#PIK3CA Mutation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
BioAdvisers said on Biotech Advisers
Loss of PTEN in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines significantly correlates with AZD8186 sensitivity
Ocosu-Brackett et al.’S Figure 6 “Effect of the combination of AZD8186 and anti-PD1 on isogenic models” is featured on the cover of “Oncotarget” issue 11.
In vitro cell viability assays and immunoblots showed that loss of PTEN in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines was significantly associated with AZD8186 sensitivity.
AZD8186 combined with paclitaxel and eribulin has a synergistic effect on the growth inhibition of PTEN-losing cells.
AZD8186 significantly enhanced the antitumor efficacy of anti-PD1 antibodies in a melanoma xenograft model of PTEN-deficient BP mice, but not in a PTEN wild-type CT26 xenograft model.
In vitro, cell proliferation and colony formation assays were performed to determine the sensitivity of the cells to AZD8186.
AZD8186 has single-agent efficacy in TNBC cell lines lacking PTEN, but has limited single-agent efficacy in vivo.
“Phosphatidylinositol,” said the University of Texas Medical Anderson Cancer Center’s Department of Surgical Oncology, the Department of Research Cancer Therapy, the Department of Breast Cancer Surgery, and the Dr. Franka Meric-Bernstam Research Center in Houston, Texas, USA The 3-kinase (PI3K) / AKT / mTOR pathway is an important regulator of many physiological cellular processes that promote normal cell differentiation, proliferation, and survival. ”
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) / AKT / mTOR pathway is an important regulator of many physiological cell processes that promote normal cell differentiation, proliferation, and survival.
——Dr. Funda Meric-Bernstam, Department of Cancer Therapy, Department of Breast Surgery, Oncology and Sheikh Khalifa Bin Zayed Al Nahyan Personalized Cancer Therapy Institute
MiRNA mutation, loss of copy number, epigenetic silencing, and downregulation of PTEN protein can lead to inactivation of PTEN function, leading to activation of the PI3K / AKT / mTOR pathway, which in turn increases tumor growth in a variety of solids, invades and metastases tumors including the breast Cancer, endometrial cancer, prostate cancer, renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, glioblastoma and colorectal cancer.
Loss of PTEN and increased PI3K signaling are related to the resistance of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab and endocrine therapy, and the poor prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer.
In vitro, they consumed PIK3CB, which encodes PI3K, to reveal the significant growth inhibitory effect of PTEN-deficient tumors, whereas in corresponding PTEN-deficient tumors, to inhibit PIK3CA or encodes PI3K respectively. For PI3K, it did not have this growth inhibitory effect.
Therefore, the PI3K subtype is a driver of abnormal proliferation in PTEN-deficient cancers, and therefore, PI3K is a promising target for the treatment of PTEN-deficient TNBC. AZD8186 is a selective and potent small molecule inhibitor of PI3K with additional activity on PI3K isoforms.
The Merrick-Bernstam research team concluded in their Oncotarget paper, “These results provide preclinical evidence for the antitumor efficacy of AZD8186 in PTEN-deficient solid tumors. AZD8186 has a single drug in TNBC cell lines lacking PTEN Efficacy, with a modest single-agent effect in the body. In addition, AZD8186 enhances the antitumor effect of paclitaxel, but the use of this combination in an immunosuppressive model can observe stable and progressive disease. In an immune-capable model, AZD8186 Combination with anti-PD1 can lead to regression of PTEN-deficient BP tumors. We realize that although AZD8186 sensitivity is associated with PTEN loss, we can only speculate on causality. In conclusion, although further understanding of the mechanism of action of these combinations is required. ”
Abbkine specializes in the fields of proteinology and cytology, and is committed to innovating and developing various antibodies, proteins, analytical reagents and kits, with a view to becoming a key promoter in the fields of life science research and development, and drug development. We provide you with the favorite products of protein and immune research users, from basic immunological products such as protein extraction and quantification, to internal reference label antibodies, primary antibodies and secondary antibodies for immunological experiments; favorite products of cell research users, from Dyes and kits for detecting cell status, organelle extraction kits, cell substructure staining and cell metabolism detection products, and cytokine and protein detection kits for cell culture, just to help your research career !
About Abbkine
Our positioning: Serve global users of cell and protein research, and provide users with economical and technical product solutions by applying processes and product portfolios.
Our mission: to inspire our inherent creativity, provide competitive biomedical products and services, and continue to create maximum value for our customers.
Our vision: to be a respected, world-class supplier of biomedical products and services.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Bioadvisers shared on Biotech Advisers
Loss of PTEN in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines significantly correlates with AZD8186 sensitivity
Ocosu-Brackett et al.’S Figure 6 “Effect of the combination of AZD8186 and anti-PD1 on isogenic models” is featured on the cover of “Oncotarget” issue 11.
In vitro cell viability assays and immunoblots showed that loss of PTEN in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines was significantly associated with AZD8186 sensitivity.
AZD8186 combined with paclitaxel and eribulin has a synergistic effect on the growth inhibition of PTEN-losing cells.
AZD8186 significantly enhanced the antitumor efficacy of anti-PD1 antibodies in a melanoma xenograft model of PTEN-deficient BP mice, but not in a PTEN wild-type CT26 xenograft model.
In vitro, cell proliferation and colony formation assays were performed to determine the sensitivity of the cells to AZD8186.
AZD8186 has single-agent efficacy in TNBC cell lines lacking PTEN, but has limited single-agent efficacy in vivo.
“Phosphatidylinositol,” said the University of Texas Medical Anderson Cancer Center’s Department of Surgical Oncology, the Department of Research Cancer Therapy, the Department of Breast Cancer Surgery, and the Dr. Franka Meric-Bernstam Research Center in Houston, Texas, USA The 3-kinase (PI3K) / AKT / mTOR pathway is an important regulator of many physiological cellular processes that promote normal cell differentiation, proliferation, and survival. ”
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) / AKT / mTOR pathway is an important regulator of many physiological cell processes that promote normal cell differentiation, proliferation, and survival.
——Dr. Funda Meric-Bernstam, Department of Cancer Therapy, Department of Breast Surgery, Oncology and Sheikh Khalifa Bin Zayed Al Nahyan Personalized Cancer Therapy Institute
MiRNA mutation, loss of copy number, epigenetic silencing, and downregulation of PTEN protein can lead to inactivation of PTEN function, leading to activation of the PI3K / AKT / mTOR pathway, which in turn increases tumor growth in a variety of solids, invades and metastases tumors including the breast Cancer, endometrial cancer, prostate cancer, renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, glioblastoma and colorectal cancer.
Loss of PTEN and increased PI3K signaling are related to the resistance of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer to trastuzumab and endocrine therapy, and the poor prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer.
In vitro, they consumed PIK3CB, which encodes PI3K, to reveal the significant growth inhibitory effect of PTEN-deficient tumors, whereas in corresponding PTEN-deficient tumors, to inhibit PIK3CA or encodes PI3K respectively. For PI3K, it did not have this growth inhibitory effect.
Therefore, the PI3K subtype is a driver of abnormal proliferation in PTEN-deficient cancers, and therefore, PI3K is a promising target for the treatment of PTEN-deficient TNBC. AZD8186 is a selective and potent small molecule inhibitor of PI3K with additional activity on PI3K isoforms.
The Merrick-Bernstam research team concluded in their Oncotarget paper, “These results provide preclinical evidence for the antitumor efficacy of AZD8186 in PTEN-deficient solid tumors. AZD8186 has a single drug in TNBC cell lines lacking PTEN Efficacy, with a modest single-agent effect in the body. In addition, AZD8186 enhances the antitumor effect of paclitaxel, but the use of this combination in an immunosuppressive model can observe stable and progressive disease. In an immune-capable model, AZD8186 Combination with anti-PD1 can lead to regression of PTEN-deficient BP tumors. We realize that although AZD8186 sensitivity is associated with PTEN loss, we can only speculate on causality. In conclusion, although further understanding of the mechanism of action of these combinations is required. ”
Abbkine specializes in the fields of proteinology and cytology, and is committed to innovating and developing various antibodies, proteins, analytical reagents and kits, with a view to becoming a key promoter in the fields of life science research and development, and drug development. We provide you with the favorite products of protein and immune research users, from basic immunological products such as protein extraction and quantification, to internal reference label antibodies, primary antibodies and secondary antibodies for immunological experiments; favorite products of cell research users, from Dyes and kits for detecting cell status, organelle extraction kits, cell substructure staining and cell metabolism detection products, and cytokine and protein detection kits for cell culture, just to help your research career !
About Abbkine
Our positioning: Serve global users of cell and protein research, and provide users with economical and technical product solutions by applying processes and product portfolios.
Our mission: to inspire our inherent creativity, provide competitive biomedical products and services, and continue to create maximum value for our customers.
Our vision: to be a respected, world-class supplier of biomedical products and services.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Asian Countries are witnessing an Increasing Demand for Breast Cancer Drugs
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women after lung cancer. Advancements in screening and treatment for breast cancer have improved survival rates in the last few decades. Breast cancer is a kind of cancer formed in tissues of the breast. The most common types of breast cancer are ductal carcinoma, which begins in the lining of the milk ducts and lobular carcinoma, which starts in the lobules (milk glands) of the breast.
In the US, around 12% of women develop breast cancer over the course of their lifetime. In Canada, an estimated 26,900 women were expected to be diagnosed with breast cancer in 2019 and breast cancer accounts for nearly 25% of new cases of cancer among Canadian women.
North America was leading the global breast cancer drug market with more than 45% of the revenue in 2018. The presence of standard healthcare infrastructure, increasing awareness about early disease diagnosis, and the presence of established players are among the factors that make North America a major shareholder in the market.
Product approvals, collaboration, and development of new drugs are among the strategies followed by dominant companies to strengthen their position in the market. For instance, in May 2019, Novartis announced the US FDA approval for Piqray in combination with fulvestrant for the treatment of postmenopausal women and men with hormone receptor-positive, PIK3CA-mutated, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 negative (HR+/HER2-), advanced or metastatic breast cancer
Expiration of patents, high development cost of the drug, and strict regulatory guidelines are hampering the growth of the market. By considering all the above facts and figures and an in-depth analysis of the market, the market research company predicts that global breast cancer drugs market is going to reach revenue of around $36.7 billion, and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.4% during the forecast ed period of 2019- 2025.
Read the full report summary @ breast cancer drugs market or Download sample report @ breast cancer drugs market sample report.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Is Molecular Testing?
Molecular testing is a laboratory method that checks a sample of tissue, blood, or other body fluid for certain genes, proteins, or other molecules that may be a sign of a disease or condition. It can be done alone or with other procedures such as biopsies to help diagnose cancer or other diseases. Molecular tests can also help plan treatment, find out how well treatment is working, and predict whether cancer will spread or return. Here is some more information about molecular testing.
Whether you have heard these terms during the COVID-19 pandemic or not, molecular diagnostics (MDx) is an important and rapidly developing area of medical laboratory science. Molecular diagnostics utilizes techniques from molecular biology, such as PCR and other nucleic acid amplification tests, to help diagnose disease.
The earliest molecular techniques were developed in the 1950s to study genetic markers, but it took decades for these methods to be applied to medical laboratory diagnosis. MDx is now the basis for many routine tests that help to identify infectious agents and guide antimicrobial therapy.
A common example is the rapid detection of influenza or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) using a real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). This test can detect many different kinds of bacteria or viruses in a sample, usually within an hour. View here: https://www.jantdx.com for more details about this service.
Molecular tests are also used to diagnose some types of cancer, including mutations in the BRAF and PIK3CA genes that can increase your risk of getting a certain type of thyroid cancer. These tests can also help determine if you have a gene that makes it easier for your tumor to grow or spread.
Other molecular tests look for specific proteins or other biomarkers that can be useful in predicting how a tumor will respond to various treatments. For example, a gene expression signature that predicts benefit from tyrosine kinase inhibitors can help choose the best medication for advanced breast cancer.
Some large-scale genetic tests look at whole sections of DNA called chromosomes rather than individual genes. These include karyotypes and chromosomal microarrays. These tests can also have findings unrelated to the reason they were ordered (secondary findings).
The availability of these new tests has led some to recommend that all thyroid nodules be molecularly tested before surgery. However, prospective studies assessing the effect of molecular testing on surgical rates and outcomes are lacking. Those studies that do exist are correlative in nature and show that fewer surgeries were performed during the time period when molecular testing was introduced, but they do not prove that the tests caused this change. Learn more about the above topic by clicking this link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Molecular_diagnostics.
0 notes
Text
New Blood-Vessel-on-a-Chip Can Help Researchers Further Understand Vascular Malformations
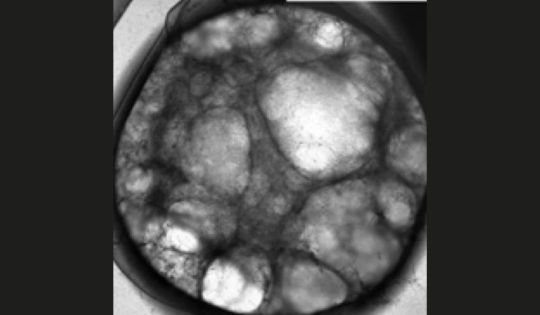
New Blood-Vessel-on-a-Chip Can Help Researchers Further Understand Vascular Malformations. A research team led by William Polacheck, Ph.D., at the UNC School of Medicine, has engineered a microfluidic model that mimics a rare genetic disorder affecting the structure of veins, arteries, capillaries, and lymphatic vessels. February 24, 2023, CHAPEL HILL, N.C. - Our bodies are made up of 60,000 miles of complex pipes that play a vital role in transporting nutrients throughout our bodies, performing waste disposal, and supplying our organs with fresh oxygen and blood. Several things can go wrong with this complex system, including vascular malformations (VMs), a group of rare genetic disorders that causes an abnormal formation of veins, arteries, capillaries, or lymphatic vessels at birth. VMs can interfere with the duties of our precious pipes by causing blockages, poor drainage, and the formation of cysts and tangles.

William Polacheck, PhD To address a need for further study, William Polacheck, Ph.D., assistant professor in the UNC-NCSU Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering and the Department of Cell Biology and Physiology, and his team from across the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, have developed a model that mimics VMs specifically caused by a mutation of PIK3CA – a gene that has been implicated in multiple types of lymphatic, capillary, and venous malformations. Their work was published in Science Advances, an open-access multidisciplinary journal from the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). “There are number of ‘chicken and the egg problems’ of the PIK3CA mutation,” said Polacheck. “Is it causing something else to go wrong? Or is there something else in the environment causing the mutation to have more severe effects? Working in a much more controlled environment, such as a microfluidic model, allows us to isolate and figure out how the genetics of the disease relate to what’s happening in the cells.” VMs are caused by mutations in the genes that direct the development of vasculature throughout the body. Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) is one of those genes. Activating mutations in PIK3CA commonly contribute to malformations of the smaller blood vessels, causing blood to pool underneath the skin. This specific type of vascular malformation is usually discovered at birth. These diseases start as the baby is developing. Since there is a multitude of changes happening at this point in the child’s development, it can be a difficult condition for researchers to study.
A Team in the Making
Julie Blatt, MD, professor of pediatric hematology-oncology in the UNC Department of Pediatrics, saw the need for a new approach to model the disease, which affects a majority of her patients. She has had a long-standing interest in the clinical management of patients with vascular malformations, as well as an interest in repurposing cancer drugs for the disease. Impressed with his prior manuscripts, Dr. Blatt picked up the phone and cold-called Polacheck, who is a biomedical engineer by trade, to ask if he could create a microfluidic model of PIK3CA-specific vascular malformations. “I think the transdisciplinary aspect keeps the possibility of application to patients at the forefront, said Dr. Blatt. “The Polacheck lab has prioritized introduction of genetic mutations that are relevant to patients and to studying drugs which we know or think will have benefit.”

Wen Yih Aw, PhD Around the same time, Wen Yih Aw, Ph.D., was working as a postdoctoral researcher at UNC Catalyst, a research group focused on understanding rare diseases in the Eshelman School of Pharmacy. Aw was collaborating with the Polacheck lab on a vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome project. Eventually, Aw joined the Polacheck lab and used her molecular biology expertise to help develop the VMs model. In addition to Dr. Blatt and Aw, the lab has an ongoing collaboration with Boyce Griffith, Ph.D. in the Department of Mathematics and the Computational Medicine Program at the UNC College of Arts and Sciences, who is helping with analyzing the structures of the networks. “All those pieces were necessary to complete the work,” said Polacheck. “It does say something about UNC-Chapel Hill because there were multiple departments across campus involved. There were no barriers whatsoever to working together on this project.”
How a Microfluidic Model Works
Microfluidic models are incredibly small – about the size of a millimeter – three-dimensional devices that can be used to control or simulate the environment within the body. In this case, a small piece of blood vessel composed of healthy human endothelial cells or endothelial cells expressing the PIK3CA mutation is centered inside of the device. From there, the researchers can look into the process of vascular formation, and introduce specific chemicals and mechanical forces to the model to simulate the conditions of the body. They observed the formation of enlarged and irregular vasculature with the introduction of PIK3CA mutation. To confirm whether or not their model accurately portrays the manifestation of the disease, the team next conducted a drug efficacy study.

Images of control (Top) and PIK3CAE542K vascular networks (Bottom). Vascular networks were labeled with fibrin (magenta), 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (white), actin (green), and endothelial cell–specific CD31 staining (cyan). There are two drugs currently used for the treatment of vascular malformations: rapamycin and alpelisib. The latter is a newly discovered PIK3CA-specific inhibitor recently approved by the FDA to treat certain types of breast cancer and PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum. So far, pre-clinical studies in mouse models and in patients have shown that alpelisib is more effective in reversing vascular malformation defects. After selecting the two drugs, Polacheck and Aw applied the treatment to their devices. The study was a success. “The blood vessels used to be really dilated and large,” said Aw, first author of the study. “By imaging the vessels before and after treating with drugs, we observed the vessels shrink and, more or less, revert it back to a normal shape and function. We were very excited to be able to replicate some of the results in vitro with the model we built.” Moving forward, Aw and Polacheck are looking to replicate the finding in tissues from vascular malformation patients, especially those who don’t have the PIK3CA mutation or don’t have clear genetic information. Their model can now be used to evaluate new medications or to perform synergistic drug studies.
Multiple Paths for Future Study
Now that they know that their model works, Aw and Polacheck plan to use it to study the behavior of the mutated cells over time, as well as how the mutation affects malformations of the lymphatic tissue. The disease initially begins with an individual cell that acquires the PIK3CA mutation. Then, much like a chain reaction, the effects of the mutation in that one cell spreads to the surrounding cells until the malformation is fully formed. As their model currently stands, the lab cannot mimic that natural process. Aw is currently working on a new and different approach for a microfluidic model. She aims to create a platform that will allow them to start with cells that are healthy, and then “flip on” the mutation, and watch it progress across the tissue of interest. Ultimately, it will help them understand how the mutation is able to affect other cells and move throughout space. Vascular malformations can also occur in lymphatic tissue. As opposed to blood vessels, lymphatic vessels have a duty to recycle excess fluid throughout the body and acts as a superhighway for immune cells to get to sites of infection. Very little is known about the basic cell biology of lymphatic endothelial cells, so Polacheck is hoping to do a study that is similar to his most recent one. “The outputs are slightly different because the function of the lymphatics is different from blood vessels,” said Polacheck. “By comparing and contrasting what happens on the blood side and the lymphatic side, we will also be able to learn something about the basic biology of those two types of tissues.” Source: UNC School of Medicine Read the full article
0 notes
Text
How a new blood-vessel-on-a-chip can help researchers further understand vascular malformations
Control cells and endothelial cells expressing PIK3CA-activating mutations cultured in 3D fibrin matrices and imaged at 0 and 168 hours after seeding. Scale bars, 1000 μm. Credit: Aw et al. Our bodies are made up of 60,000 miles of complex pipes that play a vital role in transporting nutrients throughout our bodies, performing waste disposal, and supplying our organs with fresh oxygen and…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
IJMS, Vol. 24, Pages 1799: An Overview of Circulating Cell-Free Nucleic Acids in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Triple-Negative Breast #cancer
Triple-negative breast #cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive subtype of breast #cancer due to its molecular heterogeneity and poor clinical outcomes. Analysis of circulating cell-free tumor nucleic acids (ctNAs) can improve our understanding of TNBC and provide efficient and non-invasive clinical biomarkers that may be representative of tumor heterogeneity. In this review, we summarize the potential of ctNAs to aid TNBC diagnosis and prognosis. For example, tumor fraction of circulating cell-free DNA (TFx) may be useful for molecular prognosis of TNBC: high TFx levels after neoadjuvant chemotherapy have been associated with shorter progression-free survival and relapse-free survival. Mutations and copy number variations of TP53 and PIK3CA/AKT genes in plasma may be important markers of TNBC onset, progression, metastasis, and for clinical follow-up. In contrast, the expression profile of circulating cell-free tumor non-coding #RNAs (ct#ncRNAs) can be predictive of molecular subtypes of breast #cancer and thus aid in the identification of TBNC. Finally, dysregulation of some circulating cell-free tumor #miRNAs (miR17, miR19a, miR19b, miR25, miR93, miR105, miR199a) may have a predictive value for chemotherapy resistance. In conclusion, a growing number of efforts are highlighting the potential of ctNAs for future clinical applications in the diagnosis, prognosis, and follow-up of TNBC. https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/2/1799?utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=tumblr
0 notes
Text
Pip3 pathway

#PIP3 PATHWAY SKIN#
Each has been implicated in a variety of cell signaling responses, either as a necessary cofactor or a regulator, although direct regulatory roles remain unproven. PIP 2 and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate are the respective products of PI 5-kinase and PI 3-kinase, as shown in Fig. 1. J.David Lambeth, Sung Ho Ryu, in New Comprehensive Biochemistry, 1996 5.1 Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP 2) and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate as potential signal molecules 96 The relevance of PIK3CA mutations to the clinical activity of anti-HER2-directed therapy by trastuzumab and lapatinib is under active investigation. Furthermore, PIK3CA mutations are twice as common in HER2-positive or ER-positive tumors, suggesting that more than one aberration upstream of AKT may be necessary to overcome the effect of an intact PTEN. 95 Recent data elucidating the relationship between presence of PIK3CA mutations and PTEN status show that they are inversely correlated. 94 In addition, PTEN loss has been associated with a decreased likelihood of response to anti-HER2 therapy with trastuzumab. 93 PTEN loss is associated with genetic instability, and primary breast tumors that lack PTEN have increased aneuploidy. 92 PTEN is inactivated in a wide variety of human tumors as a result of either mutation or, more commonly, epigenetic silencing through methylation, including in breast cancer.
#PIP3 PATHWAY SKIN#
Germline PTEN mutations cause a hereditary cancer predisposition syndrome known as Cowden syndrome, characterized by a high incidence of breast, uterine, thyroid, and skin neoplasms. 91 This signal is inactivated by the opposing phosphatase action of the tumor suppressor gene PTEN. Approximately 25% of human breast cancers harbor oncogenic activating mutations in the p110α catalytic subunits of PI3K ( PIK3CA). PIP 3 activates AKT and other related pathways to induce proliferation and inhibit apoptosis. Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PIP 3) is a lipid second messenger formed by PIP 3 kinase (PI3K) in response to receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Beryl McCormick, in Abeloff's Clinical Oncology (Fifth Edition), 2014 PI3K and PTEN

0 notes
Text
Targeted Therapy for Advanced Hurthle Cell Carcinoma of the Thyroid Gland
Targeted Therapy for Advanced Hurthle Cell Carcinoma of the Thyroid Gland
• The recent report by Ganly et al:• They identified the importance of the:• RTK / RAS /RAF / MAPK and PIK3 / AKT / mTOR pathways in this disease• At least one receptor tyrosine kinase:• Was mutated in 20% of HCC tumors, including:• EGFR (2%)• ERBB2 (11%)• PDGFR (2%)• TSHR (4%)• MET (4%)• RET (4%)• PIK3CA mutations:• Were found in 2% of HCC tumors and were:• Mutually exclusive with PTEN mutations…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Genetic Testing Market Growth & Trends | Analysis by 2030
Genetic testing is one of the rapidly evolving segments in the healthcare sector. It is estimated that the global genetic testing market will evolve at 10.25% of the CAGR between 2022 and 2030. The increasing incidence of genetic diseases and the rising applications build the groundwork for the market’s opportunistic progression.
Genetic testing helps identify changes in proteins, chromosomes, or genes. The results can rule out or confirm a suspected genetic condition and determine the chances of passing or developing a genetic disorder.

The top trend-setting factors in the market are the rise in the aging population and technological advancements. As per the United Nations’ World Population Prospects 2020 Highlights, more than 1.5 billion will be aged over 65 by 2050. The aging population is vulnerable to chronic diseases, thereby raising the demand for preventive diagnostics, especially genetic testing. Further, the growing cases of inherited diseases like hemophilia, cystic fibrosis, and sickle cell anemia are pushing the need for genetic testing.
Genetic Testing Market by Segmentation | Trends 2022
The global genetic market report scope includes the segmentation analysis of disease, application, technology, and type. The government initiatives in terms of genetic testing awareness, the rising disposable income, and technological advancements facilitate the growth of key segments like type and disease. For instance, genetic testing is increasingly being used in pharmacogenomics, also called drug-gene testing. This is also attributed to the genetic testing techniques advancements.
The cancer segment is expected to have the largest revenue share in the global genetic testing market by disease.
Cancer is the second-leading cause of death, with almost 70% of deaths occurring in low-and-middle-income countries. Genetic testing aids in estimating the chances of developing cancer by assessing the specific changes in genes, chromosomes, and proteins. This leads to increased surviving probability, cost-effective treatment, and minimal morbidity.
The increasing awareness about personalized medicine and preventive diagnosis, and the growing cancer burden, contribute to the segment growth. According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), the new cancer incidence is predicted to reach 30.2 million by 2040.
Furthermore, the growing technological advancements and product launches boost the cancer segment’s growth. For instance, Roche launched the Cobas PIK3CA Mutation Test in December 2020 for detecting PIK3CA mutations in advanced or metastatic breast cancer patients.
Moreover, the rising popularity of direct-to-consumer channels, the growing adoption of self-testing kits, increased consumer expenditure on healthcare, and easy access to genetic testing services boost growth opportunities in the type segment.
The prenatal & newborn testing segment is evaluated to be the fastest-growing test type.
This is accredited to surging demand to identify health complications in newborn or prenatal babies, particularly in developed countries. Also, prenatal screening helps identify several health conditions like Down syndrome, Edward syndrome, and patau syndrome. Further, as per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the perinatal mortality was stable, with stillbirth affecting almost 1% of all pregnancies in the US in 2012.
In addition, extensive research associated with genomics and proteomics and heavy investments in research activities has resulted in substantial technological advancements.
Asia-Pacific is expected to project more growth opportunities given the increased government initiatives, the rising research activities, large population, awareness of early screening of genetic disorders, growing medical tourism, and increasing demand for quality healthcare. Whereas North America is estimated to fare more in terms of revenue share due to the presence of key players like 23andMe, Myriad Genetics Inc, PerkinElmer Inc, Illumina Inc, etc., a strong base of healthcare facilities, and a surging pregnancy rate.
Future Potential
Some aspects of most diseases are influenced by changes in the patient’s genome. In this regard, there is immense potential for genetic testing in promising applications like tumor molecular profiling like liquid biopsies to select cancer treatment, sequencing for rare diseases, and non-invasive prenatal diagnostics. Additionally, the increasing acceptance and accessibility of non-targeted sequencing among consumers and patients are evaluated to offer growth opportunities for the global genetic testing market.
#Genetic Testing Market#genetic testing#healthcare#inkwood research#market research report#market research reports#market research
0 notes
Text
Breast cancer drug shows promise in treating young infants with PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum
Breast cancer drug shows promise in treating young infants with PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum
PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum (PROS) is a group of rare, incurable disorders caused by mutations in the PIK3CA gene that result in the malformation and overgrowth of various parts of the body. A new report to be published January 26 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM) describes the successful treatment of two young infants with PROS using the breast cancer drug alpelisib. PROS…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Liquid Biopsy Market to Surpass $3,535.1 Million, Globally by 2027 Expand at a 27.3% Exclusive Report by CMI
Liquid biopsy can be divided into four categories based on the sort of material they contain: tumor cells, Exosomal DNA, free DNA, and miRNAs. Liquid biopsies can be divided into four categories based on the type of analysis: small-scale mutation analysis and targeted deep sequencing, structural changes analysis, large-scale mutation analysis by next-generation sequencing, and copy number alteration analysis. For liquid biopsies, there are two separate test categories, one depending on the material type evaluated in the test and the other focusing on the type of analysis used to monitor or detect cancer.
Request Here Sample Report (Get Full Perceptions in PDF - 140+ Pages) @ https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/insight/request-sample/1223
Statistics:
The global liquid biopsy market is expected to be worth US$ 3,535.1 million by the end of 2027.
Global Liquid Biopsy Market: Drivers
Over the forecast period, the global liquid biopsy market is expected to rise due to rising demand for non-invasive diagnostic techniques. Liquid biopsy is a non-invasive diagnostic test for cancer detection. When compared to traditional biopsy, it has a lower morbidity rate. Furthermore, liquid biopsy could provide a clear insight of a patient's tumor characteristics and genetic alterations. Over the forecast period, these benefits are projected to increase demand for the liquid biopsy.
Global Liquid Biopsy Market: Opportunities
To increase the usage of the liquid biopsy, cooperation between bioinformatics experts, physicians, and biochemists is needed. To examine the efficacy of liquid biopsy in cancer diagnosis, a parallel examination of the liquid biopsy and traditional biopsy is necessary.
Global Liquid Biopsy Market: Restraints
The availability of an inadequate number of genes will limit the global liquid biopsy market growth. Doctors and Oncologists can use tissue biopsy to look at numerous genes at once. In the liquid biopsy, however, urine and blood tests only allow access to a single gene at a time, and may not provide a reliable companion diagnosis to begin treatment.
Buy This Research Report Now @ https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/insight/buy-now/1223
Key Takeaways:
The CTC (Circulating Tumor Cells) segment of the global liquid biopsy market was worth US$ 416.7 million in 2019 and is expected to grow at a rate of 19.3 % CAGR to US$ 1,710.8 million by 2027. Over the forecast period, rising cancer prevalence is a key driver propelling the global liquid biopsy market growth.
In 2019, the segment of blood sample accounted for the largest share in the global liquid biopsy market, and accounted 93.6% of market value, following by the segment of urine sample. Over the forecast period, the global liquid biopsy market is expected to rise due to a growing preference of non-invasive diagnostic techniques.
Market Trends:
Use of the liquid biopsy in lung cancer diagnosis has increased in recent years. Blood tests are used by doctors to diagnose lung cancer, particularly in individuals having non-small cell lung cancer. Artificial Intelligence is being more widely used in the liquid biopsy. For instance, a U.S. based AI genomics firm, Freenome, is working on creating blood tests that utilize Ai to identify the body's early-warning indications of cancer. The company offered preliminary data in Research and Development in October 2018 to apply machine learning for discovering colorectal cancer in its early stages.
Global Liquid Biopsy Market: Competitive Landscape
The following companies are key players in the global liquid biopsy market: Silicon Biosystems, Pathway Genomics Corporation, Biocept, Inc., Natera, Inc., Sysmex Corporation, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Limited., Trovagene, Inc., Qiagen N.V., MDxHealth SA, and Janssen Global Services. Global Liquid Biopsy Market: Key Developments
• February 2020: In Europe, QIAGEN N.V. introduced its FFPE and liquid biopsy PIK3CA diagnostic as a tool for identifying patients having a phosphatidyl 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) alteration in breast cancer.
• January 2020: A veterinary diagnostics and pharmaceutical firm, Zomedica Pharmaceuticals Corporation, has announced the completion of development and production of its canine cancer reference lab liquid biopsy platform.
Need Customize Report? Please Visit @ https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/insight/request-customization/1223
0 notes
Text
Familial Nonmedullary Thyroid Carcinoma (Fnmtc): Molecular Advances with the New Sequencing Technologies- Juniper Publishers
Introduction
Approximately 3-9% of the thyroid neoplasms are hereditary. Familial non-medullary thyroid cancer (FNMTC) is diagnosed when three or more first-degree relatives are affected and is classified into Syndromic familial adenomatous polyposis, Gardner’s syndrome, Cowden’s disease, Carney’s complex type 1, Werner’s syndrome) and Nonsyndromic (thyroid cancer). Several candidate chromosomal loci and susceptibility genes have been reported but these results are not replicated in subsequent studies. As the Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) now offers a powerful new diagnostic approach of the goal of this article was to review the current knowledge the new approaches used for the molecular characterization of FNMTC cases.
Familial predisposition of nonmedullary thyroid carcinoma (FNMTC) is diagnosed when three or more first-degree relatives are affected. It occurs in about 3-9% of the follicular cell-derived neoplasms and is classified into Syndromic and Nonsyndromic because encompasses a heterogeneous group of diseases [1]. The Syndromic group is characterized by a predominance of non-thyroidal tumors. Some syndromes are more frequently observed, such as familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), Cowden syndrome, Werner syndrome and Carney complex, with thyroid cancer prevalence of 2-12%, 35%, 18% and 15%, respectively. Except for Werner’s syndrome, all syndromes related with FNMTC are autosomal dominant. Several driver-genes have been identified, APC gene was associated to FAP and PTEN, SDH, PIK3CA, AKT1 and KLLN were related to Cowden syndrome; PRKAR1α was related to Carney complex and WRN gene was associated to Werner’s syndrome [1].
The Nonsyndromic form accounts for 95% of all FNMTC cases and is characterized by the presence of thyroid cancer and the absence of other known associated syndromes [2]. The Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (PTC) subtype is the most commonly observed and may or may not be associated with benign thyroid neoplasms (multinodular goiter) or autoimmunity thyroid disease (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis). Several candidate chromosomal loci and susceptibility genes have been reported (1q21, 2q21, 6q22, 8p23.1-p22 and 19p13.2, NKX2‐1, FOXE1, SRGAP1, TERT, HABP2 and C14orf93) suggesting that it is a polygenic familial cancer syndrome [1,3-5]. As subsequent studies failed to identify segregation of these candidates with the disease and due to the clinical variability of the patients, the molecular profile of each FNMTC family may be unique [6-9]. Furthermore, important cancer-related genes (APC, PTEN, TSHR, RET, TRK, c‐MET, BRAF and H‐K‐N‐RAS) were also excluded as the cause of FNMTC [10]. In the last decade, techniques for single-target detection have been replaced by the Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), which allows simultaneous analysis of a large group of genes generating a large volume of data in parallel [11-13]. The NGS high-throughput platforms are more efficient, less expensive and provides information that is not provided by Sanger DNA sequencing analysis or by hot spot mutation gene targeted assays (MLPA - Multiplex Ligation Probe-dependent Amplification or Taqman Genotyping) [10–12]. Analysis of the generated data is a complex process. In familial diseases with clinical heterogeneity, as observed in FNMCT, a careful selection of the individuals to be submitted to the NGS is necessary. The inclusion of unaffected individuals improves diagnostic rates by facilitating variants selection and mutations identification due to the exclusion of regional polymorphisms. The definition of a suitable pipeline for the identification and classification of the variants is also an essential step [11,12]. In silico predictive analysis provided by specific programs such as Polyphen2, SIFT, Mutation Assessor and Mutation Taster is a valuable tool to distinguish between the pathological and benign variants associated with the phenotype, taking into account the evolutionary conservation of the amino acid or nucleotide residue, biochemical impact of the amino acid substitution considering the physicochemical properties, and the variant localization [11,12]. As there is no rule, the use a more stringent filtering criterion are more appropriate as the first approach while less strict selection may be adequate when no candidate variant was identified [13-16]. It is noteworthy that a consensus among the prediction results leads to a better accuracy, as in CONDEL, PON-P and Meta-SNP algorithms [11,17,18]. Information obtained from population databases (1000 Genomes Project, ExAc and Exome Variant Server (EVS)) are frequently used to exclude variants that are deemed polymorphic/benign based on a global minor allele frequency (MAF) cut off of ~1% (0.01).
However, it is important to consider ethnicity-specific MAFs that depend on the ethnic background of the population, particularly in populations with high miscegenation as observed in Brazilians, underrepresented in most of the genomic databases, however data made available by local consortiums as ABraOM [19] and EPIGEN-BRAZIL [20] unravel this problem. In the literature, it is already possible to observe the benefits of new generation sequencing in the FNMTC. Recently, a group sought to identify previously undescribed cancer-predisposing gene(s) in a Cowden Syndrome family enriched for thyroid cancer across 4 generations, who had tested negative for PTEN, SDHB-D and KLLN, via an approach combining exome sequencing and family study. They found a variant in SEC23B gene and suggested that this germline heterozygous variant is associate with cancer predisposition [21]. Moreover, when whole-genome approach was conducted in sporadic FAP patient in which any pathogenic APC mutations was found by the conventional Sanger sequencing, a mosaic mutation in ~12% of his peripheral leukocytes was identified. Demonstrating that NGS is an effective tool to identify genetic mosaicism in hereditary diseases [22]. A variant on WRN gene was identified by exome-wide sequencing in a 16-year-old girl with an atypical syndrome without diagnosis after 10 years of the first symptoms. The variant has been previously reported in Werner’s syndrome (WS) and when the patient was re-evaluated several features of WS were detected, allowing the early diagnosis of a recessive disease and the early use of adequate therapies and interventions [23]. Using Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) a germline variant in the HABP2 gene was identified in a family with seven PTC patients of a FNMTC kindred and in 4.7% of 423 sporadic PTC cases. This variant increased protein expression in the tumor samples and functional studies showed that the loss of function p.G534E rs7080536 variant leads to increased colony formation and cell migration, characteristics of malignant transformation, suggesting that the HABP2 gene may be involved in susceptibility to thyroid cancer [4]. Because the authors did not report the ethnicity of the family and for having used only one database to determine MAF (1000 Genomes), this result was questioned by others groups [24]. Furthermore, this variant was considered a polymorphism in other populations (United Kingdom, USA, Saudi Arabia, Colombia, Spain, Italy, Australia and Brazil) [24].
Only Zhang et al identified the rs7080536 variant in 4/29 (13.8%) of unrelated FNMTC kindreds [25]. In other study, through linkage analysis and exome-sequencing the genes C14orf93 (RTFC), PYGL and BMP4 were identified as candidate genes in a FNMTC family with 5 cases of PTC. However, the functional studies showed that only the p.V205M mutation of the C14orf93 gene led to increased migration rate and colony formation in a PTC cell line [5]. Next Generation Sequencing allied to capture of expressed sequences from genomic DNA now offers a powerful new diagnostic approach. Barriers to use this technology still include cost and the complexity of interpreting results arising from simultaneous identification of large numbers of variants. Thus, cost reductions and new friendly analysis of this big data are necessary. Even so, the results obtained through this new generation sequencing technology have opened doors to new possibilities in the search for the molecular bases of thyroid familial cancer.
For more about Juniper Publishers please click on:https://twitter.com/Juniper_publish
For more about Journal of Thyroid Research please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/jetr/index.php
#Thyroid Research#thyroid nodules#endocrinology impact factor#Metabolic Syndrome#Juniper publishers e-books
0 notes
Text
Red meat consumption, colon cancer, and the environment - Dr. Antonio Giordano

Consumption of red and processed meats has long been linked to an increased risk of colorectal cancer, according to epidemiological research.
A study conducted by the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston looked into the link between a red meat-based diet, DNA damage, and colorectal cancer. The findings would have confirmed DNA damage that could affect the Kras gene, specifically two mutations (G12D and G13D), as well as the PIK3CA gene, which are both linked to the onset of colorectal cancer.
For the first time, researchers have discovered an alkylating mutational signature in colon cells, which they relate to red and processed meat intake. The discovery of this mutation might have far-reaching implications: for example, if it were feasible to identify those genetically susceptible to alkylating damage by screening, they could be safeguarded against the dangers associated with a diet high in red meat. Colorectal cancer is caused by a habit that, when combined with other hereditary factors, contributes to the disease's onset.
Read more: https://www.drantoniogiordano.com/post/red-meat-consumption-colon-cancer-and-the-environment
0 notes
Text
Alpelisib
In this article, we will discuss Alpelisib (Dosage Overview). So, let’s get started. Alpelisib is indicated in combination with fulvestrant for the treatment of postmenopausal women, and men,with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative, PIK3CA-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer as detected by an FDA-approved test following progression…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo

The PIK3CA mutation occurs in breast, colon, lung, and other cancers. Clinical trials with new targeted therapies are available for eligible patients to enroll in. Get genetic testing to see if you have the PIK3CA or other gene mutations present. Learn more about how these clinical trials can benefit PIK3CA positive cancers below. #clinicaltrials #genomics #genetictesting #cancerawareness #BeatingCancerTogether
0 notes