#Data Privacy Laws Around the World: What Marketers Need to Know
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Data Privacy Laws Around the World: What Marketers Need to Know

In today’s digital age, data privacy laws are more important than ever. As marketers, it’s crucial to stay informed about the regulations that govern how we collect and use personal information. From the GDPR in Europe to CCPA in California, understanding these laws can help protect your customers’ data and build trust with your audience. In this blog post, we’ll explore key data privacy laws around the world and discuss what marketers need to know to ensure compliance and safeguard their reputation. Let’s dive in!
Introduction to data privacy laws and their importance for marketers
In today’s digital age, the use of personal data is a central aspect of marketing strategies. Companies collect and analyze vast amounts of consumer information to tailor their advertisements and promotions, with the goal of increasing sales and revenue. However, with this increased reliance on data comes the responsibility to protect it and respect individuals’ privacy rights.
Data privacy laws are regulations put in place by governments to safeguard personal information from being misused or shared without consent. These laws vary in scope and complexity across different countries, but they all share a common goal: to protect individuals’ sensitive data from exploitation by businesses.
The rise of online platforms and social media has made it easier for companies to gather user data through various channels such as cookies, browsing history, location tracking, and more. This has raised concerns about how this data is collected, stored, and used by organizations. In response to these concerns, many countries have implemented strict data privacy laws that require companies to follow specific guidelines when handling personal information.
One of the most well-known data privacy laws is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. It applies to all companies that process personal data of EU citizens, regardless of where the company is located. The GDPR gives individuals more control over their personal data and requires businesses to obtain explicit consent before collecting, using, or sharing it.
Overview of different data privacy laws around the world, including GDPR, CCPA, and others
In today’s digital world, data privacy has become a major concern for individuals and businesses alike. With the increasing amount of personal information being collected and shared online, governments around the world have implemented various data privacy laws to protect their citizens’ rights.
One of the most well-known data privacy laws is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which was implemented by the European Union (EU) in 2018. This law applies to all companies that collect or process personal data of EU citizens, regardless of where they are located. Under GDPR, individuals have the right to know what personal data is being collected about them, how it will be used, and who it will be shared with. They also have the right to access their data, request its deletion, and give or withdraw consent for its use.
Another important piece of legislation is the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which went into effect in 2020. Similar to GDPR, CCPA gives California residents more control over their personal information held by businesses. It requires companies to disclose what personal data they collect and how it is used, as well as giving consumers the option to opt-out of having their data sold.
Other data privacy laws around the world include:
1. Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA): This law applies to all organizations that collect, use or disclose personal information in the course of commercial activities. It requires companies to obtain consent before collecting, using or disclosing personal information and to provide individuals with access to their personal information.
2. Australia’s Privacy Act 1988: This law regulates how private sector organizations handle personal information. It requires companies to have a privacy policy outlining how they collect, use, and disclose personal information and to give individuals the right to access their data.
3. Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (LGPD): This is Brazil’s answer to GDPR and it went into effect in September 2020. LGPD applies to all companies that process personal data in Brazil, regardless of where they are located. It gives individuals the right to access, correct, delete, and limit the use of their personal data.
4. Japan’s Act on the Protection of Personal Information (APPI): This law regulates the handling of personal data by businesses in Japan. It requires companies to obtain consent before collecting or using personal information and gives individuals the right to request disclosure or correction of their data.

How these laws impact marketing strategies and tactics
Data privacy laws have a significant impact on marketing strategies and tactics, as they dictate how businesses can collect, use, and store personal information of their customers. These laws are constantly evolving and becoming more stringent in order to protect the sensitive data of individuals. As a marketer, it is crucial to stay informed about these laws to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal repercussions.
One major way in which data privacy laws impact marketing strategies is through the limitations on data collection. In the past, marketers had access to vast amounts of personal information collected from various sources such as cookies, social media platforms, and third-party data brokers. However, with the implementation of laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, businesses now need explicit consent from individuals before collecting their personal data. This has led to a shift towards building first-party data through opt-in forms or loyalty programs rather than relying on third-party sources. Additionally, data privacy laws also restrict the use of personal information for marketing purposes. Marketers must carefully consider how they use the data collected from consumers and ensure that it aligns with the purpose for which it was originally collected. For example, if a customer provides their email address to receive updates about a specific product, businesses cannot use that email address to send them promotional emails for other products without their explicit consent.
These laws also impact marketing tactics such as targeted advertising and personalization. Marketers must be transparent about the data they collect and how it will be used, and they must provide individuals with the option to opt-out of targeted advertising. This means that businesses need to be more strategic in their targeting efforts, using only the data that is necessary and relevant for their campaigns.
Key compliance requirements and best practices for marketers to follow
As marketers, it is important to understand and comply with data privacy laws around the world. Failure to do so can result in hefty fines, loss of consumer trust, and damage to your brand’s reputation. In this section, we will discuss key compliance requirements and best practices that marketers should follow to ensure they are meeting data privacy laws.
1. Consent and Transparency: One of the fundamental principles of data privacy laws is obtaining consent from individuals before collecting or processing their personal information. This means that as a marketer, you must clearly communicate what personal data you are collecting, why you are collecting it, how it will be used, and who it will be shared with. Additionally, the consent must be freely given, specific, informed and unambiguous. Make sure your opt-in forms are easy to understand and have a clear affirmative action from the individual.
2. Data Minimization: Data minimization refers to the practice of only collecting and retaining the minimum amount of personal information necessary for a specific purpose. As a marketer, you must ensure that you are not collecting more data than required for your marketing activities. Avoid requesting sensitive information such as race or ethnicity unless absolutely necessary.
3. Security Measures: With an increase in cyber threats and data breaches, governments around the world have implemented strict regulations on how organizations should protect personal information. It is crucial for marketers to implement appropriate security measures such as encryption techniques, firewalls, access controls etc., especially when dealing with sensitive personal information.
4. Cross-Border Transfers: Many countries prohibit cross-border transfers of personal information without adequate protection measures in place. Before transferring any data outside of your country/region of operation make sure you understand the applicable transfer restrictions and take appropriate steps such as implementing Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) or obtaining explicit consent from individuals.
5.Data Subject Rights: Under most data privacy laws like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), individuals have the right to access, correct, delete or restrict the processing of their personal information. As a marketer, you must be prepared to fulfill these requests and have systems in place to respond within the required time frame.
Case studies of companies that have faced consequences for violating data privacy laws
Data privacy laws are becoming increasingly stringent around the world, with governments and regulatory bodies cracking down on companies that violate these laws. In this section, we will discuss some notable case studies of companies that have faced severe consequences for their failure to comply with data privacy laws.
1. Facebook’s Cambridge Analytica Scandal:
In 2018, social media giant Facebook made headlines when it was revealed that Cambridge Analytica, a political consulting firm, had gained unauthorized access to the personal information of millions of Facebook users. This data was then used for targeted political advertising during the 2016 US Presidential election. The scandal resulted in several investigations and lawsuits against Facebook, including a $5 billion settlement with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) – the largest penalty ever imposed on a tech company for violating consumer privacy.
2. British Airways Data Breach:
In 2018, British Airways suffered a massive data breach where hackers gained access to personal and financial data of over 400,000 customers. The breach occurred due to vulnerabilities in the airline’s website and mobile app and resulted in a fine of £20 million by the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This incident served as a warning to companies about their responsibility to protect customer data and implement strong security measures.
These case studies highlight the serious repercussions companies can face for not complying with data privacy laws. This emphasizes the need for businesses to prioritize data protection and implement robust security measures to avoid similar consequences.
Future of data privacy laws and potential changes in the marketing landscape
The future of data privacy laws is a topic that is constantly evolving and has a direct impact on the marketing landscape. With the ever-increasing use of technology and data collection, governments around the world are taking steps to protect individuals’ personal information. As a marketer, it is crucial to stay informed about these changes and understand how they may affect your strategies and tactics.
One potential change in the marketing landscape due to data privacy laws is an increase in consumer trust. With stricter regulations in place, consumers may feel more confident that their personal information will be handled with care and not sold to third parties without their consent. This could lead to a more positive perception of brands that prioritize data privacy, resulting in increased loyalty and engagement.
On the other hand, there may also be challenges for marketers when it comes to targeted advertising and personalized messaging. Data privacy laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) require explicit consent from individuals for their data to be collected and used for targeted advertising purposes. This means that companies will need to find alternative ways to reach their target audience without relying heavily on collecting personal information.
Another potential change in the marketing landscape could be an increase in transparency regarding data usage. Many countries are introducing laws that require companies to disclose how they collect, use, store, and share customer data. This level of transparency can build trust with consumers by providing them with more control over their personal information.
Conclusion:
In today’s digital age, data is a valuable commodity that fuels the success of businesses. As marketers, we rely heavily on collecting, analyzing, and utilizing consumer data to create effective marketing strategies and campaigns. However, with the increasing concern over privacy breaches and unauthorized use of personal information, governments around the world have implemented strict data privacy laws to protect individuals from potential harm.
It is crucial for marketers to stay updated on these ever-evolving data privacy laws as non-compliance can result in hefty fines and damage to a brand’s reputation. With the rise of global interconnectedness and cross-border data transfers, it is not enough for businesses to just comply with their local regulations; they must also adhere to international standards.
#Data Privacy Laws Around the World: What Marketers Need to Know#web devlopment#app development#software devlopment company#webdevelopment#app devlopment#graphic design#digital marketing#web development
0 notes
Text
What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (known as fiat currencies like the US Dollar or Euro), cryptocurrencies are decentralized, meaning they are not controlled by any central authority such as a central bank or government. Instead, they operate on blockchain technology, which ensures transparency, immutability, and security through a distributed network of computers (called nodes).
History and Origin
The concept of digital currency predates cryptocurrency, but it wasn't until 2008 that cryptocurrency as we know it emerged. That year, an anonymous individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published a whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”. In 2009, Bitcoin was launched as the first cryptocurrency.
Since then, thousands of other cryptocurrencies have been created, often referred to as altcoins (alternative coins), including Ethereum, Litecoin, Ripple (XRP), and Cardano.
Blockchain Technology
At the heart of most cryptocurrencies is blockchain, a decentralized ledger that records all transactions across a network. Key features include:
Transparency: All participants in the network can view the ledger.
Immutability: Once data is recorded, it cannot be changed or deleted.
Security: Uses cryptographic techniques to secure data and transactions.
Each transaction is verified by network participants using consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), making the system resistant to fraud and tampering.
Common Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most valuable cryptocurrency by market cap.
Ethereum (ETH): Known for its smart contract functionality, allowing developers to create decentralized applications (dApps).
Binance Coin (BNB): Used on the Binance exchange for trading and transaction fee discounts.
Ripple (XRP): Designed for fast, low-cost international payments.
Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), Polkadot (DOT): Emerging platforms focused on scalability, efficiency, and interoperability.
Use Cases of Cryptocurrency
Digital Payments: Fast, low-fee global transactions without needing intermediaries.
Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with conditions written in code, used in DeFi (Decentralized Finance).
DeFi: Financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading that operate without banks.
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): Unique digital assets verified using blockchain, used in art, gaming, and entertainment.
Remittances: Sending money across borders more efficiently than traditional services.
Tokenization: Turning real-world assets like real estate or art into digital tokens.
Privacy: Some cryptocurrencies like Monero and Zcash offer enhanced anonymity.
Advantages of Cryptocurrency
Decentralization: No single point of control or failure.
Security: Advanced cryptographic techniques protect users and transactions.
Lower Fees: Especially for cross-border transactions.
Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can participate.
Transparency: All transactions are publicly verifiable.
Innovation: Enables new technologies like DeFi, DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations), and NFTs.
Challenges and Risks
Volatility: Prices can be highly unpredictable.
Regulatory Uncertainty: Different countries have varying stances, and laws are still evolving.
Security Threats: Hacking, phishing, and scams are common.
Environmental Impact: Mining (especially Bitcoin's PoW) consumes large amounts of energy.
Lack of Consumer Protections: Lost funds in hacks or fraud are often unrecoverable.
Complexity: Understanding wallets, keys, and blockchain technology can be intimidating for newcomers.
Regulation Around the World
Governments are taking different approaches to crypto regulation:
United States: Regulatory bodies like the SEC and CFTC are involved, but legal frameworks are still evolving.
European Union: The MiCA (Markets in Crypto-Assets) regulation aims to standardize crypto laws across member states.
China: Has banned most crypto activities, including mining and trading.
El Salvador: Became the first country to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender in 2021.
The Future of Cryptocurrency
The future of crypto is both exciting and uncertain. Key developments to watch include:
Institutional Adoption: More banks and companies are integrating crypto.
CBDCs (Central Bank Digital Currencies): Governments creating digital versions of fiat money.
Scalability Solutions: Innovations like Layer 2 solutions (e.g., Lightning Network, Optimism) aim to make blockchains faster and more efficient.
Integration with AI and IoT: Expanding crypto's role in smart devices and automation.
Global Regulation: More consistent legal frameworks may improve stability and trust.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency represents a revolutionary shift in how people think about money, value, and trust. While it offers many advantages over traditional systems—such as decentralization, privacy, and financial inclusion—it also comes with significant risks and challenges. As technology matures and regulation evolves, crypto could play a foundational role in the future of finance, technology, and global economies.
0 notes
Text
Why B.Tech Cyber Security Is Your Gateway to a Future-Proof Career?

In today’s digital-first world, data is the new oil—and cyber threats are the new oil spills. As technology races ahead, the demand for digital bodyguards—cybersecurity experts—is surging. That’s where a B.Tech in Cyber Security comes into play, offering a blend of computer science, ethical hacking, cryptography, and risk management. If you're someone who dreams of protecting critical information infrastructure and fighting the silent battles of cyberspace, this program might be your perfect match.
Why B.Tech in Cyber Security is the Talk of the Tech Town
From government agencies to fintech firms, from healthcare giants to e-commerce platforms—everyone is investing heavily in cybersecurity. A B Tech Cyber Security Admission today means stepping into a career that isn’t just high in demand but also offers significant societal impact. Students are not only taught to detect, analyze, and neutralize cyber threats but also encouraged to innovate secure systems from the ground up.
youtube
Understanding the B.Tech Cyber Security Eligibility Criteria
Before diving into the cyber world, it’s crucial to know if you meet the B Tech Cyber Security Eligibility. Generally, candidates must have completed their 10+2 with Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics as core subjects, scoring a minimum of 50-60%, depending on the university. Some institutions may conduct entrance exams like JEE or their own aptitude tests to evaluate students’ analytical and technical skills.
Pro tip: A background in computer science or prior exposure to programming languages like Python or C++ can give you an edge during the admission process.
What Does It Cost to Be a Digital Defender?
Let’s talk numbers. The B Tech Cyber Security Fees can vary widely depending on the institute. In private universities, it generally ranges between INR 1.5 to 2.5 lakhs per year, while in government institutions, the fees can be considerably lower. Though it might seem like a significant investment, it’s one that pays off handsomely through solid career returns and job security in a constantly evolving digital ecosystem.
Many universities also offer scholarships based on merit or economic background, making this futuristic education more accessible to passionate learners.
The Real Deal: B.Tech Cyber Security Placement
What truly sets this course apart is its impressive B Tech Cyber Security Placement record. Graduates are snapped up by top-tier companies like Infosys, Wipro, Accenture, Deloitte, and even international tech firms like Cisco, IBM, and Palo Alto Networks. Roles offered include Information Security Analyst, Cyber Security Engineer, Network Security Administrator, and Ethical Hacker, with packages starting from INR 6 LPA and going upwards of INR 15 LPA for high-performing students.
In fact, due to the increasing global awareness around data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA, even international placement opportunities are opening up for Indian graduates.
Bonus: Future-Proof and Crisis-Resistant
Unlike traditional jobs that fluctuate with economic cycles, cybersecurity professionals often see steady demand even during downturns. With cyber crimes increasing year after year, organizations are placing a premium on talent trained in digital defense. Hence, B Tech Cyber Security Admission not only equips you with technical skills but also ensures you're always one step ahead in the job market.
Final Thoughts
If you're looking for a career that combines technology, strategy, and an adrenaline rush of solving real-world problems, B.Tech in Cyber Security is the path to pursue. It’s more than a course—it’s a commitment to safeguarding the digital future.
From eligibility to fees, from admissions to placements—this is your all-access pass to becoming a cyber-sentinel in the age of information warfare. So, gear up and apply—because the future needs fearless defenders, and they might just be wearing your shoes.
0 notes
Text
```markdown
The Rise of Cryptocurrency: Navigating the Complexities of Data Scraping
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital currencies, cryptocurrencies have emerged as a transformative force in the financial sector. With their decentralized nature and potential for high returns, they have captured the attention of investors, technologists, and regulators alike. However, amidst this excitement, one critical aspect often overlooked is the process of data scraping—how information about these digital assets is collected, analyzed, and utilized.
Understanding Cryptocurrency Data Scraping
Data scraping, in the context of cryptocurrencies, involves the automated collection of data from various sources such as exchanges, forums, social media platforms, and news outlets. This data can include trading volumes, price movements, sentiment analysis, and more. The primary goal is to gain insights that can inform investment decisions, market trends, and regulatory policies.
Why is Cryptocurrency Data Scraping Important?
1. Market Analysis: By scraping data from multiple exchanges, analysts can get a comprehensive view of market trends and price movements. This helps in identifying patterns and making informed trading decisions.
2. Sentiment Analysis: Social media platforms are rich sources of public opinion and sentiment towards different cryptocurrencies. Analyzing this data can provide valuable insights into investor behavior and market sentiment.
3. Regulatory Compliance: As governments around the world grapple with how to regulate cryptocurrencies, data scraping can help in monitoring transactions and ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations.
Challenges in Cryptocurrency Data Scraping
While the benefits are clear, there are also significant challenges associated with data scraping in the cryptocurrency space:
1. Data Quality: Not all data sources are reliable or accurate. Ensuring the quality and integrity of scraped data is crucial.
2. Privacy Concerns: Collecting personal data without consent can lead to legal issues. It’s important to respect user privacy and adhere to data protection laws.
3. Technical Complexity: Cryptocurrency data is often complex and requires advanced algorithms to process and analyze effectively.
Future Trends in Cryptocurrency Data Scraping
As the cryptocurrency market matures, we can expect to see advancements in data scraping technologies. These may include:
AI and Machine Learning: Enhanced algorithms that can better predict market trends and identify fraudulent activities.
Blockchain Integration: Utilizing blockchain technology to ensure the authenticity and security of scraped data.
Regulatory Adaptation: Developing solutions that comply with evolving regulatory frameworks while still providing valuable insights.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency data scraping is a powerful tool that can unlock a wealth of information for investors, analysts, and regulators. However, it also comes with its set of challenges that need to be addressed. As the industry continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how data scraping technologies adapt and improve to meet these challenges.
What do you think are the most promising areas for future development in cryptocurrency data scraping? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
```
加飞机@yuantou2048

蜘蛛池出租
EPP Machine
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to QR Codes for Vehicles: Enhancing Safety and Efficiency
Introduction
Overview of QR Codes in Modern Technology
Importance of QR Codes for Vehicles
What Are QR Codes?
Definition and Functionality
Evolution of QR Codes in the Automotive Industry
Why Use QR Codes for Vehicles?
Enhancing Vehicle Safety
Improving Emergency Response Times
Facilitating Maintenance and Repairs
Types of QR Codes for Vehicles
Emergency QR Codes
Purpose and Benefits
How They Work During Emergencies
Tracking QR Codes
Vehicle Tracking and Monitoring
Benefits for Fleet Management
Maintenance and Service QR Codes
Accessing Vehicle Maintenance History
Facilitating Efficient Service Scheduling
How to Generate a QR Code for Your Vehicle
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a QR Code
Tools and Software for QR Code Generation
Customizing Your QR Code
Implementing QR Codes in Vehicles
Best Practices for QR Code Placement
Ensuring Durability and Longevity
Integrating with Vehicle Information Systems
Real-Life Applications of QR Codes in Vehicles
Case Studies from the Automotive Industry
Success Stories from Emergency Services
The Future of QR Codes in the Automotive Industry
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
How QR Codes Could Evolve with Smart Vehicles
Security and Privacy Concerns
Protecting Personal Data with Vehicle QR Codes
Avoiding Common QR Code Scams
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Compliance with Local and International Laws
Guidelines for Publicly Accessible QR Codes
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using QR Codes in Vehicles
Incorrect Placement and Scanning Issues
Overlooking Updates and Maintenance
How to Educate Drivers and Passengers on QR Codes
Training for Emergency Situations
Encouraging Regular Use and Awareness
The Role of QR Codes in Vehicle Recalls
Simplifying the Recall Process
Communicating with Vehicle Owners Effectively
Integrating QR Codes with Mobile Apps
Enhancing User Experience with Vehicle Apps
Using QR Codes for In-App Features
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
The Growing Importance of QR Codes for Vehicle Safety
FAQs
What Information Can Be Stored in a Vehicle QR Code?
How Secure Are Vehicle QR Codes?
Can QR Codes Be Scanned in All Weather Conditions?
How Often Should Vehicle QR Codes Be Updated?
Are QR Codes for Vehicles a Legal Requirement?
The Ultimate Guide to QR Codes for Vehicles: Enhancing Safety and Efficiency
In a world where technology is rapidly transforming every aspect of our lives, the automotive industry is no exception. From self-driving cars to advanced navigation systems, vehicles are becoming smarter and more connected than ever before. One of the latest innovations making its way into the automotive scene is the use of QR codes. While QR codes have been around for a while, their application in vehicles is gaining traction, especially for enhancing safety, improving emergency responses, and streamlining maintenance. In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about QR codes for vehicles and how they can benefit you.
What Are QR Codes?
QR codes, short for Quick Response codes, are two-dimensional barcodes that can store a significant amount of information. When scanned with a smartphone or a QR code reader, they can instantly provide access to data, websites, contact information, and more. Initially developed in the 1990s for the automotive industry in Japan, QR codes have evolved into a versatile tool used across various sectors, including marketing, retail, and now, vehicle management.
Why Use QR Codes for Vehicles?
QR codes offer several benefits when used in
started on it right away! get a qr code tracking emergency qr code for vehicle vehicle qr emergency qr qr for cars prepare a guest post for this website https://kavachqr.live/
Title: The Power of QR Codes in Enhancing Vehicle Safety and Efficiency
Outline:
Introduction
Overview of QR Codes in Modern Vehicle Management
The Growing Need for QR Codes in the Automotive Industry
Understanding QR Codes
What Are QR Codes?
How QR Codes Function in Different Contexts
The Role of QR Codes in Vehicle Safety
Emergency QR Codes for Vehicles
Definition and Purpose
How They Assist in Emergency Situations
Tracking QR Codes for Vehicles
Vehicle Tracking and Monitoring
Benefits for Fleet Management and Individual Owners
How to Get a QR Code for Your Vehicle
Step-by-Step Guide to Generating a Vehicle QR Code
Best Tools and Resources for QR Code Generation
Customization Options for Vehicle QR Codes
Implementing QR Codes on Vehicles
Best Practices for QR Code Placement on Vehicles
Ensuring Scannability and Durability
Integrating QR Codes with Vehicle Information Systems
Real-World Applications of Vehicle QR Codes
Case Studies: How Emergency QR Codes Have Saved Lives
Success Stories: Fleet Management with QR Tracking Codes
Security and Privacy with Vehicle QR Codes
Protecting Sensitive Information in QR Codes
Avoiding Scams and Ensuring Safe Use of QR Codes
Future Trends: QR Codes in Smart Vehicles
The Evolution of QR Code Technology in the Automotive Industry
Potential Innovations and Future Applications
Conclusion
Recap of the Benefits of QR Codes for Vehicles
Encouraging the Adoption of QR Technology for Vehicle Safety
FAQs
What Information Should Be Included in a Vehicle QR Code?
How Can QR Codes Improve Emergency Responses?
Are QR Codes Durable Enough for Long-Term Use on Vehicles?
Can QR Codes Be Customized for Specific Vehicle Types?
How Secure Are QR Codes for Tracking Vehicles?
The Power of QR Codes in Enhancing Vehicle Safety and Efficiency
In today’s fast-paced world, the need for quick access to crucial information is more important than ever, especially when it comes to vehicle safety and management. QR codes, known for their ability to store and quickly deliver information, are emerging as a powerful tool in the automotive industry. Whether for tracking, emergency situations, or routine vehicle management, QR codes offer a versatile solution that can significantly enhance both safety and efficiency.
Understanding QR Codes
Before diving into how QR codes are transforming vehicle management, it’s essential to understand what they are. A QR code, or Quick Response code, is a type of barcode that can be scanned using a smartphone or QR code reader to instantly access information. These codes can store a wide range of data, including URLs, contact details, and even vehicle-specific information, making them incredibly versatile.
The Role of QR Codes in Vehicle Safety
QR codes are playing a pivotal role in enhancing vehicle safety, particularly through their use in emergency situations and vehicle tracking.
Emergency QR Codes for Vehicles
An emergency QR code is designed to store critical information about the vehicle and its occupants. In the event of an accident, first responders can scan the code to access details like the driver’s medical history, emergency contacts, and vehicle specifications. This can significantly reduce response times and ensure that appropriate care is provided on the spot.
Imagine you’re in an accident, and you’re unconscious. With an emergency QR code on your vehicle, paramedics can quickly scan the code and gain access to your medical history, allergies, or any special instructions. This information can be crucial in saving your life.
Tracking QR Codes for Vehicles
Another significant application of QR codes in vehicles is tracking. Whether you’re managing a fleet of delivery trucks or simply want to keep tabs on your personal car, a tracking QR code can provide real-time data on the vehicle’s location, speed, and condition. This is especially useful for businesses that rely on efficient fleet management, as it helps in monitoring vehicle performance and optimizing routes.
How to Get a QR Code for Your Vehicle
Getting a QR code for your vehicle is easier than you might think. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Choose a QR Code Generator: Start by selecting a reliable QR code generator. There are many free and paid options available online.
Enter the Necessary Information: Depending on the purpose of the QR code (emergency, tracking, etc.), input the relevant data. For an emergency QR code, this might include medical information and contact details. For a tracking QR code, you would include the tracking URL or data.
Customize the QR Code: Many QR code generators allow you to customize the appearance of your QR code. You can choose different colors, add a logo, or adjust the shape to match your vehicle’s branding.
Download and Print the QR Code: Once you’ve generated your QR code, download it in a high-resolution format. You can then print it on a sticker or decal that can be affixed to your vehicle.
Implementing QR Codes on Vehicles
Once you have your QR code, proper implementation is key to ensuring it functions as intended.
Best Practices for QR Code Placement on Vehicles
Visibility: Place the QR code in a visible area where it’s easily accessible for scanning. Common spots include the windshield, rear window, or near the vehicle’s registration plate.
Durability: Use materials that can withstand various weather conditions. The QR code should remain scannable in rain, snow, or intense sunlight.
Integration: Consider integrating the QR code with the vehicle’s information system if applicable. This can help in maintaining up-to-date data without manual updates.
Real-World Applications of Vehicle QR Codes
QR codes are already making a significant impact in real-world scenarios.
Case Studies: How Emergency QR Codes Have Saved Lives
In several documented cases, emergency QR codes have played a crucial role in saving lives. For instance, during a multi-car pileup, paramedics were able to quickly scan the QR codes on the vehicles involved, allowing them to prioritize care based on the occupants’ medical needs. This not only saved time but also improved the quality of care provided on the scene.
Success Stories: Fleet Management with QR Tracking Codes
Fleet managers have reported increased efficiency and reduced operational costs after implementing QR tracking codes on their vehicles. By monitoring real-time data, they’ve been able to optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, and ensure timely maintenance, all of which contribute to a more streamlined operation.
Security and Privacy with Vehicle QR Codes
While QR codes offer numerous benefits, it’s essential to address security and privacy concerns. To protect sensitive information stored in QR codes:
Use Encryption: Ensure that any personal or sensitive data is encrypted before being encoded into the QR code.
Regular Updates: Update the QR code data regularly to prevent outdated information from being accessed.
Scam Awareness: Be aware of potential scams involving QR codes, such as codes being replaced with malicious ones. Regularly check your vehicle’s QR codes to ensure they haven’t been tampered with.
Future Trends: QR Codes in Smart Vehicles
As vehicles continue to evolve into smart, connected machines, the role of QR codes is likely to expand. We can expect to see QR codes being used for more advanced functions, such as initiating self-diagnostic checks, connecting with IoT devices, or even interacting with autonomous vehicle systems. The possibilities are vast, and the integration of QR codes into smart vehicles could redefine how we interact with our cars.
Conclusion
QR codes are more than just a convenient tool—they’re becoming an integral part of vehicle safety and management. Whether you’re looking to enhance emergency responses, streamline vehicle tracking, or simply make your car more user-friendly, QR codes offer a versatile solution that’s easy to implement and highly effective.
As technology continues to advance, the role of QR codes in the automotive industry will only grow. By embracing this technology today, you’re not just keeping up with the times—you’re actively contributing to a safer, more efficient future on the road.
FAQs
What Information Should Be Included in a Vehicle QR Code?A vehicle QR code can include various types of information, such as emergency contact details, medical history, vehicle identification numbers, and links to vehicle tracking systems.
How Can QR Codes Improve Emergency Responses?Emergency QR codes allow first responders to quickly access crucial information about the vehicle and its occupants, significantly reducing response times and improving the quality of care provided at the scene.
Are QR Codes Durable Enough for Long-Term Use on Vehicles?Yes, QR codes can be printed on durable materials that are resistant to weather conditions, ensuring they remain scannable for extended periods.
Can QR Codes Be Customized for Specific Vehicle Types?Absolutely. QR codes can be customized in terms of size, shape, color, and the type of information they store, making them suitable for various vehicle types and purposes.
How Secure Are QR Codes for Tracking Vehicles?QR codes used for tracking vehicles can be secured using encryption and other security measures to protect against unauthorized access and tampering.
By incorporating QR codes into your vehicle, you’re not just adding a piece of technology—you’re enhancing safety, efficiency, and the overall driving experience. Consider implementing a QR code on your vehicle today and take advantage of the many benefits it offers.
0 notes
Text
ATS Pious Orchards Noida Home to Future Investment

The first thing you need to know about buying properties from bankruptcy auctions is that, given in hand, it is one of the most profitable forms of investment that the modern market can offer us. A concept, this, which seems obvious for the numerous professionals but which, at the same time, is precious for all those entrepreneurs or private citizens who appear for the first time in the world of buying property for investment properties in Noida. ATS Pious Orchards, And it is to them, to all those who intend to understand where to invest in real estate, that the advantages that can be used by participating in a bankruptcy auction of real estate must be as clear as possible. ATS Pious Orchards Price / ATS Pristine Golf Villas Price / ATS Happy Trails Price / ATS Picturesque Reprieves Phase 2 Price
In five adjectives, the whole truth about a successful investment: Advantageous. In economic terms, the realization prices which can be used in bankruptcy auctions have no comparison with the typical sale and purchase of the real estate market. The opportunities follow each other day by day and the right opportunity is always around the corner, ready to be seized. All the auctions on the online portals are authorized by the respective courts of jurisdiction and, therefore, are in compliance with the provisions of the relevant jurisprudence in every detail. Sure. ATS Pious Orchards, The online auction sites offer maximum security in terms of the quality of the property auctioned, the sale and purchase transactions and the protection of sensitive data. Privacy is guaranteed as established by law.
Transparent. The above in consideration of the fact that all the registration, participation, relaunch and award procedures of the property take place in full transparency. The software developed for these IT platforms allows each potential buyer to follow all the information flow that entails, from the announcement of the auction base to the beating of the sale. Simple . The same software has been developed in a streamlined and intuitive way even for beginners in the sector and therefore can be used from any location or mobile device with a few simple operations, always keeping up to date on what is going on in a given auction.
What are the best areas to invest in real estate? To understand how to invest in real estate, you need to be aware of which areas, or cities, in this case, with the highest return on initial investment compared to the others. Nationally, more than a third of the cities with the highest return on investment are located on the coast, both north and south of the boot. ATS Pious Orchards, According to the latest surveys, the Noida city with the best ratio between the purchase price and the rental price of a property is ATS Pious Orchards, The centers of the Adriatic coast, where prices per square meter are much higher, occupy more secluded positions. But for all buyers who wish to invest in Sector 150, the cities and towns of the hinterland, often real jewels of tradition and culture, cannot be forgotten. In addition to the enchanting historic cities of Sector 150, are also well placed in the special ranking.
#ATS Pious Orchards#ATS Pious Orchards Noida#ATS Pious Orchards floor plan#ATS Pious Orchards price list#ATS Pious Orchards resale#ats noida flats#ats luxury flats
0 notes
Text
Ultimate Guide For Contracts Translation Services

Business partnerships are based on contracts that spell out exactly what each party's rights, duties, and obligations are. When doing business around the world, these contracts must be translated properly to avoid confusion and legal problems. Legal documents depend on Contract agreement translation services a lot to make sure they keep their purity and meaning when they are translated into other languages.
Things you should keep in mind
When writing contracts, accuracy is very important because you need to be very precise and pay close attention to every detail. Legal effects can be big, even for language changes that don't seem important. Look for a translation service that has a past of happy clients and a good name for being accurate.
Legal knowledge is important:
contracts can include complicated legalese and details that only a lawyer can understand. When looking for a translation service, make sure the people who work there know both the law and the language you need.
Respect for Other Cultures:
Contracts can be seen in different ways by people from different cultures. A professional translation service will be aware of these details and make sure that the translated contract fits the culture and language of the people who will be reading it.
Protecting privacy and security:
A lot of contracts have private information in them. Select a translation service that values privacy and data security and works hard to keep your information safe.
How to Choose the Best Service Provider
When looking for a translation service, you must make sure that they have translated papers before. Pre-existing experience in your area and a good understanding of the laws that apply are both very helpful.
To sum up
Good communication is the key to building strong business relationships in the global market. To make sure that legal documents are translated correctly across countries and languages, Contract agreement translation services are very important. Companies can handle the complicated parts of international contracts with confidence and clarity if they know how important it is to be accurate, know the law, be aware of other cultures, and choose the right provider. This will make it possible for growth and teamwork to happen in new ways.
#legal translation services#Rent Agreement Translation Services#Contract agreement translation services
0 notes
Text
A Quick Guide to Launching Your Mobile App

Introduction
In the fast-paced world of mobile applications, launching a successful app requires a strategic approach and meticulous implementation. This quick but comprehensive guide will walk you through each step of the process, from initial market research to maintaining a thriving user base.
Market Research: Know Your Audience and Competitors
Understanding your target audience is the foundation of a successful app. Define your user personas, identify their needs, and conduct a thorough competitor analysis to set your app apart in the crowded marketplace.
Define Unique Selling Proposition (USP)

Clearly articulate what makes your app unique. Highlight key features and benefits that address user needs, giving your app a compelling reason to stand out. Consider one to two main points of differentiation, coupled with one or two points of parity.
Prototyping and Design: Bringing Ideas to Life
Create wireframes, mockups, and prototypes to visualize your app’s interface and features. Seek user feedback for improvements, ensuring a user-friendly design.
Development: Turning Vision into Reality
Choose your development platform, select a suitable framework, and adopt an agile development approach. Thoroughly test your app to identify and fix bugs, ensuring a seamless user experience. Develop the application in an agile and lean manner, to incrementally improve the application during development and to better ensure product-market fit. Ensure you have a feedback loop in place with multiple stakeholders (include end users) to continuously improve the app.
App Monetization: Turning Downloads into Revenue
Decide on your revenue model and implement a secure payment system. Whether it’s freemium, subscription, ads, or in-app purchases, choose what aligns best with your app and audience.
App Store Optimization (ASO): Rise to the Top

Optimize your app’s visibility in app stores with effective keyword research, compelling visual assets, and a focus on positive reviews. Make your app stand out from the competition.
Marketing and Promotion: Building Buzz
Establish a strong social media presence, create engaging content, and consider influencer marketing. Plan a launch event or promotion to generate excitement around your app.
User Acquisition and Retention: Keeping Users Engaged
Utilize various user acquisition strategies, including paid advertising and partnerships. Ensure a smooth onboarding process and implement retention strategies to keep users returning. Ensure your app provides real utility to its users.
Analytics and Iteration: Data-Driven Success
Implement analytics tools to track user behavior and app performance. Regularly analyze data and user feedback to make informed updates and release new features.
Legal Considerations: Ensure Compliance

Navigate app permissions, adhere to app store guidelines, and prioritize user privacy. Clearly communicate your terms of service and privacy policy. Ensure you understand where the app’s users are located and comply with local laws and regulations. Data privacy laws and regulations are becoming more important than ever before. Make sure to figure out what you must do to maintain compliance without the risk of significant penalty.
Customer Support: Building Trust
Provide efficient customer support through in-app help, email, or chat. Address user concerns promptly to build trust and credibility.
Scale and Maintenance: Growing Responsibly
Prepare to scale infrastructure as your user base grows. Regularly update and maintain the app to ensure compatibility with new operating system versions. Have plans in place for “what if” scenarios, such as what if a server goes down or what if the database gets corrupted. Backups and disaster recovery are a must.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement: Stay Agile
Encourage user feedback through various channels. Continuously improve the app based on feedback and emerging trends to stay ahead in the dynamic app market. Seek to continuously delight users, to increase retention and customer lifetime value.
Final Thoughts
Launching a mobile app is a multifaceted journey that requires careful planning and execution. By following this quick yet comprehensive guide, you can navigate the complexities of bringing your app to market and increase your chances of success. Remember, adaptability and responsiveness to user feedback are key elements throughout this exciting process. Good luck with your app launch!
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Privacy Without Monopoly, EU edition
Tech monopoly apologists insist that there’s something exceptional about tech that makes it so concentrated: “network effects” (when a product gets better because more people use it, like a social media service).
They’re wrong.
Tech is concentrated because the Big Tech companies buy up or crush their nascent competitors — think of Facebook’s predatory acquisition of Instagram, which Zuckerberg admitted (in writing!) was driven by a desire to recapture the users who were leaving FB in droves.
Google’s scale is driven by acquisitions — Search and Gmail are Google’s only successful in-house products. Everything else, from Android to Youtube to their entire ad-tech stack, was once a standalone business that Google captured.
Monopolies extract monopoly rents — like those delivered by Googbook’s crooked ad-tech marketplaces, or Apple/Google’s 30% app shakedown — and use them to maintain their monopolies. Google gives Apple billions every year so it will be the default Ios and Safari search.
These are the same tactics that every monopolist uses — high-stakes moneyball that creates a “kill-zone” around the monopolist’s line of business that only a fool would try to enter. Tech DOES have network effects, but that’s not what’s behind tech monopolies.
We see monopolies in industries from bookselling to eyeglasses, accounting to cheerleading uniforms, pro wrestling to energy, beer to health insurance. These monopolies all follow Big Tech’s template of mobilizing monopoly rents to buy or crush all competition.
The differences between the anticompetitive tactics that monopolized these industries are largely cosmetic — swap out a few details and you might well be describing how John D Rockefeller and Standard Oil monopolized the oil markets in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Big Tech does have network effects, but these are actually a tool that can be used to dismantle monopolies, as well as maintaining them. Network effects are double-edged swords: if a service gets more valuable as users join, it also gets less valuable as users leave.
If you want to understand the anticompetitive structure of the tech industry, you’d be better off analyzing switching costs, not network effects. Switching costs are the things you have to give up when you leave a service behind.
If your customers, community, family members or annotated photos and other memories are locked up in Facebook’s walled garden (or if you’ve got money sunk in proprietary media or apps on Apple’s, etc), then the switching cost is losing access to all of that.
Here’s where tech really is different: tech has intrinsically low switching costs. Latent in all digital technology is the capacity to interoperate, to plug a new service into an old one, to run an old app inside a simulator (“runtime”).
There’s no good technical reason you can’t leave Facebook but take your treasured photos with you — and continue to exchange messages with the people you left behind.
True, Facebook has gone to extraordinary lengths to keep its switching costs high, deploying technical countermeasures to block interoperability. But these aren’t particularly effective. Lots of people have figured out how to reverse-engineer FB and plug new things into it.
Power Ventures created an app that aggregated your FB feed with feeds from rival services, giving you a single dashboard. NYU’s Ad Observer scraps the political ads FB shows you for analysis to check whether FB is enforcing its own paid political disinformation rules.
And there’s a whole constellation of third-party Whatsapp clients that add features FB has decided Whatsapp users don’t deserve, like the ability to block read-receipts or run multiple accounts on the same device.
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2020/03/african-whatsapp-modders-are-masters-worldwide-adversarial-interoperability
Most of these are technical successes, but they’re often legal failures. FB has used the monopoly rents it extracted to secure radical new laws and new interpretations of existing laws to make these tactics illegal.
Power Ventures was sued into oblivion. Ad Observer is fighting for its life. The Whatsapp mods are still going strong, but that may be down to the jurisdictions where they thrive — sub-Saharan Africa — where FB has less legal muscle.
With low switching costs, much of FB’s monopoly protection evaporates. Lots of people hate FB, and FB knows it. You’re on FB because your friends are there. Your friends are there because you’re there. You’ve taken each other hostage, and FB benefits.
With low switching costs, you could leave FB — but not your friends. The kill zone disappears. All we need is interoperability.
Enter the EU’s Digital Services Act and Digital Markets Act, proposed regulations to force interop on the biggest Big Tech players.
The EU has recognized that mandating interop can reduce switching costs, and reducing switching costs can weaken monopoly power.
Some critics (like me!) of the EU proposals say they don’t go far enough, asking for “full interop” for rival services.
Against these calls for broader interop come warnings about the privacy implications of forcing FB to open up its servers to rivals. It’s hard enough to keep FB from abusing its users’ privacy, how will we keep track of a constellation of services that can access user data?
Last Feb, Bennett Cyphers and I published “Privacy Without Monopoly,” for EFF, describing how interoperability can enhance privacy.
Interop means that users can choose services that have better privacy policies than Facebook or other incumbent platforms.
https://www.eff.org/wp/interoperability-and-privacy
But in theory, it means that users could choose worse services — services that have worse privacy policies, services that might be able to grab your friends’ data along with your own (say, the pictures you took of them and brought with you, or their private messages to you).
That’s why, in our paper, we say that interop mandates have to be backstopped by privacy rules — democratically accountable rules from lawmakers or regulators, not self-serving “privacy” limitations set by the Big Tech companies themselves.
For example, Facebook aggressively imports your address books when you sign up, to connect you to the people you know (this isn’t always a good experience — say, if your stalker has you in their address book and automatically gets “friended” with you).
If you try to take your address book with you when you quit, FB claims your contact list isn’t “yours” — it belongs to your contacts. To protect their privacy, FB has to block you from exporting the data — making it it much harder to establish social ties on a new service.
It’s not obvious who that contact info “belongs to” (if “belong to” is even the right way to talk about private information that implicates multiple people!).
But what is obvious is that Facebook can’t be trusted to make that call.
Not only has Facebook repeatedly disqualified itself from being trusted to defend its users’ privacy, but it also has a hopeless conflict of interest, because privacy claims can be used to raise switching costs and shore up its monopoly.
In our paper, Bennett and I say that these thorny questions should be resolved democratically, not in a corporate boardroom.
Now, as it happens, there’s a region where 500M people are protected by a broad, democratically enacted privacy law: Europe, home of the GDPR.
Today, in a new appendix to “Privacy Without Monopoly,” EFF has published “The GDPR, Privacy and Monopoly,” my analysis of how the GDPR makes interoperability safer from a privacy perspective.
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2021/06/gdpr-privacy-and-monopoly
Working with EFF’s Christoph Schmon and Bennett Cyphers, we develop a detailed analysis of the GDPR, and describe how the GDPR provides a lawful framework for resolving thorny questions about consent and blended title to data.
The GDPR itself seeks to promote interoperability; it’s right there in Recital 68: “data controllers should be encouraged to develop interoperable formats that enable data portability.” But loopholes in the rules have allowed dominant companies to stymie interop.
For years, Europeans have had the “right” to port their data, but nowhere to port that data to. The DMA closes the loopholes and dismantles the hurdles that kept switching costs high.
The GDPR’s consent/security/minimization framework sets out the parameters for any interoperability, meaning we don’t have to trust Facebook (or Google, or Amazon, or Apple) to decide when interop must be blocked “to defend users’ privacy” (and also shareholders’ profits).
Big Tech platforms already have consent mechanisms (and must continue to build them) to create the legal basis for processing user data. An interoperable FB could be a consent conduit, letting your friends decide when and whether you can take their data to a new service.
And the GDPR (not a tech executive) also determines when a new service meets the privacy standards needed for interop. It governs how that new service must handle user data, and it gives users a way to punish companies that break the rules.
Today, if you leave Facebook, your friends might not even notice. But in a world where FB is a consent conduit to manage your departure and resettlement, all your friends get signals about your departure — perhaps prompting them to consider whether they should go, too.
Far from prohibiting interop, the GDPR enables it, by creating an explicit privacy framework that is consistent across all services, both the old monopolies and the new co-ops, startups, public utilities, and other alternatives that interop would make possible.
Monopolies distort the world in two ways. The most obvious harm is to competition, choking out or buying out every alternative, so you have to live by whatever rules the monopolist sets.
But the other kind of harm is even worse: monopolists can use their political power to get away with terrible abuses.
Ad-tech concentration produced monopoly rents that blocked or weakened privacy law for decades, allowing for a grotesque degree of commercial surveillance.
We don’t want competition in surveillance.
Opening space for interop poses a legitimate risk of creating a contest to see who can violate your human rights most efficiently.
https://pluralistic.net/2021/06/08/leona-helmsley-was-a-pioneer/#monkeys-paw
Yet, it’s obvious that monopolists themselves shouldn’t get to decide where they should be subjected to competition and where they should be subjected to regulation. That’s a job for democratic institutions, not autocratic board-rooms.
Adding privacy regulation (strong privacy regulation, with a private right of action allowing users to sue companies for breaking the rules) to interop is how we resolve this conundrum, how we make sure we’re banning surveillance, rather than “democratizing” it.
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Great Reset Demands Firing All Unvaccinated Employees Analysis by Dr. Joseph Mercola
Story at-a-glance
The Great Reset has been called a conspiracy theory by many, despite specific plans published on the World Economic Forum (WEF) website and partnerships between the WEF and global organizations like the United Nations and World Health Organization
An investigative report asserts that the ongoing restructuring of processes that control food and data are upending traditional practices so private corporations have more control and influence than democratically elected government
A part of the Great Reset is a reset of the economy, including jobs. Many across the U.S. are facing unemployment if they do not choose to take a genetic therapy experiment in the form of a COVID-19 vaccine
Employees of six major hospitals in Cincinnati, Ohio, have filed a lawsuit, hoping to stop the mandated vaccine, which health experts are promoting with inconsistent messages, first claiming it does not stop community transmission; yet, requiring it for employment under the guise of preventing the spread of infection
Over the past year and a half, I’ve written many articles detailing the evidence supporting the claim that the COVID pandemic is a ruse to usher in a new system of global centralized governance by unelected leaders, the so-called Great Reset.
The recent release of the House Foreign Affairs Committee report1 entitled, “The Origins of COVID-19: An Investigation of the Wuhan Institute of Virology,” presented solid evidence that many of the “conspiracy theories” about the virus were in fact true. For example, using some intelligence reports and other public documents, the committee found that:2
“… we now believe it’s time to completely dismiss the wet market as the source of the outbreak. We also believe the preponderance of the evidence proves the virus did leak from the WIV and that it did so sometime before September 12, 2019.”
They presented evidence of genetic modification and wrote this:3
“This report also lays out ample evidence that researchers at the WIV, in conjunction with U.S. scientists and funded by both the PRC [People’s Republic of China] government and the U.S. government, were conducting gain of-function research on coronaviruses at the WIV …
In many instances, the scientists were successful in creating 'chimeric viruses' — or viruses created from the pieces of other viruses — that could infect human immune systems.
With dangerous research like this conducted at safety levels similar to a dentist’s office, a natural or genetically modified virus could have easily escaped the lab and infected the community.”
The idea of the Great Reset may feel like a conspiracy theory, especially if life as you know it where you live has not dramatically changed. You still go to work, buy food, go to the gym, go out to eat and attend events. There may be people wearing masks, and you may see or hear news reports about vaccine mandates and vaccine passports, but it hasn’t reached your employer and you may not be personally affected … yet.
But, make no mistake, unless we all do our part to peacefully protest the changes being planned, write to our legislatures, and talk to our neighbors and friends, what is happening in New York,4 France,5 Germany6 and Israel,7 will soon be knocking on your front door.
Does ‘Great Reset’ Sound Like a Conspiracy? It May Be Worse
An article titled, “Welcome To 2030: I Own Nothing, Have No Privacy and Life Has Never Been Better” appeared in Forbes Magazine8 in November 2016. It was written by Ida Auken, a member of the Denmark Parliament9 and agenda contributor at the World Economic Forum (WEF).10
The article was frightening in the simplistic way it describes the dissolution of society as we know it. And, as time marches forward, we see more evidence of what the WEF has proposed as “perfect sense”11 coming true.
Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau suggested in September 2020 what other world leaders have also promoted12 — that the COVID-19 virus, that has killed and devastated the health of many people, provided the world is an:13
"… opportunity for a reset ... our chance to accelerate our pre-pandemic efforts to re-imagine economic systems that actually address global challenges like extreme poverty, inequality and climate change."
More than 20 world leaders came together to suggest, "At a time when COVID-19 has exploited our weaknesses and divisions, we must seize this opportunity and come together as a global community for peaceful cooperation that extends beyond this crisis."14 And while that sounds noble, altruistic and humanitarian, it is the plan for the future that is in stark contrast to the statement.
Ivan Wecke, a journalist from Open Democracy, did a deep dive into some of what lies behind the WEF’s Great Reset plan and found what he called something “almost as sinister hiding in plain sight. In fact, more sinister because it’s real and it’s happening now. And it involves things as fundamental as our food, our data and our vaccines.”15
Although Wecke discounts the plans of the Great Reset to abolish private property, use the virus to solve overpopulation and enslave the remainder of humanity as “nebulous and hard to pin down,” he goes on to illustrate in detail how the fundamental structure of the world that controls food and data, and ultimately humanity, is being upended and restructured so that private corporations have more control and influence than governments.
WEF Calls It ‘Stakeholder Capitalism’
It comes down to “stakeholder capitalism,” which are the magic words that Klaus Schwab, WEF chairman, has been promoting for decades, and is a central theme in the organization's Great Reset plan.16 The concept as Wecke describes it is to transform global capitalism, so corporations create value for stakeholders.17
These stakeholders can be consumers, employees, communities and others. This will be carried out through multi-stakeholder partnerships of governments and private-sector businesses across the globe. As he dug deeper into the concept, it became more apparent that this means giving corporations more power and taking that influence away from democratically elected institutions.
The initial plan was drafted after the 2008 economic crisis and included the vision that governments around the world would be only one influencer in a multi-stakeholder model. When he asked himself who would be the other nongovernmental stakeholders, Wecke only had to look at the WEF partners that meet each year in Davos, Switzerland.
These partners are some of the biggest companies in oil, food, technology and pharmaceuticals. In other words, the companies that could ultimately restructure society and control the supply chain are those that provide everyday necessities. These proposed concepts appear to have started taking shape in a strategic partnership agreement which the WEF signed with the United Nations in 2019.
Harris Gleckman, senior fellow at the Center for Governance and Sustainability from the University of Massachusetts18 calls this move an inroad to creating a place for corporations inside the United Nations.19
The WEF is using the concept of multi-stakeholders to change the current system that countries use today to work together. This multilateral system may not always be effective and may have too many layers of bureaucracy, but Wecke says it is “theoretically democratic because it brings together democratically elected leaders of countries to make decisions in the global arena.”20
Big Tech May Run the Roadmap for Digital Cooperation
What’s really happening here, though, is the move toward placing unelected stakeholders in positions of power does not deepen democracy but, rather, puts decision making in the hands of financially focused corporations. As Wecke points out, this will have real-world implications for how medications are distributed, food systems are organized and how Big Tech is governed.
Under a democratic rule of law, six corporations already control 90% of the news media consumed by Americans. Tech Startups calls this an “illusion of choice and objectivity.”21 How much more propaganda will be thrown in the face of consumers when Big Tech is monitoring and controlling Big Tech?
The year 2030 holds significance for the WEF’s vision22 which is to scale technology and facilitate “inclusive growth.” In the fall of 2021, the UN will bring together the Food Systems Summit to achieve sustainable development goals by 2030.23 Yet, Sofia Monsalve of FIAN International, a human rights organization focused on food and nutrition, told Wecke:24
“’Abandoning pesticides is not on the table. How come?’ asks Sofia Monsalve of FIAN International, a human rights organisation focused on food and nutrition.
'There is no discussion on land concentration or holding companies accountable for their environmental and labour abuses.’ This fits into a bigger picture Monsalve sees of large corporations, which dominate the food sector, being reluctant to fix the production system. ‘They just want to come up with new investment opportunities.’”
Wecke also dug into a long list of participants in the 2020 Roadmap For Digital Cooperation25 and found influencers included Microsoft, Google, Facebook and the WEF.26 The functions for the group appear to be vague, but if the group comes to fruition, it will be a decisive victory for those Big Tech companies that have been pushing to expand their power,27 are fighting antitrust rules28 and are facing accusations of tax evasion.29
The move by the UN and WEF has not gone unnoticed. A group of more than 170 civil organizations have signed an open letter30 detailing why they oppose the plan. At a time when stronger regulations are needed to protect consumers, it appears that the new UN digital roadmap may be seeking less.
Firing the Unvaccinated Is the Start of the Great Job Reset
Finally, Wecke addresses the issue of global vaccine distribution.31 Instead of the World Health Organization, which is “the directing and coordinating authority for health within the United Nations system,”32 being responsible for vaccine access, another initiative was created called COVAX. According to the WHO, COVAX is co-led by the WHO, UNICEF, CEPI and GAVI.33
As a quick reminder, GAVI (the Vaccine Alliance) and CEPI (Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations) have strong ties with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the WEF and are connected with large pharmaceutical companies such as Pfizer, AstraZeneca and more.34
The influence these groups have on the global distribution of the COVID vaccine may have been best illustrated when South Africa and India requested a temporary lift on the rules governing intellectual property to increase manufacturing and distribution to developing countries. Wecke reports35 that although the WHO director-general publicly said that he backed a proposal, others in the COVAX initiative strongly opposed it, and it didn’t happen.
There appears to be enough vaccines available in industrialized nations for the WEF to support any and all employees being fired if they choose not to take the vaccine. The National File36 published a tweet the WEF made in May 2021 which said, “Get your COVID-19 jab — or you could face consequences from your employer #COVID19 #JobsReset21.”
Additionally, the WEF had posted an article37 on their website that made a variety of claims about the percentage of companies that would require employees to be vaccinated and juxtaposed mental health concerns and burnout through the pandemic with being unvaccinated in the article.
After intense backlash, the tweet was deleted and replaced with a question, “Will employees be required to get the COVID-19 vaccination?”38 The new post quickly filled with screen shots of the original post.
Two Cities Promising to Fire Employees
Even before the FDA announced their approval of the Pfizer vaccine,39 Cincinnati, Ohio, area hospital systems had announced that starting October 1, 2021, all health care workers and volunteers are required to be vaccinated. Among those participating in the vaccine mandate are the University of Cincinnati Health, Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center and the Christ Hospital Health Network.40
Health care workers in Cincinnati have now filed a lawsuit against six of the hospital systems saying requiring vaccines for employment is unlawful and violates workers’ Constitutional rights. The lawsuit says, "When there was no vaccine, the workers had to go to work. They were heroes. Now that there is a vaccine, they have to get the vaccine or be fired. Now they are ‘zeros.’"41
April Hoskins is a lab assistant at St. Elizabeth Edgewood who has worked for 20 years in family practice and hospital oncology. She told a reporter from WLWT5,42 "You've trusted us this whole time to take care of these patients, unvaccinated, without the proper PPE. And now out of nowhere, you have to get it or you're going to be terminated? Like, something is wrong with that picture.”
August 23, 2021, New York City Mayor Bill de Blasio announced that all public school teachers and staff would be required to have at least one dose of the vaccine by September 27, 2021, or they would no longer have a job. Not soon afterward, the United Federation of Teachers union issued a statement from union president Michael Mulgrew reiterating their desire and priority to keep the students and teachers safe. He went on to say:43
“While the city is asserting its legal authority to establish this mandate, there are many implementation details, including provisions for medical exceptions, that by law must be negotiated with the UFT and other unions, and if necessary, resolved by arbitration."
It Is Important to Point Out the Inconsistencies
This was the second announcement from de Blasio, who first mandated vaccinations for approximately 400,000 employees in the Department of Education, New York Police Department and the Fire Department of New York.44 In tandem with New York, California Long Beach Unified School District also announced mandatory vaccinations, as has Chicago Mayor Lori Lightfoot for all Chicago Public School employees by October 15, 2021.
New Jersey Gov. Phil Murphy also announced mandatory vaccinations or twice-weekly testing requirements for all state employees, effective October 18. It is clear that as different states and municipalities add their own mandates, it’s essential to be aware of what is happening in your local and regional areas, as well as to speak up at public meetings and demand public hearings on the matter.
The mayor of Orland Park, Illinois, a suburb of Chicago, describes an example of how decisions behind closed doors can have a different outcome than those in public.45 He also says what is happening now is about “our processes, Constitutionality and the rule of law.”
The inconsistencies from health experts are deafening. Even the World Health Organization advises people who are vaccinated to continue wearing masks due to the Delta variant because “vaccine alone won’t stop community transmission.”46 Simultaneously, the public is told that everyone needs the vaccine to prevent spread of the infection47 and if you have the vaccine, you can still spread the virus and put others at risk.48
Each person has a responsibility to speak up, share information and ensure that as people make up their minds about vaccination, vaccine passports, civil liberties and the right to free speech, they have all the information they need and not just what’s shared in mainstream media.
To that end, I encourage you to share my articles with your friends and family. As you know, they are removed from the website 48 hours after publication. Please copy and paste the information, with the sources, and share it!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to End Up Being an Inventor (In 5 Actions).

We consulted with numerous expert inventors to boil down the tricks of the craft. Some have made jobs out of an invention, others have found markets. If you're sitting on an idea that might be the next terrific American invention, below's your playbook.
1. Cultivate an Idea.
The record of the invention is studded with one-hit marvels, inventors whose solitary blockbuster suggestion made them a fortune. However one of the most prolific inventors can not switch off the idea maker. They are also troubled as well as creative. Inventors just see life's many obstacles in a different way than the average person, according to medical-devices inventor Robert Fischell. "The key to inventing is the awareness that a problem is a trigger from which an invention can be created," says Fischell, who holds more than 200 patents for advancements such as an implantable heart defibrillator and also enhanced stents. "When I'm in the operating room as well as a doctor tosses a device against the wall in irritation, I claim, 'Great, here's an opportunity.'".
Fischell, who at the elevation of his profession filed a new patent application every six weeks, wastes no time in determining whether his most recent concept satisfies the patent test of being brand-new, beneficial, and also nonobvious. He goes right to the U.S. Patent as well as Hallmark Workplace's database of released patents (patft.uspto.gov) and performs a search. "If you review a patent, as well as someone, has currently resolved the issue, after that you're still an inventor. You just arrived late," he says.
If, after an initial search, your idea verifies unique, after that continue developing it. Be reasonable concerning what you're obtaining right into. "The moment you commit will be dual what you believe it will be, as well as the buck amounts you devote will be 4 times what you assumed," Leatherman states.
Make drafts, execute examinations, expand principles, and keep comprehensive notes. Patent lawyers suggest their customers preserve a visit a completely bound notebook that obtains stamped by a notary public frequently. A logbook becomes essential in cases before the U.S. Patent and also Trademark Workplace including similar technologies, as the burden of proof is up to patent applicants to demonstrate that they were the initial to conceive of an invention.
At this onset in the video game, your investment of personal time and money will have been minor compared with what is around the bend. Before the case, you'll need to ask some hard questions about both your concept as well as on your own: Is my idea significantly different than any that precede it? Exists a large market for the product? Can it be developed and made at a reasonable expense? That is the client, and why should they get my product as well as not a competitor's? Am I prepared to devote myself fully to making this concept do well?
Inventors who have been via the process care not to undervalue the psychological and mental determination called for. "If you can't afford mentally and intellectually to fail if your vanity would certainly be wiped out after that don't do it.". see also InventHelp TV Commercial
2. Develop a Model.
With the schedule of powerful computing and computer-assisted layout software application like Autodesk Inventor as well as SolidWorks 3D CAD, inventors today live in what Kamen describes as "the utmost sweet-shop." The earliest versions of Kamen's first invention, a wearable mixture pump that provides specific dosages of medicines such as insulin, sprang to life out a computer system display yet in a workshop set up in the basement of his parents' home on Long Island, N.Y. Kamen was a teenager at the time.
Also when made in a highly exact digital CAD atmosphere, an item ultimately has to leap to the genuine globe in the kind of a model. Depending on the materials entailed and the complexity of an invention, the expense of making a high-quality prototype can empty a financial institution account as well as compel an inventor to look for financing at an extremely early stage.
Tim Leatherman supports taking a DIY technique. During an experimental phase lasting three years, he constructed prototypes of his groundbreaking multitool from cardboard, wood, as well as steel till he picked advanced layout. "By collaborating with my hands," he says, "I found out about barriers to performance as well as manufacturability.".
When you have your prototype, it's time to repair your invention. Obtain outside your head and go-to experts in the field, Fischell suggests. "Ask, 'Do you believe my suggestion has business benefit? Would certainly you utilize it?' Make them authorize a privacy arrangement," he says. For inventors, the possibility of copyright burglary is very actual, but way too much caution can become immobilizing. Privacy, or nondisclosure, the contract permits you to field-test in confidence.
Responses from Mario Salazar's target audience-- woodworkers-- compelled the Colorado Springs inventor to adjust his digital miter gauge. The mechanical prototype he constructed in the cellar with a blowpipe, an oscilloscope, and also a milling maker noticed eBay worked efficiently as well as felt ideal to Salazar, yet the tradespersons wanted it bigger as well as much more inexpensive. "You can't fall for your invention," he states. "Obtain responses and also make alterations accordingly.".
In the agitated company world, a patent protects the inventor by providing the unique right to leave out others from making, making use of, or offering his invention for 20 years. "When other people see you making cash, your patent will be the only methods you have for keeping control of the market," claims Lonnie Johnson, founder of Johnson ElectroMechanical types of equipment as well as the inventor of the Super Soaker water weapon. Follow inventhelp for more advice:
https://www.linkedin.com/company/inventhelp
https://twitter.com/inventhelp
3. Submit a Patent.
Patent law is made complex things, so get an experienced patent lawyer to write and also file your patent application. Anticipate to pay in between $3000 as well as $10,000. "Work with a patent lawyer who additionally has a level in the field you're making an application for a patent in and who understands your market," Salazar encourages.
A knowledgeable lawyer can prepare a wide patent that safeguards an invention against violation from any angle. In the case of Richard Phillips, proprietor of International Survival, his well-crafted patent application made it impossible for anybody to replicate the slim, shock-absorbing material he developed for his protective paintball vest. "My legal representative spread out the patent out thus far over and below my laminated foam product's residential properties that a competitor's vest would certainly have to be so hefty the wearer couldn't walk approximately light that the vest falls apart when struck," Phillips states.
On standard, patent authorization takes 3 years and may call for going back as well as forth several times with patent examiners. From the moment a patent application arrives at the USPTO up until it is either provided or abandoned, an invention is covered by patent-pending standing. In the situation of John Marsden, that created Pour 'N Shop, a bartending system of plastic containers, and also put spouts for beverage mixers, a pending patent amounted to a suit of paper armor.
According to Salazar, any kind of inventor has to be all set to do battle. "I'll have my attorney send out a cease-and-desist letter if somebody infringes on my patent. As well as in the end, a patent is just as great as the thickness of your pocketbook.".
4. Examine the Market.
When the patent application is in total, the inventor needs to change from developing a suggestion of developing a service. Rare is the innovative brilliant behind an invention that likewise has business chops-- or the interest-- to look after the manufacture, advertising, and also selling of his production. Even the brightest innovative minds can drop victim to the countless rip-offs and also doubtful invention-promotion companies whose advertisements clutter the Internet. Many expert inventors urge care with any kind of attire that requests for cash upfront to shop your suggestions about.
Tim Leatherman built up important know-how in business and also production by joining with Steve Berliner. John Marsden, the Pour 'N Store designer, partnered early on with service school grad Ed Harrigan. "If I had not had Ed, I probably would not have made it," he says.
Marketing research studies-- perform your own or appoint a market research company-- will certainly provide you data concerning market patterns and customer demographics. There is no substitute, nevertheless, for putting your invention in front of potential consumers as well as manufacturers, providers, and distributors to get a sense of its market value. For the inventor, this is an anxious time.
Salazar is a big believer in showing your items at trade shows. "You'll figure out who is doing what, whether you'll be able to contend and if somebody wants to get what you have," he claims. "However you're additionally dropping your cabinets and every person will see what you've obtained. Your item had better be 95 percent complete. Be ready to answer concerns: Just how huge is the market? That's mosting likely to buy it?".
5. Sell It or Make It.
Inventors make cash in two means: collecting aristocracies by certifying the right to produce their invention or production, distributing, and marketing the invention themselves. Louis J. Foreman, owner, and also the primary executive of Enventys, an item style as well as a design firm in Charlotte, N.C., and writer of The Independent Inventor's Handbook, has personally encountered that problem several times as the holder of 10 licenses as well as has encouraged many inventors as a lead court on the PBS program Everyday Edisons.
Then it's time to ask yourself one more round of questions: First, exists enough upside potential to merit the threat of bringing the item to market on your own? "Consider opportunity costs also," Foreman says. "If you have to quit a job that pays $100,000, can you make enough to counter that?" Second, do you have the financial resources to pull it off? If you don't, then where is the money most likely to originate from? And lastly, do you have the competence to run an organization? "It's one point to come up with a remarkable item, however, are you comfy marketing it, can you distribute it, restore it as well as satisfy orders if Walmart offers you a 5-million-piece purchase order?" Supervisor claims.
No question licensing is the less complicated path to getting an invention to market. It requires less dedication of time as well as up-front resources and frees inventors to do what they do best: invent. However, expedience comes with an expense. Royalty prices on patents-- created on the list price, production run, as well as various other variables-- average less than 2 to 7 percent of retail sales. Still, for a first-time inventor brief on funds and also know-how, a licensing contract can be the pot of gold at the end of the rainbow.
#InventHelp#InventHelp phone number#InventHelp address#InventHelp locations#InventHelp twitter#InventHelp linkedin#InventHelp blog
133 notes
·
View notes
Text
data entry firm
Data Entry Services
Perfect Data Entry offers outsource data entry services that your business need. With 300+ professionals working for you, you can concentrate on what you do best while depending on our team of diverse professionals to take care of the rest. Any business owner can have access to a team that rivals the back office of a large corporation. Our expert team can handle it all – from coding and marketing to data entry, graphic design, and project management – we offer a full range of services, at competitive rates.
The data entry process is additionally impacted when the operations of departments, subsidiaries, and clients involve multiple languages and time zones. Even when all data entry tasks are localized, the process is typically labor-intensive and costly – often preventing key employees from accomplishing high-priority assignments.
Trusted and Respected Around the World
Ever since our inception all those years ago, we have only grown in strength and reputation. Today Perfect Data Entry is home to a team of 300+ data entry professionals who have the skills and expertise needed to deliver top-notch services to our clients. We are also the go-to data entry outsourcing firm for many companies listed amongst the Fortune 500 list.
Perfect Data Entry is an American owned and operated business. This ensures that we will respect all privacy laws and strictly abide by all non-competitive and non-disclosure agreements. When clients sign with us for our services, they can rest assured knowing they are getting into an agreement with a trusted American company.
We Succeed when Our Clients Do.
We at Perfect Data Entry have worked diligently over the years to offer only the best and secure data entry services to our many satisfied clients with high accuracy and faster turnaround time in mind. Together, we have helped our clients manage their data and ultimately grow their business to exponential heights. We see our success in the success of our clients. You can scoot over to our testimonials section to check out what our clients have to say about us.
For those who want quick relief from the overwhelming burden of data entry, contact us now and we will get in touch with you in no time.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Lenovo TechWorld 2019
Disclosure: I attended Lenovo TechWorld 2019 in Beijing as Lenovo’s Guest. I sat in a super fan / brand advocate seat, and attended in that capacity. Lenovo asks that, as part of my participation, I follow all FTC disclosure laws relative to sponsored content. All opinions are my own.
Disclosure: I consumed the majority of Lenovo TechWorld 2019 via an earbud, translators working hard to turn Chinese into English on the other end. Something may have gotten lost in the translation, and I’ve tried my best to get clarity in those cases where I suspect that happened.
Lenovo HQ Tour - Day Zero
The tour wasn’t what I was expecting. It was definitely a marketing experience, designed to influence influencers and the media. It was well produced, had something for everyone, and a little more.

I write extensively about identity and digital identity in my speculative science fiction series. I’ve read Derek Parfit’s work, and Christine M. Korsgaard’s “Self-Constitution”. The philosophical implications of identity are something I’ve explored in great depth. To that end, Lenovo may be one of a precious few tech companies looking to empower (as opposed to exploit) the user, via their identity.
In philosophy, whenever someone is merely a means in the process of your decision making, you’re probably a jerk, or in the process of acting like one. Lenovo sees a person’s identity as more than a means to create markets for themselves, and is looking through the eyes of the user for how they would relate to potential markets instead.
When I stepped into Lenovo’s unmanned employee store, using my face, it sort of hit home what they were wanting to do. The store had a curious assortment of snacks, food, and drinks. Were the contents curated based on the patronage? I wished I’d asked, but I suspect that’s the cases. Instead of a marketing edifice trying desperately to contrive demand, the store felt more like the corner market that served a neighborhood.
It was an odd sensation to have in a high tech store that didn’t have personnel, but still had personality. That of the folks that shopped there, perhaps? There was the quick bite to eat for lunch, necessities people might grab to avoid a trip to the market on the way home, and the afternoon snack. Nothing was arranged to market the goods in a specific way. It felt more like a community pantry that had contents aggregated over time, to suit the needs of the patrons.
I haven’t had that sensation since I was a young person, standing in the corner market of an old neighborhood where some of my extended family dwelled. That’s where the familiarity ended, though.

In China, commerce is just handled differently. On the outside, it feels a little impersonal to use WeChat or Alipay on your phone to make a transaction. However, I saw the flip side, while I was shopping at Lenovo’s pop up store at the TechWorld venue. They had a Lenovo Legion backpack I wanted (well, needed. It was red!), but I didn’t have WeChat set up to pay, or enough cash.
Nevertheless, the young woman helping me was determined to make the transaction happen. The other employees gathered around, and we talked it over. In the end, she became the handler in the exchange. I gave her the money using Alipay, and she used her WeChat to complete the transaction at the point of sale. This sort of economic decentralization happens at the user level in China.
Having based my book series around a global fiscal collapse, it was interesting to see how Lenovo (and to some degree, China) is making sure the future I’m somewhat afraid of, never happens. Where technology doesn’t reach all the way to the ground, to the common person, it will generally either fail at best, or at worst, exploit the common person.
There were other demonstrations of this notion in the home, and workplace, throughout the tour. The extreme care taken to make sure Lenovo’s products don’t interfere with the user, or their other devices shed light on why I keep buying from them. From a very high developmental level, Lenovo’s products put the user first.
TechWorld - Day 1: Commercial
During the commercial keynote, there was a lot of marketing babble, buzzwords, and hype. It was hard to pick out the gems, the bits that really will resonate in the industry. This is to be expected whenever a company goes large on the stage to sell themselves. This isn't criticism of Lenovo, it's a realization of all that is at stake.

Lenovo wants to change China, and by virtue of that, influence change in the rest of the world.
Lenovo has realized what many companies in the West have not. Decentralizing processes, beside transparent data acquisition, has tremendous potential. This is particularly true for countries with large populations. Each person represents an opportunity to create or serve particular markets.
The assumption is that automation will take jobs from humans, and give them to robots. That edge computing will make people in the field obsolete. I don’t think that is the case. Lenovo has seen that the optimization of processes is one of the last ways technology can improve the profits of companies, while helping preserve the environment. We don’t need less people and more robots, we need more efficient processes underlying the work done by both man and machine.
This is marketable both for companies that want to go greener by reducing waste, while saving money on power consumption. The sum of that vision rests with edge computing built on system agnostic, easy to produce hardware, with software to match. So that data acquisition isn't reliant on crafting new products for each industry.
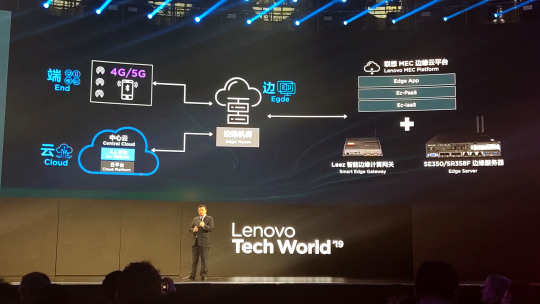
During the first day I wondered if this approach would trickle down to the regular consumer, with edge computing coming to the home. People already struggle to trust that technology in their homes. Lenovo understands that anxiety; from toggles on webcams, to the hardware switches on microphone-equipped smart home devices.
They intend to start building that trust by using block-chain to track the food supply in China. If they can make the delivery of necessities in China safer, people will learn to trust the technology. In the United States, there is deep distrust of anything resembling this kind of data acquisition. Worldwide, trust is often the barrier to reaching out to better industry practices and economic models.
If Lenovo pulls it off in China, a billion people on the planet will be closer to trusting the decentralization of data, and data acquisition, via edge computing. The counter argument is that it all requires data centers, something on the other side of the edge computing bridge from the Internet of Things. Something to manage that data acquisition, that isn’t necessarily transparent to end users, outside of the institutional control of said data centers.
I know the above paragraphs looks like a lot of buzzwords and technobabble, but decentralizing data will lead to the democratization of technology, economies, and greater control of one’s personal data. The reason underlying this is that Lenovo is using open source type hardware (ARM) and software (Linux) in their edge computing solutions.
I would be the first to point out that this is likely by necessity as opposed to genuinely held benevolent intent if not for a conversation with Lenovo’s Chief Communications Officer, Torod Neptune. I was, perhaps, a little more vocal during the round table than I should have been, but I wanted to know where Lenovo really stood. If their push for the democratization of technology would be inclusive to all people. Mister Neptune assured me that it was, and that the notion was at the top of their ethics hierarchy.
I’m very skeptical when it comes to the good intentions of corporations. If you’ve read my speculative science fiction series, I do not cast corporations, or the government entities responsible for regulating them, in a very good light. I designed the series during the Occupy Wall Street movement. I spent some of the trip looking for where Lenovo had deviated from what Torod Neptune was pitching at the meeting with him. I see problems in the industry, but Lenovo isn’t at the root of them, and they may even swing things the other way at the commercial and institutional level.
That said, Lenovo has some challenges where inclusive access to technology is concerned.
TechWorld - Day 2: Consumer, Small Business, Consultancy
The second day was full of epic wins, and some missteps. Lenovo seemed conflicted, sending a mixed message on stage. I’ll break it down as best as I can.
The Good: There was talk of making technology more democratic, edge computing in the residential consumer market, bespoke cloud services, and access to technology, artificial intelligence, and data privacy for people with special needs. The decentralization of the Internet is the next step, the next big thing, and Lenovo is keenly aware of this. They understand that the market for such is emerging, regardless, and that there is an opportunity for every single person in that market.
The narrative from day one, about leveraging AI, smart data center management, and edge computing data acquisition would trickle down to the average user of tech in the home, and on the street. Lenovo’s message wasn’t that they were creating that market, but that they were ready to provide products thereof, almost like it was an evolutionary imperative that they were merely ready for.
I didn’t think much of the Thinkbook and Thinkplus line until I understood it a little better and who it is being marketed to. If you want to start your own global tech consultancy with automated customer care, and a small office staff, Lenovo is trying to provide hardware, and language translation support to that end. They are making big things for the little guy, and I approve.
The Bad: The second day was sprinkled with casual sexism, with a decidedly male-focused keynote, then capped off with Lenovo announcing a very respectful sponsorship of the Chinese Women’s Volleyball Team. I clapped, I cringed, I wanted to cry, and for various reasons. I feel like a few product managers and executives hadn’t gotten Torod Neptune’s memo about inclusivity.
Others, thankfully, were on point.
Lenovo is far from the only tech company grappling with these issues. Stating that there are many attractive females employed in a particular division of the company shouldn’t be an acceptable means to sell product. The message delivered for Thinkbook, and Thinkplus, were that they were “The Young Man” of the workplace, looking to start his consultancy, or small business venture. That he’d have hardware options for himself, and his female assistant.
The appeal of the Thinkbook / Plus product lines transcends gender, and the marketing should have reflected that. That women were excluded as customers during the keynote was a mistake. Hopefully, when those products start reaching the US, Lenovo doesn’t continue the tragic narrative put forward at TechWorld.
The two women they put on the stage as product managers were there, as directed by the man leading the keynote. One was the product manager for the Yoga Book 2, or Yoga Book C930 as it is also called. I’d have really liked to see her up there by herself, pitching the product, without a guy as the conversational prompt.

It’s important to note that what I saw is not the trend at Lenovo. They released their 2nd annual Diversity and Inclusion report a few days after Techworld. Lenovo’s workforce is 36.2 percent female, up 1.2 percent from 2018.
Traditionally under-represented racial and ethnic groups are on the rise in the executive ranks in the U.S. workforce, at 27.4 percent. Lenovo wants to make it 28 percent by 2020.
When I attended CES earlier this year, I was able to sit in at a conference, hosted by Lenovo, for women in the tech industry to meet and discuss the challenges they face in the workforce. It is these things that stand in contrast to what I saw on stage at TechWorld in China. Definitely, I’ll be paying close attention to whether Lenovo pushes the needle toward inclusion, and equity.
In that, I am hopeful.
Conclusion: TechWorld 2019 Overview
Getting to see the connected narrative of days one and two between artificial intelligence, data acquisition, and edge computing was something I needed. I don’t think people in the consumer market understand the influence of these things in their daily lives, and as a result, are afraid of those influences.
Sadly, companies like Google and Amazon do an excellent job of making it worse by lacking transparency in their data acquisition in a residential setting.
Lenovo talked about GPU virtualization in the cloud during the Day 1 Keynote. I’m giddy at all the possible applications thereof. I hope one day to have an extremely thin and light drawing tablet in hand, 5G connected, that can handle commercial applications, rendering done quickly in the cloud. The primary barrier to that being a reality, is trust.
Lenovo has a genuine opportunity to change the narrative at an industry level if they can make data collection via edge computing transparent, and democratic. Will Lenovo hold to that narrative? It starts with the people making decisions within, and there is every indication that Lenovo is struggling to move in that direction, in all markets.
That said, there is a genuine effort at high levels of the company to that end.
Thanks for reading.
For More TechWorld 2019 coverage, check out these other Lenovo Insiders, and the Hashtag #LenovoTechWorld #LenovoIN
Adam Fowler
https://twitter.com/AdamFowler_IT
https://www.adamfowlerit.com/
Onica Cupido
https://twitter.com/OnicaCupido
Vernon Chan
https://twitter.com/vernieman
https://vernonchan.com/
Lawrence Mann
https://twitter.com/LAWRENCEcanDRAW
https://www.youtube.com/LAWRENCEcanDRAW
And, our friends from the Lenovo Champions ;-D
https://www.instagram.com/tecnolaura/
https://www.youtube.com/technikfaultier
https://twitter.com/TecnoLocura
https://www.instagram.com/leotechmaker/

1 note
·
View note
Text
Zuck calls Apple a monopolist
The copyright scholar James Boyle has a transformative way to think about political change. He tells a story about how the word "ecology" welded together a bunch of disparate issues into a movement.
Prior to "ecology," there were people who cared about owls, or air pollution, or acid rain, or whales, and while none of these people thought the others were misguided, they also didn't see them as being as part of the same cause.
Whales aren't anything like owls and acid rain isn't anything like ozone depletion. But the rise of the term "ecology," turned issues into a movement. Instead of being 1,000 causes, it was a single movement with 1,000 on-ramps.
Movements can strike at the root, look to the underlying economic and philosophical problems that underpin all the different causes that brought the movement's adherents together. Movements get shit done.
Which brings me to monopolies. This week, Mark Zuckerberg, one of the world's most egregious, flagrant, wicked monopolists, made a bunch of public denunciations of Apple for...monopolistic conduct.
Or, at least, he tried to. Apple stopped him. Because they actually do have a monopoly (and a monoposony) (in legal-economic parlance, these terms don't refer to a single buyer or seller, they refer to a firm with "market power" - the power to dictate pricing).
Facebook is launching a ticket-sales app and the Ios version was rejected because it included a notice to users that included in their price was a 30% vig that Apple was creaming off of Facebook's take.
https://www.theverge.com/2020/8/28/21405140/apple-rejects-facebook-update-30-percent-cut
Apple blocked the app because this was "irrelevant" information, and their Terms of Service bans "showing irrelevant" information.
This so enraged Zuck that he gave a companywide address - of the sort that routinely leaks - calling Apple a monopolist (they are), accused them of extracting monopoly rents (they do), and of blocking "innovation" and "competition" (also true).
https://www.buzzfeednews.com/article/pranavdixit/zuckerberg-apple-monopoly
Now, there are a bunch of Apple customers who consider themselves members of an oppressed religious minority who'll probably stop here (perhaps after an angry reply), and that's OK. You do you. But I have more to say.
Apple is a monopolist, sure, but more importantly, they are monoposonists - these are firms with "excessive buying power," gatekeepers who control access to purchasers. Monoposony power is MUCH easier to accumulate than monopoly power.
In the econ literature, we see how control over as little as 10% of the market can cement a firm's position, giving it pricing power over suppliers. Monopsony is the source of "chickenization," named for the practices of America's chicken-processing giants.
Chickenized poultry farmers have to buy all their chicks from Big Chicken; the packers tell them what to feed their birds, which vets to use, and spec out their chicken coops. They set the timing on the lights in the coops, and dictate feeding schedules.
The chickens can only be sold to the packer that does all this control-freaky specifying, and the farmer doesn't find out how much they'll get paid until the day they sell their birds.
Big Chicken has data on all the farmers they've entrapped and they tune the payments so that the farmers can just barely scratch out a living, teetering on the edge of bankruptcy and dependent on the packer for next year's debt payments.
Farmers who complain in public are cut off and blackballed - like the farmer who lost his contract and switched to maintaining chicken coops, until the packer he'd angered informed all their farmers that if they hired him, they would also get cancelled.
Monopsony chickenizes whose groups of workers, even whole industries. Amazon has chickenized publishers. Uber has chickenized drivers. Facebook and Google have chickenized advertisers. Apple has chickenized app creators.
Apple is a monopsony. So is Facebook.
Market concentration is like the Age of Colonization: at first, the Great Powers could steer clear of one another's claims. If your rival conquered a land you had your eye on, you could pillage the one next door.
Why squander your energies fighting each other when you could focus on extracting wealth from immiserated people no one else had yet ground underfoot?
But eventually, you run out of new lands to conquer, and your growth imperative turns into direct competition.
We called that "World War One." During WWI, there were plenty of people who rooted for their countries and cast the fighting as a just war of good vs evil. But there was also a sizable anti-war movement.
This movement saw the fight as a proxy war between aristocrats, feuding cousins who were so rich that they didn't fight over who got grandma's china hutch - they fought over who got China itself.
The elites who started the Great War had to walk a fine line. If they told their side that Kaiser Bill is only in the fight to enrich undeserving German aristos, they risked their audience making the leap to asking whether their aristos were any more deserving.
GAFAM had divided up cyberspace like the Pope dividing the New World: ads were Goog, social is FB, phones are Apple, enterprise is Msft, ecommerce belongs to Amazon. There was blurriness at the edges, but they mostly steered clear of one another's turf.
But once they'd chickenized all the suppliers and corralled all the customers, they started to challenge one another's territorial claims, and to demand that we all take a side, to fight for Google's right to challege FB's social dominance, or to side with FB over Apple.
And they run a risk when they ask us to take a side, the risk that we'll start to ask ourselves whether ANY of these (tax-dodging, DRM-locking, privacy invading, dictator-abetting, workforce abusing) companies deserve our loyalty.
And that risk is heightened because the energy to reject monopolies (and monoposonies) needn't start with tech - the contagion may incubate in an entirely different sector and make the leap to tech.
Like, maybe you're a wrestling fan, devastated to see your heroes begging on Gofundme to pay their medical bills and die with dignity in their 50s from their work injuries, now there's only one major league whose owner has chickenized his workers.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m8UQ4O7UiDs&list=FLM6hLIAIO-KfsNFn8ENnftw&index=767
Maybe you wear glasses and just realized that a single Italian company, Luxottica, owns every major brand, retailer, lab and insurer and has jacked up prices 1,000%.
https://www.latimes.com/business/lazarus/la-fi-lazarus-glasses-lenscrafters-luxottica-monopoly-20190305-story.html
Or maybe the market concentration you care about it in healthcare, cable, finance, pharma, ed-tech, publishing, film, music, news, oil, mining, aviation, hotels, automotive, rail, ag-tech, biotech, lumber, telcoms, or a hundred other sectors.
That is, maybe you just figured out that the people who care about owls are on the same side as the people who care about the ozone layer. All our markets have become hourglass shaped, with monop(olists/sonists) sitting at the pinch-point, collecting rents from both sides, and they've run out of peons to shake down, so they're turning on each other.
They won't go gently. Every Big Tech company is convinced that they have the right to be the pinchpoint in the hour-glass, and is absolutely, 100% certain that they don't want to be trapped in the bulbs on either side of the pinch.
They know how miserable life is for people in the bulbs, because they are the beneficiaries of other peoples' misery. Misery is for other people.
But they're in a trap. Monopolies and monopsonies are obviously unjust, and the more they point out the injustices they are EXPERIENCING, the greater the likelihood that we'll start paying attention to the injusticies they are INFLICTING.
Much of the energy to break up Big Tech is undoubtedly coming from the cable and phone industry. This is a darkly hilarious fact that many tech lobbyists have pointed out, squawking in affront: "How can you side with COMCAST and AT&T to fight MONOPOLIES?!"
They have a point. Telcoms is indescribably, horrifically dirty and terrible and every major company in the sector should be shattered, their execs pilloried and their logomarks cast into a pit for 1,000 years.
Their names should be curses upon our lips: "Dude, what are you, some kind of TIME WARNER?"
But this just shows how lazy and stupid and arrogant monopolies are. Telcoms think that if they give us an appetite for trustbusting Big Tech, that breaking up GAFAM will satiate us.
They could not be more wrong. There is no difference in the moral case for trustbusting Big Tech and busting up Big Telco. If Big Tech goes first, it'll be the amuse-bouche. There's a 37-course Vegas buffet of trustbustable industries we'll fill our plates with afterward.
Likewise, if you needed proof that Zuck is no supergenius - that he is merely a mediocre sociopath who has waxed powerful because he was given a license to cheat by regulators who looked the other way while he violated antitrust law - just look at his Apple complaints.
Everything he says about Apple is 100% true.
Everything he says about Apple is also 100% true OF FACEBOOK.
Can Zuck really not understand this? If not, there are plenty of people in the bulbs to either side of his pinch who'd be glad to explain it to him.
The monopolized world is all around us. That's the bad news.
The good news is that means that everyone who lives in the bulbs - everyone except the tiny minority who operate the pinch - is on the same side.
There are 1,000 reasons to hate monopolies, which means that there are 1,000 on-ramps to a movement aimed at destroying them. A movement for pluralism, fairness and solidarity, rather than extraction and oligarchy.
And just like you can express your support for "ecology" by campaigning for the ozone layer while your comrade campaigns for owls, you can fight oligarchy by fighting against Apple, or Facebook, or Google, or Comcast, or Purdue Poultry...or Purdue Pharma.
You are on the same side as the wrestling fan who just gofundemed a beloved wrestler, and the optician who's been chickenized by Luxottica, and the Uber driver whose just had their wages cut by an app.
115 notes
·
View notes
Text
Will augmented reality make people indulge in the virtual world? ——several problems of AR
youtube
Nowadays, people have designed a lot of applications of AR in different areas. The Pokémon Go is one of the most famous AR games which is also a very successful application of AR in real life. And we can say that AR is going to play an important role in the future. Under this circumstance, many people expect that the AR technology can bring us many improvements in our daily life. And along with the improvement of AI technology, more and more people believe the game company can use AI as a heart and then create many amazing and playful games in the near future. Until now, the AR can only connect with the physical environment by cameras in the daily life. And with AI, game designers can come up with more ways for people to link the virtual world to the real-life.
However, the combination of AI and AR technology can also make a lot of negative effects to people. Sometimes the AR technology may lead to addition because some people can’t distinguish between the real world and the virtual reality. If that really happens, then less people will be willing to work hard. As a result, the productivity of the whole society may decrease. But before we show you the negative side of that technology, maybe we can know the specific meaning of the AR.
What’s is AR?
Augmented reality (AR) is an “interactive experience of a real-world environment where the objects that reside in the real-world are enhanced by computer-generated perceptual information, sometimes across multiple sensory modalities, including visual, auditory, haptic, somatosensory and olfactory.” - From Wikipedia.
Will you live in a virtual world?

Pokémon go AR is one of the most popular games around the world. You can use your phone’s camera to show a Pokémon in real world, trapping them to get their attention and make them pose accordingly.
Let’s imagine one day the AR is everywhere in our life---- You wear a AR glasses, it will show you the famous TV shows to you. Then, you need to attend a meeting, AR glasses make a virtual meeting room and your colleagues are all sit here. After that, you want to go to a restaurant and have a meal. You see a map on your AR glasses and you just need to follow the instructions. You can do everything you can image by AR. In that case, will you live without AR?
You might think it is really a wonderful thing. However, spending more time in virtual life means less time in real life. There is a research shows the mobile phone makes people feel less connected. The experience shows more than 500000 of people don’t get out of their house for half of a year.
These people don’t have many friends, they rarely have communication with people. And they have bad health. That’s all because they are indulge in the virtual world. So how can we avoid to addicted to virtual world? Many psychologists believe that people should have more communications with others and do more sports. Don’t forget you are living in the real world.

And there are some other social problems which caused by the AR by NOW. For example, sometimes people may get injured while playing the Pokémon game since they may be too excited to run to the Pokémon but ignore the latent dangers on the streets and roads. According to the report of Screenrant news, a Pokémon player fell into a ditch while searching for a Pokémon and one of the bones in her foot was broken and she needs 6-8 weeks to recover from her injury. Moreover, some people even use their phone to try to capture the Pokémon even if they are driving! That behavior can easily lead to car accidents, cause huge property lost and casualties. To avoid that problem, the government may need to enhance the effects of these laws which prohibit people from using their phones when they are driving cars and in the meantime the game company should remind their customers to be careful while they are looking for the Pokémon to capture in some downtown areas or dangerous places which means there are many roads and the traffic condition is always busy there.
Another Obstacle

As the developing of AR, a big problem comes out, hacking. Although this problem has existed for decades, it seems more destructive in AR’s world. When we are building a new reality in a more digital way, we need to care about out digital property, too. No matter you believe or not, augmented reality is adding your risk of losing your privacy.
As a fan of Pokémon Go, I will go crazy if someone else steal my pokémons by hacking into your smartphone. People’s privacy in the digital world is not only about money but also about the time costs in the game. If you spend a hundred hours catching and cultivating your pokémons, your account should not be worthless just because you have not pay to the game. Otherwise, it should be valuable since you can exchange money with this account. In the future, AR will keep developing and foreseeable, it will create a digital world based on the physical reality. When more and more people spending more money in AR world, the government most pay attention on it because it may become a big part of the national economy.
Nowadays, the market for “intangible personal property” (in-game items) in the gaming world already commands billions of U.S. dollars and continues to grow substantially every year. People pay for in-game goods with real cash, but generally whoever owns the intellectual property rights to the game itself actually owns the property. Different from today’s digital game, AR is easier to confuse reality because it’s built on the physical world. This means it’s very likely to attract more cash than traditional digital games.
If the government doesn’t do something like making laws and setting a fine to prevent hacking to these properties, more and more conflicts will arise In order to solve this problem, it’s important to call on people to think about the legal issues at stake AR virtual world.
Conclusion
Although AR already shows us a fascinating future, there are a lot of new problems come out and need to be solved. Treating them sensibly and logically, believing the potential of human, we can build an unbelievable world with AR.
youtube
References: [1] the explanation of Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AR [2] data from sino caijing (Sina Caijing 2017, https://finance.sina.com.cn/roll/2017-01-14/doc-ifxzqhka3024216.shtml ) [3] the accident is reported by Screenrant, https://screenrant.com/pokemon-go-dangers/ [4] Do you own your virtual property? | Vanderbilt Journal of Entertainment & Technology Law, http://www.jetlaw.org/2018/11/03/do-you-own-your-virtual-property/
[5] HYPER-REALITY - YouTube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YJg02ivYzSs
[6] Minecraft Earth: Apple WWDC Gameplay Reveal - YouTube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GNo38kNy_EU
Written by: Avan, Andy, Mike
1 note
·
View note