#CNC Router 4 axis
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Video
youtube
STARMA 3 axis 4 axis cnc router 6060 Milling And Engraving Machine
#youtube#STARMA 3 axis 4 axis cnc router 6060 Milling And Engraving Machine Main specifications: 2.2kw water cooling spindle DSPA11 control system S
0 notes
Text
EXPLORING THE 5 COOL PARTNER SELLER ELECTRONICS PRODUCTS-Part1
Exploring the 5 Cool Partner Seller Electronics Products
Prologue
Are you an electronics enthusiast looking to expand your electronics project repertoire? Want to take your skills to the next level by exploring new and exciting products? Look no further than our list of five cool electronics products from partner sellers!
Whether you’re interested in building your own smart home devices, experimenting with sensors, or creating your own robot, these products are sure to inspire you. They cover a lot of application areas, from loop detectors used to monitor vehicle count in parking garages to Arduino CNC shields used in CNC machines, from simple pulse sensors used to detect cardiovascular pulse signals from fingertip to RGB LED panel light used in smart home, these products are unique, compact, and functional. Not only are these products fun to build and use but they’re also designed to help you learn new skills and techniques along the way.
What’s more, these products all come from trusted partner sellers who are committed to developing high-quality products. They’re happy to provide technical support for customers who have questions, so you can be sure you’re getting the best in electronics.
So get ready to dive into the world of electronics and explore these five cool partner seller products. You’re sure to find something that piques your interest and takes your own electronics projects to the next level.
Inductive Loop Vehicle Detector by Elektronika-ba
Whether you need to monitor occupancy and count vehicles in parking garages, control vehicle access at door and barrier controls, or facilitate traffic light installations and traffic controllers, the inductive loop detector is the perfect solution. It can even detect the direction and speed of vehicle traffic, making it an invaluable tool for a variety of traffic-related applications. In addition, this device can function as a stand-alone speed trap and can be easily interfaced with Arduino.
We can also provide a pre-programmed PIC chip to meet your project requirements.
Specifications
Number of operating modes: 4
Tuning: Automatic
Detection type: Presence/Pulse
Presence time: Adjustable in 3 steps
Pulse duration: 250 ms / 500 ms
Signal filtering: Adjustable in 2 steps (NORMAL, HIGH)
Loop inductance: 20 uH — 1000 uH
Frequency range: 20 kHz — 145 kHz
Frequency selection: 2 combinations (LOW, HIGH)
Sensitivity: Maximum 0.0025% Δf/f, adjustable in 8 steps
Detection speed: 10 ms by default, adjustable
Start-up time: ~ 1 second per channel (or longer if the frequency is not stable)
Temperature range: -35°C — 120°C
Sensor protection: Galvanic isolation + gas discharge tube for lightning protection
Don’t settle for less — click here to learn more about the Inductive Loop Vehicle Detector and experience the compact, yet cool detector!
Arduino CNC Shield V3.51 by Protoneer
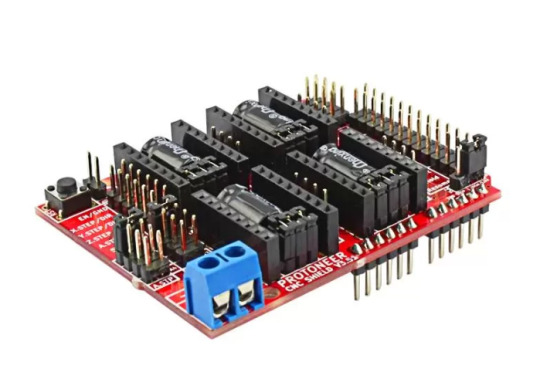
Designed by Protoneer, this kit is packed with features to ensure high precision control of your stepper motors, you can use it to easily build small CNC routers, DIY laser cutters, 3D printers, or any project that requires precise stepper motor control.
Our latest version 3.51 includes several enhancements to make assembly and installation even easier. We’ve added end-stop and probe signal filtering circuitry to eliminate false triggers and allow the use of unshielded cables for end-stops and probes. We’ve also increased the size of the solder pads for easier assembly and updated the probe pin labels to make installation a breeze.
With the Arduino CNC Shield Kit, you’ll have everything you need to build your own CNC router or mill with ease.
Features
Includes Noise Filers on all end stops and the probing pin. (New in V3.51)
GRBL 0.9 compatible. (Open source firmware that runs on an Arduino UNO that turns G-code commands into stepper signals https://github.com/grbl/grbl)
4-Axis support (X, Y, Z, A-Can duplicate X, Y, Z or do a full 4th axis with custom firmware using pins A4 and A3)
2 x End stops for each axis (6 in total)
Coolant enable
Uses removable Pololu A4988 compatible stepper drivers. (A4988, DRV8825 and others)(Not Included)
Jumpers to set the Micro-Stepping for the stepper drivers. (Some drivers like the DRV8825 can do up to 1/32 micro-stepping )
Compact design.
Stepper Motors can be connected with 4-pin molex connectors or soldered in place.
Runs on 12–36V DC. (At the moment only the Pololu DRV8825 drivers can handle up to 36V so please consider the operation voltage when powering the board.)
Don’t wait — click here to see more about the Arduino CNC Shield V3.51 and start your next project today!
Easy Pulse Mikro by Embedded Lab
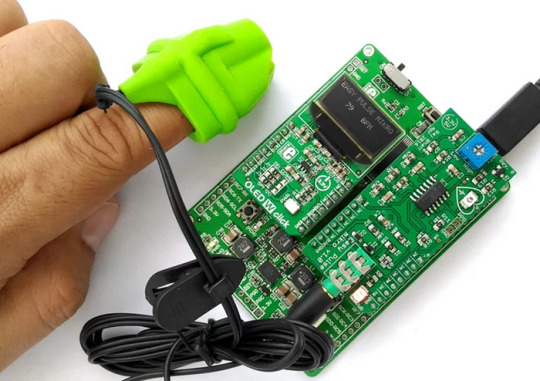
What’s more, the Easy Pulse Mikro is designed in the convenient Mikro bus form factor, making it easy to integrate with a wide range of mikroElektronika’s development boards. With all necessary instrumentation and amplification built right in, this powerful sensor provides a clean and precise analog PPG waveform output that’s routed to the AN pin of the mikroBus connector.
Whether you’re a hobbyist, student, or professional developer, the Easy Pulse mikro is the perfect tool for monitoring heart rate and other vital signs.
Click here to see more about the Easy Pulse mikro.
Features
Compatible with mikroBus socket.
Filtered and amplified analog PPG signal output
On-board potentiometer for adjusting amplifier gain, if needed (rotate clock-wise for increasing gain)
Onboard LED for indicating heartbeat. It flashes synchronously with the heartbeat on detecting the pulse from the fingertip.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How CNC Machining Services Work: An Overview

CNC machining is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering high precision, speed, and flexibility for producing intricate parts and components. From aerospace to automotive, electronics to industrial machinery, CNC machining services are critical in fabricating parts that meet exact specifications. Whether you're a product designer or a manufacturing engineer, understanding how CNC machining works can help you leverage its benefits effectively.
What Is CNC Machining?
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process where material is removed from a solid block—known as a blank or workpiece—using a variety of cutting tools. The process is controlled by pre-programmed computer software that dictates the movement of machines such as mills, lathes, routers, and grinders. Unlike manual machining, CNC systems operate with extraordinary precision and repeatability, making them ideal for high-tolerance, complex parts.
Key Components of CNC Machining Systems
Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Everything starts with a 3D model or a technical drawing of the desired part. Engineers or designers use CAD software to define dimensions, geometries, and tolerances.
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM): The CAD file is then imported into CAM software, which generates a toolpath and converts the design into G-code—a programming language that CNC machines understand.
CNC Machine: The G-code is uploaded to the CNC machine, which follows the programmed instructions to execute precise movements and tool changes. Machines may be 3-axis, 4-axis, or even 5-axis, depending on the complexity of the part and the number of simultaneous movements required.
Cutting Tools: Depending on the material and design, different cutting tools are used, such as end mills, drills, or turning tools. The choice of tool affects surface finish, cutting speed, and overall efficiency.
Workholding: Fixtures and vises secure the workpiece in place during machining, ensuring stability and accuracy.
The CNC Machining Workflow
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the typical CNC machining process:
1. Design & Planning
The journey of custom CNC machined parts begins with a detailed design. Engineers define all technical requirements, including geometry, material selection, surface finish, and tolerance. This stage is crucial because the CAD model directly influences machining feasibility and cost.
2. Programming
CAM software interprets the CAD model to produce G-code. This code tells the CNC machine what actions to perform—movements along the X, Y, and Z axes, spindle speeds, feed rates, tool changes, and more.
3. Setup
A technician sets up the machine by loading the workpiece, installing the required tools, and configuring the machine based on the program. This step may also involve calibrating the tool offsets and checking initial positions.
4. Machining
Once everything is set up, the machine starts removing material as per the G-code instructions. The process could involve multiple operations such as drilling, milling, turning, or tapping. Multi-axis machines can produce complex geometries in a single setup, reducing lead time and improving precision.
5. Inspection & Quality Control
After machining, the part is inspected using precision measurement tools such as calipers, micrometers, or Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM). This step ensures that the final product meets all specified dimensions and tolerances.
6. Finishing Operations
Depending on the application, post-machining processes like deburring, anodizing, or powder coating may be applied. These finishing steps enhance durability, corrosion resistance, or aesthetics.
Types of CNC Machining
There are several types of CNC machining processes, each suited for specific applications:
Milling: A rotating cutting tool moves along multiple axes to remove material.
Turning: The workpiece rotates while a stationary cutting tool shapes its exterior or interior.
Drilling: Straight holes are created using a rotating drill bit.
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): Material is removed using electrical sparks—ideal for hard materials or intricate cavities.
Grinding: A rotating wheel removes material to achieve high surface finish and tight tolerances.
Advantages of CNC Machining
Precision: CNC machines can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.001 inches, ideal for high-performance industries.
Repeatability: Once programmed, the machine can produce thousands of identical parts with minimal variation.
Flexibility: CNC services can handle one-off prototypes or high-volume production runs.
Efficiency: Faster turnaround times and reduced manual labor.
Material Versatility: Supports a wide range of materials including metals (aluminum, steel, titanium), plastics (nylon, ABS, PEEK), and composites.
Applications of Custom CNC Machined Parts
Custom CNC machined parts are essential in industries where performance and reliability are non-negotiable:
Aerospace: Complex components such as turbine blades, housings, and brackets.
Medical Devices: Surgical instruments, prosthetics, and diagnostic equipment.
Automotive: Engine components, transmission parts, and custom performance mods.
Robotics & Automation: Gears, end-effectors, and structural parts.
Consumer Electronics: Housings, frames, and connectors.
At MS Machining, our team specializes in producing high-quality custom CNC machined parts tailored to exact client specifications. Whether you need prototypes or full-scale production, MS Machining delivers consistent quality with fast lead times.
Why Choose MS Machining?
When it comes to custom CNC machined parts, choosing the right partner can make all the difference. Here's what sets MS Machining apart:
State-of-the-Art Equipment: We operate a fleet of advanced 3-, 4-, and 5-axis CNC machines.
Experienced Technicians: Our machinists have years of hands-on experience across multiple industries.
Fast Turnaround: We streamline production timelines without compromising quality.
Material Expertise: From exotic alloys to engineering plastics, we handle diverse materials with precision.
Quality Assurance: Every part undergoes rigorous inspection to ensure it meets or exceeds your requirements.
Whether you're a startup developing your first prototype or a large enterprise needing scalable production, MS Machining is your trusted source for dependable CNC machining services.
The Future of CNC Machining
CNC machining is constantly evolving, with emerging technologies like AI, machine learning, and automation pushing the boundaries further. Predictive maintenance, adaptive toolpath optimization, and real-time quality monitoring are enhancing productivity and reliability. As industries continue to demand higher performance and customization, CNC machining will remain a foundational technology for manufacturing innovation.
Final Thoughts
CNC machining is more than just a fabrication method—it's a bridge between concept and reality. With its unparalleled accuracy, versatility, and efficiency, it enables manufacturers to produce everything from simple fixtures to complex aerospace components. Companies like MS Machining are at the forefront, delivering precision-crafted custom CNC machined parts that help bring ambitious designs to life.
Whether you're exploring rapid prototyping or full-scale manufacturing, understanding how CNC machining services work empowers you to make informed decisions and achieve superior results.
0 notes
Video
youtube
4 axis cnc stone marble granite carving machine, 4 axis stone cnc router...
0 notes
Text
5 Common CNC Router Controller Issues and How to Fix Them

In the world of modern manufacturing, CNC routers are indispensable for achieving precision and efficiency. However, even the most advanced machines are vulnerable to technical glitches—particularly with their controllers. A CNC router controller is essentially the command center that translates software instructions into physical movement. When something goes wrong here, it can bring your entire operation to a halt.
This article dives deep into the five most common CNC router controller issues, how to troubleshoot them effectively, and what you can do to prevent them in the future. Whether you're running a small shop or managing a high-volume production line, these insights will help keep your machine in top shape.
1. Controller Won’t Power On
You hit the switch—and nothing. No lights, no motion, no signs of life.
Why It Happens:
Blown fuses or breakers.
Loose or disconnected power cables.
Malfunctioning power supply unit (PSU).
Incorrect input voltage or surge damage.
How to Fix It:
Check and replace any blown fuses.
Make sure power cords are firmly connected and not frayed.
Test the PSU with a multimeter to verify correct output voltage.
Use a voltage regulator or surge protector to prevent future damage.
Pro Tip: Label your power supply connections clearly during setup. It makes troubleshooting faster and easier.
2. Freezing or Crashing During Jobs
Midway through a cut, your router suddenly locks up. Job ruined, material wasted.
Why It Happens:
Controller overheating due to poor airflow.
Bugs or incompatibility in the firmware/software.
Memory overload from excessive G-code complexity.
EMI (electromagnetic interference) or loose data connections.
How to Fix It:
Keep the controller clean and properly ventilated.
Ensure all software and firmware are updated to stable versions.
Break up large files into smaller toolpaths.
Use shielded cables and ensure proper grounding to eliminate EMI.
Maintenance Hack: Consider using CNC Control Retrofits that come with improved cooling and processing power to reduce these occurrences significantly.
3. Axis Movement Not Working
If your CNC router won’t move along the X, Y, or Z axis, you’re essentially grounded.
Why It Happens:
Stepper driver failure.
Motor or cable disconnects.
Faulty G-code or coordinate settings.
Loose or stripped motor couplings.
How to Fix It:
Double-check driver and motor connections.
Test drivers individually by swapping them between axes.
Inspect and fix any loose mechanical parts.
Review your CAM setup to ensure proper motion commands are being sent.
Upgrade Tip: If your machine frequently suffers from axis issues, consider CNC Control Retrofits that upgrade your stepper systems to more reliable and powerful servo motors.
4. Controller Doesn’t Connect to Computer
You plug in the USB cable and nothing happens—no connection, no control.
Why It Happens:
Outdated or missing drivers.
Cheap or damaged USB cables.
Wrong COM port selected in software.
Firmware and software version mismatch.
How to Fix It:
Install the correct drivers (often CH340 or FTDI).
Replace USB cable with a short, shielded one.
In your control software, manually select the correct COM port.
Verify the firmware on your controller is compatible with your software version.
Pro Note: Avoid USB hubs. Connect directly to your PC's port whenever possible.
5. Spindle Won’t Start or Has Speed Issues
Spindle problems can cause major setbacks—especially when cuts rely on consistent speeds.
Why It Happens:
No PWM or analog control signal.
Misconfigured spindle driver or VFD.
Incorrect G-code spindle commands (e.g., M3, S1000).
Motor overload or faulty wiring.
How to Fix It:
Ensure all spindle control wiring is secure and accurate.
Verify VFD settings align with your spindle motor specs.
Use test commands (M3 S1000, M5) to isolate the problem.
Test spindle motor directly to confirm it’s functional.
Expert Insight: CNC Control Retrofits often include improved spindle control systems, allowing for smoother and more reliable speed regulation across various materials.
Bonus: Preventing CNC Controller Problems
Fixing problems is good. Preventing them is better. Here’s how:
Regular Cleaning: Dust buildup is the silent killer of electronics.
Firmware Updates: Always run the most stable versions—not betas.
Cable Management: Keep power and signal wires separated.
Surge Protection: Always use voltage regulators or UPS systems.
Monthly Checklist: Schedule a 15-minute inspection every month to check connections, clean filters, and back up your machine settings.
Conclusion
CNC routers are amazing tools—but only when the controller is functioning flawlessly. Whether you're dealing with power issues, motion problems, or connectivity failures, the key is understanding what’s going wrong and how to fix it efficiently.
As we've seen, many common problems can be traced back to simple issues like loose wires or outdated software. But if you're constantly struggling with performance or compatibility, it's worth considering CNC Control Retrofits to upgrade aging systems with modern, more reliable hardware.
By applying the strategies in this guide, you'll not only be ready to fix issues quickly, but you'll also be in a strong position to prevent future downtime, maximize efficiency, and get the most out of your CNC investment.
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
CNC Router Carving Machine 4 axis tilting 180 degree and with Saw Cuttin...
0 notes
Text
4 Axis CNC Router for Foam, Aluminum, Wood Mold Processing
The 4 axis CNC router has become an indispensable tool in the fields of mold processing and fabrication. Whether working with foam, aluminum, or wood, these machines offer unparalleled precision, versatility, and efficiency.
4 Axis CNC Router
A 4 axis CNC router is a computer-controlled machine that can move along four different axes: X, Y, Z, and an additional rotational axis (A-axis). This additional axis allows for more complex and intricate cuts, making it ideal for mold processing and other detailed fabrication tasks.
The 4 axis machining centre at a good price, provide several configurations to meet different requirement, perfect for several kinds of foam and mould router, the innovation model designed by iGOLDENCNC, combined with a competitive set of configurations. Hot applications include:
>Carving all kinds of non-metal materials processing such as foam, lost foam, automobile foam mold, yacht mold, large ship wooden mold, cast wooden mold, engineering plastic materials, aviation wooden mold, propeller, train wooden mold, etc. >Foam processing of automotive stamping molds, casting wood molds, automotive interiors, processing of engineering plastic materials; >Other industry molds: electrical appliance molds, lighting molds, ceramic sanitary ware, three-dimensional curved surfaces for large musical instruments, instrument molds, home appliance molds, air-conditioning molds, automotive molds, automotive interior molds, automotive bumper molds, automotive instrument table molds, etc.
Benefits of Using a 4 Axis CNC Router for Mold Processing
Precision and Accuracy
4 axis CNC routers offer exceptional precision and accuracy, allowing for the creation of intricate designs and complex shapes. The computer-controlled movements ensure consistent and high-quality cuts.
Versatility
These machines can work with various materials, including foam, aluminum, and wood. This versatility makes them ideal for a wide range of mold processing projects.
Complex Geometries
The additional rotational axis (A-axis) allows for the creation of complex geometries and detailed features that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional 3 axis routers.
Efficiency
4 axis CNC routers can operate at high speeds, significantly reducing production time. The automation of the cutting process allows for continuous operation, increasing overall productivity.
Material Efficiency
CNC routers minimize material waste by producing precise cuts and shapes. This efficiency is particularly beneficial when working with expensive materials like aluminum.
4 Axis CNC Router for Foam Parameter
ModeliGW-MC-2060Working area2000*6000*1100mmSpindleChina HQD 9kw atc air cooling spindle + swing 180 degreeInverterFulingMotorJapan Yaskawa 850W servo motorDriverJapan Yaskawa 1kw servo driverControl SystemSyntec 6MB control system + hand wheelTableVacuum & T-slot table with 7.5kw air vacuum pumpTransmissionXY helical rack, Z Taiwan TBI ball screwGuide railTaiwan linear guideBall screwZ TBI ball screwBodyThick steel tube Welded bodyBeamSteel beamColumnsSteel columnsControl boxIndependent control boxColourCustom madeLubricationAutomatic oilingTool SettingAutomatic Tool Calibration SensorDust collectorDouble bag dust collectorVoltage3 Phase/380V/50HZRotary axisOptional part
Applications of 4 Axis CNC Routers in Mold Processing
4 axis CNC routers are used in various applications within mold processing, including:
Foam Molds: Creating detailed foam molds for casting and prototyping.
Aluminum Molds: Fabricating precise aluminum molds for injection molding and other manufacturing processes.
Wood Molds: Producing custom wood molds for casting, forming, and other applications.
Prototyping: Rapid prototyping of complex designs and geometries.
Custom Tooling: Creating custom tooling and fixtures for specialized manufacturing processes.

Choosing the Right 4 Axis CNC Router for Mold Processing
Consider Your Needs
Identify the specific requirements for your mold processing projects, such as the types of materials you will be working with, the complexity of the designs, and the production volume. Choose a machine that meets these needs.
Machine Size and Capacity
Consider the size of the materials you will be cutting and choose a machine with an appropriate bed size and cutting capacity. Larger machines can handle bigger projects, while smaller machines are suitable for detailed work.
Spindle Power
The spindle power determines the cutting capability of the CNC router. Higher power spindles can cut through thicker and harder materials more efficiently. Choose a spindle power that matches your specific cutting requirements.
Software Compatibility
Ensure the CNC machine is compatible with the CAD and CAM software you plan to use. Compatibility ensures seamless design and toolpath generation.
What is the 4 axis CNC Router?
4 axis CNC router is an automatic computer-controlled machine tool whose spindle rotates 180° along the X-axis or the Y-axis to do 3D arc milling and cutting, which is based on the ordinary 3 axis machine tool. 4th axis CNC router is an automated machine tool kit with computer numerical controller for relief carving and sheet cutting, as well as adding the fourth axis (rotary axis) for 3D cylinders milling.
In addition, the 4-axis CNC machine is divided into four-axis three-linkage and four-linkagel, not to say that the rotation is added, it is a four-axis linkage machine tool, and a computer-controlled system with a rotating axis and a four-axis linkage can be called as a real 4 axis CNC machine. Because of the rotation movement of the 4th rotary axis, 3D machining of cylindrical, arc, and circular surfaces is realized.
CNC FOAM CUTTERHot Wire Foam Cutter
3D CNC ROUTER, CNC FOAM CUTTER, CNC ROUTER2060 3d Foam Milling Machine Carving Eps Foam Polystyrene
3D CNC ROUTER, ATC CNC ROUTER, CNC FOAM CUTTER, CNC ROUTERTop 3d CNC Foam Cutting & Carving Machine
HOT4 AXIS CNC ROUTER, CNC FOAM CUTTER, CNC ROUTER, CNC WOOD ROUTER4 Axis Machining Centre CNC Milling Machine for Foam, Aluminum, Wood Mold Processing5.00 out of 5
3D CNC ROUTER, 4 AXIS CNC ROUTER, CNC FOAM CUTTER, CNC ROUTER, CNC WOOD ROUTERDetachable 4 Axis CNC Foam Cutting Machine for EPS, Wood, Metal Carving
HOT4 AXIS CNC ROUTER, CNC FOAM CUTTER, CNC ROUTER, CNC WOOD ROUTER1530 EPS Foam Cutting Machine Mold Making
HOT4 AXIS CNC ROUTER, CNC FOAM CUTTER, CNC ROUTER, CNC WOOD ROUTERDouble Layer 4 Axis CNC Machine for Foam, Aluminum, Wood Mold Making
HOTREAD MOREQUICK VIEWCNC FOAM CUTTER, CNC ROUTERCNC Foam Cutting Machine for EPS, EPP, XPS
A real 4-axis machine tool can cut wood, foam, stone, white marble, human body, Buddha statues, sculptures, handicrafts, furniture. 4-axis is refer to X-Y-Z-A, X-Y-Z-B or X-Y-Z-C, 4 axis are linked, the four axis can work at the same time. If the machine has only three feed axes (X, Y, Z), the Y-axis can be manually replaced with a rotating axis, and it can only be three-axis linkage at most. This is a 4th axis CNC machine, and it is also the usual fake four axis. In terms of use, it can process planes, reliefs, and cylinders. If the machine has four feed axes (X, Y, Z, A), it can be processed with four-axis linkage, and can process planes, reliefs, cylinders, non-standard three-dimensional patterns, and corners of 3D patterns.
1530 CNC Foam Cutter for 3D Foam Mold Carving
3D Carving CNC Router Machine with Three Heads
3D Engraving 5 Axis CNC Machining Center
5 Axis CNC Router Woodworking for Sale
4 Axis CNC Foam Carving Router with Rotary Device
4 Axis EPS/Foam CNC Router Carving Machine
4 Axis Rotary 1325 Wood Carving Cnc Router
CNC 5 Axis Gantry Machining Center
CNC Foam Cutting Machine Hot Wire
Foam Hot Wire Cutter
Customized 1325 CNC Foam Carving&Cutting Machine
Double Work Table 4 Axis CNC Router Machine
0 notes
Text
How CNC Machine Parts Work Together to Create Masterpieces

The precision and efficiency of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines, marvels of modern engineering, are revolutionizing the industry. At the core of these machines is a symphony of interrelated components, each essential to creating complex patterns and works of art. CNC machines provide unmatched accuracy in converting raw materials into completed products, ranging from creative sculptures to aerospace components.
This article explores how a CNC machine's many parts cooperate to produce excellent outcomes.
Understanding CNC Machines
A CNC machine controls its components and tools by adhering to a pre-programmed set of instructions known as G-code. This automated method ensures accuracy and consistency, lowering the possibility of human error.
Although there are many different kinds of CNC machines, such as routers, plasma cutters, lathes, and mills, they all have similar essential parts and purposes.
Essential Components of a CNC Machine and Their Functions
1. The Control Panel
The CNC machine's brain is the control panel, where users enter commands and monitor things.
Role: Its function is to interpret the G-code and convert commands into machine operations.
Features: Features include buttons, touchscreens, and real-time feedback displays.
2. Frame
The CNC machine is structurally stable thanks to the frame.
Role: Provides support for all other parts and dampens vibrations while in use.
Materials: Cast iron, steel, or aluminum are usually used for durability.
3. Spindle
The spindle is the revolving axis that cuts, drills, or mills materials.
Function: Provides the cutting tool with the power to form the material.
Adjustability: Depending on the material and operation, speed and power can be changed.
4. Cutting Instruments
Cutting tools work directly with the material and are replaceable components.
Function: Mold, drill, or engrave materials into desired shapes.
Types: Types include router bits, drill bits, end mills, and lathe tools.
5. Worktable
During machining, the worktable holds the material firmly in place.
Function: Prevents material movement and guarantees stability.
Features: Depending on the machine, it may be fixed or mobile.
6. System of Axes (X, Y, Z)
Thanks to the axis system, the CNC machine can move the workpiece and cutting tool in various directions.
Role: Shapes the material and allows for precise movements.
Types:
X-axis: Horizontal movement on the X-axis.
Y-axis:Vertical movement is the Y-axis.
Z-axis: Movement of depth.
7. Motors
Motors power the spindle and axis movements.
Function: Supply the strength and accuracy required for machining operations.
Types:Types include servo motors and stepper motors.
8. System of Coolant
The cutting tool and material are prevented from overheating by the coolant system.
Function: Ensures smooth cuts, prolongs tool life, and lowers friction.
Types:Types include air jets, lubricants, and water-based coolants.
9. Sensors
Sensors provide feedback to guarantee seamless operation.
Role: Monitor the machining process, measure tool wear, and identify faults.
10. Tool Switch
When performing multi-step tasks, the tool changer automatically switches cutting tools.
Role: Reduces downtime and increases efficiency.
How CNC Parts Work Together
Below, I will describe the following explanation:
1. Machine Programming
First, CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software designs the parts. From this architecture, G-code, which acts as the machine's instructions, is created. This code is sent to the control panel, synchronizing all component movements.
2. Material Positioning
Clamps or a vacuum system secure the material after it is placed on the worktable. Sensors check alignment to guarantee precision.
3. Shaping and Cutting
The spindle begins to work with the proper cutting tool attached. Motors drive the axis system to move the tool in relation to the material. The coolant system guarantees smooth cutting by lowering heat and friction.
4. Automatic Modifications
If the procedure calls for changing tools, the tool changer swaps out the existing tool for a new one. Sensors monitor tool wear and notify the user when a replacement is required.
5. Completing and Examining
Once machining is finished, the component is given final touches, like polishing or deburring. Sensors and inspection systems check accuracy and quality assurance.
CNC Machine Applications
Numerous applications are made possible by the smooth integration of CNC machine elements, such as:
Automotive: Prototypes, gears, and engine parts.
Aerospace: Precision parts, structural elements, and turbine blades.
Healthcare: Prosthetics and surgical tools.
Art & Design: Personalized engravings, sculptures, and furniture.
Electronics: enclosures and circuit boards.
Benefits and CNC Machine
Below, I will describe the benefits of cnc machine:
High Precision: Reliable in creating complex patterns.
Efficiency: Reduced downtime and quicker production.
Versatility: Adaptable to a range of substances and uses.
Automation: Cuts down on errors and manual work.
Cost-Effectiveness: Increases production while reducing material waste.
CNC Machining Challenges
Beside their effectiveness, CNC machines have many drawbacks:
High Initial Cost: Software and machines can be costly.
Complex Setup: Programming and maintenance call for knowledgeable operators.
Material Restrictions: Machining certain materials can be complex.
CNC Machining's Future
CNC machines are becoming more innovative and effective in integrating robots, AI, and IoT. In manufacturing, sophisticated automation, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance are establishing new benchmarks. CNC machines will remain essential to innovation as hybrid technologies develop.
Faqs
1. Is it possible for a single CNC machine to do several tasks?
Indeed, automated tool changers and multi-axis systems allow current CNC machines to transition between tasks, making them incredibly adaptable.
2. What kinds of materials are suitable for a CNC machine?
CNC machines can process materials such as metals (aluminum, steel, titanium), polymers, wood, and composites.
3. How long does it take to learn CNC programming?
Learning the fundamentals of CNC programming may take a few weeks, but months of practice and instruction may be necessary to master more complex techniques.
4. Are CNC machines eco-friendly?
CNC machines are typically environmentally benign because of their high accuracy and low material waste. Nonetheless, coolant disposal and energy use need to be well controlled.
Conclusion
CNC machines demonstrate the effectiveness of precise engineering. These machines can produce masterpieces in various industries by fusing state-of-the-art technology with a beautiful interplay of elements. When CNC parts integrate flawlessly, the possibilities range from intricate aeronautical components to creative designs.
Knowing how CNC machines work can help you realize their full potential and stimulate creativity in your ideas, whether as a manufacturer or a hobbyist.
0 notes
Text
Stone CNC Machine for Perfect Finishes
In the world of stone carving and machining, precision is everything. Whether it's creating intricate sculptures, countertops, or architectural features, a stone CNC machine is the key to achieving flawless results. These machines bring cutting-edge technology into traditional stonework, making processes faster, more efficient, and highly accurate. Using a stone CNC machine can improve the quality of your work, and investing in a CNC machine can greatly improve your business.
What is a Stone CNC Machine?
Stone CNC machine is a computer-controlled system that is designed to cut, carve, and engrave stone with precision. CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control, meaning the machine follows precise instructions given by computer software to perform specific tasks. This automation allows for a level of accuracy that manual methods simply cannot match.
Stone CNC machines come in various types, including routers and mills, with some models offering 3, 4, or even 5-axis capabilities. These machines can work with a variety of materials, including granite, marble, limestone, and even synthetic stones, to create everything from simple engravings to complex, three-dimensional sculptures.

The Advantages of Using a Stone CNC Machine
1. Precision and Accuracy
The most obvious benefit of using a stone CNC machine is the precision it offers. Manual carving, engraving, or cutting stone can be incredibly challenging and time-consuming, especially when aiming for high levels of detail. With a CNC machine, your designs are created with millimeter accuracy, ensuring consistent results with every project. This is especially useful for businesses that require repetitive tasks, such as cutting countertops or engraving gravestones.
The ability to work with complex 3D designs also sets CNC machines apart from traditional methods. Whether you're creating intricate patterns or highly detailed stone sculptures, the CNC machine can bring your vision to life without compromising on quality.
2. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
The automation of a stone CNC machine means faster production times and higher output. Once you input your design into the system, the machine does the rest. This significantly reduces the time spent on manual labor, allowing your business to take on more projects and increase revenue.
Moreover, CNC machines often operate 24/7 with minimal supervision. Once set up, they can continue to work on multiple pieces simultaneously, maximizing productivity and keeping costs low.
3. Cost-Effective in the Long Run
While the initial cost of purchasing a stone CNC machine might seem high, it is a sound investment for businesses looking to scale. The automation process reduces labor costs, lowers material wastage, and improves production efficiency. Over time, these savings will far outweigh the initial purchase price.
Additionally, the precision of CNC machines helps minimize errors during production. With less rework and waste, you’ll save money in the long term. The machines also require minimal maintenance, further reducing operational costs.
4. Versatility Across Various Applications
Stone CNC machines are incredibly versatile, making them useful in a variety of industries. Whether you're in the construction, monument, or artistic stone carving sector, these machines can handle it all. Some of the most common applications include:
Monument and Tombstone Engraving: Whether it's a traditional or contemporary design, CNC machines offer the precision needed for memorial stone engraving.
Countertop Fabrication: With the ability to cut and shape granite, marble, and other hard stones, CNC machines are perfect for creating countertops with intricate designs.
Architectural Features: From columns to ornate stone carvings, CNC machines can carve intricate architectural features that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Sculpture and Artwork: Artists and sculptors can use CNC machines to create highly detailed sculptures and relief carvings, offering a level of artistry that manual tools simply cannot replicate.

Key Features to Look for in a Stone CNC Machine
When selecting a stone CNC machine, it's crucial to evaluate several factors to ensure you choose the right one for your business. The number of axes is an essential consideration. Stone CNC machines come in 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis CNC stone machining center. A 3-axis machine is suitable for basic cutting, engraving, and carving tasks. For more complex shapes and deeper carvings, a 4-axis machine offers additional rotational capabilities. However, if you're looking for maximum flexibility and the ability to work on all sides of the stone, a 5-axis machine is ideal for creating intricate 3D shapes with precision.
Additionally, the software compatibility of the machine plays a significant role in its functionality. Machines that work with popular CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) programs, such as AutoCAD, Rhino, and Mastercam, allow for seamless design-to-production workflows, ensuring the accuracy of your designs. The quality of cutting tools is also vital for achieving smooth, precise cuts. Look for machines that are compatible with diamond-tipped tools to guarantee high-quality finishes on your stone materials.
Machine Stability and Durability for High-Precision Work
The stability of the CNC machine is critical for precise stone cutting and carving. A solid, stable frame made from durable materials like steel or cast iron ensures minimal vibration during operation. This reduces errors and ensures smoother, more accurate cuts. Stone CNC machines are subjected to significant forces during operation, so choosing a machine with a sturdy construction will not only enhance cutting precision but also extend the longevity of the machine. Machine stability is a key factor in producing consistent, high-quality results across various stone projects.
Maintenance and Care for Your CNC Stone Machine
While stone CNC machines are generally low-maintenance, it’s important to follow a regular maintenance routine to ensure longevity and optimal performance. Here are some tips:
Regular Cleaning: Stone cutting generates dust and debris, which can clog up the machine. Clean the machine regularly to keep it running smoothly.
Lubrication: Ensure the moving parts of the machine are well-lubricated to prevent friction and wear over time.
Check for Wear and Tear: Regularly inspect the machine for any signs of wear, especially on cutting tools. Replacing worn-out parts will ensure the machine continues to produce high-quality results.
Calibration: Periodically recalibrate the CNC machine to ensure it maintains its accuracy and precision.
Conclusion
Stone CNC machine can revolutionize the way you approach stone carving, cutting, and engraving. The precision, efficiency, and versatility it offers can drastically improve your production capabilities and the quality of your work. Whether you’re creating complex sculptures, countertops, or architectural features, a CNC machine can help you achieve perfect finishes with minimal effort.
If you're in the market for a stone CNC machine, it's essential to choose a machine that suits your specific needs and budget. Look for key features like the number of axes, software compatibility, and cutting tools to make the best decision for your business.
By incorporating a stone CNC machine into your production process, you can stay ahead of the competition, improve your workflow, and deliver top-notch stonework to your clients every time.
FAQ
1. How accurate are stone CNC machines? Stone CNC machines are incredibly accurate, capable of producing cuts and carvings down to millimeter precision. This level of detail ensures high-quality results, especially for intricate designs.
2. What types of stone can a CNC machine cut? CNC machines can cut a variety of stones, including granite, marble, limestone, and sandstone. They are also capable of working with synthetic stones and composites.
3. How long does it take to complete a project with a CNC stone machine? The time required for a project depends on its complexity and size. However, CNC machines can complete tasks much faster than manual methods, improving production time significantly.
4. Do CNC stone machines require a lot of maintenance? CNC stone machines are relatively low-maintenance. Regular cleaning, lubrication, and tool replacement are all that’s needed to ensure the machine runs efficiently.
5. Can I use the same CNC machine for both cutting and engraving stone? Yes, many stone CNC machines are versatile enough to handle both cutting and engraving tasks. Ensure that your machine has the appropriate tooling and software to perform both functions.
0 notes
Text
What You Need To Know About The Different Types Of CNC Milling Machines?
In factories and workshops, getting things done quickly and accurately is really important. CNC milling machines are like the superheroes of technology because they're super precise and can adapt to different tasks. Let's explore the different kinds of machines that are helping industries come up with cool new stuff, making CNC milling easier to understand.
1. Vertical Mills:
- An easily accessible workpiece from above is made possible by the vertical axis used on vertical milling machines. Flat surfaces, slots, and pockets are frequently created using them. For tasks like mould production and prototyping, where accessibility and precision are important, vertical mills are perfect.
2. Horizontal Mills:
- Horizontal milling machines have a spindle aligned horizontally, in contrast to vertical mills. These configurations are ideal for heavy-duty machining activities and batch production because they allow the cutting of numerous sides of a workpiece without requiring repositioning. Manufacturing sectors including aerospace, automotive, and marine are strongholds for horizontal mills.
3. Multi-Axis Mills:
- Advanced features of multi-axis milling machines include simultaneous movement along several axes. These devices have unmatched accuracy and productivity when it comes to carrying out intricate machining tasks. Multi-axis mills are essential in sectors like jewellery manufacture, medical, and aerospace because they can create complex geometries and shapes by adding extra axes of movement, such as rotational or tilting axes.
4. CNC Router Mills:
- To cut and shape wood, plastic, and other non-metallic materials, specialised milling machines known as CNC router mills are used. Signage, cabinetry, and woodworking businesses will find them perfect because of their big work envelopes and high-speed spindles. For small-scale producers, artists, and hobbyists, CNC router mills are great.
5. Benchtop Mills:
- Benchtop milling machines are compact and portable, making them ideal for small workshops, educational institutions, and prototype laboratories. Despite their diminutive size, these machines provide precision and adaptability that rival bigger industrial mills. Benchtop mills are popular among amateurs, DIY enthusiasts, and students learning the principles of machining.
CNC milling machines are available in a wide range of designs that satisfy a variety of industrial requirements, from vertical mills to multi-axis machining centres. Understanding the strengths and capabilities of each kind enables producers to pick the best machine for their individual applications, enabling innovation and efficiency in the ever-changing world of contemporary production.
Why choose HLH Rapid?
HLH Rapid is a remarkable team that combines the best of the West and East. It was founded by Vader Yu from China and Director James Murphy from the United Kingdom, both of whom have extensive industry expertise.
We help companies globally by promptly producing high-quality prototypes and parts. Our skills as well as expertise promote innovation, making it easier for businesses to develop new products swiftly.
We are pleased to provide a wide range of services, including rapid injection moulding, CNC machining, and numerous 3D printing technologies (such as SLA, SLS, and SLM), all in one stop.
To know more about cnc milling services, talk to our experts today by sending an email at [email protected] or visit our website: www./hlhrapid.com
0 notes
Text
Unlocking Precision: Understanding CNC Machine Configuration
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines have revolutionized manufacturing by automating and streamlining the production of intricate parts with unparalleled precision and efficiency. At the heart of every CNC machine lies its configuration – a carefully orchestrated combination of components and parameters that determine its capabilities and performance. In this blog, we'll delve into the essential elements of CNC machine configuration, shedding light on the key components that drive its functionality and versatility.
Machine Type: CNC machines come in various types, each designed for specific machining operations and applications. Common types include:
CNC Milling Machines: Used for cutting and shaping solid materials, such as metal, wood, and plastics, using rotating cutting tools.
CNC Lathes: Ideal for machining cylindrical parts by rotating the workpiece against stationary cutting tools.
CNC Routers: Employed for cutting and carving materials like wood, foam, and composites using computer-controlled routing heads.
CNC Plasma Cutters: Utilized for cutting metal sheets and plates using a high-velocity jet of ionized gas (plasma). Selecting the appropriate machine type depends on factors such as the desired machining operations, material types, part complexity, and production volume.
Axis Configuration: The axis configuration of a CNC machine refers to the number and orientation of its motion control axes. Common configurations include:
3-Axis Machines: Capable of moving along three linear axes (X, Y, Z) to perform 2D and 3D machining operations.
4-Axis Machines: Incorporate an additional rotary axis (typically A or B) for rotating the workpiece, enabling more complex machining operations and angular cuts.
5-Axis Machines: Feature two additional rotary axes (typically A and B or A and C), allowing for simultaneous movement and rotation in multiple directions, expanding the range of machining possibilities and enhancing precision.
Multi-Axis Machines: Combine three or more linear and rotary axes to achieve intricate machining capabilities, such as simultaneous milling, turning, and grinding. The axis configuration determines the machine's flexibility, precision, and suitability for specific machining tasks.
Control System: The control system is the brain of the CNC machine, responsible for interpreting the part design data (usually in the form of G-code) and translating it into precise movements and commands for the machine's motors and actuators. Key components of the control system include:
CNC Controller: The central unit that processes the G-code instructions and coordinates the motion of the machine axes.
Motor Drives: Power the machine's motors and provide precise control over their speed and position.
Feedback Systems: Include encoders and sensors that provide feedback on the position, velocity, and acceleration of the machine axes, ensuring accurate motion control.
Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Allows operators to interact with the CNC machine, input machining parameters, monitor the machining process, and troubleshoot any issues. Modern CNC machines may utilize proprietary control systems or industry-standard platforms such as Fanuc, Siemens, or Mitsubishi, each offering unique features and capabilities.
Tooling and Workholding: Tooling and workholding play a critical role in CNC machining, enabling the secure fixation of workpieces and the precise execution of machining operations. Key components include:
Cutting Tools: End mills, drills, inserts, and other cutting tools tailored to specific materials and machining operations.
Tool Changers: Automatic or manual systems for changing cutting tools during machining processes, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
Workholding Devices: Vises, clamps, fixtures, and chucks that securely hold the workpiece in place during machining, ensuring stability and accuracy. Proper selection and setup of tooling and workholding solutions are essential for achieving optimal machining results and minimizing setup time.
CNC machine configuration encompasses a myriad of components and parameters that determine the machine's capabilities, performance, and versatility. By understanding the machine type, axis configuration, control system, and tooling/workholding options, manufacturers can select and configure CNC machines to meet their specific machining requirements and production goals. Whether producing precision parts for aerospace, automotive, or medical applications, CNC machines stand ready to unlock the potential of modern manufacturing with their unparalleled precision and efficiency.
0 notes
Video
youtube
4 axis waving head ATC Foam Carving CNC Router machine with rotary#foamm...
0 notes
Text
CNC MACH3 USB 4 Axis Motion Controller card breakbout board 100KHz
USB MACH3 100Khz Breakout Board 4 Axis Interface Driver Motion Controller for cnc router MACH3 4 Axis 100KHz USB Smooth Stepper Motion Controller card breakout board for CNC MACH3 4 Axis 100KHz USB CNC Smooth Stepper Motion Controller card breakout board for CNC Engraving 12-24V Specification: 1. Support for 4-axis linkage, you can connect four stepper motor drives or servo drives; 2. Maximum…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Video
youtube
Routerstar 4 axis cnc router with 180 degree rotating spindle
0 notes
Text
CNC Wood Router
Do you have a thought to DIY or buy a reliable CNC Wood Router? Browse the 2024 new Wood Router buyer’s guide as follows, we’ll provide you with the competitive Wood Routers of 2024 with expert customer service to satisfied your requirements.
What is a CNC Wood Router? CNC Wood Router is a wood router machine controlled by the computer. It can process 2D/3D, milling, carving (relief, plane engraving, hollow carving, 3D carving), cutting, slotting and drilling of most popular wood materials and other soft materials, including woodworking crafts, wood carving, wooden marks, wooden toys, wooden gifts, cabinet making, wooden door making, wooden modelling, production of wooden furniture such as wardrobe.
The main structure of CNC Wood Router includes spindle, bed, gantry, servo motor and actuator, CNC operating system, CNC software, rack guide, screw, worktable, power supply, limit switch and so on.
CNC Wood Router is also known as wood CNC machine, woodworking CNC router, wood CNC router, CNC wood carving machine, wood CNC cutter, CNC wood milling machine, wood CNC table, CNC wood table, CNC wood router machine, CNC woodcarver, CNC wood engraver, CNC woodcutter, CNC wood cutting machine, c and c wood router, CNC woodworking machine, CNC wood engraver, wood c and c machine.
ATC CNC ROUTER SERIES
ATC CNC router is the first choice for enterprises with large production volume. According to the different tool changing methods, automatic tool changing engraving machines can be subdivided into linear ATC CNC machine and disc ATC engraving machines.Compared with the traditional manual tool change production method, this type of ATC CNC engraving machine has an independent tool magazine with different tool bits.Request a Quote
Small CNC Machine for Small Business
IGW-ATC 1325(PRO)ATC CNC Machine
ATC CNC Wood Router Table Kit
Wood CNC Router and Laser Engraver Combo
4×8 Wood CNC Router for Sale
Linear ATC CNC Router with Oscillating Knife Cutting
3d Atc Auto Tool Changer Wood Woodworking Machine
Wood CNC Router Rotation Head With Rotation Table
ATC CNC ROUTER SERIES
ATC CNC router is the first choice for enterprises with large production volume. According to the different tool changing methods, automatic tool changing engraving machines can be subdivided into linear ATC CNC machine and disc ATC engraving machines.Compared with the traditional manual tool change production method, this type of ATC CNC engraving machine has an independent tool magazine with different tool bits.Request a Quote
Small CNC Machine for Small Business
IGW-ATC 1325(PRO)ATC CNC Machine
ATC CNC Wood Router Table Kit
Wood CNC Router and Laser Engraver Combo
4×8 Wood CNC Router for Sale
Linear ATC CNC Router with Oscillating Knife Cutting
3d Atc Auto Tool Changer Wood Woodworking Machine
Wood CNC Router Rotation Head With Rotation Table
ATC CNC ROUTER, CNC ROUTER MACHINE, CNC WOOD ROUTERCNC Wood Router Machine
CNC ROUTER, CNC WOOD ROUTERBest Wood CNC Machine for Small Business
CNC WOOD ROUTERBest CNC Router Machines for Woodworking
CNC WOOD ROUTERLatest 1325 Wood CNC Machine 4×8
CNC WOOD ROUTERCNC Wood Router Manufacturers and Supplier
ATC CNC ROUTER, CNC ROUTER MACHINE, CNC WOOD ROUTERCNC Wood Carving Machine
3 AXIS CNC ROUTER, CNC WOOD ROUTER3 Axis CNC Router with automatic tool changer
HOT3 AXIS CNC ROUTER, CNC ROUTER, CNC WOOD ROUTER3 Axis ATC CNC Router with Automatic Tool Changer for Wood Furniture5.00 out of 5
HOT3 AXIS CNC ROUTER, CNC ROUTER, CNC WOOD ROUTERWood 3 Axis 4*8 CNC Router Machine for Sale
3D CNC ROUTER, 4 AXIS CNC ROUTER, CNC ROUTER, CNC WOOD ROUTERMulti Use 4 Axis Woodworking CNC Router with Rotary Axis
3D CNC ROUTER, 4 AXIS CNC ROUTER, CNC ROUTER, CNC WOOD ROUTER4 Axis CNC Wood Engraving Machine with Spindle Swing 180 Degree
READ MOREQUICK VIEW3D CNC ROUTER, 4 AXIS CNC ROUTER, CNC ROUTER, CNC WOOD ROUTERRotary Spindle 4 Axis CNC Wood Engraving Machine with Auto Tool Change
0 notes
Video
youtube
3D foam column cutting engraving on 4 axis cnc router More details or free tutorials ,please contact on whatsapp :008618053182392/ [email protected], Our website : jxautocnc.com
0 notes