#SortedSet interface
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
SortedSet Interface in Java With Program Example
SortedSet is a child interface of Set Interface. It exhibits similar behaviour to its parent interface like not allowing duplicates and preserving insertion order. As its name suggests, the elements present in sortedSet, are always stored in sorting order. By default, it applies natural sorting to arrange the elements in a specific order. For example, in the case of numbers, the elements are…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Java Collection
Java libraries are indispensable tools that streamline development by providing pre-written code for common tasks. "The Ultimate Guide to Java Libraries" explores a myriad of libraries that enhance Java programming, from handling data structures to implementing complex algorithms.
A key feature covered is collections in Java, which offer efficient ways to manage groups of objects, improving code efficiency and readability.
TpointTech is a valuable resource for developers seeking in-depth tutorials and examples on using these libraries effectively. Leveraging these libraries can significantly reduce development time and improve application performance.
Overview of Java Collections
The Java Collections Framework includes interfaces, implementations, and algorithms. The core interfaces include Collection, List, Set, Queue, and Map, each serving different purposes.
Collection Interface:
The root interface of the framework, representing a group of objects known as elements. It is extended by List, Set, and Queue interfaces.
List Interface:
An ordered collection that allows duplicate elements. Common implementations are ArrayList, LinkedList, and Vector. Lists are ideal when you need to access elements by their index.
ArrayList: Resizable array implementation, offering constant-time positional access but slower for insertion and deletion.
LinkedList: Doubly-linked list implementation, providing efficient insertion and deletion but slower access time.
Vector: Synchronized version of ArrayList, rarely used due to performance overhead.
Set Interface:
A collection that does not allow duplicate elements. It models mathematical sets and provides implementations like HashSet, LinkedHashSet, and TreeSet.
HashSet: Uses a hash table for storage, offering constant-time performance for basic operations.
LinkedHashSet: Maintains insertion order, slightly slower than HashSet.
TreeSet: Implements the SortedSet interface, ensuring elements are in ascending order, based on their natural ordering or a specified comparator.
Queue Interface:
Designed for holding elements prior to processing, typically ordered in a FIFO (first-in-first-out) manner. Common implementations include LinkedList, PriorityQueue, and ArrayDeque.
PriorityQueue: Elements are ordered according to their natural ordering or a provided comparator, useful for creating priority-based tasks.
ArrayDeque: Resizable-array implementation of the Deque interface, providing efficient insertion and deletion from both ends.
Map Interface:
Represents a collection of key-value pairs, where each key maps to one value. Popular implementations are HashMap, LinkedHashMap, and TreeMap.
HashMap: Provides constant-time performance for basic operations, assuming a good hash function.
LinkedHashMap: Maintains a doubly-linked list of its entries, preserving the order of insertion.
TreeMap: Implements the SortedMap interface, ensuring keys are in ascending order.
Advantages of Java Collections Framework
Reduces Programming Effort: With a set of ready-made data structures and algorithms, JCF eliminates the need for developers to implement complex data structures from scratch.
Increases Program Speed and Quality: Standardized interfaces and optimized implementations ensure high performance and reliability.
Interoperability: Collections can be easily passed across APIs, reducing the complexity of integration.
Ease of Maintenance: Well-documented and widely-used classes make it easier for developers to maintain and enhance code.
Common Algorithms in JCF
Java Collections Framework includes various algorithms to perform routine tasks, such as sorting, searching, and shuffling. These algorithms are static methods in the Collections utility class.
Sorting: Collections.sort(List list), sorts the specified list into ascending order.
Shuffling: Collections.shuffle(List list), randomly permutes the elements in the list.
Searching: Collections.binarySearch(List> list, T key), performs binary search on a sorted list.
Conclusion
The Java Collections Framework is indispensable for any Java developer. It offers a standardized and efficient way to manage groups of objects, making code more robust and maintainable.
By leveraging the various interfaces and implementations, such as lists, sets, queues, and maps, developers can handle data structures effectively.
Understanding collections in Java, as detailed on resources like TpointTech, is crucial for building high-performance applications. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, mastering Java collections will significantly enhance your programming capabilities.
0 notes
Text
CS314 Programming Assignment 8: Solved
CS314 Programming Assignment 8: Solved
The purposes of this assignment are: to practice implementing data structures to use ArrayLists and Iterators to implement sorting and searching algorithms by modifying pre-existing algorithms. To develop code that makes use of encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, interfaces, and abstract classes. Summary: Implement three classes: AbstractSet, UnsortedSet, and SortedSet. Recall that the…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Java Collections Interview Questions and Answers
Here are some Java Collections Interview Questions and Answers to prepare your interview.
Java Collections Framework is the fundamental aspect of java programming language. It’s one of the important topic for java interview questions. Here I am listing some important java collections interview questions and answers for helping you in interview.
Here is the list of mostly asked java collections interview questions with answers.
1. What is difference between ArrayList and vector?
1) Synchronization – ArrayList is not thread-safe whereas Vector is thread-safe. In Vector class each method like add(), get(int i) is surrounded with a synchronized block and thus making Vector class thread-safe.
2) Data growth – Internally, both the ArrayList and Vector hold onto their contents using an Array. When an element is inserted into an ArrayList or a Vector, the object will need to expand its internal array if it runs out of room. A Vector defaults to doubling the size of its array, while the ArrayList increases its array size by 50 percent.
2. How can Arraylist be synchronized without using Vector?
Ans) Arraylist can be synchronized using:
Collection.synchronizedList(List list)
Other collections can be synchronized:
Collection.synchronizedMap(Map map) and Collection.synchronizedCollection(Collection c)
3. If an Employee class is present and its objects are added in an arrayList. Now I want the list to be sorted on the basis of the employeeID of Employee class. What are the steps?
Ans) 1) Implement Comparable interface for the Employee class and override the compareTo(Object obj) method in which compare the employeeID
2) Now call Collections.sort() method and pass list as an argument.
Now consider that Employee class is a jar file.
1) Since Comparable interface cannot be implemented, create Comparator and override the compare(Object obj, Object obj1) method .
2) Call Collections.sort() on the list and pass comparator as an argument.
4. What is difference between HashMap and HashTable?
Both collections implements Map. Both collections store value as key-value pairs. The key differences between the two are
Hashmap is not synchronized in nature but hshtable is.
Another difference is that iterator in the HashMap is fail-safe while the enumerator for the Hashtable isn’t. Fail-safe– “if the Hashtable is structurally modified at any time after the iterator is created, in any way except through the iterator’s own remove method, the iterator will throw a ConcurrentModificationExceptionâ€?
3. HashMap permits null values and only 1 null key, while Hashtable doesn’t allow key or value as null.
5. What are the classes implementing List interface?
There are three classes that implement List interface: 1) ArrayList : It is a resizable array implementation. The size of the ArrayList can be increased dynamically also operations like add,remove and get can be formed once the object is created. It also ensures that the data is retrieved in the manner it was stored. The ArrayList is not thread-safe.
2) Vector: It is thread-safe implementation of ArrayList. The methods are wrapped around a synchronized block.
3) LinkedList: the LinkedList also implements Queue interface and provide FIFO(First In First Out) operation for add operation. It is faster if than ArrayList if it performs insertion and deletion of elements from the middle of a list.
6. Which all classes implement Set interface?
Ans) A Set is a collection that contains no duplicate elements. More formally, sets contain no pair of elements e1 and e2 such that e1.equals(e2), and at most one null element. HashSet,SortedSet and TreeSet are the commnly used class which implements Set interface.
SortedSet – It is an interface which extends Set. A the name suggest , the interface allows the data to be iterated in the ascending order or sorted on the basis of Comparator or Comparable interface. All elements inserted into the interface must implement Comparable or Comparator interface.
TreeSet – It is the implementation of SortedSet interface.This implementation provides guaranteed log(n) time cost for the basic operations (add, remove and contains). The class is not synchronized.
HashSet: This class implements the Set interface, backed by a hash table (actually a HashMap instance). It makes no guarantees as to the iteration order of the set; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order will remain constant over time. This class permits the null element. This class offers constant time performance for the basic operations (add, remove, contains and size), assuming the hash function disperses the elements properly among the buckets
7. What is difference between List and a Set?
1) List can contain duplicate values but Set doesnt allow. Set allows only to unique elements. 2) List allows retrieval of data to be in same order in the way it is inserted but Set doesnt ensures the sequence in which data can be retrieved.(Except HashSet)
8. What is difference between Arrays and ArrayList ?
Ans) Arrays are created of fix size whereas ArrayList is of not fix size. It means that once array is declared as :
int [] intArray= new int[6];
intArray[7] // will give ArraysOutOfBoundException.
Also the size of array cannot be incremented or decremented. But with arrayList the size is variable.
Once the array is created elements cannot be added or deleted from it. But with ArrayList the elements can be added and deleted at runtime.
List list = new ArrayList(); list.add(1); list.add(3); list.remove(0) // will remove the element from the 1st location.
ArrayList is one dimensional but array can be multidimensional.
int[][][] intArray= new int[3][2][1]; // 3 dimensional array
To create an array the size should be known or initalized to some value. If not initialized carefully there could me memory wastage. But arrayList is all about dynamic creation and there is no wastage of memory.
9. When to use ArrayList or LinkedList ?
Ans) Adding new elements is pretty fast for either type of list. For the ArrayList, doing random lookup using “get” is fast, but for LinkedList, it’s slow. It’s slow because there’s no efficient way to index into the middle of a linked list. When removing elements, using ArrayList is slow. This is because all remaining elements in the underlying array of Object instances must be shifted down for each remove operation. But here LinkedList is fast, because deletion can be done simply by changing a couple of links. So an ArrayList works best for cases where you’re doing random access on the list, and a LinkedList works better if you’re doing a lot of editing in the middle of the list.
10. Consider a scenario. If an ArrayList has to be iterate to read data only, what are the possible ways and which is the fastest?
Ans) It can be done in two ways, using for loop or using iterator of ArrayList. The first option is faster than using iterator. Because value stored in arraylist is indexed access. So while accessing the value is accessed directly as per the index.
11. Now another question with respect to above question is if accessing through iterator is slow then why do we need it and when to use it.
Ans) For loop does not allow the updation in the array(add or remove operation) inside the loop whereas Iterator does. Also Iterator can be used where there is no clue what type of collections will be used because all collections have iterator.
12. Which design pattern Iterator follows?
Ans) It follows Iterator design pattern. Iterator Pattern is a type of behavioral pattern. The Iterator pattern is one, which allows you to navigate through a collection of data using a common interface without knowing about the underlying implementation. Iterator should be implemented as an interface. This allows the user to implement it anyway its easier for him/her to return data. The benefits of Iterator are about their strength to provide a common interface for iterating through collections without bothering about underlying implementation.
Example of Iteration design pattern – Enumeration The class java.util.Enumeration is an example of the Iterator pattern. It represents and abstract means of iterating over a collection of elements in some sequential order without the client having to know the representation of the collection being iterated over. It can be used to provide a uniform interface for traversing collections of all kinds.
13. Is it better to have a HashMap with large number of records or n number of small hashMaps?
Ans) It depends on the different scenario one is working on: 1) If the objects in the hashMap are same then there is no point in having different hashmap as the traverse time in a hashmap is invariant to the size of the Map. 2) If the objects are of different type like one of Person class , other of Animal class etc then also one can have single hashmap but different hashmap would score over it as it would have better readability.
14. Why is it preferred to declare: List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); instead of ArrayList<String> = new ArrayList<String>();
Ans) It is preferred because:
If later on code needs to be changed from ArrayList to Vector then only at the declaration place we can do that.
The most important one – If a function is declared such that it takes list. E.g void showDetails(List list); When the parameter is declared as List to the function it can be called by passing any subclass of List like ArrayList,Vector,LinkedList making the function more flexible
15. What is difference between iterator access and index access?
Ans) Index based access allow access of the element directly on the basis of index. The cursor of the datastructure can directly goto the ‘n’ location and get the element. It doesnot traverse through n-1 elements.
In Iterator based access, the cursor has to traverse through each element to get the desired element.So to reach the ‘n’th element it need to traverse through n-1 elements.
Insertion,updation or deletion will be faster for iterator based access if the operations are performed on elements present in between the datastructure.
Insertion,updation or deletion will be faster for index based access if the operations are performed on elements present at last of the datastructure.
Traversal or search in index based datastructure is faster. ArrayList is index access and LinkedList is iterator access.
16. How to sort list in reverse order?
Ans) To sort the elements of the List in the reverse natural order of the strings, get a reverse Comparator from the Collections class with reverseOrder(). Then, pass the reverse Comparator to the sort() method.
List list = new ArrayList(); Comparator comp = Collections.reverseOrder(); Collections.sort(list, comp)
17. Can a null element added to a Treeset or HashSet?
Ans) A null element can be added only if the set contains one element because when a second element is added then as per set defination a check is made to check duplicate value and comparison with null element will throw NullPointerException. HashSet is based on hashMap and can contain null element.
18. How to sort list of strings ,case insensitive?
Ans) using Collections.sort(list, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
19. How to make a List (ArrayList,Vector,LinkedList) read only?
Ans) A list implemenation can be made read only using Collections.unmodifiableList(list). This method returns a new list. If a user tries to perform add operation on the new list; UnSupportedOperationException is thrown.
20. What is ConcurrentHashMap?
Ans) A concurrentHashMap is thread-safe implementation of Map interface. In this class put and remove method are synchronized but not get method. This class is different from Hashtable in terms of locking; it means that hashtable use object level lock but this class uses bucket level lock thus having better performance.
21. Which is faster to iterate LinkedHashSet or LinkedList?
Ans) LinkedList.
22. Which data structure HashSet implements?
Ans) HashSet implements hashmap internally to store the data. The data passed to hashset is stored as key in hashmap with null as value.
23. Arrange in the order of speed – HashMap,HashTable, Collections.synchronizedMap, concurrentHashmap ?
Ans) HashMap is fastest, ConcurrentHashMap,Collections.synchronizedMap,HashTable.
24. What is identityHashMap?
Ans) The IdentityHashMap uses == for equality checking instead of equals(). This can be used for both performance reasons, if you know that two different elements will never be equals and for preventing spoofing, where an object tries to imitate another.
25. What is WeakHashMap?
Ans) A hashtable-based Map implementation with weak keys. An entry in a WeakHashMap will automatically be removed when its key is no longer in ordinary use. More precisely, the presence of a mapping for a given key will not prevent the key from being discarded by the garbage collector, that is, made finalizable, finalized, and then reclaimed. When a key has been discarded its entry is effectively removed from the map, so this class behaves somewhat differently than other Map implementations.
#Java Collections Interview Questions and Answers#Java Collections Interview Questions#java interview questions#Java tutorials#india
0 notes
Text
http://www.sudotutorials.com
Check http://www.sudotutorials.com/ for all java tutorials
http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/contents.html : Table of Contents http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-hello-world.html : Write a Java Program http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-operator.html : Learn Java Operators http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-literals.html : Java Literals http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-datatypes.html : Java Data Types http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-class-object.html : Create Class and Object in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-constructor.html : Java Constructor http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-control-statement.html : Java Control Statement http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-access-control.html : Access Control in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-inheritance.html : Java Inheritance Example http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-method-overloading.html : Java Method Overloading Example http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-method-overriding.html : Java Method Overriding Example http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-package.html : Java Package Example http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-interface.html : Java Interface Example http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-abstract-class.html : Java Abstract Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-composition.html : Java Composition Example http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-exception-handling.html : Exception Handling in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-custom-exception.html : Create Custom Exception Class in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-chained-exception.html : Chained Exception in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-static-method.html : Static Method in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/basics/java-final-keyword.html : Use of final Keyword in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/contents.html : Table of Contents http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-collection-interface.html : Java Collection Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-set-interface.html : Java Set Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-hashset-class.html : Java HashSet Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-treeset-class.html : Java TreeSet Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-linkedhashset-class.html : Java LinkedHashSet Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-navigableset-interface.html : Java NavigableSet Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-sortedset-interface.html : Java SortedSet Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-queue-interface.html : Java Queue Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-deque-interface.html : Java Deque Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-list-interface.html : Java List Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-arraylist-class.html : Java ArrayList Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-linkedlist-class.html : Java LinkedList Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-hashmap-class.html : Java HashMap Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/how-hashmap-works-internally-in-java.html : How HashMap Works Internally in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-linkedlist-vs-arraylist.html : Java LinkedList vs ArrayList Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/java-comparable-interface.html : Java Comparable Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/use-comparator-for-custom-sorting.html : Use Comparator For Custom Sorting http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/collections/comparator-vs-comparable-in-java.html : Difference Between Comparator and Comparable Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/contents.html : Table of Contents http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/what-is-stream-in-java.html : What is Stream in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/byte-stream-in-java.html : Java Byte Stream Classes http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-inputstream-class.html : Java InputStream Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-outputstream-class.html : Java OutputStream Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-fileinputstream-class.html : Java FileInputStream Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-fileoutputstream-class.html : Java FileOutputStream Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-bytearrayinputstream-class.html : Java ByteArrayInputStream Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/character-stream-in-java.html : Java Character Stream Classes http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-reader-class.html : Java Reader Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-writer-class.html : Java Writer Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-filereader-class.html : Java FileReader Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/java-file-handling/java-filewriter-class.html : Java FileWriter Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/contents.html : Table of Contents http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/create-thread-in-java.html : Create Thread in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/create-multiple-thread-in-java.html : Create Multiple Thread in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-thread-lifecycle.html : Java Thread Lifecycle http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/thread-priority-in-java.html : Thread Priority in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/what-is-daemon-thread-in-java.html : Daemon Thread in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/synchronization-in-java.html : Thread Synchronization in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/difference-between-synchronized-block-and-method-in-Java.html : Difference Between Synchronized Block and Method in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-thread-interthread-communication.html : Java Interthread Communiction http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-thread-join-isalive-method.html : Java Thread join(), isAlive() Method http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-use-of-volitile-variable-in-thread.html : Use of Volatile Variable in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/object-level-locking-vs-class-level-locking-in-java.html : Object Level Locking and Class Level Locking in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/difference-between-wait-sleep-yield-in-java.html : Difference Between wait(), sleep() and yield() in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/how-to-create-a-immutable-class-in-java.html : How to Create Immutable Class in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-concurrent-api.html : Java Concurrent API http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-semaphore.html : Semaphore in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-countdownlatch.html : Java CountdownLatch Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-cyclicbarrier.html : Java CyclicBarrier Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-thread-exchanger.html : Java Exchanger in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-phaser.html : The Java Phaser Class http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-executor-interface.html : Java Executor Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-concurrent-collection.html : Java Concurrent Collection http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-blocking-queue.html : Java BlockingQueue Interface http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-concurrent-map.html : Java Concurrent Map http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-concurrentnavigablemap.html : Java ConcurrentNavigableMap Concurrent Collection http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-fork-join-framework.html : Java Fork/Join Framework http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-locks.html : The Lock object in Java http://sudotutorials.com/tutorials/java/multithreading-in-java/java-atomicinteger.html : Java AtomicInteger Class
0 notes
Text
TreeSet Class in Java With Program Example
TreeSet is an implementation class of NavigableSet interface which is a child interface of SortedSet. It is a class in the collection framework that stores and manipulates elements in some sorting order. It represents self-balancing binary tree as its underlying data structure which makes it a good choice for search and retrieving operations. Syntax: Set<T> set = new TreeSet<T>(); It stores…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
NavigableSet Interface in Java With Program Example
NavigableSet is a child interface of SortedSet that provides navigation methods to navigate through a set. It showcases the same behaviour as SortedSet with some additional navigable attributes & behaviour. It provides several methods that are only applicable to the implementation classes of NavigrableSet interface such as lower(), floor(), and ceiling methods to get elements less than or equal,…
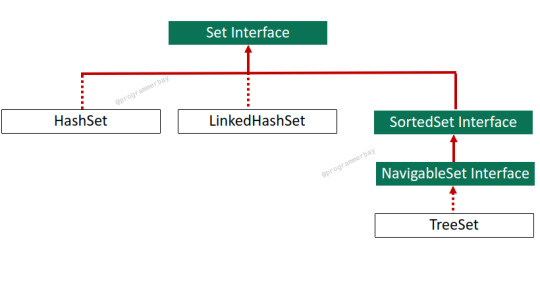
View On WordPress
0 notes