#Food Processing Unit Subsidy
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Tomato Powder Business: कम लागत में अधिक मुनाफे वाला बिज़नेस
Tomato Powder Business:-कम लागत में अधिक मुनाफे वाला बिज़नेस परिचय भारत एक कृषि प्रधान देश है, जहाँ सब्जियों और फलों की खेती बड़े पैमाने पर होती है। टमाटर (Tomato) भारतीय रसोई में सबसे अधिक उपयोग किए जाने वाले उत्पादों में से एक है। मौजूदा समय में झारखंड में टमाटर की कीमत मात्र ₹2 प्रति किलो और बिहार में ₹4 प्रति किलो हो गई है, जिससे किसानों को बड़ा नुकसान हो रहा है। ऐसे में, टमाटर पाउडर (Tomato…
#MahaKumbh2025 EconomicGrowth ReligiousTourism IndiaTourism Prayagraj Ayodhya Varanasi YogiAdityanath UPDevelopment#Food Processing Unit Subsidy#Government Schemes for Food Processing#How to Make Tomato Powder#Tomato Powder#Tomato Powder Business#Tomato Powder Export#Tomato Powder Manufacturing Process
0 notes
Text
Outgoing special rapporteur David Boyd says ‘there’s something wrong with our brains that we can’t understand how grave this is’
The race to save the planet is being impeded by a global economy that is contingent on the exploitation of people and nature, according to the UN’s outgoing leading environment and human rights expert.
David Boyd, who served as UN special rapporteur on human rights and the environment from 2018 to April 2024, told the Guardian that states failing to take meaningful climate action and regulating polluting industries could soon face a slew of lawsuits.
Boyd said: “I started out six years ago talking about the right to a healthy environment having the capacity to bring about systemic and transformative changes. But this powerful human right is up against an even more powerful force in the global economy, a system that is absolutely based on the exploitation of people and nature. And unless we change that fundamental system, then we’re just re-shuffling deck chairs on the Titanic.”
The right to a clean, healthy and sustainable environment was finally recognised as a fundamental human right by the United Nations in 2021-22. Some countries, notably the US, the world’s worst historic polluter, argue that UN resolutions are legally influential but not binding. The right to a healthy environment is also enshrined into law by 161 countries with the UK, US and Russia among notable exceptions.
Boyd, a Canadian environmental law professor, said: “Human rights come with legally enforceable obligations on the side of states, so I believe that this absolutely should be a game-changer – and that’s why states have resisted it for so long.
Boyd said: "By bringing human rights into the equation, we now have institutions, processes and courts that can say to governments this isn’t an option for you to reduce your greenhouse gas emissions and phase out fossil fuels. These are obligations which include regulating businesses, to make sure that businesses respect the climate, the environment and human rights."
Over the course of his six-year mandate, Boyd met thousands of people directly affected by rising sea levels, extreme heat, plastic waste, toxic air, and dwindling food and water supplies, while undertaking fact-finding missions to Fiji, Norway, St Vincent and the Grenadines, Portugal, Slovenia, Chile, Botswana and Maldives.
“Powerful interconnected business and political elites – the diesel mafia – are still becoming wealthy from the existing system. Dislodging this requires a huge grassroots movement using tools like human rights and public protest and every other tool in the arsenal of change-makers.”
On his first trip as special rapporteur to Fiji, Boyd met with community members from Vunidogoloa, a coastal village left uninhabitable by rising sea water, who were forced to relocate to higher ground. Last year in Botswana, he met with Indigenous people from the Kalahari desert no longer able to handle the worsening heat and water scarcity.
Over the past 30 years, the world has pinned its hopes on international treaties - particularly the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Paris accords – to curtail global heating. Yet they do not include mechanisms for holding states accountable to their commitments, and despite some progress, greenhouse-gas emissions have continued to rise and climate breakdown is accelerating.
It’s not just taxpayer subsidies propping up polluting industries and delaying climate action. The same multinationals are involved in negotiating – or at least influencing – climate policy, with a record number of fossil-fuel lobbyists given access to the UN Cop28 climate talks last year.
Boyd said: “There’s no place in the climate negotiations for fossil-fuel companies. There is no place in the plastic negotiations for plastic manufacturers. It just absolutely boggles my mind that anybody thinks they have a legitimate seat at the table.
“It has driven me crazy in the past six years that governments are just oblivious to history. We know that the tobacco industry lied through their teeth for decades. The lead industry did the same. The asbestos industry did the same. The plastics industry has done the same. The pesticide industry has done the same.”
In his final interview before handing over the special rapporteur mandate, Boyd said he struggles to makes sense of the world’s collective indifference to the suffering being caused by preventable environmental harms.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Business Opportunities for Agri & Food Processing Sector in Rajasthan: Col Rajyavardhan Rathore

Rajasthan, known for its rich cultural heritage and vast arid landscapes, is rapidly emerging as a hub for the agriculture and food processing sector. With its unique agricultural produce, favorable policies, and increasing investment in food processing infrastructure, the state offers a wealth of business opportunities for entrepreneurs and investors. Col Rajyavardhan Rathore, a prominent leader from Rajasthan, has consistently emphasized the importance of leveraging this sector to drive sustainable economic growth and uplift rural livelihoods.
Why Rajasthan is a Prime Destination for Agri & Food Processing Ventures
Rajasthan’s diverse agro-climatic zones and rich agricultural traditions make it a prime destination for ventures in agriculture and food processing. Key factors driving this growth include:
Abundant Agricultural Produce: Rajasthan is a leading producer of crops like millet, wheat, mustard, and pulses, as well as horticultural produce like guava, pomegranate, and ber (Indian jujube).
Strategic Location: Proximity to major markets like Delhi, Gujarat, and Maharashtra enhances logistics efficiency.
Government Support: Favorable policies and incentives to promote food processing industries.
Key Opportunities in Rajasthan’s Agri & Food Processing Sector
1. Cereal and Grain Processing
Rajasthan is the largest producer of bajra (pearl millet) and a significant producer of wheat and barley.
Opportunities include milling, packaging, and exporting these staples to domestic and international markets.
2. Oilseed Processing
The state is India’s top producer of mustard seeds, making it ideal for setting up mustard oil extraction and processing units.
Value-added products like mustard oil cakes for animal feed also present lucrative business opportunities.
3. Dairy Industry
With a strong livestock population, Rajasthan has immense potential in milk production and processing.
Opportunities include setting up dairy plants for products like butter, cheese, and flavored milk.
4. Horticulture-Based Businesses
Rajasthan is known for its high-quality pomegranates, kinnows, and dates.
Processing units for juices, jams, and dried fruits can tap into both domestic and export markets.
5. Spice Production and Processing
The state is a significant producer of spices like coriander, cumin, and fenugreek.
Setting up spice grinding and packaging units can cater to increasing demand from urban markets and exports.
6. Herbal and Medicinal Plants
Rajasthan’s arid climate supports the cultivation of medicinal plants like aloe vera, isabgol, and ashwagandha.
Opportunities include producing herbal extracts, essential oils, and ayurvedic medicines.
7. Organic Farming and Products
With growing awareness of health and sustainability, organic farming is gaining traction.
Export of organic grains, vegetables, and processed foods is a high-potential area.
8. Cold Storage and Logistics
Lack of adequate cold storage infrastructure poses a challenge, creating an opportunity for investment.
Businesses can also invest in modern logistics systems for efficient transportation of perishable goods.
Policy Support for Agri & Food Processing in Rajasthan
The Rajasthan government has introduced a host of initiatives to promote investment in the sector:
Rajasthan Agro-Processing, Agri-Business & Agri-Export Promotion Policy: Offering incentives like capital subsidies, tax rebates, and single-window clearances.
Mega Food Parks Scheme: Establishment of food parks to support processing industries with shared infrastructure.
Cluster-Based Development: Promotion of crop-specific clusters like the mustard cluster in Bharatpur and spice cluster in Jodhpur.
Subsidies for Startups: Financial support for agri-tech startups and small-scale food processing units.
The Role of Technology in Driving Growth
1. Precision Farming
Use of drones, IoT devices, and satellite imagery for better crop management.
2. Food Processing Automation
Adoption of automated equipment for sorting, grading, and packaging ensures efficiency and quality.
3. Blockchain in Agri-Supply Chains
Enhancing transparency and traceability from farm to fork.
4. Digital Marketplaces
Platforms like eNAM are helping farmers connect directly with buyers, ensuring better prices.
Col Rajyavardhan Rathore: Advocating for Agri-Business Growth
Col Rathore has been a strong advocate for leveraging Rajasthan’s agricultural strengths to create employment and boost the economy. His initiatives include:
Promoting Agri-Entrepreneurship: Encouraging youth to explore opportunities in modern farming and food processing.
Farmer Outreach Programs: Regular interactions with farmers to address challenges and introduce them to new technologies.
Policy Advocacy: Ensuring that government policies align with the needs of farmers and agri-businesses.

Challenges and Solutions in the Sector
Challenges
Water Scarcity: Dependence on rain-fed agriculture in many regions.
Post-Harvest Losses: Lack of proper storage and transportation facilities.
Market Access: Difficulty in connecting small farmers to larger markets.
Solutions
Drip Irrigation and Water Conservation: Efficient irrigation methods to tackle water scarcity.
Investment in Cold Chains: Preventing wastage of perishable goods.
Digital Platforms for Farmers: Expanding access to markets through e-commerce and digital supply chains.
A Promising Future for Agri & Food Processing in Rajasthan
Rajasthan is poised to become a leader in the agriculture and food processing sector, thanks to its diverse produce, supportive policies, and visionary leadership. With growing investments and technological advancements, the state offers endless opportunities for entrepreneurs and businesses.
Under the guidance of leaders like Col Rajyavardhan Rathore, Rajasthan is moving steadily toward a future where its agricultural wealth is fully harnessed to benefit farmers, consumers, and the economy at large.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Integrated Cluster Development Scheme: A Visionary Initiative by Col Rajyavardhan Rathore

The Integrated Cluster Development Scheme (ICDS), launched under the leadership of Colonel Rajyavardhan Rathore, marks a significant milestone in fostering economic growth and social development across Rajasthan. Focused on empowering small-scale industries, artisans, and rural entrepreneurs, this initiative is set to transform traditional production clusters into engines of innovation, employment, and sustainability.
In this article, we’ll explore the goals, features, and potential impact of this scheme on Rajasthan’s economy and its people.
What is the Integrated Cluster Development Scheme?
The ICDS aims to modernize and strengthen production clusters in Rajasthan, encompassing sectors like handicrafts, textiles, food processing, and small-scale manufacturing. By integrating infrastructure development, skill training, and financial incentives, this scheme provides a holistic framework to promote regional growth.
Col Rajyavardhan Rathore’s Vision Behind the Scheme
Col Rajyavardhan Rathore, a staunch advocate for rural development and economic empowerment, believes that: “Clusters are the backbone of our economy. Strengthening them means empowering our artisans, entrepreneurs, and communities for a brighter, self-reliant Rajasthan.”
His leadership in shaping the scheme reflects a commitment to harnessing the state’s cultural heritage and industrial potential for sustainable development.
Key Objectives of the ICDS
Economic Growth: Enhance the productivity and profitability of Rajasthan’s traditional and emerging clusters.
Job Creation: Generate employment opportunities, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas.
Skill Development: Provide training to workers and entrepreneurs in modern techniques and global standards.
Sustainability: Promote eco-friendly practices in production and infrastructure.
Global Competitiveness: Enable clusters to compete effectively in national and international markets.
Highlights of the Integrated Cluster Development Scheme
1. Infrastructure Upgradation
Establishment of common facility centers (CFCs) equipped with modern tools and machinery.
Development of dedicated industrial parks and cluster zones.
Improved connectivity through roads, railways, and digital infrastructure.
2. Financial Support
Subsidies and Grants: Financial assistance for purchasing equipment and upgrading technology.
Cluster Development Funds: Allocation of funds for infrastructure, marketing, and research.
Low-Interest Loans: Easy access to credit for small businesses and artisans.
3. Capacity Building
Skill Training Programs: Workshops on modern production techniques, quality control, and innovation.
Entrepreneurship Development: Training in business management and digital marketing.
Global Exposure: Participation in national and international trade fairs.
4. Promoting Innovation and Technology
Establishment of innovation hubs within clusters to encourage research and development.
Integration of digital tools such as e-commerce platforms and management software.
5. Focus on Key Sectors
Handicrafts and Textiles: Revitalizing traditional crafts with modern designs.
Food Processing: Expanding the scope of agro-based industries with value addition.
Renewable Energy Clusters: Promoting solar and wind energy production units.
Impact of the Scheme on Rajasthan
Economic Benefits
An estimated 20–30% increase in cluster productivity within the first three years.
Boost in state GDP through enhanced industrial output and exports.
Social Empowerment
Improved livelihood opportunities for over 50,000 workers and artisans.
Empowerment of women and marginalized communities through focused support programs.
Sustainability
Adoption of eco-friendly production techniques, reducing the environmental footprint.
Examples of Targeted Clusters
Jaipur Handicrafts Cluster
Known for its exquisite jewelry, blue pottery, and textiles, Jaipur’s cluster will benefit from marketing support and infrastructure development.
Jodhpur Furniture Cluster
Famous for its wooden furniture, this cluster will see investments in modern tools and export promotion.
Bikaner Agro Cluster
A hub for food processing and agricultural produce, Bikaner’s cluster will receive funding for value-added processing units.
How the Scheme Promotes Self-Reliance
Aligned with the “Make in India” and “Atmanirbhar Bharat” initiatives, the ICDS focuses on reducing import dependency by enhancing local production capabilities. By enabling small businesses to scale up and reach global markets, it fosters a self-reliant ecosystem.
Col Rajyavardhan Rathore’s Commitment to Progress
Col Rathore has been instrumental in advocating policies that blend tradition with technology. His leadership ensures that the ICDS not only preserves Rajasthan’s cultural identity but also propels it into the future.
In his words: “This scheme is a tribute to the hardworking people of Rajasthan who keep our traditions alive while embracing the opportunities of the modern world.”
A New Dawn for Rajasthan’s Clusters
The Integrated Cluster Development Scheme is a game-changer for Rajasthan’s economy. By focusing on modernization, skill enhancement, and financial support, it promises to uplift thousands of artisans, workers, and entrepreneurs while showcasing Rajasthan’s rich heritage to the world.
This initiative is not just about economic development; it’s about empowering communities, celebrating culture, and creating a sustainable future for all.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
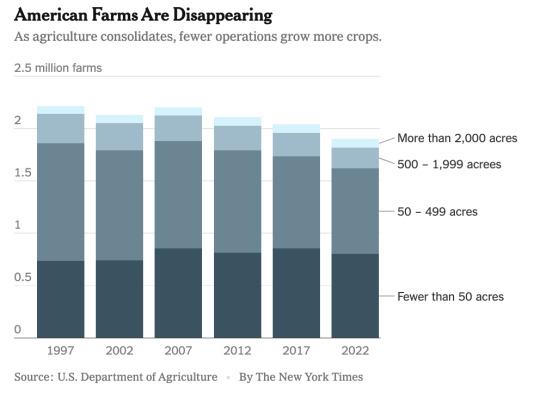
Excerpt from this story from the New York Times:
Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack has a line about the state of small-scale agriculture in America these days.
It’s drawn from the National Agricultural Statistics Service, which shows that as the average size of farms has risen, the nation had lost 544,000 of them since 1981.
“That’s every farm today that exists in North Dakota and South Dakota, added to those in Wisconsin and Minnesota, added to those in Nebraska and Colorado, added to those in Oklahoma and Missouri,” Mr. Vilsack told a conference in Washington this spring. “Are we as a country OK with it?”
Even though the United States continues to produce more food on fewer acres, Mr. Vilsack worries that the loss of small farmers has weakened rural economies, and he wants to stop the bleeding. Unlike his last turn in the same job, under former President Barack Obama, this time his department is able to spend billions of dollars in subsidies and incentives passed under three major laws since 2021 — including the biggest investment in conservation programs in U.S. history.
The plan in a nutshell: Multiply and improve revenue streams to bolster farm balance sheets. Rather than just selling crops and livestock, farms of the future could also sell carbon credits, waste products and renewable energy.
“Instead of the farm getting one check, they potentially could get four checks,” Mr. Vilsack said in an interview. He is also helping schools, hospitals and other institutions to buy food grown locally, and investors to build meatpacking plants and other processing facilities to free farmers from powerful middlemen.
But it’s far from clear whether new policies and a cash infusion will be enough to counteract the forces that have pushed farmers off the land for decades — especially since much of the money is aimed at reducing carbon emissions, and so will also go toward large farming operations because they are the biggest polluters.
The number of farms has been declining since the 1930s, in large part because of migration from rural areas to cities and greater mechanization of agriculture, which allowed operators to cultivate larger tracts with fewer people. Over time, the federal government abandoned a policy of managing production to support prices, prompting growers to become more export-oriented while local distribution networks atrophied.
The last half-decade has been more disruptive than most. First came a trade war against China under former President Donald J. Trump, which drew retaliatory tariffs that cut into U.S. exports of farm products like soybeans and pork. Then came the pandemic, which scrambled supply chains and sapped farm labor, leaving crops to rot in the fields.
After Congress cushioned the blow with relief for farmers hurt by pandemic disruptions, things started to turn around. Even as the cost of supplies like fertilizer and seed rose, so did food prices, and farm incomes increased. In 2023, default rates on farm loans neared record lows.
“Farm balance sheets are the healthiest they’ve ever been in the aggregate,” said Brad Nordholm, the chief executive of Farmer Mac, a large secondary market for agricultural credit. “The tools available to American farmers to have a more predictable return, even when commodity prices change and input prices change, is greater than it’s ever been before.”
But wholesale crop prices are expected to decline over the coming year. Rising interest rates have made it more difficult to finance planting and harvesting, borrow for an expansion or just get into agriculture — especially since land values jumped 29 percent from 2020 to 2023.
That’s especially true for the smallest farmers, who are far less likely to be tapped into Department of Agriculture assistance programs and are more vulnerable to adverse weather, labor shortages and consumer whims.
“I think in some ways they’re in a worse position than before the pandemic,” said Benneth Phelps, executive director of the nonprofit Carrot Project, which advises small farmers in New England. “We see a lot of farmers making hard decisions right now about whether to stay in or get out, because they’ve run out of steam.”
That’s where the American Rescue Plan, the Inflation Reduction Act and the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law come in.
The laws have collectively provided about $60 billion to the Agriculture Department, which has parceled it out across a variety of priorities, from relieving farmers’ debt to paying them to reduce their carbon emissions.
The biggest chunk — about $19.5 billion — has breathed new life into subsidies to encourage conservation practices that improve the land, like cutting back on plowing and planting cover crops to sequester carbon in the soil. Some of the programs had shrunk in successive Farm Bills, which are five-year legislative packages that covers most agricultural subsidies, and about two-thirds of farmers who applied each year got nothing.
The new funding has added 16,000 recipients over the past two years. Preliminary data shows the expansion is allowing smaller farms to take part.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

ANGC Group India Pvt Ltd Leading Top 10 Msme Small Sc St Startup Business Machinery Loan Msme Industrial Hotel Hospital Food Processing Unit Subsidy Consultants
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Biogas in Thrissur: Powering a Greener Future Through Sustainable Waste Management

As cities grow and energy demands rise, the need for sustainable alternatives becomes more urgent. In this context, biogas in Thrissur has emerged as a powerful solution that addresses both waste management and clean energy production. Thrissur, known for its strong community values and environmental awareness, is leading the way in adopting biogas technology across homes, institutions, and farms.
What is Biogas and How Does it Work?
Biogas is a renewable source of energy produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic waste such as kitchen scraps, food waste, agricultural residue, and cow dung. The process produces methane-rich gas, which can be used for cooking, heating, or generating electricity. The byproduct, called slurry, can be used as a nutrient-rich organic fertilizer.
Why Thrissur is Adopting Biogas Technology
Thrissur, with its mix of urban and semi-rural communities, generates a significant amount of biodegradable waste daily. Rather than letting it end up in landfills, many households, schools, and public institutions have started adopting biogas plants as a smart alternative. This shift not only reduces waste but also cuts down on LPG usage and electricity bills.
Benefits of Biogas in Households and Institutions
✅ Reduces waste volume at the source
✅ Lowers dependency on conventional fuels like LPG
✅ Produces organic fertilizer for gardens and farms
✅ Minimizes greenhouse gas emissions
✅ Promotes self-sufficiency and eco-conscious living
From small-scale kitchen digesters to community-level biogas plants, there are models suitable for every space and need in Thrissur.
Government Support and Subsidy Schemes in Kerala
The Kerala State Biodiversity Board and local bodies in Thrissur encourage biogas adoption through subsidies and awareness programs. These schemes make biogas plant installation more affordable for families, institutions, and agricultural entrepreneurs. Some of the popular government-supported models include portable biogas units and fixed dome-type plants.
Local Manufacturers and Installation Options in Thrissur
Several reliable manufacturers and service providers offer biogas installation and maintenance services in Thrissur. From site inspection to plant commissioning and after-sales support, these providers ensure a hassle-free transition to clean energy.
Conclusion
Biogas in Thrissur isn’t just a trend — it’s a movement toward sustainability and self-reliance. With government support, community participation, and growing environmental awareness, biogas is shaping a cleaner and greener future for the city. Now is the right time to embrace biogas technology and become part of Thrissur’s eco-revolution.
#biogas in kerala#biogas plant for home#incinerator manufacturers in kerala#biogas#kerala#portable biogas plant for home#incinerators in kerala
0 notes
Text
Biogas Plant: A Sustainable Energy Solution for the Future

Introduction to Biogas Plants
A biogas plant is an eco-friendly facility that produces renewable energy by processing organic waste materials such as agricultural residues, animal manure, food waste, and sewage sludge. Through anaerobic digestion, these materials are broken down by microorganisms to produce biogas—a mixture primarily composed of methane (CH₄) and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
As the world shifts toward clean energy alternatives, biogas plants play a crucial role in waste management, energy generation, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
How a Biogas Plant Works
The core process of a biogas plant involves the following stages:
Feedstock Collection – Organic waste such as crop leftovers, food scraps, and animal waste are gathered.
Anaerobic Digestion – The waste is placed in a sealed digester, where bacteria break it down in an oxygen-free environment.
Biogas Generation – Methane-rich gas is produced and collected for use as fuel.
Digestate Separation – The remaining material, known as digestate, is separated and used as a nutrient-rich organic fertilizer.
Types of Biogas Plants
There are different types of biogas plants, each designed to meet specific needs:
Fixed Dome Biogas Plant – Cost-effective and durable, commonly used in rural areas.
Floating Drum Biogas Plant – Provides easy gas measurement and storage.
Plug Flow Digester – Suitable for high-solids waste like cow dung or crop waste.
Industrial Biogas Plant – Large-scale facilities designed for cities, factories, or agricultural cooperatives.
Benefits of Biogas Plants
1. Renewable Energy Production
Biogas is a clean, renewable fuel that can replace fossil fuels for electricity generation, heating, and even vehicle fuel when upgraded to biomethane.
2. Waste Reduction
Biogas plants convert waste into energy, significantly reducing landfill usage and mitigating methane emissions.
3. Climate Change Mitigation
By capturing methane—a potent greenhouse gas—biogas plants help reduce global warming and promote carbon neutrality.
4. Soil Enrichment
The by-product, digestate, serves as an excellent organic fertilizer, enhancing soil fertility and crop yields.
5. Energy Independence
Communities and industries using biogas can reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels, promoting energy security.
Applications of Biogas
Electricity and Heat Generation via Combined Heat and Power (CHP) units
Cooking Fuel in households and commercial kitchens
Vehicle Fuel (Biomethane for CNG engines)
Industrial Energy for processing plants and greenhouses
Challenges and Solutions
While biogas plant installation can be capital-intensive and technically demanding, the long-term benefits outweigh the initial costs. Government incentives, carbon credits, and technological advancements have made biogas more accessible and cost-effective.
Common challenges:
High upfront costs
Technical expertise for operation
Seasonal variation in feedstock
Solutions:
Government subsidies and feed-in tariffs
Training programs for operators
Diversified feedstock sourcing
Biogas Plants and Sustainability Goals
Biogas technology aligns with several UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), including:
Affordable and Clean Energy (SDG 7)
Climate Action (SDG 13)
Sustainable Cities and Communities (SDG 11)
Responsible Consumption and Production (SDG 12)
Conclusion
Investing in a biogas plant is a smart step toward a cleaner, greener future. Whether for individual farms, businesses, or municipalities, biogas offers a powerful combination of sustainable energy, waste management, and climate action. As demand for renewable energy grows, biogas plants are poised to become a key player in the global energy transition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main purpose of a biogas plant?
To convert organic waste into renewable energy (biogas) and organic fertilizer.
How much biogas can be produced from 1 ton of food waste?
Approximately 100–200 cubic meters, depending on the composition and digestion conditions.
Is biogas plant installation expensive?
Initial setup costs can be high, but government incentives and energy savings offer strong long-term returns.
Can biogas be used for cooking?
Yes, biogas is an excellent fuel for household and commercial cooking applications.
0 notes
Text
What’s the Best Way to Start a Palm Leaf Plate Wholesale Business

Let’s be honest — finding a business idea that’s both profitable and meaningful isn’t easy. But every once in a while, something comes along that checks both boxes. That’s exactly what palm leaf plates offer: a chance to make good money while doing something that’s genuinely good for the planet.
If you’ve been thinking about starting your own wholesale business, palm leaf plates wholesale might be your golden ticket — especially now, as more people shift toward sustainable living and eco-friendly products.
Let’s walk through how you can actually get started — from understanding the product to setting up your operations and landing your first customers.
Why Palm Leaf Plates? Why Now? In a world drowning in plastic, palm leaf plates offer something refreshingly different.
They’re made from naturally fallen Areca palm leaves — no trees are cut, and no chemicals are used. They’re biodegradable, compostable, and surprisingly strong. That means they’re perfect for restaurants, events, catering companies, and even exports.
What makes this even more exciting is the timing. Countries are banning single-use plastics, and businesses are looking for planet-friendly options. That creates a real demand — and real opportunity — for smart entrepreneurs like you to step in.
Step 1: Understand What You're Selling Before you jump in, take time to really understand the product. Palm leaf plates come in all sorts of shapes and sizes — round dinner plates, square lunch plates, bowls, trays, and even compartment thalis.
Think about:
What kind of buyers you want to target (restaurants? event companies? exporters?)
Which styles and sizes are in high demand
What kind of quality and price range you want to offer
Knowing your product makes you a better seller — and it builds trust with your customers.
Step 2: Choose Your Business Model — Source or Manufacture Here’s the big decision: Do you want to source your plates from a manufacturer or make them yourself?
Option 1: Source and Sell This is the easier and faster route. You buy palm leaf plates in bulk from a trusted manufacturer and resell them to your customers. It’s low investment, and great if you're just starting out or want to focus on sales and marketing.
Option 2: Set Up a Manufacturing Unit This route takes more effort and money — but gives you full control. You’ll need machines, raw materials (palm leaves), and workers. A small setup in India can cost around ₹6–7 lakhs.
The process itself is straightforward:
Collect naturally fallen palm leaves
Wash and dry them
Press them into shape using heat molds
Trim, check quality, and pack
If you're based in southern India (Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu), where palm leaves are abundant, this could be a smart long-term play.
Step 3: Handle the Legal Stuff Don’t worry — this part sounds more intimidating than it is. Here’s what you’ll typically need to run a legit wholesale business:
GST registration (mandatory in India)
Udyam/MSME registration (helps with bank loans and subsidies)
FSSAI license (since these plates are used with food)
If you're thinking about exports, you might also need certifications like:
Compostability certification (BPI or EN13432)
ISO or food safety standards
These add credibility and help you access international markets.
Step 4: Figure Out Who You’re Selling To Since this is a wholesale business, you’ll be selling in bulk. So who are your ideal buyers?
Restaurants and cafés going plastic-free
Wedding and event planners
Organic stores and retailers
Exporters targeting markets in Europe, the U.S., or the Middle East
Each type of buyer will have different needs. An exporter might care more about certifications. A restaurant may want fast delivery and consistent quality. Learn what your customers want — and deliver it better than the next guy.
Step 5: Build a Basic Online Presence No need for a fancy e-commerce website (at least not yet). But having a clean, simple site or landing page makes a big difference.
Here’s what it should include:
Product photos and descriptions
Your story — what makes your business eco-conscious
How to place bulk orders
Contact form or WhatsApp link for quick inquiries
Also list your business on platforms like IndiaMART, TradeIndia, or ExportersIndia — many wholesale buyers use these sites to find suppliers.
And don’t underestimate Instagram and LinkedIn. Posting real photos, customer stories, or even short videos of how the plates are made can go a long way.
Step 6: Don’t Ignore Packaging and Shipping Palm leaf plates are tough, but smart packaging still matters. Go for simple, eco-friendly cartons — they look good and match your values. Include care instructions if needed.
As for logistics:
For local deliveries, use couriers like Delhivery, DTDC, or India Post
For exports, partner with freight forwarders who understand food-grade and eco-packaged products
If possible, always send a few samples first — it builds confidence and helps close the deal.
Step 7: Promote Smart, Not Loud Marketing doesn’t mean spending lakhs on ads. You can start small and still make an impact.
Here’s what works:
Send free samples to local restaurants or event planners
Share your story on social media (authentic always beats “salesy”)
Write short blog posts with keywords like “palm leaf plates wholesale” — Google loves helpful content
Follow up with leads from B2B marketplaces and always respond quickly
The more human and real your brand feels, the more people will trust you.
Final Thoughts: At the end of the day, this business isn’t just about plates. It’s about solving a real-world problem: plastic waste. You’re offering an alternative that’s better for the earth — and still practical, affordable, and beautiful.
With smart sourcing, the right connections, and a little hustle, starting a palm leaf plates wholesale business can be both rewarding and impactful. And the best part? You don’t need a huge investment to get going — just the right mindset and a clear plan.
FAQs 1. Are palm leaf plates microwave-safe? Yes! They’re heat-resistant and perfectly safe for microwaves and even ovens (up to a certain temperature).
2. How long can I store palm leaf plates? If kept dry and sealed, they can last up to 18 months without any problem.
3. Can I sell these plates internationally? Absolutely. Just make sure you get the right certifications and understand the import rules of your target countries.
4. What’s the minimum investment to start this business? If you're reselling, you can start with ₹1–2 lakhs. If you're manufacturing, expect around ₹6–7 lakhs for a basic unit setup.
5. Where can I find good suppliers? IndiaMART is a great starting point. You can also visit manufacturing hubs in South India to meet suppliers in person — that’s always a plus.
#ecofriendlytableware#sustainabledinnerware#palmleafplateswholesale#ecodisposableplateseurope#arecaleafplates#compostableplatesusa#arecaleafplatesuppliers#disposablearecaleafplates#naturalpalmleafplates
0 notes
Text
Government Schemes for Food Processing Units: Subsidy & Bank Loan Interest Details
Government Schemes for Food Processing Units: Subsidy & Bank Loan Interest Details Food Processing उद्योग भारत में तेजी से बढ़ रहा है और सरकार इसे और अधिक बढ़ावा देने के लिए विभिन्न schemes लेकर आई है। यदि आप एक Food Processing Unit स्थापित करना चाहते हैं, तो भारत सरकार की विभिन्न योजनाओं के तहत आपको Subsidy, Bank Loan और अन्य financial assistance मिल सकती है। इस blog में हम विस्तार से इन…
#Food Processing Loan Interest#Food Processing Unit Subsidy#Government Schemes for Food Processing#Indian Government Subsidy Schemes#MSME Loan Scheme#Mudra Yojana for Food Industry
0 notes
Text
Can Switching to Bio-CNG Make Your Business Carbon-Neutral?

In an era where sustainability is no longer optional but essential, businesses are increasingly exploring cleaner energy alternatives. One such promising option is Bio-CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) — a renewable fuel derived from organic waste. But can switching to Bio-CNG truly make your business carbon-neutral? Let’s explore.
What is Bio-CNG and How is it Produced?
Bio-CNG is purified biogas primarily composed of methane. It’s created from organic waste through anaerobic digestion — a natural process where microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. The raw biogas is then upgraded by removing carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, and moisture, resulting in Bio-CNG.
This entire process is typically carried out at a bio gas plant, which receives waste such as agricultural residue, food waste, cattle dung, or municipal solid waste and converts it into useful fuel.
Why Bio-CNG is Gaining Momentum
Renewable & Sustainable Bio-CNG comes from waste — something every industry produces. Using it turns waste into a resource, reducing landfill burden and greenhouse gas emissions.
Reduces Carbon Footprint Unlike fossil fuels, Bio-CNG emits almost zero net carbon dioxide, making it ideal for companies aiming to lower their carbon emissions.
Cost-Effective in the Long Run Though setup might require initial investment, the operational and fuel costs are significantly lower, especially if the company produces a steady stream of organic waste.
Government Incentives Governments are encouraging green fuel use by offering subsidies and tax benefits for businesses that source fuel from a certified bio gas plant.
How Bio-CNG Helps Achieve Carbon Neutrality
Carbon neutrality means balancing emitted carbon with an equivalent offset. Here’s how Bio-CNG helps:
● Closed Carbon Loop: The carbon dioxide emitted during Bio-CNG combustion is reabsorbed by the crops or organic sources that later become waste, creating a circular system.
● Displacement of Fossil Fuels: Replacing diesel or LPG with Bio-CNG cuts direct emissions from fossil fuels, which are otherwise non-renewable.
●️ Waste-to-Energy Efficiency: Businesses generating large volumes of organic waste can install or collaborate with a bio gas plant to turn that waste into usable energy, reducing methane release into the atmosphere.
Industries That Benefit the Most
● Food Processing Units — generate high organic waste.
● Transport Fleets — can convert vehicles to run on Bio-CNG.
● Hotels & Resorts — with food waste and heating/cooking requirements.
● Dairy & Agro-Based Businesses — already have the raw material needed for Bio-CNG production.
Challenges to Consider
● Infrastructure & Investment: Initial setup of a bio gas plant or Bio-CNG sourcing network requires capital and planning.
● Logistics: Transportation and storage of Bio-CNG need specialized equipment.
● Regulatory Compliance: Meeting environmental and safety standards is crucial.
However, these hurdles are quickly reducing with technological advances and rising demand.
Conclusion: A Step Towards a Greener Business Future
Switching to Bio-CNG is not just a fuel change — it’s a strategic move toward carbon neutrality, operational efficiency, and future-proofing your business against environmental regulations.
If your business generates organic waste or runs on heavy fuel consumption, integrating Bio-CNG into your energy mix can be a game-changer. By partnering with a reliable bio gas plant, you not only reduce your environmental impact but also join the global movement toward sustainability.
Final Thought: In a world driven by conscious consumption and green goals, Bio-CNG offers a practical, scalable, and impactful solution. The question isn’t if you should switch — it’s when.
0 notes
Text
Food Waste Recycling Machine Market Growth Fueled by Rising Environmental Awareness and Stringent Waste Management Policies
Introduction
The Food Waste Recycling Machine Market is experiencing substantial growth driven by heightened environmental awareness and increasingly stringent governmental policies on waste management. With global food waste contributing significantly to environmental degradation, the adoption of food waste recycling machines has become a pivotal solution for sustainable waste disposal. This article explores the factors propelling the market growth, the key technologies involved, and future outlooks.

Rising Environmental Awareness
Globally, environmental concerns such as climate change, pollution, and depletion of natural resources are prompting governments, organizations, and individuals to rethink waste management strategies. Food waste, which accounts for a significant portion of municipal solid waste, poses both environmental and economic challenges. When improperly disposed of, food waste emits methane, a potent greenhouse gas contributing to global warming.
In response, public awareness campaigns and sustainability initiatives have amplified the demand for eco-friendly waste management solutions. Recycling machines designed specifically for food waste allow for efficient on-site processing, reducing landfill use and turning waste into valuable by-products like compost and biogas.
Impact of Stringent Waste Management Policies
Regulatory frameworks worldwide have tightened, focusing on waste reduction, segregation, and recycling targets. Many countries have implemented bans on organic waste landfill disposal, mandatory waste segregation rules, and incentives for adopting green technologies.
For example, the European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan encourages member states to minimize food waste and invest in recycling technologies. Similarly, regions in North America and Asia are enacting policies that support the integration of food waste recycling machines in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
These policies drive investments in advanced recycling machines, fostering innovation and adoption across sectors. Government incentives such as subsidies, tax benefits, and grants further support market growth.
Technological Advancements in Food Waste Recycling Machines
Innovations in food waste recycling machines have enhanced efficiency, usability, and environmental impact. Modern machines utilize aerobic and anaerobic digestion, dehydration, and composting technologies to process food waste rapidly and hygienically.
Energy-efficient designs, compact models, and smart features like IoT integration for real-time monitoring and operation optimization have made these machines suitable for diverse environments—from large-scale industrial facilities to small households.
The development of hybrid systems combining multiple technologies also contributes to improved waste conversion rates and energy recovery, aligning with sustainable development goals.
Market Segmentation and Key Applications
The Food Waste Recycling Machine Market is segmented based on type, end-user, and geography.
By Type: Machines are broadly categorized into composters, dehydrators, digesters, and hybrid systems. Each offers unique benefits and suits different waste types and volumes.
By End-User: Key sectors include residential, commercial (restaurants, hotels, supermarkets), and industrial (food processing units, agricultural sectors). Commercial adoption is notably rising due to increasing waste volumes and regulatory pressures.
By Geography: North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific lead the market due to progressive regulations and awareness. Emerging economies are also witnessing growth as infrastructure improves.
Challenges and Market Resilience
Despite promising growth, the market faces challenges such as high initial costs, lack of consumer awareness in certain regions, and logistical constraints in waste segregation. However, continuous technological improvements and increasing environmental campaigns are mitigating these barriers.
Companies are focusing on cost-effective, user-friendly models to enhance market penetration. Educational initiatives and collaborations between public and private sectors are also playing vital roles in boosting adoption.
Future Outlook
The future of the Food Waste Recycling Machine Market looks promising, driven by the convergence of environmental imperatives and technological progress. Increasing global commitments to reduce carbon footprints and achieve sustainable development targets will sustain market momentum.
Emerging trends such as AI-driven waste sorting, blockchain for supply chain transparency, and integration with smart city initiatives are expected to revolutionize the market further. Additionally, rising investments in circular economy frameworks and waste-to-energy projects will create new growth avenues.
Conclusion
The Food Waste Recycling Machine Market's growth is intrinsically linked to the escalating environmental concerns and regulatory frameworks emphasizing sustainable waste management. As governments and industries continue to prioritize eco-friendly solutions, the demand for efficient food waste recycling machines is set to soar, fostering a greener and more sustainable future.
#FoodWasteRecyclingMachine#WasteManagement#EnvironmentalSustainability#RecyclingTechnology#GreenTechnology#WasteReduction#CircularEconomy#SustainableDevelopment#OrganicWaste#FoodWasteRecycling
0 notes
Text
Rainbow Trout Market Grows With Surge In Global Aquaculture Development And Investment
The rainbow trout market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness about healthy eating, rising demand for sustainable seafood, and the expanding aquaculture industry. Rainbow trout, a species native to North America, is now farmed worldwide due to its high adaptability and commercial value. With a growing global appetite for protein-rich, low-fat, and omega-3-rich food sources, rainbow trout has emerged as a favored choice for health-conscious consumers and food service industries alike.

Market Overview
Rainbow trout farming, primarily carried out in freshwater environments such as ponds, raceways, and tanks, is practiced extensively in countries like the United States, Chile, Iran, Norway, and the European Union. The aquaculture segment dominates the market share, thanks to technological advancements in breeding, feeding, and disease control. Wild catch, although still present, is significantly lower due to regulatory concerns and environmental sustainability measures.
The market has diversified with the production of fresh, frozen, smoked, and processed rainbow trout products. Fresh and chilled rainbow trout remain the most popular among consumers, accounting for the highest revenue segment. The retail sector, including supermarkets, hypermarkets, and online platforms, plays a key role in the distribution of rainbow trout, along with direct sales to restaurants and catering services.
Key Drivers
Several factors are propelling the rainbow trout market forward. First, increasing awareness of the health benefits of fish consumption is influencing consumer choices. Rainbow trout is rich in essential nutrients such as high-quality protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins B12 and D, making it a desirable option in a balanced diet. This trend aligns with the growing emphasis on healthy lifestyles and preventive healthcare.
Second, government initiatives and investments in aquaculture infrastructure and research have stimulated market expansion. Many countries now promote sustainable fish farming as a strategy to ensure food security and economic development. Supportive regulations, subsidies, and training programs for fish farmers have encouraged both small-scale and industrial players to invest in rainbow trout cultivation.
Third, the rise in demand for exotic and gourmet seafood products in emerging economies is opening new growth avenues. As middle-class populations grow and disposable incomes rise, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, the appetite for premium fish like rainbow trout has increased significantly.
Challenges in the Market
Despite promising growth, the rainbow trout market faces some challenges. Disease outbreaks, particularly in intensive aquaculture settings, can lead to significant losses. The use of antibiotics and chemicals to combat diseases has raised concerns about food safety and environmental impact. Regulatory scrutiny and the push for antibiotic-free aquaculture practices are forcing industry players to adopt improved biosecurity and disease management techniques.
Additionally, climate change poses a risk to aquaculture operations by altering water temperatures and increasing the frequency of extreme weather events. Trout farming is sensitive to water quality and temperature, and any significant shifts can affect yield and fish health.
Trade regulations, tariffs, and import-export restrictions also influence market dynamics. Producers and exporters must navigate varying food safety standards and certifications across countries, which can complicate international trade and limit market access.
Regional Insights
North America remains a major market for rainbow trout, driven by strong consumer demand and well-established aquaculture infrastructure. Europe is also a significant player, with countries like Italy, France, and the UK leading in trout production and consumption.
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, thanks to increased investments in aquaculture and a growing population base. In particular, China, India, and Iran are ramping up trout production capacities to meet both domestic and export demands.
Future Outlook
The future of the rainbow trout market looks optimistic, with technological innovations and sustainable practices shaping its development. The integration of recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS), automated feeding systems, and genetic improvements in trout breeds is expected to enhance productivity and sustainability.
In addition, consumer preferences are shifting toward traceable and responsibly sourced seafood. Certifications such as GlobalG.A.P. and ASC (Aquaculture Stewardship Council) are gaining traction, prompting producers to adopt ethical farming practices.
E-commerce and direct-to-consumer sales are also creating new opportunities for market expansion. Online platforms offering fresh and processed fish products with quick delivery are gaining popularity, especially in urban areas.
In summary, the rainbow trout market is thriving on the back of health trends, technological progress, and sustainable aquaculture practices. With ongoing innovations and expanding global demand, the market is poised for continued growth in the coming years.
0 notes
Text
Exposing the Widespread Cruelty of Factory Farming: A Comprehensive, Eye
Opening Investigation into Animal Suffering, Environmental Harm, and Public Health Risks
The Hidden Cruelty of Factory Farming: What “cruelty.farm/gu/” Reveals
Factory farms—also known as intensive or industrial animal production facilities—inflict profound suffering on animals, devastate ecosystems, and pose mounting risks to human health. The website cruelty.farm/gu/ (likely a Gujarati-language resource) exposes the full scale of these injustices—from cramped living conditions to environmental degradation. This article synthesizes the key themes and calls readers to reflect on the consequences of their food choices.
1. Severe Physical and Psychological Impact on Animals
Animals on factory farms endure extreme confinement. Chickens are packed into battery cages with barely room to move; pigs are crammed into gestation crates too small even to turn around; dairy cattle are confined for continuous milking; fish are crowded in aquaculture tanks with deteriorating conditions .
These setups cause chronic pain, respiratory illnesses, skeletal problems, infections, and high stress.
Behavioral issues—like feather pecking, bar-biting, or cannibalism—are common, manifestations of both psychological distress and physical dysfunction .
Fundamental needs—grazing, exploration, maternal bonding—are denied, turning living beings into production units instead of sentient creatures.
2. Routine Mutilations and Mechanical Interventions
To manage crowded conditions and curb natural behaviors, farms commonly perform painful procedures without anesthesia. These include tail docking and ear notching in pigs, debeaking of chickens, mulesing of sheep, and other mutilations .
These actions often serve purely production-centric ends—not welfare.
3. Cruel Slaughter, Transport, and Health Risks
Transport to slaughterhouses adds more suffering. Animals may travel long distances without food, water, or rest; many arrive weakened or injured . The slaughter processes themselves—if not strictly regulated—can be rough and frightening. Combined with overcrowding, poor hygiene, and chemical use, the result is a heightened risk of disease outbreaks, including zoonotic infections, E. coli, Salmonella, and antibiotic-resistant bacteria
4. Environmental Toll of Intensive Farming
Factory farming isn’t only cruel—it’s ecologically disastrous. Large volumes of animal waste contaminate soil and waterways, contributing to algal blooms and dead zones; methane emitted by livestock, especially cattle, is a powerful greenhouse gas; clearing land for feed crops fuels deforestation and biodiversity loss; pesticide and fertilizer runoff further erodes ecosystems
5. Public Health and Human Consequences
For farm workers, conditions include exposure to harmful gases like ammonia and hydrogen sulfide, long hours, low wages, and psychological stress .
The environmental fallout—polluted water and air—also impacts nearby communities, raising rates of respiratory diseases and gastrointestinal illnesses
The widespread use of antibiotics to prevent disease in overcrowded animals is accelerating the rise of drug-resistant bacteria—an urgent global health crisis
6. Economic Pressures and Market Dynamics
Factory farms thrive on economies of scale, producing cheap food by externalizing costs—welfare, health, and environmental damages ignored. Subsidies, lax regulations, and weak labeling enable this system to persist. Meanwhile, small farmers struggle to compete, further consolidating agribusiness control
Labels like "free-range" or "organic" may offer better welfare—but are sometimes misleading or inconsistently regulated
Awareness about the horrors of factory farming has driven many to reevaluate dietary and purchasing habits. Movements promoting vegan, vegetarian, or reduced-meat diets are gaining traction .
Choosing plant-based foods, supporting small farmers dedicated to humane and sustainable practices, or advocating for policy reform are all impactful actions.
Conclusion: A Call to Ethical Responsibility
The data on cruelty.farm/gu/ offers a striking portrait of the industry’s brutality. Animals are robbed of dignity; ecosystems suffer; human health is compromised. Yet consumers hold transformative power. By opting for plant-based meals, demanding transparent welfare standards, and supporting sustainable farmers, individuals can help dismantle a harmful system.
Every meal is a moral choice. As public awareness grows, so does the potential for reform. Moving toward compassion isn’t just about individual ethics—it’s a pathway to healing animals, communities, and the planet.
0 notes
Text
How to Create a Strong Project Report for a Loan Application in 2025
In 2025, obtaining financial support for a new or existing business—whether through traditional banking channels or government-backed schemes like PMEGP, CMEGP, or Mudra—requires one crucial document: a Project Report. A well-structured and comprehensive Project Report for a Loan is the foundation of a successful loan application. It reflects the business potential, financial planning, and repayment capacity of the applicant.

Project Report for Bank Loan, including insights for PMEGP Project Report, CMEGP Project Report, Mudra Loan Project Report, and how to structure both a Detailed Project Report for Bank Loan and a Feasibility Project Report.
What is a Project Report?
A Project Report is a structured business document that outlines the objectives, operations, market analysis, funding requirements, and financial projections of a proposed business or an existing one seeking expansion. This report is necessary whether you are applying for a Bank Loan, PMEGP, CMEGP, or a Mudra Loan.
The Project Report for the Loan demonstrates the practicality of the business idea and includes both qualitative and quantitative data. It is also used as a base document to prepare a Feasibility Report or a Feasibility Project Report.
Importance of a Project Report for a Bank Loan
A Project Report for Bank Loan is the primary document reviewed by banks and financial institutions to judge the viability and risk of the proposal. It includes:
Projected revenues and profits
Required loan amount
Usage of loan funds
Business sustainability
Repayment capability
Without a strong Detailed Project Report, loan sanction becomes difficult. This is especially true for schemes like the PMEGP Project Report (for rural and unemployed entrepreneurs), the CMEGP Project Report (a state-level subsidy scheme), and the Mudra Loan Project Report (for micro and small enterprises).
Key Sections in a Detailed Project Report for Bank Loan
When creating a Detailed Project Report for a Bank Loan or a Feasibility Project Report, the following components must be included:
1. Executive Summary
An overview of the business, highlighting the key features of the proposal and loan requirements. This section sets the tone for the entire Project Report.
2. Promoter Profile
Details about the business owner(s), their qualifications, experience, and management capabilities. A solid profile adds credibility to any PMEGP Project Report, CMEGP Project Report, or Mudra Loan Project Report.
3. Business Overview
Detailed description of the business model, services or products offered, and their USP. A must-have for any type of Project Report for a Loan.
4. Market Analysis
Include industry trends, customer segmentation, competition, pricing strategy, and market potential. This helps in building a convincing Feasibility Report.
5. Technical and Operational Plan
Outline of infrastructure, location, machinery, manpower, and production process. This is crucial for preparing a Detailed Project Report for sectors such as manufacturing, food processing, or textiles.
6. Financial Projections
This is the most critical part of any Project Report for a Bank Loan:
Estimated cost of the project
Funding requirements and means of finance
5-year projections of Balance Sheet, P&L, and Cash Flow
Break-even analysis
Loan repayment schedule
These details are essential in the Mudra Loan Project Report, PMEGP Project Report, and Feasibility Project Report formats.
Differences Between Project Report and Feasibility Report
A Project Report gives an overall plan and roadmap of your business.
A Feasibility Report or Feasibility Project Report specifically focuses on whether the business idea is practical and financially sound.
Banks often require both, especially when evaluating larger loans under schemes like the Detailed Project Report for Bank Loan for new industrial units.
Tips to Prepare a Strong Project Report for a Loan
Customize for the Loan Type Each scheme (e.g., PMEGP, CMEGP, Mudra) has unique requirements. Tailor the Project Report accordingly.
Use Realistic Data Don’t overestimate profits or underestimate costs. Your Feasibility Report must look practical.
Include Government Scheme Benefits In your PMEGP Project Report or CMEGP Project Report, mention subsidy amounts, contribution percentage, and implementing agencies like KVIC or DIC.
Consult Financial Experts Use Chartered Accountants or certified consultants to prepare a compliant Detailed Project Report.
Follow the Latest Guidelines In 2025, financial institutions will be more stringent. Update your Project Report for Bank Loan as per RBI and scheme-specific changes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Using generic templates for every loan type
Ignoring scheme-specific details in the PMEGP Project Report or the Mudra Loan Project Report
Incomplete financial projections
Missing the Feasibility Report altogether
Submitting outdated formats not accepted by banks or implementing agencies
Conclusion
A well-drafted Project Report for a Loan in 2025 is more than just a formal requirement—it’s the key to unlocking credit for your business. Whether you’re preparing a PMEGP Project Report, CMEGP Project Report, Mudra Loan Project Report, or a Detailed Project Report for Bank Loan, ensure it is realistic, data-backed, and aligned with the scheme or lender's expectations.
Remember, a solid Feasibility Project Report or Feasibility Report adds weight and professionalism to your application, helping you stand out in a competitive funding environment.For additional information or assistance, please contact us at +91-8989977769.
0 notes
Text
Biogas Plants in Kerala: Powering the State Towards a Sustainable Future

Kerala, known for its ecological richness and progressive environmental policies, is taking major strides in sustainable energy. One of the key innovations leading this change is the growing adoption of biogas plants in Kerala, which are helping manage organic waste while producing clean, renewable energy for homes, farms, and institutions.
What Are Biogas Plants?
Biogas plants convert organic waste — like food scraps, agricultural residue, and animal manure — into usable energy through anaerobic digestion. The process produces methane gas (used as fuel) and slurry (used as organic fertilizer), making it a win-win for waste management and energy needs.
Why Biogas Plants Matter in Kerala
Waste Management Solution: With high levels of household and agricultural waste, biogas plants in Kerala offer an eco-friendly way to manage it.
Renewable Energy Generation: The methane-rich gas generated is used for cooking, electricity, and even heating water, reducing reliance on LPG and grid electricity.
Government Support: Kerala’s local bodies and agencies offer financial subsidies and technical assistance to promote biogas adoption.
Sustainability Drive: With rising climate concerns, biogas offers a clean, decentralized energy source aligned with Kerala’s green initiatives.
Types of Biogas Plants in Kerala
Household Biogas Plants: Ideal for urban and rural homes, using kitchen and garden waste.
Institutional Biogas Plants: Installed in schools, hospitals, and religious places for large-scale waste conversion.
Portable Biogas Units: Compact and mobile, suitable for smaller spaces and quick installations.
Community Biogas Plants: Managed by panchayats or NGOs to serve entire neighborhoods or markets.
Benefits of Biogas Adoption in Kerala
Reduces methane emissions and landfill use
Promotes organic farming with high-quality bio-slurry
Reduces monthly fuel expenses
Creates rural employment and self-sufficiency
Strengthens Kerala’s climate-resilient infrastructure
Popular Regions Promoting Biogas in Kerala
Districts like Thrissur, Palakkad, Ernakulam, and Kozhikode are at the forefront of this green energy revolution, with thousands of functioning biogas plants installed through government and private efforts.
Final Thoughts
With rising environmental consciousness and the push for self-sustaining energy solutions, biogas plants in Kerala are becoming an essential part of the state’s green infrastructure. Whether you’re a homeowner, a farmer, or an institution, investing in a biogas plant is a step towards cleaner energy and a healthier planet.
#biogas in kerala#biogas plant for home#incinerator manufacturers in kerala#biogas#kerala#portable biogas plant for home#incinerators in kerala
0 notes