#Maltego
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Maltego: Desentrañando Redes y Relaciones en el Mundo de la Ciberseguridad
En un mundo digital cada vez más interconectado, la capacidad de identificar y analizar patrones, relaciones y conexiones es crucial para proteger sistemas y prevenir amenazas. Entre las herramientas más potentes en el arsenal de los profesionales de ciberseguridad, investigadores y analistas forenses, destaca Maltego: una solución innovadora diseñada para revelar y mapear datos ocultos en redes,…
0 notes
Text
Maîtriser l’OSINT en France : Une opportunité d’apprentissage stratégique
Dans un monde numérique en perpétuelle évolution, apprendre osint France est devenu une compétence incontournable pour les professionnels de la sécurité, de la veille stratégique, du journalisme d’investigation, mais aussi pour les curieux souhaitant développer leur esprit d’analyse. L’intelligence open source, ou OSINT (Open Source Intelligence), fait référence à la collecte et à l’analyse d’informations accessibles au public. Apprendre l’OSINT en France permet donc d’acquérir une capacité précieuse pour détecter, comprendre et anticiper les menaces ou opportunités dans divers secteurs.
La formation en intelligence open source s’impose comme une démarche structurée et rigoureuse pour ceux qui souhaitent exploiter intelligemment les données disponibles sur Internet, les réseaux sociaux, les bases de données publiques et bien d’autres sources ouvertes. Contrairement à une simple recherche sur le Web, l’OSINT exige une méthodologie spécifique, des outils spécialisés et une solide éthique d’utilisation. Cela en fait une compétence à la fois technique et stratégique.
L’intérêt croissant pour la formation en intelligence open source en France est directement lié à la numérisation massive de l’information et à la complexité croissante des enjeux sécuritaires et économiques. Des secteurs aussi vari��s que la cybersécurité, le renseignement d’entreprise, les ressources humaines ou encore le marketing digital intègrent désormais les compétences OSINT dans leurs pratiques quotidiennes. Cette approche permet d’obtenir une vision plus complète des environnements concurrentiels, sociaux ou géopolitiques.
De nombreuses initiatives de formation voient le jour, allant de simples introductions aux outils OSINT jusqu’à des cursus avancés incluant des études de cas, des simulations et des ateliers pratiques. Ces programmes permettent non seulement de développer une compréhension approfondie des techniques de collecte et d’analyse, mais aussi de maîtriser des outils tels que Maltego, TheHarvester, ou encore SpiderFoot. La qualité de ces formations dépend toutefois grandement de l’expertise des formateurs et de leur capacité à relier la théorie aux situations concrètes rencontrées sur le terrain.
Dans ce contexte, Academie-digitale.eu propose une approche pédagogique pensée pour les apprenants francophones souhaitant se spécialiser dans l’OSINT. Sans se limiter à un simple catalogue d’outils, les parcours offerts permettent de comprendre les logiques d’investigation, de structurer ses recherches et de vérifier la fiabilité des sources. Cela favorise l’autonomie et la rigueur, deux qualités essentielles dans la pratique de l’intelligence open source.
Il est essentiel de souligner que la formation en intelligence open source ne se limite pas à un usage technique ou professionnel. Elle touche aussi à la responsabilité citoyenne et à la capacité de chacun à faire preuve de discernement face à l’infobésité ambiante. Savoir identifier une désinformation, retracer une origine douteuse ou comprendre une campagne d’influence sont autant de compétences utiles dans un monde où l’information est devenue un levier de pouvoir.
Apprendre l’OSINT en France, c’est donc aussi s’armer intellectuellement pour faire face aux enjeux actuels de transparence, de cybersécurité et de veille concurrentielle. Cela suppose de sortir d’une logique passive de consommation d’information pour adopter une posture active et critique.
En intégrant ce type de formation dans un parcours professionnel ou académique, les apprenants s’ouvrent à de nouvelles perspectives d’évolution et de spécialisation. Qu’il s’agisse de rejoindre une cellule de veille stratégique, de travailler pour une organisation non gouvernementale, une entreprise ou une institution publique, les compétences en OSINT sont aujourd’hui de plus en plus valorisées.
Academie-digitale.eu s’inscrit ainsi dans cette dynamique de transformation numérique et de montée en compétences, en offrant un accompagnement adapté aux réalités du marché francophone. En investissant dans cette expertise, les apprenants participent activement à la construction d’un environnement informationnel plus transparent, fiable et sécurisé.
0 notes
Text
UNC4057 LOSTKEYS Malware Targets Western NGOs

UNC4057 LOSTKEYS
The Russian government-backed outfit COLDRIVER targets Western and non-governmental organisations with its latest spyware, LOSTKEYS.
The Russian government-backed threat organisation COLDRIVER (also known as UNC4057, Star Blizzard, and Callisto) has stolen data from NGOs and Western targets using LOSTKEYS, a new virus. The Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) been tracking COLDRIVER for years, including its SPICA malware in 2024, and believes LOSTKEYS is a new tool.
COLDRIVER focusses on credential phishing targeting well-known targets. People at NGO or personal email addresses are generally targeted. They steal login passwords, emails, and contact lists after gaining access to a target's account. COLDRIVER may also access system files and infect devices with malware.
COLDRIVER has attacked journalists, think institutes, NGOs, and past and current Western government and military advisors. Plus, the gang has kept targeting Ukrainians. COLDRIVER's principal goal is to acquire intelligence for Russia's strategic goals. In several cases, the gang hacked and leaked NGO and UK official data.
January, March, and April 2025 saw the discovery of LOSTKEYS malware. The malicious application may take files from a hard-coded set of folders and extensions and transmit the attacker system details and active processes. COLDRIVER normally utilises credentials to access contacts and emails, although they have utilised SPICA to access target system documents. LOSTKEYS has a unique purpose and is utilised in certain scenarios.
The multi-step LOSTKEYS infection chain begins with a tempting website featuring a fake CAPTCHA. After the CAPTCHA is “verified,” the PowerShell code is transferred to the user's clipboard and the page invites them to execute it using Windows' “run” prompt. The “ClickFix” approach includes socially engineering targets to copy, paste, and run PowerShell scripts. Google Threat Intelligence Group said many APT and financially driven attackers use this method, which has been well documented.
PowerShell does the first stage's second step. In numerous instances, the IP address 165.227.148[.] provided this second step.68. The second step computes the display resolution MD5 hash and stops execution if it matches one of three specified values. This step may avoid virtual machine execution. The request must contain IDs unique to each observed instance of this chain to proceed. In every observation, the third stage comes from the same host as the previous phases.
Base64-encoded blobs decode into additional PowerShell in the third phase. This step requires retrieving and decoding the latest LOSTKEYS payload. It does this by downloading two additional files from the same host using different identities for each infection chain. The first-downloaded Visual Basic Script (VBS) file decodes the second file. Each infection chain is decoded with two keys. One unique key is in the decoder script, while stage 3 saves the second. Keys are used to replace cypher the encoded data.
The final payload is LOSTKEYS VBS. File theft and system data collection are its purposes.
Two more LOSTKEYS samples dated December 2023 were uncovered during this behaviour investigation. These previous PE files posing as Maltego files change greatly from the execution chain starting in 2025. It is unclear if these December 2023 samples are related to COLDRIVER or if the malware was reused from another operation into January 2025. Exchanged Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) include binary hashes and C2 addresses like njala[.]dev and 80.66.88[.]67.
Google Threat Intelligence Group uses threat actor research like COLDRIVER to improve product security and safety to safeguard consumers. Once detected, hazardous websites, domains, and files are added to Safe Browsing to protect users. Government-backed attacker warnings alerted Gmail and Workspace users. Potential targets should enrol in Google's Advanced Protection Program, enable Chrome's Enhanced Safe Browsing, and update all devices.
Google shares its findings with the security community to raise awareness and help targeted companies and people. Sharing methods and approaches improves threat hunting and sector user protections. The original post comprises YARA rules and compromise indicators and is available as a Google Threat Intelligence collection and rule bundle.
#UNC4057LOSTKEYS#UNC4057#COLDRIVER#GoogleThreatIntelligence#virtualmachines#VisualBasicScript#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Guia de Treinamento Modular em Investigação Cibernética Forense com Foco em Criptomoedas e Operações Clandestinas.(rascunho)
Guia de Treinamento Modular – Criptomoedas, Inteligência e Forense Cibernética
Objetivo Geral:
Capacitar investigadores a identificar, rastrear e analisar transações com criptoativos utilizadas em operações de inteligência, terrorismo, financiamento ilícito ou guerra híbrida, com foco em Bitcoin e ativos correlatos.
Módulo 1 – Fundamentos Operacionais
Objetivo: Compreender os usos estratégicos de criptomoedas por entidades estatais e paraestatais.
Conteúdo:
Histórico do uso de criptografia em inteligência.
Bitcoin, Monero e ZCash: propriedades e vulnerabilidades.
O papel de SHA-256 e suspeitas sobre backdoors.
TOR, mixers e atomic swaps em cenários reais.
Estudos de caso: Crypto AG, Silk Road, Venezuela e Irã.
Atividade prática:
Leitura dirigida + questionário crítico sobre o artigo “Crypto” de Steven Levy e relatórios da NSA revelados por Snowden.
Módulo 2 – Técnicas de Rastreamento Blockchain
Objetivo: Aplicar ferramentas e heurísticas para rastrear carteiras suspeitas.
Ferramentas:
Blockchair, Mempool.space, Chainalysis Reactor (ou simulador), WalletExplorer.
Python com web3.py, etherscan-python, bitcoinlib.
Procedimentos:
Clusterização de endereços.
Detecção de padrões de comportamento.
Heurística de co-gasto e reuso de endereço.
Identificação de canais Tor, VPN e proxies.
Exercício prático:
Fornecer ao aluno um conjunto de endereços com padrões ocultos de movimentação ligados a uma ONG fachada.
Módulo 3 – Correlacionamento Geopolítico e SIGINT
Objetivo: Integrar eventos globais e inteligência aberta para contextualizar transações suspeitas.
Conteúdo:
Mapeamento de eventos (guerras, sanções, blackouts).
Uso de cronologia comparada com dados blockchain.
Integração com relatórios do OFAC, Wikileaks, Bellingcat.
Ferramentas:
Pandas, Matplotlib para análise temporal.
OSINT Framework, Maltego, Tracelabs.
Estudo de caso:
Atividade com o caso simulado GhostWire, onde o aluno cruza transações com deslocamentos aéreos e metadados de aparelhos de comunicação.
Módulo 4 – Engenharia Reversa de Ferramentas e Códigos Suspeitos
Objetivo: Avaliar a possibilidade de implantes ou armadilhas (trapdoors) em clientes Bitcoin ou funções criptográficas.
Conteúdo:
SHA-256 e testes de entropia modificada.
Fingerprinting de compiladores.
Modificação de builds e auditoria de código-fonte.
Ferramentas:
Ghidra, IDA Pro, Hashpump, Binwalk, Radare2.
Exercício técnico:
Análise de um node bitcoind suspeito e detecção de artefatos que indicam compilação orientada a rastreabilidade.
Módulo 5 – Modelagem de Risco e Redação de Relatórios Forenses
Objetivo: Comunicar achados técnicos de forma estruturada e acionável.
Inclui:
Modelo de relatório (como você propôs).
Técnicas de escrita objetiva e escalável (inteligência analítica).
Formulação de hipóteses falsificáveis (baseada em Popper).
Estratégias de validação cruzada e alertas de falsos positivos.
Simulação final:
Cada aluno recebe um dossiê de inteligência, endereços em blockchain e precisa produzir um relatório de 6 páginas com recomendações operacionais.
Certificação e Continuidade
Ao final, os investigadores poderão receber um selo de "Analista Cibernético Forense em Criptoativos e Operações Irregulares", com possibilidade de continuidade em módulos avançados (ex.: Dark Finance em Atos de Guerra Híbrida).
PS.: Não deixa o Haddad ver isso, ele é burro e pode afetar a autoestima dele.
0 notes
Text
Learn the 5 Stages of Ethical Hacking
With threats on the digital platform ever-present today, ethical hacking has emerged as an essential method for protecting systems, networks, and information. As malicious hackers use vulnerabilities to carry out crime, ethical hackers (or white hat hackers) utilize their craft for good purposes — finding and fixing vulnerabilities before threat actors have the chance to do so. But ethical hacking is not a random process. It follows a methodical process to make every step legal, efficient, and in accordance with the security goals of the organization. This process is typically in five stages, which are very specific and trace ethical hackers from reconnaissance to reporting. Let us dive into detail about what these stages involve and why they're crucial for a successful cyber defense strategy. Phase 1: Reconnaissance (Information Gathering) Also known as: Footprinting Reconnaissance is the first and, arguably, the most important phase of ethical hacking. It's akin to the "research" phase. Ethical hackers find out as much as they can about the target before they try to break into it. This phase lays the groundwork for everything that follows. Aims: •Get familiar with the digital footprint of the target •Identify weak spots and vulnerable entry points • Steal away undetected while gathering information Methods Used: • Passive Reconnaissance – No contact with the target (e.g., use of WHOIS lookup, DNS records, social media, public databases). • Active Reconnaissance – Direct contact with the system (e.g., ping sweeps, port scanning, traceroutes). Tools: •Maltego •Nmap •Recon-ng •Google Dorking Why it matters: Proper reconnaissance saves time and makes the rest of the hacking process easier. It also replicates the first steps taken by real-world cyber attackers.
Phase 2: Scanning (Probing for Weaknesses) After the ethical hacker has sufficient surface information, scanning is the next phase where more intensive probing is done to identify particular vulnerabilities in the system. Objectives: • Discover open ports and services • Detect live systems • Identify running OS and applications • Discover known vulnerabilities
Methods: • Port Scanning – Scanning which ports are open and what services are running.
• Network Mapping – Knowledge of the network topology and the identification of the hosts. • Vulnerability Scanning – System scanning for known configuration or software vulnerabilities. Tools: • Nessus • Nikto • OpenVAS • Wireshark Why it matters: Scanning gives the hacker a technical snapshot of how healthy the system is and assists the hacker in determining which vulnerabilities to exploit during the exploitation phase.
Phase 3: Access Gaining (Exploitation) This is where ethical hacking really gets to work and occurs. The hacker attempts to break into the system by taking advantage of the weaknesses revealed in the scanning. It sounds like the climax, but it's a very choreographed and strategic move that makes ethical hacking. Objectives: • Use a known exploit to gain access • Increase privileges (for example, from guest to admin) • Identify the amount of potential damage that an actual perpetrator might do Methods • Buffer overflow attacks • tSQL injection • Brute-force password cracking • Misconfiguration exploitation Tools: • Metasploit • Hydra • John the Ripper • SQLMap Why it matters: Access that is gained allows organizations to see how much access an attacker would have, giving them a chance to cut off critical points of access before damage is being caused.
Phase 4: Maintaining Access (Persistence) During this phase, the ethical hacker mimics what an actual attacker would do once they have compromised the system — maintain access to keep gathering data or installing malware. Objectives: •Create backdoors or remote access tools •Mimic advanced persistent threats (APT) •Illustrate long-term risk exposure Methods: •Installing Trojans or rootkits (ethically and with permission) •Creating rogue user accounts •Altering system services for covert access Tools: •Netcat •Backdoor Factory •MSFVenom Why it matters: This stage assists in determining how long a system might remain compromised undetected — an important consideration when analyzing incident response measures. Phase 5: Covering Tracks & Reporting While malicious hackers attempt to cover their tracks, ethical hackers do the opposite — they make sure all actions taken are logged, traced, and completely documented. Reporting is the last and possibly most useful step of the ethical hacking process.
Goals: • Restore the system to normal • Report to the organization • Deliver remediation steps that are actionable What's in the Report: • Disclosed vulnerabilities • Attacks tried and success rates • Possible impact of each vulnerability • Fix recommendations and improvements Why it matters: The final-report is a blueprint that the organization can use to make its defenses harder. It transforms an ethical hack from a test into an actionable business tool.
The Legal and Ethical Side It's important to emphasize: Ethical hacking should be done with the right permission. That is, written permission, well-delineated scope, and test boundaries. Unapproved hacking—no matter what "noble cause"—is against the law and punishable by it. Why the 5 Phases are Important Together, these five phases create a repeatable, effective cycle of security testing. They: •Echo the methods of actual attackers •Detect potential threats prior to exploitation •Enhance organizational cybersecurity stance •Meet standards such as ISO/IEC 27001, PCI-DSS, etcFinal Thoughts Ethical hacking is not merely about cracking open systems—it's about learning them, enhancing them, and helping to make the internet a more secure place. From IT managers to aspiring cybersecurity analysts to entrepreneurs, recognizing the five stages of ethical hacking can assist you in making better, more secure decisions. With increasing cybercrime, ethical hacking is no longer a choice — it's a necessity. And as with any strategic process, its success depends on how systematically and responsibly it's carried out.
Website: https://www.icertglobal.com/course/ceh-certification-training/Classroom/62/3044

0 notes
Text
Best Tools & Software You Will Learn in an Ethical Hacking Course in CRAFT Dehradun

In today’s digital world, cybersecurity threats are on the rise, making ethical hacking a crucial skill for IT professionals. If you're looking for a top-rated Ethical Hacking Course in Dehradun, CRAFT Empowering Careers offers a hands-on program covering all the essential tools and software used by ethical hackers. Join now and kickstart your journey in cybersecurity!
Why Learn Ethical Hacking?
Ethical hackers play a key role in securing networks, applications, and data from cyber threats. Learning ethical hacking opens doors to exciting career opportunities in cybersecurity, penetration testing, and network security. By enrolling in our Ethical Hacking Course in Dehradun, you'll gain real-world experience with industry-standard tools and techniques.
Essential Tools & Software Covered in the Course
At CRAFT Empowering Careers, our ethical hacking course includes practical training on some of the most powerful tools used in cybersecurity.
1. Kali Linux – The Ultimate Penetration Testing OS
Pre-installed with top security tools like Nmap, Metasploit, and Wireshark.
Used by professionals for ethical hacking and penetration testing.
2. Metasploit Framework – Mastering Exploits
A must-have tool for penetration testers.
Helps in identifying vulnerabilities and launching simulated cyberattacks.
3. Wireshark – The Best Network Analysis Tool
Monitors and captures network traffic to detect unauthorized activities.
Essential for network security assessments.
4. Nmap (Network Mapper) – Scanning & Auditing Networks
Helps in network discovery, identifying open ports, and running security audits.
Used by professionals to map out network vulnerabilities.
5. Burp Suite – Web Application Security Testing
An advanced tool for detecting vulnerabilities like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
Essential for web security professionals.
6. Aircrack-ng – Wireless Security Assessment
Tests the security of Wi-Fi networks.
Helps in cracking WEP and WPA-PSK encryption for security analysis.
7. SQLmap – Automated SQL Injection Detection
Detects and exploits SQL injection vulnerabilities in databases.
A must-have tool for database security testing.
8. John the Ripper – Password Cracking Made Easy
Helps test the strength of passwords.
Supports various encryption techniques and algorithms.
9. Nikto – Web Server Security Scanner
Scans web servers for outdated software, misconfigurations, and vulnerabilities.
Ensures website security against cyber threats.
10. Maltego – Cyber Intelligence & Investigation Tool
Used for information gathering and mapping relationships between entities.
Helps cybersecurity professionals in reconnaissance and intelligence gathering.
Enroll in the Best Ethical Hacking Course in Dehradun
At CRAFT Empowering Careers, we provide practical training with real-world hacking scenarios to help you master cybersecurity skills. Our course is designed for beginners and professionals looking to build a strong foundation in ethical hacking.
Key Features of Our Ethical Hacking Course:
✔ Hands-on training with real-world tools.
✔ Expert guidance from cybersecurity professionals.
✔ Certification upon course completion.
✔ 100% placement assistance for career growth.
Enroll Now and take the first step toward a rewarding cybersecurity career!
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is a booming field, and ethical hackers are in high demand. By mastering tools like Kali Linux, Metasploit, Wireshark, and more, you can boost your cybersecurity skills and land high-paying jobs in the IT sector. Join the Ethical Hacking Course in Dehradun at CRAFT Empowering Careers and start your journey today!
For more details, visit: CRAFT Empowering Careers Ethical Hacking Course
0 notes
Text
Ethical Hacker Course: Key Skills You Will Learn
With the increasing number of cyber threats and data breaches worldwide, the demand for skilled ethical hackers is higher than ever since the past two decades. An ethical hacker course equips professionals with the knowledge and hands-on experience needed to identify, exploit, and fix the security vulnerabilities in networks & systems. If you are looking for career in cyber security, here’s a very depth analysis at the important skills you will learn in an ethical hacking course.
Core Modules in an Ethical Hacker Course
An ethical hacking course covers various modules designed to provide a solid foundation in cybersecurity. Some of the core modules include:
1. Introduction to Basics of Ethical Hacking
Understanding the role & responsibilities of an ethical hacker
Legal & ethical considerations in cybersecurity
Different types of cyber threats and attack methodologies
2. Footprinting and Reconnaissance
Gathering information about a target system using open-source intelligence (OSINT)
Using tools like Nmap, Maltego, and Google Dorking to identify vulnerabilities
Techniques such as passive and active reconnaissance
3. Scanning Networks and System Hacking
Identifying open ports, services, and vulnerabilities
Exploiting security loopholes using vulnerability scanners
Password cracking techniques, privilege escalation, and maintaining access
4. Malware Threats & Attack Vectors
Understanding types of malware: viruses, worms, ransomware, and trojans
Analyzing malware behavior & prevention strategies
Using sandboxing & endpoint protection tools
5. Web Application Security
Detecting common web vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF)
Security testing methodologies for web applications
Understanding Secure Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
6. Wireless Network Security
Understanding Wi-Fi encryption standards (WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA3)
Conducting wireless penetration testing
Preventing wireless network intrusions
7. Cryptography and Network Security
Basics of encryption, hashing, and digital signatures
Implementing secure communication channels
Understanding of VPNs, firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Hands-On Learning: Practical Exercises and Real-World Scenarios
Ethical hacking courses emphasize hands-on learning to prepare professionals for real-world cybersecurity challenges. Some key practical aspects include:
Penetration Testing Labs: Simulated environments where students can practice exploiting vulnerabilities.
Capture The Flag (CTF) Challenges: Gamified cybersecurity competitions to test hacking skills.
Incident Response Simulations: Handling real-world cybersecurity incidents, including data breaches and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
Reverse Engineering and Exploit Development: Analyzing malicious code and writing exploits for vulnerabilities.
By working on real-world cybersecurity scenarios, ethical hackers develop real time problem solving skills and learn to think like attackers to defend systems very effectively.
Important Tools & Tactics Used by Ethical Hackers
Ethical hackers used the various tools and techniques to perform security assessments. Some of the essential tools include:
Kali Linux: A penetration testing operating system with a wide range of security tools.
Metasploit Framework: A very powerful tools for developing and executing exploit any code.
Burp Suite: A web vulnerability scanner used for security testing of web applications.
Wireshark: A network protocol analyzer for capturing & analyzing network traffic in the systems.
John the Ripper and Hashcat: Password cracking tools.
Nmap and Zenmap: Network scanning tools for identifying vulnerabilities.
SQLmap: A tool that used for detecting & exploiting My SQL injection vulnerabilities.
Using these tools, ethical hackers perform penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and forensic analysis to strengthen an organization’s security posture.
Complement Certifications CEH for Career & Growth:
While the Certified Ethical Hacker certification is a highly demanding credential, comparing it with other certifications can further improve your career opportunities. Some of the complementary certifications include:
1. Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
Focuses & Improve on hands-on penetration testing skills.
Requires candidates to complete a challenging 24-hour practical exam.
Those who are looking to specialize in offensive security.
2. GIAC Penetration Tester (GPEN)
Covers advanced penetration testing techniques.
Recognized by government and enterprise cybersecurity teams.
Focuses on exploit development, privilege escalation, and password attacks.
3. Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
Covers broad cybersecurity domains, including risk management and governance.
Ideal for those aspiring to take on security management roles.
Highly valued by employers worldwide.
4. CompTIA PenTest+
Covers penetration testing methodologies, tools, and reporting.
A good alternative for those starting in ethical hacking.
5. EC-Council Certified Security Analyst (ECSA)
Advanced ethical hacking certification that builds on CEH.
Covers in-depth penetration testing methodologies.
Ideal for professionals looking to specialize in vulnerability assessment and red teaming.
Conclusion
An ethical hacker course provides professionals with in-depth knowledge and hands-on experience in cyber security programs. From network scanning and malware analysis to penetration testing and web security, ethical hackers develop a very powerful skill set to protect organizations from cyber threats. With the right combination of certifications and in depth practice, ethical hackers can advance their careers and contribute to strengthening global cyber security defenses. Are you ready to take on your ethical hacking journey? Start learning today and build a rewarding career in cybersecurity!
#ceh certification requirements#ethical hacking course#hacking course#ethical hacking courses#ethical hacker course
0 notes
Video
tumblr
Gestern Abend wurde es spät bei der Aufzeichnung der neuen OSINT Studio Folge. Matthias und ich folgten einer Spur, die uns immer tiefer ins Handelsregister führte. Was als einfache Recherche begann, wurde schnell zu einer brisanten Frage: Ist Maltego wirklich ein deutsches OSINT Tool? In diesem Clip bekommst du einen ersten Einblick in unsere Recherche. Wem gehört Maltego wirklich? Die vollständige Episode mit all unseren Erkenntnissen erscheint nächste Woche – also jetzt #OSINTStudio abonnieren, um nichts zu verpassen! 💬 Erinnerst du dich noch an Paterva? Schreib es in die Kommentare!
0 notes
Text
youtube
Summary
🌐 Introduction to Dark Web OSINT:
Kirby Plessas, a former military intelligence analyst, shares her methodology for conducting OSINT investigations on the dark web.
Focused on leveraging tools and techniques to collect and analyze data while maintaining operational security (OPSEC).
🔍 Key Topics and Techniques:
Tools and Environment:
Use of virtual machines (VMs), VPNs, and the Tor browser for safe exploration.
Bookmarking important sites to maintain continuity in investigations.
Recon Techniques:
Analyze vendor profiles, transaction histories, and product listings to identify patterns.
Reverse image searches and metadata extraction to trace images back to their origins.
Social Network Analysis Tools:
Tools like Maltego, Case File, and Aeterna Notebook are used to map connections and identify relationships.
Integration of disparate datasets to uncover hidden linkages.
🛠️ Investigative Workflow:
Scraping and indexing dark web sites using add-ons like Scrapbook for offline analysis.
Using tools like Stolen Camera Finder and blockchain explorers to trace digital assets.
Leveraging Google Dorks and RSS feeds for real-time monitoring of dark web activities.
🎯 Challenges and Recommendations:
The dark web's dynamic nature requires constant adaptation of tools and techniques.
Emphasized the importance of ethical practices to ensure data collection remains lawful and respectful of privacy.
0 notes
Text
Best Practices for Conducting Penetration Testing with Burp Suite and Maltego
Penetration testing is a critical aspect of information security, enabling organizations to identify vulnerabilities and strengthen their defenses against potential threats. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the best practices for conducting penetration testing using the Burp Suite and Maltego. We will cover the technical background, implementation guide, code examples, best practices,…
0 notes
Text
Criminal IP and Maltego Collaborate to Broaden Threat Intelligence Data Search
http://securitytc.com/TBq3W8
0 notes
Text
OSINT là viết tắt của “open source intelligence”. Khái niệm này ám chỉ việc tìm kiếm thông tin mà bạn có thể truy cập hợp pháp, thông qua các phương tiện hợp pháp. OSINT chủ yếu được thực hiện trực tuyến, nhưng nó cũng có thể được thực hiện ngoại tuyến. Pentesters sử dụng OSINT để nghiên cứu các mục tiêu của họ và các chuyên gia tình báo về mối đe dọa sử dụng OSINT để tìm hiểu về các mối đe dọa mạng. OSINT là một công cụ quan trọng cho cả đội đỏ và đội xanh. Dưới đây là một số công cụ phổ biến nhất cho OSINT. 10 công cụ OSINT mà hacker cần biết Shodan Shodan là một công cụ tìm kiếm các thiết bị mạng có thể khai thác trên internet, chẳng hạn như máy chủ và thiết bị IoT. Có thể khai thác tức là có thể truy cập công khai. Có thể đặt một máy chủ, thiết bị ngoại vi IoT hoặc thiết bị mạng trên internet và định cấu hình nó tương đối riêng tư và khó lấy dấu vân tay. Nhưng nếu một thiết bị được kết nối với Internet mà không có cấu hình bảo mật cẩn thận, bạn có thể tìm thấy thiết bị đó thông qua Shodan với các tìm kiếm phù hợp. Sử dụng Shodan mà không có tài khoản trả phí sẽ trả về một số lượng kết quả tìm kiếm rất hạn chế. Tài khoản trả phí hữu ích hơn rất nhiều nếu loại nghiên cứu không gian mạng OSINT mà bạn thực hiện yêu cầu khám phá máy chủ, thiết bị mạng và thiết bị ngoại vi IoT (chẳng hạn như máy ảnh). Maltego Maltego chạy như một ứng dụng dành riêng cho máy tính để bàn Windows, Mac và Linux, cho phép người dùng truy cập vào nhiều nguồn dữ liệu cho các mục đích OSINT, nghiên cứu báo chí và pháp y. Có hơn 58 nguồn dữ liệu trong Maltego tính đến thời điểm mình viết bài này, bao gồm mã hóa địa lý Google Maps, AlienVault OTX, ATII Hades Darkweb Intelligence, Blockchain.info, Crowdstrike, VirusTotal, và nhiều nguồn khác. Mình hy vọng số lượng nguồn dữ liệu được tích hợp vào Maltego sẽ tăng lên theo thời gian. Giá trị mà Maltego cung cấp cho các nhà nghiên cứu không chỉ ở bộ sưu tập nguồn dữ liệu khổng lồ mà còn ở cách nền tảng của nó có thể hiển thị cho người dùng các mẫu và xu hướng dữ liệu thông qua biểu đồ hình ảnh có thể tùy chỉnh cao. Lên đến một triệu thực thể có thể được vẽ trong biểu đồ mà Maltego tạo. Tất nhiên, bạn có thể tận dụng tất cả các tính năng của Maltego nhưng không phải là miễn phí, mặc dù họ sẽ cho phép bạn xem bản demo trước khi bạn quyết định đăng ký. Nhưng nếu bạn không muốn trả tiền, Maltego Community Edition miễn phí vẫn có thể rất hữu ích. Google Dorks Google Dorks không phải là một ứng dụng. Đúng hơn, đó là một kỹ thuật sử dụng công cụ tìm kiếm Google mà mọi người đều sử dụng hàng ngày. Đừng đi tìm ứng dụng Google Dorks chính thức, ứng dụng này không tồn tại đâu. Nhưng có những nhà phát triển đã phát triển các công cụ phần mềm mã nguồn mở cho Google Dorking mà bạn có thể thử, chẳng hạn như Pagodo và GoogleDorker. Một chiến lược Google Dorking điển hình bắt đầu bằng việc sử dụng các truy vấn tìm kiếm đơn giản và sau đó chuyển sang các truy vấn phức tạp hơn. Hầu hết mọi người chỉ nhập các chuỗi văn bản vào tìm kiếm của Google, chẳng hạn như “dự báo thời tiết” hoặc “abc xyz”. Nhưng có một số toán tử tìm kiếm có thể được sử dụng trong tìm kiếm của Google để trả lại nhiều kết quả đúng ý định của bạn hơn. Ví dụ: bạn có thể thử “site: anonyviet.com” để tìm kiếm cụ thể trên trang web của mình hoặc sử dụng các dấu ngoặc kép xung quanh một cụm từ tìm kiếm để chỉ trả về kết quả có sử dụng cụm từ tìm kiếm chính xác đó. Google cung cấp danh sách các mẹo để tinh chỉnh các tìm kiếm trên Google của bạn tại đây. Rất nhiều trang web được cấu hình rất kém khi nói đến an ninh mạng. Các bot thu thập thông tin web của Google hoạt động hiệu quả nhất trên web khi chúng có quyền truy cập để khám phá. Vì vậy, Google Dorking có thể là một kỹ thuật để tìm dữ liệu như địa chỉ email, thông tin đăng nhập và số ngân hàng chưa được bảo mật đúng cách. Recon-ng Recon-ng là một công cụ do thám web mã nguồn mở. Sức mạnh của nó sẽ được tăng lên bởi các mô-đun mà bạn có thể cài đặt cho nó. Nếu bạn sử dụng Recon-ng một cách hiệu quả, bạn có thể tiết kiệm rất nhiều thời gian trong việc nghiên cứu OSINT.
Recon-ng có thể chạy từ dòng lệnh. Nếu bạn muốn làm cho Recon-ng hữu ích cho mục đích của mình, hãy chọn tùy chọn Marketplace từ menu chính và khám phá những gì có sẵn. Có một số lượng lớn các mô-đun mà bạn có thể thử, với nhiều mô-đun được cải tiến và bổ sung liên tục. Nếu bạn cảm thấy thoải mái với dòng lệnh và bạn muốn OSINT hoạt động hiệu quả hơn nhiều, Recon-ng có thể trở thành một trong những công cụ yêu thích của bạn. Ahmia.fi Ahmia.fi là một công cụ tìm kiếm đặc biệt để tìm các trang web trên Mạng Tor, mặc dù bản thân công cụ tìm kiếm này cũng có thể truy cập được trên “clearnet”. Nhưng bạn sẽ cần Tor Browser để mở kết quả tìm kiếm Tor của bạn. Rất nhiều chỗ mua bán và diễn đàn nằm trên Mạng Tor, vì vậy việc sử dụng hiệu quả công cụ tìm kiếm Ahmia.fi có thể là một phương pháp tuyệt vời cho công việc pháp y OSINT của bạn. Wayback Machine Các trang web cũ đã chết giờ nằm ở đâu? Wayback Machine là một công cụ tìm kiếm của hơn 632 tỷ trang web và đang tăng lên, nhiều trang web bắt nguồn từ những năm 1990. Archive.org đang sử dụng Wayback Machine để lưu trữ nhiều web nhất có thể. Bạn cũng có thể sử dụng trang web của họ để tự lưu trữ các trang web hiện đang trực tuyến theo cách thủ công. Nếu và khi các trang web và máy chủ web bị xóa hoặc chuyển sang chế độ ngoại tuyến, một bản sao đã lưu trữ có thể được tìm thấy thông qua Wayback Machine. Cá nhân mình đã tìm thấy các trang web được lưu trữ từ năm 1994 đến năm 2021 thông qua công cụ này. Và điều thực sự thú vị là bạn thường có thể sử dụng các liên kết trong các trang web đã lưu trữ để chuyển đến kho lưu trữ của các trang web khác đó. theHarvester theHarvester là một công cụ do thám mã nguồn mở hữu ích khác mà bạn có thể cài đặt từ GitHub. Nó có thể được sử dụng để lấy địa chỉ email, máy chủ, tên miền phụ, tên nhân viên và mở các cổng internet từ nhiều nguồn công cộng khác nhau như công cụ tìm kiếm, máy chủ khóa PGP và Shodan. Khi Harvester được cài đặt, bạn có thể dễ dàng chạy ứng dụng từ dòng lệnh của mình. Có một bộ tùy chọn đặc biệt phong phú để khám phá dữ liệu trong máy chủ DNS. Máy chủ DNS có tất cả các loại thông tin rất hữu ích vì chúng liên kết tên miền với các địa chỉ IP cụ thể. Một số nguồn dữ liệu yêu thích của mình mà bạn có thể khám phá vớiHarvester bao gồm LinkedIn, Bing, Google và VirusTotal. TinEye TinEye là một công cụ mạnh mẽ để nghiên cứu hình ảnh trực tuyến. Nếu bạn có một hình ảnh trên thiết bị cục bộ của mình, bạn có thể tải nó lên TinEye và xem hình ảnh đó có được sử dụng trên các web khác hay không và như thế nào. Một trường hợp sử dụng rõ ràng nhất là nếu bạn có ảnh của ng��ời nào đó mà bạn không biết danh tính và bạn muốn tìm hiểu họ là ai. Nhưng có nhiều trường hợp sử dụng khác, chẳng hạn như "bức ảnh này được chụp ở đâu?" hoặc "đây là ảnh chụp màn hình của ứng dụng nào?" Ngược lại, nếu bạn có URL của hình ảnh trên web, bạn cũng có thể tiến hành nghiên cứu theo cách đó. TinEye cũng hữu ích để duy trì sự riêng tư của bạn. Ví dụ: có lẽ bạn nên bảo vệ quyền riêng tư của con mình. TinEye có thể thông báo cho bạn biết nếu và khi nào ảnh của con bạn được chia sẻ trực tuyến. OSINT Framework OSINT Framework là ứng dụng web hoàn hảo nếu bạn không chắc mình sẽ cần sử dụng nguồn dữ liệu OSINT nào để tìm thông tin bạn muốn. Vì vậy, OSINT Framework giới thiệu cho bạn một cây khổng lồ các nguồn dữ liệu tiềm năng mà bạn có thể khám phá. Bạn có muốn phân tích tệp độc hại, tên người dùng, vị trí địa lý, địa chỉ IP, tên miền, IRC, Dark Web, siêu dữ liệu, thông tin về mối đe dọa, số điện thoại hoặc có thể là thứ gì khác không? Tiếp tục nhấp qua cây biểu đồ cho đến khi bạn tìm thấy nguồn mà bạn cần. OSINT Framework có thể là bước đầu tiên của bạn trong tất cả quá trình OSINT.
0 notes
Text
Essential Ethical Hacking Tools and Software for Beginners

In the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity, ethical hacking plays a crucial role in identifying vulnerabilities, securing systems, and protecting digital assets. Whether you're a cybersecurity enthusiast or aspiring ethical hacker, having the right tools and software is essential to effectively simulate attacks and assess security posture. In this blog post, we'll explore some fundamental ethical hacking tools and software that every beginner should know.
Understanding Ethical Hacking Tools and Software
Ethical hacking tools and software are designed to assist security professionals in testing and evaluating the security of systems and networks. These tools simulate real-world attacks to identify weaknesses and help organizations strengthen their defenses. For beginners entering the field of ethical hacking, mastering these tools is a critical step toward building foundational skills. Here are some essential ethical hacking tools and software every beginner should be familiar with:
Nmap: Nmap (Network Mapper) is a powerful network scanning tool used for discovering hosts and services on a computer network. It's essential for port scanning, detecting open ports, and identifying potential entry points for attackers.
Wireshark: Wireshark is a network protocol analyzer that captures and displays network packets. It helps ethical hackers analyze traffic, identify vulnerabilities, and troubleshoot network issues.
Metasploit: Metasploit is a penetration testing framework that allows ethical hackers to exploit known vulnerabilities in systems. It provides a range of tools for developing and executing exploits, making it an indispensable tool for security assessments.
Burp Suite: Burp Suite is a web application security testing tool used for scanning and testing web applications. It helps identify security flaws such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF).
John the Ripper: John the Ripper is a password-cracking tool used to perform brute-force attacks and dictionary attacks on password hashes. It's commonly used to assess password strength and test authentication mechanisms.
Aircrack-ng: Aircrack-ng is a suite of tools for assessing Wi-Fi network security. It includes tools for capturing packets, performing dictionary attacks on Wi-Fi passwords, and testing WEP/WPA encryption vulnerabilities.
Hydra: Hydra is a popular password-cracking tool that supports various protocols, including SSH, FTP, Telnet, and HTTP. It's used for performing brute-force attacks on login credentials.
Nikto: Nikto is a web server scanner that identifies potential security vulnerabilities in web servers. It checks for outdated software versions, misconfigurations, and common vulnerabilities.
Snort: Snort is an open-source intrusion detection system (IDS) that detects and logs suspicious network traffic. It's used for real-time monitoring and alerting of potential security threats.
Maltego: Maltego is a data visualization tool used for gathering and analyzing information about targets. It helps ethical hackers perform reconnaissance and map relationships between entities.
Best Hacker in the World:
While ethical hacking emphasizes responsible and legal practices, renowned best hacker in the world such as Kevin Mitnick, Kevin Poulsen, and Adrian Lamo have gained fame for their expertise in cybersecurity and ethical hacking.
It's important to note that ethical hacking is not about achieving notoriety but rather about using skills for constructive purposes, such as securing systems, protecting data, and promoting cybersecurity awareness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering ethical hacking tools and software is essential for beginners looking to pursue a career in cybersecurity. By familiarizing themselves with tools like Nmap, Wireshark, Metasploit, and Burp Suite, aspiring ethical hackers can gain practical experience in penetration testing, vulnerability assessment, and network security. Ethical hacking is ultimately about using skills and knowledge responsibly to defend against cyber threats and safeguard digital assets. Start exploring these tools and software today to embark on an exciting journey into the world of ethical hacking!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Accretion & Discretion
The content in my Evernote has been accumulating for the last 38 months, like a planetesimal expanding with each new asteroid it encounters. Those that grow large enough to become actual planets are in hydrodynamic equilibrium – rounded due to their gravity being sufficient to compact any type of mineral in their makeup. They all differentiate to some degree, with dense minerals sinking, and gasses escaping. This collection is now at the point of differentiation, only with a network sorting rather than vertical stratification.
This process has been … educational for me. Like my computer science education, my first career of handling enterprise LAN administration, and my move to service provider networking. My non-telecom pursuits have been similar – renewable energy, Democratic politics, and my meandering progress in all things sense making. Reading piles up around my interest of the moment, but those are all profit oriented.
As an autist of the more functional sort, I still do some very autismal things, I just don’t talk about them as much. The most visible among them was my two year pursuit of western history. Between that and the studies related to my conversion to Buddhism I spent quite a bit of time on the intersection of hypnosis and formal linguistic analysis. I wrote a great deal on food and water security with a focus that happened to be roughly the boundaries of the Ottoman empire at its peak, which was uncharacteristically noisy of me.
Over the years I’ve been described as: aloof, secretive, unknowable, and otherwise inaccessible. This is typically not a conscious act, it’s just my personal perch on the autism spectrum. But this time is different. What would normally be a private pursuit, perhaps occasionally surfacing in conversation, is now an intentional matryoshka, a riddle within a mystery, wrapped in my purportedly enigmatic ways.
I took a break in the middle of writing this to fiddle with the graph. I’ve discovered, and perhaps solved, a significant problem. If you’re counting noses there are eleven additional green dots, but that’s not eleven additional names. There are six new names and the outermost arc of those dots are just a bit darker than all the rest – they’re well known aliases.
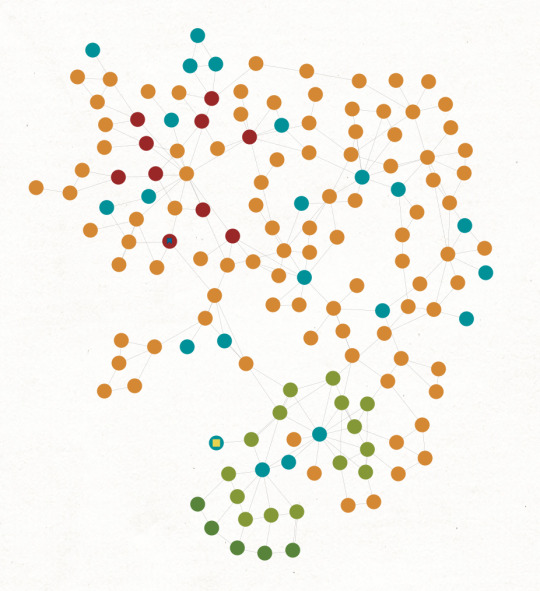
Right now they are quite close on the graph. That’s not an accurate representation of reality, there’s a sharp divide between those first nine names and the six who just joined the mix.
And since this is Maltego, there isn’t really a good way to represent the temporal component. One group came first, and then the second arose, with just one “cross patched” between both groups. There’s a sense of betrayal in that crossing, but I’m not sure how, or even if I should say anything about it.
0 notes
Text
CompTIA CySA+ CS0-003: Maltego
Maltego is a data mining and information gathering tool that can provides automatic merging of data to provide visual maps. It is a open source intelligence tool with graphical link analyses tool. Maltego is a great tool to identify relationships and it is extremely useful when you deal with big data. It helps visualize relationships with data and see connections that you would have otherwise…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
0 notes