#Coronavirus Across nation
Text
Alarm bells ring in Japan as experts warn of fast-spreading new Covid variant KP. 3 - Published July 19, 2024
Paywalled at the South China Morning Post: Unpaywalled by Covidsafehotties.
The country reported a 39 per cent week-on-week surge in infections from July 1 to 7, with Okinawa the hardest hit
Japan is grappling with a new and highly contagious coronavirus variant that is fuelling the country’s 11th wave of Covid-19 infections, health experts warn.
The KP. 3 variant is spreading rapidly, even among those who are vaccinated or have recovered from previous infections, according to Kazuhiro Tateda, president of the Japan Association of Infectious Diseases.
“It is, unfortunately, the nature of the virus to become more resilient and resistant each time it changes into a different form,” Tateda told This Week in Asia. “People lose their immunity quite quickly after being vaccinated, so they have little or no resistance.”
Tateda, who sits on Japan’s advisory panel formed at the start of the pandemic, said the coming weeks will be critical as authorities monitor the variant’s spread and impact.
While hospitals have reported a sharp uptick in Covid-19 admissions, Tateda said he is “relieved that not many of these cases are severe”. Typical symptoms of the KP. 3 variant include high fever, sore throat, loss of smell and taste, headaches, and fatigue.
According to the health ministry, medical facilities across Japan logged a 1.39-fold – or 39 per cent – increase in infections from July 1 to 7, compared to the previous week.
Okinawa prefecture has been the hardest hit by the new strain of the virus, with hospitals reporting an average of nearly 30 infections per days. The KP. 3 variant has accounted for more than 90 per cent of Covid-19 cases nationwide, the Fuji News Network reported, leading to renewed concerns about bed shortages at medical facilities.
Since Japan’s first detected Covid-19 case in early 2020 involving a man who returned from the Chinese city of Wuhan, East Asian nation has recorded a total of 34 million infections and around 75,000 related deaths. The country’s Covid-19 caseload peaked on August 5, 2022, when more than 253,000 people were receiving treatment.
Japan’s uptick in cases coincides with similar increases being observed globally. In the US, the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention reported a 23.5 per cent week-over-week rise in the number of people visiting hospitals with Covid-19 symptoms during the week ending July 6.
High-profile US.figures such as President Joe Biden and Doug Emhoff, husband of Vice-President Kamala Harris, have recently tested positive and gone into isolation. Meanwhile, several riders in the ongoing Tour de France cycling race have also returned positive test results.
Experts say it is too early to determine the full impact of the new variant on Japanese businesses or cross-border activities like travel. Precautionary measures are already in place at the country’s air and seaports to monitor the health of incoming arrivals. However, the global spike in cases may deter some Japanese from venturing abroad this summer.
A recent survey by Nippon Life insurance found that just 3.2 per cent of Japanese plan to travel abroad in the coming months, which is likely to depress annual travel figures once again. In 2023, Japan saw 9.62 million outbound travellers, a recovery after three years of extremely low pandemic-era numbers, but still far below the 20.01 million outbound travellers recorded in 2019.
Despite the latest surge, infectious disease expert Tateda insists there is no need for panic in Japan. However, he emphasised the importance of following precautions implemented during the pandemic’s peak, such as mask-wearing in public, handwashing, and social distancing.
Tateda also stressed that anyone testing positive should immediately isolate themselves.
#covid#mask up#pandemic#covid 19#coronavirus#wear a mask#sars cov 2#still coviding#public health#wear a respirator
207 notes
·
View notes
Text

The coronavirus that spread across the United States and became a pandemic in March 2020 will go down as one of the most difficult times in our nation’s history. Nearly every American experienced significant disruptions to their daily lives, with financial issues and physical isolation often leaving permanent scars. It was a terrible time, and one we will never forget. Today, however, things are looking up. President Biden recently declared that Covid is no longer a national emergency. What does that mean? Well, I’ll tell you.
We are post-pandemic. We are immortal. Those still alive cannot die.
It is time to bask in the knowledge that we have defeated the feverish viral scourge. Go forth without fear, because those malevolent RNA intruders can harm you no longer. You are the chosen Americans. The virus has been banished from every corner of our great nation, even stupid fucking Arkansas, who never listened to me, and you have emerged from the other side as survivors. Join me in celebrating mask-less in a very crowded room, my friends, for nothing—nothing—can take your life now.
Full story.
784 notes
·
View notes
Text
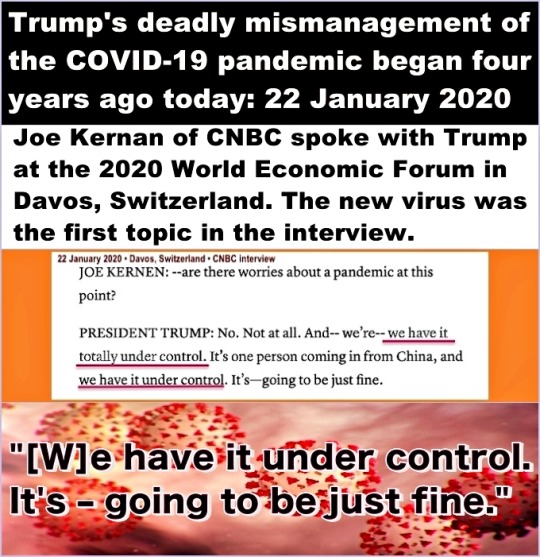
Just so nobody can say this is out of context, here's a vid of the entire interview.
The Obama administration successfully contained the Ebola outbreak in the United States. The death toll for Ebola in the US was under a dozen. So before leaving office, the Obama National Security Council created a 69-page handbook on how to deal with a pandemic. Trump and his flunkies ignored it with disastrous results.
Trump team failed to follow NSC’s pandemic playbook
The US death toll from COVID-19 is in seven digits. Other industrialized countries with advanced technological infrastructure such as Canada, Taiwan, Germany, and New Zealand had lower fatality rates per capita.
Trump largely ignored the virus until well into March when it had a chance to spread across the US.
The missing six weeks: how Trump failed the biggest test of his life
The president was aware of the danger from the coronavirus – but a lack of leadership has created an emergency of epic proportions
The Trump administration, at best, was in denial; at worst, it sabotaged the pandemic response.
youtube
Trump White House made 'deliberate efforts' to undermine Covid response, report says
Trump zombies who claim the economy was marvelous under Trump conveniently forget about everything that happened after February of 2020. Trump's early bungling of the pandemic plunged the economy into recession. The COVID supply chain problems and the economic stimulus required to prevent a depression led to the spurt in inflation which is finally receding.
People who are nostalgic about taking hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin, drinking bleach, and sticking UV lights up their butts must be excited about the opportunity to vote for Trump again.
#donald trump#botched pandemic response#covid-19#coronavirus#public health#anniversary of trump's awful covid-19 response#gross incompetence of the trump administration#the trump recession#trump tanked the economy#trump is a loser#vote blue no matter who#election 2020#election 2024
122 notes
·
View notes
Text
Evidence is mounting that Europe’s far right will score better than ever before in the upcoming European Parliament elections on June 6 to June 9—and that the continent’s young voters will fuel its ascent. The young adults now gravitating to far right aren’t Nazis or xenophobic racists, but they may have a hand in an outcome that will, at the very least, shift the European Union’s priorities and accents to the right. A particularly solid right-wing finish—and cooperation across the hard-right spectrum—could rattle EU unity and throw a wrench into the bloc’s workings at a time when it is confronting acute crises on several fronts, not least the war in Ukraine.
Since new laws mean that even people under 18 will be eligible to vote in some countries—16-year-olds in Austria, Germany, Malta, and Belgium, and 17-year-olds in Greece—there had been hope that these new voters would put a brake on the populist surge engulfing Europe. The idea behind giving 16- and 17-year-olds the vote was partly based on their long-term investment in politics. The policies designed today will affect them for many decades, in contrast to their grandparents.
And in the 2019 European Parliament election, young voters showed great promise by turning out in record numbers, a hopeful sign that reflected their enthusiasm for the common European project. With the climate movement rocking the streets, their votes went disproportionately to green parties that championed strong climate protection and deeper EU integration—two sets of long-term interests. This landed green representatives from Portugal to Latvia in the Brussels parliament and prompted the EU administration to approve the European Green Deal in 2020.
But the democratic exuberance of voters in their late teens, 20s, and early 30s could boost a very different trend this June, as growing numbers of younger voters are siding with far-right populist parties—the very ones that want to scupper the Green Deal and rein in the EU. In recent national votes conducted in Portugal, Sweden, the Netherlands, Italy, Finland, and France, young people voted in unprecedented numbers for extreme nationalist and euroskeptic parties. (Though some observers have argued that reporting about these trends is incomplete or oversimplified.) And surveys in Germany show the youth vote becoming ever more sympathetic to the Alternative for Germany (AfD), a far-right party that has undergone a radicalization that makes it among Europe’s fiercest, hard-right electoral parties.
“There’s no doubt that these parties have been making inroads to younger voters,” said Catherine de Vries, a Dutch political scientist. “The parties don’t look so extreme anymore, as they’ve been around for a while now. And young people think that the mainstream parties have had their chance. The system still doesn’t work for them, so let the other guys have a try.”
A German study published this year by a team led by youth researcher Simon Schnetzer showed that a full 22 percent of the young people (in this case, ages 14 through 29) surveyed would vote for the AfD if German elections were held today—twice as many as just two years ago. The tally for the Green Party fell by a third during that time frame. A full quarter of those asked said they weren’t sure who’d they vote for—another all-time high result.
The grounds for the pronounced shift are vague: Researchers tend to cite a general unhappiness with the post-pandemic economic and political conditions. “It seems as if the coronavirus pandemic left [young people] irritated about our ability to cope with the future, which is reflected in deep insecurity,” wrote the study’s authors. The issues described by participants that most impact this insecurity included their personal finances, professional opportunities, the health sector, and social recognition. They expressed less concern about the climate crisis and more about inflation, the economy, and old-age poverty.
“We can speak of a clear shift to the right in the young population,” said Klaus Hurrelmann, one of the study’s authors and a professor at the Hertie School in Berlin. The AfD’s foremost campaign priority of stopping immigration and refugee relief plainly struck a chord: Compared to a separate study conducted five years ago, about half as many (26 percent) of the young participants (26 percent) in the 2024 study said they were not in favor of taking in refugees. But just as important as the content of immigration policies, the authors underlined, was the idea that young people feel unheard or involved in the political process.
The change in sympathy in many young Germans reflects survey results, elections, and the statements of other young people across Europe. In the Netherlands’ elections last year, the most popular party among people under 35 (at 17 percent) was the Party for Freedom, led by Geert Wilders, a far-right populist with a long record of EU-trashing.
The explanation provided by many Dutch experts: It’s all about bestaanszekerheid, a Dutch word translated as “livelihood security.” This refers to having a decent and regular income, a comfortable home, access to education and health care, and a buffer against unexpected problems, de Vries told the Guardian. Young peoples’ leading concerns in the Netherlands are housing, overcrowded classes, and struggling hospitals, she said, which Wilders addressed in his campaign.
In Portugal’s March legislative elections, the far-right Chega party, which prioritized courting young people, raked in more of their votes than any other party. The meaning of chega, which can be translated as “that’s enough,” accurately describes many young voters’ motive for supporting it. Their gripes: “a very low average wage and an economy that cannot absorb educated young people,” according to political scientist António Costa Pinto in an interview with Euronews
“In the past, right-wing sympathizers accused immigrants of taking their jobs,” said Eberhard Seidel, the managing director of a Berlin-based nongovernmental organization called Schools Without Racism. “Now there are enough jobs but not enough housing for people who work. They still have to live with their parents.”
Observers say that the far right has excelled at grabbing the youth’s attention, not least with the social media platform TikTok. The recent German study found that 57 percent of young people imbibe their news and politics through social media. More than 90 percent use messaging service WhatsApp, followed by Instagram (80 percent) and YouTube (77 percent). TikTok stands at 51 percent; more than half of all 14- to 29-year-olds now use the app regularly, compared to 44 percent last year. The epiphany prompted an immediate response from German Health Minister Karl Lauterbach, who on declared in his first video on the platform, posted on March 19: “Revolution on TikTok: It starts today.”
Other opinion surveys show that young voters are diverse, divided, and undecided. A YouGov poll conducted in August 2023 showed that young Europeans are overwhelmingly concerned about the climate crisis and its likely effects, and more willing than older people to change behavior to mitigate those effects. Another poll, conducted in Germany, showed human rights violations at the top of younger people’s lists, followed by climate change, sexual harassment, and child abuse.
Younger voters still aren’t the drivers of xenophobia in the way that their parents’ generation was, Seidel said. A vote for the AfD doesn’t necessarily mean that they favor expelling immigrants from Germany or exiting the EU. “They take the basics of democracy and the social system for granted,” he said. “And they’re not fully aware of the implications of a rightward lurch in their political systems.”
Neither were Brexit’s voters, Seidel noted. And they found out the hard way.
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
Irene Yazzie can’t think of anyone who lives within 10 miles of her farm in the Navajo Nation who has drinking water flowing into their homes, hers included. In the far reaches of the reservation in Northeastern Arizona, near where the red-rock buttes of Monument Valley rise above the desert floor, indoor plumbing can feel like a luxury.
“I don’t know that people understand how hard of a life we have here,” said Yazzie, 71.
Help could be on the way if Congress approves a historic agreement reached between the Navajo, Hopi and San Juan Southern Paiute Tribes and the state of Arizona that would settle all of their outstanding water rights claims to the Colorado River Basin.
The deal, which all three tribes have now approved, marks a historic milestone for Indigenous nations that have fought for decades for their fair share of the water coursing through their ancestral lands.
Water claims with New Mexico and Utah had already been settled. Arizona had been the lone holdout. The 27,400-square-mile Navajo reservation, the nation’s largest, stretches across parts of all three states, with huge distances between towns and even individual homes.
While millions of people in the interior Southwest and Southern California draw from the Colorado River to sustain their cities and crops, Yazzie’s tribe has lacked pipelines connecting it to this precious — and overtaxed — waterway.
Several days a week, Yazzie or one of her two adult children makes the hour-long drive along bumpy dirt and gravel roads to reach a tribal community center that allows residents to pump water for a fee. Once back home, Yazzie has her son refill a cistern in the family’s yard.
“I’m always hauling water,” Yazzie said recently by phone.
Yazzie and her neighbors outside the Navajo hamlet of Dennehotso aren’t alone in living with water scarcity. An estimated 30% of households on the Navajo reservation don’t have indoor plumbing, and many who live in remote areas have to power their homes with generators because they’re also not connected to the power grid.
During a signing event in the tribal capital of Window Rock, Ariz., Navajo Nation President Buu Nygren said the water agreement is especially meaningful for residents on the reservation who are forced to haul water simply to access a basic necessity of life. In some cases, residents share water supplies with relatives and friends, while others get relief from nonprofits that offer free water system installations.
While the deal has been a long time in the making, the effort to bring safe drinking water into tribal members’ homes has taken on a new urgency in recent years due to droughts caused by climate change, the coronavirus pandemic and the battle among Southwestern states to secure their share of water from the river basin.
The country’s volatile politics and the looming presidential election are also top of mind for Indigenous leaders. The tribes will need both congressional approval and a presidential signature before the new agreement can take effect.
Some tribal officials see the Democratic administration of President Biden as more favorable to water rights claims and the protection of ancestral lands than Biden’s predecessor and presumptive Republican nominee, Donald Trump, though both as president have acted in support of expanding water access. In 2020, the Trump administration backed a deal between the Navajo Nation and Utah that settled all water rights claims in state and authorized about $220 million in federal funding to help build water infrastructure. Since Biden took office in 2021, his administration has directed hundreds of millions of dollars to Indigenous tribes for water projects.
In 2023, however, the majority-conservative U.S. Supreme Court dealt a blow to Navajo efforts to expand water access when it ruled that the federal government is not legally obligated to aid in the building of pipelines and other infrastructure to bring safe drinking water to reservation residents.
“Last year it was a hit to the belly that the (U.S. Supreme Court) was not going to help us,” Nygren said at the signing ceremony. “But now we have our own attorneys, water experts, hydrologists, and we can figure out how much water belongs to us.”
Under the finalized agreement, the Navajo will receive “a substantial amount of the Colorado River Upper Basin water, some Lower Basin water, all groundwater underlying the Navajo Nation, all surface water that reaches the Navajo Nation from the Little Colorado River, and all wash water that reaches the Nation south of the Hopi reservation,” according to the Navajo Nation Council.
The deal calls for the federal government to allocate $5 billion toward the building of critical infrastructure to link the territory’s surface water and groundwater sources to the communities that need them. It also gives the Navajo the flexibility to move Arizona water from the Colorado River’s upper basin to the lower basin and to divert water in New Mexico and Utah to Navajo communities in Arizona if that’s the closest source to those residents.
“Obviously, living on the Navajo reservation, we don’t have boundaries — this is just one piece of our homeland — so building out large infrastructure for water, sewer and electric lines, that’s huge,” said Joelynn Ashley, who chairs the Navajo Nation Water Rights Commission and represents areas that border the river.
Ashley said that while many Navajo have long depended on groundwater, contamination from uranium and arsenic, as well high salinity levels, make some of it unsafe to use. And some wells simply don’t yield enough water to meet demand.
“We just want to be able to use all of our water because we’ve got a lot of places where either water quantity or water quality is not there,” Ashley said.
Yazzie says the arrival of pipelines and water pouring from a tap in her home could not happen soon enough. She’s looking forward to the day when she doesn’t have to drive 16 miles each way to fill up on water for her family, as well as her 18 cows, 15 goats and two horses.
“It’s a hassle,” she said.
#us politics#news#los angeles times#2024#water rights#indigenous tribes#Navajo#San Juan Southern Paiute#hopi#Colorado River#arizona#new mexico#utah#California#Dennehotso#us supreme court#us congress
22 notes
·
View notes
Text

[Link to the Reuters article. From June 14th, 2024]
"At the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. military launched a secret campaign to counter what it perceived as China’s growing influence in the Philippines, a nation hit especially hard by the deadly virus.
The clandestine operation has not been previously reported. It aimed to sow doubt about the safety and efficacy of vaccines and other life-saving aid that was being supplied by China, a Reuters investigation found. Through phony internet accounts meant to impersonate Filipinos, the military’s propaganda efforts morphed into an anti-vax campaign. Social media posts decried the quality of face masks, test kits and the first vaccine that would become available in the Philippines – China’s Sinovac inoculation.
Reuters identified at least 300 accounts on X, formerly Twitter, that matched descriptions shared by former U.S. military officials familiar with the Philippines operation. Almost all were created in the summer of 2020 and centered on the slogan #Chinaangvirus – Tagalog for China is the virus.
“COVID came from China and the VACCINE also came from China, don’t trust China!” one typical tweet from July 2020 read in Tagalog. The words were next to a photo of a syringe beside a Chinese flag and a soaring chart of infections. Another post read: “From China – PPE, Face Mask, Vaccine: FAKE. But the Coronavirus is real.”
After Reuters asked X about the accounts, the social media company removed the profiles, determining they were part of a coordinated bot campaign based on activity patterns and internal data.
The U.S. military’s anti-vax effort began in the spring of 2020 and expanded beyond Southeast Asia before it was terminated in mid-2021, Reuters determined. Tailoring the propaganda campaign to local audiences across Central Asia and the Middle East, the Pentagon used a combination of fake social media accounts on multiple platforms to spread fear of China’s vaccines among Muslims at a time when the virus was killing tens of thousands of people each day. A key part of the strategy: amplify the disputed contention that, because vaccines sometimes contain pork gelatin, China’s shots could be considered forbidden under Islamic law.
The military program started under former President Donald Trump and continued months into Joe Biden’s presidency, Reuters found – even after alarmed social media executives warned the new administration that the Pentagon had been trafficking in COVID misinformation. The Biden White House issued an edict in spring 2021 banning the anti-vax effort, which also disparaged vaccines produced by other rivals, and the Pentagon initiated an internal review, Reuters found.
The U.S. military is prohibited from targeting Americans with propaganda, and Reuters found no evidence the Pentagon’s influence operation did so.
Spokespeople for Trump and Biden did not respond to requests for comment about the clandestine program.
A senior Defense Department official acknowledged the U.S. military engaged in secret propaganda to disparage China’s vaccine in the developing world, but the official declined to provide details.
A Pentagon spokeswoman said the U.S. military “uses a variety of platforms, including social media, to counter those malign influence attacks aimed at the U.S., allies, and partners.” She also noted that China had started a “disinformation campaign to falsely blame the United States for the spread of COVID-19.”
In an email, the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs said that it has long maintained the U.S. government manipulates social media and spreads misinformation.
Manila’s embassy in Washington did not respond to Reuters inquiries, including whether it had been aware of the Pentagon operation. A spokesperson for the Philippines Department of Health, however, said the “findings by Reuters deserve to be investigated and heard by the appropriate authorities of the involved countries.” Some aid workers in the Philippines, when told of the U.S. military propaganda effort by Reuters, expressed outrage.
Briefed on the Pentagon’s secret anti-vax campaign by Reuters, some American public health experts also condemned the program, saying it put civilians in jeopardy for potential geopolitical gain. An operation meant to win hearts and minds endangered lives, they said.
“I don’t think it’s defensible,” said Daniel Lucey, an infectious disease specialist at Dartmouth’s Geisel School of Medicine. “I’m extremely dismayed, disappointed and disillusioned to hear that the U.S. government would do that,” said Lucey, a former military physician who assisted in the response to the 2001 anthrax attacks.
The effort to stoke fear about Chinese inoculations risked undermining overall public trust in government health initiatives, including U.S.-made vaccines that became available later, Lucey and others said. Although the Chinese vaccines were found to be less effective than the American-led shots by Pfizer and Moderna, all were approved by the World Health Organization. Sinovac did not respond to a Reuters request for comment.
Academic research published recently has shown that, when individuals develop skepticism toward a single vaccine, those doubts often lead to uncertainty about other inoculations. Lucey and other health experts say they saw such a scenario play out in Pakistan, where the Central Intelligence Agency used a fake hepatitis vaccination program in Abbottabad as cover to hunt for Osama bin Laden, the terrorist mastermind behind the attacks of September 11, 2001. Discovery of the ruse led to a backlash against an unrelated polio vaccination campaign, including attacks on healthcare workers, contributing to the reemergence of the deadly disease in the country.
“It should have been in our interest to get as much vaccine in people’s arms as possible,” said Greg Treverton, former chairman of the U.S. National Intelligence Council, which coordinates the analysis and strategy of Washington’s many spy agencies. What the Pentagon did, Treverton said, “crosses a line.”
Together, the phony accounts used by the military had tens of thousands of followers during the program. Reuters could not determine how widely the anti-vax material and other Pentagon-planted disinformation was viewed, or to what extent the posts may have caused COVID deaths by dissuading people from getting vaccinated.
In the wake of the U.S. propaganda efforts, however, then-Philippines President Rodrigo Duterte had grown so dismayed by how few Filipinos were willing to be inoculated that he threatened to arrest people who refused vaccinations.
“You choose, vaccine or I will have you jailed,” a masked Duterte said in a televised address in June 2021. “There is a crisis in this country … I’m just exasperated by Filipinos not heeding the government.”
When he addressed the vaccination issue, the Philippines had among the worst inoculation rates in Southeast Asia. Only 2.1 million of its 114 million citizens were fully vaccinated – far short of the government’s target of 70 million. By the time Duterte spoke, COVID cases exceeded 1.3 million, and almost 24,000 Filipinos had died from the virus. The difficulty in vaccinating the population contributed to the worst death rate in the region.
A spokesperson for Duterte did not make the former president available for an interview.
Some Filipino healthcare professionals and former officials contacted by Reuters were shocked by the U.S. anti-vax effort, which they say exploited an already vulnerable citizenry. Public concerns about a Dengue fever vaccine, rolled out in the Philippines in 2016, had led to broad skepticism toward inoculations overall, said Lulu Bravo, executive director of the Philippine Foundation for Vaccination. The Pentagon campaign preyed on those fears.
“Why did you do it when people were dying? We were desperate,” said Dr. Nina Castillo-Carandang, a former adviser to the World Health Organization and Philippines government during the pandemic. “We don’t have our own vaccine capacity,” she noted, and the U.S. propaganda effort “contributed even more salt into the wound.”
The campaign also reinforced what one former health secretary called a longstanding suspicion of China, most recently because of aggressive behavior by Beijing in disputed areas of the South China Sea. Filipinos were unwilling to trust China’s Sinovac, which first became available in the country in March 2021, said Esperanza Cabral, who served as health secretary under President Gloria Macapagal Arroyo. Cabral said she had been unaware of the U.S. military’s secret operation.
“I’m sure that there are lots of people who died from COVID who did not need to die from COVID,” she said.
To implement the anti-vax campaign, the Defense Department overrode strong objections from top U.S. diplomats in Southeast Asia at the time, Reuters found. Sources involved in its planning and execution say the Pentagon, which ran the program through the military’s psychological operations center in Tampa, Florida, disregarded the collateral impact that such propaganda may have on innocent Filipinos.
“We weren’t looking at this from a public health perspective,” said a senior military officer involved in the program. “We were looking at how we could drag China through the mud.”
In uncovering the secret U.S. military operation, Reuters interviewed more than two dozen current and former U.S officials, military contractors, social media analysts and academic researchers. Reporters also reviewed Facebook, X and Instagram posts, technical data and documents about a set of fake social media accounts used by the U.S. military. Some were active for more than five years.
Clandestine psychological operations are among the government’s most highly sensitive programs. Knowledge of their existence is limited to a small group of people within U.S. intelligence and military agencies. Such programs are treated with special caution because their exposure could damage foreign alliances or escalate conflict with rivals.
Over the last decade, some U.S. national security officials have pushed for a return to the kind of aggressive clandestine propaganda operations against rivals that the United States’ wielded during the Cold War. Following the 2016 U.S. presidential election, in which Russia used a combination of hacks and leaks to influence voters, the calls to fight back grew louder inside Washington.
In 2019, Trump authorized the Central Intelligence Agency to launch a clandestine campaign on Chinese social media aimed at turning public opinion in China against its government, Reuters reported in March. As part of that effort, a small group of operatives used bogus online identities to spread disparaging narratives about Xi Jinping’s government.
COVID-19 galvanized the drive to wage psychological operations against China. One former senior Pentagon leader described the pandemic as a “bolt of energy” that finally ignited the long delayed counteroffensive against China’s influence war.
The Pentagon’s anti-vax propaganda came in response to China’s own efforts to spread false information about the origins of COVID. The virus first emerged in China in late 2019. But in March 2020, Chinese government officials claimed without evidence that the virus may have been first brought to China by an American service member who participated in an international military sports competition in Wuhan the previous year. Chinese officials also suggested that the virus may have originated in a U.S. Army research facility at Fort Detrick, Maryland. There’s no evidence for that assertion.
Mirroring Beijing’s public statements, Chinese intelligence operatives set up networks of fake social media accounts to promote the Fort Detrick conspiracy, according to a U.S. Justice Department complaint.
China’s messaging got Washington’s attention. Trump subsequently coined the term “China virus” as a response to Beijing’s accusation that the U.S. military exported COVID to Wuhan.
“That was false. And rather than having an argument, I said, ‘I have to call it where it came from,’” Trump said in a March 2020 news conference. “It did come from China.”
China’s Foreign Ministry said in an email that it opposed “actions to politicize the origins question and stigmatize China.” The ministry had no comment about the Justice Department’s complaint.
Beijing didn’t limit its global influence efforts to propaganda. It announced an ambitious COVID assistance program, which included sending masks, ventilators and its own vaccines – still being tested at the time – to struggling countries. In May 2020, Xi announced that the vaccine China was developing would be made available as a “global public good,” and would ensure “vaccine accessibility and affordability in developing countries.” Sinovac was the primary vaccine available in the Philippines for about a year until U.S.-made vaccines became more widely available there in early 2022.
Washington’s plan, called Operation Warp Speed, was different. It favored inoculating Americans first, and it placed no restrictions on what pharmaceutical companies could charge developing countries for the remaining vaccines not used by the United States. The deal allowed the companies to “play hardball” with developing countries, forcing them to accept high prices, said Lawrence Gostin, a professor of medicine at Georgetown University who has worked with the World Health Organization.
The deal “sucked most of the supply out of the global market,” Gostin said. “The United States took a very determined America First approach.”
To Washington’s alarm, China’s offers of assistance were tilting the geopolitical playing field across the developing world, including in the Philippines, where the government faced upwards of 100,000 infections in the early months of the pandemic.
The U.S. relationship with Manila had grown tense after the 2016 election of the bombastic Duterte. A staunch critic of the United States, he had threatened to cancel a key pact that allows the U.S. military to maintain legal jurisdiction over American troops stationed in the country.
Duterte said in a July 2020 speech he had made “a plea” to Xi that the Philippines be at the front of the line as China rolled out vaccines. He vowed in the same speech that the Philippines would no longer challenge Beijing’s aggressive expansion in the South China Sea, upending a key security understanding Manila had long held with Washington.
“China is claiming it. We are claiming it. China has the arms, we do not have it.” Duterte said. “So, it is simple as that.”
Days later, China’s foreign minister announced Beijing would grant Duterte’s plea for priority access to the vaccine, as part of a “new highlight in bilateral relations.”
China’s growing influence fueled efforts by U.S. military leaders to launch the secret propaganda operation Reuters uncovered.
“We didn’t do a good job sharing vaccines with partners,” a senior U.S. military officer directly involved in the campaign in Southeast Asia told Reuters. “So what was left to us was to throw shade on China’s.”
U.S. military leaders feared that China’s COVID diplomacy and propaganda could draw other Southeast Asian countries, such as Cambodia and Malaysia, closer to Beijing, furthering its regional ambitions.
A senior U.S. military commander responsible for Southeast Asia, Special Operations Command Pacific General Jonathan Braga, pressed his bosses in Washington to fight back in the so-called information space, according to three former Pentagon officials.
The commander initially wanted to punch back at Beijing in Southeast Asia. The goal: to ensure the region understood the origin of COVID while promoting skepticism toward what were then still-untested vaccines offered by a country that they said had lied continually since the start of the pandemic.
A spokesperson for Special Operations Command declined to comment.
At least six senior State Department officials responsible for the region objected to this approach. A health crisis was the wrong time to instill fear or anger through a psychological operation, or psyop, they argued during Zoom calls with the Pentagon.
“We’re stooping lower than the Chinese and we should not be doing that,” said a former senior State Department official for the region who fought against the military operation.
While the Pentagon saw Washington’s rapidly diminishing influence in the Philippines as a call to action, the withering partnership led American diplomats to plead for caution.
“The relationship is hanging from a thread,” another former senior U.S. diplomat recounted. “Is this the moment you want to do a psyop in the Philippines? Is it worth the risk?”
In the past, such opposition from the State Department might have proved fatal to the program. Previously in peacetime, the Pentagon needed approval of embassy officials before conducting psychological operations in a country, often hamstringing commanders seeking to quickly respond to Beijing’s messaging, three former Pentagon officials told Reuters.
But in 2019, before COVID surfaced in full force, then-Secretary of Defense Mark Esper signed a secret order that later paved the way for the launch of the U.S. military propaganda campaign. The order elevated the Pentagon’s competition with China and Russia to the priority of active combat, enabling commanders to sidestep the State Department when conducting psyops against those adversaries. The Pentagon spending bill passed by Congress that year also explicitly authorized the military to conduct clandestine influence operations against other countries, even “outside of areas of active hostilities.”
Esper, through a spokesperson, declined to comment. A State Department spokesperson referred questions to the Pentagon.
In spring 2020, special-ops commander Braga turned to a cadre of psychological-warfare soldiers and contractors in Tampa to counter Beijing’s COVID efforts. Colleagues say Braga was a longtime advocate of increasing the use of propaganda operations in global competition. In trailers and squat buildings at a facility on Tampa’s MacDill Air Force Base, U.S. military personnel and contractors would use anonymous accounts on X, Facebook and other social media to spread what became an anti-vax message. The facility remains the Pentagon’s clandestine propaganda factory.
Psychological warfare has played a role in U.S. military operations for more than a hundred years, although it has changed in style and substance over time. So-called psyopers were best known following World War II for their supporting role in combat missions across Vietnam, Korea and Kuwait, often dropping leaflets to confuse the enemy or encourage their surrender.
After the al Qaeda attacks of 2001, the United States was fighting a borderless, shadowy enemy, and the Pentagon began to wage a more ambitious kind of psychological combat previously associated only with the CIA. The Pentagon set up front news outlets, paid off prominent local figures, and sometimes funded television soap operas in order to turn local populations against militant groups or Iranian-backed militias, former national security officials told Reuters.
Unlike earlier psyop missions, which sought specific tactical advantage on the battlefield, the post-9/11 operations hoped to create broader change in public opinion across entire regions.
By 2010, the military began using social media tools, leveraging phony accounts to spread messages of sympathetic local voices – themselves often secretly paid by the United States government. As time passed, a growing web of military and intelligence contractors built online news websites to pump U.S.-approved narratives into foreign countries. Today, the military employs a sprawling ecosystem of social media influencers, front groups and covertly placed digital advertisements to influence overseas audiences, according to current and former military officials.
China’s efforts to gain geopolitical clout from the pandemic gave Braga justification to launch the propaganda campaign that Reuters uncovered, sources said.
By summer 2020, the military’s propaganda campaign moved into new territory and darker messaging, ultimately drawing the attention of social media executives.
In regions beyond Southeast Asia, senior officers in the U.S. Central Command, which oversees military operations across the Middle East and Central Asia, launched their own version of the COVID psyop, three former military officials told Reuters.
Although the Chinese vaccines were still months from release, controversy roiled the Muslim world over whether the vaccines contained pork gelatin and could be considered “haram,” or forbidden under Islamic law. Sinovac has said that the vaccine was “manufactured free of porcine materials.” Many Islamic religious authorities maintained that even if the vaccines did contain pork gelatin, they were still permissible since the treatments were being used to save human life.
The Pentagon campaign sought to intensify fears about injecting a pig derivative. As part of an internal investigation at X, the social media company used IP addresses and browser data to identify more than 150 phony accounts that were operated from Tampa by U.S. Central Command and its contractors, according to an internal X document reviewed by Reuters.
“Can you trust China, which tries to hide that its vaccine contains pork gelatin and distributes it in Central Asia and other Muslim countries where many people consider such a drug haram?” read an April 2021 tweet sent from a military-controlled account identified by X.
The Pentagon also covertly spread its messages on Facebook and Instagram, alarming executives at parent company Meta who had long been tracking the military accounts, according to former military officials.
One military-created meme targeting Central Asia showed a pig made out of syringes, according to two people who viewed the image. Reuters found similar posts that traced back to U.S. Central Command. One shows a Chinese flag as a curtain separating Muslim women in hijabs and pigs stuck with vaccine syringes. In the center is a man with syringes; on his back is the word “China.” It targeted Central Asia, including Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan, a country that distributed tens of millions of doses of China’s vaccines and participated in human trials. Translated into English, the X post reads: “China distributes a vaccine made of pork gelatin.”
Facebook executives had first approached the Pentagon in the summer of 2020, warning the military that Facebook workers had easily identified the military’s phony accounts, according to three former U.S. officials and another person familiar with the matter. The government, Facebook argued, was violating Facebook’s policies by operating the bogus accounts and by spreading COVID misinformation.
The military argued that many of its fake accounts were being used for counterterrorism and asked Facebook not to take down the content, according to two people familiar with the exchange. The Pentagon pledged to stop spreading COVID-related propaganda, and some of the accounts continued to remain active on Facebook.
Nonetheless, the anti-vax campaign continued into 2021 as Biden took office.
Angered that military officials had ignored their warning, Facebook officials arranged a Zoom meeting with Biden’s new National Security Council shortly after the inauguration, Reuters learned. The discussion quickly became tense.
“It was terrible,” said a senior administration official describing the reaction after learning of the campaign’s pig-related posts. “I was shocked. The administration was pro-vaccine and our concern was this could affect vaccine hesitancy, especially in developing countries.”
By spring 2021, the National Security Council ordered the military to stop all anti-vaccine messaging. “We were told we needed to be pro-vaccine, pro all vaccines,” said a former senior military officer who helped oversee the program. Even so, Reuters found some anti-vax posts that continued through April and other deceptive COVID-related messaging that extended into that summer. Reuters could not determine why the campaign didn’t end immediately with the NSC’s order. In response to questions from Reuters, the NSC declined to comment.
The senior Defense Department official said that those complaints led to an internal review in late 2021, which uncovered the anti-vaccine operation. The probe also turned up other social and political messaging that was “many, many leagues away” from any acceptable military objective. The official would not elaborate.
The review intensified the following year, the official said, after a group of academic researchers at Stanford University flagged some of the same accounts as pro-Western bots in a public report. The high-level Pentagon review was first reported by the Washington Post. which also reported that the military used fake social media accounts to counter China’s message that COVID came from the United States. But the Post report did not reveal that the program evolved into the anti-vax propaganda campaign uncovered by Reuters.
The senior defense official said the Pentagon has rescinded parts of Esper’s 2019 order that allowed military commanders to bypass the approval of U.S. ambassadors when waging psychological operations. The rules now mandate that military commanders work closely with U.S. diplomats in the country where they seek to have an impact. The policy also restricts psychological operations aimed at “broad population messaging,” such as those used to promote vaccine hesitancy during COVID.
The Pentagon’s audit concluded that the military’s primary contractor handling the campaign, General Dynamics IT, had employed sloppy tradecraft, taking inadequate steps to hide the origin of the fake accounts, said a person with direct knowledge of the review. The review also found that military leaders didn’t maintain enough control over its psyop contractors, the person said.
A spokesperson for General Dynamics IT declined to comment.
Nevertheless, the Pentagon’s clandestine propaganda efforts are set to continue. In an unclassified strategy document last year, top Pentagon generals wrote that the U.S. military could undermine adversaries such as China and Russia using “disinformation spread across social media, false narratives disguised as news, and similar subversive activities [to] weaken societal trust by undermining the foundations of government.”
And in February, the contractor that worked on the anti-vax campaign – General Dynamics IT – won a $493 million contract. Its mission: to continue providing clandestine influence services for the military."
12 notes
·
View notes
Text

deAdder
* * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
August 11, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Aug 12, 2024
Vice President Kamala Harris’s choice of Minnesota governor Tim Walz to be her running mate seems to cement the emergence of a new Democratic Party.
When he took office in January 2021, President Joe Biden was clear that he intended to launch a new era in America, overturning the neoliberalism of the previous forty years and replacing it with a proven system in which the government would work to protect the ability of ordinary Americans to prosper. Neoliberalism relied on markets to shape society, and its supporters promised it would be so much more efficient than government regulation that it would create a booming economy that would help everyone. Instead, the slashing of government regulation and social safety systems had enabled the rise of wealthy oligarchs in the U.S. and around the globe. Those oligarchs, in turn, dominated poor populations, whose members looked at the concentration of wealth and power in the hands of a few people and gave up on democracy.
Biden recognized that defending democracy in the United States, and thus abroad, required defending economic fairness. He reached back to the precedent set by Democratic president Franklin Delano Roosevelt in 1933 and followed by presidents of both parties from then until Ronald Reagan took office in 1981. Biden’s speeches often come back to a promise to help the parents who “have lain awake at night staring at the ceiling, wondering how they will make rent, send their kids to college, retire, or pay for medication.” He vowed “to finally rebuild a strong middle class and grow our economy from the middle out and bottom up, giving hardworking families across the country a little more breathing room.”
Like his predecessors, he set out to invest in ordinary Americans. Under his administration, Democrats passed landmark legislation like the American Rescue Plan that rebuilt the economy after the devastating effects of the coronavirus pandemic; the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law that is rebuilding our roads, bridges, ports, and airports, as well as investing in rural broadband; the CHIPS and Science Act that rebuilt American manufacturing at the same time it invested in scientific research; and the Inflation Reduction Act, which, among other things, invested in addressing climate change. Under his direction, the government worked to stop or break up monopolies and to protect the rights of workers and consumers.
Like the policies of that earlier era, his economic policies were based on the idea that making sure ordinary people made decent wages and were protected from predatory employers and industrialists would create a powerful engine for the economy. The system had worked in the past, and it sure worked during the Biden administration, which saw the United States economy grow faster in the wake of the pandemic than that of any other developed economy. Under Biden, the economy added almost 16 million jobs, wages rose faster than inflation, and workers saw record low unemployment rates.
While Biden worked hard to make his administration reflect the demographics of the nation, tapping more women than men as advisors and nominating more Black women and racial minorities to federal judicial positions than any previous president, it was Vice President Kamala Harris who emphasized the right of all Americans to be treated equally before the law.
She was the first member of the administration to travel to Tennessee in support of the Tennessee Three after the Republican-dominated state legislature expelled two Black Democratic lawmakers for protesting in favor of gun safety legislation and failed by a single vote to expel their white colleague. She has highlighted the vital work historically Black colleges and universities have done for their students and for the United States. And she has criss-crossed the country to support women’s rights, especially the right to reproductive healthcare, in the two years since the Supreme Court, packed with religious extremists by Trump, overturned the 1973 Roe v. Wade decision.
To the forming Democratic coalition, Harris brought an emphasis on equal rights before the law that drew from the civil rights movements that stretched throughout our history and flowered after 1950. Harris has told the story of how her parents, Dr. Shyamala Gopalan, who hailed from India, and Donald J. Harris, from Jamaica, met as graduate students at the University of California, Berkeley and bonded over a shared interest in civil rights. “My parents marched and shouted in the Civil Rights Movement of the 1960s,” Harris wrote in 2020. “It’s because of them and the folks who also took to the streets to fight for justice that I am where I am.”
To these traditionally Democratic mindsets, Governor Walz brings something quite different: midwestern Progressivism. Walz is a leader in the Minnesota Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party, which formed after World War II, but the reform impulse in the Midwest reaches all the way back to the years immediately after the Civil War and in its origins is associated with the Republican, rather than the Democratic, Party. While Biden’s approach to government focuses on economic justice and Harris’s focuses on individual rights, Walz’s focuses on the government’s responsibility to protect communities from extremists. That stance sweeps in economic fairness and individual rights but extends beyond them to recall an older vision of the nature of government itself.
The Republican Party’s roots were in the Midwest, where ordinary people were determined to stop wealthy southern oligarchs from taking over control of the United States government. That determination continued after the war when people in the Midwest were horrified to see industrial leaders step into the place that wealthy enslavers had held before the war. Their opposition was based not in economics alone, but rather in their larger worldview. And because they were Republicans by heritage, they constructed their opposition to the rise of industrial oligarchs as a more expansive vision of democracy.
In the early 1870s the Granger movement, based in an organization originally formed by Oliver H. Kelley of Minnesota and other officials in the Department of Agriculture to combat the isolation of farm life, began to organize farmers against the railroad monopolies that were sucking farmers’ profits. The Grangers called for the government to work for communities rather than the railroad barons, demanding business regulation. In the 1870s, Minnesota, Iowa, Wisconsin, and Illinois passed the so-called Granger Laws, which regulated railroads and grain elevator operators. (When such a measure was proposed in California, railroad baron Leland Stanford called it “pure communism” and hired former Republican congressman Roscoe Conkling to fight it by arguing that corporations were “persons” under the Fourteenth Amendment.)
Robert La Follette grew up on a farm near Madison, Wisconsin, during the early days of the Grangers and absorbed their concern that rich men were taking over the nation and undermining democracy. One of his mentors warned: “Money is taking the field as an organized power. Which shall rule—wealth or man; which shall lead—money or intellect; who shall fill public stations—educated and patriotic free men, or the feudal serfs of corporate capital?”
In the wake of the Civil War, La Follette could not embrace the Democrats. Instead, he and people like him brought this approach to government to a Republican Party that at the time was dominated by industrialists. Wisconsin voters sent La Follette to Congress in 1884 when he was just 29, and when party bosses dumped him in 1890, he turned directly to the people, demanding they take the state back from the party machine. They elected him governor in 1900.
As governor, La Follette advanced what became known as the “Wisconsin Idea,” adopted and advanced by Republican President Theodore Roosevelt. As Roosevelt noted in a book explaining the system, Wisconsin was “literally a laboratory for wise experimental legislation aiming to secure the social and political betterment of the people as a whole.” La Follette called on professors from the University of Wisconsin, state legislators, and state officials to craft measures to meet the needs of the state’s people. “All through the Union we need to learn the Wisconsin lesson,” Roosevelt wrote.
In the late twentieth century, the Republican Party had moved far away from Roosevelt when it embraced neoliberalism. As it did so, Republicans ditched the Wisconsin Idea: Wisconsin governor Scott Walker tried to do so explicitly by changing the mission of the University of Wisconsin system from a “search for truth” to “improve the human condition” to a demand that the university “meet the state’s workforce needs.”
While Republicans abandoned the party’s foundational principles, Democratic governors have been governing on them. Now vice-presidential nominee Walz demonstrates that those community principles are joining the Democrats’ commitment to economic fairness and civil rights to create a new, national program for democracy.
It certainly seems like the birth of a new era in American history. At a Harris-Walz rally in Arizona on Friday, Mayor John Giles of Mesa, Arizona, who describes himself as a lifelong Republican, said: “I do not recognize my party. The Republican Party has been taken over by extremists that are committed to forcing people in the center of the political spectrum out of the party. I have something to say to those of us who are in the political middle: You don’t owe a damn thing to that political party…. [Y]ou don’t owe anything to a party that is out of touch and is hell-bent on taking our country backward. And by all means, you owe no displaced loyalty to a candidate that is morally and ethically bankrupt…. [I]n the spirit of the great Senator John McCain, please join me in putting country over party and stopping Donald Trump, and protecting the rule of law, protecting our Constitution, and protecting the democracy of this great country. That is why I’m standing with Vice President Harris and Governor Walz.”
Vice President Harris put it differently. Speaking to a United Auto Workers local in Wayne, Michigan, on Thursday, she explained what she and Walz have in common.
“A whole lot,” she said. “You know, we grew up the same way. We grew up in a community of people, you know—I mean, he grew up… in Nebraska; me, Oakland, California—seemingly worlds apart. But the same people raised us: good people; hard-working people; people who had pride in their hard work; you know, people who had pride in knowing that we were a community of people who looked out for each other—you know, raised by a community of folks who understood that the true measure of the strength of a leader is not based on who you beat down. It’s based on who you lift up.”
—
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Letters from an american#Heather Cox Richardson#American History#political history#Joe Biden#for the people#democracy#civil rights#economic opportunity
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
A noted historian, demographer and author is warning that the United States is on the verge of another civil war.
Neil Howe, who co-authored the book "The Fourth Turning: An American Prophecy," noted that four out of five predictors for a crisis have already happened, leaving the country on the edge of unparalleled internal conflict. (Related: The catalyst for the next US civil war?)
In a recent interview with the Daily Signal, Howe summarized the factors he considers are pushing the American nation toward a possible civil war.
He said the first of four that have come to pass is a "crisis over debt," which Howe referred to as a "new tea party movement," which manifested during the 2010 political conflicts under the same name.
The second is a WMD (weapon of mass destruction) attack on a major American city, this being the Sept. 11, 2001 terrorist attack on New York City. Howe said the terrorist attacks accomplished this prediction by bringing destruction and enduring consequences.
The third was the pandemic, specifically the Wuhan coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic which swept across the world beginning in 2020.
The fourth one was Russia invading a former soviet republic. This was fulfilled when Russia began its special military operation in Ukraine in February 2022, and it connects with his prediction of international tensions reaching a fever pitch.
Nullification crisis could be the tipping point that drops America into chaos
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pentagon ran secret anti-vax campaign to undermine China during pandemic
CHRIS BING and JOEL SCHECTMAN at Reuters:
At the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. military launched a secret campaign to counter what it perceived as China’s growing influence in the Philippines, a nation hit especially hard by the deadly virus.
The clandestine operation has not been previously reported. It aimed to sow doubt about the safety and efficacy of vaccines and other life-saving aid that was being supplied by China, a Reuters investigation found. Through phony internet accounts meant to impersonate Filipinos, the military’s propaganda efforts morphed into an anti-vax campaign. Social media posts decried the quality of face masks, test kits and the first vaccine that would become available in the Philippines – China’s Sinovac inoculation.
Reuters identified at least 300 accounts on X, formerly Twitter, that matched descriptions shared by former U.S. military officials familiar with the Philippines operation. Almost all were created in the summer of 2020 and centered on the slogan #Chinaangvirus – Tagalog for China is the virus.
“COVID came from China and the VACCINE also came from China, don’t trust China!” one typical tweet from July 2020 read in Tagalog. The words were next to a photo of a syringe beside a Chinese flag and a soaring chart of infections. Another post read: “From China – PPE, Face Mask, Vaccine: FAKE. But the Coronavirus is real.”
After Reuters asked X about the accounts, the social media company removed the profiles, determining they were part of a coordinated bot campaign based on activity patterns and internal data.
The U.S. military’s anti-vax effort began in the spring of 2020 and expanded beyond Southeast Asia before it was terminated in mid-2021, Reuters determined. Tailoring the propaganda campaign to local audiences across Central Asia and the Middle East, the Pentagon used a combination of fake social media accounts on multiple platforms to spread fear of China’s vaccines among Muslims at a time when the virus was killing tens of thousands of people each day. A key part of the strategy: amplify the disputed contention that, because vaccines sometimes contain pork gelatin, China’s shots could be considered forbidden under Islamic law.
The military program started under former President Donald Trump and continued months into Joe Biden’s presidency, Reuters found – even after alarmed social media executives warned the new administration that the Pentagon had been trafficking in COVID misinformation. The Biden White House issued an edict in spring 2021 banning the anti-vax effort, which also disparaged vaccines produced by other rivals, and the Pentagon initiated an internal review, Reuters found.
The U.S. military is prohibited from targeting Americans with propaganda, and Reuters found no evidence the Pentagon’s influence operation did so.
Spokespeople for Trump and Biden did not respond to requests for comment about the clandestine program.
A senior Defense Department official acknowledged the U.S. military engaged in secret propaganda to disparage China’s vaccine in the developing world, but the official declined to provide details.
A Pentagon spokeswoman said the U.S. military “uses a variety of platforms, including social media, to counter those malign influence attacks aimed at the U.S., allies, and partners.” She also noted that China had started a “disinformation campaign to falsely blame the United States for the spread of COVID-19.”
[...]
The effort to stoke fear about Chinese inoculations risked undermining overall public trust in government health initiatives, including U.S.-made vaccines that became available later, Lucey and others said. Although the Chinese vaccines were found to be less effective than the American-led shots by Pfizer and Moderna, all were approved by the World Health Organization. Sinovac did not respond to a Reuters request for comment.
Academic research published recently has shown that, when individuals develop skepticism toward a single vaccine, those doubts often lead to uncertainty about other inoculations. Lucey and other health experts say they saw such a scenario play out in Pakistan, where the Central Intelligence Agency used a fake hepatitis vaccination program in Abbottabad as cover to hunt for Osama bin Laden, the terrorist mastermind behind the attacks of September 11, 2001. Discovery of the ruse led to a backlash against an unrelated polio vaccination campaign, including attacks on healthcare workers, contributing to the reemergence of the deadly disease in the country.
[...]
By summer 2020, the military’s propaganda campaign moved into new territory and darker messaging, ultimately drawing the attention of social media executives.
In regions beyond Southeast Asia, senior officers in the U.S. Central Command, which oversees military operations across the Middle East and Central Asia, launched their own version of the COVID psyop, three former military officials told Reuters.
Although the Chinese vaccines were still months from release, controversy roiled the Muslim world over whether the vaccines contained pork gelatin and could be considered “haram,” or forbidden under Islamic law. Sinovac has said that the vaccine was “manufactured free of porcine materials.” Many Islamic religious authorities maintained that even if the vaccines did contain pork gelatin, they were still permissible since the treatments were being used to save human life.
The Pentagon campaign sought to intensify fears about injecting a pig derivative. As part of an internal investigation at X, the social media company used IP addresses and browser data to identify more than 150 phony accounts that were operated from Tampa by U.S. Central Command and its contractors, according to an internal X document reviewed by Reuters.
“Can you trust China, which tries to hide that its vaccine contains pork gelatin and distributes it in Central Asia and other Muslim countries where many people consider such a drug haram?” read an April 2021 tweet sent from a military-controlled account identified by X.
The Pentagon also covertly spread its messages on Facebook and Instagram, alarming executives at parent company Meta who had long been tracking the military accounts, according to former military officials.
One military-created meme targeting Central Asia showed a pig made out of syringes, according to two people who viewed the image. Reuters found similar posts that traced back to U.S. Central Command. One shows a Chinese flag as a curtain separating Muslim women in hijabs and pigs stuck with vaccine syringes. In the center is a man with syringes; on his back is the word “China.” It targeted Central Asia, including Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan, a country that distributed tens of millions of doses of China’s vaccines and participated in human trials. Translated into English, the X post reads: “China distributes a vaccine made of pork gelatin.”
Reuters reports that The Pentagon launched an anti-vaxx campaign in the Philippines and Central Asia to foment anti-Chinese sentiments against their Sinovac vaccine.
#The Pentagon#China#Sinophobia#Sinovac#Coronavirus Vaccines#Vaccines#Vaccine Hesitancy#Coronavirus#Philippines#Donald Trump#Joe Biden#Biden Administration#Trump Administration#Central Asia
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) didn't report a staggering $7 billion in award-level obligations and outlays during fiscal year 2022, according to an inspector general audit released this week.
The EPA Office of the Inspector General (OIG) determined that the agency underreported its award-level outlays by $5.8 billion, or 99.9%, and its award-level obligations by $1.2 billion, or 12.9% during FY22, the period between October 2021 and September 2022. The agency further failed to report any of its Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act outlays and under-reported its coronavirus pandemic-related outlays.
"The lack of complete and accurate reporting also led to taxpayers being initially misinformed about the EPA’s spending, and policy-makers who relied on the data may not have been able to effectively track federal spending," the OIG report concluded.
In response to the audit, House Energy and Commerce Committee Chair Cathy McMorris Rodgers, R-Wash., blasted the EPA and called for increased transparency into its activities.
"It’s outrageous and unacceptable that the EPA cannot keep track of its spending or inform Congress — and the American people — of how it is using taxpayer dollars," McMorris Rodgers said in a statement Thursday. "This eye-opening report only further highlights the need for more transparency at the EPA."
"It also raises questions about whether the agency is incapable of managing its record-high budget or if the agency is attempting to hide the amount of taxpayer dollars it is spending to advance the administration’s radical rush-to-green agenda," she added. "The Energy and Commerce Committee will continue holding this administration accountable for its actions that are driving up costs across the board and hurting Americans."
MICHIGAN DEMOCRAT SIGNED NDA INVOLVING CCP-TIED COMPANY, DOCUMENTS SHOW, CONTRADICTING HER PAST CLAIMS
The EPA ultimately corrected its FY22 figures in May 2023 as a result of the OIG audit while making configuration changes a month later. Overall, the inspector general made five recommendations which it said the agency agreed to make.
The report, meanwhile, comes as the EPA both manages a massive green energy fund and continues to request a larger budget. The Inflation Reduction, Democrats' massive climate and tax bill passed in 2022, created the $27 billion Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund, which in turn establishes a national green bank to fund green projects nationwide.
HOUSE REPUBLICANS OPEN PROBE INTO BIDEN ADMIN FOR OPENING PUBLIC LANDS TO FOREIGN OWNERSHIP
And the White House is requesting that Congress approve a FY24 EPA budget of more than $12 billion, a record level. Republicans have aimed to reduce the EPA budget to about $6 billion, which would be the agency's smallest budget since the early 1990s.
"The Biden administration is using EPA as a pass through for taxpayer dollars to fund left-wing groups that aim to get Democrats elected, not improve the environment," Mandy Gunasekara, a Heritage Foundation visiting fellow who served as the EPA's chief of staff during the Trump administration, told Fox News Digital.
"A failure to report $7 billion is absurd and unacceptable, but also symbolic of how Team Biden operates: prioritizing their political goals over the needs of the American people," she continued. "I’m glad Chair Rodgers is monitoring this and hope the committee brings forth the agency’s Chief Financial Officer to account for this serious oversight."
The EPA did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Experts Call Long COVID in Kids a Public Health Crisis. Why Is It Being Ignored? - Published Aug 26, 2024
For years, public health experts have said that COVID-19 infections in children are “mild.” According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the most common symptoms of COVID in kids are a fever and cough. While some children with the coronavirus are admitted to the ICU and there are pediatric deaths, studies have found that underlying medical conditions including obesity, diabetes, cardiac and lung disorders, increase the risk of severe outcomes.
This research has contributed to how COVID is managed in schools. However, a new study in the Journal of the American Medical Association sheds light on the effect a coronavirus infection can have on children over a longer period. While many people recover quickly from COVID, some don’t, experiencing symptoms that can last for months or years. This condition, known as long COVID, not only affects adults but also children. The new research helps us understand the extent kids experience these debilitating conditions — and how we can treat it.
“This is one of the first large-scale national studies to do research related to long COVID across the entire lifespan, with a particular focus on children and understanding the differences in long COVID in different aged children,” Dr. Rachel Gross, an associate professor in the Departments of Pediatrics and Population Health at NYU Langone and the study’s principal investigator, told Salon.
In the study, led by the National Institutes of Health’s RECOVER Initiative, researchers asked caregivers to tell them about the symptoms that their children or teenagers had been experiencing more than four weeks after a coronavirus infection. For some children in the study, that meant their symptoms went on for three months after their COVID infection. For others, it was up to two years. Researchers looked at the symptoms in those children with persisting symptoms and compared them to children who had never been infected with the coronavirus in the past. They then identified similarities in the prolonged symptoms and found they were distinguishable based on age.
“In school-aged children, we heard commonly that children were experiencing trouble with their memory, focusing, headaches, having trouble sleeping, and stomach pain,” Gross told Salon. “And in the teenagers, we were hearing about symptoms related to fatigue and pain, having body or muscle or joint pain, being very tired or sleepy, having low energy, as well as having trouble with memory and focusing.”
A unique symptom the researchers saw in the teenage group was changes in or a loss of smell or taste. Additionally, researchers found clusters of symptoms that are unique to school-aged children and teenagers. The first were symptoms that affect every organ system in the body.
“These are the children with the highest burden of symptoms,” Gross said, adding that caregivers described these children as having a “lower quality of life and more impact on their overall health.” “The second type of long COVID we also saw across both the ages was predominantly characterized by fatigue and pain.”
Studies estimating its prevalence in pediatric populations are limited and conflicting, estimating up to 25% of children infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus could go on to develop long COVID. A study published in 2024 estimated that up to 5.8 million young people have long COVID.
“This is a public health crisis for children,” Gross said. “We know that child health is so critically important for how children grow and even as they become adults, that chronic illness during childhood and adverse experiences during childhood greatly affects the adults that they can become.”
Gross said the U.S. will see the “long-term impacts of experiencing long covid In childhood for decades to come.”
Dr. Dean Blumberg, chief of pediatric infectious diseases and associate professor in the Department of Pediatrics at the University of California, Davis, told Salon he agreed long COVID is a “public health crisis” for children.
“Some of these kids with long COVID, they are severely affected, they can’t do their normal activities, they fall behind school, they can’t go to school,” Blumberg said. “And then in this study, they highlighted a lot have had some neurocognitive effects, and that really interferes with with learning.”
For Blumberg, the takeaway from this study, he told Salon, is a “call to arms to increase vaccination rates,” which among children, he said are “abysmal.”
According to a recent KFF survey, while both flu and COVID vaccines are recommended for school-aged children, flu vaccination rates were over three times higher than COVID vaccination rates. While COVID-19 vaccines are recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices in the pediatric immunization schedule, they aren’t required for school attendance. According to one study published in the journal Pediatrics, vaccination reduced the risk of an acute infection, but it is less clear whether it protects against long COVID. The latest COVID vaccines were approved by the Food and Drug Administration last week, which the CDC recommends for anyone six months or older.
Now, researchers will be tasked with figuring out why long COVID affects children differently based on their age. When it comes to adults, some studies have shown that subsequent COVID infections increase a person’s risk of getting long COVID. The CDC estimates that one in 13 adults in the United States currently have long COVID symptoms.
Gross told Salon she hopes this research raises awareness for both healthcare providers, as well as schools and educators, that “long COVID in children is not rare.”
“That they are likely to have children experiencing these prolonged symptoms within their healthcare systems and their schools,” Gross said. “And that many of the symptoms that I’ve described, trouble with memory and focusing, headache, trouble sleeping, these are symptoms that you know can impact a child and their schooling.”
#covid#mask up#pandemic#covid 19#sars cov 2#wear a mask#coronavirus#public health#still coviding#wear a respirator#long covid
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
“The future belonged to the showy and the promiscuous”: Why the 21st Century Loves Edith Wharton
Emily J. Orlando
E. Gerald Corrigan Chair in the Humanities & Social Sciences and Professor of English
Fairfield University

Photo: John Singer Sargent, Sybil Frances Grey, later Lady Eden 1905.
If ever there were a good time to read the American writer Edith Wharton (1862-1937), who published over forty books across four decades, it’s now. Since the Wharton revival of the late 20th century, when directors were adapting (the Pulitzer-Prize winning) The Age of Innocence, Ethan Frome, The Buccaneers, and The House of Mirth, her star has continued to rise. As I yesterday prepared to teach The Custom of the Country, which many have called Wharton’s greatest novel, a friend texted me Sofia Coppola’s article on the surprising appeal of its social-climbing heroine. Coppola is developing Undine Spragg’s story for Apple TV. A kind of Gilded Age Material Girl, Undine has been ready for her close-up for years.
Coppola joins an impressive roster of contemporary admirers of Wharton that includes Roxane Gay, Laura Bush, Lisa Lucas, Peggy Noonan, Jennifer Egan, Stephin Merritt, Claire Messud, Meg Wolitzer, Mindy Kaling, Doug Hughes, Brandon Taylor, Ta-Nehisi Coates, Ali Benjamin, Vendela Vida, Ottessa Moshfegh, and Kristin Hannah. At a time when publishing houses are compelled to scale back, new editions of Wharton’s books are appearing in print with introductions by Coppola, Egan, and Taylor.

Photo: Sofia Coppola.
Those who think they don’t know Wharton might be surprised to learn they do. A reverence for Wharton’s writings informs Sex and the City (whose pilot welcomes us to “the Age of Un-Innocence”), Gossip Girl, Downtown Abbey (whose “Lady Edith” suggests a nod to Wharton), and HBO’s The Gilded Age which, like Downton, is created by the Wharton-appreciating Julian Fellowes. His Bertha and George, after all, are named for the power couple from The House of Mirth.
But why Wharton? Why now? Perhaps it’s because for all its new technologies, conveniences, and modes of travel and communication, our own “Gilded Age” is a lot like hers. For the post-war and post-flu-epidemic climate that engendered The Age of Innocence is not far removed from our post-COVID-19 reality. In both historical moments, citizens of the world have witnessed a retreat into conservativism and a rise of white supremacy. Fringe groups like the “Proud Boys” and “QAnon” and deniers of everything from the coronavirus to climate change and Sandy Hook are invited to the table in the name of free speech, and here Wharton’s distrust of false narratives resonates particularly well. Post-9/11 calls for patriotism and the alignment of the American flag with one political party harken back to Wharton’s poignant questioning, in a 1919 letter, of the compulsion to profess national allegiance:
how much longer are we going to think it necessary to be “American” before (or in contradistinction to) being cultivated, being enlightened, being humane, & having the same intellectual discipline as other civilized countries?[i]
Her cosmopolitan critique of nationalist fervor remains instructive to us today.
Edith Wharton seems to have foreseen the excesses, obsessions, and spectacles of our current moment. The scandals documented in Wharton’s narratives serve as harbingers of the sensations that flash across our hand-held screens. Jeffrey Epstein’s sex trafficking touches on the same nerve as the sexual exploitation of minors in Wharton’s Summer (1917) and The Children (1928). The quid pro quo run-in between Wharton’s Lily Bart and Gus Trenor looks uncomfortably forward to Harvey Weinstein and #MeToo. The rise to power of Donald Trump would not surprise Edith Wharton.

Photo: “Vanity,” by Auguste Toulmouche, circa 1870.
Wharton’s tenacious Undine Spragg—as horrifying to progressive era readers as she is admired by Generation Z—can be conceived of as the original social media influencer conscious of her brand. For Undine and her creator know that “the future belonged to the showy and the promiscuous”[ii] and that the turn-of-the-century “world where conspicuousness passed for distinction”[iii] foreshadows our own. Wharton would describe Undine in terms we might use for a “Real Housewife of Park Avenue”: “If only everyone would do as she wished she would never be unreasonable” (162). Undine’s world encourages her to aspire to the rank of trophy wife and the sexual double standard dictating that “genius is of small use to a woman who does not know how to do her hair”[iv] would apply to Wharton herself who, on the 150th anniversary of her birth, would be assessed by a male novelist in terms of how she sizes up to Grace Kelly or Jackie Kennedy.[v] The writer who would declare, in her wildly popular interior design manual The Decoration of Houses, privacy “one of the first requisites of civilized life”[vi] would be appalled by what is broadcast across social media. Wharton also would’ve anticipated the racism directed at Meghan Markle and why granting Oprah an interview would not help relations with her spouse’s family. Children forcibly separated from families due to morally dubious immigration policies echo the plight of war refugees for whose welfare Edith Wharton labored, while the distrust of the cultural other echoes the writer’s own complicated nationalist allegiances.[vii]
Ten years ago, Lev Raphael took the temperature of Wharton studies declaring in the Huffington Post: “Edith Wharton is hot.” She is now positively on fire. I offer below a short excerpt from the introduction to The Bloomsbury Handbook to Edith Wharton, which appears in print today.
*********************

The image gracing the cover of The Bloomsbury Handbook to Edith Wharton, capturing a scene on the terrace of Edith Wharton’s French home, reflects the cultural work that this book takes as its task. The writer is in her element: she cradles in her lap her beloved dogs, she sits outdoors at a well-appointed property she lovingly transformed, she surrounds herself with fashionably dressed cosmopolitans, and she smiles. The moment validates an idea expressed in The Age of Innocence: that “the air of ideas is the only air worth breathing.” As host, Wharton, by this point an internationally acclaimed artist, has brought together representatives of an admiring generation from diverse backgrounds that would outlive and perhaps learn from her. That sunlit terrace is doing something we hope this book will do: provide a foundation for future conversations with Edith Wharton at the center.

Photo: Edith Wharton publicity shot.
Around the time this photograph was taken, Wharton would reflect in A Backward Glance that “[t]he world is a welter and has always been one; but though all the cranks and the theorists cannot master the old floundering monster, . . . here and there a saint or a genius suddenly sends a little ray through the fog, and helps humanity to stumble on, and perhaps up” (379). Wharton’s writings arguably send a ray and help humanity stumble on and up in our own Gilded Age. It is the aim of this collection of essays, produced by leaders in the field at a time of global crisis, to make a meaningful contribution to the scholarship on and dialogue about the work of Edith Wharton and to open up new possibilities for understanding and embracing a writer whose corpus is as enormous as it is resonant. To borrow from Wharton’s preface to her anthology The Book of the Homeless (1916), in which she conceives of her volume, as she so often does, as a house: “You will see from the names of the builders what a gallant piece of architecture it is. . . . So I efface myself from the threshold and ask you to walk in.”[viii]
Emily J. Orlando is the E. Gerald Corrigan Chair in the Humanities & Social Sciences and Professor of English at Fairfield University. She is the author of Edith Wharton and the Visual Arts and editor of The Bloomsbury Handbook to Edith Wharton. She is currently preparing for publication a new edition of Edith Wharton’s first book, The Decoration of Houses.
[i]Lewis, Letters, 424.
[ii]Edith Wharton, The Custom of the Country, New York, Penguin, 2006, 117.
[iii]Edith Wharton, The House of Mirth, ed. Elizabeth Ammons, 2nd Norton Critical ed. (New York: Norton, 2018), 186.
[iv]Edith Wharton, The Touchstone, in Wharton, Edith, Collected Stories, 1891-1910, ed. Maureen Howard (New York: Library of America, 2001), 170.
[v]Jonathan Franzen, “A rooting interest: Edith Wharton and the problem of sympathy,” The New Yorker, February 5, 2012.
[vi] Edith Wharton and Ogden Codman, Jr., The Decoration of Houses (New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons, 1897), 22.
[vii]See Melanie Dawson, “The Limits of Cosmopolitan Experience in Wharton’s The Buccaneers.” Legacy 31.2 (2014): 258-80. Print.
[viii]Edith Wharton, Preface to The Book of the Homeless (Le Livre des Sans-foyer) (New York, Charles Scribner’s Sons, 1916), xxiv-xxv.
#Emily J. Orlando#Fairfield University#Edith Wharton#Gossip Girl#The Custom of the Country#Sofia Coppola#The Age of Innocence#Undine Spragg#Summer#The Book of the Homeless
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
News you won't find on Fox News or other far right outlets.
Official crime statistics are only released after a substantial delay, so for nearly a decade I’ve collected and compiled big-city crime data as a way to assemble a more real-time picture of national murder trends. And this spring, I’ve found something that I’ve never seen before and that probably has not happened in decades: strong evidence of a sharp and broad decline in the nation’s murder rate.
The United States may be experiencing one of the largest annual percent changes in murder ever recorded, according to my preliminary data. It is still early in the year and the trend could change over the second half of the year, but data from a sufficiently large sample of big cities have typically been a good predictor of the year-end national change in murder, even after only five months.
It's in the interests of extremist Republicans to get white people in particular to think that out of control minorities are out to murder them. So when crime goes down, the GOP ramps up other things like culture war issues.
Murder is down about 12 percent year-to-date in more than 90 cities that have released data for 2023, compared with data as of the same date in 2022. Big cities tend to slightly amplify the national trend—a 5 percent decline in murder rates in big cities would likely translate to a smaller decline nationally. But even so, the drop shown in the preliminary data is astonishing.
True, there is still the sensational murder here or there which will get a disproportionate amount of coverage. But murder rates across the board are down notably.
[T]he good news is, well, good. Murder is down 13 percent in New York City, and shootings are down 25 percent, relative to last year as of late May. Murder is down more than 20 percent in Los Angeles, Houston, and Philadelphia. And, most significantly, murder is down 30 percent—30 percent!—or more in Jackson, Mississippi; Atlanta, Georgia; Little Rock, Arkansas; Minneapolis, Minnesota; Milwaukee, Wisconsin; and others.
The last significant drop in crime took place in the 1990s during the Clinton administration.
The cause of the Great Crime Decline of the 1990s, when murder fell 37 percent over six years, is still not fully understood, so any explanations of the current trend must remain in the hypothesis phase for now.
I hate to rub it in, but there seems to be at least a modest correlation. In the 1970s and 1980s when 16 of those 20 years were under Republican administrations, the crime rate in the US soared. The crime decline of the 1990s and the current murder nosedive are under Democratic administrations.
The current dip is despite the number of police officers being the same or just slightly down.
Murder is down in Chicago, New Orleans, and New York, for example, but Chicago’s number of police officers is virtually unchanged from last summer, while New Orleans’s is down more than 8 percent and New York has roughly 2 percent fewer officers.
The end of the emergency phase of the coronavirus pandemic may also be contributing to the decline in murder.
The murder rate went up during the COVID-19 emergency. Perhaps that's another result of Donald Trump's botched handling of the pandemic.
It's been finally dawning on people that Republicans aren't great for the economy. Eventually it may also become conventional wisdom that the GOP is bad for public safety.
When the de facto leader of the Republican Party is an indicted lying crook with the mindset of a petty mobster, that sends a message to American society that such behavior is acceptable. No wonder criminal behavior is down since Trump's departure from office.
No honest person can call the GOP the party of "law and order" any more.
#public safety#crime#murder rate in the us#2023 murder stats#decrease in murder rate#crime is rampant under republicans#clinton administration#biden administration#donald trump#trump's botched handling of covid-19 emergency
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
The U.S. defense industrial base just got a $20 billion shot in the arm from the national security supplemental bills passed by Congress last week. But although officials and experts believe the funding will provide a much-needed jolt to military production and help open up new factory lines, some say it’s still not enough to respond to China, Russia, and terror threats at the same time.
“We have begun—begun—to rebuild the industrial base with the supplementals,” Bill LaPlante, the Pentagon’s acquisition chief, said at an event last week. “Calling it a wartime footing, no.”
The biggest need? Money. Officials and experts say that the United States needs more of it, lots more, to make the real investments. At the peak of World War II, the United States was spending nearly 40 percent of its GDP on defense. It’s down to less than a tenth of those spending levels now. And the need to spend more has gone up with the Chinese spending more—and with Russian factories working around the clock.
“It’s still shy by quite a bit [for] what you would need to get our stockpiles in the right shape, get our industrial base in the right shape, help the Taiwanese, and get the Ukrainians in a position that they can get some leverage in negotiations,” said Jeb Nadaner, a former U.S. deputy assistant secretary of defense for industrial policy. “If the benchmark is against the calendar and the clock, we’re still falling behind every month. And that can’t go unnoticed by China.”
But the jolt will allow the United States to surge artillery production and solve key bottlenecks.
One is the production of solid rocket motors used for everything from Javelin anti-tank weapons that can hit a tank from a little over a mile away to intercontinental ballistic missiles that can propel warheads across the Atlantic and Pacific oceans if a U.S. war with Russia or China ever went nuclear.
Aerojet Rocketdyne, which was recently bought out by L3Harris Technologies for nearly $5 billion, was one of only a few suppliers. But the supplemental gives several billions of dollars for companies, such as Orbital ATK, to expand their solid rocket motor facilities.
And it provides money from the Defense Production Act—the same law that Washington used to force U.S. manufacturers to produce more masks, gloves, and face shields during the coronavirus pandemic—to build out a second tier of rocket motor suppliers, including X-Bow Systems in Texas; Ursa Major in Colorado; and Adranos in Mississippi, which was recently bought out by defense technology company Anduril. The idea is to fast-track work that wasn’t going to be done until at least 2026, if not 2027 or 2028, according to a congressional aide, who spoke on condition of anonymity to talk about military contracts that hadn’t been made public.
There’s also about $100 million to help Williams, one of the only American makers of cruise missile motors, speed up production in Michigan. Those motors are used in the long-range anti-ship missile that might one day help Taiwan fend off Chinese landings; the armor-piercing joint air-to-surface standoff missile; the Tomahawk land attack missile that is the U.S. Navy’s weapon of choice; and the Harpoon missile that the Ukrainians have used in the Black Sea.
There’s also money to build factories for ball bearings, printed circuit boards, and other subcomponents for the $311 billion that the Pentagon wants to spend in the upcoming year to develop new weapons. Processor assemblies, castings, forgings, microelectronics, and seekers for munitions have been major bottlenecks. And there are recruitment and attrition problems almost across the board, from welders at shipyards to rocket engineers, a generational problem that might need vocational-training fixes at the high school level and up.
But with some Democrats pushing back on the Biden administration’s $850 billion Pentagon budget proposal as too costly, there’s also a focus on smaller attritable capabilities that don’t need a whole lot of start-up capital or defense industrial muscle to get moving.
There’s a ton of counter-drone money, about $600 million, that will go toward Coyotes, a small drone capable of intercepting other drones, and Roadrunners, an air defense munition that takes off vertically—just like the F-35 fighter jet variant flown by the U.S. Marines.
Some members, such as House Armed Services Committee ranking member Adam Smith, have advocated for ending production of ground-launched nuclear weapons. Congress is also trying to scrap old weapons, including F-15 fighter jets, the A-10 Warthog aircraft, and littoral combat ships used by the Marines. Smith is even curious about using microwaves as the next generation of air defense instead of directed energy.
The United States is also torn between near-term needs, like 155 mm artillery ammunition, and long-term needs—like a sixth-generation fighter jet that will follow the F-35. “There are going to have to be some trade-offs between preparing for a near-term fight and near-term deterrence and probably making some trade-offs on some next-generation weapons systems,” said Seth Jones, the senior vice president and director of the international security program at the Center for Strategic and International Studies in Washington, D.C.
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine is still going to be a major factor in setting requirements for the U.S. military. “We’re going to be selling 155 [mm] like a drunken sailor for a few years,” said Mark Montgomery, a senior fellow at the Foundation for Defense of Democracies. “The Western alliance needs the U.S. to crank 155 [mm] for a decade.”
Other weapons used in the early days of Ukraine’s defense of Kyiv are likely to hit a plateau in production. Those include Javelin systems; the High Mobility Artillery Rocket System, or HIMARS; and Stinger anti-aircraft missiles, which the Pentagon sent to Ukraine in large numbers early in the war and are also included in the supplemental, but which have taken on a secondary role as the fight has been bogged down in trench warfare for months and months.
Allies can help solve some of the bottleneck problems. The United States is co-developing new glide-phase interceptors with Japan as well as co-producing guided multiple-launch rockets with Australia and guidance-enhanced missiles for Patriot air defenses with the Germans. But after the political fights that took the supplemental more than six months to get through Congress, LaPlante and other officials acknowledged that the United States now has an image problem in showing itself to be a reliable torch-bearer for the global defense industrial base.
There’s another major production plateau that members of Congress are trying to stave off: attack submarines. The Biden administration’s proposed budget for the upcoming year slashed funding for one attack submarine. For years, producing two a year had been the standard, even though U.S. shipyards only produce between 1.2 and 1.4 Virginia-class submarines each year, and new variants are 24 to 36 months behind schedule.
And there are dependencies that are difficult—if not impossible—to cut. The United States still buys a significant amount of its titanium from Russia, which is used for everything from landing gears to tank armor, and is only slowly ramping up production of rare earth minerals, which are dominated by China. But the U.S. military’s weapons are ravenous for rare earths: The F-35 needs 900 pounds of rare earths to run, and the Virginia-class submarines need more than 10 times that amount. The military also needs lithium ions used in advanced battery production that China also dominates.
Where Congress and the Pentagon are having more trouble jolting the defense industrial base to life is for weapons that might be used in the Indo-Pacific. The U.S. Army’s precision strike missile that would be used to hit incoming Chinese ships from more than 600 miles out, for instance, is still being developed—the seeker that would find enemy vessels isn’t finished—so there’s no way to ramp up capacity, at least not yet.
But before the United States ramps up industrial capacity, some members of Congress want the Pentagon to take a good, hard look at what’s already on the books.
“Where can we look within the budget and say, wouldn’t we be better to spend more money on these things that we really do need?” Smith said. “So before I get into a discussion about, ‘Gosh, it’d be great if we had another $50 billion,’ where are we spending the money that we have? I think that’s the first question.”
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Letters in Your Last Name- Chapter 11

A/N: So the next several chapters center in the COVID universe. A fun dynamic of Kevin has to leave and Sam has to stay. Our lil babes are gonna go through it a lil bit now 🥺
Word Count: 4.6k
Warnings: COVID talk, swearing, angsty
NHL suspends season indefinitely as coronavirus outbreak continues.
The air in the apartment is almost giddy despite the unknown of what is to come of the 2019-2020 NHL season. With the Coronavirus beginning to grip the world more fiercely, all large events in the United States have come to a screaming halt, seemingly overnight. As disappointing as it is for obvious reasons, it is even more so for the Wild specifically as they were really beginning to turn their season around. The last game against the Ducks in Anaheim was a dynamic game for Kevin with two power play goals to lead the team to their latest, and maybe last, win of the season. For now, players, and their families, have no choice but to wait in limbo to see what the next steps will be.
Now with all that, why are we giddy? Because since October, we haven’t spent more than 7 consecutive days together. Therefore, the idea of getting extra, almost borrowed time, has us both on a comfortable high. Kevin and I are having a lazy day, a rarity during the late season that we are taking advantage of now. We already ate a delicious dinner of grilled cheese and tomato soup. Now we are catching up on a few Netflix releases we have missed in the last few weeks. To All The Boys Part 2 is playing on our living room TV. My hand loosely fingers the strands of Kevin’s hair. I can tell he is drifting in and out of sleep on my lap.
The shrill sound of his phone ringing jolts both Kevin and I from our relaxed positions. He reaches for it on the coffee table, flipping the screen. We both see the picture of him and his mother. He clears his throat and rubs the sleep from his eyes.
“Ahoj?” Kevin answers in Czech. I can hear the rushed sound of talking over the other end and furrow my brows inquisitively. Kevin stands and walks out of the room to our bedroom, listening intently. When he returns a few minutes later, he is off the phone and has a worried expression. “The U.S. is banning air traffic to and from Europe on Friday.”
“What? No way… that can’t be true.” I say, becoming alert. How has this already escalated to a point where we would essentially shut down commerce and travel between continents? Fear grips my throat at the look on Kevin’s face.
“My mother just told me.” He motions to his phone. He reaches for the remote for the TV and flips to one of the national news programs. There, the President is confirming what Kevin’s mom told him just now. A travel ban will begin on Friday. All non-US citizens are restricted from entering the United States if they are coming from 26 different European countries- including Switzerland and Sweden. For now it seems, Kevin would be able to return to Europe from the United States. How long that will last is unknown at this time.
Kevin and I grow dead silent as we watch the press conference play out on NBC.
“Does this mean you need to go?” I wonder what we are both thinking out loud.
“I… Don’t know…” He trails off. I faintly hear a sound and I know it’s the fictitious noise of our bubble of bliss giving way to the cold, dreadful reality of a global pandemic.
“Kev, I’m getting nervous.” I admit to him. He reaches for me and pulls me across the couch, into his chest.
“Me too.” He whispers against my head. “I’ll call around tomorrow and figure out what I should do.” He assures me. I know his words are meant to soothe me, but they don’t. Instead, the lump of fear in my chest expands until I feel like I’m suffocating.
The next day, I sit quietly at the island in the kitchen as Kevin makes his calls. The kitchen is filled with smells of soup simmering in the crock pot and my latest bath and body works candle burns in the center of the counter. It feels like any other, winter day, but it isn’t. His first call is to Andy Heydt, Director of Hockey Operations for the Wild. Andy is still unsure of the exact direction the NHL is advising for players, but he promises to follow up with Kevin once he hears more. The next call is to his agent, who echos the same thing to Kevin- they still don’t know what to advise players to do at this time. The next few calls are to his parents, a few friends in Sweden including his trainer, Andreas. Life seems to be going on normally in Sweden despite the news from across the pond.
“This seems to be a lot of hurry up and wait.” Kevin shrugs as he tosses his phone down and sits next to me. He reaches for a piece of granola from the bowl in front of me and crunches on it. “I can’t really do anything until the NHL decides what we can do.”
“Well, they have already suspended the season, so it’s highly likely they would support players returning home.”
“Yeah, it’s just tough because we don’t know how long that will be. A few weeks, a month? No one knows at this point and if they let us leave, we likely won’t be able to return until the travel ban is lifted.”
“What a mess.” I murmur, grabbing a cluster of granola. I bring it to my lips, but can’t stand the idea of eating anything else while my stomach summersaults inside of me. I drop it back into my bowl and push the rest to Kevin. “If you can go, do you think you will?”
“I’m not sure. Honestly, I might have to with my VISA. If the league isn’t running, that means I’m not authorized to be here longer than 90 days. This shutdown could be longer than that.” Kevin explains to me, letting out a frustrated sigh. “At least we can spend some time together.” I nod in agreement. Yet, I can’t help but reflect on how long we will have.
Kevin and I pass the time snuggling on the couch under a large blanket, watching HGTV. I’m a sucker for Love it or List it even though the entire show seems staged and fake. At least it is a distraction from the heaviness of what is happening in the world right now. Kevin has fallen into a brief cat nap when his phone begins to buzz again. He puts it on speaker as Andy’s voice rings out.
“Hi guys. I just got word from the NHL & NHLPA that they are making moves to allow for players to return home. An announcement will likely be coming in the next few hours. Because of VISA expirations, the NHLPA is recommending all Non-U.S. Citizens return home. Kevin, at this time you are required to return to Sweden and self-quarantine for now. Start looking for tickets for the first flight you can find. They’re going fast. If you need help, let me know and we can get our office on it as well. The NHL & NHLPA will be meeting again in the next few weeks to decide on additional next steps for resuming the season. There is optimist talk for that to begin at the end of this month, but the likelihood of that is looking slimmer by the hour.”
“Okay.” Kevin confirms. I don’t look at him while he wraps up the conversation.
“Be safe, Kevin.” Andy ends the call with a click, off to call the other international players on the Wild.
“I guess I’m going.” Kevin whispers, pulling me into his lap. He buries his face into my body and I hold him close. I don’t want him to go. I am so afraid that he can’t stay with me. The idea of no set date of a return for the league, and therefore Kevin, makes my stomach twist into an uncomfortable knot. The way this seems to be coming together- the talk of visa expirations and leaving despite a travel ban- the league is preparing for an extended break. Kevin lifts his face and looks into my eyes. A pained expression flashes across when he takes in my tears. Now that they have started, I can’t stop them.
“I know.” He tells me, pulling me forward and resting his cheek against mine. “I’m sorry.” I nod and a hiccup sob escapes my lips. “It will be okay.” He assures me. We both know he can’t guarantee that, but it eases a bit of the pressure in my body to know he believes it.
The rest of the day is awful. Kevin begins to make his arrangements to leave and soon we can’t hide from the truth. He leaves tomorrow for Sweden on a one-way ticket. Kevin releases a heavy sign when his purchase is confirmed and flips his phone to the other side of the couch. He looks at me, but I can’t bring myself to meet his gaze. I know I should at least be pretending to be supportive in this, but it’s difficult. There is so much unknown in this world. It’s scary, yet I felt like if we were together, we could make it through. Now he is leaving and the loneliness is hovering. I can feel it descending on me like a despondent shadow trying to steal my joy.
The crockpot beeps in the kitchen signaling the Chicken Wild Rice soup is done. We both glance in that direction before our eyes meet in a loaded look. I feel tears stinging my eyes and I have to look away. I don’t want to cry again. I want to be strong for now and then completely fall apart after he leaves tomorrow.
Kevin stands and slowly walks over to the windows, looking out at the Minnesota skyline. The sun has set and the city lights twinkle in the cold winter night. I know we are both thinking similar things. This morning when the sun rose, everything was okay. Different, but okay. Now, when the sun rises tomorrow, Kevin will leave for an undetermined amount of time. I swallow the lump in my throat and slowly rise to finish the soup. I stir in the heavy cream and spoon us both up a small bowl, handing Kevin his at the window. He turns to me, grabbing it from my hands and pulling me into his arms.
“Sam, I don’t want to go. I need you to know that…” He trails off, whispering into my hair. All I can do is nod my head in acknowledgement.
“This is going to be really hard.” I whisper to him. I’m afraid if I talk any louder, my voice will break.
“I know, baby.” Kevin rests his mouth on the top of my head. We stay like that for minutes- until the soup is cold and the show ends and the sadness has begun to suffocate us. I pull away first to look into his beautiful face.
“I love you.” I say simply. It won’t fix anything or change this pandemic, but at least we have that.
“I love you too.” He responds. I grab his soup bowl from the table and walk back into the kitchen. I set the bowl down on the counter and frown at all the soup in the crockpot. The last thing I’m interested in right now is eating. The only thing I feel right now is nothing at all. I’ve evidently gone numb in the last hour.
“Baby.” Kevin calls to me from the hallway. “Let’s go to bed.” He holds his hand out for me and I take it, following him slowly down to our room. But I don’t want to go to bed. I don’t want to fall asleep and wake up knowing he will be gone in a matter of hours. Kevin throws the comforter back on our bed and pulls me into him. He settles me deep into his chest and holds on tightly. No wandering hands. No sexy smooches. Just the deep intimacy of holding one another close.
“Maybe it won’t be that long.” Kevin murmurs to me. I shake my head no. My heart can’t take the speculation of the what ifs tonight. I tilt my face up to look at him, wanting to memorize every bit of this moment together. “Even when I leave tomorrow, a part of me is staying here with you.” He tells me, brushing a strand of my hair behind my ear and holding my face in his hand. I close my eyes and lean into his touch. His thumb brushes against my lips before I feel him kiss me. It’s emotional-filled with pain, sorrow, and a deep love that leaves me aching. His hands pull me in tighter and I lace my hands behind his head.
I don’t know how I will possibly let him go tomorrow.
_ _ _
“Alright. I think that’s it.” Kevin says as he grabs the final suitcase from my SUV. He sets it on the ground and closes my trunk. Between the multiple suitcases and all of his hockey equipment, he has the luggage cart overflowing. I can’t imagine how much that all costs to fly across the ocean.
“Do you need help?” I ask him, fidgeting with my keys.
“No, I got it.” He assures me, sliding each of his arms into his backpack. “Come here.” He demands, tugging me into his chest and squeezing me tightly. We stay like that for several moments. I realize that I’m crying and I don’t even care. What is the point in being strong now? This entire week, this entire virus, has been exhausting, terrifying, and at times, heartbreaking. I want to go back to yesterday morning. The blissful, ignorance of it all was reassuring and safe.
“I don’t want to let go.” Kevin whispers to me. I just shake my head in response; there are no words left to say.
His hand rubs comfortingly up and down my back through my winter jacket. I blink rapidly as I pull away, rubbing the sleeves of my sweatshirt under my eyes. Kevin’s arms stay around me as he looks down into my face.
“I don’t know what to say to make this less hard.” He admits to me. “All I know is that I miss you so much and I’m not even gone.”
“Kev, we can’t change this. Just be safe.” I mumble to him, standing on my toes and bringing our lips together. He immediately opens his lips and his tongue finds my mouth. The kiss is passionate and painful. I never want it to end. His hands pull me tighter to him. I grip his jacket firmly, trying to stay as close and held by him as possible.
“I love you.” I tell him earnestly when we pull apart.
“I love you too.” He repeats to me. The sadness on his features breaks my heart all over again. “Be safe, okay?” I nod my head as my bottom lip quivers again.
With all my remaining resolve, I step from his arms completely. Kevin stays there for a moment, just looking at me. I’ve never seen his face so sullen, his eyes so desperate and his demeanor so damn sad.
“Kev… just go.” I encourage him, knowing it’s what he needs to hear. A final, dark expression crosses his face but he nods in response.
“Bye.”
“Bye. Have a safe flight.” I watch as he puts his mask on. I swallow hard, determined to keep it somewhat together until he has disappeared into the airport.
“I’ll call you when I get there.” He tells me as he puts his hands on the cart. It takes all my will power to not step towards him and beg for him to hold me just a few moments longer. Instead I look at his shoes, because if I look at his face, I’ll be done.
“Okay.” I whisper to him. When I lift my eyes to his, I’m right. I’m done. Tears fall from my eyes in a steady stream. Kevin’s eyes are getting glassy and he’s trying hard not to let his tears fall. He reaches for me and I rush into his arms one final time. My tears soak into the shoulder of his jacket. When we release each other again, we know it has to be the last time.
With a final longing look, he turns and pushes the cart towards the door. I watch his retreating back, eating up every second that I can get of him. When he disappears through the door, a strangled sob escapes my lips. God damn it. Leaving him at this airport might just kill me. I suck in a breath of air and it immediately comes out as another sob. I press my hand to my lips and turn, jumping into my SUV and resting my head on the steering wheel. I don’t care that I’m sitting in a space someone else could use. I don’t care that security is walking along the sidewalk encouraging people to keep moving. I can’t think of anything beyond the deep, aching pain in my chest.
This is not how it’s supposed to be.
_ _ _
In July, the ringing of a FaceTime call pulls me away from my intense concentration of coloring in my adult coloring book. Entertainment is tough to come by when most of the city is shut down still due to COVID. Living in downtown was warm and homey prior to COVID. Now, it’s just cold and industrial without people around. I miss the constant stream of cars and noise. In April, I had to buy a white noise machine just to be able to get to sleep every night.
I reach for my phone, smiling when I see Kevin’s face.
“Hi!” I say excitedly, “Tell me you have good news!”
There have been rumblings in the hockey and media circles that the NHL is close to resuming. It’s been almost five months since the NHL season was paused. It’s been over 100 days since I’ve seen Kevin. To say it’s been difficult would be an understatement. What feels more difficult is that Kevin is able to live relatively normal in Sweden, while we have been under various mandates and lock downs to mitigate the spread of this virus. When Kevin first returned, he was cautious. He spent most of his time in his apartment or training at the local arena. However, as the months have dragged on, he’s gotten pretty loose. Part of me worries for him and the other part of me is insanely jealous.
“Relatively good.” He confirms. “I’ll be back soon!”
“Yay!” I yell, kicking my legs in excitement.
“And then I’ll be leaving for Canada in three weeks.”
“What? No.” The smile drops from my face. “The league is doing the bubble?” I groan, throwing myself back down onto the couch.
“Yeah.” He sighs deeply. “Sorry, babe. But at least we will have some time together.” I watch as Kevin walks out of the arena and into the bright sunlight. Sweden looks gorgeous today. Kevin waves to someone out of the camera view, then looks back down at his phone. “I’m heading back to my place to look at flights. I can let you know what a few of the options are to see what works best?”
“Whatever gets you to me the fastest and soonest.” I say to him. He grins in response, nodding. “I miss you so much, Kev. I’m so excited to see you!”
“Me too, baby. What are you up to?”
“Coloring.” I show him my coloring book. It’s a black and white page filled with different types of flowers. In the middle in loopy calligraphy are the words eat a bag of dicks. “For Alex.” I wink at Kevin who bursts out laughing.
“I want to be there when you give that to him.”
“You better get here soon then. I think I’m going to frame it and give it to him for his birthday next week.” I giggle wickedly at that. “Speaking of birthdays, what are you doing for yours tomorrow?” I wonder, tossing my art project to the side and focusing in on him.
“Andreas is taking me to a good pizza place here.” He mentions his off-season coach as he settles into the driver seat of his car. “I wish you were here though.” He gives me a small, sad tilt of his lips.
“Stupid COVID.” I pout at him. “I hope someone gets you a princess cake!”
“I actually got myself one already.” He admits somewhat sheepishly. “I’ve been dying for a piece all day but forced myself to wait until after training.”
“Cake for breakfast is definitely a birthday tradition for you.” I wiggle my eyebrows at him. We both grin as we remember his birthday last year in Sweden. Frosting everywhere, his sheets being ruined and us not caring at all.
“Just doesn’t taste as good without you though.” He beams at me.
We chat a little bit longer as Kevin drives back to his place. Eventually, we end the call as Kevin gets ready to hop into the shower. He has a meeting with a company for a potential sponsorship opportunity. It’s an athletic, energy drink that we do not have in the United States. He says he will bring some back for me to try.
Once our call ends, I busy myself with completing Alex’s picture. I search around various websites for a frame, finding one on Amazon that can be delivered tomorrow. Satisfied with my purchase, I begin the chores I’ve been putting off for the last few days, including laundry, dishes, and cleaning the bathroom. Once I’ve accomplished those, I turn my attention to dinner. I found a soup recipe on Pinterest that seems light enough for summer. Even though the summer heat in Minnesota feels oppressive at times, there is something about soup that comforts me. I could use some of that as I wait out the last few weeks before Kevin arrives. I ponder when he may be back. Hopefully it’s within the next week or so. It’s hard to know what options are available with how limited the flight choices are these days.
My phone jingles as I’m cutting up the onion for my soup. I glance down, seeing it’s the front desk of our building. I click the green button and shove my phone between my cheek and shoulder so I can continue working on dinner.
“Hi Dave.” I answer. We have a few people who work the front desk here, but I know it's Dave today. With limited interaction with the outside world, I've gotten to know the front desk people and their schedules well. Dave is my favorite though. He's in his second career after retiring from the Postal Service at an early age.
“Hi Sam, you have a food delivery here.”
“Oh, really? I didn’t order anything. Does it say from where?” I ask adjusting the phone from my shoulder to my hand.
“Not sure. It’s just a white bag.”
“Okay, I’ll be down in a second.”
I end the call as I’m stuffing my feet into my sandals. I grab my keys from the bowl, trying not to frown at the sight of Kevin’s keys. Soon. He will be home soon. I take the elevator to the lobby. Dave is waiting for me outside the elevator and hands me the white bag.
“I figured I’d save you a few steps.” He smiles kindly at me.
“Thanks, Dave. Are you heading home soon?”
“I am, but I’ll be back tomorrow- same time and place.”
“Well, I’ll stop by with some soup. I’m trying a new recipe tonight.”
“I’d like that. Goodnight, Sam.”
I wave goodbye and hit the 15th floor again before peering into the bag. I can see a gold, Wuollet’s Bakery sticker on the white box along with a red ribbon securing the sides. It’s sizable and heavy, but I’m unsure what is in it or who it could be from. When I enter the apartment, I set the bag on the counter and carefully lift the box out of the bag. Beneath the box is a white card with my name on it. I open the envelope and flip the card over to read the message.
Save some for when I’m home on Friday. I love you!- Kevin
My stomach drops to my knees and I let out an excited squeal. I carefully undo the ribbon from the box and open the top to reveal a Princess Torte. Although not completely the same, it’s very similar to what Kevin will be having tomorrow for his birthday. I glance at the time, seeing it is after midnight in Sweden, meaning it’s officially his birthday. I grab my phone and click on his name to begin the FaceTime call. Kevin picks up after one ring.
“Hi birthday boy.” I murmur to him through my large grin. He cheeses back to me in his dark apartment.
“Hi beautiful.” He tells me as he sits up, pausing the show he is watching.
“It’s your birthday, but I’m getting cake?” I ask him, flipping the camera so he can see the cake.
“Well, it is technically for both of us.” He insists, his smile somehow grows larger.
“You’re really coming back that soon?”
“Yep!”
“Baby…” I trail off, looking back at the princess cake.
“Friday.” He confirms to me.
“Two more sleeps.” I respond.
“I have to quarantine…” He reminds me.
“Shush. Don’t ruin it.” I tell him, grabbing a knife to cut into the cake.
“Okay.” He laughs. “Hey, that’s a big piece.” He scolds me jokingly, watching me cut into the green fondant. “At this rate, you’re going to eat it all without me.”
“Oh my god, Kevin. You like this cake more than me.” I tisk at him, turning the camera so it’s back on me.
“Eh.. It’s good, but not that good.”
“Uh huh.“ I roll my eyes at him while savoring the bite of sugary goodness.
“It’s really doing something for me watching you suck on that fork.” Just to tease him, I flick my tongue up the fork and giggle. “You’re gonna have to pay for teasing me like this.”
“Looking forward to it.” I tell him, running my tongue along my lips tantalizingly slow. I watch him gulp before I take another slow bite of the cake.
“Damn.” He mutters to me, blowing out a quick breath. “I can’t wait to kiss that mouth.”
I take a sip of my water from my Yeti and laugh lightly. When I return my gaze to him, he’s watching me through sleepy eyes.
“You should go to sleep. Just because it’s your birthday doesn’t mean you get a day off from training.” I tease him. Kevin yawns and rubs a hand over his face.
“That’s true. If anything, I’m probably going to get my ass kicked.”
“That’s how you know Andreas cares.” I give him a sweet smile, pushing the cake away to lean against the counter. “I’ll see you soon though.”
“So soon.” He whispers back to me. “I’ll call you tomorrow.”
“Okay. I love you. Happy birthday, babe.”
“Thank you. Love you.” He smiles before I end the call.
My heart swells as I glance at the clock.
Only 48 more hours of living in different countries.
But who’s counting?
#letters in your last name au#kevin fiala#Kevin Fiala Fic#los angeles kings#my writing#hockey fan fiction#hockey writing#NHL writing
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
ICYMI last week
"The Department of Justice (DOJ) announced Wednesday the launch of two new COVID-19 fraud strike forces, as 371 people were charged over offenses in connection to the alleged theft of more than $800 million in coronavirus aid.
Out of the 371 defendants charged with pandemic-related fraud, 119 of them either pleaded guilty or were convicted at trial, according a DOJ press release. Authorities also said that more than $57 million in court-ordered restitution was imposed, and 117 civil matters occurred during the federal sweep, with more than $10.4 million in judgments.
Federal prosecutors also worked with law enforcement authorities to secure forfeiture of more than $231.4 million, the DOJ said.
“The Justice Department has now seized over $1.4 billion in COVID-19 relief funds that criminals had stolen and charged over 3,000 defendants with crimes in federal districts across the country,” Attorney General Merrick Garland said in a statement.
“This latest action, involving over 300 defendants and over $830 million in alleged COVID-19 fraud, should send a clear message: the COVID-19 public health emergency may have ended, but the Justice Department’s work to identify and prosecute those who stole pandemic relief funds is far from over.”
The department also announced the launch of two additional coronavirus fraud strike forces: one at the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the District of Colorado and one at the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the District of New Jersey.
The department said that the two new strike forces add to the three strikes launched last September in California, Florida and Maryland.
“The law enforcement actions announced today reflect the Justice Department’s focus — working with our law enforcement partners nationwide — on bringing to justice those who stole from American businesses and families at a time of national emergency,” Deputy Attorney General Lisa Monaco said. “The two new Strike Forces launched today will increase our reach as we continue to pursue fraudsters and recover taxpayer funds, no matter how long it takes.”
8 notes
·
View notes