#Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Hackers Exploiting LiteSpeed Cache Plugin Flaw to Hijack WordPress Sites

Cybercriminals are actively exploiting a high-severity vulnerability in the widely-used LiteSpeed Cache plugin for WordPress to take over websites, according to researchers at WPScan. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2023-40000 with a CVSS score of 8.3, is an improper input neutralization flaw that allows stored cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. LiteSpeed Cache for WordPress (LSCWP) is an all-in-one site acceleration plugin with over 5 million active installations. It features server-level caching and various optimization capabilities. However, the recently disclosed vulnerability enables unauthenticated attackers to escalate privileges and create rogue admin accounts named "wpsupp‑user" and "wp‑configuser" on vulnerable sites. Once the malicious actors gain administrative access, they have complete control over the compromised WordPress website. Patchstack originally discovered the stored XSS vulnerability in February 2024, which can be triggered through specially crafted HTTP requests.
Surge in Exploitation Attempts Detected
WPScan reported a significant spike in access attempts to a malicious URL on April 2nd and April 27th, likely indicating widespread exploitation efforts. The researchers identified two prominent IP addresses involved in scanning for vulnerable sites: 94.102.51.144 with 1,232,810 requests, and 31.43.191.220 with 70,472 requests. The vulnerability was addressed by LiteSpeed Technologies in October 2023 with the release of version 5.7.0.1. However, unpatched sites remain at risk of compromise. WPScan has provided indicators of compromise (IoCs) for these attacks, including malicious URLs like https//dnsstartservicefounds.com/service/fphp, https//apistartservicefoundscom, and https//cachecloudswiftcdncom. Additionally, users should watch out for the IP address 45.150.67.235, which has been associated with the malware campaign.
Urgent Patching Recommended
WordPress site owners and administrators are strongly advised to update their LiteSpeed Cache plugin to the latest patched version as soon as possible to mitigate the risk of exploitation and potential website takeover. Read the full article
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cyber Threat Intelligence: Staying Ahead of Attacks

Cyber threats are continuously increasing and reaching new heights in their level of complexity and sophistication in today's interconnected digital landscape. From state-sponsored attacks to organized cyber-crimes, each of these threats keeps evolving to bombard organizations through new avenues. Treating breaches after the occurrence is an outdated strategy. In interventional terms, this is where Cyber Threat Intelligence plays an important role, giving businesses and security experts the ability to convert raw data into actionable insights so as to stay ahead of attacks.
In essence, CTI is a prerequisite for proactive cybersecurity because it facilitates decision-making and risk mitigation in the face of a continuously abreast foe. Instead of spending all their time fighting fires, organizations should be looking ahead to anticipate threats, rather than basing themselves back against the wall.
What is Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)?
At its core, Cyber Threat Intelligence (or CTI, threat intelligence) is detailed, contextual, actionable knowledge about existing or emerging cybersecurity threats. It is more than just raw threat data (like an IP address associated with an attack); it also provides context, analysis, and recommendations.
If we consider:
Threat Data: Suspicious IP addresses.
Threat Information: Those IP addresses were used in a phishing campaign last week.
Cyber Threat Intelligence: Those IP addresses were used by a known cybercriminal group (we'll call them "RedFox") that targets organizations in your industry using spear-phishing techniques. Here are the more common Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) and Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) of these adversaries, and this is how you can defend against them proactively.
It is this transformation of raw data into actionable intelligence that really makes Cyber Threat Intelligence valuable.
Why CTI is Essential for Staying Ahead of Attacks:
Proactive Defense: CTI helps organizations anticipate and prevent attacks before they happen. Knowing that knowing the adversary's motives, methods (TTPs), and targets-the-security teams can highlight weaknesses in defense and thus reduce their potential attack surface.
Informed Decision-Making: At a strategic level, in terms of the threat landscape, this can allow CISOs and executives to make informed decisions about security investments, risk management, and resource
Swift Incident Response: CTI can also provide the relevant context during the incident to help the response team ascertain the nature of the attack, assess the scope and potential impact, and thereby initiate containment and remediation much faster.
Resource Optimization: Knowing which threats are most relevant and critical to their organization, security teams can then focus their attention and resources on them as opposed to spending time on issues that offer little risk.
Enhanced Situational Awareness: CTI provides insight into the threats of the global domain as well as the concerned industry so that organizations keep abreast of emerging risks and change their security posture according to them.
Types of Cyber Threat Intelligence:
CTI is typically categorized into different types based on its audience and purpose:
1. Strategic Threat Intelligence:
Focus: High-level, non-technical overview of the global threat landscape.
Audience: Executives, Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs), and board members.
Purpose: To inform long-term cybersecurity strategy, risk management, and budgetary allocation. Some reports may cover geopolitical cyber warfare; others may focus on threat trends affecting specific industries or large ransomware campaigns.
2. Operational Threat Intelligence:
Focus: On threat actors' TTPs, motivations, and campaigns.
Audience: Security operations teams, incident responders, and threat hunters.
Purpose: To predict attacks for identified adversaries and provide enabling information during an incident investigation; for example, details about how a particular threat group "APT" operates and breaches networks.
3. Tactical Threat Intelligence:
Focus: Technical details about specific Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) – the "fingerprints" of an attack.
Audience: Security analysts, security engineers.
Purpose: Immediately actionable data to detect and block threats. Examples include malicious IP addresses, domain names, file hashes of known malware, and specific phishing email subject lines. This is often integrated directly into security tools like SIEMs and firewalls.
Implementing and Leveraging CTI:
Typically, organisations implement the consequent steps to put the CTI into practice:
Collect Data: Obtain raw data outputs and threat activity from various sources (open-source intelligence, dark web forums, threat intelligence feeds, internal security logs, human intelligence).
Process & Analyze: Convert raw data into intelligence by excluding irrelevant data, correlating pertinent data, and uncovering patterns to define adversary behavior.
Integrate: Integrate the intelligence with existing security solutions (SIEM, SOAR, EDR, firewalls) to perform automatic detection and response.
Disseminate: Disseminate relevant intelligence among stakeholders (executives, security teams) in an easily understandable manner.
Continuous Improvement: Remember that CTI is never a set-it-and-forget-it toolkit; it needs constant monitoring, updates, and adaptation as the threat landscape keeps evolving.
With this era being an ever-increasing and ever-changing challenge posed by cyber threats, Intelligence is no longer a luxury but an absolute necessity on the side of cybersecurity. Actively working with CTI allows organizations to move on the offensive rather than sit in a reactive position defending against a digital onslaught, keeping their digital assets secure and ensuring uninterrupted business operations in the hostile cyber world.
Contact us
Call now on +91 9825618292
Visit Our Website: http://tccicomputercoaching.com/
0 notes
Text
What Makes EDSPL’s SOC the Nerve Center of 24x7 Cyber Defense?

Introduction: The New Reality of Cyber Defense
We live in an age where cyberattacks aren’t rare—they're expected. Ransomware can lock up entire organizations overnight. Phishing emails mimic internal communications with eerie accuracy. Insider threats now pose as much danger as external hackers. And all this happens while your teams are working, sleeping, or enjoying a weekend away from the office.
In such an environment, your business needs a Security Operations Center (SOC) that doesn’t just detect cyber threats—it anticipates them. That’s where EDSPL’s SOC comes in. It’s not just a monitoring desk—it’s the nerve center of a complete, proactive, and always-on cyber defense strategy.
So, what makes EDSPL’s SOC different from traditional security setups? Why are enterprises across industries trusting us with their digital lifelines?
Let’s explore, in depth.
1. Around-the-Clock Surveillance – Because Threats Don’t Take Holidays
Cyber attackers operate on global time. That means the most devastating attacks can—and often do—happen outside regular working hours.
EDSPL’s SOC is staffed 24x7x365 by experienced cybersecurity analysts who continuously monitor your environment for anomalies. Unlike systems that rely solely on alerts or automation, our human-driven vigilance ensures no threat goes unnoticed—no matter when it strikes.
Key Features:
Continuous monitoring and real-time alerts
Tiered escalation models
Shift-based analyst rotations to ensure alertness
Whether you’re a bank in Mumbai or a logistics firm in Bangalore, your systems are under constant protection.
2. Integrated, Intelligence-Driven Architecture
A SOC is only as good as the tools it uses—and how those tools talk to each other. EDSPL’s SOC is powered by a tightly integrated stack that combines:
Network Security tools for perimeter and internal defense
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) for collecting and correlating logs from across your infrastructure
SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) to reduce response time through automation
XDR (Extended Detection and Response) for unified visibility across endpoints, servers, and the cloud
This technology synergy enables us to identify multi-stage attacks, filter false positives, and take action in seconds.
3. Human-Centric Threat Hunting and Response
Even the best tools can miss subtle signs of compromise. That’s why EDSPL doesn’t rely on automation alone. Our SOC team includes expert threat hunters who proactively search for indicators of compromise (IoCs), analyze unusual behavior patterns, and investigate security gaps before attackers exploit them.
What We Hunt:
Zero-day vulnerabilities
Insider anomalies
Malware lateral movement
DNS tunneling and data exfiltration
This proactive hunting model prevents incidents before they escalate and protects sensitive systems like your application infrastructure.
4. Multi-Layered Defense Across Infrastructure
Cybersecurity isn’t one-size-fits-all. That’s why EDSPL’s SOC offers multi-layered protection that adapts to your unique setup—whether you're running on compute, storage, or backup systems.
We secure:
Switching and routing environments
On-premise data centers and hybrid cloud security models
Core network devices and data center switching fabric
APIs, applications, and mobility endpoints through application security policies
No layer is left vulnerable. We secure every entry point, and more importantly—every exit path.
5. Tailored Solutions, Not Templates
Unlike plug-and-play SOC providers, EDSPL dives deep into your business architecture, industry regulations, and operational needs. This ensures our SOC service adapts to your challenges—not the other way around.
Whether you’re a healthcare company with HIPAA compliance needs, or a fintech firm navigating RBI audits, we offer:
Custom alert thresholds
Role-based access control
Geo-fencing and behavioral analytics
Industry-specific compliance dashboards
That’s the EDSPL difference—we offer tailored SOC services, not templated defense.
6. Fully Managed and Maintained – So You Focus on Business
Hiring, training, and retaining a cybersecurity team is expensive. Most businesses struggle to maintain their own SOC due to cost, complexity, and manpower limitations.
EDSPL eliminates that burden with its Managed and Maintenance Services. From deployment to daily operations, we take complete ownership of your SOC infrastructure.
We offer:
Security patch management
Log retention and archiving
Threat intelligence updates
Daily, weekly, and monthly security reports
You get enterprise-grade cybersecurity—without lifting a finger.
7. Real-Time Visibility and Reporting
What’s happening on your network right now? With EDSPL’s SOC, you’ll always know.
Our customizable dashboards allow you to:
Monitor attack vectors in real time
View compliance scores and threat levels
Track analyst responses to incidents
Get reports aligned with Services KPIs
These insights are vital for C-level decision-makers and IT leaders alike. Transparency builds trust.
8. Scalable for Startups, Suitable for Enterprises
Our SOC is designed to scale. Whether you’re a mid-sized company or a multinational enterprise, EDSPL’s modular approach allows us to grow your cybersecurity posture without disruption.
We support:
Multi-site mobility teams
Multi-cloud and hybrid setups
Third-party integrations via APIs
BYOD and remote work configurations
As your digital footprint expands, we help ensure your attack surface doesn’t.
9. Rooted in Vision, Driven by Expertise
Our SOC isn’t just a solution—it’s part of our Background Vision. At EDSPL, we believe cybersecurity should empower, not limit, innovation.
We’ve built a culture around:
Cyber resilience
Ethical defense
Future readiness
That’s why our analysts train on the latest attack vectors, attend global security summits, and operate under frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK and NIST CSF.
You don’t just hire a service—you inherit a philosophy.
10. Real Impact, Real Stories
Case Study 1: Ransomware Stopped in Its Tracks
A global logistics client faced a rapidly spreading ransomware outbreak on a Friday night. Within 15 minutes, EDSPL’s SOC identified the lateral movement, isolated the infected devices, and prevented business disruption.
Case Study 2: Insider Threat Detected in Healthcare
A hospital’s employee tried accessing unauthorized patient records during off-hours. EDSPL’s SOC flagged the behavior using our UEBA engine and ensured the incident was contained and reported within 30 minutes.
These aren’t hypothetical scenarios. This is what we do every day.
11. Support That Goes Beyond Tickets
Have a concern? Need clarity? At EDSPL, we don't bury clients under ticket systems. We offer direct, human access to cybersecurity experts, 24x7.
Our Reach Us and Get In Touch teams work closely with clients to ensure their evolving needs are met.
From technical walkthroughs to incident post-mortems, we are your extended cybersecurity team.
12. The Future Is Autonomous—And EDSPL Is Ready
As cyberattacks become more AI-driven and sophisticated, so does EDSPL. We're already integrating:
AI-based threat intelligence
Machine learning behavioral modeling
Predictive analytics for insider threats
Autonomous remediation tools
This keeps us future-ready—and keeps you secure in an ever-evolving world.
Final Thoughts: Why EDSPL’s SOC Is the Backbone of Modern Security
You don’t just need protection—you need presence, prediction, and precision. EDSPL delivers all three.
Whether you're securing APIs, scaling your compute workloads, or meeting global compliance benchmarks, our SOC ensures your business is protected, proactive, and prepared—day and night.
Don’t just react to threats. Outsmart them.
✅ Partner with EDSPL
📞 Reach us now | 🌐 www.edspl.net
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
APT41’s Actions Highlight the Need for Threat Monitoring

This blog post discusses malware attack chain technology, delivery tactics, and other APT41 operations. We also explain indications of compromise (IOCs) to help security professionals protect against similar attacks. GTIG used customised detection signatures, stopped attacker-controlled infrastructure, and strengthened Safe Browsing to defeat this attempt.
APT41
APT41, a Chinese cyber threat group, commits both commercial cybercrime and state-sponsored espionage. Group uses modern espionage software for its own gain. China promotes its economic interests through high-tech and healthcare strategic espionage and profits from video gaming. APT41 is skilled, persistent, and agile, using malware, supply chain breaches, and spear-phishing. Cybercrime and government are complex, as APT41's criminal acts may have government ties.
Chinese Cyber Group APT41 Blends Personal Crime with State Espionage
According to a detailed FireEye Intelligence study published on Google Cloud Blog, APT41, a well-known Chinese cyber threat cell, is purportedly conducting state-sponsored espionage and financially driven operations. This group is notable among China-based entities being watched because it appears to exploit private malware, generally used for espionage, for personal gain. Evidence suggests APT41 has been committing cybercrime and cyberespionage since 2014.
APT41's espionage targets match China's five-year economic growth goals. They have established key access to telecommunications, high-tech, and healthcare companies. Targeting telecom firms' call record data and targeting news/media corporations, travel agencies, and higher education institutions shows that the organisation tracks people and conducts surveillance. APT41 may have targeted a hotel's reservation systems before Chinese authorities came for security reconnaissance.
APT41 has targeted the video game sector with ransomware and virtual currency manipulation. They can switch between Linux and Windows to reach game production environments. The cryptographic certificates and source code needed to sign malware are taken from these settings. Importantly, it has used this access to put malicious code into trustworthy files and disseminate them to victim firms using supply chain breach techniques.
These supply chain compromises have defined APT41's most notorious espionage. APT41 restricts the deployment of follow-on malware in multi-stage operations by matching against unique system IDs, considerably obfuscating the intended targets and limiting delivery to only the targeted victims, notwithstanding the effort.
The malware families and tools used by APT41 include public utilities, shared malware with other Chinese espionage organisations, and unique tools. Spear-phishing emails with HTML attachments often compromise. After entering, they can utilise rootkits, credential stealers, keyloggers, and backdoors. APT41 sparingly uses rootkits and MBR bootkits to mask malware and maintain persistence on high-value targets. This adds stealth because the function runs before OS initialisation.
The group is fast and relentless. They quickly find and break intermediary systems to access network portions. In two weeks, they breached hundreds of systems across segments and regions. In addition, they are persistent and quick to adapt. After a victim company makes changes or users download infected attachments, APT41 can gather new malware, register new infrastructure, and re-establish itself in compromised systems across numerous locations within hours.
APT41 may be linked to Chinese-language forum users “Zhang Xuguang” and “Wolfzhi”. These people suggested publicising their skills and services to be hired.
Comparing online gaming goals to APT41's working hours, “Zhang Xuguang” recommended “moonlighting.” These individuals are suspected of espionage due to persona data, programming proficiency, and targeting of Chinese-market online games. Operational activity mapping since 2012 suggests APT41 conducts financially motivated operations outside of workdays.
APT41's originality, expertise, and resourcefulness are shown by their unique use of supply chain breaches, regular use of compromised digital certificates to sign malware, and infrequent use of bootkits among Chinese APT groups. Since 2015, APT41, like other Chinese espionage organisations, has shifted from direct intellectual property theft to strategic information gathering and access management, despite their continued financial interest in the video game sector. As their targeting and capabilities have grown, supply chain compromises in various industries may increase.
APT41 may receive safeguards to conduct for-profit operations or be ignored due to its linkages to state-sponsored and underground markets. They could have also avoided notice. These operations show a blurred line between government and crime, which threatens ecosystems and is exemplified by APT41.
For more details visit govindhtech.com
#APT41#supplychain#cybercrime#Chinesecyberthreat#MasterBootRecord#indicatorsofcompromise#technology#technews#technologynews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Hiring Entry-Level Cyber Talent? Start with CSA Certification
In today's increasingly digital landscape, the threat of cyberattacks looms larger than ever. Businesses of all sizes are grappling with sophisticated threats, making robust cybersecurity defenses not just a luxury, but a necessity. At the forefront of this defense are Security Operations Center (SOC), and the unsung heroes within them: SOC Analysts.
However, a critical challenge many organizations face is bridging the talent gap in cybersecurity. The demand for skilled professionals far outstrips the supply, particularly at the entry-level. This is where strategic hiring practices, coupled with valuable certifications like the Certified SOC Analyst (C|SA) certification, become paramount.
The Ever-Growing Need for SOC Analysts
The role of a SOC analyst is pivotal. They are the frontline defenders, tirelessly monitoring an organization's systems and networks for suspicious activity, detecting threats, and initiating rapid responses to mitigate potential damage. From analyzing logs and alerts to investigating incidents and implementing containment measures, their work is continuous and critical.
The job outlook for information security analysts, which includes SOC analysts, is incredibly strong. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 33% growth from 2023 to 2033, a rate significantly faster than the average for all occupations. This translates to approximately 17,300 job openings each year, highlighting the immense demand for these professionals. As cyber threats evolve in sophistication and frequency, and as businesses increasingly embrace digital transformation and remote work, the need for skilled SOC analysts will only intensify.
What Does an Entry-Level SOC Analyst Do?
An entry-level SOC analyst, often referred to as a Tier 1 analyst, serves as the first line of defense within a Security Operations Center. Their primary responsibilities include:
Monitoring Security Alerts: Continuously observing security alerts generated by various systems such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management), IDS/IPS (Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems), and endpoint protection1 tools.
Initial Triage and Prioritization: Assessing the severity and legitimacy of alerts, distinguishing between false positives and genuine threats, and prioritizing them for further investigation.
Log Analysis: Examining logs from different sources (servers, workstations, network devices) to understand security events and identify indicators of compromise (IoCs).
Following Playbooks: Executing established procedures and playbooks for common security scenarios and incident response.
Documentation: Meticulously documenting findings, actions taken, and the progression of security incidents.
Escalation: Escalating confirmed or complex threats to higher-tier SOC analysts (Tier 2 or Tier 3) for deeper investigation and remediation.
While a bachelor's degree in computer science or a related field can be beneficial, it's not always a strict prerequisite for entry-level SOC roles. Many successful SOC analysts enter the field through dedicated cybersecurity courses, bootcamps, or relevant certifications.
Key Skills for Aspiring SOC Analysts
To excel as an entry-level SOC analyst, a combination of technical and soft skills is essential:
Technical Skills:
Network Fundamentals: A solid understanding of network protocols (TCP/IP, DNS, DHCP), network architecture, and common network devices (firewalls, routers).
Operating System Knowledge: Familiarity with various operating systems (Windows, Linux) and their security configurations.
Security Technologies: Practical knowledge of security tools like SIEM systems, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), antivirus software, and vulnerability scanners.
Log Analysis: The ability to effectively analyze security logs from diverse sources to identify anomalies and malicious activities.
Incident Response Basics: Understanding the fundamental steps of incident response, including detection, containment, eradication, and recovery.
Threat Intelligence: An awareness of current cyber threats, attack methodologies, and indicators of compromise.
Basic Scripting (Optional but beneficial): Familiarity with scripting languages like Python can help automate tasks and analyze data more efficiently.
Soft Skills:
Analytical and Problem-Solving: The ability to think critically, analyze complex information, and identify root causes of security incidents.
Attention to Detail: Meticulousness in examining logs and alerts to avoid missing crucial details.
Communication: Clear and concise written and verbal communication skills to document incidents and collaborate with team members and other departments.
Adaptability: The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, so the ability to learn new technologies and adapt to emerging threats is vital.
Teamwork: SOC operations are often a collaborative effort, requiring effective communication and coordination with colleagues.
The Value of SOC Certifications for Entry-Level Talent
For individuals looking to break into the cybersecurity field as a SOC analyst, and for employers seeking to identify qualified entry-level talent, SOC certifications play a crucial role. These certifications validate a candidate's foundational knowledge and practical skills, providing a standardized benchmark of competence.
While several certifications can aid an aspiring SOC analyst, the Certified SOC Analyst (C|SA) certification by EC-Council stands out as a strong starting point, particularly for those targeting Tier I and Tier II SOC roles.
Why CSA Certification is a Game-Changer for Entry-Level SOC Hiring
The Certified SOC Analyst (C|SA) certification is specifically engineered to equip current and aspiring SOC analysts with the proficiency needed to perform entry-level and intermediate-level operations. Here's why the C|SA certification is a significant asset for hiring entry-level cyber talent:
Tailored for SOC Operations: Unlike broader cybersecurity certifications, C|SA is designed with the explicit needs of a Security Operations Center in mind. Its curriculum covers the end-to-end SOC workflow, from initial alert monitoring to incident response and reporting.
Comprehensive Skill Development: The C|SA program delves into critical areas such as:
Security Operations and Management: Understanding the principles and practices of managing a SOC.
Understanding Cyber Threats, IoCs, and Attack Methodology: Gaining knowledge of common cyber threats, indicators of compromise, and attack techniques.
Incidents, Events, and Logging: Learning about log management, correlation, and the significance of various security events.
Incident Detection with SIEM: Mastering the use of Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions for effective incident detection.
Enhanced Incident Detection with Threat Intelligence: Integrating threat intelligence feeds into SIEM for proactive threat identification.
Elaborate Understanding of SIEM Deployment: Gaining practical insights into deploying and configuring SIEM solutions.
Hands-On, Practical Learning: The C|SA program emphasizes practical skills through lab-intensive sessions. Candidates get hands-on experience with incident monitoring, detection, triaging, analysis, containment, eradication, recovery, and reporting. This practical exposure is invaluable for entry-level professionals who often lack real-world experience.
Real-time Environment Simulation: The labs in the C|SA program simulate real-time SOC environments, allowing candidates to practice identifying and validating intrusion attempts using SIEM solutions and threat intelligence, mirroring actual job scenarios.
Compliance with Industry Frameworks: The C|SA certification aligns 100% with the National Initiative for Cybersecurity Education (NICE) framework, specifically under the "Protect and Defend (PR)" category for the role of Cyber Defense Analysis (CDA). This alignment ensures that C|SA-certified individuals possess skills recognized and valued across the industry.
Global Recognition: Accredited by EC-Council, a globally recognized authority in cybersecurity certifications, the C|SA credential enhances career prospects and demonstrates proficiency to potential employers worldwide.
Clear Career Pathway: For aspiring SOC analyst professionals, the C|SA serves as the foundational step, providing them with the necessary skills and knowledge to enter a SOC team at Tier I or Tier II level. This creates a clear and achievable career path.
Beyond Certification: What Else to Look For
While the C|SA certification is an excellent indicator of a candidate's readiness for an entry-level SOC analyst role, employers should also consider other factors during the hiring process:
Passion and Curiosity: Cybersecurity is a rapidly evolving field. Look for candidates who demonstrate genuine enthusiasm for continuous learning and a strong desire to stay updated on the latest threats and technologies.
Problem-Solving Aptitude: Assess their ability to think critically and approach challenges systematically.
Communication Skills: Strong communication is vital for collaborating within the SOC team and explaining technical issues to non-technical stakeholders.
Any Relevant Experience: Even internships, personal projects, or volunteer work in cybersecurity can demonstrate practical application of skills.
Cultural Fit: A candidate's ability to integrate into the team dynamics and contribute positively to the SOC environment.
Conclusion
As the cybersecurity landscape continues to grow in complexity and threat sophistication, the demand for skilled SOC analysts will only intensify. For organizations seeking to build a robust and responsive security team, investing in entry-level talent is crucial. The Certified SOC Analyst (C|SA) certification offers a highly relevant and practical pathway for aspiring professionals to gain the necessary skills, making them a valuable asset from day one. By prioritizing candidates with foundational certifications like C|SA, employers can confidently onboard individuals who are not just theoretically knowledgeable, but also practically equipped to contribute to their security operations and safeguard their digital assets.
0 notes
Text
Enhancing Cybersecurity Resilience
Discover how a modern Threat Intelligence Platform empowers organizations with actionable insights, proactive defense, and next-gen cybersecurity capabilities.
In the ever-evolving digital world, cybersecurity threats have grown in complexity, frequency, and scale. From ransomware and phishing attacks to data breaches and nation-state cyber espionage, the digital threat landscape has expanded into a vast, dynamic battlefield. For organizations aiming to remain secure, simply reacting to threats after they happen is no longer a viable option.

Today, security teams must be proactive, predictive, and precise in their threat response strategies. This is where a Threat Intelligence Platform (TIP) plays a vital role. Rather than operating in silos or relying solely on isolated security tools, a modern TIP serves as a centralized hub for collecting, analyzing, and distributing threat data in real-time—empowering cybersecurity professionals to make informed decisions faster.
In this article, we delve deep into what makes a Threat Intelligence Platform essential in the modern age, how it integrates with other security protocols, and why forward-looking organizations are investing in it to build stronger cyber defenses.
Understanding the Role of a Threat Intelligence Platform
A Threat Intelligence Platform is not just another security tool—it is a strategic asset. It aggregates threat data from multiple sources, correlates information, and offers context-rich insights that help in identifying and mitigating cyber threats before they manifest into breaches.
The core functions of a TIP include:
Data Aggregation: Collects structured and unstructured threat data from external feeds, internal systems, and global cybersecurity communities.
Analysis and Correlation: Uses advanced algorithms, machine learning, and contextual linking to correlate data points across diverse threat vectors.
Threat Prioritization: Automatically ranks threats based on relevance, severity, and business impact.
Actionable Intelligence Delivery: Integrates with SIEMs, firewalls, and incident response platforms to deliver real-time alerts and automated response actions.
Ultimately, a TIP transforms raw data into actionable threat intelligence, reducing the burden on security analysts and enabling faster incident detection and response.
The Increasing Complexity of the Cyber Threat Landscape
Cybercriminals today use sophisticated methods to infiltrate networks. Techniques like spear-phishing, zero-day exploits, and AI-driven malware are growing in prevalence. Furthermore, the lines between criminal groups, hacktivists, and nation-state actors are increasingly blurred, adding layers of complexity.
Key trends include:
Multi-Stage Attacks: Attackers often use a chain of exploits to gain access and maintain persistence in a system.
Supply Chain Threats: Vendors and third-party providers are now frequent targets, becoming indirect entry points.
Living-off-the-Land Attacks: Cybercriminals use legitimate tools (e.g., PowerShell, Windows Management Instrumentation) to avoid detection.
To counter such tactics, organizations need visibility not just within their internal environments but across the global threat ecosystem. This is where the strategic advantage of a TIP comes into play.
Features of an Effective Threat Intelligence Platform
Not all TIPs are created equal. The most effective platforms provide a range of features that enhance detection, analysis, and response:
1. Automated Data Collection
A TIP should automatically collect data from various threat feeds, security logs, dark web sources, and open databases. Automation reduces manual workload and ensures real-time threat visibility.
2. Advanced Threat Correlation
The platform must be capable of correlating indicators of compromise (IOCs) such as IP addresses, file hashes, domain names, and malware signatures across different incidents to uncover patterns.

3. Integration with Security Ecosystems
A TIP that integrates with SIEM, SOAR, EDR, and firewall solutions ensures that insights are not siloed but can trigger immediate security actions.
4. Contextual Threat Enrichment
Context is key. The TIP should enrich threat data with geographical, behavioral, and historical insights to aid faster and more accurate decision-making.
5. Collaborative Intelligence Sharing
Sharing threat intelligence across industry groups, ISACs, and global cyber communities strengthens collective security.
Use Case: Proactive Defense in Financial Services
Financial institutions are a prime target for cybercriminals due to the high-value data they hold. Let’s consider a mid-size bank integrating a TIP into its security framework.
Scenario:
A suspicious domain is flagged on a global threat feed. The TIP correlates this IOC with phishing attempts targeting banking customers in Asia. Upon further analysis, the platform uncovers malware strains associated with credential theft. The platform alerts the SOC (Security Operations Center) and triggers automated rules to block the domain at the firewall level.
This real-time detection and action, driven by the TIP, prevents a potential breach and demonstrates how actionable intelligence can drastically reduce incident response time and damage.
How TIPs Leverage Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT)
Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) refers to data collected from publicly available sources such as news reports, forums, blogs, social media, code repositories, and more. When integrated with a Threat Intelligence Platform, OSINT enhances the scope and depth of intelligence gathering.
For example, attackers often discuss vulnerabilities or leak data on underground forums. A TIP that harvests OSINT can pick up on these signals early, offering preemptive insights before the threat becomes widespread.
Additionally, by analyzing chatter patterns, sentiment, and keywords, TIPs can identify emerging attack vectors or vulnerable sectors—enabling organizations to prepare in advance.
The Power of Cyber Threat Analysis in TIPs
Cyber Threat Analysis is the heart of any effective threat intelligence strategy. A TIP streamlines this process by offering analytics dashboards, pattern recognition engines, and predictive modeling tools. It breaks down raw data into:
Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) of attackers.
Attack timelines and kill chain mapping.
Threat actor attribution based on behavior and tools used.
This deep analysis enables security teams to distinguish between random noise and real threats, reducing alert fatigue and boosting operational efficiency.
Moreover, advanced platforms use AI and machine learning to improve over time, identifying new threat variants and behavioral patterns that may otherwise go unnoticed.
Importance of Digital Risk Protection in TIP Integration
Today’s attack surfaces extend beyond corporate firewalls. Executives, employees, vendors, and third-party platforms create a digital footprint that’s often unmonitored. This is where Digital Risk Protection (DRP) comes into play.

By integrating DRP capabilities into a TIP, organizations gain visibility into:
Brand impersonation attempts.
Leaked credentials on the dark web.
Domain spoofing and phishing sites.
Social media threats and impersonation.
This holistic visibility allows organizations to safeguard their brand reputation, intellectual property, and customer trust more effectively.
Threat Intelligence Platform Deployment: Challenges and Solutions
While the advantages of TIPs are compelling, implementing them does come with challenges. Let’s explore a few and how organizations can address them:
1. Data Overload
Many TIPs collect vast amounts of data, which can become overwhelming. The solution lies in deploying machine learning filters and customizable threat scoring models to highlight what matters most.
2. False Positives
Too many false positives can waste time and resources. A TIP with behavior-based analysis and contextual enrichment significantly reduces such noise.
3. Integration Issues
Legacy systems might not integrate well with newer TIPs. Opt for platforms with strong API support and modular architecture for smoother interoperability.
4. Skilled Workforce
Threat intelligence requires expertise. While TIPs automate many functions, upskilling teams and investing in regular training ensures that organizations derive maximum value from their platforms.
Future of Threat Intelligence Platforms
With the increasing digitization of services and rise in remote work, the importance of real-time, predictive cybersecurity has never been greater. The future of TIPs lies in:
AI-Driven Threat Prediction: Using neural networks and behavioral analytics to forecast threats before they manifest.
Cloud-Native Architecture: Offering scalable, elastic intelligence solutions for hybrid and cloud-native enterprises.
Blockchain for Threat Data Integrity: Ensuring the immutability and trustworthiness of shared intelligence.
Global Threat Intelligence Sharing Consortiums: Encouraging collective intelligence sharing to counter global threats collaboratively.
Organizations that invest early in TIPs are setting themselves up for long-term resilience and competitiveness.
Conclusion
In an age where cyber threats evolve by the minute, waiting for an incident to happen is no longer a luxury any organization can afford. A modern Threat Intelligence Platform doesn’t just help organizations react—it equips them to anticipate, prepare, and act swiftly.
From aggregating data to conducting in-depth Cyber Threat Analysis, from tapping into Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) to enhancing Digital Risk Protection, a TIP acts as a central nervous system for proactive cybersecurity defense.
At DeXpose, we believe in empowering enterprises with cutting-edge threat intelligence solutions. Our mission is to help businesses stay a step ahead of adversaries by providing tools and insights that foster cyber resilience.
Are you ready to strengthen your organization’s cyber defense posture? Reach out to DeXpose today and explore how our intelligence-driven solutions can transform your approach to cybersecurity.
0 notes
Text
Cyber Clues You Shouldn’t Miss – What Are IoCs?
Indicators of Compromise are like breadcrumbs hackers leave behind. Find out how to detect them, understand IoA vs IoC, and keep your AWS, Azure, and Veeam backups secure. Click here to read the full article : What Are Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)?
1 note
·
View note
Text
This image gives a solid, compact breakdown of what a Next Generation Firewall (NGF) actually does. It’s way more than just blocking ports like the old-school firewalls. These bad boys are the Swiss Army knife of cybersecurity—combining multiple tools into one powerhouse of a system. Here’s a detailed look at each feature shown:
⸻
Core Capabilities of a Next Generation Firewall (NGF):
1. Antivirus
Blocks known malware and viruses at the perimeter.
2. Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
Detects and prevents malicious traffic using signatures and behavior analysis.
3. Mobile Security
Extends firewall protection to mobile users and endpoints.
4. Threat Intelligence Service
Feeds live data about current threats into the NGF for real-time defense.
5. Antispam
Blocks phishing and spam-based attacks, especially in emails.
6. Vulnerability Management
Identifies and manages security flaws in systems or software.
7. Virus Outbreak Protection Service
Early detection of new virus variants through heuristic analysis and sandboxing.
8. IP Reputation
Blocks or flags traffic from known malicious IPs.
9. Content Disarm & Reconstruction (CDR)
Strips potentially dangerous content from documents and reconstructs safe versions.
10. Industrial Security
Secures SCADA/ICS systems often used in factories and utilities.
11. Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
Monitors cloud service use and enforces security policies for SaaS apps.
12. Application Control
Manages and restricts access to applications by user, group, or device.
13. Web Filtering
Blocks access to malicious or inappropriate websites.
14. Security Rating Service
Gives your network or firewall a security score based on current configurations and threats.
15. Web Security
Protects against threats from web browsing like drive-by downloads and malicious scripts.
16. Indicators of Compromise (IoC)
Detects subtle signs that a system may be compromised.
⸻
Why This Matters:
Next-Gen Firewalls don’t just filter traffic—they analyze behavior, apply AI-based detection, and adapt in real-time. Whether you’re working in cybersecurity, IT management, or penetration testing, understanding NGF features helps you:
• Design layered defenses
• Troubleshoot with more context
• Detect threats earlier
• Improve security posture assessments
⸻
Want to go deeper into how NGFs are implemented or maybe compare top vendors like Fortinet, Palo Alto, or Cisco Firepower
0 notes
Text
Experts Reveal: "Hacking of Moroccan Platforms" Just a "False Flag" Operation, Global Campaign Targeted "Oracle Cloud"
Rabat – Cybersecurity experts, after extensive research and verification, have revealed that the narrative circulating about Algerian hackers breaching Moroccan online platforms is merely a “false flag operation” that lacks any digital forensics evidence or Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) to substantiate the claim. The experts clarified that the actual breach targeted the Oracle Cloud IaaS…
0 notes
Text
Akira Ransomware Breaches Over 250 Global Entities, Rakes in $42 Million
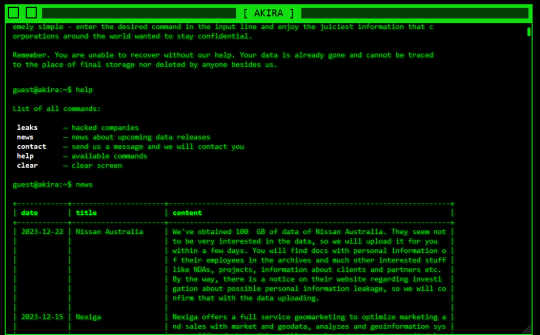
A joint cybersecurity advisory issued by CISA, FBI, Europol, and the Dutch NCSC-NL has uncovered the staggering scale of the Akira ransomware campaign. Since early 2023, the nefarious Akira operators have compromised more than 250 organizations worldwide, extorting a whopping $42 million in ransom payments. Akira's Prolific Targeting Across Industries The Akira ransomware group has been actively infiltrating entities across diverse sectors, including education, finance, and real estate. Staying true to the double extortion playbook, the threat actors exfiltrate sensitive data before encrypting the victims' systems, amplifying the pressure for a ransom payment. Early Akira versions, coded in C++, appended the .akira extension to encrypted files. However, from August 2023 onward, certain attacks deployed Megazord, a Rust-based variant that encrypts data with the .powerranges extension. Investigations reveal the perpetrators interchangeably using both Akira and Megazord, including the updated Akira_v2. Initial Access and Privilege Escalation The cybercriminals exploit various entry points, such as unprotected VPNs, Cisco vulnerabilities (CVE-2020-3259 and CVE-2023-20269), RDP exposures, spear phishing, and stolen credentials. Post-compromise, they create rogue domain accounts, like itadm, to elevate privileges, leveraging techniques like Kerberoasting and credential scraping with Mimikatz and LaZagne. Disabling Security Controls and Lateral Movement To evade detection and facilitate lateral movement, Akira operators disable security software using tools like PowerTool to terminate antivirus processes and exploit vulnerabilities. They employ various tools for reconnaissance, data exfiltration (FileZilla, WinRAR, WinSCP, RClone), and C2 communication (AnyDesk, Cloudflare Tunnel, RustDesk, Ngrok). Sophisticated Encryption The advisory highlights Akira's "sophisticated hybrid encryption scheme" combining ChaCha20 stream cipher with RSA public-key cryptography for efficient and secure encryption tailored to file types and sizes. As the Akira ransomware campaign continues to wreak havoc, the joint advisory provides crucial indicators of compromise (IoCs) to help organizations bolster their defenses against this formidable threat. Read the full article
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Empowering Cybersecurity with AI: A Smarter Approach to Digital Defense

In today’s digital world, where cyber threats are becoming more complex and evolving rapidly, traditional cybersecurity methods can no longer keep up. The rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming how we approach cybersecurity, offering smarter, faster, and more proactive defense strategies. This article explores how AI is revolutionizing cybersecurity, providing a more efficient and predictive way to protect digital assets and systems.
The Need for Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
As businesses and individuals continue to rely heavily on digital platforms, they face an increased risk of cyber threats. The vast amount of data being generated, combined with increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks, means traditional security systems often struggle to keep up. AI presents a promising solution, offering advanced capabilities to detect, analyze, and respond to threats more effectively than conventional methods.
Complexity of Modern Cyber Threats
Cyberattacks today are not only more frequent but also more sophisticated. Cybercriminals have access to advanced techniques that can easily bypass traditional security defenses. Modern threats range from ransomware attacks to zero-day vulnerabilities and advanced persistent threats (APTs). Traditional systems, which rely on predefined rules and signatures, often fall short in identifying and mitigating these new and complex attacks.
AI, however, can process vast amounts of data in real time, detecting anomalies and unusual behavior patterns that may signal an attack. By using machine learning and advanced algorithms, AI can identify these threats much more efficiently than human-based or rule-based systems, allowing organizations to respond before an attack causes significant damage.
Speed and Efficiency
Cyberattacks can occur in a matter of seconds, making it essential to detect and respond quickly. The speed of AI-powered systems is one of their most significant advantages. By analyzing vast amounts of data in real-time, AI can generate alerts and take automated actions to mitigate threats before they escalate. This ability to react swiftly dramatically reduces the window of opportunity for cybercriminals, ultimately preventing many attacks from succeeding.
AI-Driven Cybersecurity Solutions
Artificial Intelligence is already being applied in various cybersecurity solutions, providing smarter and more proactive defenses for businesses. Here are some of the key ways AI is enhancing cybersecurity:
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
AI-powered Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are among the most widely used AI-driven solutions in cybersecurity. These systems monitor network traffic, looking for unusual patterns or signs of an attack. Unlike traditional IDS, which rely on signature-based detection, AI-powered systems can learn and adapt to recognize new threats by analyzing massive datasets. By detecting potential intrusions in real time, AI allows businesses to respond to threats as they happen, rather than after the fact.
Behavioral Analysis
AI is also being used to analyze user and system behavior to detect insider threats and compromised accounts. By creating baseline profiles for users and systems, AI can identify any deviation from normal behavior, flagging it as suspicious. This form of behavioral analysis helps organizations detect threats that may otherwise go unnoticed, such as unauthorized access or credential theft, which often occur inside the network.
Automated Threat Hunting
Manual threat hunting is a time-consuming and resource-intensive process. AI can streamline this task by continuously scanning an organization’s network for vulnerabilities and indicators of compromise (IoCs). AI can process vast amounts of security data, identify potential threats, and even recommend actionable steps to mitigate risks. With automated threat hunting, organizations can ensure they are always on the lookout for new threats without the need for constant human oversight.
Fraud Detection
In industries such as banking and e-commerce, AI plays a critical role in detecting and preventing fraudulent activities. AI systems analyze patterns in transaction data to identify fraudulent transactions and prevent financial losses. By learning from historical data and continuously adapting to new methods used by fraudsters, AI can provide an extra layer of protection against financial crimes.
Phishing Detection
Phishing attacks, where attackers impersonate legitimate entities to steal sensitive information, are one of the most common cybersecurity threats. AI can analyze emails, websites, and other communication methods to detect phishing attempts. By identifying suspicious content, such as unusual email addresses, links, or attachments, AI can protect users from falling victim to phishing schemes.
Challenges and Considerations in AI-Powered Cybersecurity
While AI brings immense advantages to cybersecurity, it is not without its challenges. Organizations looking to integrate AI into their cybersecurity infrastructure need to consider several key factors.
Data Privacy and Security
AI systems require access to vast amounts of data to function effectively. This raises concerns about data privacy and security, as AI must be trained on sensitive information. Ensuring that AI systems adhere to strict data protection regulations, such as GDPR, is essential to avoid privacy breaches and data misuse.
False Positives
AI-powered systems are not perfect and can sometimes generate false positives, where benign activities are mistakenly identified as threats. This can lead to unnecessary alerts and responses, creating additional workload for security teams. Continuous fine-tuning and optimization of AI models are required to minimize false positives and ensure that the system remains effective in identifying real threats.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating AI into an organization’s existing cybersecurity infrastructure can be a complex process. AI solutions must be compatible with legacy systems and seamlessly integrate with current security tools and protocols. Organizations must ensure that their AI solutions work in tandem with other cybersecurity measures to maximize efficiency and effectiveness.
Expertise and Training
Managing AI-powered cybersecurity solutions requires specialized knowledge and expertise. Organizations must invest in training their security teams to understand and utilize AI tools effectively. Additionally, ongoing training is necessary to keep up with the rapid advancements in AI technology and the evolving nature of cyber threats.
Conclusion
AI is undoubtedly reshaping the landscape of cybersecurity, offering smarter, faster, and more proactive defenses against ever-evolving cyber threats. By harnessing the power of AI, organizations can stay one step ahead of cybercriminals, identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited, and respond to attacks more efficiently. However, to fully realize the potential of AI in cybersecurity, businesses must address challenges such as data privacy, false positives, integration, and the need for specialized expertise.
As cyber threats continue to grow in sophistication, adopting AI-powered cybersecurity solutions is no longer just an option; it is a necessity. Organizations that invest in AI-driven defenses will be better prepared to protect their digital assets, ensuring a safer and more secure future for their operations.
#Cybersecurity#ArtificialIntelligence#AICyberSecurity#DigitalDefense#SmartCyberSecurity#AIinCyberDefense
0 notes
Text
How Sharing Cyber Attack Insights Can Prevent Future Breaches

Introduction
Cyber threats are evolving rapidly, with attackers constantly refining their techniques to exploit vulnerabilities. Organizations that operate in isolation often struggle to keep up with these threats. However, by sharing cyber attack insights, businesses, governments, and cybersecurity professionals can collectively strengthen their defenses and prevent future breaches. In this article, we explore how sharing cyber threat intelligence can enhance security and reduce cyber risks.
1. Strengthening Cyber Defenses Through Shared Intelligence
Cybercriminals often use similar attack strategies across different organizations. By sharing attack patterns, indicators of compromise (IoCs), and vulnerabilities, companies can learn from each other’s experiences and implement proactive security measures.
Key Benefits:
✅ Helps organizations stay ahead of emerging threats. ✅ Enables real-time updates to firewalls and security protocols. ✅ Reduces the chances of repeated attacks using the same methods.
For example, if a company identifies a phishing campaign targeting its employees, sharing details about the email templates, malicious URLs, and sender information can help other organizations block similar attempts.
2. Faster Detection and Response
When organizations share cyber attack insights, it accelerates threat detection and response times. Security teams can act swiftly based on real-time data instead of waiting for an attack to occur.
How It Helps:
🔹 Faster response to zero-day vulnerabilities. 🔹 Reduced damage from ransomware and malware outbreaks. 🔹 Better coordination between cybersecurity teams and law enforcement.
For instance, a banking institution that detects a new form of credential-stuffing attack can alert other financial institutions, preventing widespread financial fraud.
3. Preventing Attacks from Spreading
A cyber attack on one organization can quickly spread to others if security vulnerabilities remain unpatched. By sharing attack details, businesses can prevent similar breaches and limit the damage.
Real-World Example:
The WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017 spread globally, affecting thousands of organizations. If companies had widely shared details of the exploit used (EternalBlue vulnerability), many others could have patched their systems before the attack escalated.
Best Practices for Containment:
✔ Report threats to cybersecurity communities and Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs). ✔ Implement automated threat-sharing solutions to notify others in real-time. ✔ Conduct cross-industry security drills to test response capabilities.
4. Enhancing Industry-Wide Cybersecurity Collaboration
Cyber threats don’t discriminate based on industry. Whether it’s healthcare, finance, or retail, all sectors face cyber risks. By collaborating and sharing insights, industries can work together to improve overall security.
Initiatives That Promote Threat Intelligence Sharing:
ISACs (Information Sharing and Analysis Centers): Sector-specific groups that share cyber threat intelligence.
MITRE ATT&CK Framework: A global knowledge base of attacker tactics and techniques.
Government-Led Cybersecurity Programs: The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the EU’s ENISA provide resources for sharing threats.
By participating in these networks, organizations gain access to valuable intelligence that can prevent large-scale cyber incidents.
5. Overcoming Challenges in Sharing Cybersecurity Insights
Despite the benefits, many companies hesitate to share cyber attack information due to concerns about:
❌ Privacy & Confidentiality: Fear of exposing sensitive business information. ✅ Solution: Share only essential IoCs and anonymized data to protect privacy.
❌ Legal & Compliance Issues: Regulations like GDPR and HIPAA restrict data sharing. ✅ Solution: Work with cybersecurity and legal teams to ensure compliance-friendly threat sharing.
❌ Competitive Concerns: Businesses worry that sharing insights may benefit competitors. ✅ Solution: Cybersecurity is a collective effort—everyone benefits from stronger defenses.
6. The Future of Threat Intelligence Sharing
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, the future of cybersecurity lies in automation and artificial intelligence-driven threat intelligence sharing. Machine learning algorithms can analyze shared threat data in real-time, predicting and mitigating attacks before they occur.
Additionally, governments and cybersecurity alliances are pushing for more open threat intelligence platforms, allowing organizations to collaborate securely without risking sensitive data exposure.
Conclusion
Sharing cyber attack insights is no longer optional—it’s a necessity for preventing future breaches. By working together, organizations can strengthen their defenses, reduce attack success rates, and create a more resilient cybersecurity ecosystem. While challenges exist, the benefits far outweigh the risks.
Cyber threats evolve, but so must our response. The more we share, the safer we become. Let’s build a future where cybersecurity is a collective effort, not an individual struggle.
1 note
·
View note
Text
youtube
Summary
🕵️ What is Threat Hunting?
A proactive process of identifying potential threats in a network before they escalate.
Focuses on detecting behaviors and anomalies, not just relying on automated tools or indicators of compromise (IoCs).
🔍 Key Concepts:
Proactive vs. Reactive: Unlike incident response, threat hunting actively seeks out threats before alerts trigger.
Behavioral Focus: Uses tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) rather than relying solely on signatures or known IoCs.
Human-Centric Approach: Augments tools with human expertise to identify patterns, reducing "alert fatigue" from excessive automated warnings.
🔧 Core Steps in Threat Hunting:
Hypothesis Creation: Identify potential gaps in detection and craft informed hypotheses about possible attacker behaviors.
Data Collection: Gather relevant logs and telemetry to support the investigation.
Investigation: Analyze the collected data, using statistical methods and pattern recognition to pinpoint anomalies.
Output: Document findings, report vulnerabilities, and propose mitigations.
🔒 Importance and Benefits:
Reduces dwell time, limiting the period an attacker remains undetected in the network.
Fills gaps in existing security controls, providing a supplementary layer of defense.
Improves team collaboration by involving cross-functional expertise.
0 notes
Text
UNC4057 LOSTKEYS Malware Targets Western NGOs

UNC4057 LOSTKEYS
The Russian government-backed outfit COLDRIVER targets Western and non-governmental organisations with its latest spyware, LOSTKEYS.
The Russian government-backed threat organisation COLDRIVER (also known as UNC4057, Star Blizzard, and Callisto) has stolen data from NGOs and Western targets using LOSTKEYS, a new virus. The Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) been tracking COLDRIVER for years, including its SPICA malware in 2024, and believes LOSTKEYS is a new tool.
COLDRIVER focusses on credential phishing targeting well-known targets. People at NGO or personal email addresses are generally targeted. They steal login passwords, emails, and contact lists after gaining access to a target's account. COLDRIVER may also access system files and infect devices with malware.
COLDRIVER has attacked journalists, think institutes, NGOs, and past and current Western government and military advisors. Plus, the gang has kept targeting Ukrainians. COLDRIVER's principal goal is to acquire intelligence for Russia's strategic goals. In several cases, the gang hacked and leaked NGO and UK official data.
January, March, and April 2025 saw the discovery of LOSTKEYS malware. The malicious application may take files from a hard-coded set of folders and extensions and transmit the attacker system details and active processes. COLDRIVER normally utilises credentials to access contacts and emails, although they have utilised SPICA to access target system documents. LOSTKEYS has a unique purpose and is utilised in certain scenarios.
The multi-step LOSTKEYS infection chain begins with a tempting website featuring a fake CAPTCHA. After the CAPTCHA is “verified,” the PowerShell code is transferred to the user's clipboard and the page invites them to execute it using Windows' “run” prompt. The “ClickFix” approach includes socially engineering targets to copy, paste, and run PowerShell scripts. Google Threat Intelligence Group said many APT and financially driven attackers use this method, which has been well documented.
PowerShell does the first stage's second step. In numerous instances, the IP address 165.227.148[.] provided this second step.68. The second step computes the display resolution MD5 hash and stops execution if it matches one of three specified values. This step may avoid virtual machine execution. The request must contain IDs unique to each observed instance of this chain to proceed. In every observation, the third stage comes from the same host as the previous phases.
Base64-encoded blobs decode into additional PowerShell in the third phase. This step requires retrieving and decoding the latest LOSTKEYS payload. It does this by downloading two additional files from the same host using different identities for each infection chain. The first-downloaded Visual Basic Script (VBS) file decodes the second file. Each infection chain is decoded with two keys. One unique key is in the decoder script, while stage 3 saves the second. Keys are used to replace cypher the encoded data.
The final payload is LOSTKEYS VBS. File theft and system data collection are its purposes.
Two more LOSTKEYS samples dated December 2023 were uncovered during this behaviour investigation. These previous PE files posing as Maltego files change greatly from the execution chain starting in 2025. It is unclear if these December 2023 samples are related to COLDRIVER or if the malware was reused from another operation into January 2025. Exchanged Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) include binary hashes and C2 addresses like njala[.]dev and 80.66.88[.]67.
Google Threat Intelligence Group uses threat actor research like COLDRIVER to improve product security and safety to safeguard consumers. Once detected, hazardous websites, domains, and files are added to Safe Browsing to protect users. Government-backed attacker warnings alerted Gmail and Workspace users. Potential targets should enrol in Google's Advanced Protection Program, enable Chrome's Enhanced Safe Browsing, and update all devices.
Google shares its findings with the security community to raise awareness and help targeted companies and people. Sharing methods and approaches improves threat hunting and sector user protections. The original post comprises YARA rules and compromise indicators and is available as a Google Threat Intelligence collection and rule bundle.
#UNC4057LOSTKEYS#UNC4057#COLDRIVER#GoogleThreatIntelligence#virtualmachines#VisualBasicScript#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Security Information And Event Management Market: Key Trends and Growth Drivers
The global security information and event management market size is expected to reach USD 11.62 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 14.5% from 2023 to 2030, according to the new reports of Grand View Research, Inc. Security information and event management (SIEM) systems enhance threat detection capabilities through the utilization of advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms.
By analyzing vast volumes of security data, these platforms can proactively identify and respond to emerging risks by identifying patterns, anomalies, and correlations. Integrating with threat intelligence feeds and services offers significant advantages for SIEM platforms. By incorporating up-to-date threat intelligence data, SIEM systems can effectively recognize and respond to established attack vectors, emerging threats, and indicators of compromise (IOCs), thereby bolstering their ability to safeguard against potential security breaches.
In today's ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, organizations face a multitude of complex threats, including malware, ransomware, phishing, and insider risks. To effectively combat these challenges, a robust security infrastructure must include a SIEM solution, providing users with real-time threat detection and response capabilities.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Security Information And Event Management Market
Security Information and Event Management Market Report Highlights
• The software segment accounts for the largest market share of over 65.1% in 2022 and is anticipated to maintain its dominance over the forecast period owing to extensive event correlation, alerting, and process automation capabilities of software solution to enable effective incident response features across organizations
• The cloud segment is expected to observe the highest CAGR of 15.8% during the forecast period. In cloud environments such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), security events can be monitored and analyzed with the help of cloud-based SIEM solutions, thereby enabling organizations to have complete visibility and control over the entirety of their IT infrastructure
• The small & medium enterprises enterprise segment is anticipated to witness an exceptional CAGR of 15.2% during the forecast period. SIEM technology offers SMEs a centralized and economical way to improve their security posture and safeguard their valuable assets and sensitive data, thereby surging the market demand across organizations
• The IT & telecom segment is anticipated to register a considerable CAGR of 16.3% over the forecast period. An ecosystem that combines edge computing, cloud services, on-premise architecture, Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and other cutting-edge technologies is complicated and diverse. Due to the high risk of cyberattacks in such a setting, Security information and event management (SIEM) solutions must be used by the IT & telecom sector
• North America accounted for the largest market share of over 32.7% in 2022 and is expected to retain its position over the forecast period. Due to the highly developed IT infrastructure in the region, the dangers and complexity of cyberattacks are increasing, which is driving the demand for security information and event management
• Key players in the SIEM market have an extended operating history, a large customer base, and significant competitive strengths. In addition to the inorganic growth strategies, vendors emphasize improving after-sale service offerings to ensure periodic maintenance of installed products
Security Information And Event Management Market Segmentation
Grand View Research has segmented the global security information and event management (SIEM) market based on solution, deployment, enterprise size, vertical, and region:
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Solution Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
• Software
• Service
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Deployment Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
• Cloud
• On-premise
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Organization Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
• Small And Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs)
• Large Enterprises
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Vertical Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
• BFSI
• IT and Telecom
• Retail & E-commerce
• Healthcare and Life Sciences
• Manufacturing
• Government & Defense
• Energy & Utilities
• Others
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2018 - 2030)
• North America
o U.S.
o Canada
• Europe
o UK
o Germany
o France
o Italy
o Spain
• Asia Pacific
o China
o India
o Japan
o Australia
o South Korea
• Latin America
o Brazil
o Mexico
o Argentina
• Middle East and Africa
o UAE
o Saudi Arabia
o South Africa
Order a free sample PDF of the Security Information And Event Management Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
#Security Information And Event Management Market#Security Information And Event Management Market Size#Security Information And Event Management Market Share#Security Information And Event Management Market Analysis#Security Information And Event Management Market Growth
0 notes