#ImmutableObjects
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Exploring Record Classes in Java: The Future of Immutable Data Structures
A record in Java is a special type of class designed specifically for holding immutable data. Introduced in Java 14 as a preview feature and made stable in Java 16, records eliminate the need for writing repetitive boilerplate code while still providing all the essential functionalities of a data model.
Key Characteristics of Java Records
Immutable by Default – Once created, the fields of a record cannot be modified.
Automatic Methods – Java automatically generates equals(), hashCode(), and toString() methods.
Compact Syntax – No need for explicit constructors and getters.
Final Fields – Fields inside a record are implicitly final, meaning they cannot be reassigned.
How to Define a Record Class in Java
Defining a record class is straightforward. You simply declare it using the record keyword instead of class.
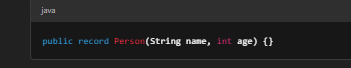
Example: Creating a Simple Record
java
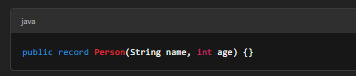
Using the Record Class
java
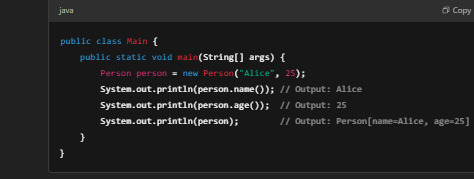
Notice how we access fields using methods like name() and age() instead of traditional getter methods (getName() and getAge()).
Comparing Records vs. Traditional Java Classes
Before records, we had to manually write constructors, getters, setters, and toString() methods for simple data structures.
Traditional Java Class (Without Records)
java
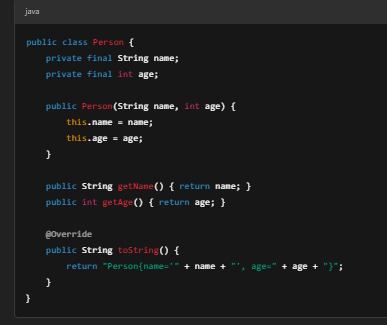
This approach requires extra lines of code and can become even more verbose when dealing with multiple fields.
With records, all of this is reduced to just one line:
java
When to Use Records?
Records are ideal for: ✔ DTOs (Data Transfer Objects) ✔ Immutable Data Representations ✔ Returning Multiple Values from a Method ✔ Reducing Boilerplate Code in Simple Models
Customizing Records: Adding Methods and Static Fields
Though records are immutable, you can still add methods and static fields for additional functionality.
Example: Adding a Custom Method
java
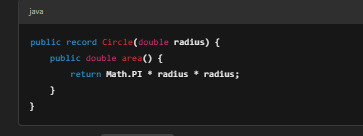
Now you can call circle.area() to calculate the area of a circle.
Using Static Fields in Records
java
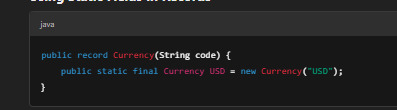
Limitations of Java Record Classes
While records are powerful, they do have some limitations: ❌ Cannot Extend Other Classes – Records implicitly extend java.lang.Record, so they cannot inherit from any other class. ❌ Immutable Fields – Fields are final, meaning you cannot modify them after initialization. ❌ Not Suitable for Complex Objects – If your object has behavior (methods that modify state), a traditional class is better.
Conclusion: Are Java Record Classes the Future?
Record classes offer a modern, efficient, and elegant way to work with immutable data structures in Java. By removing repetitive boilerplate code, they improve code readability and maintainability.
If you’re working with data-heavy applications, DTOs, or immutable objects, adopting records is a great way to simplify your Java code while ensuring efficiency.
What’s your experience with Java records? Share your thoughts in the comments! 🚀
FAQs
1. Can I modify fields in a Java record?
No, records are immutable, meaning all fields are final and cannot be changed after object creation.
2. Are Java records faster than regular classes?
Performance-wise, records are similar to normal classes but offer better readability and maintainability due to their compact syntax.
3. Can a record extend another class?
No, records cannot extend any other class as they already extend java.lang.Record. However, they can implement interfaces.
4. How are records different from Lombok’s @Data annotation?
While Lombok’s @Data generates similar boilerplate-free code, it requires an external library. Java records, on the other hand, are built into the language.
5. What Java version supports records?
Records were introduced as a preview feature in Java 14 and became a stable feature in Java 16. For more Info : DevOps with Multi Cloud Training in KPHB
#Java#CoreJava#JavaProgramming#JavaDeveloper#LearnJava#Coding#Programming#Tech#SoftwareDevelopment#ImmutableObjects#JavaRecords#OOP#CleanCode#CodeNewbie#DevLife#BackendDevelopment#Java21#TechBlog#CodeWithMe#100DaysOfCode#CodeSnippet#ProgrammingTips#TechTrends
0 notes