#Real-world PDCA application
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
PDCA in IATF 16949: Beyond Compliance – A Practical Automotive Perspective
The PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle isn’t just a theoretical model in IATF 16949—it’s a discipline that drives defect prevention, customer satisfaction, and operational excellence. But too many suppliers stop at compliance, missing the real value: process maturity and zero-defect culture. Here’s how to truly live the PDCA cycle in an IATF 16949 environment. 🧩 1. PLAN: Go Beyond Quality—Integrate…
#Automotive QMS best practices#Automotive quality management#IATF 16949 continuous improvement#IATF 16949 corrective action#IATF 16949 implementation guide#IATF 16949 process approach#IATF compliance strategy#Lean manufacturing PDCA#PDCA audit preparation#PDCA cycle in manufacturing#PDCA for automotive suppliers#PDCA IATF 16949#PDCA in automotive industry#PDCA methodology in IATF#Plan Do Check Act IATF#Practical PDCA IATF examples#Quality improvement IATF 16949#Real-world PDCA application
0 notes
Text
Achieving Environmental Excellence: A Comprehensive Guide to ISO 14001 Certification

In an era where environmental concerns dominate public discourse, businesses face increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices. Climate change, resource depletion, and pollution are not just abstract concepts; they have real-world implications for both society and business operations. Consequently, organizations are recognizing the necessity of implementing effective Environmental Management Systems (EMS) to manage their environmental responsibilities. This is where the ISO 14001 Standard comes into play.
ISO 14001 is a globally recognized standard that provides a framework for organizations to manage their environmental impacts systematically. By achieving ISO 14001 certification, businesses not only comply with regulations but also demonstrate their commitment to sustainability, enhancing their reputation and competitiveness in the marketplace. As a leading consulting company with extensive experience in ISO standards, 4C Consulting Private Limited has successfully helped over 2,500+ clients implement ISO standards, with more than 15,000 hours dedicated to ISO training.
What is the ISO 14001 Standard?
The ISO 14001 Standard is part of the ISO 14000 family of standards focused on environmental management. It establishes the criteria for an effective EMS and is applicable to any organization, regardless of its size or sector. The standard encourages organizations to adopt a systematic approach to managing environmental responsibilities, allowing them to identify, control, and improve their environmental performance.
Central to ISO 14001 is the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) model, which promotes continuous improvement. This cyclical process enables organizations to set environmental objectives, implement processes to achieve these objectives, monitor progress, and make necessary adjustments based on performance evaluations.
Why is the ISO 14001 Standard Needed?
The need for the ISO 14001 Standard is underscored by several compelling factors:
Regulatory Compliance: Environmental regulations are becoming increasingly stringent worldwide. Implementing ISO 14001 helps organizations comply with relevant laws, reducing the risk of legal penalties and reputational damage.
Risk Management: By identifying and managing environmental risks, organizations can prevent incidents that may harm the environment and incur significant costs. An effective EMS allows businesses to proactively address potential environmental issues before they escalate.
Stakeholder Expectations: Investors, customers, and the public are increasingly prioritizing sustainability. ISO 14001 certification signals a commitment to environmental responsibility, enhancing credibility and trust with stakeholders.
Market Differentiation: In competitive markets, organizations that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices stand out. ISO 14001 certification can serve as a valuable marketing tool, attracting environmentally-conscious customers.
Continuous Improvement: ISO 14001 promotes a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging organizations to regularly assess and enhance their environmental performance.
How to Implement the ISO 14001 Standard
Implementing the ISO 14001 Standard requires a structured and strategic approach. Here are the key steps involved in the ISO 14001 implementation process:
Obtain Management Support: Gaining commitment from top management is crucial for the successful implementation of ISO 14001. Leaders must recognize the importance of environmental management and allocate necessary resources to support the process.
Conduct a Gap Analysis: Assess current environmental management practices against the requirements of ISO 14001. This gap analysis helps identify areas that need improvement and establishes a baseline for the implementation process.
Develop an ISO 14001 Manual: Create an ISO 14001 manual that outlines the organization’s environmental policies, objectives, and procedures. This manual serves as a guiding framework for the EMS and ensures that everyone in the organization is aligned with its goals.
Set Environmental Objectives: Establish clear, measurable environmental objectives that align with the organization’s overall strategic goals. These objectives should be based on the results of the gap analysis and stakeholder expectations.
Implement Processes: Develop and implement processes to achieve the established objectives. This may involve training employees, enhancing operational practices, and adopting sustainable technologies that minimize environmental impact.
Monitor and Measure Performance: Regularly monitor environmental performance against the set objectives. Utilize key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
Conduct Internal Audits: Perform internal audits to assess the effectiveness of the EMS. This helps identify non-conformities and opportunities for improvement, ensuring the organization remains compliant with ISO 14001 requirements.
Management Review: Conduct periodic management reviews to evaluate the EMS’s performance and make informed decisions regarding necessary changes or improvements.
Continual Improvement: Foster a culture of continuous improvement by regularly reviewing and updating processes based on audit findings and performance evaluations.
Benefits of ISO 14001 Implementation
Implementing the ISO 14001 Standard offers numerous benefits, including:
Enhanced Environmental Performance: Organizations can significantly reduce their environmental impact, leading to improved sustainability and compliance with regulations.
Cost Savings: By identifying inefficiencies and waste, businesses can reduce operational costs and improve resource utilization, resulting in substantial financial savings.
Improved Stakeholder Relationships: Certification enhances credibility with customers, investors, and regulators, fostering trust and loyalty. It demonstrates a commitment to responsible business practices.
Increased Employee Engagement: A robust EMS creates a culture of environmental responsibility, motivating employees to contribute to sustainability efforts and enhancing overall job satisfaction.
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that achieve ISO 14001 certification can differentiate themselves in the marketplace, appealing to environmentally-conscious customers and improving their market position.
Risk Reduction: Proactively managing environmental risks minimizes the potential for incidents that could lead to legal liabilities or reputational damage, safeguarding the organization’s long-term viability.
How 4C Consulting Can Help You Implement ISO 14001
At 4C Consulting, we specialize in providing expert guidance for organizations seeking ISO 14001 certification. Our extensive experience and commitment to excellence make us the ideal partner for your ISO 14001 implementation journey. With over 15,000 hours of ISO training and a proven track record of assisting more than 2,500 clients, our team is well-equipped to support you every step of the way.
Our comprehensive services include:
ISO 14001 Consulting: We offer tailored consulting services to help you navigate the complexities of ISO 14001 implementation. Our consultants work closely with your team to develop and implement effective EMS processes tailored to your organization’s needs.
ISO 14001 Training: We provide in-depth training programs designed to educate your employees about ISO 14001 requirements. Our training equips your team with the knowledge and skills necessary to contribute effectively to the EMS.
Gap Analysis and Planning: Our experts conduct thorough gap analyses to identify areas for improvement and develop actionable plans for compliance with ISO 14001.
Ongoing Support: We offer continuous support throughout the implementation process and beyond, ensuring your organization remains compliant and continuously improves its environmental performance.
#ISO 14001 Implementation#ISO 14001 manual#ISO 14001 certification#ISO 14001 Consulting#ISO 14001 Training#ISO 14001 Audits#ISO 14001 Standard Requirements
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding the Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) Cycle for Continuous Improvement
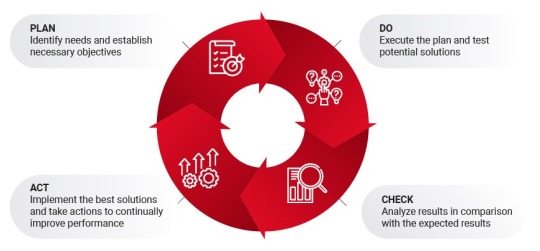
In today's fast-paced world, businesses and individuals alike strive for continuous improvement. One powerful method for achieving this is the Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) cycle. Originating in quality management, this model is a straightforward yet powerful framework to boost efficiency and effectiveness in various fields, from project management to personal development. In this article, we will delve into what PDCA is, how it works, and why it is essential for anyone looking to optimize processes and drive quality improvements in any area of life.
What is the Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) Cycle?
The PDCA cycle, also known as the Deming Cycle or Shewhart Cycle, is a four-step iterative process used for continuous improvement of products, processes, or services. Its goal is to promote ongoing assessment and refinement to achieve higher standards of quality. Each phase serves a specific purpose and involves distinct activities that lead to insights for improvement. Below, we explore each of these steps in detail.
Step 1: Plan
The first step in the PDCA model is planning. This involves defining the problem, identifying goals, and laying out a strategy to address the issue or achieve desired objectives. During this stage, it’s crucial to perform a thorough analysis of the problem, often using techniques like the 5 Whys or Root Cause Analysis. This helps to understand the underlying factors contributing to the problem.
Key activities in the Plan phase:
Define objectives and performance metrics
Conduct research and gather data
Brainstorm and evaluate potential solutions
Develop a clear action plan
Key phrase to remember: Proper planning prevents poor performance.
Step 2: Do
Once a solid plan is in place, it’s time to implement it in the "Do" phase. During this stage, small-scale implementation is recommended to minimize risks and costs. This helps to assess the feasibility of the proposed solutions in a real-world setting without committing extensive resources. While executing, it’s important to document the process carefully, as this documentation will be valuable for the later stages.
Key activities in the Do phase:
Execute the plan on a small scale
Collect relevant data on performance
Observe and record results
Step 3: Check
After implementing the plan, it’s time to evaluate its effectiveness in the "Check" phase. This stage involves comparing actual results to the expected outcomes to determine if the objectives were met. Analytical tools like Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and variance analysis are often used in this stage to measure success.
Key activities in the Check phase:
Analyze data and assess performance
Identify deviations or discrepancies
Determine the effectiveness of the solution
The Check phase provides critical insights for deciding whether to adopt the changes fully or make further adjustments.
Step 4: Act
The final stage, "Act," involves making adjustments based on the insights gained in the previous phase. If the solution was successful, it might be standardized and implemented on a larger scale. If not, the cycle may start over, with adjustments made to improve upon the initial plan.
Key activities in the Act phase:
Implement changes on a full scale if successful
Standardize the solution if viable
Re-enter the cycle if modifications are needed
Applications of the PDCA Cycle
The PDCA model is versatile and can be applied in various fields:
Manufacturing: In quality control, PDCA helps in minimizing defects and optimizing production processes.
Healthcare: Improves patient care and operational efficiency by continuously assessing and refining processes.
Education: Helps teachers and institutions improve curricula based on feedback and outcomes.
Project Management: Offers a structured approach for risk management and process optimization.
Personal Development: Encourages a proactive approach toward self-improvement and goal achievement.
Benefits of Using the PDCA Cycle
1. Continuous ImprovementThe primary advantage of Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) is its emphasis on continuous improvement, ensuring that processes or products keep evolving to meet changing needs.
2. Reduced RiskBy testing solutions on a smaller scale during the Do phase, organizations can mitigate risks associated with new initiatives.
3. Enhanced EfficiencyPDCA helps in identifying and eliminating wasteful practices, making processes leaner and more efficient.
4. Better Decision-MakingPDCA relies on data-driven insights gathered during the Check phase, leading to informed decision-making.
5. Increased AccountabilityThe PDCA framework requires documentation and review, which promotes accountability and transparency across teams.
Challenges of Implementing PDCA
Despite its simplicity, the PDCA model has certain challenges. Some of these include:
Time Consumption: Each phase, especially planning and evaluation, requires time and commitment.
Requires a Culture of Change: Successful implementation of PDCA demands an organization that values innovation and constant improvement.
Dependency on Accurate Data: The Check phase relies on accurate data collection and analysis. Inaccuracies can lead to incorrect conclusions.
How to Integrate PDCA with Other Quality Tools
PDCA and Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma focuses on reducing waste and improving quality, making it an ideal partner for PDCA. While Lean Six Sigma identifies areas needing improvement, PDCA provides a cycle to implement and sustain these improvements.
PDCA and Kaizen
In Kaizen, or "continuous improvement," small, incremental changes are made regularly. When integrated with PDCA, Kaizen becomes even more powerful, as the Plan, Do, Check, Act cycle ensures every improvement is tested and validated.
Examples of PDCA in Real-Life Scenarios
1. Improving Customer Service
A company facing customer dissatisfaction issues could apply the PDCA model by analyzing feedback (Plan), testing new response protocols (Do), reviewing customer feedback (Check), and standardizing the most effective protocols (Act).
2. Product Development
In product development, PDCA can be used to ensure each phase of development is optimized for efficiency and quality. By testing each feature on a small scale, product teams can identify issues early and avoid costly adjustments later.
Best Practices for Implementing PDCA
Engage Stakeholders: Ensuring all stakeholders understand and support the PDCA cycle is essential.
Maintain Open Communication: Transparent communication allows teams to share insights at each phase.
Focus on Data Accuracy: Reliable data is key to effective evaluation and decision-making in the Check phase.
Document Every Step: Proper documentation allows for better learning and reference in future PDCA cycles.
Conclusion
The Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) cycle is a foundational framework for anyone looking to enhance efficiency, minimize waste, and drive continuous improvement. With applications across numerous fields, it has become a cornerstone of quality management and process optimization. By embracing PDCA, organizations and individuals alike can foster a culture of ongoing assessment and refinement, achieving a higher standard of excellence and adaptability in today’s dynamic world.
0 notes
Text
Enhance Environmental Management with ISO 14001 Training by 4C Consulting

ISO 14001 Training is a crucial step for organizations aiming to improve their environmental management systems and ensure compliance with international standards. 4C Consulting offers comprehensive ISO 14001 Training designed to equip your team with the knowledge and skills necessary to implement and maintain effective environmental management practices. This blog will provide an understanding of ISO 14001 Training, its importance, and why you should choose 4C Consulting for this essential training.
Understanding ISO 14001 Training
Definition: ISO 14001 is an international standard that specifies requirements for an effective environmental management system (EMS). It provides a framework for organizations to protect the environment, respond to changing environmental conditions, and achieve continual improvement of their environmental performance.
Objective: The primary goal of ISO 14001 Training is to educate employees on the principles and requirements of the ISO 14001 standard, ensuring they understand how to implement and manage an EMS effectively.
Importance of ISO 14001 Training
Environmental Awareness: Enhances the understanding of environmental impacts and the importance of sustainability within the organization.
Regulatory Compliance: Helps ensure compliance with environmental laws and regulations, reducing the risk of legal issues.
Risk Management: Identifies and mitigates environmental risks associated with organizational activities.
Operational Efficiency: Improves processes to reduce waste and resource consumption, leading to cost savings.
Reputation and Credibility: Demonstrates a commitment to environmental responsibility, enhancing the organization’s reputation among customers and stakeholders.
Training
Understanding ISO 14001: Environmental Management Principles: Learn the core principles of environmental management, including pollution prevention, legal compliance, and continual improvement. Structure of ISO 14001: Familiarize yourself with the structure and requirements of the ISO 14001 standard, which follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) model. Importance of ISO 14001 Training: Employee Engagement: Engages employees in environmental management practices, fostering a culture of sustainability. Legal Compliance: Ensures that the organization meets all relevant environmental regulations, avoiding fines and penalties. Risk Reduction: Reduces environmental risks and potential liabilities through proactive management. Resource Efficiency: Promotes efficient use of resources, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Market Advantage: Enhances the organization’s competitive edge by demonstrating a commitment to environmental stewardship. ISO 14001 Training Process: Introduction to ISO 14001: Overview of the ISO 14001 standard, its history, and its importance. Key Requirements: Detailed explanation of the key requirements of ISO 14001, including context of the organization, leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and improvement. Implementation Strategies: Practical guidance on how to implement an effective EMS in line with ISO 14001 requirements. Documentation and Records: Importance of maintaining accurate documentation and records for the EMS. Internal Audits: Training on how to conduct internal audits to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement. Continual Improvement: Emphasis on the importance of continual improvement in environmental performance.
Why Choose 4C Consulting?
4C Consulting offers tailored ISO 14001 Training programs that cater to the unique needs of your organization. Our expert trainers provide practical insights and hands-on guidance, ensuring your team gains a thorough understanding of the ISO 14001 standard and its application. With a focus on real-world implementation and continuous improvement, 4C Consulting helps you build a robust environmental management system that drives sustainability and compliance. Choose 4C Consulting for a comprehensive, impactful training experience that empowers your organization to achieve its environmental goals. Contact us now.
0 notes
Text
iso 14001 lead auditor training online
The Imperative of ISO 14001 Lead Auditor Training: Nurturing Environmental Excellence
Introduction:
In today's global landscape, environmental sustainability has emerged as a pivotal concern for businesses worldwide. Organizations are increasingly recognizing the need to adopt robust environmental management systems to mitigate their ecological footprint. Among the most renowned frameworks for environmental management is ISO 14001. However, ensuring compliance and optimizing environmental performance demands expertise. Hence, ISO 14001 Lead Auditor Training assumes paramount significance. This article delves into the essential aspects of such training, elucidating its importance and exploring its profound impact on fostering environmental stewardship.
Understanding ISO 14001:
ISO 14001 serves as the cornerstone for environmental management systems, providing a systematic approach to address environmental challenges. Lead auditors must possess a comprehensive understanding of its principles, requirements, and implementation strategies. Through rigorous training, professionals delve into the intricacies of ISO 14001, comprehending its structure, key clauses, and the significance of continual improvement. Moreover, they explore case studies and real-world scenarios, gaining insights into practical applications and best practices. Such foundational knowledge equips auditors to assess organizational compliance effectively and recommend tailored solutions for enhancing environmental performance.
Roles and Responsibilities of Lead Auditors:
Effective environmental management necessitates competent leadership and oversight. Lead auditors play a pivotal role in evaluating an organization's environmental management system's conformity with ISO 14001 standards. During training, participants delve into the core responsibilities of lead auditors, encompassing planning, conducting audits, and reporting findings. They learn to navigate the audit process proficiently, from initiating assessments to communicating audit results. Furthermore, emphasis is placed on cultivating strong communication and interpersonal skills to engage stakeholders and facilitate constructive dialogue on environmental objectives and targets.
Risk-Based Approach to Auditing:
In today's dynamic business environment, organizations face multifaceted environmental risks that necessitate proactive mitigation strategies. ISO 14001 Lead Auditor Training underscores the importance of adopting a risk-based approach to auditing. Participants learn to identify, assess, and prioritize environmental risks, tailoring audit protocols accordingly. By focusing on high-risk areas, auditors can provide targeted recommendations for enhancing environmental resilience and compliance. Moreover, training equips auditors with the tools and methodologies to conduct thorough risk assessments, incorporating factors such as regulatory requirements, operational processes, and stakeholder expectations.
Driving Continuous Improvement:
Sustainable environmental management is a journey of perpetual improvement. ISO 14001 Lead Auditor Training instills a culture of continuous enhancement by emphasizing the principles of Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) and the pursuit of operational excellence. Auditors are trained to not only identify non-conformities but also to proactively identify opportunities for innovation and optimization. Through collaborative engagement with organizational stakeholders, lead auditors facilitate the development of actionable strategies to minimize environmental impact, conserve resources, and enhance overall sustainability performance.
Conclusion:
iso 14001 lead auditor training online In an era defined by escalating environmental concerns and regulatory scrutiny, ISO 14001 Lead Auditor Training emerges as a linchpin for nurturing environmental excellence within organizations. By equipping professionals with the requisite knowledge, skills, and competencies, such training empowers them to uphold the principles of environmental stewardship and drive meaningful change. As businesses strive to align with sustainable practices and demonstrate corporate responsibility, investing in ISO 14001 Lead Auditor Training becomes not only a strategic imperative but also a catalyst for fostering a greener, more resilient future.
0 notes
Text
Could Your Small Business Benefit From Lean Manufacturing ? |

If you use key performing indicators to measure how your business is doing, seek input from your employees about ways to continually improve, or use ERP software you are, in fact, practicing “lean manufacturing.” The question is: are there other lean principles you could be employing to further improve the performance of your business ? Lean manufacturing was popularized by Toyota back in the 1990s. It attempts to cut waste out of the job process while improving quality and maximizing value to the customer. I like to describe lean manufacturing as a philosophy comprised of 32 different ideas. Because all 32 ideas do not fit all companies, in my view, managers should pick and choose the ideas that work for their business and implement just those ideas. For instance, at a CNC Machine Shop I’m currently working with in Silicon Valley, we are in the process of implementing the “5S,” an approach for cleaning, organizing, and standardizing work areas much like the “CAN DO” program created by Henry Ford, from which the idea receives its inspiration. While the 5 S’s and creating a tool crib attendant position to stage tools & materials “just-in-time” for machinists were good fits here, because this business produces many different parts in smaller quantities, many of the lean ideas applicable to manufacturers did not fit this job shop operation. When looking at ways to be more “lean,” expect some resistance to change. At the previously mentioned machine shop, for example, the company almost talked themselves out of implementing the 5S’s until the Controller pointed out how many office supplies the old Production Manager had hoarded, in addition to the many problems they had to deal with after they terminated this manager because he buried RMAs in the cabinets of his cubical instead of placing them in a visible, designated area. Many of the small businesses I work with can benefit from better inventory management, scheduling & preventive maintenance, and lean manufacturing offers several possible solutions. What follows is a summary of the 32 lean manufacturing ideas that helped transform Toyota into the largest automobile manufacturer in the world … Perhaps your business can benefit from some of these ideas. For more information about implementing lean manufacturing principles in your business, please contact Jim Talerico today at 1-800-828-7585. 32 Lean Manufacturing Tools: The 5S System: is an effective approach for rooting out inefficiencies, improving work space organization, and implementing standard work-area practices throughout your organization. The 5S’s gets it name from the Japanese words used as guiding principles for this approach: namely, “Seiri” (tidiness,) “Seiton,” (orderliness,) “Seiso,” (cleanliness,) “Seiketsu,” (standardization,) “Shitsuke,” (discipline.) By implementing the 5S’s, employees can improve work station organization and, furthermore, become more efficient as they will be able to find tools more quickly, work safer, and improve their productivity by standardizing procedures. Boeing feels that the 5S’s have simplified operations and improved organizational efficiencies, and Harley Davidson credits the 5S’s with both streamlining their manufacturing processes and improved safety — which is sometimes referred to as the “6th” Kaizen: which translates to “continuous improvement,” encourages employees at all levels of the organization to make suggestions for improving the business to upper management. Kaizen helps employees feel more engaged, invested, and connected to the business. When Toyota implemented Kaizen at one of its plants located in the US, the auto maker received more than 75,000 suggestions from its 7,000 employees about how to improve the manufacturing process. Toyota went on to implement 99% of those ideas. Hoshin Kanri: takes a big picture look at the organization to ensure alignment of its corporate goals with middle management and front-line managers day-to-day objectives. This practice helps to ensure that the organization is working as one to tackle problems and realize its corporate vision and is implemented by upper management, who work closely with middle and front-line managers to ensure organizational focus on corporate goals and objectives. Value Stream Mapping (VSM): outlines the production process from start to finish. A flow chart is used to examine each step to find areas of waste or inefficiencies, so that steps can be taken to improve the process. Dalco Metals, Inc. used VSM to reconfigure its office space, which cut their order processing time in half, and inspired them to implement lean principles in their manufacturing process. Kanban: is a popular lean manufacturing technique that uses cards to control the flow of materials through a process. These cards are often used to trigger adjustments in inventory. Kanban, which means “visual cards,” is used to minimize waste, maximize efficiencies, and can also be used to signal when to cut back or step up production. Andon: is a visual feedback system designed to report on the status of production on the shop floor, and alert others when assistance may be needed. Andon uses a combination of lights and sounds to communicate status updates, problems & challenges. Both Toyota & Nissan use Andon in their plants to empower factory employees to provide real-time feedback about the production process. Gemba: encourages managers to connect with employees on a personal level and to seek out the real problems on the plant floor. The five – (5) guidelines governing this approach include: Having a specific purpose for taking a “Gemba walk;” Be familiar with the area on which you are focusing; Making sure you understand the overall process; and Knowing what questions to ask. Muda: is a core lean manufacturing principle and consists of seven- (7) different types of waste that organizations needs to eliminate from the work environment to maximize their bottom-line. These seven- (7) forms of waste include: The overproduction of items manufactured before they are needed in the workplace; Either too many or too few inventory items, which wastes money that could be invested in other areas of the organization; Downtime, resulting from waiting; Unnecessary motions of people and machines; Unnecessary transportation of parts or items during the process; Over processing beyond the customer’s requirements; and Rework resulting from quality issues. “SMART” Goals: are “specific,” “measurable,” “attainable,” “results-oriented,” and “time-specific.” Creating smart goals help an organization measure its success at reaching its corporate objectives. PDCA – Plan, Do, Check, Act: is a method for solving problems. During the planning phase, the problem is identified. Doing involves the act to solve the problem. Next, small scale changes are reviewed to see if the intended consequences have been reached, and to contemplate further actions needed. The last step in the process are the final actions, if any, needed to solve the problem. The process can be repeated, as needed, to focus on continuous improvement. Root Cause Analysis: is a problem-solving approach that attempts to find the underlying cause of a problem. Getting to the root of a problem ensures that a company avoids focusing on symptoms of the problem. Ishkawa (Cause & Effect Diagrams) is a “root cause analysis” technique for solving problems. Another name for this approach is the 5 whys ? By asking the question “why” up to 5 times, you ensure that you get to the root cause of an issue, so that corrective actions can be implemented to solve the problem. Ishkawa diagrams are illustrations that map out the answer to the 5 whys, and are sometimes called a “bone diagram,” because they can resemble a fish’s bones. Mind Maps: illustrates in a visual format the connection of ideas associated with a certain task. Mind maps are used to analyze both “macroscopic” and “microscopic” considerations of a problem during a “brainstorming” session. Mind maps are often used to unlock the solution to difficult problems. Poka-Yoke: translates loosely to “inadvertent error prevention.” Poka-Yoke is used to detect — and prevent — problems in the production process in “real time,” rather than after the process is completed. Proponents of Poka-Yoke maintain that it saves time and money while minimizing unnecessary waste in the production process. The Big Six- (6) Losses: helps an organization avoid the six- (6) most common reasons for productivity loses, which include: Unplanned Steps – such as when a piece of equipment goes down during the production process; Planned Stops – such as breaks, safety inspections, and planned maintenance; Small Stops – such as the time needed to unclog a machine, correct settings, or to clean up; Slow Cycles – which usually occur when a machine runs slower than designed, because it is old, worn out, or being controlled by a new operator; Production Rejects – defective parts produced during the routine course of production, usually due to operator error or incorrect settings; and Startup Rejects – defective parts produced as a machine turns on and starts up. Start-up rejects usually occur due to normal processes during equipment startups and process changeovers. Standardized Work: consists of finding the best work practices for a process and implementing that approach across the organization. When implementing a standard process, the steps involved when the tasks are to be performed and why they must be performed are carefully communicated to all parties involved. The Visual Factory: relies on visual communications to inform workers. Examples of visual communications include: electronic display boards, color coded storage systems, signs, labels, and floor markings. Studies reveal that clear, simple, and direct communications improve organizational efficiencies. Cellular Manufacturing: Is an approach that breaks down the production process into parts, and creates “cells” consisting of machines, people and processes that fit into the larger manufacturing process. The benefit of cellular manufacturing is that it can cut down on floor space, increase output, and improve productivity, when compared to a large-scale assembly line operation. Cellular manufacturing also offers flexibility, as a company can adjust certain cells without effecting the entire manufacturing process. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): is a comprehensive computer software solution that collects data throughout the production process to allow the entity to make better business decisions. Key Performing Indicators (KPIs): are important measurements that speak to the efficiency of the process. These critical measurements provide quick feedback about whether you are meeting your goals and allows management to make timely changes. Heijunka: is a scheduling approach that encourages a steady flow of small batch manufacturing instead of larger runs with more downtime between runs. The theory behind this approach is that focusing on smaller runs improves focus and, hence, efficiencies. Level Loading: is a technique that balances the manufacturing process, so that goods are produced at a steady rate. This, in turn, ensures that other stages of the production process can happen at a steady rate, independent of short-term increases or decreases in demand. Level loading reduces stresses to the process caused by big changes in demand. Continuous Flow: is a scheduling strategy that attempts to minimize interruptions in the process by anticipating shutdowns and planning around them. Minimizing downtime allows a company to maximize output, profits, and efficiencies. Takt Time: encourages a manufacturer to develop a rate of production that reflects consumer demand. Takt time measures the rate at which items must be produced to meet consumer needs, rather than the time it takes to produce an item. Takt time ensures the proper allocation of resources and offers employees flexibility, so long as consumer demands are met. Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED): SMED reduces setup times or changeover times in a manufacturing process to less than 10 minutes. SMED speeds up setups by simplifying the process, eliminating wasteful steps, and developing standard procedures. Toyota used SMED to reduce changeovers from 3 days to 10 minutes in their transfer stamping process. Zero Quality Control (ZQC): is a method for eliminating all defects from a process due to operator error or unfavorable conditions. ZQC aims to control a process’ performance, so that it is impossible to produce defects. Jidoka: is another approach for minimizing inefficiencies, slowdowns, breakdowns, etc. by empowering employees and establishing machine controls to stop the process and fix the problem without management approval. Bottleneck Analysis: looks at areas where the process backs up and then institutes changes, improvements and methods to improve the slow down, or “bottleneck.” Bottleneck analysis improves efficiencies and productivity by locating obstacles in the process and giving employees the tools to remove these obstacles. A-B-C Inventory: groups inventory into three – (3) classes of inventory using Pareto’s Law, also known as the 80:20 rule. “A items” represents the top 20% of inventory that moves the fastest; B items consist of that inventory which moves moderately; and C items are the slowest moving items. (B and C items represent the other 80%.) By separating inventory in this manner, a company can better focus on managing the more important inventory items. Just-In-Time (JIT): instead of inventorying items that can be pulled for future use, customer demand drives JIT inventory purchasing requirements. Inventory purchases are timed for when they are needed in the production process and arrive on the floor “just in time.” Total Production Maintenance (TPM): promotes proactive, preventive maintenance. By saving on maintenance costs and reducing downtime both productivity and output are improved. The seven – (7) techniques for implementing TPM include: (i) Autonomous Maintenance, which includes operators keeping tabs on their equipment and work areas; (ii) Process / Machine Improvement, which uses data provided by operators to improve preventative maintenance; (iii) Preventative Maintenance Tasks & Duties, which are documented to help ensure better maintain equipment; (iv) Early Maintenance Investments to prolong the life of equipment; (v) Process Quality Management, which ensures worker / management buy-in by assigning maintenance roles to both groups; (vi) Education & Training to improve machine operation, maintenance & safety; and (vii) actions to Sustain Success. Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): OEE provides a method for understanding the efficiency of each step in the manufacturing process. Using this method, a machine’s — or processes’– downtime, performance, and quality is measured as a percentage from 0 to 100. Knowing these percentages, allows management to look elsewhere in the production cycle for possible improvements.
0 notes
Text
PDA Startup Workshop Event #8
Bottleneck of Artificial Intelligence
Automated Emotional Analysis
PDA Abstract
Silicon valley's Professional Development Accelerator(PDA) focuses on creative talent technology acceleration service, adopts PDCA business model to provide trainees with technical diagnosis services and skills based on actual projects, technical enhancement services, and project incubation services. PDA is located in the core area of Silicon Valley, USJ, which brings together Silicon Valley FLAG scientists, 65 technical experts, 7 laboratories of various kinds, 45 of whom have doctor's degree, and they try their best to help the newly graduated college students to develop innovation and entrepreneurship activities.
PDA's main business:
1) project technical diagnosis and analysis;
2) practical project technical service;
3) special technical training services;
4) project incubation;
5) talent derivative services
PDA will make full use of the technology and talent advantages of Silicon Valley to provide high quality talent acceleration service for the majority of students.
PDA Business Workshop Schedule
-Company introduction
-Entrepreneurial lecture
-Introduction of entrepreneurial experience
-Q&A
Sponsor
University of San Jose, PDA project manager
Event Host
Joseph Xiong USJ TA
Guest Speaker
Name: Brian Wong
Company Name: Kiip
Experiences: Mr. Wong graduated from The University of British Columbia. He is currently a co-founder of Kiip. Kiip (pronounced “keep”) was a mobile consumer engagement platform that advertises in “moments” in 10,000 apps. Kiip is credited with the creation of “moments marketing”, which involves brands marketing to consumers in the right timing and mindset, based on their mobile behaviors. Mr. Wong has been recognized with many awards for his accomplishments and leadership, including:
- Forbes’ “30 under 30” for three years in a row.
- AdAge's “Creativity Top 50”
Brian launched his first book at the age of 25: The Cheat Code, published by Crown Business / Penguin Random House. The Cheat Code contains 71 bite-sized and virtually effortless shortcuts to get a leg up on the competition, garner attention for creative thinkers and their ideas, and to accelerate success. The book has been translated into Simplified Chinese and Arabic, and is featured by Forbes, CNBC, Elle, The Telegraph, The Globe and Mail, and many more publications around the world, and is quickly becoming the go-to book for entrepreneurial and intrapreneurial advice for our generation.
Artificial-Intelligence key points
Where does artificial intelligence come from?
The concept of "artificial intelligence" was proposed in the "Dartmouth College Summer Artificial Intelligence Research Program", which was initiated by John McCarthy and others on August 31, 1956, to bring together like-minded academics on "automatic computers." Topics such as "randomness" and "creative" are discussed. The conference lasted for a month, brainstorming and launched a number of groundbreaking proposals. This program can be seen as the "fire" of the artificial intelligence revolution, bringing computer technology applications to a whole new level.
what is artificial intelligence?
In computer science, artificial intelligence (AI) (sometimes called machine intelligence) is the intelligence that machines display, as opposed to the natural intelligence that humans display. In spoken language, the term "artificial intelligence" is often used to describe a machine (or computer) that mimics the "cognitive" functions (such as "learning" and "solving problems") that are related to human thinking. Artificial intelligence is divided into three categories: weak artificial intelligence, strong artificial intelligence and super artificial intelligence; weak artificial intelligence, also known as restricted domain artificial intelligence or applied artificial intelligence, is an artificial intelligence focused on solving specific domain problems; strong artificial Intelligence, also known as complete artificial intelligence, refers to artificial intelligence that can do all the work of human beings. It has the ability of logical reasoning, use strategy, decision making, problem solving, planning, common sense knowledge reasoning, natural language communication, etc. In all areas, there are artificial intelligences that perform better than the most intelligent human brains, such as research, social, and learning. Every innovation of weak artificial intelligence is a further milestone toward strong artificial intelligence and super artificial intelligence. We believe that quantitative change will be transformed into qualitative change. The crowd looked for him thousands of Baidu, and suddenly looked back at the place.
Where is artificial intelligence going?
The bottleneck of artificial intelligence technology lies in the detection and prediction of human emotions. In the Internet age, with the increase of hardware computing storage capacity, more and more artificial intelligence algorithms can be put into the real industrial production, such as: speech recognition, image recognition, natural language processing. Based on these applications and combined with the Internet of Things, big data technology completes the collection, cleaning, structuring, labeling and pattern extraction of training data. Just as human beings invented the concept of "intelligence" and "emotional intelligence", artificial intelligence should not have only one dimension of evaluation. Does the machine have the ability to perceive, generate, and control human emotions? This issue is currently undecided in academia and is in its infancy in the application of industry. Currently, the MIT Emotional Research team is developing the EQ-Radio, an emotional monitoring recognizer that measures the breathing and heartbeats, uses wireless signals and some small behaviors to determine what kind of emotion a person is in, with a prediction accuracy of 87%.
Event Time and Location
Time: Saturday, 2019/11/23, 14:00 - 15:30
Address: University of San Jose, 1631 N First Street, Suite #200, San Jose, CA, 95112
Registration
https://www.eventbrite.com/e/pda-startup-workshop-event-8-ai-talk-tickets-83068808041?aff=utm_source%3Deb_email%26utm_medium%3Demail%26utm_campaign%3Dnew_event_email&utm_term=eventurl_text
0 notes
Text
HRM 330 all Weeks discussions assignments and course project
Follow Below Link to Download File
https://homeworklance.com/downloads/hrm-330-weeks-discussions-assignments-course-project/
We also Do 100% Original and Plagiarism Free Assignment / Homework and Essay
Email us for original and Plagiarism Free Work At ( [email protected] ) or order us at (https://homeworklance.com/custom-order/ )
Devry HRM330 Week 1 Discussion DQ 1 & DQ 2
DQ 1
When efficiency, equity, voice, and other employee, union, and corporate goals conflict with each other, what should happen next? Should property rights dominate labor rights? Should labor rights dominate property rights? Should they be balanced? Defend your reasoning
DQ 2
Discuss the current pressures on the U.S. labor relations system—on the corporate side, workplace flexibility and employment involvement (stemming at least partly from globalization) and on the labor side, low union density, a representation gap, and difficulties in organizing new workers.
Devry HRM330 Week 2 Discussion DQ 1 & DQ 2
DQ 1
Like any business, labor relations require a strategic approach to create an efficient plan in support of employees. What is a key union or labor strategy that is still used today? What is a key historical strategy that should no longer be part of a labor relations plan? Thoroughly explain both responses.
DQ 2
It has been written, “The attempt of persons to understand the forces remaking their world and, by organization, to control them, constitutes the major motif of the social history of the late 19th century.” Describe how this statement applies to workers and unions in the different periods of labor history. Does this statement have applicability in today’s labor relations arena?
Devry HRM330 Week 3 Discussion DQ 1 & DQ 2
DQ 1
Human resource professionals need to ensure that employees have a voice in the employment relationship with their employers. From an HR perspective, what strategies would you consider employing to make sure employees have the ability to have a voice? Explain your reasoning for those strategies.
DQ 2
Discuss what you think are the most important challenges for both unions and management in a union workplace. Why are the challenges in a nonunion workplace? How have these challenges changed over the last 5 to 10 years?
Devry HRM330 Week 4 Discussion DQ 1 & DQ 2
DQ 1
In both private and public sectors, a sharp increase in union membership coincides with the passage of protective legislation. A long-standing debate is whether increased demand for unionization causes new legislation or vice versa. What side of this argument do you find yourself on and why? Explain your reasoning. Bring in recent examples in the news that support your stand.
DQ 2
Bargaining has resulted in many rights and benefits for all employees within the workplace. Describe your understanding of the purpose of bargaining. Conduct some additional research, and review a case study that includes union bargaining (be sure to cite your source of the case study).
HRM 330 week 5
DQ 1
List the pros and cons of interest arbitration. Why do you think the usage of interest arbitration in the private sector is so low?
DQ 2
A union-represented employee filed a grievance with her employer because she was terminated. The employer stated they were in an at-will state and had the right to terminate anyone at any time without cause. The former employee was terminated with no reason given, so the employer states he had the right to terminate her on the spot. Share your thoughts on this scenario as the labor relations professional. Detail what steps you would take, if any, and explain each step thoroughly. Be sure to cite labor law accordingly.
HRM 330 week 6
DQ 1
Some conflict management styles include avoidance, accommodation, competition, compromise, and collaboration. Which style do you think you use for conflict resolution? Share why you tend to use that approach to resolve conflicts. Also share instances when a particular style did not go so well. Why, from your view, did that happen? What, if anything, did you learn when that style did not help?
DQ 2
According to Arbitrator Daugherty (Koven and Smith, 2006), there are seven tests of just cause.
1. Was the worker given advance warning of the consequences of his or her conduct?
2. Was the rule, order, or standard reasonably related to employee performance?
3. Was the alleged violation thoroughly investigated before discipline?
4. Was the investigation fair and objective?
5. Did the investigation reveal convincing proof of guilt?
6. Was the employer’s discipline nondiscriminatory?
7. Was the discipline reasonably related to the worker’s record and the severity of the conduct?
How would you answer these questions based on the following scenario? Be thorough because you will be presenting this in front of the union.
Scenario
An employee received a disciplinary letter for her personnel file because she made a mistake on the job. This letter removes seniority points from her record. The company is in the middle of layoffs, and as a result of this letter, this employee would be next for layoff, when without the letter, she would have been safe. The mistake did not cost the business money but rather embarrassment to the supervisor, according to the employee. The contract states that the disciplinary process may be used for performance issues. The supervisor stated that the employee’s mistake was a performance issue and he had the right to issue a disciplinary letter. This employee’s previous performance appraisals have been satisfactory and above.
Reference
Koven, A., & Smith, S. (2006).
HRM 330 week 7
DQ 1
What recommendations would you make to union and management leadership in order to meet the demands of a constantly changing workplace? What are some possible warnings?
DQ 2
There is going to be a major generation shift with baby boomers leaving the workplace. Generations X and Y do not have the same ties to union activities as the baby boomers. What might unions have to offer these new generations? How would unions go about connecting with these two generations?
Written Assignment #1
HR Strategy Responding to a Union Organizing Drive
Due Week 3
Assignment Overview
There are 4 scenarios at the end of Chapter 6 of the textbook, pages 225 and 226. The purpose of this assignment is to provide you with real world exposureto the functions performed by labor relations. This assignment is worth 150 points; see rubric below.
Preparing for this Assignment
Read through each of the 4 scenarios. Spend some time analyzing what actions you would take as the HR Manager for these organizations.
Assignment Criteria
1. 1. Write a6-8 page paper (does not include title page or reference page/pages) providing a “summary” of your actions.
2. a. You are the HR Manager for each scenario.
3. b. Read through each scenario.
4. c. Read through the Plan-Do Check-Act(PDCA) process that is located in DocSharing. This will be helpful in your analysis of the issues as well as offering viable recommendations.
5. d. Outline your various alternatives in responding to the union organizing drive.
6. e. Develop and support aspecific recommended course of action to present to upper management.
7. 2. Follow APA format guidelines.
8. 3. You should be able to cover the alternatives and recommended actions in 1 1/2 to 2 pages for each scenario.
9. 4. The paper should include theory application. In other words, once you have conducted your analysis, what theories link to the Labor Relationsprocesses/functions? For example, spend a little time justifying the recommendations you made to upper management. Why should management pursue your suggestions? What analysis have you done that makes your recommendations viable? What are the pros and cons of the recommendations?
HRM 330 week 5
You Decide
Scenario SummaryYour Role/AssignmentKey Players
Scenario Summary
Carol Fern has been employed by Bainbridge Borough for 18 years as a tax clerk. The tax clerk position is part of the bargaining unit represented by Local 10 of the American Federation of State, County, and Municipal Employees (AFSCME). When Carol and her husband found out that she was unable to conceive, they decided to adopt a child. The Ferns were notified on April 22 that a 3-month-old baby girl was available and they could adopt her in three days. However, Carol told the adoption agency that she thought it was unfair to leave the company on such short notice because April was a busy tax season. Adoption was delayed until May 2. On April 27, Carol requested two weeks of paid vacation for May 2 to May 17. This request was granted. The day before she was to return from her paid vacation, Carol asked for 6 months of unpaid maternity leave. The request had to be approved by the Bainbridge Borough Council, which rejected the request by a 4-3 vote. However, the council did offer Carol two consecutive 90-day reasonable purpose leaves (amounting to 6 months of leave).
On June 1, the following grievance was filed.
According to Article X, Section 4.A—Unpaid Leaves, 5. Maternity on page 13 of the final agreement between Bainbridge Borough and Local 10: Maternity leaves not to exceed 6 months shall be granted at the request of an employee. Maternity leaves shall, upon the request of the employee, be extended or renewed for a period not to exceed 6 months. Relief or remedy sought: Granting of the just and deserved leave request.
A Potentially Relevant Contract Provision A. Leaves of absence for a limited period without pay—not to exceed 90 days—shall be granted for any reasonable purpose. Extension to be granted with approval of Borough Council.
Your Role/Assignment
The Issue
The union claims that the company violated the collective bargaining agreement by denying Carole Fern’s request for maternity leave. Carole Fern is clearly a new mother and is therefore entitled to the leave specified by the contract. The town argues that maternity leave is for mothers of naturally-born infants, not adopted children, and therefore, Carole Fern is not entitled to maternity leave.
So, decide which one is correct: Does maternity leave apply to adoptive mothers or only to mothers actually giving birth?
Key Players
Carol FernTax Clerk Town People Sally StevensCEO of company Bob SmithUnion leader
YOU DECIDE
Assignment
Assignment
You have three areas of focus for this assignment.
1. As an attorney for Bainbridge Borough, develop a case to support the council’s rejection of Carol Fern’s unpaid maternity leave request.
2. As an attorney for AFSCME Local 10, develop an argument to support your client’s contention that the council’s rejection of Carol’s unpaid maternity leave request violated the collective bargaining agreement.
3. As an arbitrator, how would you rule? Why?
Write a two- to three-page paper, (double-spaced, 12 point type, APA style) that outlines the case for Bainbridge Borough, the case for AFSCME Local 10, and how you would rule as an arbitrator based on the facts you have for this case.
CategoryPointsDescriptionBainbridge Rejection20Based on the collective bargaining agreement wording, defend why Carol’s request should be denied.Union’s Contention20Based on the collective bargaining agreement, defend why Carol’s request should be granted.Arbitrator’s Perspective30Present the issues that the arbitrator has to analyze in making a decision on the grievance.Total70You have thoroughly presented both sides of the argument and have shown the arbitrator’s rationale in the decision to sustain or deny the grievance.
HRM 330 week 7
Course Project: Beginning or End of Unions?
Submit your project to the Dropbox located on the silver tab at the top of this page. For instructions on how to use the Dropbox, read these .next.ecollege.com/default/launch.ed?ssoType=DVUHubSSO2&node=184″>step-by-step instructions or watch this Tutorial.next.ecollege.com/default/launch.ed?ssoType=DVUHubSSO2&node=232″>Dropbox Tutorial.
See the Syllabus section “Due Dates for Assignments & Exams” for due date information.
.equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/HRM330_CH_Course_Project.html#1″>Objectives| .equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/HRM330_CH_Course_Project.html#2″>Course Project Paper Topics| .equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/HRM330_CH_Course_Project.html#3″>Guidelines| .equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/HRM330_CH_Course_Project.html#4″>Milestones| .equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/HRM330_CH_Course_Project.html#5″>Grading Rubrics| .equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/HRM330_CH_Course_Project.html#6″>Best Practices
Objectives
.equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/HRM330_CH_Course_Project.html#top”>Back to Top
The purpose of this project is to apply your critical-thinking skills to address the following concepts in a comprehensive paper. Do not simply respond to these items but provide a fully reviewed paper about the future of unions.
The objective of this paper is to share your professional understanding related to labor relations and unions based on theory. Include the theories from the discussions, your readings, and the TCOs reviewed throughout the course in this paper.
See the Course Project Paper Tour below for more information and tips for writing the paper.
Course Project Paper Tour .equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/Transcripts–HRM330_CH_Course_Project_trans.html”>Transcript
Course Project Paper Topics
.equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/HRM330_CH_Course_Project.html#top”>Back to Top
These are the topics you have to choose from to write the course paper.
· In today’s economic climate, with more and more organizations continuing to shed jobs, can unions survive?
· Consider a specific union, such as the United Auto Workers, International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers, Teamsters, National Education Association, American Federation of Teachers, and so forth, and discuss their viability into the future. What does this specific union need to focus on to remain in the business world?
· What changes are needed for unions to maintain support from their membership, the community, and the employers?
· Labor unions are experiencing a decline, which includes political influence and membership. How does politics influence membership decline?
· What generational aspects (i.e., baby boomers, Generation X, Generation Y) have influenced labor unions and will continue to do so?
· What other external dynamics are impacting labor unions? For example, how does the global workforce impact union strategies? For unions, where were they, where are they, and where do they need to go to remain or regain an active and viable organization in the 21st century?
· For unions, where were they, where are they, and where do they need to go to remain or regain an active and viable organization in the 21st century?
· What is the future of public sector employees and their union membership? A number of states have focused on reducing benefits and union rights. Is this the future and will this focus spread to other organizations outside of the public sector that have unions?
· What types of bargaining strategies need to be put into place for unions to be able to survive inside organizations?
Guidelines
.equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/HRM330_CH_Course_Project.html#top”>Back to Top
· Write an 8- to 10-page paper (excluding title and reference pages) that identifies the challenges that unions face in the 21st century.
· Include all aspects of the assignment criteria outlined.
· Use a 12-point Times Roman or Arial font, double-space it, and have 1 in. margins as a standard format.
· Do not include extra lines between paragraphs and so forth.
· You should use theory throughout your paper, which covers the aspects of the TCOs reviewed in the previous weeks.
· You should use a minimum of six scholarly resources.
· DeVry University policies are in effect, including the plagiarism policy: cite in text when quoting (copying information word for word) or using words and thoughts that are not your own.
· Submit assignments in Word documents only to the Dropbox by the due date.
· Graphs and tables are not needed and should not be used in this paper.
· Grammar, punctuation, spelling, and so forth will all be taken into consideration when awarding points.
· Proofread your papers before submitting; spell check is not foolproof.
· This paper is worth 250 points and will be graded on the quality of the research topic, quality of paper information, and use of citations, grammar, and sentence structure.
· Papers are due in Week 7 of this course.
Milestones
.equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/HRM330_CH_Course_Project.html#top”>Back to Top
The Final Paper is due in Week 7.
Submit your project to the Dropbox located on the silver tab at the top of this page. For instructions on how to use the Dropbox, read these .next.ecollege.com/default/launch.ed?ssoType=DVUHubSSO2&node=184″>step-by-step instructions or watch this Tutorial.next.ecollege.com/default/launch.ed?ssoType=DVUHubSSO2&node=232″>Dropbox Tutorial.
See the Syllabus section “Due Dates for Assignments & Exams” for due date information.
Grading Rubrics
.equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/HRM330_CH_Course_Project.html#top”>Back to Top
Assignment Title: Course Project
Category
Points
%
Description
Documentation and Formatting
25
10
The paper should follow instructions as outlined under the guidelines.
Organization and Cohesiveness
50
20
The paper should have topical flow with like subjects in each paragraph. Paragraphs should flow and link from one topic to the next. Instructor feedback from throughout the session should be integrated. Paragraph transitions should be present and logical. Page count should follow guidelines.
Editing
25
10
Sentences should be complete, clear, and concise. Sentence transitions should be present and maintain the flow of thought. Rules of grammar and punctuation should be followed. Spelling should be correct. Sentence structure should be clean and clear. The writing style should follow appropriate undergraduate-level writing.
Content
150
60
The paper content should be thorough, yet concise. Information included should be relevant to the topic and provide depth and clarity of theories, as well as theory application. All key elements of the assignment should be covered in a substantive way. Concepts should be reviewed clearly, supported by specific details (examples or analysis), and organized logically. The paper should link theory to relevant examples of current concepts and industry practice. There should be correct use of vocabulary and theory.
Total
250
100
A quality paper will meet or exceed all of the above requirements.
Best Practices
.equella.ecollege.com/file/a36ab1d6-62be-47d2-9f07-53d6e4cc6e76/1/HRM330_CH_Course_Project.html#top”>Back to Top
These are suggestions for what could be included in this section.
The following are the best practices in preparing this paper.
· Cover Page—Include who you prepared the paper for, who prepared it, and the date.
· Table of Contents—List the main ideas and section of your paper and the pages in which they are located. The illustrations should be included separately.
· Introduction—Use a header on your paper. This will indicate you are introducing your paper.
The purpose of an introduction or opening should do the following.
1. Introduce the subject and why the subject is important.
2. Preview the main ideas and the order in which they will be covered.
3. Establish a tone of the document.
Include in the introduction a reason for the audience to read the paper. Also, include an overview of what you are going to cover in your paper and the importance of the material. (This should include or introduce the questions you are asked to answer on each assignment.)
· Body of Your Report—Use a header titled with the name of your project. Example: The Development of Hotel X—A World Class Resort. Then proceed to break out the main ideas. State the main ideas, state major points in each idea, and provide evidence. Break out each main idea you will use in the body of your paper. Show some type of division, such as separate sections that are labeled, separate group of paragraphs, or headers. You would include the information you found during your research and investigation.
· Summary and Conclusion—Summarizing is similar to paraphrasing but presents the gist of the material in fewer words than the original. An effective summary identifies the main ideas and major support points from the body of your report. Minor details are left out. Summarize the benefits of the ideas and how they affect the tourism industry.
· Work Cited—Use the citation format as specified in the Syllabus.
Additional hints on preparing the best possible project are as follows.
1. Apply a three-step process of writing: Plan, write, and complete.
2. Prepare an outline of your research paper before you go forward.
3. Complete a first draft and then go back to edit, evaluate, and make any changes required.
The following are the best practices in preparing this paper.
· Create a separate title page, which includes name, paper title, and university.
· Include an introductory paragraph that identifies the paper’s content: Introduce the subject and the reason it is important, preview the main ideas and the order in which they will be covered, and establish the document’s tone.
· Include a concluding paragraph that provides a summary of the major points from the paper.
· Use a formal writing style for academic writing (sharing information and facts or theory).
· Write your paper in third person.
· Fully describe the concepts and theories. (What does the information mean?)
· Apply a three-step process of writing: Plan, write, and complete.
· When making a statement, for example, all people who break the law should improve their communication skills to stay out of jail, you must substantiate that statement. If that statement is not your own thought or a statistic, cite it. If it is your opinion, state that it is and explain the information that led to that conclusion. Provide enough information to validate and explain statements.
· Minimize copied information, which just teaches you how to copy and paste. Use critical-thinking skills to understand the material researched.
0 notes
Text
PDCA in ISO 9001: Beyond the Basics – A Practical Perspective
The PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle isn’t just a theory; it’s a strategic engine behind process maturity and continuous improvement in ISO 9001. But most organizations stop at “basic compliance” — and that’s where the real opportunity is lost. Here’s how to actually live the PDCA cycle across your organization. 🧩 1. PLAN: More Than Just Procedure Writing Common Mistake: Organizations confuse…
#Continuous improvement in ISO 9001#Implementing PDCA effectively#ISO 9001 audit preparation#ISO 9001 Continuous Improvement#ISO 9001 implementation guide#ISO 9001 quality management#PDCA cycle explained#PDCA for quality improvement#PDCA in quality management system#PDCA ISO 9001#PDCA methodology in ISO#Plan Do Check Act cycle#Practical PDCA examples#Process approach ISO 9001#Quality management best practices#Real-world PDCA application
0 notes
Text
Enhance Environmental Management with ISO 14001 Training by 4C Consulting

ISO 14001 Training is a crucial step for organizations aiming to improve their environmental management systems and ensure compliance with international standards. 4C Consulting offers comprehensive ISO 14001 Training designed to equip your team with the knowledge and skills necessary to implement and maintain effective environmental management practices. This blog will provide an understanding of ISO 14001 Training, its importance, and why you should choose 4C Consulting for this essential training.
Understanding ISO 14001 Training
Definition: ISO 14001 is an international standard that specifies requirements for an effective environmental management system (EMS). It provides a framework for organizations to protect the environment, respond to changing environmental conditions, and achieve continual improvement of their environmental performance. Objective: The primary goal of ISO 14001 Training is to educate employees on the principles and requirements of the ISO 14001 standard, ensuring they understand how to implement and manage an EMS effectively.
Importance of ISO 14001 Training
Environmental Awareness: Enhances the understanding of environmental impacts and the importance of sustainability within the organization. Regulatory Compliance: Helps ensure compliance with environmental laws and regulations, reducing the risk of legal issues. Risk Management: Identifies and mitigates environmental risks associated with organizational activities. Operational Efficiency: Improves processes to reduce waste and resource consumption, leading to cost savings. Reputation and Credibility: Demonstrates a commitment to environmental responsibility, enhancing the organization’s reputation among customers and stakeholders.
Training
Understanding ISO 14001: Environmental Management Principles: Learn the core principles of environmental management, including pollution prevention, legal compliance, and continual improvement. Structure of ISO 14001: Familiarize yourself with the structure and requirements of the ISO 14001 standard, which follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) model. Importance of ISO 14001 Training: Employee Engagement: Engages employees in environmental management practices, fostering a culture of sustainability. Legal Compliance: Ensures that the organization meets all relevant environmental regulations, avoiding fines and penalties. Risk Reduction: Reduces environmental risks and potential liabilities through proactive management. Resource Efficiency: Promotes efficient use of resources, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Market Advantage: Enhances the organization’s competitive edge by demonstrating a commitment to environmental stewardship. ISO 14001 Training Process: Introduction to ISO 14001: Overview of the ISO 14001 standard, its history, and its importance. Key Requirements: Detailed explanation of the key requirements of ISO 14001, including context of the organization, leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and improvement. Implementation Strategies: Practical guidance on how to implement an effective EMS in line with ISO 14001 requirements. Documentation and Records: Importance of maintaining accurate documentation and records for the EMS. Internal Audits: Training on how to conduct internal audits to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement. Continual Improvement: Emphasis on the importance of continual improvement in environmental performance.
Why Choose 4C Consulting?
4C Consulting offers tailored ISO 14001 Training programs that cater to the unique needs of your organization. Our expert trainers provide practical insights and hands-on guidance, ensuring your team gains a thorough understanding of the ISO 14001 standard and its application. With a focus on real-world implementation and continuous improvement, 4C Consulting helps you build a robust environmental management system that drives sustainability and compliance. Choose 4C Consulting for a comprehensive, impactful training experience that empowers your organization to achieve its environmental goals. Contact us now.
0 notes
Text
Enhance Environmental Management with ISO 14001 Training by 4C Consulting

ISO 14001 Training is a crucial step for organizations aiming to improve their environmental management systems and ensure compliance with international standards. 4C Consulting offers comprehensive ISO 14001 Training designed to equip your team with the knowledge and skills necessary to implement and maintain effective environmental management practices. This blog will provide an understanding of ISO 14001 Training, its importance, and why you should choose 4C Consulting for this essential training.
Understanding ISO 14001 Training
Definition: ISO 14001 is an international standard that specifies requirements for an effective environmental management system (EMS). It provides a framework for organizations to protect the environment, respond to changing environmental conditions, and achieve continual improvement of their environmental performance.
Objective: The primary goal of ISO 14001 Training is to educate employees on the principles and requirements of the ISO 14001 standard, ensuring they understand how to implement and manage an EMS effectively.
Importance of ISO 14001 Training
Environmental Awareness: Enhances the understanding of environmental impacts and the importance of sustainability within the organization.
Regulatory Compliance: Helps ensure compliance with environmental laws and regulations, reducing the risk of legal issues.
Risk Management: Identifies and mitigates environmental risks associated with organizational activities.
Operational Efficiency: Improves processes to reduce waste and resource consumption, leading to cost savings.
Reputation and Credibility: Demonstrates a commitment to environmental responsibility, enhancing the organization’s reputation among customers and stakeholders.
Training
Understanding ISO 14001:
Environmental Management Principles: Learn the core principles of environmental management, including pollution prevention, legal compliance, and continual improvement.
Structure of ISO 14001: Familiarize yourself with the structure and requirements of the ISO 14001 standard, which follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) model.
Importance of ISO 14001 Training:
Employee Engagement: Engages employees in environmental management practices, fostering a culture of sustainability.
Legal Compliance: Ensures that the organization meets all relevant environmental regulations, avoiding fines and penalties.
Risk Reduction: Reduces environmental risks and potential liabilities through proactive management.
Resource Efficiency: Promotes efficient use of resources, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Market Advantage: Enhances the organization’s competitive edge by demonstrating a commitment to environmental stewardship.
ISO 14001 Training Process:
Introduction to ISO 14001: Overview of the ISO 14001 standard, its history, and its importance.
Key Requirements: Detailed explanation of the key requirements of ISO 14001, including context of the organization, leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and improvement.
Implementation Strategies: Practical guidance on how to implement an effective EMS in line with ISO 14001 requirements.
Documentation and Records: Importance of maintaining accurate documentation and records for the EMS.
Internal Audits: Training on how to conduct internal audits to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Continual Improvement: Emphasis on the importance of continual improvement in environmental performance.
Why Choose 4C Consulting?
4C Consulting offers tailored ISO 14001 Training programs that cater to the unique needs of your organization. Our expert trainers provide practical insights and hands-on guidance, ensuring your team gains a thorough understanding of the ISO 14001 standard and its application. With a focus on real-world implementation and continuous improvement, 4C Consulting helps you build a robust environmental management system that drives sustainability and compliance. Choose 4C Consulting for a comprehensive, impactful training experience that empowers your organization to achieve its environmental goals. Contact us now.
0 notes
Text
Enhance Environmental Management with ISO 14001 Training by 4C Consulting

ISO 14001 Training is a crucial step for organizations aiming to improve their environmental management systems and ensure compliance with international standards. 4C Consulting offers comprehensive ISO 14001 Training designed to equip your team with the knowledge and skills necessary to implement and maintain effective environmental management practices. This blog will provide an understanding of ISO 14001 Training, its importance, and why you should choose 4C Consulting for this essential training.
Understanding ISO 14001 Training
Definition: ISO 14001 is an international standard that specifies requirements for an effective environmental management system (EMS). It provides a framework for organizations to protect the environment, respond to changing environmental conditions, and achieve continual improvement of their environmental performance.
Objective: The primary goal of ISO 14001 Training is to educate employees on the principles and requirements of the ISO 14001 standard, ensuring they understand how to implement and manage an EMS effectively.
Importance of ISO 14001 Training
Environmental Awareness: Enhances the understanding of environmental impacts and the importance of sustainability within the organization.
Regulatory Compliance: Helps ensure compliance with environmental laws and regulations, reducing the risk of legal issues.
Risk Management: Identifies and mitigates environmental risks associated with organizational activities.
Operational Efficiency: Improves processes to reduce waste and resource consumption, leading to cost savings.
Reputation and Credibility: Demonstrates a commitment to environmental responsibility, enhancing the organization’s reputation among customers and stakeholders.
Training
Understanding ISO 14001:
Environmental Management Principles: Learn the core principles of environmental management, including pollution prevention, legal compliance, and continual improvement.
Structure of ISO 14001: Familiarize yourself with the structure and requirements of the ISO 14001 standard, which follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) model.
Importance of ISO 14001 Training:
Employee Engagement: Engages employees in environmental management practices, fostering a culture of sustainability.
Legal Compliance: Ensures that the organization meets all relevant environmental regulations, avoiding fines and penalties.
Risk Reduction: Reduces environmental risks and potential liabilities through proactive management.
Resource Efficiency: Promotes efficient use of resources, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Market Advantage: Enhances the organization’s competitive edge by demonstrating a commitment to environmental stewardship.
ISO 14001 Training Process:
Introduction to ISO 14001: Overview of the ISO 14001 standard, its history, and its importance.
Key Requirements: Detailed explanation of the key requirements of ISO 14001, including context of the organization, leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and improvement.
Implementation Strategies: Practical guidance on how to implement an effective EMS in line with ISO 14001 requirements.
Documentation and Records: Importance of maintaining accurate documentation and records for the EMS.
Internal Audits: Training on how to conduct internal audits to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Continual Improvement: Emphasis on the importance of continual improvement in environmental performance.
Why Choose 4C Consulting?
4C Consulting offers tailored ISO 14001 Training programs that cater to the unique needs of your organization. Our expert trainers provide practical insights and hands-on guidance, ensuring your team gains a thorough understanding of the ISO 14001 standard and its application. With a focus on real-world implementation and continuous improvement, 4C Consulting helps you build a robust environmental management system that drives sustainability and compliance. Choose 4C Consulting for a comprehensive, impactful training experience that empowers your organization to achieve its environmental goals. Contact us now.
0 notes
Text
Enhance Environmental Management with ISO 14001 Training by 4C Consulting

ISO 14001 Training is a crucial step for organizations aiming to improve their environmental management systems and ensure compliance with international standards. 4C Consulting offers comprehensive ISO 14001 Training designed to equip your team with the knowledge and skills necessary to implement and maintain effective environmental management practices. This blog will provide an understanding of ISO 14001 Training, its importance, and why you should choose 4C Consulting for this essential training.
Understanding ISO 14001 Training
Definition: ISO 14001 is an international standard that specifies requirements for an effective environmental management system (EMS). It provides a framework for organizations to protect the environment, respond to changing environmental conditions, and achieve continual improvement of their environmental performance.
Objective: The primary goal of ISO 14001 Training is to educate employees on the principles and requirements of the ISO 14001 standard, ensuring they understand how to implement and manage an EMS effectively.
Importance of ISO 14001 Training
Environmental Awareness: Enhances the understanding of environmental impacts and the importance of sustainability within the organization.
Regulatory Compliance: Helps ensure compliance with environmental laws and regulations, reducing the risk of legal issues.
Risk Management: Identifies and mitigates environmental risks associated with organizational activities.
Operational Efficiency: Improves processes to reduce waste and resource consumption, leading to cost savings.
Reputation and Credibility: Demonstrates a commitment to environmental responsibility, enhancing the organization’s reputation among customers and stakeholders.
Training
Understanding ISO 14001:
Environmental Management Principles: Learn the core principles of environmental management, including pollution prevention, legal compliance, and continual improvement.
Structure of ISO 14001: Familiarize yourself with the structure and requirements of the ISO 14001 standard, which follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) model.
Importance of ISO 14001 Training:
Employee Engagement: Engages employees in environmental management practices, fostering a culture of sustainability.
Legal Compliance: Ensures that the organization meets all relevant environmental regulations, avoiding fines and penalties.
Risk Reduction: Reduces environmental risks and potential liabilities through proactive management.
Resource Efficiency: Promotes efficient use of resources, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Market Advantage: Enhances the organization’s competitive edge by demonstrating a commitment to environmental stewardship.
ISO 14001 Training Process:
Introduction to ISO 14001: Overview of the ISO 14001 standard, its history, and its importance.
Key Requirements: Detailed explanation of the key requirements of ISO 14001, including context of the organization, leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and improvement.
Implementation Strategies: Practical guidance on how to implement an effective EMS in line with ISO 14001 requirements.
Documentation and Records: Importance of maintaining accurate documentation and records for the EMS.
Internal Audits: Training on how to conduct internal audits to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Continual Improvement: Emphasis on the importance of continual improvement in environmental performance.
Why Choose 4C Consulting?
4C Consulting offers tailored ISO 14001 Training programs that cater to the unique needs of your organization. Our expert trainers provide practical insights and hands-on guidance, ensuring your team gains a thorough understanding of the ISO 14001 standard and its application. With a focus on real-world implementation and continuous improvement, 4C Consulting helps you build a robust environmental management system that drives sustainability and compliance. Choose 4C Consulting for a comprehensive, impactful training experience that empowers your organization to achieve its environmental goals. Contact us now.
0 notes