability to do so, little by little, for decades, and that’s why a new technology that seems cool no longer excites. That’s why we feel dread — because we know that a cool technology is just bait to lure us into a prison that masquerades as a fortress.
Image: Jerry Whiting (modified) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:CueCat_barcode_scanner.jpg
CC BY-SA 3.0: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
[Image ID: A Cuecat scanner with a bundled cable and PS/2 adapter; it resembles a plastic cat and also, slightly, a sex toy. It is posed on a Matrix movie 'code waterfall' background and limned by a green 'supernova' light effect.]
7K notes
·
View notes
Link
0 notes
Text
How to Properly Check IDs
An ID card scanner displays and records the data saved on a driver's license, state ID or navy ID. This sometimes contains age, date of start, name, deal with and card expiration date. While this will simply help a bouncer weed out expired IDs and underage IDs, it does not mechanically detect faux IDs. For an ID scanner to be best at detecting pretend IDs, the operator must manually examine the information printed on the ID with the knowledge stored within the ID.
The barcode and magnetic stripe on a typical driver's license incorporates the identify, tackle, date of birth, height, weight, eye shade, hair colour, license number, and license challenge and expiration dates. The ID card scanner displays this info in a simple-to-read format on a display and data the transaction in a database.
Nevertheless, the name saved on the cardboard might read "John Smith." It's common follow for fake IDs makers to easily print new information on a card that has already been encoded with other information. Since it is much more durable to encode the information saved on a magnetic stripe or barcode than it's to print on a blank card, faux ID makers usually buy pre-encoded playing cards in bulk and print totally different names, addresses and birthdays on the entrance. These playing cards are marketed to minors as "scannable faux IDs." They will scan, but the data printed on the card will not match the data stored throughout the card.
An ID card scanner makes it doable for a bouncer, bartender or liquor retailer clerk to see the information encoded on the ID card. With out an ID scanner there isn't any strategy to access this information. An ID scanner operator should physically examine the data proven on Click here for Blog the ID to the data displayed on the ID scanner. If the information on the front of the card doesn't match the info stored within the card, it is possible that the ID is faux. On this method, an ID scanner can show a useful software for checking the authenticity of IDs.
An ID card scanner is a instrument to display and document the information saved on an Identification Card. It can help a bouncer uncover a fake ID by revealing the data encoded on the cardboard and making it out there to be in contrast with the knowledge printed on the cardboard. However, an attentive user must manually examine the 2 sets of information. A bouncer may check with other bodily safety gadgets like holograms, photos and card material to assist decide the authenticity of an ID.
Contrary to widespread belief, commercially accessible ID scanners don't run the license number against the official state database for authenticity. The state-managed databases that contain license data cannot be accessed by the general public. An ID scanner records the license number and information as evidence that age was diligently verified, but it doesn't examine to see if the license number is valid in a state database. Only authorized authorities can check to see if a license number is legitimate.
Some companies market "Faux ID Scanners." These products are purposefully deceptive. An ID scanner is an important tool for accessing identification card info, but it isn't a machine to detect fake IDs. In case you are trying to purchase an ID scanner for your small business, look for a good company that actually describes the capabilities and limitations of its merchandise.
Do a web-based seek for "pretend ids" and you will be amazed to discover how easy it can be to obtain an ID allowing you to pose as someone else. Or how easy it can be for another person http://www.club21ids.is/ to acquire an ID that can allow him or her to pose as you. Some web sites peddle poor high quality cards, others offer excellent high quality, and lots of web sites are merely scams.
The very fact is, our present identification techniques are insufficiently safe, and our identifying documents are simply copied. Anybody with a pc, scanner and printer can recreate an ID. Outdated systems exasperate the issue by making it too straightforward to acquire a real ID at the DMV, with both respectable or falsified info.
One other glitch is the potential for people to fully alter their appearances. Males with facial hair can wreak havoc on the present system. This is generally executed as a prank. In different cases, the person is trying to subvert the system to maintain a level of anonymity. New applied sciences, reminiscent of facial recognition, should eventually resolve a few of these problems, but they're nonetheless years away from being absolutely applied.
In Indianapolis, Indiana, a man was capable of obtain six totally different IDs. He accomplished this by visiting various completely different registries all through the state and using borrowed names and stolen info. He obtained job applicant knowledge from a failed physique shop enterprise he had owned. He used the false identities to open checking accounts at a number of banks and write fraudulent checks to himself. He was caught whereas Fake IDs applying for his seventh ID, because of facial recognition software program. But it is disturbing to know that he was able to purchase six completely different identities, all stolen from real folks, without detection. It was a financial institution employee who eventually observed that he had two different bank accounts beneath two totally different names. If the man hadn't been so greedy, he would have gotten away with it.
In Indianapolis and other registries the daily photographs are in comparison with hundreds of thousands of others already on file. The system continually scans the information and presents circumstances which may match, requiring further investigation by registry workers.
Some of the requirements of improving facial recognition include not smiling to your picture or smile so long as you retain your lips collectively. Different necessities meant to assist the facial recognition software program embrace protecting your head upright (not tilted), not wearing eyeglasses in the photo, not carrying head coverings, and retaining your hair from obscuring your brow, eyebrows, eyes, or ears.
As state and native authorities crack down on underage ingesting, the fines and charges on businesses that promote alcohol to minors continues to increase. Anyone underneath the age of 21 just isn't permitted to purchase or drink alcohol. Tobacco gross sales are age-restricted as effectively. Enforcement by federal, state and native officers is anticipated, and plenty of bars, grocery stores, restaurants and nightclubs are scrambling for a strategy to keep one step ahead of those sporting pretend ID playing cards to keep away from infractions. Checking IDs isn't enough. False identification is available and a few young individuals go to every effort to go to bars or buy alcohol and tobacco merchandise from legit businesses. It may be a standing symbol for the underage patron to "get away with it."
Whereas some fakes could be noticed easily, others are rather more tough to distinguish between the actual deal and people made at home on a pc. The actual fact remains that no matter what, the enterprise Wikipedia Here institution will probably be still be held responsible for serving minors if the alcoholic beverage management board or a legislation enforcement company discovers they've achieved so.
One way to fight that is by means of trendy expertise. There are now portable ID scanners obtainable that help businesses verify the age and authenticity of the individual attempting to enter or make purchases. These devices have age verification software program that documents the process. An digital readout is activated by swiping the magnetic strip on a driver's license or identification card. This protects the bar or nightclub from admitting patrons that are not allowed to be there or denying unlawful gross sales to minors. By buying these machines for hand-held or fastened use, institutions can weed out the minors and stop trouble. Most are battery-operated and decode magnetic strips by a easy swipe of the stripe. If the ID is false, an alarm will sound. The false info can be stored in the machine by way of the software program for future reference, if needed.
Because of this, these businesses are defending themselves from losing money and business on infraction enforcement. For instance, companies getting caught for serving minors can be given a stiff monetary punishment of www.club21ids.is/ several hundred dollars on the first infraction. It increases with extra violations. Authorized expenses, akin to contributing to the delinquency of a minor, include legal professional's fees and possibly extra fines.
In some states, shutting down a business for the evening after a raid on minors can cost a whole bunch or hundreds of dollars in revenue. In some states, a third infraction leads to automatic revocation of the liquor license and prison fees as properly. When a company loses its liquor license altogether, they will seemingly go out of business.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Why Automated Data Capture Solutions are a Smart Way Forward for Businesses?
Whether it’s CRM software used to track sales, ERP software for streamlining production, email software for tracking communication, advertising software used for marketing (Meta ads, LinkedIn ads, Google ads, Bing ads, etc.), or other third-party apps for streamlining business operations—organizations have customer data dispersed across a myriad of platforms.
According to Statista, the total amount of data created, copied, and consumed globally had already reached 64.2 zettabytes in 2020. The same is expected to reach more than 180 zettabytes by 2025. Organizations tapping into data-driven decision-making to pull ahead of the competition have to collect these vast amounts of data produced and extract intelligence using data analysis.
As evident, the amount of data being produced in the world is growing exponentially, but the majority of it is unstructured which makes it unfit for business consumption. Keeping a record of all the differences and working on extracting information can be extremely time-consuming.
Whether it’s the image, audio, video, text, or big data, when well collected, organized, and processed can be used to drive business success and growth through leveraging modern technologies such as Robotic Process Automation, Artificial Intelligence, and Machine Learning. Growth-focused companies understand that data collection lays the foundation for the data processing and analysis stage; thus, they automate their data aggregation process to accelerate their time to value.
The Automation Advantage
Remember cash registers where each product had to be entered manually by employees? Take another example of supply chains where passing an item from one level to the next of the chain meant filling in a ridiculous amount of paperwork. These manual tasks were made easy with the help of barcode scanners—one of the first examples of data capture systems that accelerated item identification and processing.
However, the world has now moved beyond data collection devices such as RFID readers or barcode scanners into fully automated data collection systems and smart data capture solutions. These automatic data capture platforms take all of a company’s data sources such as CRMs, ERPs, advertising software, emails, accounting software, etc., and extract valuable information without the need for a programmer to do the coding-decoding.
Smart data transformation solutions combine human expertise with AI, ML, and RPA. Hence, whether you have public or proprietary data in a raw unorganized format, automatic solutions can help you transform them into tagged and schema-compliant structured XML for data products, analytics, and AI/ML applications.
Automated Data Capture Methods
Automated data capture systems come in different methods and forms that change based on the unique needs of a business. Additionally, the level of automation can be changed to meet certain character recognition requirements. Listed below are some of the most common automated data capture methods:
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
As the first revolutionary technology in automated data capture, Optical Character Recognition is used to convert typed documents, PDF files, images, or scanned documents into editable, searchable, digital documents.
Since the 1990s, OCR has helped companies across multiple sectors including healthcare, finance, logistics, and governments, to digitize their files accurately. It is extremely helpful for sectors dealing with sensitive information such as patient information and medical claims.
Optical Mark Recognition (OMR)
This is another excellent way to manage all the documents. Optical Mark Recognition not only recognizes characters but also scans documents for marks such as filled-in bubbles and checkmarks. OMR is commonly used to expedite and facilitate capturing of human-marked details including consumer feedback or surveys, multiple-choice tests, symptoms checklists, poll results, etc.
Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR)
Intelligent Character Recognition technology leverages Machine Learning to teach machines to comprehend handwritten documents and focuses on solving complex challenges. Though the accuracy offered is not that high, ICR can save significant time processing handwritten documents.
Intelligent Document Recognition (IDR)
Intelligent Document Recognition is a highly sensitive and accurate data capture method from any part of a document, including the tags and meta description. It is more like a complex type of Optical Character Recognition, which is used to extract data from unstructured documents such as medical forms, delivery notes, and invoices.
Additionally, IDR is capable of interpreting patterns, tables, and content in both paper and electronic formats, recognizing the start and the end of a document, as well as sorting documents according to their category. This method is commonly used in legal, logistics, mailrooms, and accounting companies.
Voice Recognition
If you have Siri, Alexa, Cortana, or Google Assistant, you are already using some type of voice recognition algorithm. Voice Recognition technology leverages Natural Language Processing (NLP) embedded in Deep Learning algorithms to recognize and comprehend different voice patterns. It has countless applications when combined with smart chatbot technologies as they can provide excellent customer service, support, and security.
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR)
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition Technology is used to identify specially formatted characters printed in magnetic ink. This is commonly used in banks to speed up the processing of checks and other documents. One of the good things about this technology is that people can read the data as well.
Benefits of Automated Data Capture
Faster Turnaround Times
Processing speed is one of the unavoidable benefits of automated data capture. Imagine how a nightclub bouncer would have a difficult time trying to verify the age of a customer by looking at them or the time it would take to manually process, proofread and mail out medical claims. With ID scanning software, this process would take a few seconds.
Minimized Errors
Manual data entry includes high chances of human error. However, you can easily avoid these mistakes with automated data processing as the smart data collection software can swiftly scan through documents. They can compare these documents to templates and other files to assure data is complete and things such as names, gender, and date of birth are accurate on sensitive documents.
Boosted Efficiency
With automated data collection systems at your disposal, you can simplify complex tasks that in turn help you to increase efficiency. Besides, replacing physical files with digital files serves to eliminate workplace clutter and makes all files accessible to authorized persons from any device and at all times.
Cost Savings
Numerous organizations have turned to automation because of its cost-saving benefits. You can eliminate costs related to ongoing training, extra labor, equipment maintenance, document storage, and system updates with automation.
Greater Employee Satisfaction
Outdated manual processes like prolonged data entry are both mentally and physically taxing, which makes it difficult for employees to focus on such arduous tasks for a long duration. Automating such processes facilitates employees to better focus on more engaging tasks or core competencies.
Endnote
Among the benefits of automated data capture solutions include faster turnaround times, cost-optimization, reduced human errors, enhanced customer experience, and greater employee satisfaction.
The Statista reports proved the same as most respondents agreed that automation reduced the risk of equipment failure, performance issues, data breaches, and regulatory compliance violations, as of 2021. At the same time, 50 percent of respondents agreed that automation processes give more space to the IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives. Hence, you already know what to do next.
READ HERE INSPIRED BLOG: https://www.datasciencesociety.net/why-automated-data-capture-solutions-are-a-smart-way-forward-for-businesses/
0 notes