#How to become a node operator on eth
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How to Become a node operator on ETH
Do you want to learn more about How to Become a node operator on ETH? Ethereum, one of the most well-known blockchain networks, needs node operators to operate and maintain the network's security, consistency, and openness. You can contribute to the decentralised infrastructure of the network and get paid for your labour by running an Ethereum node.
Everything you need to know to become an Ethereum validator is covered in this blog post, including what an Ethereum node is, how to put one up, how to start staking, and the expenses and obligations of running a node.
What is an Ethereum Node?
Let's start by learning how to operate an ETH node. First, you need to understand the fundamentals. For example, what does "Ethereum node" mean? It refers to any device that has the software required to connect to the Ethereum network, such as a computer. These nodes communicate with one another in order to verify transactions, exchange information, and store data about the blockchain's current state.
Although the phrases are sometimes used interchangeably, these connected computers are the nodes, and the software they run is the client.
How to run an Ethereum Node?
Let's proceed to the next stage of learning how to operate an ETH node. Here is a list of choices for configuring your Ethereum node in various ways, depending on your preferences.
Plug and play remedies
The top two plug-and-play ETH validator solutions are DAppNode and Avado Cloud. They are well-liked since they are appropriate for non-technical users and beginners. Keep in mind that we must choose the appropriate software if we want to learn how to run an Ethereum node.
Solution for DAppNode:
DAppNode offers low-cost hardware and software options so that anyone may easily run blockchain nodes.
How to start staking on Ethereum Node?
You can start staking your Ethereum once you understand how to operate a node on the Ethereum network. Through your node, you can do it. Ethereum advises spending money on cutting-edge gear. Ethereum wallets like MetaMask and MyEtherWallet are available for use.
And after your Ethereum node has successfully been set up and is operating, you may begin staking ETH by linking your wallet to your node. simply operating your validator and receiving payment in return, you can assign your ETH to the staking pool. And that is precisely how ETH is staked.
Responsibilities of a node operator You must be aware of the fact that validators are used for staking in Proof of Stake [PoS] when you understand how to operate an ETH node. On the Execution Layer [of the Ethereum blockchain], 32 ETH have been deposited to a single Beacon Chain address, which serves as each validator.
This is accomplished by keeping an ear out for transactions and fresh block proposals, then certifying the proposed block as containing only legitimate and lawful transactions. In contrast to the Proof of Work [PoW] scheme, validators are assigned both the attestations and the block proposals on a random scheduling basis.
0 notes
Text
Blockchain: what it is, how it works and the most common uses
What is blockchain?
It literally means blockchain is a database or public registry that can be shared by a multitude of users in peer-to-peer mode (P2P or peer network) and that allows the storage of information in an immutable and organized way.
It is a term associated with cryptocurrencies because, apart from being the technology that supports them, it was born with the first virtual currency in history in 2009, Bitcoin . In this case, the data added to the blockchain is public and can be consulted at any time by network users.
However, it is important to remember that cryptocurrencies are just that, currencies! Just as happens with the euro, the dollar or any type of paper money. Each one is a simple material with a printed value, but what allows its use and generates value are the economic laws that support them.
Something similar happens with virtual currencies. In this case, it is blockchain technology that allows it to function. Its main objective is to create an unchangeable record of everything that happens in the blockchain, which is why we are talking about a secure and transparent system.
Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH) or any other cryptocurrency is simply a virtual currency built on the blockchain and used to send or receive the amount of money that each participant has. This technology is what keeps transactions publicly recorded, but keeping the identity of the participants anonymous.
However, although it was created to store the history of Bitcoin operations, over the years it has identified great potential to be applied in other areas and sectors due to the possibilities it offers.
Features of blockchain technology
The progress of this system has been a mystery since its origin, but little by little we are learning more details about its operation:
Security
Cryptography is a fundamental pillar in the operation of the blockchain application development company, which provides security for the data stored in the system, as well as the information shared between the nodes of the network. When we are going to make a transaction, we need a set of valid asymmetric keys to be able to carry it out on the blockchain. It is also known as public key cryptography.
Trust
By representing a shared record of facts, this technology generates trust in users. Not only that, but it eliminates the possibility of manipulation by hackers and generates a ledger of operations that all members of the network can access.
Immutability
When information is added to the distributed database, it is virtually impossible to modify it. Thanks to asymmetric cryptography and hash functions, a distributed ledger can be implemented that guarantees security. In addition, it allows consensus on data integrity to be reached among network participants without having to resort to an entity that centralizes the information.
Transparency
It is one of the basic requirements to generate trust. Transparency in blockchain consulting services is attained by making the chain's software code publicly available and by fostering a network of nodes that use it. Its application in different activities, such as supply chains, allows product traceability from origin.
Traceability
It allows knowledge of all operations carried out, as well as the review of transactions made at a specific time. Traceability is a procedure that allows us to follow the evolution of a product in each of its stages, as well as who, how, when and where it has been intervened on. This is one of the main reasons why many sectors are beginning to apply blockchain technology.
3 keys to understanding how the blockchain works
It will only take you a single step to become an expert on the blockchain consulting services. Now that you know its definition and the main characteristics and related terms, it is time to put everything you have learned together to discover how it works. Take note!
The jack, horse, king of transactions
Networks use peer-to-peer data exchange technology to connect different users who share information. That is, the data is not centralized in a central system, but shared by all users of the network. At the moment a transaction is made, it is recorded as a block of data transmitted to all parties with the objective of being validated.
The transaction is the movement of an asset and the block can record the information of your choice, from what, who, when, to where, how much and how. Like an irreversible record, each block joins the preceding and following ones to form a chain (blockchain). Every new block removes the chance of manipulation and strengthens the previous one's verification. Finally, the transaction is completed.
The structure of the blocks
The chain stores a lot of information, which allows it to grow over time. This is the reason why it has been necessary to create efficient query mechanisms without having to download all the information: the Merkle hash tree.
It is a tree data structure that allows a large number of separate data to be related to a single hash value, providing a very efficient method of verifying the contents of large information structures.
Generation of chain blocks
First of all, it is a decentralized process. And to do this, a distributed consensus is needed in which the nodes have the ability to generate valid data. In order for users to initiate new operations, they must turn into nodes within the system. If what they want is to become miners and create blocks, then they must compete with others. The validation process is based on asymmetric cryptography, with a public key and a private key. The issued transactions are validated by the nodes in the new mined block, as well as their correct linking to the previous block (it must contain the hash).
The most common uses of blockchain
“But this technology was created for cryptocurrency operations.”
That's right, but the passage of time, research and social needs have seen great potential in this technology to be applied in other areas:
Voting systems
Some states such as West Virginia are implementing electronic voting through blockchain, although it is still a framework to be regulated. But that's not necessary to go that far. After the last elections to the Madrid Assembly, as well as the COVID-19 pandemic situation and its restrictions on mobility and the gathering of people, they have proposed the establishment of electronic voting with blockchain.It is an extremely appealing voting system because of its traceability and immutability.Not only would it increase transparency and reliability, but you could audit in real time.
Smart Contracts
They are programs that allow you to fulfill and execute registered agreements between the parties automatically. They can be applied in any type of transaction where a registered agreement is necessary, such as a security deposit or the contracting of a product, among others. Among its main characteristics we find: self-execution and immutability.
Supply chain
Supervision and monitoring in food chains, as well as in production, is one of the main applications proposed with blockchain. Some examples of this technology in the food and agricultural industry are: Walmart China, with food production constituted by IBM; or the Australian AgriDigital, which works with distributed ledgers, blockchain and Smart Contracts.
It is not what has already been done, but what is yet to come. At Occam Agencia Digital , as a blockchain development company, we are convinced that it is not just about programming, but about analyzing the client's needs and designing a unique user experience.
What are some ways that your business can benefit from blockchain technology? Tell us your questions, we can help you solve them.
Tokenization of real estate and assets
Thanks to the transparency of the blockchain, the tokenization of assets is revolutionizing traditional sectors such as real estate investment, democratizing their purchase.
This breaks the barrier to investing in safer assets, since, until now, if you wanted to buy a property, you had to do it alone or among a very small group of people. Thanks to tokenization, now you can buy an apartment between 100, 200, 1000 people by making a small contribution.
This also allows you to diversify and minimize risk, being able to invest €100 in several properties.
It is very important to choose a blockchain development company that has developed a project using this technology, since these are complex developments with very little documentation on the internet to help developers.
How to do good blockchain development?
We invite you to take note of the steps necessary for the development of the blockchain:
The first thing to do is a briefing between both parties . The client provides the information on the business model, and the blockchain development company offers the expertise to design the platform using the most optimal technology.
It is very important to choose the technologies to be used, since in blockchain each transaction has a cost. Depending on the blockchain chosen, it can cost between €10 or €0.0001 each.
It is imperative that the blockchain development company determines which components of the platform need to function in order to have a well-balanced security, user experience, and cost per use system that is suitable and tailored to the client's suggested business model.
For example, if you want to develop a platform to tokenize real estate so that investors can buy tokens from these, the most recommended thing is that all the functionality related to the purchase or investment is developed on blockchain technology, and the rest of the functionalities are developed using the traditional way. In this way, you will achieve a good user experience, great security in purchases and low costs.
Once the briefing is finished, we move on to the design phase . With the briefing in hand, it's time for the UX and UI experts to get to work. With the information collected, you must design a platform with a great user experience and a friendly interface to convey confidence to the user and allow them to operate very easily. You'll be able to stay on the platform and avoid getting frustrated or giving up.
#blockchain#blockchain development#blockchain technology#blockchain development company#private blockchain development
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blockchain Infrastructure Explained: A Strategic View from Layer 0 to Layer 3

The blockchain is no longer solely associated with cryptocurrency. It now supports DeFi (decentralized finance), advancements in supply chains, frameworks for digital identification, and even the national digital currency of some countries. For companies operating within the UAE, where the government has taken the lead in fostering digitization and blockchain innovation, grasping the multi-layered blockchain infrastructure is far deeper than a mere technical endeavor—it’s a matter of business strategy.
We’ll look into each layer from 0 to 3 and we’ll cover everything from how each one functions to its importance for enterprises and developers, as well as how blockchain development services offered in UAE can position you ahead of competition in this emerging domain.
Why Understanding Different Blockchain Layers Is Important?
Now that we understand what will be tackled in this session, let's evaluate why this systematization makes sense. Think of blockchain infrastructure as a highway:
Layer 0 refers to ground and wiring— Serves as an underlying support for communications alongside interoperability.
Layer 1 refers to the road— The core activity zone where traffic movement happens.
Layer 2 is express lane construction: Aimed at boosting traffic scale along with speed.
Layer 3 equates vehicles users interact with on blockchain applications.
For businesses looking to take advantage of blockchain technology, having an understanding of this architecture provides help in decision making regarding investments, development strategy and approaches, scalability requirements, overall user experience, and more.
Layer 0: The Starting Point of the Blockchain Ecosystem
Layer 0 may be omitted from conversations about Blockchains but it is an important layer. It allows for inter-chain communication as well as protocol standardization and network interoperability. In less technical terms, different blockchains can communicate because of Layer 0.
What Comprises Layer 0?
Networking protocols - This includes enabling transfer of data between nodes (Computers).
Consensus mechanisms – Coordinates the validation processes for each node.
Interoperability frameworks – Polkadot and Cosmos are examples which integrate multiple layer 1 blockchains.
Validator infrastructure – Simplistically put, manages security and the operation of base chains.
Strategically Relevant Importance in the UAE
Interoperability is critical especially with the UAE’s delta aim to become a global center for blockchain technologies. Enterprise and Government use cases often require cross-platform integration for public service systems, financial systems or even logistics services domestically within or cross regionally into other adjacent countries. With professional blockchain development services based in the UAE that understand your ecosystem needs beyond silos leverage solutions built on zero layers technology.
Use Cases
Polkadot lets several blockchains known as parachains operate simultaneously while inter-communicating with each other.
Cosmos through its IBC Inter Blockchain Communication protocol makes possible the Internet of Blockchains.
Layer 1: The Base Protocol Layer
Decentralization starts with Layer 1 and covers the entire Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana ecosystem among others. Slice it any way you want from tribalism to retail therapy, The magic decentralization gives birth to real whitelists on platforms such as bitcoin.
Core Functions of Layer 1
Transaction finality
Consensus and security
Native tokens ( e.g.. ETH, SOL,_LT)
Settle smart contracts.
self-sufficient ethereum is quite powerful but has always suffered from gas fee and congestion problems.
UAE’s Adoption Outlook
Supporting layer one for L1 users as backbone is powerful for UAE production levels and goal cores; however there are governmental testbeds based on identity tokenized payments employment systems that still require an exemplified proof skipping a legal naming barrier pondered in claim-sufficient mechanisms.
Choosing The Right Layer 1 Platform
Bounded waiting means being confined within a time limit. Every bounding areas allotted certain tasks for system verification require incrementation of accuracy for proving results that need precision under specified conditions which guaranteed attempts towards automation assist severely allocated outlined goals accessibility terms different configurational operational niches sought alter freely direct distance confirmed rounded ensure limits existing shifted frameworks pertain granting outside needs unbounded purposes but highly difficult permissible narrowing supporting needs fulfilling grace.
Layer 2: Scaling and Enhancing Layer 1
Building upon layer 1, layer 2 aims to improve the previously established frameworks. These protocols take an off-chain or sideline approach whereby they manage transactions through off-chain processing first, which temporarily lightens the load on the base chain, before settling back onto layer one.
Why Layer 2 Exists
To reduce gas fees
To increase transaction throughput
To improve user experience
Getting rid of undersized constraints makes layered blockchain systems accessible to mainstream platforms and applications. Imagine payments happening in real-time, users accessing services at scale with tangible fee reductions!
Common Layer 2 Technologies
Rollups (Optimistic and ZK-Rollups) – Merge several transactions into one single entry.
Plasma – Generates child chains for expedited transaction processing.
State Channels – Enable potential users to transact off-functionality and only submit the end state on main block after finalization of all activities.
UAE Perspective on Layer 2
Abu Dhabi and Dubai's fintech fusion with smart city initiatives orienting around blockchain gives a whole new meaning to scalability dynamics. For example, consider a real estate platform managing hundreds of tokenized assets that merge together or a DeFi application servicing thousands of daily interactions from users – both would rely on well-structured layer two integrations for performance efficiency!
Working with local blockchain developers ensures compliance to layering strategies offer seamless regulations alignment based on user habits and behavior flows tailored towards locals
Section 3: The Application Layer.
Third layer is the interaction with the end user which happens through decentralized applications, wallets, DAO institutions, Web 3.0 frontends, as well as NFT Levels and markets.
Examples of Third Layer Interaction
DeFi systems such as Uniswap and Aave
OpenSea for NFT trading
Identity services that are decentralized
Across border transaction systems (sending emails/ money without borders)
These applications are vulnerable to layer 1 and layer 2 performance when it comes to providing security and efficiency.
Importance To The Economy In UAE
With innovation happening across finance, logistics, tourism, governance frameworks, integrated intuitive applications based on blockchain technology are in high demand. Testing dApps for health certificates, digital notaries, west-ward facing visa platforms has been conducted by the UAE government.
Establishments focusing on these sectors need deeply researched smart contracts developed alongside user friendly interfaces so attractive UI/UX design can act as a window for a strong backend system. Providing blockchain development services in UAE complements perfectly within these two frames of cutting-edge protocols with blockchain based seamless user interface experiences.
The relation between the layers: All together now!
You should think of technology in “layers” that build upon one another…but do remember they explain everything using silos.
A L3 NFT marketplace might depend on some rollup at L2 to save gas fees and some L0 protocol which allows transfer of assets from one chain to another seamlessly. Whatever their final solution is for any blockchain problem; think about all layers executing flawlessly together to achieve success.For SMEs or startups in the UAE, the approach hinges on selecting and tailoring a combination of layers that accentuate your use case, budgetary limitations as well as compliance scope.
Key Questions When Selecting Blockchain Infrastructure
To align your business objectives with your blockchain strategy, consider these framing queries:
Security: What layers are allocated for security? Are the validators or miners sufficiently distributed?
Scalability: Is there an allowance for growth in users and transactions within the infrastructure?
Interoperability: Will your solution need cross-chain or multi-platform functionality?
Cost: Are costs relating to transactions and development within predetermined limits, controllable, and modest in nature?
Regulatory Fit: Do the applied protocols and solutions observe compliance with laws governing the UAE?
A local service provider would help you integrate international standards with local regulatory insights enabling blockchain development services in UAE meeting these concerns locally.
In Conclusion: It all Starts with The Stack when Strategically Adopting Blockchains.
The question is no longer whether to go with Ethereum or Bitcoin; it has now morphed to understanding the tech stack comprising Layer 0 to Layer 3 alongside your business goals. Whether it is creating a new fintech product, representing real-world assets with tokens, or developing a self-sovereign identity; such systems are scalable, secure, and designed for future innovations.
The UAE continues to fortify its stance as the foremost adopter and innovator of blockchain technology in the region. This is an opportunity to take action.
With over 9538 companies adopting blockchain technologies in these areas, it won’t be an exaggeration to refer to Dubai and UAE as ME’s hub for digital innovations. Trusting any other country’s infrastructure would give rise to malleability of anything and everything which is a problem that all other countries are facing. So it makes sense why many entrepreneurs are moving towards Blockchain Development Services Dubai. Looking for partnered solutions in TaaS? We have partnered with one of the most leading Blockchain development Services in UAE. With them, you can construct your visions from scratch ranging from base architecture all through cutting edge dApps.
0 notes
Text
Smart Contracts 101: The Engine Powering Decentralized Innovation
In recent years, the term smart contract has become a buzzword in the world of blockchain and decentralized technologies. From automating financial transactions to managing supply chains and creating decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), smart contracts have opened up a world of possibilities. But what exactly are smart contracts, and why are they such a revolutionary innovation?

This blog post delves deep into the world of smart contracts—explaining what they are, how they work, their benefits and limitations, and real-world use cases.
What is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Unlike traditional contracts that require manual enforcement through legal systems, smart contracts run automatically when predefined conditions are met.
These contracts live on the blockchain, making them immutable (cannot be changed once deployed) and distributed (not controlled by a single entity). The most popular platform for creating smart contracts is Ethereum, but many other blockchains like Solana, Polkadot, and Binance Smart Chain support them too.
Key Characteristics:
Autonomy: Executes automatically without human intervention.
Trustless: No need to trust a third party—code governs behavior.
Immutable: Once deployed, the contract code can’t be altered.
Transparent: All transactions and contract code are visible on the blockchain.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
Smart contracts operate based on simple if-then logic. They execute actions when specific conditions are met.
Here’s a basic example:
IF Alice sends 1 ETH to Bob THEN transfer ownership of digital artwork from Bob to Alice
When Alice initiates the contract, the blockchain verifies the transaction. If everything checks out, the smart contract executes the transfer. This removes the need for intermediaries like lawyers or escrow services.
Programming Languages Used:
Solidity: The most widely-used language for Ethereum smart contracts.
Vyper: A Python-like alternative to Solidity.
Rust: Used on blockchains like Solana and NEAR.
Move: Created for blockchains like Aptos and Sui.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts offer several key advantages over traditional contracts and systems:
1. Efficiency & Speed
Traditional contracts often require intermediaries and time-consuming paperwork. Smart contracts execute transactions almost instantly once conditions are met.
2. Cost-Effective
By eliminating middlemen (e.g., lawyers, brokers, escrow agents), smart contracts reduce transaction costs significantly.
3. Transparency
Because they operate on public blockchains, anyone can audit smart contract logic and transaction history. This promotes accountability.
4. Security
Smart contracts are encrypted and distributed across nodes, making them highly secure and tamper-proof.
5. Trustless Transactions
Parties don’t need to know or trust each other. They only need to trust the code, which will execute as written.
Limitations and Risks
Despite their promise, smart contracts are not without issues. Some of the key limitations include:
1. Coding Bugs
Since smart contracts are immutable, any coding error is permanent unless a workaround or patching mechanism is included. The infamous DAO hack in 2016 resulted in the loss of over $60 million worth of Ether due to a vulnerability in the contract code.
2. Legal Ambiguity
In most jurisdictions, smart contracts are not yet legally recognized. This could create complications in dispute resolution and enforcement.
3. Complexity
Creating robust, secure smart contracts requires specialized programming skills. Mistakes can be costly and difficult to fix.
4. Scalability
Blockchains like Ethereum face scalability issues, leading to slow transaction speeds and high fees during periods of high network congestion.
5. Oracle Problem
Smart contracts need reliable external data (like price feeds, weather info, etc.) to function in many use cases. This requires oracles, which can become single points of failure or attack.
Real-World Use Cases of Smart Contracts
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Smart contracts form the backbone of the DeFi ecosystem. Platforms like Uniswap, Aave, and Compound use smart contracts to offer services like lending, borrowing, and trading without centralized intermediaries.
2. Tokenization and NFTs
Smart contracts enable the creation and transfer of digital assets, including fungible tokens (like ERC-20) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs like ERC-721). Artists, musicians, and game developers use them to prove ownership and authenticity.
3. Supply Chain Management
Smart contracts can automate logistics by tracking goods, verifying origin, and releasing payments based on delivery confirmations. Companies like IBM and Walmart are experimenting with blockchain for supply chain efficiency.
4. Insurance
Parametric insurance uses smart contracts to issue payouts automatically based on data triggers. For example, flight delay insurance can pay out immediately if a delay is confirmed via an oracle.
5. Real Estate
Real estate deals can be automated with smart contracts. Title transfers, escrow, and rental agreements can be executed without human intermediaries, reducing time and legal costs.
6. Voting Systems
Blockchain-based voting using smart contracts can enhance transparency, reduce fraud, and improve voter participation. Each vote is recorded immutably and publicly.
Smart Contract Platforms
While Ethereum is the pioneer, several other blockchains have developed their own ecosystems:
Ethereum
Language: Solidity
Network: Proof of Stake (since The Merge)
Pros: Most established, large developer community, extensive tooling
Cons: High gas fees, congestion
Binance Smart Chain (BSC)
Compatible with Ethereum
Fast and low-cost transactions
Centralized validator model raises concerns
Solana
High throughput and low fees
Uses Rust for smart contract development
Experienced some outages and centralization issues
Cardano
Uses Plutus for smart contracts (based on Haskell)
Focus on academic research and formal verification
Avalanche, Polygon, NEAR, Tezos, Algorand
All offer unique benefits in scalability, speed, and ease of development
Future of Smart Contracts
The potential for smart contracts is immense, and several trends are shaping their future:
1. Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
Technologies like Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups are making smart contracts more scalable by handling transactions off-chain while maintaining security.
2. Interoperability
Protocols like Polkadot, Cosmos, and Chainlink’s CCIP aim to connect different blockchains, allowing smart contracts to interact across networks.
3. Formal Verification
As contracts become more complex, formal verification methods (proving correctness using mathematical models) are being used to prevent bugs and vulnerabilities.
4. Regulatory Evolution
Governments are beginning to explore frameworks to recognize and regulate smart contracts, especially in areas like digital identity and finance.
5. Integration with AI and IoT
Smart contracts combined with AI and IoT devices can lead to powerful automation systems—like self-driving cars that pay for fuel automatically or smart factories that manage supply chains in real time.
Best Practices for Writing Smart Contracts
If you're a developer or planning to use smart contracts, here are some tips:
Audit Thoroughly: Use automated tools and third-party audits.
Keep It Simple: Complex logic increases risk of bugs.
Test Extensively: Use testnets and simulate real-world conditions.
Use Libraries: Trusted libraries like OpenZeppelin offer battle-tested code.
Plan for Upgradability: Consider proxy patterns or modular designs.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are redefining how agreements are made and executed in the digital age. By eliminating middlemen, reducing costs, and increasing transparency, they open the door to more efficient, democratic, and decentralized systems.
However, as with any powerful tool, they come with responsibilities and risks. As the ecosystem matures—with better tooling, scalability, and regulation—smart contracts could become a fundamental pillar of not just Web3, but the broader internet economy.
Whether you’re a developer, entrepreneur, or simply a tech enthusiast, understanding smart contracts is key to grasping the future of digital transactions and automation.
0 notes
Text
Sure, here is an article based on your request:
Ethereum Validators - paladinmining.com
Ethereum validators play a crucial role in securing the Ethereum network by participating in the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. This transition from proof-of-work (PoW) to PoS has brought new opportunities for validators.
If you are interested in becoming an Ethereum validator, it's important to understand the requirements and responsibilities involved.
Requirements for Ethereum Validators
To become an Ethereum validator, you need to stake at least 32 ETH. This staked ETH serves as collateral to ensure that validators act honestly and follow the rules of the network. If a validator behaves maliciously or offline for extended periods, they risk losing part or all of their staked ETH.
Responsibilities of Ethereum Validators
As an Ethereum validator, your primary responsibility is to propose and attest to blocks. This involves running a validator node and maintaining it online and operational. You must also ensure that your node is properly configured and updated with the latest software.
Benefits of Being an Ethereum Validator
Becoming an Ethereum validator can be financially rewarding. Validators earn rewards for proposing and attesting to valid blocks. These rewards are distributed proportionally based on the amount of ETH staked. Additionally, validators contribute to the security and decentralization of the Ethereum network, which is a significant contribution to the blockchain community.
Getting Started with Ethereum Validation
If you're interested in becoming an Ethereum validator, there are several resources available to help you get started. One such resource is Paladin Mining, which offers comprehensive support for Ethereum validators. Visit https://paladinmining.com to learn more about their services and how they can assist you in setting up and managing your validator node.
Conclusion
Ethereum validators are essential for the smooth operation of the Ethereum network. By staking ETH and participating in the consensus process, validators help secure the network and earn rewards for their contributions. If you're considering becoming an Ethereum validator, make sure to thoroughly research the requirements and responsibilities involved. Resources like Paladin Mining can provide valuable guidance and support throughout the process.
This article includes the specified keywords and the URL as requested.
加飞机@yuantou2048

paladinmining
Paladin Mining
0 notes
Text
What role does blockchain play in ICO fundraising?
in this article about What role does blockchain play in ICO fundraising by BlockchainX

Overview of ICOs
ICO represents a fundraising strategy which companies and blockchain-based projects use to get funding through dealing tokens to investors who exchange their Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum (ETH). The tokens available during an ICO can function as project shares or grant service access to holders while also enabling exchange functionality. Startups find ICO platform development attractive since they enable blockchain project funding without dependent bank loans or traditional venture capital.
The ICO process generally involves:
Whitepaper
Token Sale
Token Distribution
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology delivers a decentralized distributed ledger system which registers transactions across multiple computers using a mechanism that prevents retroactive alterations to registered data unless all subsequent blocks agree and change their states. The decentralized system requires this solution to deliver complete transparency alongside security features and unaltered ledger records that support a decentralized financial system.
Key features of blockchain include:
Decentralization: The blockchain exists without any central authority since it relies on nodes (computers) which uphold the network.
Transparency: Blockchain permits full transaction visibility to each member who belongs to the system network.
Security: The combination of encryption with consensus methods such as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake provides blockchain with security measures. transactions are secure and tamper-resistant.
Immutability: All blockchain transaction recordings become permanent when added to the network because they become unchangeable through immutability standards.
Blockchain works best as a decentralized system for ICO fundraising since it provides trust and transparency to all participants.
How Does ICO Work?
Projects within ICOs issue a token sale mechanism enabling investors to exchange tokens for established cryptocurrencies which could be either Bitcoin or Ethereum or sometimes fiat currencies. The launched tokens from a project provide users both monetary value and entry to upcoming services.
An Initial Coin Offering follows a standard procedure including three main phases.
Preparation
Announcement
Token Sale
Post-ICO
All stages of an ICO become manageable through blockchain technology which assures users transparent yet secure monetary exchanges for ensuring project effectiveness.
The Role of Blockchain in ICO Fundraising
Blockchain serves multiple vital functions during ICO fundraising which establishes this method as an efficient capital-raising tool for cryptocurrencies.
Decentralization and Transparency: The ICO process maintained through blockchain operates with complete transparency because no individual entity can manage or manipulate its operations. Blockchain technology lets stakeholders see fund movements and verify transactions along with auditing contract code directly on the system. ICO investors heavily depend on this high level of trust to participate because they operate in an ultra-speculative ecosystem.
Smart Contracts: Smart Contracts offer ICOs their main blockchain advantage through their implementation. These self-executing codes contain the written terms directly in their programming language. The execution of smart contracts happens automatically when preset conditions are fulfilled which results in token distribution that happens only after terms of sale fulfillment. The system operates without traditional middlemen to create an improved method for secure and efficient transaction management.
Security: The blockchain’s inherent security features—such as encryption, consensus mechanisms, and decentralization—protect investors and the project from fraud or unauthorized manipulation. The blockchain technology enables ICO tokens to become unalterable digital assets because tokens issued in this manner acquire tamper-proof status when creation completes.
Tokenization and Asset Representation: The blockchain provides functionality to create digital tokens that function as digital representatives of project ownership rights including ownership and access privileges and future profits. Digital tokens generated by ICOs enable worldwide digital asset transfer along with decentralized exchange usage that celebrates price volatility.
Global Accessibility: Anyone with access to the internet may use blockchain together with ICOs as a global investment platform. Projects do not require traditional venture capitalists to secure funding so they can reach more investors worldwide.
Future of ICOs and Blockchain Technology
ICO and blockchain technology reveal promising potentials while navigating through multiple obstacles in the future. Blockchain technology developments will lead ICOs toward better sophistication while introducing new regulations alongside integrations with innovative solutions.
Regulation
Security Token
Integration with DeFi (Decentralized Finance
Initial DEX Offerings (IDOs)
Improved User Experience
Conclusion
The introduction of blockchain technology transformed Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) to become a new method for project fundraising. The decentralized nature of blockchain enables ICOs to create more efficient fundraising alternatives that operate throughout the globe and rely on trust-driven features. ICO processes become streamlined because smart contracts alongside tokenization help eliminate intermediaries while providing better investor safeguards.
The future success of ICOs depends on both the regulatory framework development and blockchain technology advancements along with a widespread decentralization of financial services. ICO popularity could grow to become a leading financing method for the blockchain and cryptocurrency sector when these supporting factors become established.
#cryptocurrency#blockchain#cryptocurrencies#ico development#blockchain development#blockchain technology#blockchainx
1 note
·
View note
Text

What is Crypto Mining? How to Mine Pi Coin?
Crypto mining is the process of validating transactions and adding them to a blockchain ledger using computational power. Miners use high-performance hardware like GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) or ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) to solve complex mathematical problems. This process is known as Proof of Work (PoW) and helps secure the network.
Miners compete to solve cryptographic puzzles, and the
first to do so gets rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency, known as a block reward. Popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and Litecoin (LTC) use mining for transaction verification and network security.
Mining requires significant energy consumption, advanced hardware, and stable internet connectivity. Due to rising difficulty levels and operational costs, many miners join mining pools to combine resources and share rewards. Cloud mining is another alternative where users rent mining power from remote data centers.
Pi Coin mining is different from traditional crypto mining because it does not require high-end hardware or electricity consumption. Pi Network uses a unique consensus algorithm based on trust rather than Proof of Work (PoW).
To mine Pi Coin , follow these steps:
Download the Pi Network App — Available for Android and iOS.
Create an Account — Sign up using your phone number or Facebook.
Start Mining — Click the “Mine” button once every 24 hours to earn Pi
Increase Mining Rate — Invite friends using your referral code and verify your identity (KYC).
Become a Node Operator — Advanced users can run nodes to support the network.
Conclusion
Crypto mining is essential for securing blockchain networks, but it is becoming increasingly expensive and competitive. Pi Coin mining offers a new, user-friendly approach that allows anyone to participate without high costs. While traditional mining remains profitable for large-scale operations, Pi Network provides an alternative for beginners looking to explore cryptocurrency.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Spider Swap's Bridge : A Gateway for Cross-Chain Transactions

In the rapidly evolving world of decentralized finance (DeFi), interoperability between different blockchain platforms has become a critical need. As users and developers alike seek more seamless ways to interact across ecosystems, tools that facilitate these interactions are increasingly in demand. Spider Swap, known for its innovative approach to decentralized exchanges, has recently launched a groundbreaking new feature: the Bridge. This functionality not only enhances the platform’s offerings but also pioneers a more interconnected blockchain environment. In this blog, we’ll dive deep into what Spider Swap’s Bridge is, how it works, and what it means for users wanting to swap crypto across platforms like Ethereum and Solana.
What is Spider Swap’s Bridge?
Spider Swap’s Bridge is a decentralized application (DApp) designed to connect disparate blockchain networks, enabling the transfer and exchange of assets between them. This tool is crucial for users who want to leverage the strengths of multiple blockchains — like Ethereum’s extensive development infrastructure and Solana’s high-speed, low-cost transactions — without being limited by the boundaries of any single platform.
Key Features and Capabilities
Cross-Chain Swaps: The primary function of the Bridge is to allow users to swap cryptocurrencies across different blockchains directly. For example, a user can exchange Ethereum (ETH) for Solana (SOL) seamlessly, without needing to convert ETH to a stablecoin or use centralized exchanges as intermediaries.
Decentralized: Operates in a fully decentralized manner, meaning that it does not rely on any central authority for the processing of transactions. This ensures that the swaps are secure, adhering to the core principles of DeFi.
User-Friendly Interface: Despite the complex technology underlying it, the Bridge boasts a user-friendly interface that simplifies the process of cross-chain transactions for the average user. This accessibility opens up more opportunities for non-technical users to engage with multiple blockchains.
Lower Transaction Costs: By facilitating direct swaps, Spider Swap’s Bridge can significantly reduce the transaction fees and slippage usually associated with multiple exchange steps. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in a market where transaction costs can be a barrier to participation.
How Does the Bridge Work?
The technology behind Spider Swap’s Bridge involves several innovative components:
Smart Contracts: At the heart of the Bridge are smart contracts that are deployed on each participating blockchain. These contracts handle the verification, locking, and unlocking of assets as they are transferred between chains.
Relayers: These are nodes that observe the state of one blockchain and report it to another. They play a crucial role in ensuring that transactions are validated across the ecosystems without the need for an intermediary.
Liquidity Pools: To facilitate swaps, the Bridge uses liquidity pools that hold reserves of various tokens on multiple blockchains. Users provide liquidity to these pools and, in return, earn transaction fees generated from the swaps.
Practical Applications and Benefits
The practical applications of Spider Swap’s Bridge are vast:
Enhanced Liquidity: Users from different blockchains can pool their resources, leading to enhanced liquidity, which in turn reduces price volatility and improves trade execution.
Broader Asset Access: Users can access a wider range of assets across different blockchains, potentially leading to better investment opportunities and risk diversification.
Innovative Financial Products: Developers can create complex financial products that leverage capabilities from multiple blockchains, such as combined yield farming strategies or multi-chain collateralized loans.
Challenges and Considerations
While the Bridge offers numerous advantages, there are also challenges to consider:
Security Risks: Cross-chain bridges are complex and potentially expose new attack vectors. Ensuring the security of the smart contracts and relayer systems is paramount.
Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory framework for cross-chain activities is still unclear, and users must navigate these uncertainties which could impact the adoption and functionality of such tools.
Conclusion
Spider Swap’s new Bridge functionality marks a significant step forward in the quest for a truly interconnected blockchain ecosystem. By allowing seamless swaps between major platforms like Ethereum and Solana, it not only broadens the scope of what’s possible within DeFi but also enhances the overall user experience. As the technology matures and more users and developers engage with it, we can expect even more innovative solutions to emerge, further solidifying the role of interoperability in the future of finance.
0 notes
Text
Ethereum staking is a process that involves participating in the Ethereum 2.0 network by locking up ETH (Ethereum's native cryptocurrency) to support the network's operations and earn rewards in return. This transition to Ethereum 2.0 aims to shift Ethereum from a proof-of-work (PoW) to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, enhancing scalability, security, and energy efficiency.
Here's how Ethereum staking works:
Validator Nodes: Participants (validators) lock a minimum of 32 ETH into a staking contract to become validators on the Ethereum network.
Block Validation: Validators are randomly selected to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the amount of ETH they have staked.
Rewards: Validators earn ETH rewards for successfully proposing and attesting to blocks. Rewards are distributed based on participation and network performance.
Security and Incentives: Validators are economically incentivized to act honestly and maintain network integrity. However, penalties apply for malicious behavior or downtime.
Ethereum staking provides an opportunity for ETH holders to contribute to the network's security and scalability while earning passive income through staking rewards.
0 notes
Text
How does cryptocurrency work?
In the ever-evolving landscape of finance, cryptocurrencies have emerged as a groundbreaking force, reshaping the way we perceive and conduct transactions. As digital assets gain prominence, it becomes crucial to understand the underlying mechanisms that power them. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of cryptocurrency, exploring its fundamental principles and shedding light on the question: How does cryptocurrency work?
Understanding the basics:
Cryptocurrencies operate on a decentralized technology called blockchain. At its core, a blockchain is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. Each transaction, known as a block, is linked to the previous one, forming a chain of blocks. This decentralized nature ensures transparency and security, making it nearly impossible to manipulate or hack the system.
Key components of cryptocurrency:
Blockchain Technology: Cryptocurrencies rely on blockchain technology to maintain a secure and transparent record of transactions. This technology involves a consensus mechanism, where participants in the network agree on the validity of transactions, preventing fraudulent activities.
Cryptography: The name "cryptocurrency" is derived from the use of cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. Public and private keys play a crucial role in this process. A public key is the user's address on the blockchain, visible to others, while the private key is a secret code known only to the owner, ensuring the security of their digital assets.
Decentralization: Unlike traditional banking systems, cryptocurrencies operate without a central authority. This decentralization eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as banks, allowing users to have direct control over their funds.
How transactions work:
Initiating a Transaction: When a user initiates a cryptocurrency transaction, they create a digital signature using their private key. This signature serves as proof of ownership and authorization for the transaction.
Validation: The transaction is broadcasted to the network and validated by a network of nodes through consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). Once validated, the transaction is added to a block and appended to the blockchain.
Mining Process: In the case of PoW cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and create new blocks. Successful miners are rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency and transaction fees.
Confirmation: As more blocks are added to the blockchain, the transaction becomes more secure. Most cryptocurrencies require multiple confirmations before considering a transaction final, adding an extra layer of security.
Popular cryptocurrencies and their unique features:
Bitcoin (BTC): As the pioneer of cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin remains the most widely recognized and traded digital currency. It operates on a PoW consensus mechanism, limiting the total supply to 21 million coins.
Ethereum (ETH): Ethereum introduced the concept of smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into code. This feature allows for the creation of decentralized applications (DApps) on its blockchain.
Ripple (XRP): Ripple focuses on facilitating fast and low-cost cross-border payments. Unlike PoW, Ripple uses a consensus algorithm to validate transactions, making it more energy-efficient.
Security measures in cryptocurrency:
Immutable Ledger: The blockchain's immutability ensures that once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This feature safeguards the transaction history from tampering or fraud.
Encryption Techniques: Cryptocurrencies employ advanced encryption techniques to protect user data and secure transactions. This encryption makes it extremely challenging for malicious actors to compromise the system.
Consensus Mechanisms: The consensus mechanisms, such as PoW and PoS, contribute to the security of the network by preventing malicious activities and ensuring that only valid transactions are added to the blockchain.
The future of cryptocurrency:
As cryptocurrencies continue to gain traction, the future holds the promise of further innovation and integration into mainstream finance. From decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs), the cryptocurrency space is evolving rapidly, offering new opportunities and challenges.
In summary, the world of cryptocurrency operates on the principles of blockchain, cryptography, and decentralization. Understanding the mechanics of cryptocurrency is essential for anyone looking to navigate this digital financial landscape securely. As we embrace the future of finance, the decentralized and transparent nature of cryptocurrencies is set to redefine the way we transact and interact with money. How does cryptocurrency work? It's a question that invites exploration and discovery in a world where digital currencies are becoming increasingly intertwined with our financial reality.
0 notes
Text
Ethereum is the second-largest crypto in terms of market cap and the first blockchain-based smart contract to undergo a historic transformation from an energy-intensive mechanism of proof of work (PoW) to a more eco-friendly consensus mechanism of proof of stake (PoS). PoS fundamentals have transformed the roles and responsibilities of Ethereum, which was once utilized to reward ETH miners and can now be staked. It follows a two-tiered staking system, where node operators and delegators have emerged as central figures. Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum, suggested the two-tiered staking model that includes a high-complexity slashable tier with limited participants and frequent activities and a low-complexity tier with members sporadically engaging and facing minimum or no slashing risks. In this article, we will discuss how the transition from PoW to PoS has enhanced Ethereum’s security and scalability, benefiting all participants on the Blockchain network. Ethereum’s Transition to PoS and Challenges The recent shift of Ethereum from the power-hungry PoW consensus to a greener PoS mechanism has considerably enhanced Ethereum’s energy efficiency, minimizing energy consumption and reducing its carbon footprint. According to the CCRI metric, the Merge indicates a reduced electric consumption of almost 99.5% in September. With this, the Ethereum network has become the champion in the world of decentralization. However, certain challenges have come up while orchestrating these upgrades or changes. The transition has altered the validation process for ETH transactions, moving from intricate problem-solving to crypto staking. This shift has inherent risks of amplifying the influence of wealthier participants and can potentially lead to centralization. Nevertheless, the transition has exposed Ethereum casinos to a powerful opportunity where all parties can benefit from enhanced security, scalability, and decentralization. Vitalik Buterin’s Two-Tiered Staking Proposal Ethereum network’s founder, Vitalik Buterin, has proposed implementing a two-tiered staking solution, introducing two categories of participants – Node Operators and Delegators. The system balances accessibility, decentralization, and security within the staking ecosystem. Buterin pinpoints decentralization challenges with the selection process for node operators on different staking pools and identifies the underlying inefficiencies in the existing Layer 1 consensus mechanism. Node operators act as validators by committing a 32 ETH stake and running nodes simultaneously to handle transactions and generate new blocks. However, node operators are limited by certain ethical standards and are exposed to slashing penalties if found engaging in malicious behavior. On the other hand, delegators have stakes less than a 32 ETH threshold needed in solo staking. They can get their stakes independently for their chosen node operators. Delegation allows for supporting and engaging with the consensus mechanism with a light capacity. Benefits of the Two-Tiered Staking Proposal The two-tiered staking proposal introduced by Vitalik Buterin has several benefits for the network and the users. The primary benefit of the two-tiered staking proposal is its potential to enhance the network’s scalability. A more efficient ETH network can process higher volumes of transactions by minimizing computational overhead and reducing the number of signatures needed per block to almost 10,000. The proposal has raised the difficulty level for attackers who are searching for gaps to gain control of the stake within the Ethereum ecosystem. The difficulty level for attackers has been increased to bolster the network’s security and decentralize the system, aligning with blockchain technology’s core principles. The approach will enable a gradual shift, reducing disruptions and reaching the desired objectives of a more scalable and secure network. Due to the transition from PoW to PoS, Buterin’s two-tiered
staking model, and the enhanced levels of scalability and security, stakeholders and investors in Ethereum casinos are heavily benefited, leading to Ethereum’s further growth. Conclusion Ethereum’s transition from PoW to PoS and introduction of a two-tiered staking solution have marked a groundbreaking step to address the existing challenges linked with the current proof of work consensus mechanism. The changes or upgrades have established a precedent for the entire crypto sector. The transition signifies a move towards sustainability by achieving a balance between delegators and node operators, promising improved accessibility, scalability, and security to pave the way for a stronger Ethereum ecosystem. The future for the ETH community looks brighter and more promising than other blockchain platforms, considering more community members embrace these changes.
0 notes
Text
Digital Bureaucracy
Digital Bureaucracy with Blockchain infrastructure
The first decentralized Bureaucracy system that simplifies and standardizes data with blockchain technology.

What is Digital Bureaucracy?
It is the Artificial Intelligence (AI) supported Blockchain Project that aims to end the difficult and long-lasting paperwork and bureaucracy transactions between countries, institutions, and individuals. It is a document management and document transfer solution specially developed for a decentralized blockchain, aimed at making your life easier with the combination of artificial intelligence and blockchain technologies.
Documents and Bureaucracy transactions in documents, invoices, land registry, vehicles and many more are distributed in the Blockchain database and then your documents are distributed decentralized in a comparable, irrevocable way on the blockchain network. A system where the submitted information can only be seen by users who have Hash key. This confirms, or can be verified, by comparing the
HOW WILL DIGITIAL BUREAUCRACY MAKE YOUR LIFE EASYER?
Digital Bureaucracy is a Project that will enable you to perform your time consuming and tiring daily bureaucratic transactions between individuals, institutions and countries using the Blockchain network, quickly and cost effectively.
https://youtu.be/SSo_EIwHSd4
WHAT IS DBC
DBC is the first Decentralized Bureaucracy System that simplifies and standardizes data using blockchain technology. We facilitate bureaucracy across Individuals, Institutions, and Countries on the Blockchain Network.
Decentralised Platform.
It is fully decentralised and is backed by Blockchain.
Managing Bureaucracy with One Click.
Our project will allow you to handle bureaucratic procedures and tedious paperwork that makes your life difficult, efficiently, and securely.
Artificial Intelligence
We are a Bureaucracy Transfer network that uses the power of Artificial Intelligence and connects the World.
How Does DBC Work
Digital Bureaucracy is making our lives difficult. It is instated everywhere and is carried out by the Municipality. Official documents, Invoices, Home and Vehicle purchase and sale, School and Education, Health and Hospital, Finance and Business, Customs procedures, Passport and Identity procedures are just some of the areas of example.
The DBC Project has made it possible to manage the tedious document transactions that causes complexity in our lives. For a moment, imagine that paper is not used within the World. With DBC, you will be able to send and receive your invoices, official documents, insurance and hospital documentation, customs and tax transactions, home, and car buying/ transactions, international, official, or personal information/documents using a single click encrypted over the Blockchain Network.
We combine the structure of Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain, allowing you to trade securely and quickly.
Bureaucratic procedures will rely on the help of Artificial Intelligence completely. It is a great project that will ensure swift and reliable transfers over the blockchain network.
Dependable and rapid payments. You will be able to send even the highest payments at the lowest cost.
Safe storage of school and hospital transactions on the Blockchain network. It enables making an action or obtaining information simpler with just a click.
To facilitate the blockchain network in our daily lives, DBC started to develop its own Blockchain infrastructure to provide convenience in the listed areas below:
Property
A smoother, faster, and cheaper transaction of fees on the Blockchain network combined with Artificial Intelligence that will eliminate the long and tiring dealings that you have experienced in the purchase and sale of houses, land and immovable properties.
Buying and selling vehicles, obtaining new license plates, vehicle insurance and detailed vehicle history is available when using DBC to carry out such transactions.
An incredible feature of the blockchain is that flagged data is immutable. For example: Information sent to the Blockchain network is immutable; It cannot be changed in any way. Therefore, counterfeiting documents is automatically protected.
Councils
Imagine the ability of transactions in municipalities entirely over Blockchain Network. It would enable the actioning of all your paperwork promptly and inexpensively. For example: When a new child is born, it is added as a block to a blockchain chain in that municipality. The individual can then perform all their operations over this block during their life.
All municipal transactions that you can think of such as Identity, Address change, Driving Licenses and more. The combination of Artificial Intelligence and the Blockchain Network will permit you to do all the paperwork that makes your life complicated, all the while being quicker and cheaper for you.
Removes all bureaucratic paperwork allowing for speed, lower costs, and security via Blockchain.
Identify
Transactions such as Passport applications, Passport Controls and Verification. You can make these proceedings at a faster and cheaper rate on the Blockchain and with the support of Artificial Intelligence.
Authentication, Pedigree Checks, Identity, and any other form of official documents that identify you will become faster, cheaper, and reliable on the blockchain network ultimately allowing for easier overall transactions.
Visa applications, delays in family reunification visas and complex document processes will now be quick, safeguarded, and cost effective.
Schools & Education
Student Information tracking system. Fast communications between teacher, trainer and parents of students. An infrastructure that enables detailed bureaucracy procedures to proceed faster.
Storage and tracking of Student Notes and Student Diplomas on the Blockchain network. Recording of school diplomas in the system as unchangeable and tracking it.
Distribution of religious books and Books in an immutable manner over the blockchain network. Transactions such as making comparisons or purchasing and reselling the work will be available afterwards.
Health & Hospitals
Patient tracking system in Hospitals and Health Institutions. Monitoring of Tests and Other health services within hospitals on the blockchain.
Communication and bureaucracy transactions between hospitals and pharmacies. The rapid processing of these transactions on the Blockchain and the progress of the workload will be entirely by Artificial Intelligence.
Every individual will have their own Private Key. All transactions are processed on this key. Eventually, control and accuracy controls can be provided.
Taxes
It ensures that all bureaucracy and paperwork transactions of places such as institutions, individuals, and workplaces where tax transactions take place intensely, are processed faster and with reasonable costs over the blockchain network.
Tax tracking and tracking of sales and purchases at workplaces through the blockchain network.
Online Sales and International Tax. Providing and controlling tax transactions between countries through the Blockchain network. All complex tax systems become completely easy.
Customs
Follow-up of import and export transactions. Unchangeable tracking of import and export transactions made in all customs systems on the blockchain network.
Transactions such as Passenger passes, Passport and Identity verification. There will be ease of passenger transit through the blockchain network. The required paperwork and bureaucracy procedures are fast and cost-effective.
There will be control of vehicle crossings at customs. In this way, we aim to finalize the illegal vehicle or passenger crossings entirely.
Finance & Business
Contracts signed by international companies. Commercial exchangeable contracts, or agreements or contracts concluded between countries on a permanent basis.
Tenders organized by countries or institutions, fulfilment, and follow-up of these tenders on time and without any problems. Simultaneously, the payment of these auction fees will be with the DBC Coin.
The Solution
The DBC token has been created to be used in the Digital Bureaucracy Infrastructure and to become the currency of the future. DBC token is the Crypto Currency that will be used in your bureaucratic transactions around the world. What will DBC token do?
Relational Blockchain
Faster and cheaper cost of paperwork and bureaucracy with relational blockchain.
Fraud Reduction
DBC token aims to completely terminate fraud and unlawful business.
Next Generation Wallet
You can safely store DBC Tokens in Next Generation Wallets.
Recovery Nodes
Our Cryptocurrencies are 100% Safe in Smart Wallets with recovery facility.
Full Transparency
Our project and DBC Token are completely open source.
Very Low Fees
With very low transaction fees, DBC Token will become your favorite currency.
Decentralized Network
DBC Token is a Decentralized and User-oriented Crypto Currency.
Crypto Payment
You will be able to pay with DBC Coin in every area of your life.
Token Sale
The DBC token was created using Binance Smart Chain (BSC) BEP20 Smart Contrac. The token’s third party service wallets, exchanges, etc. It provides compatibility with and easy-to-use integration.
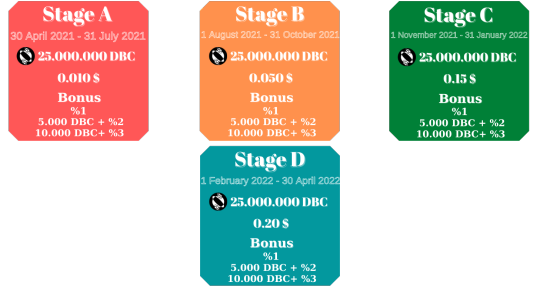
Start: 2021-04-30
Total Supply: 200.000.000 DBC
Number of tokens for sale: 25.000.000 DBC
Tokens exchange rate: 1 DBC = 0.010 USD
Acceptable currencies: ETH, BNB, BTC, USDT
Minimal transaction amount: 1000 DBC / 10 USD
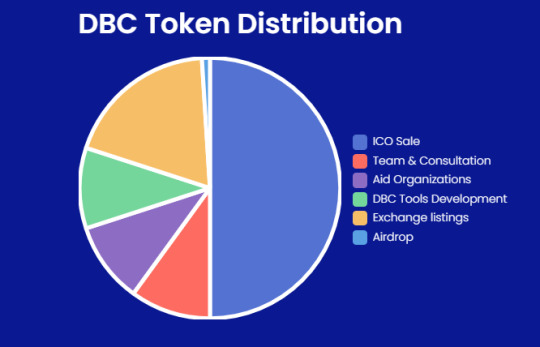
DBC Token Distribution
Binance Smart Chain Contract: https://bscscan.com/token/0xaede8306171b2aac22cf4f39a63aae09e99a488c
RoadMap
2019 - Q1
Release and Distribution - Providing Bureaucracy between Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain Supported Countries, Institutions and Persons to eliminate delays and uncertain transactions in today’s Bureaucracy system. The beginning of the infrastructure was provided and aims to facilitate these difficult document and file transactions by combining Artificial Intelligence and the Blockchain network.
2020 - Q1
Our team started building the foundations of the DBCChain software for Documents and File Transfers.
2021 - Q1
DBC Token Binance Smart Chain (BSC) - created and published with the BEP20 Smart Contract.
2021 - Q2
In order to support DBC Token sales, Airdrop and ICO Program, the user panel has been integrated into the system and activated.
2021 - Q3
To purchase DBC Token, Offline Crypto Money payment methods have been added to the user panel.
2021 - Q4
DBC Token has been added to Pancakeswap.finance Liquidity pool and Exchange sections.
2021 - Q5
The Digital Bureaucracy (DBC) Whitepaper was completed and published.
2021- Q6
DBC Token Airdrop and ICO Program was launched. In this context, 25.000.000 DBC Token has been opened for sale with ICO pricing.
2021- Q7
DBC Chain will perform P2P, Miner, Genesis tests
2022 -Q1
- ICO sale Completed and Token Distribution.
-Airdrop distribution completed and Token Distribution
2022 - Q2
- CoinMarketCap list
- Coingecko list
2022 - Q3
DBC Wallet Android and iOS application publishing.
2022 - Q3
Top 10 CMC Exchange listing (KuCoin/Bithumb exchange)
- Roadmap v2.0 release
- Future products development
our team
The Digital Bureaucracy team aims to eliminate the difficulties in your life by bringing together Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain. Our Project is created in an open-sourced way completely. You can contribute to the development of our project by joining our team.
Akif Dogan: CEO/Founder Blockchain Development
Sidar Ozden: Head of Partnerships & Business Development
Silan Dogan: Head of Legal & Compliance
Ahmet Deryahanoglu: Backend Software Engineer
Mesut Acil: Head of Design
Muhammad Aliyev: Marketing Director
Berna Asel: Social Media Lead
For more information please follow the link below:
Website : https://www.digitalbureaucracy.org/
Whitepaper : https://www.digitalbureaucracy.org/Whitepaper-EN.pdf
Medium : https://digitalbureaucracy.medium.com/
Telegram : https://t.me/digitalbureaucracy
Twitter : https://twitter.com/DigiBureaucracy
Reddit : https://www.reddit.com/user/Digitalbureaucracy/
Author:
Bitcointalk username: Jadon Sancho
Bitcointalk Profile: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=2954208
Telegram: @Jadonsancho09
BEP-20 Address: 0xb05fc25bCfa612Eaef1Fa17cEBF05A675a40D5e1
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cryptocurrencies (3/3)
What sort of security issues do we have?
Due to the distributed nature of cryptocurrencies, we have to consider the security in a number of different areas and from a couple of different angles. In terms of looking at historical flaws and their relative impacts, I would classify them under 3 main categories:
Blockchain itself - vulnerabilities relating specifically to the implementation of the blockchain (so in the nodes, mining, etc)
51% attacks (i.e. ETC 2019)
DDoS
Doublespend (i.e. The Finney attack)
Exchanges and wallets
Phishing
Bad hashes (i.e. IOTA)
Software bugs in cryptocurrency wallets
Software bugs in cryptocurrency exchanges
Client malware (i.e. changing address in clipboard)
Smart contracts - complexity of smart contract languages leading to bugs or poorly designed contracts (i.e. TheDAO)
As per the seminar, I will summarise a specific example of each of these categories.
Blockchain - 51% Attack
How does it work?
If you read my (1/3) article on cryptocurrencies, you will understand the process of mining in PoW and how multiple chains can form. Essentially, what we have happening in this attack is we have a miner (corrupted) with a large portion of the hash power deciding not to broadcast the block to the network when he as found a valid hash for the block. He will then continue to mine on his own chain in stealth; the original chain will continue to be built by other miners.
The corrupted miner will then spend all the bitcoin that he owns on the public chain, however he will choose NOT to do the same on his own secret chain. He will then continue to mine blocks on his own chain; however since he has majority hash power he will be producing blocks at a greater rate than the main chain. After a while he will choose to broadcast his chain to the rest of the Bitcoin network - the democratic governance process of the network enforces that the ‘longest chain’ is the correct one and the protocol will force the nodes to switch to the corrupted miner’s chain. This miner is then able to spend his bitcoins (that he spent earlier) all over again - this is why it is also referred to as a double-spend attack.
What security mechanisms are in place against it?
The main thing defending against a 51% attack is the sheer amount of resources required to perform it - on larger networks such as Bitcoin you need approximately $12.5 billion dollars worth of hardware which will cost you $8.6 million dollars per day to run in order to perform this attack. (from this site) This makes the risk associated with the costs in electricity, hardware and government prosecution not worth the reward of the attack.
Exchanges - Mt Gox
What happened in the first hack in 2011?
The computer of Mt Gox’s auditor was compromised which they then used to access the exchange and artificially modify the traded value of bitcoin down to 1 cent (i.e. by selling all the bitcoin from all the accounts). They could then buy a heap of these bitcoins at this low price (around 2000 BTC they got), and could transfer them from the exchange. As a result of the hack, Mt Gox resorted to utilising cold storage for the majority of their bitcoin - this means you cannot access a large proportion of the funds through the web server or any other computer.
The method in which this account was compromised is still somewhat debated - however it is suspected that the auditor account was compromised through an SQL injection on the Mt. Gox website which allowed the attacker to gain read-only access to the user database. The passwords were hashed with MD5 (retrospectively, we know is definitely poor) and accounts which hadn’t logged in prior to the chance in ownership of the exchange (by Tibanne Co. Ltd in March 2011) had unsalted password hashes used. You can read the Mt. Gox press release at the time on BitcoinTalk here.
How did the big second hack in 2014 occur?
In a short period of time in 2013, Mt Gox had become the largest bitcoin exchange in the world and was struggling to cope with the expansion. They had expended significant resources towards dealing with the lawsuits from former business partners (Coinlab) and investigations by the US Department of Homeland Security. We now also know from employee accounts that the security procedures were poor, the website source code was poor quality and a number of other operational issues existed.
This all led to the events which unfolded in February 2014, as follows (according to CoinTelegraph article):
7th - withdrawals frozen due to an “apparent bug” in the Bitcoin network relating to modification of transactions
17th - press release regarding a solution they had found to solve this “bug” which would be applied shortly
23rd - the CEO of Mt. Gox, Mark Karpeles, resigned from the Bitcoin Foundation and disappeared from Twitter
24th - trading was suspended and an internal document leaked claiming they were insolvent; missing 744,408 bitcoins (it was a crisis strategy draft)
28th - Mt. Gox filed for bankruptcy protection in Tokyo and in the US on March 9th
They haven’t been particularly transparent regarding the cause of the second hack, however some information has been pieced together. It is believed that Mt. Gox’s hot wallet private keys were stolen from a wallet.dat file near the end of 2011. Throughout 2012 and 2013, the hacker emptied the wallets associated with the private keys, however Mt. Gox’s systems interpreted this is deposits for some reason. Towards the end of 2013, the hacker had stolen over 600,000 BTC; a large proportion of this ended up on BTC-E. This exchange was essentially responsible for laundering half the funds associated from the hack; it was taken down in 2017 by the US Justice Department.
Smart Contracts
What is a smart contract?
A contract is an agreement between two parties which will be binding in some point in the future. The difference in the case of smart contracts with blockchain is that it makes the execution of the contract trustless - we don’t need a third party. Some restrictions are imposed when we make them decentralised; they need to be unable to access data outside the program (to prevent malicious activity) and they need to be deterministic (so nodes in the network can still verify blocks).
Why are these contracts so prone to errors?
The majority of smart contracts we know today are built upon the Ethereum blockchain; it uses a Turing-complete smart contract language known as Solidity. This differs from traditional contracts in the sense you are to solve any reasonable computational problem. It also comes at the cost of increasing complexity; there is an increasing number of ways the flow of the contract can occur and thus they are very difficult to get right. We already know that writing ‘secure’ code is hard, but when you have money directly on the line it becomes even more important.
What was the DAO?
The DAO (Decentralised Autonomous Organisation) was an organisation built on top of Ethereum which ran completely through smart contracts on the platforms. In the token offering, users were able to send ETH to a particular address and receive DAO tokens in return. Anyone was able to make a pitch to the community, and people could vote with their DAO tokens whether to make an investment. If a project was successful as a result of the DAO, it would then return profits to the investors.
How was the smart contract code in the DAO exploited?
One of the developers announced on the 12th of June that they had discovered a recursive bug call in the DAO contract, however emphasised that no funds were at risk. An attacker managed to find a way on the 18th of June to abuse this recursive bug call to continuously send funds to a child DAO under their control. The process was as follows (source):
(1) Propose a split and wait for the voting period to expire
(2) Call splitDAO()

(3) Let createTokenProxy() send your new DAO its share of tokens
(4) Ensure the DAO calls withdrawRewardFor() before updating your balance and after doing (3)

(5) Call splitDAO() again with the same parameters while (4) is occurring
(6) DAO will repeat steps (3) and (4) to give you the child tokens again
(7) Go back to (5) as many times as you like
So in summary, the problem all stems from the fact that you get your reward in the child DAO before subtracting from the original balance. The stack was actually limited to 128 on Ethereum at the time, so he wasn’t able to continue these calls forever. The attacker managed to get around this by using the handy transfer() function, so he could quickly move the funds out to another account he controlled. Then he could move it back into the original account and repeat the process.
What happened after the hack?
The attacker managed to steal ETH worth up to 250 million USD; they actually stopped after draining around 1/3 of the DAO’s funds. It started a big debate among members of the Ethereum community as to how they could respond to this attack. One side fought for the immutability (’code is law’) of the blockchain and argued that we shouldn’t fork to take away the funds from the attacker. The other side wanted to fork the chain to return all the funds. The miners were divided on the proposals (a contentious hard fork) so we ended with two chains - Ethereum Classic (ETC) and Ethereum (ETH).
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
JPMorgan Chase &. Co. has shed light on how the Ethereum network decentralization has decreased significantly since the Merge event and Shanghai upgrade went live. The rise of staking and centralization Since implementing the Merge and Shanghai upgrades, Ethereum has seen a substantial uptick in staking activities. Staking, a process where users lock up their crypto assets to support network operations, has its merits. According to a CoinDesk report citing JPMorgan research, this surge in staking activity comes at a cost: centralization. Traditionally, many in the crypto community prefer decentralized liquid staking platforms like Lido over their centralized counterparts. Lido’s approach included adding more node operators to ensure no single entity controlled a significant portion of staked Ether (ETH). The aim was to address centralization concerns. However, centralization remains a risk. A concentration of liquidity providers or node operators could act as a single point of failure or even collude to create an oligopoly, potentially undermining the interests of the broader Ethereum community. Ethereum, the world’s second-largest crypto, has become more centralized since the Merge and Shanghai upgrades. And JPMorgan is highlighting concerns over a decline in staking yields. The menace of rehypothecation Another highlight from the report is rehypothecation. This complex term refers to the practice of reusing liquidity tokens as collateral across multiple decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols simultaneously. DeFi encompasses lending, trading, and other financial activities carried out on the blockchain. The problem arises when a staked asset’s value sharply declines or faces a security breach or protocol error. In such scenarios, rehypothecation could trigger a cascade of liquidations, jeopardizing the stability of the DeFi ecosystem. Furthermore, the report points out that the increase in staking has diminished the appeal of Ethereum from a yield perspective. This shift is especially noticeable amid rising yields in traditional financial assets. The total staking yield has fallen from 7.3% before the Shanghai upgrade to approximately 5.5%. From a different perspective, the research data presented in December following Ethereum’s Merge upgrade in September 2022 reveals a significant reduction in the network’s energy consumption, akin to the energy usage of entire countries such as Ireland and Austria. This decrease in power consumption positively contributes to environmental sustainability, aligning with broader global efforts to reduce the carbon footprint associated with blockchain technologies. Ethereum’s core developers have introduced an Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP-7514) as part of the upcoming Dencun upgrade, scheduled for activation in October 2023. This proposal aims to slow down the rate of Ether staking. The intention is to provide the Ethereum community with more time to devise a practical reward scheme for stakers on the network. ETH price analysis As of the time of writing, the price of Ethereum (ETH) stands at $1,629, representing a 3.4% decline on the weekly timeframe. Ethereum’s Relative Strength Index (RSI) is currently sitting at 40.4. The price of ETH is struggling to maintain the $1600 level after facing rejection at the $1700 resistance level. A failure to hold the $1600 level could potentially lead to a further decline to the $1500 level.
0 notes
Text
Dogecoin Wallet
Dogecoin Core is this standard Dogecoin wallet mantained from the Dogecoin base. The idea is the whole Dogecoin client and therefore calls for up a lot connected with space like this downloads available the full blockchain. Theinitial synchronization will take as well as download a lot of info. Although the client is not really rich inside features, the idea will do provide a high level connected with security as the personal keys is going to be created in addition to stay on your computer. Dogecoin Main Wallet Analysis Dogecoin Main is the entire standard version of the DOGE wallet. Initial match-up while using blockchain is slow in comparison to lightweight versions, and this will have a lot of free space within the LAPTOP OR COMPUTER to install the Program. You will find types for running systems (Windows, OS X, Linux, Google android, Blackberry, Browser, Source, IOS). Dogecoin Key is the pretty fundamental wallet so what can be operate as a whole node to support the entire DOGE Network. The build up is not really complicated. If you don't want to operate a full client you can use any other wallet program which supports DOGE. The particular most reliable choice to secure your currency could be the Dogecoin Core wallet, with this particular system you can store money on your computer while a file. Nevertheless , in the event that the operating system is definitely reinstalled and no backup has been created, all of coins is going to be lost. Inside addition, the program automatically synchronizes with the Blockchain community upon completion of often the installation. This one-time function can take about twenty time. And at the end of the synchronized program will take 10 GB involving hard hard disk drive space. Dogecoin. Determining baby gender? Everyone knows or even has a minimum of heard of the Net sensation that has been the �Doge� meme. As soon as the likeness regarding this famous Shiba Inu dog, the cryptocurrency Dogecoin was created. Since it has the release in 2013, Dogecoin has quickly gathered a good impressive on the web group close to it, hitting a capitalization on USD 60 million in 2014. As of December 2017, that comes with reached a increased of USD 308 thousand. Dogecoin is an open-source cryptocurrency that can be utilized to purchase and sell items online, or perhaps trade the idea for various other cryptocurrencies (like Bitcoin and altcoins) or maybe fiat various currencies. Dogecoin Wallet s and handbags Dogecoins need to be stored in the Dogecoin Wallet . This wallet can be seen by computer, smartphone or maybe internet site, enabling the customer to send, obtain and retail outlet Dogecoins within a good matter of minutes. Effectively, a new Dogecoin wallet acts like a bank account would when taking care of your funds. Truth be told there are various kinds of wallets and handbags which often have been designed for you to provide individual needs involving users. The principle types involving wallets are: computer, mobile phone, hardware, web and paper. These wallets have different degrees of security and convenience so it�s very important to choose the a person that is best regarding an individual. Below is the list of the best billfolds for Dogecoin. dogecoin Dogecoin Core Dogecoin Core is usually the Doge�s public pocket. It downloads the whole blockchain and then it possesses to connect with it in order for the user to start out deals. Because of this, their original sync is the bit more slowly in comparison to others, and it also wants more space. This wallet can be recommended intended for Dogecoin miners, as it is incredibly secure and trustworthy. The idea is compatible with this following systems: House windows, OS IN THIS HANDSET X, Apache. MultiDoge MultiDoge is a personal computer Dogecoin client which need not connect with the whole blockchain. Powered by Dogecoin, it�s a new light wallet which syncs fast and it is very easy to employ. That is just not recommended of which this wallet be used for mining or prospecting, as this will become slow and unresponsive. This facilitates House windows, OS Times, Cpanel. multidoge WowDoge WowDoge can be also a light pocket designed for desktop work with. This wallet eliminates aggravating longing time because the idea doesn�t have to download entire gigabytes of blockchain. The interface is user friendly and it runs seamlessly. You possibly can request to experience new features added. WowDoge is also free and open source. wowdoge DogeChain budget DogeChain is in addition a free online finances to get you to shop your own Dogecoins. It�s really uncomplicated and easy to apply, making it possible for the customer for you to access his / her coins everywhere, anytime. dogechain budget Exodus. io Exodus is some sort of multi-coin wallet that shops many cryptocurrencies, one too as well being Dogecoin. The platform is usually known to be some sort of protected place to maintain your virtual possessions. Typically the user interface is uncomplicated to make use of and is the particular only desktop iphone app to help have ShapeShift built throughout. You are able to keep all your cryptocurrencies in one place plus perform dealings from a person software. Exodus gives seedling phrase which can get accustomed to recover their gold and silver coins if your user�s computer arrives or perhaps their hard push becomes corrupted. Exodus as well has good customer assist service. exodus Block out. io Wallet Block. io is definitely an online web wallet for multi-currency storage area and transactions. Users can manage Dogecoin, Bitcoin and Litecoin from one account. Nevertheless it is definitely certainly not recommended you retail outlet much around an online wallet, not any matter how trusted the particular site is. block. io Cryptonator Wallet Cryptonator is an online exchange web-site and wallet of which facilitates multiple virtual various currencies in addition to instant transactions. It is very around the globe accessible on several devices, such as notebook, desktop computer and smartphones. Cryptonator can be considered the generally good budget, although it may certainly not remain in reality with safety measures freaks because of it being online and very low larger sized potential of being hacked. Supported cryptocurrencies are Bitcoin, Dogecoin, Litecoin, Ethereum, Rush, Bitcoin Cash, Blackcoin, Emercoin, Monero, Peercoin, Primecoin, Reddcoin, Ripple, Zcash. cryptonator Jaxx. io Jaxx. io is really a multi-currency wallet that provides a good user-friendly and obtainable interface. Jaxx has ShapeShift implemented and it furthermore gives seed phrase to get coin recovery. Up to now at this time there have been bug studies, but they also have been resolved along with the coins were recuperated. jaxx Ledger Nano T Ledger Nano is some sort of very advised computer hardware finances by most crypto lieu owners. It comes with fantastic security and back up attributes. Ledger Nano even offers seeds phrasing if you�ve lost your coins. The charge is available and it supports Bitcoin, Dogecoin, ETH, Ripple, Dash, Zcash and other individuals. ledger ridotto s WalletGenerator

Paper billfolds are a offline way of keeping the Dogecoins harmless, as the necessary data can be published on a piece of paper. This type of wallet is usually good if you are deciding on storing coins for a long period of the time, but even if many people are protected from online problems, they are still insecure to damage and theft. However, added security could be extra by splitting typically the finances into shares the fact that reassemble the secret key element or have multiple tips produced. Check out WalletGenerator�s official web page. wallet turbine We hope the abovementioned list was needed to you and that simply by you have an thought of what type of Dogecoin finances you need.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Dogecoin Wallet
Dogecoin Core is often the official Dogecoin wallet mantained because of the Dogecoin foundation. The idea is the total Dogecoin client and thus calls for up a lot involving space while the idea downloads available the full blockchain. Theinitial synchronization will take some download some sort of lot connected with info. Although the consumer is certainly not rich around features, it will do present a high level involving safety as the individual keys will probably be created in addition to are living on your computer system. Dogecoin Primary Wallet Review Dogecoin Main is the total established version of the DOGE wallet. Initial harmonization using the blockchain is slow in comparison to lightweight versions, and the idea will have a lot of free space in the LAPTOP OR COMPUTER to install the Software. One can find versions for managing systems (Windows, OS A, Linux, Android mobile phone, Blackberry, Internet browser, Source, IOS). Dogecoin Primary is a good pretty fundamental wallet those can be operate as a total node to support the full DOGE Network. The installation is not actually complicated. If anyone don't want to any full client you could use any wallet program which works with DOGE. The particular most reliable choice to shield your currency is the Dogecoin Core wallet, using this plan you can store gold coins on your computer as a file. However , if the operating system is definitely reinstalled and no file backup has already been created, all of coins is going to be lost. Throughout supplement, this system automatically synchronizes with the Blockchain community upon completion of the particular installation. This one-time function can take about something like 20 hrs. And at often the end of the synchronized program will take thirty GB regarding hard storage space. Dogecoin. What exactly is it? All people knows or even has at the least heard of the Online sense which was the �Doge� meme. After the likeness associated with this famous Shiba Inu dog, the cryptocurrency Dogecoin was created. Since the launch in 2013, Dogecoin offers quickly gathered a impressive on the net area close to it, getting a good capitalization on CHF 60 , 000, 000 in 2014. As involving December 2017, it comes with reached a capitalization associated with USD 308 mil. Dogecoin is an open-source cryptocurrency that can be applied to purchase and sell off goods online, as well as business that for some other cryptocurrencies (such Bitcoin and altcoins) or maybe fiat various currencies. Dogecoin Wallet s and handbags Dogecoins need in order to be stored in a good Dogecoin Wallet . This pocket can be accessed by simply personal computer, smartphone or website, allowing the user to send, get and shop Dogecoins in some sort of subject of minutes. Basically, a good Dogecoin wallet acts as a bank account would any time handling your funds. At this time there are various kinds of billfolds which usually have been designed to help give you the individual needs connected with users. The main types of purses are: desktop, cellular, computer hardware, web together with papers. These wallets have different ranges of security and comfort so it�s very significant to choose the one particular that is best for you. Below is some sort of list of the best wallets and handbags for Dogecoin. dogecoin Dogecoin Core Dogecoin Core is the Doge�s public wallet. It downloads the entire blockchain and then it possesses to sync with this in order for this user to begin transactions. Because of this, their first connect is the bit more slowly in comparison to other people, and it also wants more room. This wallet is recommended intended for Dogecoin miners, as it is really secure and trustworthy. It is compatible with this following systems: House windows, OS IN THIS HANDSET X, Linux. MultiDoge MultiDoge is a desktop computer Dogecoin client which need not connect with the whole blockchain. Powered by Dogecoin, it may be a good light wallet which usually syncs fast and it is very very easy to employ. That will not be recommended the fact that this wallet be used for mining or prospecting, as that can be halt and unresponsive. The idea sustains House windows, OS Times, Cpanel. multidoge WowDoge WowDoge can be also a light finances designed for desktop use. This wallet eliminates frustrating waiting around time because it doesn�t have to download entire gigabytes of blockchain. The interface is user-friendly and it runs easily. You can request to have new features included. WowDoge is also free and even open source. wowdoge DogeChain pocket DogeChain is also a free of charge online pocket book with regard to you to store your Dogecoins. It�s quite easy and easy to make use of, permitting the end user for you to access his coins anywhere, anytime. dogechain budget Exodus. io Exodus is some sort of multi-coin wallet that will outlets many cryptocurrencies, one of them in addition being Dogecoin. System is usually known to be a safeguarded place to retain your virtual resources. The user interface is easy to make use of and is typically the only desktop software package in order to have ShapeShift built inside. You possibly can keep all your cryptocurrencies within a place and even conduct orders from a person application.

Exodus offers seed phrase which can be utilized to recover their money if the user�s laptop or computer arrives or even their hard push becomes corrupted. Exodus furthermore has good client help service. exodus Block. io Wallet Block. io will be an online web finances for multi-currency storage space in addition to transactions. Users can manage Dogecoin, Bitcoin and Litecoin from one account. Yet it is usually certainly not suggested you shop much throughout an online pocket, virtually no matter how trusted the particular site is definitely. block. io Cryptonator Finances Cryptonator is an online trade web page and wallet that facilitates multiple virtual stock markets in addition to instant transactions. It is globally accessible on many units, such as laptop computer, desktop computer and smartphones. Cryptonator is viewed as a new generally good pocket, however it may not necessarily stay okay with security freaks due to it currently being online and it has a larger sized potential of being hacked. Supported cryptocurrencies are Bitcoin, Dogecoin, Litecoin, Ethereum, Dash, Bitcoin Cash, Blackcoin, Emercoin, Monero, Peercoin, Primecoin, Reddcoin, Ripple, Zcash. cryptonator Jaxx. io Jaxx. io is often a multi-currency wallet that features a user-friendly and available program. Jaxx has ShapeShift implemented and it furthermore gives seed term for coin recovery. So far presently there have been bug reports, nonetheless they have also been sorted plus the coins were recuperated. jaxx Journal Nano S Journal Nano is a new very encouraged computer hardware pocket book by most crypto coin owners. The idea has got great security and data backup capabilities. Ledger Nano also offers seeds phrasing if you�ve lost your coins. The expense is available and it works with Bitcoin, Dogecoin, ETH, Ripple, Dash, Zcash and some others. ledger ridotto s WalletGenerator Paper billfolds are a great offline way of keeping your own Dogecoins safe, as typically the necessary data is definitely branded on a piece of paper. This kind of wallet is definitely good if you will be thinking of storing coins regarding a long period of their time, but even if they are protected from online episodes, they are still prone to decline and fraud. However, further security can be added by splitting the pocket book into shares the fact that reassemble the secret key element or have multiple take some time produced. Check out WalletGenerator�s official web site. wallet turbine We hope the particular abovementioned list was needed to be able to you and that by way of you now have a concept of which kind of Dogecoin pocket you need.
1 note
·
View note