#Mobile Sortation System
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Link
0 notes
Text
Global Logistics Automation Market is projected to reach the value of USD 55.36 billion by 2030.
Global Logistics Automation Market is projected to reach the value of USD 55.36 billion by 2030.
logistics automation market crossed USD 34 billion, with automated solutions cutting operational costs by an average of 28% across industries. Companies deploying end-to-end automation reported a 29.3% boost in warehouse productivity within the first year alone. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) surged by 34% year-on-year, reshaping warehouse layouts with flexible, scalable operations.
With e-commerce order volumes growing 5x faster than traditional retail and labor shortages driving logistics costs up by over 18%, automated systems have shifted from a “nice-to-have” to a “must-have” for competitive survival.
This report offers actionable segmentation by component, automation type, and end-user industry; uncovers pricing trends; analyzes deployment models; and provides country-specific insights including North America, Asia-Pacific, and Europe.
2025–2030 marks a critical window. Companies acting now can secure operational advantages, reduce risks, and achieve 3–5x faster returns on automation investments compared to late adopters.
Download Sample @ https://tinyurl.com/cuwv5ahk
The logistics automation market has experienced remarkable growth in 2024, revolutionizing supply chain operations across industries through advanced technological integration. This transformation is characterized by the increasing adoption of robotics, artificial intelligence, warehouse management systems, and autonomous vehicles designed to streamline logistics processes. Companies worldwide are recognizing the competitive advantages offered by automation technologies, including enhanced operational efficiency, reduced labor costs, and improved accuracy in inventory management. The market is witnessing a significant shift from traditional manual processes to sophisticated automated solutions that can handle complex logistics tasks with minimal human intervention. The current market landscape reflects a strong emphasis on end-to-end automation solutions that provide seamless connectivity between different stages of the supply chain. Major industry players are focusing on developing integrated platforms that combine various automation technologies to offer comprehensive logistics management capabilities. The rise of e-commerce has been a pivotal factor driving demand for logistics automation, as businesses strive to meet increasingly stringent customer expectations regarding delivery speed and accuracy. Additionally, the push toward sustainability has influenced market growth, with automated systems demonstrating superior energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional methods. In 2024, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have become more prominent participants in the logistics automation market, facilitated by the availability of scalable and cost-effective solutions. Cloud-based logistics automation platforms have gained substantial traction, enabling businesses of all sizes to access advanced capabilities without significant upfront investments.
Key Market Insights:
Studies indicate that companies implementing comprehensive logistics automation solutions report an average productivity increase of 29.3% within the first year of deployment. The adoption rate of automated guided vehicles (AGVs) has surged by 47% in 2024 compared to the previous year, reflecting the growing preference for mobile robotics in warehouse environments.
Approximately 62% of logistics providers are currently utilizing some form of artificial intelligence to optimize route planning and inventory management.
Automated sortation systems have demonstrated an impressive 32.6% reduction in order processing time across industries.
The pharmaceutical sector has emerged as a significant adopter of logistics automation, with 71.5% of pharmaceutical companies investing in automated storage and retrieval systems.
Market Drivers:
Increasing E-commerce Demands
The explosive growth of e-commerce has fundamentally transformed consumer expectations around delivery speed, accuracy, and flexibility, creating unprecedented pressures on supply chain operations. Modern consumers demand same-day or next-day delivery options, accurate order fulfilment, and real-time tracking capabilities — requirements that are virtually impossible to meet consistently through manual processes alone. Logistics automation technologies address these challenges directly by enabling high-speed order processing, reducing picking errors through guided systems, and facilitating rapid sortation and dispatch operations. The ability to handle high-volume, high-variety order profiles efficiently has become essential for e-commerce success, particularly during peak seasons when order volumes can increase exponentially. Additionally, the rise of omnichannel retail strategies requires seamless integration between physical and online sales channels, necessitating sophisticated automated inventory management systems that maintain accurate stock visibility across all points of sale. Companies leveraging advanced logistics automation have demonstrated their ability to reduce order fulfilment times by up to 70% while simultaneously improving accuracy rates to over 99.9%, creating significant competitive advantages in the rapidly evolving e-commerce landscape.
Labor Shortages and Rising Costs
The logistics industry is facing severe workforce challenges characterized by persistent labor shortages, high turnover rates, and steadily increasing wage costs, creating compelling incentives for automation adoption. In many developed markets, logistics operations struggle to attract and retain qualified personnel for physically demanding roles in warehouses and distribution centers, particularly for night shifts and peak seasons. This workforce gap has been exacerbated by demographic shifts including aging populations and changing career preferences among younger workers. The financial implications are substantial, with labor typically representing 50–70% of operational costs in traditional logistics facilities. Automation technologies directly address these challenges by reducing dependence on manual labour while improving working conditions for remaining staff. Tasks that once required extensive human intervention — such as heavy lifting, repetitive picking, and long-distance walking within facilities — can now be performed by automated systems operating continuously without fatigue or performance variation. This transition allows human workers to be reallocated to higher-value roles requiring judgment and problem-solving skills, often resulting in increased job satisfaction and reduced turnover. The economic case for automation becomes increasingly compelling as labour costs rise, with many companies reporting that automation investments reach positive ROI significantly faster in regions with high labour costs.
Market Restraints and Challenges:
The logistics automation market faces significant barriers including high initial investment requirements and technical integration complexities. Many existing facilities require extensive structural modifications to accommodate automation systems, increasing implementation costs. Legacy IT systems often prove incompatible with modern automation platforms, necessitating additional investments in digital infrastructure. Furthermore, workforce resistance and training requirements can delay adoption and reduce projected returns, particularly in organizations with limited change management capabilities.
Market Opportunities:
Emerging technologies including artificial intelligence and machine learning present substantial opportunities for predictive logistics optimization. The growing middle class in developing regions is driving demand for efficient distribution networks, creating new markets for automation solutions. Sustainability initiatives provide openings for energy-efficient automation systems that reduce environmental impact while improving operational efficiency. Additionally, the increasing availability of automation-as-a-service models is making sophisticated technologies accessible to smaller organizations, significantly expanding the potential customer base for logistics automation providers.
Buy Now @ https://tinyurl.com/bdet4j3k
Market Segmentation:
By Component:
Hardware: • Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) • Conveyor Systems • Sortation Systems • Palletizing and Depalletizing Systems • Robotic Picking and Packing Systems • Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) • Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) • Industrial Sensors • Barcode and RFID Scanners • Others (Cranes, Carousels, Shuttle Systems) Software: • Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) • Transportation Management Systems (TMS) • Yard Management Systems (YMS) • Inventory Management Systems • Order Management Systems • Others (Fleet Management, Labor Management Software) Services: • Consulting • System Integration and Deployment • Support and Maintenance
Autonomous Mobile Robots represent the fastest-growing hardware component within logistics automation, experiencing 34% year-over-year growth. Unlike fixed automation or traditional AGVs, these flexible systems require minimal infrastructure modifications and can be rapidly deployed and reconfigured. AMRs leverage advanced navigation capabilities, machine learning, and sophisticated sensor arrays to navigate dynamic environments without predefined paths. Their modular design and scalable implementation allow organizations to start with limited deployments and expand incrementally, creating adoption advantages for operations with uncertain future requirements or space constraints.
Warehouse Management Systems maintain their position as the dominant software component within logistics automation, representing approximately 43% of total software expenditures. These systems serve as the central nervous system for automated operations, orchestrating workflows, resource allocation, and information flows across diverse automation technologies. WMS functionality has expanded beyond inventory control to incorporate sophisticated optimization algorithms, labor management, yard operations, and seamless integration with enterprise systems. Cloud-based deployment models have democratized access to enterprise-grade capabilities, accelerating adoption across organization sizes. The strategic importance of WMS continues to grow as automation complexity increases, requiring sophisticated coordination between human operators and diverse automated systems.
By End-Use Industry:
• Retail and E-commerce • Manufacturing • Automotive • Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals • Food and Beverages • Aerospace and Defense • Consumer Electronics • Logistics and Transportation • Others (Textiles, Chemicals, Oil & Gas)
0 notes
Text
Warehouse Automation Market Growth Driven by E-commerce Expansion and Smart Logistics Integration Globally
In recent years, warehouse automation has emerged as a critical component of modern supply chain management. With global commerce expanding and customer expectations rising, businesses are under increasing pressure to enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and streamline operations. The warehouse automation market has responded to this demand with innovative technologies that are reshaping the way goods are stored, sorted, picked, and shipped.

The Driving Forces Behind Warehouse Automation
The surge in e-commerce has been one of the most significant catalysts for warehouse automation. Consumers now expect rapid order fulfillment and real-time tracking, which necessitates precise inventory management and faster logistics. Manual processes, while still common in many warehouses, can no longer keep pace with the volume and speed of modern retail. Automation technologies fill this gap by providing scalable, data-driven solutions that improve accuracy and throughput.
Labor shortages have also played a role in accelerating automation adoption. Warehousing jobs often involve repetitive tasks and physically demanding work, leading to high turnover rates and recruitment challenges. Automated systems such as robotic arms, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) can handle these tasks efficiently while reducing the dependency on human labor.
Moreover, the increasing availability of affordable sensors, AI-driven software, and cloud-based warehouse management systems (WMS) has made automation more accessible to businesses of all sizes. Even small and mid-sized companies are now exploring automation solutions to remain competitive in a rapidly changing marketplace.
Key Technologies Shaping the Market
Several technologies are central to the transformation of warehouse operations:
Robotics: Robotic systems are being widely used for picking, packing, and transporting goods within warehouses. These systems use machine learning and computer vision to navigate and perform tasks with high precision.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): AS/RS use cranes, shuttles, and conveyors to store and retrieve products efficiently. These systems are especially beneficial in high-density storage environments.
Conveyor and Sortation Systems: These enable rapid sorting of packages based on size, weight, destination, or priority, which is essential in high-volume distribution centers.
Warehouse Management Software (WMS): A robust WMS integrates with hardware systems to provide real-time visibility into inventory, order status, and workforce productivity.
Internet of Things (IoT): Sensors and connected devices provide data on equipment performance, warehouse temperature, and stock levels, allowing predictive maintenance and better resource management.
Market Outlook and Growth Trends
According to market analysts, the warehouse automation market is expected to continue its robust growth trajectory over the next decade. Valued at approximately $22 billion in 2024, it is projected to surpass $60 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 14%.
Geographically, North America and Europe have been early adopters of warehouse automation, driven by well-established logistics infrastructure and high labor costs. However, Asia-Pacific is rapidly catching up, fueled by booming e-commerce sectors in countries like China and India, as well as a strong push toward industrial modernization.
Industries beyond retail are also embracing automation. Sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and electronics are increasingly investing in warehouse technologies to meet stringent quality standards and ensure traceability throughout the supply chain.
Challenges to Implementation
Despite its benefits, warehouse automation is not without challenges. High upfront investment remains a significant barrier for many companies, particularly in emerging markets. Additionally, the complexity of integrating new technologies into existing systems can lead to downtime and operational disruptions during the transition phase.
There is also the issue of workforce displacement. While automation reduces the need for manual labor, it also necessitates upskilling workers to manage and maintain automated systems. Companies must invest in training and change management to ensure a smooth technological transition.
Cybersecurity is another growing concern. As warehouses become more digitally connected, the risk of cyberattacks increases. Ensuring robust data protection and system security is critical for preventing operational disruptions and safeguarding sensitive information.
The Road Ahead
The warehouse automation market is at a pivotal juncture. As technological capabilities expand and the cost of automation continues to decline, its adoption will become increasingly widespread. Businesses that embrace automation early stand to gain a competitive edge through improved efficiency, reduced operational costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
However, success in this space requires more than just investment in hardware and software. It demands a holistic strategy that includes employee training, supply chain integration, and a commitment to continuous innovation. By reimagining warehouse operations through the lens of automation, companies can not only meet today’s demands but also build a more agile and resilient logistics ecosystem for the future.
0 notes
Text
Warehouse Automation: 2025 Trends, Types, and Best Practices

Warehouse automation, a cornerstone of the fourth industrial revolution, is transforming logistics by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. Technologies like robotic pickers, conveyor belts, and AI-driven systems reduce manual labor and streamline operations to meet soaring e-commerce demands. As global retail sales are projected to hit $7.4 trillion by 2025, automation is critical for staying competitive. This 700-word guide explores the benefits, types, trends, and best practices for warehouse automation in 2025.
What is Warehouse Automation?
Warehouse automation leverages advanced technologies—robotics, software, and automated systems—to optimize tasks with minimal human involvement. It replaces repetitive, error-prone manual processes with faster, more accurate solutions. For instance, robotic arms sort goods, while conveyor systems move items seamlessly, saving time, cutting costs, and boosting efficiency in today’s fast-paced logistics landscape.
Benefits of Warehouse Automation
Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity
Automation streamlines workflows, accelerating tasks like storage and retrieval. Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) maximize space, while robotic pick-and-pack stations enable rapid order fulfillment, supporting services like overnight shipping. Operating 24/7, automated systems reduce bottlenecks and boost productivity.
Reducing Errors and Improving Accuracy
Technologies like barcode readers achieve near-100% data capture, eliminating picking and tracking errors. Real-time monitoring ensures accurate inventory, and precise systems deliver 99.9% picking accuracy, minimizing costly mistakes and enhancing order reliability.
Lowering Operational Costs
Automation reduces labor and material waste, offering significant savings. AS/RS systems provide a 3–5-year payback period and can last 30 years, optimizing resources. By automating repetitive tasks, businesses lower operational expenses and achieve sustainable cost reductions.
Scaling Operations Seamlessly
Automated solutions adapt to seasonal spikes or growth without major overhauls. Scalable systems like Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) integrate new technologies, ensuring warehouses remain agile in dynamic markets.
Types of Warehouse Automation Technologies
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots work alongside humans, handling repetitive tasks like sorting or packing. Equipped with safety sensors, they prevent collisions and free workers for complex duties, such as quality checks, improving efficiency and safety.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
AMRs use AI and sensors to navigate warehouses, transporting goods precisely. Integrated with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), they enhance inventory tracking, reduce labor costs, and operate 24/7 to support peak periods.
Conveyor and Sortation Systems
Conveyor belts and sortation systems use barcode scanners and RFID to move and sort goods efficiently, streamlining picking, packing, and shipping while reducing manual labor.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
AS/RS use robots or cranes to store and retrieve items, maximizing vertical space and speeding up inventory management. Integrated with WMS, they reduce congestion and boost throughput.
Key Trends in Warehouse Automation for 2025
Advancements in Robotics
Robots now handle picking, packing, and sorting with 99.9% accuracy. AI and machine learning enable them to manage complex tasks, like handling delicate items. The robotic picking market is expected to reach $5.7 billion by 2028.
Growth of AI Applications
AI optimizes restocking and demand forecasting, preventing stockouts and overstocking. AI-driven systems enhance quality control and adapt to customer demands, integral to modern WMS.
Increasing IoT Connectivity
IoT sensors provide real-time data on equipment and inventory, minimizing downtime via predictive maintenance and streamlining workflows for seamless operations.
Adoption of Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics tools forecast demand, reducing inventory costs (averaging $3.7 million annually). They drive smarter decisions and faster ROI.
Sustainable Automation
Energy-efficient conveyors and AI-driven energy management reduce environmental impact, aligning with green logistics demands.
Steps to Implement Warehouse Automation
Assess Processes: Identify inefficiencies, like slow picking, to prioritize automation’s impact.
Set Goals: Define targets, such as 20% higher order accuracy, aligned with business needs.
Choose Tools: Select scalable solutions like AGVs or robotic arms, balancing cost and ROI.
Pilot Test: Start small in a low-traffic area, measuring metrics like processing time.
Train Workforce: Upskill staff on WMS and robotics for smooth adoption.
Implement in Phases: Begin with simple tasks like barcode scanning, progressing to robotic sorting.
Monitor and Optimize: Track KPIs like order accuracy and adjust workflows to maintain efficiency.
Overcoming Challenges
High Costs: Use financing or grants to offset investments. Solutions like Pio achieve 99.9% accuracy, reducing long-term costs.
Change Resistance: Involve staff, highlight benefits like less physical strain, and share success stories.
Compatibility: Assess systems and test integrations to ensure seamless operation.
Downtime: Schedule implementations during low-demand periods and monitor early stages.
Calculating ROI
Cost Savings: Automation cuts labor and error-related costs, with savings outweighing investments in 2–3 years.
Productivity: Sorting systems process thousands of packages hourly, far surpassing manual labor.
Error Reduction: Accurate systems boost customer retention, as 17% of consumers abandon brands after one error.
Scalability: Dynamic systems handle growth without reinvestment.
Conclusion
Warehouse automation delivers faster, more accurate, and cost-effective operations. Technologies like cobots, AMRs, and AI enable warehouses to meet e-commerce demands and scale efficiently. By starting small, integrating with WMS, and training staff, businesses can maximize ROI and overcome challenges. With the automation market projected to reach $69 billion by 2025, now is the time to invest for sustainable success.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Automated Sortation System Market
📦 𝐅𝐫𝐨𝐦 𝐂𝐡𝐚𝐨𝐬 𝐭𝐨 𝐂𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐲 ➡️ 𝐎𝐧𝐞 𝐒𝐜𝐚𝐧 𝐚𝐭 𝐚 𝐓𝐢𝐦𝐞 🔄
Automated Sortation System Market size is estimated to reach $12 Billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 9.2% during the forecast period 2025–2031.
🔗 𝐆𝐞𝐭 𝐑𝐎𝐈-𝐟𝐨𝐜𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐢𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐭𝐬 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝟐𝟎𝟐𝟓-𝟐𝟎𝟑𝟏 → 𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐍𝐨𝐰
Automated Sortation System Market is a rapidly growing segment within the logistics and material handling industry, driven by the increasing demand for speed, accuracy, and efficiency in supply chain operations. These systems are used to identify, categorize, and route products or packages using technologies such as barcode scanners, RFID, sensors, and advanced software algorithms.
Key industries adopting automated sortation systems include e-commerce, retail, postal and courier services, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals, where high-volume handling and timely delivery are critical. The surge in online shopping and global trade has significantly contributed to market expansion, with warehouses and distribution centers investing in automation to manage the growing volume and complexity of operations.
Technological advancements - such as AI-powered sorting, IoT integration, and real-time data analytics - are enhancing the performance of these systems, offering greater flexibility, scalability, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Moreover, the emphasis on labor cost reduction, operational efficiency, and error minimization is accelerating adoption across developed and emerging economies.
Regionally, North America and Asia-Pacific are leading markets, with substantial investments in infrastructure modernization. The market is expected to maintain strong growth momentum, supported by continuous innovation and the global push toward digital and automated supply chains.
𝐓𝐨𝐩 𝐊𝐞𝐲 𝐏𝐥𝐚𝐲𝐞𝐫𝐬:
Daifuku North America, INCAS - SSI SCHÄFER GROUP, BEUMER Group, Interroll Group, Körber, Siemens Logistics, Fives Intralogistics , Murata Machinery USA, Inc, Dematic Mobile Automation, Vanderlande, Bastian Solutions, TGW Logistics, System Logistics Corporation - Vertique (Krones Group), Equinox MHE, MHS Global, Conveyco Technologies, Intralox, FlexLink
#AutomatedSortation #SortationSystems #WarehouseAutomation #SmartLogistics #MaterialHandling #IndustrialAutomation #SupplyChainTech #AutomationSolutions #Intralogistics #LogisticsInnovation

0 notes
Text
Automated Material Handling Equipment Market: Innovations and Technological Advancements Reshaping Industries Worldwide
The Automated Material Handling Equipment (AMHE) market is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in technology and an increasing demand for efficient and cost-effective solutions in various industries. These systems are designed to automate processes such as the transportation, storage, and retrieval of materials in warehouses, manufacturing plants, distribution centers, and other industrial settings. AMHE includes a broad range of equipment, such as conveyors, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), cranes, robots, and sortation systems, all of which work together to streamline material flow and improve operational efficiency.

Market Drivers
Several key factors are contributing to the rapid expansion of the Automated Material Handling Equipment market. One of the main drivers is the increasing demand for automation in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, e-commerce, and retail. The need for faster and more accurate material handling solutions, as well as the growing pressure to meet customer demands for quick deliveries, is pushing companies to adopt automation technologies.
The rising labor costs and the shortage of skilled labor are also influencing the market. Many businesses are turning to automated systems to reduce reliance on human labor, thereby lowering operational costs and improving productivity. Additionally, automated systems can work around the clock, ensuring higher efficiency and reducing the chances of human error. This results in enhanced throughput, better utilization of resources, and improved safety.
Technological advancements in robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are also playing a crucial role in the growth of the market. AMHE systems are becoming increasingly intelligent and capable of performing complex tasks, such as inventory management, predictive maintenance, and real-time data analysis. These innovations make automation systems more versatile and adaptable to a variety of industries, thus broadening their applications.
Market Segmentation
The Automated Material Handling Equipment market can be segmented based on the type of equipment, end-user industry, and region.
By Type of Equipment:
Conveyors: These are commonly used in manufacturing and distribution centers for transporting goods and materials. Conveyors offer an efficient means of material handling by reducing the need for manual labor and enhancing operational efficiency.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): AGVs are mobile robots used to transport materials within a facility. They follow pre-programmed paths and are equipped with sensors to avoid obstacles, improving the flow of materials while ensuring safety.
Robotic Systems: Robotic systems, such as robotic arms, are widely used in material handling for tasks such as sorting, picking, and packaging. They are often used in combination with other automated equipment to optimize processes.
Cranes and Hoists: These systems are used for lifting and transporting heavy materials in industrial settings. Cranes and hoists are vital in sectors such as construction and manufacturing.
Sortation Systems: These systems are designed to sort products based on predefined criteria such as size, color, or destination. They are typically used in warehouses and distribution centers for efficient order fulfillment.
By End-User Industry:
E-commerce and Retail: The e-commerce industry is one of the largest adopters of automated material handling systems. With the increase in online shopping, there is a growing need for efficient fulfillment centers that can handle large volumes of orders quickly and accurately.
Manufacturing: In manufacturing, AMHE systems are used to streamline processes such as assembly, packaging, and delivery. The automotive and electronics industries, in particular, rely heavily on automated material handling to improve production efficiency.
Logistics and Warehousing: The logistics industry is also a major consumer of AMHE, as it allows companies to optimize their supply chains, reduce transit times, and improve inventory management.
Food and Beverage: In the food and beverage sector, automated systems are used for tasks such as sorting, packaging, and palletizing. These systems ensure that products are handled hygienically and meet safety standards.
Pharmaceuticals: Automated systems in the pharmaceutical industry are crucial for ensuring the accuracy and safety of products. They help with tasks such as inventory management, sorting, and packaging of sensitive pharmaceutical products.
Regional Insights
The Automated Material Handling Equipment market is experiencing significant growth across various regions, with North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific being key players.
North America: North America, especially the United States, is one of the largest markets for AMHE, driven by the high adoption rate of advanced technologies in industries such as e-commerce, manufacturing, and logistics. The region's strong focus on research and development, along with the presence of several key market players, is also contributing to market growth.
Europe: Europe is another prominent region in the AMHE market, with countries like Germany, the UK, and France leading the way. The European market is characterized by a high demand for automation in manufacturing, logistics, and e-commerce, particularly in countries with strong industrial sectors.
Asia Pacific: The Asia Pacific region is expected to see the highest growth in the Automated Material Handling Equipment market. This can be attributed to the rapid industrialization in countries like China, Japan, and India. The increasing demand for automation in manufacturing and logistics, coupled with the region’s large population and growing e-commerce sector, is driving market expansion.
Challenges
Despite the significant growth potential, the AMHE market faces several challenges. One of the main obstacles is the high initial cost of implementing automated systems, which can be a barrier for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Additionally, the complexity of integrating new automated systems with existing infrastructure can lead to disruptions in operations.
Moreover, the rapid pace of technological advancements in automation means that businesses must constantly invest in upgrading their systems to remain competitive. This presents a challenge for companies in terms of budget allocation and resource management.
Conclusion
The Automated Material Handling Equipment market is poised for substantial growth, driven by the need for efficiency, cost reduction, and technological advancements. As industries continue to embrace automation to meet the demands of modern supply chains, the market for AMHE is expected to expand significantly in the coming years. However, businesses must carefully consider factors such as initial costs and system integration to ensure successful adoption.
0 notes
Text
What Is Automation in Operations? A Deep Dive into Its Impact on Palatine, Illinois Businesses
In recent years, automation in operations has emerged as a powerful force reshaping how businesses across Illinois function. In Palatine—a growing village within the Chicago metropolitan area—industries are rapidly adapting automation technologies to streamline workflows, boost efficiency, and enhance scalability.
Whether it’s a manufacturing plant using automated machinery or a logistics center implementing smart tracking systems, the transformation is visible across sectors. Businesses in Palatine, Illinois, are now recognizing that automation is no longer optional but essential for remaining competitive and agile in today's fast-paced market.
What Does Automation in Operations Actually Mean?
At its core, automation in operations refers to the use of technology—like machines, control systems, and software—to perform tasks that were traditionally done manually. These tasks may involve manufacturing, processing, monitoring, or even decision-making.
By integrating automation into operations, companies in Palatine can:
Reduce human error
Minimize repetitive labor
Increase productivity
Save time and money
Improve customer satisfaction through consistent output
From robotic process automation (RPA) in administrative tasks to programmable logic controllers (PLCs) in assembly lines, automation is making every facet of business more responsive and resilient.
Key Industries in Palatine Benefiting from Automation
Palatine is home to a mix of manufacturing, distribution, healthcare, and tech-based businesses. Automation plays a distinct role in each of these sectors, helping them scale while maintaining quality and cost-efficiency.
Manufacturing and Assembly Palatine’s proximity to industrial hubs in Illinois makes it ideal for manufacturers looking to modernize. With automation, local facilities can now rely on CNC machines, robotic arms, and automated conveyors to handle tasks that once took multiple shifts to complete. These systems also reduce the risk of injury and ensure higher output consistency.
Warehousing and Logistics The demand for faster delivery and real-time tracking has pushed logistics companies in Palatine to invest in warehouse automation. This includes:
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) Smart inventory management systems Automated sortation and packaging equipment
With these tools, operations become more efficient, and human workers are freed up for tasks requiring judgment and flexibility.
Healthcare and Medical Devices Palatine’s healthcare facilities and medical device manufacturers are also leveraging automation to handle high-volume processes with precision. From sterile packaging lines to automated diagnostic equipment, these solutions improve both patient safety and operational efficiency.
Food and Beverage Processing Automation ensures consistency in quality, taste, and safety in food production—something that’s critical to food manufacturers operating in and around Palatine. Automated mixers, dispensers, and inspection systems can significantly increase throughput while meeting strict regulatory standards.
Advantages of Adopting Automation in Local Operations
Integrating automation into day-to-day operations offers many advantages that go beyond simple productivity gains. For businesses in Palatine, Illinois these benefits include:
Enhanced Accuracy and Reliability Machines don’t tire, lose focus, or skip steps. By reducing manual intervention, automation ensures greater consistency and accuracy—especially important in industries like pharmaceuticals and electronics.
Cost Savings Over Time Though automation may require a higher upfront investment, it often results in long-term cost reductions by decreasing labor costs, minimizing waste, and reducing downtime.
Scalability and Flexibility Automated systems can easily adapt to different product lines or changing workloads. This scalability allows Palatine businesses to grow without a complete overhaul of their infrastructure.
Improved Data and Decision-Making Many automated systems provide real-time data and analytics, empowering businesses to make informed decisions. This insight is vital for continuous improvement and optimizing resource allocation.
Challenges Faced and How Palatine Businesses Are Overcoming Them
Despite its numerous benefits, automation isn’t without challenges—especially for small to mid-sized enterprises (SMEs). Concerns include:
Initial cost of installation Integration with existing systems Employee resistance to change
However, businesses in Palatine are actively overcoming these hurdles through phased implementation and workforce training. Community colleges and technical institutes in the area also offer courses in automation technology, helping bridge the skills gap and prepare workers for the future of industry.
Automation in Operations and the Human Workforce
One common misconception is that automation replaces human jobs entirely. In reality, it often transforms them.
In Palatine, we’re seeing a shift where routine tasks are automated, allowing workers to focus on more strategic, creative, or safety-critical roles. For example, instead of manually inspecting each unit on an assembly line, workers now oversee quality control systems and use data dashboards to make decisions.
By automating low-value tasks, companies also improve job satisfaction and reduce burnout, creating a healthier work environment.
The Future of Operational Automation in Palatine, Illinois
Looking ahead, the automation trend in Palatine is only expected to grow. With technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) gaining traction, the possibilities for automation are expanding every day.
Imagine predictive maintenance systems that can fix equipment before it fails, or AI-driven scheduling tools that adapt production in real time based on customer demand. These aren’t distant dreams—they’re becoming a reality right here in Palatine.
To fully benefit, businesses must continue to invest in innovation, prioritize workforce development, and collaborate with trusted automation experts.
Start Your Automation Journey Today
If your business in Palatine, Illinois is ready to integrate smarter systems into your daily operations, professional support is key. Partnering with an experienced automation provider ensures smooth planning, installation, and maintenance of your systems.
One such reliable partner is Xtreme Automation LLC. With a focus on engineering excellence, smart control systems, and industrial automation, they serve businesses across Illinois with customized automation solutions built for real-world performance.
0 notes
Text
Optimizing Efficiency: The Benefits of Warehouse Automation Services
In today’s fast-paced logistics and supply chain industry, efficiency and accuracy are critical for businesses aiming to stay competitive. Warehouse automation services have emerged as a game-changer, helping companies streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance overall productivity. In this blog, we explore the key benefits and applications of warehouse automation services.
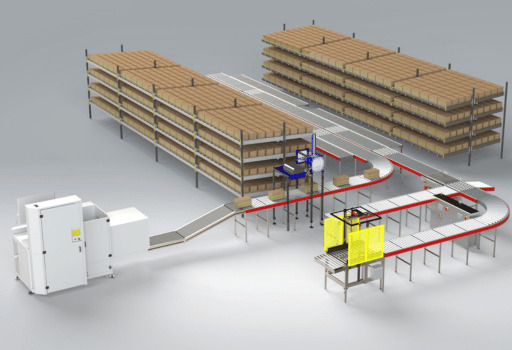
What is Warehouse Automation?
Warehouse automation involves the use of technology, robotics, and software systems to manage warehouse tasks with minimal human intervention. It includes automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), robotic picking solutions, conveyor systems, and warehouse management software (WMS). These technologies work together to optimize material handling, inventory management, and order fulfillment.
Key Benefits of Warehouse Automation
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Automated systems perform repetitive tasks at a much faster pace than human workers. With robots and AI-driven solutions handling order picking, packing, and sorting, warehouses can process higher volumes of goods efficiently, reducing labor-intensive operations.
2. Improved Accuracy and Reduced Errors
Automation significantly minimizes human errors in order fulfillment. AI-powered warehouse management systems ensure accurate picking and packing, reducing returns due to incorrect shipments. Barcode scanning and RFID tracking also enhance inventory accuracy.
3. Cost Savings and Labor Optimization
By reducing reliance on manual labor, businesses can lower operational costs. Automation helps redistribute human resources to more strategic roles while mitigating challenges related to labor shortages and workforce fatigue.
4. Better Space Utilization
Automated storage and retrieval systems enable warehouses to optimize vertical space, allowing for higher storage capacity within the same footprint. This maximizes storage efficiency and improves warehouse organization.
5. Enhanced Safety
Warehouse automation reduces the risk of workplace injuries by minimizing the need for employees to perform physically demanding or hazardous tasks. Autonomous robots and conveyor systems transport goods safely, preventing accidents associated with manual handling.
Popular Warehouse Automation Technologies
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): These self-navigating robots transport goods within the warehouse, improving picking and sorting efficiency.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): AGVs follow predefined paths to move inventory between locations.
Conveyor and Sortation Systems: Automated conveyor belts and sorting systems accelerate order processing and distribution.
Pick-to-Light and Put-to-Light Systems: These systems use LED lights to guide warehouse workers in picking and placing items, reducing errors and increasing speed.
AI-Powered Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): AI-driven software solutions optimize inventory tracking, demand forecasting, and workflow automation.
Future of Warehouse Automation
The future of warehouse automation is driven by AI, IoT, and machine learning. Smart warehouses are adopting predictive analytics, real-time tracking, and robotic process automation to improve decision-making and operational efficiency. As technology advances, fully autonomous warehouses are becoming a reality, revolutionizing supply chain logistics.
Conclusion
Warehouse automation services are transforming logistics by increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing accuracy. As businesses continue to invest in automation technologies, they will gain a competitive edge in an ever-evolving market. If you’re looking to optimize your warehouse operations, now is the time to explore automation solutions tailored to your business needs.
Ready to automate your warehouse? Contact us today to learn how our warehouse automation services can elevate your operations.
0 notes
Text
Automated Sortation System Market : Technology Advancements, Industry Insights, Trends And Forecast 2033
The automated sortation system global market report 2024 from The Business Research Company provides comprehensive market statistics, including global market size, regional shares, competitor market share, detailed segments, trends, and opportunities. This report offers an in-depth analysis of current and future industry scenarios, delivering a complete perspective for thriving in the industrial automation software market.
Automated Sortation System Market, 2024 report by The Business Research Company offers comprehensive insights into the current state of the market and highlights future growth opportunities.
Market Size - The automated sortation system market size has grown strongly in recent years. It will grow from $6.60 billion in 2023 to $7.09 billion in 2024 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.4%. The growth in the historic period can be attributed to increased handling capacity, increased demand for speed and efficiency, labor costs and availability, competitive pressures, and demonstrated ROI.
The automated sortation system market size is expected to see strong growth in the next few years. It will grow to $9.56 billion in 2028 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8%. The growth in the forecast period can be attributed to rising labor costs, supply chain resilience and agility, globalization and trade dynamics, data analytics and optimization, and E-commerce expansion. Major trends in the forecast period include autonomous sorting technologies, advanced robotics integration, AI-driven optimization, predictive maintenance, and dynamic sortation networks.
Order your report now for swift delivery @ https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/automated-sortation-system-global-market-report
The Business Research Company's reports encompass a wide range of information, including:
1. Market Size (Historic and Forecast): Analysis of the market's historical performance and projections for future growth.
2. Drivers: Examination of the key factors propelling market growth.
3. Trends: Identification of emerging trends and patterns shaping the market landscape.
4. Key Segments: Breakdown of the market into its primary segments and their respective performance.
5. Focus Regions and Geographies: Insight into the most critical regions and geographical areas influencing the market.
6. Macro Economic Factors: Assessment of broader economic elements impacting the market.
Market Drivers - Rising e-commerce sales are expected to propel the growth of the automated sortation system market going forward. E-commerce sales refer to online transactions where goods or services are bought and sold electronically, often through websites or mobile applications, bypassing traditional brick-and-mortar stores. The increasing convenience of online shopping, coupled with a broader range of products and competitive pricing, has fueled the rise in e-commerce sales. Automated sortation systems in e-commerce streamline order processing by efficiently sorting and routing packages, enhancing operational efficiency and order fulfillment speed. For instance, in February 2024, according to the United States Census Bureau, a US-based government agency, e-commerce sales reached $1,118.7 billion in 2023, an increase of 7.6% from 2022. Therefore, rising e-commerce sales are driving the growth of the automated sortation system market.
Market Trends - Major companies operating in the automated sortation system market are adopting innovative automation and robotic products for warehousing, such as sorting and order retrieval solutions, to gain a competitive edge in the market. Sorting and order retrieval solutions are technologies and systems designed to streamline and automate sorting items and retrieving orders in warehouses, distribution centers, and fulfillment centers. For instance, in March 2024, OPEX Corporation, a US-based developer of automation solutions, launched two new solutions: OPEX Sure Sort X and OPEX Xtract, a new automated sortation and order retrieval solution designed to enhance automated sorting and order retrieval processes. The OPEX Sure Sort automated sorting system is a high-speed, small-item robotic sorting system that reduces the number of excessive touches associated with existing manual sorters, increasing productivity without increasing labor needs.
The automated sortation system market covered in this report is segmented –
1) By Component: Hardware, Software 2) By System: Unit Sorters, Case Sorters, Combo Sorters 3) By Sorting: Linear Sorters, Divert Systems, Circular Sorters 4) By End-Use Industry: Retail And E-commerce, Food And Beverages, Transportation And Logistics, Pharmaceutical, Other End-Users
Get an inside scoop of the automated sortation system market, Request now for Sample Report @ https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/sample.aspx?id=15128&type=smp
Regional Insights - Europe was the largest region in the automated sortation system market in 2023. Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing region in the forecast period. The regions covered in the automated sortation system market report are Asia-Pacific, Western Europe, Eastern Europe, North America, South America, Middle East, Africa.
Key Companies - Major companies operating in the automated sortation system market report are Siemens AG; Mitsubishi Electric Corporation; Daifuku Co. Ltd.; Dematic Corp; SSI Schaefer; Vanderlande Industries; Murata Machinery Ltd.; Fives Group; Honeywell Intelligrated; Beumer Group GmbH; Interroll Group; Eisenmann SE; Bastian Solutions Inc.; Knapp AG; Viastore Systems GmbH; Grenzebach Group; Cimcorp; TGW Logistics Group; Berkshire Grey Inc.; SDI Group; Swisslog Holding AG; Datex Corporation; Conveyco Technologies; Eurosort Systems; Fortna Inc.
Table of Contents 1. Executive Summary 2. Automated Sortation System Market Report Structure 3. Automated Sortation System Market Trends And Strategies 4. Automated Sortation System Market – Macro Economic Scenario 5. Automated Sortation System Market Size And Growth ….. 27. Automated Sortation System Market Competitor Landscape And Company Profiles 28. Key Mergers And Acquisitions 29. Future Outlook and Potential Analysis 30. Appendix
Contact Us: The Business Research Company Europe: +44 207 1930 708 Asia: +91 88972 63534 Americas: +1 315 623 0293 Email: [email protected]
Follow Us On: LinkedIn: https://in.linkedin.com/company/the-business-research-company Twitter: https://twitter.com/tbrc_info Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/TheBusinessResearchCompany YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC24_fI0rV8cR5DxlCpgmyFQ Blog: https://blog.tbrc.info/ Healthcare Blog: https://healthcareresearchreports.com/ Global Market Model: https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/global-market-model
0 notes
Text
Warehouse Optimization: Key Techniques for Maximizing Space and Efficiency
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business environment, efficient warehouse management is crucial for operational success. Warehouses are not just storage spaces; they are dynamic hubs that play a critical role in the supply chain. Optimizing warehouse operations can lead to significant improvements in productivity, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. This blog explores key techniques for maximizing space and efficiency in warehouse management best logistics institute in kochi
The Importance of Warehouse Optimization Warehouse optimization involves the strategic planning and management of warehouse operations to ensure the best use of space, labor, and equipment. Effective warehouse optimization can lead to:
Increased Storage Capacity: By maximizing the use of available space, warehouses can store more inventory without the need for expansion. Improved Efficiency: Streamlined processes and optimized layouts reduce the time and effort required for tasks such as picking, packing, and shipping. Cost Savings: Efficient use of resources reduces operational costs, including labor, energy, and equipment expenses. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Faster and more accurate order fulfillment leads to improved customer experiences and loyalty. Key Techniques for Warehouse Optimization Space Utilization Effective space utilization is the foundation of warehouse optimization. Techniques for maximizing space include:
Vertical Storage: Utilizing vertical space with high-rise racking systems and mezzanines can significantly increase storage capacity. This approach allows for more efficient use of floor space and reduces the need for warehouse expansion. Narrow Aisle Shelving: Narrowing aisle widths can free up additional space for storage. Advanced material handling equipment, such as narrow aisle forklifts, can navigate these tighter spaces efficiently. Optimized Layout Design: A well-designed warehouse layout minimizes travel time and enhances workflow. Grouping similar items together, placing high-demand products near shipping areas, and creating clear paths for material handling equipment can improve overall efficiency. Inventory Management Effective inventory management is crucial for warehouse optimization. Key strategies include:
ABC Analysis: Classifying inventory into A, B, and C categories based on demand and value helps prioritize storage and handling. High-demand items (A) should be easily accessible, while lower-demand items (C) can be stored in less accessible areas. Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Implementing JIT inventory practices reduces excess stock and minimizes storage requirements. By receiving goods only as needed, warehouses can maintain lower inventory levels and reduce carrying costs. Automated Inventory Tracking: Utilizing barcode scanning, RFID technology, and inventory management software enhances accuracy and reduces manual errors. Real-time inventory tracking ensures that stock levels are optimized and helps prevent overstocking or stockouts. Warehouse Automation Automation technologies can greatly enhance warehouse efficiency. Key automation solutions include:
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): AS/RS technology automates the storage and retrieval of goods, reducing labor costs and improving accuracy. These systems are particularly useful for high-density storage and can operate in tight spaces. Conveyor Systems: Conveyor belts and automated sortation systems streamline the movement of goods within the warehouse. This reduces manual handling, speeds up order processing, and minimizes the risk of damage. Robotics: Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) can perform tasks such as picking, packing, and transportation. These robots enhance efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve safety by minimizing human intervention in hazardous areas. Efficient Order Picking Order picking is one of the most labor-intensive and time-consuming tasks in a warehouse. Optimizing the order picking process can lead to significant efficiency gains. Key techniques include:
Zone Picking: Dividing the warehouse into zones and assigning workers to specific areas reduces travel time and increases picking speed. Orders are picked in stages as they move through the different zones. Batch Picking: Grouping multiple orders together and picking items in batches reduces the number of trips made by workers. This method is particularly effective for small, high-volume items. Pick-to-Light Systems: Pick-to-light technology uses light indicators to guide workers to the correct picking locations. This reduces errors and speeds up the picking process. Labor Management Efficient labor management is crucial for warehouse optimization. Key strategies include:
Labor Scheduling: Using labor management software to schedule shifts and allocate resources based on demand ensures that the right number of workers are available when needed. This minimizes downtime and maximizes productivity. Training and Cross-Training: Providing comprehensive training and cross-training for employees enhances their skills and flexibility. Cross-trained workers can perform multiple tasks, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall efficiency. Incentive Programs: Implementing performance-based incentive programs motivates employees to work more efficiently and achieve productivity targets. Sustainability Practices Incorporating sustainability practices into warehouse operations can lead to cost savings and environmental benefits. Key techniques include:
Energy-Efficient Lighting: Using LED lighting and motion sensors reduces energy consumption and lowers utility costs. Renewable Energy Sources: Installing solar panels or wind turbines can provide a sustainable source of energy for warehouse operations. Recycling and Waste Reduction: Implementing recycling programs and reducing packaging waste minimizes the environmental impact of warehouse operations.
Warehouse optimization is a critical component of efficient supply chain management. By implementing key techniques such as effective space utilization, inventory management, warehouse automation, efficient order picking, labor management, and sustainability practices, companies can maximize space and efficiency in their warehouse operations. These strategies not only lead to cost savings and improved productivity but also enhance customer satisfaction and support long-term business success. As technology continues to evolve, the future of warehouse optimization will likely see even more innovative solutions that drive efficiency and sustainability in the logistics industry best logistic training in kochi
0 notes
Text
Warehouse Robotics Market - Forecast(2024 - 2030)
Warehouse Robotics Market Overvie
The Global Warehouse Robotics Market size is projected to reach US$6.2 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 12% from 2024 to 2030. The Warehouse Robotics Market encompasses the automation sector dedicated to developing, deploying, and utilizing robotic systems within warehouse and distribution center settings. These robots undertake tasks like picking, sorting, packing, and transportation, aiming to boost operational efficiency, enhance order accuracy, ensure safety, and minimize labor costs. A pivotal trend influencing this market is the integration of cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). These advancements empower robots to operate autonomously, make real-time decisions, and communicate seamlessly with other warehouse systems, driving higher productivity, accuracy, and adaptability. E-commerce's surge significantly propels the warehouse robotics market forward. With online shopping's exponential growth, retailers and logistics firms face mounting pressure to swiftly and accurately fulfill orders. Warehouse robots offer a scalable solution to manage these demands, enabling companies to optimize order fulfillment processes and navigate peak periods efficiently. Moreover, there's a mounting emphasis on warehouse digitalization and inventory management, spurred by the quest for enhanced visibility and control over inventory levels. Robotics technologies such as automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) and sortation robots play a pivotal role in optimizing warehouse space usage and inventory tracking. The factors such as the proliferation of advanced technologies, the expansion of e-commerce, and the increasing focus on operational efficiency and safety are expected to drive market expansion in the foreseeable future.
Report Coverage
The report: “Warehouse Robotics Industry Outlook – Forecast (2024-2030)” by IndustryARC, covers an in-depth analysis of the following segments in the Warehouse Robotics industry.
By Product Type: Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR), Articulated Robots, Cylindrical Robots, SCARA Robots, Collaborative Robots, Parallel Robots, Cartesian Robots and Others.
By Payload Capacity: less than 20Kg, 20-100Kg, 100-300Kg and greater than 300Kg.
By System Type: Knapp Open Shuttle, Locus Robotics System, Fetch Robotics Freight, Scallog System and Swisslog Carrypick.
By Components: Programmable Logic Controller, Microprocessors and Microcontrollers, Actuators, Sensors and RF Module.
By Software: Warehouse management system, Warehouse execution system, Warehouse control system and Others.
By Function: Pick & Place, Assembling & Dissembling, Transportation, Sorting & Packaging and Others.
By End-use Industry: E-commerce, Automotive, Consumer Electronics, Food & Beverages, Healthcare, Metal & Machinery, Textile, Chemical and Others.
By Geography: North America (the US, Canada and Mexico), South America (Brazil, Argentina and Others), Europe (the UK, Germany, France, Italy, Spain and Others), APAC (China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia and Others) and RoW (the Middle East and Africa).

Key Takeaways
• In the Warehouse Robotics market report, the autonomous mobile robots’ segment is analyzed to grow at a significant CAGR of 14.9% due to its high accuracy, increased efficiency and widespread applications across industry verticals.
• The E-commerce industry is expected to grow at the highest rate with a CAGR of 15.2% owing to factors such as rising demand for distribution center automation, fulfillment automation, growing demand for order accuracy and rising competition among the companies.
• North America held the largest market share of 34% in 2023 in the global Warehouse Robotics Market, owing to factors such as rapid R&D investments towards robotics and increasing adoption of robots for process automation.
0 notes
Text
Custom Warehouse Management System
Drive efficiency in warehouse operations with Adverb's cutting-edge automation technologies. Our solutions cover material movement, sortation, picking, storage, and reverse logistics, featuring mobile robots, ASRS, and warehouse management software designed for pharma, e-commerce, grocery, cold storage, solar, and battery industries.
#How to build Warehouse Management Software#Warehouse Management System Software Development#Warehouse Management System Development
0 notes
Text
Revolutionizing Supply Chains: How Adverb Technologies Redefines Efficiency
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, the efficiency of supply chains plays a pivotal role in determining success. With the advent of advanced technologies, companies are constantly seeking innovative solutions to streamline their operations and gain a competitive edge. At the forefront of this transformation stands Adverb Technologies, a leading provider of robotics and automation solutions dedicated to redefining efficiency in supply chains.
Understanding the Need for Efficiency
Efficiency in supply chains is not merely about moving goods from point A to point B—It encompasses a spectrum of processes that span from procurement to delivery. Each link in the supply chain must operate seamlessly to ensure timely and cost-effective movement of goods. However, traditional methods often fall short in meeting the demands of today's dynamic marketplace.
The Role of Adverb Technologies
Enter Adverb Technologies, a trailblazer in the field of robotics and automation. With a deep understanding of the intricacies of supply chain management, Adverb Technologies offers a range of cutting-edge solutions designed to optimize efficiency at every stage of the supply chain.
Material Movement
One of the key areas where Adverb Technologies excels is in material movement. By leveraging state-of-the-art robotics, Adverb Technologies streamlines the process of moving goods within warehouses and distribution centers. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and mobile robots equipped with advanced navigation systems ensure swift and precise movement of inventory, reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing errors.
Sortation and Picking
Sorting and picking are critical tasks in any warehouse operation, and Adverb Technologies' solutions are engineered to maximize efficiency in these areas. Through the integration of intelligent sorting systems and robotic picking technologies, Adverb Technologies enables companies to process orders faster and with greater accuracy. This not only improves order fulfillment times but also enhances customer satisfaction.
Storage Optimization
Effective storage management is essential for maintaining an efficient supply chain. Adverb Technologies offers innovative solutions for optimizing storage space, such as automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS). These systems utilize vertical storage space efficiently, allowing companies to maximize their warehouse capacity while minimizing handling time.
Reverse Logistics
In addition to forward logistics, Adverb Technologies addresses the complexities of reverse logistics—the process of handling returns and exchanges. By implementing automated systems for reverse logistics, companies can streamline the return process, reduce processing times, and improve inventory visibility.
The Impact of Adverb Technologies
The impact of Adverb Technologies' solutions on supply chain efficiency is undeniable. By automating repetitive tasks, minimizing errors, and accelerating processes, Adverb Technologies empowers companies to operate leaner and more agile supply chains. This not only translates to cost savings but also enhances competitiveness in the marketplace.
Conclusion
As supply chains continue to evolve in response to changing consumer demands and market dynamics, the need for efficiency has never been greater. Adverb Technologies stands at the forefront of this revolution, offering transformative robotics and automation solutions that redefine efficiency in supply chains. By embracing innovation and leveraging cutting-edge technology, companies can unlock new levels of productivity, reliability, and agility in their supply chain operations—with Adverb Technologies leading the way.
Got questions? Click now! https://addverb.com/contact-us/
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding the Benefits of Autonomous Mobile Robots in Warehouses

The unprecedented advancements in technology have consistently driven industries to adapt, innovate, and optimize their processes to maintain a competitive edge. The warehouse industry, a cornerstone in the global supply chain, has witnessed transformative changes with automation leading the revolution. The integration of technology in warehouse operations has opened avenues for efficiency, speed, and reliability, attributes that are crucial in the high-demand consumer market today. One of the most significant innovations reshaping the logistics sector is the deployment of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs). These sophisticated pieces of technology symbolize a new era, offering solutions to the complexities and challenges that have long plagued warehouse operations. The journey toward automation in warehouses did not happen overnight. It has been an evolutionary process, propelled by the necessity to address labor shortages, reduce operational costs, and meet the escalating demands of e-commerce. From the early stages of conveyor belts and basic mechanical aids to the sophisticated systems that orchestrate today's mega-warehouses, automation has become the backbone of logistics operations. This transformation reflects the industry’s response to the modern consumer’s expectation for speed, accuracy, and reliability in delivery services. In this comprehensive examination, we delve deep into how AMRs represent the culmination of years of technological advancement. This article will navigate through the specifics of their roles, their growing importance in the current market landscape, and the undeniable benefits of autonomous mobile robots in warehouses. It serves as a lens into the future, showcasing how AMRs are not just a temporary trend but a key investment for logistics companies aiming for longevity and success in a digitally dominated era. Brief History of Automation in Logistics The concept of automation within the logistics and warehouse industry has its roots firmly planted in the late 1950s and early 1960s when the first automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and conveyor systems were introduced. These early forms of technology were basic, designed primarily to transport goods from point A to B, yet they laid the groundwork for complex automated solutions that would follow. The primary drive behind these innovations was to improve workplace safety, increase productivity, and optimize storage, directly addressing the operational challenges of the time. Over the subsequent decades, the industry witnessed an evolutionary leap in terms of technological integration. The 1990s marked a paradigm shift with the onset of computerized warehouse management systems (WMS), which brought about improved inventory control and order processing. These systems were the precursors to the sophisticated, fully integrated solutions seen today, significantly enhancing accuracy and efficiency within warehouse operations. The era was characterized by a growing reliance on technology, setting the stage for advanced robotics and automation. The turn of the century saw an acceleration in innovation due to the explosion of e-commerce, requiring logistics to scale up and meet unprecedented demand. Warehouses faced immense pressure for faster, accurate order fulfillment, which traditional manual processes could no longer support. This period heralded the introduction of more advanced automation systems, including high-speed sortation systems, pick-to-light/put-to-light systems, and advanced robotics—each contributing to incremental improvements in speed, accuracy, and throughput capabilities. The history of automation in logistics is one of gradual but transformative change, marked by technological advancements that have continuously refined processes. Each developmental stage served as a building block for the next, culminating in the emergence of AMRs. These robots represent the epitome of decades of innovation, embodying the efficiency, safety, and speed required to drive the warehouses of the future. Definition of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are state-of-the-art robots that, unlike their predecessors, are not bound by fixed routes or pre-defined grid systems. These intelligent machines use sensors, cameras, and software to understand their environment, making decisions in real-time about the most efficient routes for material transportation. This level of autonomy and flexibility stands in stark contrast to the earlier automated guided vehicles (AGVs), which required physical guides or markers to navigate warehouse spaces. AMRs are equipped with sophisticated software allowing for real-time decision-making, route optimization, and seamless integration with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS). This ability to communicate with other systems and adapt to new instructions in real-time represents a significant leap forward in warehouse automation technology. They are designed to work collaboratively with human workers, taking over mundane, repetitive, and strenuous tasks, thereby reshaping the role of the workforce in logistics operations. The defining characteristic of AMRs—autonomy—ushers in a new level of operational efficiency. By interpreting data captured through their sensors, AMRs can navigate dynamic environments, identify obstacles, and choose the most efficient paths. This adaptability makes them particularly suitable for the ever-changing landscape of warehouses, where they can significantly reduce operational delays and human error, highlighting the core benefits of autonomous mobile robots in warehouses. The Growing Relevance of AMRs in the Current Market Landscape The current market landscape, characterized by a surge in online shopping, next-day delivery expectations, and a global pandemic, has put unparalleled pressure on warehouse operations. Companies are grappling with the challenges of maintaining efficiency, meeting escalating customer demands, and ensuring safety for their workforce. In this high-stakes environment, AMRs are emerging as indispensable allies. Their deployment addresses critical pain points, from workforce limitations due to social distancing requirements to the need for round-the-clock operations during peak seasons. AMRs are not just a solution; they are a strategic asset in the competitive e-commerce arena. By assuming roles that were previously bottlenecked by human limitations, such as picking, sorting, transporting, and packing, these robots enhance productivity. They operate tirelessly, which is particularly beneficial for meeting the tight deadlines associated with same-day or next-day deliveries, a service standard that has become a market norm. The ongoing technological advancements in AMRs, such as improved machine learning algorithms, enhanced sensory technology, and better energy efficiency, contribute to their growing relevance. These innovations are tailored to the evolving needs of warehouses, requiring systems that can effortlessly scale, adapt, and integrate with existing technological infrastructures. Consequently, AMRs are proving crucial for businesses looking to maintain agility and resilience in the face of market fluctuations and consumer demand trends. Another driving factor for AMRs' integration is the significant reduction in their cost due to advancements in manufacturing, economies of scale, and heightened competition among suppliers. This affordability has made them accessible to not just large corporations but also small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). As a result, a broader segment of the industry can now reap the benefits of autonomous mobile robots in warehouses, leveling the playing field in an otherwise competitive market space. The role of AMRs is pivotal in the current scenario, where companies are striving for sustainability. These robots, with their precision and efficiency, contribute to energy savings and reduce wasteful practices within operations. Their ability to accurately pick and transport products minimizes damages and returns, two aspects directly linked to environmental impact. In this way, AMRs are not only optimizing operations but also steering them towards greener practices. What You Will Learn With this Article In this insightful journey, we will unfold the various dimensions associated with the adoption of AMRs in warehouses, emphasizing their transformative impact. The forthcoming sections delve into specific benefits, including cost reduction, enhanced worker safety, scalability, and how they contribute to meeting and exceeding customer service expectations. Each benefit will be explored comprehensively to provide a holistic understanding of the value proposition presented by AMRs. As we proceed, we will highlight case studies from pioneering companies that have successfully integrated AMRs into their logistics operations. These real-world examples will illustrate the tangible positive outcomes and return on investment (ROI) that businesses have witnessed, reinforcing the strategic importance of embracing this technology. The section promises an in-depth look at practical implementations, shedding light on various operational models and configurations adopted by different types of businesses. We will explore the future trajectory of AMRs in logistics, considering emerging trends, anticipated technological enhancements, and potential new applications within and beyond warehouse settings. This forward-looking perspective will underscore the importance of adaptability and continuous innovation in maintaining operational excellence and competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving market landscape. The article will encapsulate the critical considerations businesses must contemplate when adopting AMRs, including investment evaluation, integration challenges, and the cultural shift within organizations. This conclusive segment aims to equip decision-makers with the necessary insights for a calculated and strategic transition towards automation, ensuring they harness the full potential of the benefits of autonomous mobile robots in warehouses. Understanding Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) The foray into understanding Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) within warehouse environments necessitates a deep dive into the multifaceted technologies that empower these systems. As the backbone of modern automated warehouses, AMRs epitomize a significant shift from manual labor to sophisticated, tech-driven operations. This transformation hinges on the robots' ability to self-navigate, make decisions, and interact within a dynamic environment, significantly amplifying the benefits of autonomous mobile robots in warehouses. AMRs operate on a confluence of technologies that imbue them with intelligence and functionality. Their design philosophy pivots on enhancing efficiency, safety, and consistency in warehouse operations, qualities that are often compromised in traditional, labor-intensive settings. The complexity of tasks they can undertake and the speed and precision with which these tasks are executed underline the pivotal role of AMRs in redefining logistical workflows. To fully leverage the advantages of AMRs, it's crucial for industry players to understand the intricate mechanics behind these robots. This knowledge not only facilitates informed decision-making regarding AMR integration but also optimizes their operation, ensuring businesses can extract maximum utility. More importantly, as these technologies continue to evolve, staying abreast of the latest developments can offer competitive advantages in a market propelled by innovation. Comprehending the technology behind AMRs is essential for troubleshooting, maintenance, and future upgrades, ensuring sustained operational excellence. With the landscape of logistics witnessing rapid transformations, companies equipped with an in-depth understanding of AMRs are better positioned to adapt, innovate, and lead in their respective markets. This section aims to unravel these technological aspects, shedding light on the intricate workings that continue to propel AMRs to the forefront of warehouse automation. The Technology Behind AMRs Autonomous mobile robots are marvels of modern engineering, integrating various advanced technologies to perform tasks autonomously and interact with their surroundings effectively. Understanding the components that constitute an AMR is essential to grasp their capabilities and the unique benefits they bring to warehouse operations. Sensor Technology The eyes and ears of any AMR are its sensors, which play a critical role in how these robots understand and engage with their environment. Various sensor technologies are integrated into AMRs, each serving a unique purpose. For instance, Lidar sensors (Light Detection and Ranging) help in forming a 3D map of the robot's surroundings, enabling it to identify obstacles, determine its position, and plan routes accordingly. Another crucial technology is machine vision, which equips AMRs with the ability to recognize objects, read labels, and ensure correct handling of goods. These systems use cameras and image recognition algorithms to interpret visual information, akin to how humans use their eyes and brain. The precision and reliability of machine vision systems are integral to maintaining the accuracy of tasks such as picking and sorting. AMRs employ various other sensors for tasks like measuring distance, detecting motion, and assessing environmental conditions. These include ultrasonic sensors, infrared sensors, and tactile sensors, which collectively contribute to the robot's understanding of its operational context. This sensory information is crucial for real-time decision-making and is central to the autonomous functionality of these robots, contributing significantly to the benefits of autonomous mobile robots in warehouses. Navigation Systems Navigation is the cornerstone of AMR functionality, enabling these robots to move within complex, dynamic environments without human intervention. This autonomy is facilitated by sophisticated systems that combine sensor data, software algorithms, and digital maps to create a comprehensive navigation solution. The primary navigation method employed by AMRs is Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). This technology enables a robot to map its environment while keeping track of its location within that space. SLAM combines data from various sensors, creating a unified, accurate representation of the environment that is essential for path planning and obstacle avoidance. AMRs use waypoint navigation, where they follow a series of pre-defined points on a map. This method is particularly effective in structured environments like warehouses, where specific routes need to be adhered to for operational efficiency. The robot's sensors continuously scan the environment to ensure it stays on course, making necessary adjustments in real-time to avoid obstacles or choose faster paths. With navigation systems, AMRs may use beacon-based navigation, where they triangulate their position using signals from fixed beacons placed around the warehouse. This system is highly reliable, ensuring precise navigation even in areas where other signals might be weak or disrupted. These navigation technologies are fundamental to AMR operations, empowering them to move materials efficiently, reduce transit times, and adapt to changes in their environment. By minimizing human involvement in these processes, AMRs significantly enhance operational efficiency, safety, and consistency. Machine Learning and AI Components The intelligence of autonomous mobile robots is powered by machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI), making them capable of learning from their environment and improving over time. These technologies form the brain of the AMR, enabling it to make decisions in real-time, a feature that distinguishes AMRs from traditional automated guided vehicles (AGVs). Machine learning in AMRs is exemplified through their ability to recognize patterns, adapt to new scenarios, and even predict future outcomes based on historical data. For instance, in a warehouse setting, an AMR can learn the most efficient routes over time, adapting to changes like new layouts or increased traffic, thus continually optimizing its paths and workflows. Artificial intelligence comes into play in more complex decision-making scenarios. It allows AMRs to understand contextual commands, make choices that would typically require human intelligence, and autonomously carry out sophisticated tasks. This level of autonomy is particularly evident in situations where AMRs interact with other systems or robots, requiring real-time communication and coordination. By leveraging AI and ML, AMRs can significantly minimize errors, reduce downtime, and increase overall warehouse productivity. These self-optimizing capabilities ensure that the benefits of autonomous mobile robots in warehouses continue to grow over time, adapting to new challenges and requirements in the ever-evolving logistical landscape. Communication Protocols and IoT Integration Interconnectivity is a major facet of AMR functionality, made possible through various communication protocols and integration with the Internet of Things (IoT). These robots are not standalone units but are part of a larger, interconnected ecosystem within the warehouse, involving other robots, management systems, and various IoT devices. AMRs rely on standard communication protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and sometimes more industry-specific ones like Zigbee, to interact with central management systems, other AMRs, and different devices within their operational perimeter. This constant communication is crucial for tasks like coordinating movements, updating task statuses, and reporting anomalies. IoT integration takes this interconnectivity a step further. By being part of the IoT ecosystem, AMRs can share data with a broader range of devices and systems, contributing to big data analytics and enabling more informed decision-making at the managerial level. This integration means that everything, from inventory levels to the operational status of each AMR, can be monitored in real-time, providing a comprehensive overview of warehouse operations. This seamless communication and IoT integration are pivotal in creating a synchronized warehouse environment. The ability to relay and receive information in real-time is one of the key benefits of autonomous mobile robots in warehouses, leading to more streamlined operations, enhanced situational awareness, and improved response times to changing operational demands. Advanced Safety Features Safety remains a paramount concern in any industrial setting, and warehouses are no exception. AMRs are ingrained with advanced safety features ensuring they operate harmoniously within a workspace shared with human workers. These robots are equipped with a variety of sensors and software designed to recognize human presence and take necessary precautionary actions to avoid collisions. One such feature is the automatic emergency braking system, which is activated the moment an obstacle is detected in the robot's path. AMRs are designed with preset speed limits to match the pace of the surrounding environment, ensuring they do not pose any threats by moving too fast within human-centric operations. Features like audio and visual indicators are standard, providing human workers with clear signals of an AMR's intentions, be it a change in direction or halting for an obstacle. Some AMRs are also equipped with edge detection to prevent falls from loading docks or ledges. By prioritizing safety, AMRs contribute to creating a hazard-free work environment, reducing workplace accidents, and ensuring the well-being of human workers. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Embracing the Era of Automated Warehouse Robots

With a focus on warehouse automation and the implementation of cutting-edge mobile robotic solutions, Hitachi is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape.
Central to this transformation is robotic palletizing, where advanced robots take charge of precise and efficient stacking of goods. This automation streamlines warehouse operations, optimizing productivity and minimizing errors.
Hitachi's expertise extends to logistics automation, incorporating robotic sorting and warehouse picking technologies. These robotic systems facilitate seamless order fulfillment, ensuring faster and error-free processes. By harnessing intelligent warehouse technology, Hitachi enhances overall inventory management, enabling accurate and efficient warehouse sorting. To further elevate efficiency, Hitachi has developed automated warehouse robots tailored for logistics tasks. These robots navigate warehouse spaces, facilitating smooth transportation and handling of goods.
Hitachi's dedication to excellence encompasses robotic inventory systems, harnessing the power of robotics and AI-driven technologies. These systems enable real-time tracking and monitoring of inventory levels, resulting in precise stock management and reduced discrepancies.
Hitachi's logistics and warehouse automation solutions encompass robotic depalletizing and palletizing solutions, warehouse picking, robotic warehouse sortation systems, automated guided vehicles and autonomous mobile robots.
Through these cutting-edge advancements, Hitachi is driving the future of warehousing, propelling it toward efficient, accurate, and technologically advanced operations.
Learn more on how scalable mobile robotic solutions manage the picking, sorting, and palletizing, making warehouse operations more efficient, cost-effective and safe:
Discover how Hitachi is enabling data-driven manufacturing automation to achieve sustainability and profitability:
#warehouse automation#warehouse robotics#logistics automation market#warehouse robots#warehouse technology#digital innovation#robotics#sustainability
0 notes
Text
FULFILMENT CENTRE VS. DISTRIBUTION CENTRE
What is a Fulfilment Centre?
A fulfilment centre is a type of warehouse, storing inventory from various sellers and distributing the products through an order fulfilment process. Fulfilment centres are different than warehouses, though, as they’re usually operated by third-party logistics providers. These third-party logistics providers offer a variety of services to clients like e-commerce companies and retail stores, by handling e-commerce orders and offering fulfilment solutions. Fulfilment centre are more focused on business-to-consumer operations.
Amazon is a good example of what fulfilment centres look like. A small business might choose to work with a fulflment centre rather than operate their own warehouses, performing their own order fulfilment services and handling of customer orders. Fulfilment centre often negotiates discounted shipping rates, so shipping costs could be lower than the e-commerce business would get on its own. They may not have a choice, however, in shipping carriers. A fulfilment centre might also handle reverse logistics, as suggested by one of the best Shipping freight forwarding companies in India.
.
Factors To Consider When Looking To Use A Fulfillment Center
While using fulfillment centers seems like a no-brainer in certain circumstances, there are a few factors that should be considered before signing any contracts.
Importance of value-added services: Are services like packaging, labeling customer orders, and faster shipping to customers necessary for your company’s current goals.
Cost of service: Can your business afford to use a fulfillment center at your particular stage?
Expected Sales: Is your business expecting a high volume of orders, or will your products need to sit for a while?
Location of fulfillment centers: Are there fulfillment centers near where your target customers live?
Knowing who your customers are and where they are will allow you to get the most out of your experience with a fulfillment center.
What is a Distribution Centre?
So distribution centre and fulfilment centre are they one and the same? Not necessarily… A distribution centre (not to be confused with “centre of a distribution” – a term used in statistics) is more of a business-to-business storage facility than a fulfilment centre. A distribution centre is used to receive inventory, temporarily store the goods and redistribute them. It may be owned directly by the retailer or it could be leased. The distribution centre focuses on the retail store customer, receiving items from the supplier and sending them on to the various stores. Hence sometimes this is also referred to as “retail distribution centre”. Consider the distribution centre as a bridge between the supplier and the stores. Products arrive on pallets and are moved in on a forklift, but then items are removed from the pallets as order processing demands. Smaller quantities of goods are sent on to the ultimate customers, the stores. These centres are part of a distribution network of facilities located closer to retail locations, and don’t typically house inventory for an extended period of time. Distribution centres might also ship items to fulfilment centres as needed for e-commerce fulfilment.
Types Of Distribution Centres
There are three different types of distribution centres:
Conventional – Material movement is performed by people and mobile equipment.
Mechanized – Material movement is assisted by mechanized, conveyance and sortation systems.
Automated – Material movement is performed in part or in full by machines or robotics.
Factors To Consider Before Using A Distribution Center
Since many e-commerce merchants are strictly B2C and don’t necessarily have a physical store, the use of a distribution center may not make sense depending on your specific circumstance.
Distribution centers generally store and ship products in bulk. The products aren’t individually wrapped and packaged. However, the location of distribution centers allow you to hold inventory closer to your target market.
According to Shipping freight forwarding companies, understanding your offerings and your clientele will be key in deciding if distribution centers are right for your business.
What Are Warehouses?
Quite simply, warehouses are used to store goods for an extended period of time. They are also used to organize and manage inventory. While it may sound simple, modern warehouses are sophisticated in their processes and use warehouse management systems (WMS) to ensure a smooth operation.
This allows them to track how many products you currently have, where they are, where they are going, who’s handling them, etc.
E-commerce merchants can rent space within a warehouse via short-term and long-term leases depending on their specific needs.
Factors to Consider Before Using A Warehouse For Your Online Store
Before you decide to use a warehouse for your e-commerce business, there are several factors you’ll need to weigh:
Seasonality of your business: Will you need the storage space after your company’s peak season?
Location location location: Will the location of the warehouse need to be close to your customer base or can it be located further away?
Cost of storage: How many SKUs do you have and what will the cost of storing them be?
How long will inventory sit: Will these products need to be shipped soon or will they need to be housed for a while?
Again, warehouses aren’t typically made for quick turnaround. Rather they’re a way to make sure your products are stored safely, organized efficiently, and are overseen in a way to make sure you never run out of inventory.
The Verdict
When looking at all three options you’ll see there really isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer. As your e-commerce business grows, your needs regarding inventory management and fulfillment will change.
Your inventory management and fulfillment decisions should depend on factors such as the size of your business, your forecasted sales, budget and goals, where your target consumers live, and more.
If your primary need is to get your products packaged and shipped quicker, a fulfillment center may be best for you.
If your primary need is to store your products safely and have your inventory managed more effectively, then a warehouse may be the better option.
And if your e-commerce business is trying to optimize inventory levels at a physical store, then a distribution center may be your best option.
How AFM Fits Into the Equation
One common theme of all these storage options is that any e-commerce storage method will require shipping at some point, whether that be warehouses shipping to fulfillment centers, or fulfillment centers shipping out to customers.
AFM is there every step of the way as it not only integrates directly with your e-commerce platform, but has also partnered with both third-party logistics companies (3PLs and fulfillment companies) and with warehouse management system companies to help manage end-to-end fulfillment operations.
Creating shipping labels with Shipping freight forwarding companies also allows you to track your packages throughout their journey so that you know if they’re inside of a fulfillment center, distribution center, or if they’re on their way to your customer.
0 notes