#TactileSensors
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

𝗗𝗜𝗗 𝗬𝗢𝗨 𝗞𝗡𝗢𝗪? 𝗠𝗮𝗹𝗮𝘆𝘀𝗶𝗮 𝗧𝗮𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗹𝗲 𝗦𝗲𝗻𝘀𝗼𝗿𝘀 𝗠𝗮𝗿𝗸𝗲𝘁 is quietly shaping the future of robotics, prosthetics, and smart devices — and investors are taking notice! 𝗗𝗼𝘄𝗻𝗹𝗼𝗮𝗱 𝗙𝗥𝗘𝗘 𝗦𝗮𝗺𝗽𝗹𝗲
𝗪𝗵𝗮𝘁’𝘀 𝗗𝗿𝗶𝘃𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗦𝘂𝗿𝗴𝗲? 1. Rising demand for precision robotics in manufacturing 2. Increasing adoption of AI-integrated healthcare devices 3. Growing investments in automotive automation and smart touch tech
𝗠𝗮𝗿𝗸𝗲𝘁 𝗜𝗻𝘀𝗶𝗴𝗵𝘁 : The Malaysia Tactile Sensors Market is projected to witness impressive growth in the coming years, driven by technological innovation, smart city development, and a push for Industry 4.0 adoption.
𝗞𝗲𝘆 𝗣𝗹𝗮𝘆𝗲𝗿𝘀 : Tekscan Inc., ForceN, Contactile, Sensobright, X-Sensors, Barrett Technology and others.
𝗢𝗽𝗽𝗼𝗿𝘁𝘂𝗻𝗶𝘁𝘆 𝗔𝗹𝗲𝗿𝘁: As industries shift towards automation and intelligent systems, tactile sensor technology is at the forefront of innovation. From detecting subtle pressure changes to enabling human-like touch in robots — this market holds the key to the next wave of smart solutions.
𝗔𝗰𝗰𝗲𝘀𝘀 𝗙𝘂𝗹𝗹 𝗥𝗲𝗽𝗼𝗿𝘁
𝗔𝗿𝗲 𝘆𝗼𝘂 𝗿𝗲𝗮𝗱𝘆 𝘁𝗼 𝗶𝗻𝘃𝗲𝘀𝘁 𝘄𝗵𝗲𝗿𝗲 𝘁𝗲𝗰𝗵 𝗺𝗲𝗲𝘁𝘀 𝘁𝗼𝘂𝗰𝗵? The time is now to explore opportunities in Malaysia’s emerging tactile tech landscape!
#TactileSensors#MalaysiaTech#InvestorAlert#SmartTechnology#Robotics#Innovation#Industry40#FutureOfTouch#SensorTechnology
0 notes
Text
#industrialautomation#automation#sensortechnology#automationsolutions#manufacturing#TactileSensors#SensorTechnology#WearableTech#SmartDevices#IoTSensors#Robotics#Automation#AI#TouchTechnology
0 notes
Text

𝐓𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐥𝐞 𝐒𝐞𝐧𝐬𝐨𝐫 𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭: 𝐂𝐮𝐫𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐭 𝐓𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐈𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐭𝐬
The 𝐓𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐥𝐞 𝐒𝐞𝐧𝐬𝐨𝐫 𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 is experiencing significant growth due to advancements in robotics, healthcare, and consumer electronics. Tactile sensors, which mimic the human sense of touch, are essential for applications requiring precision and sensitivity.
𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐅𝐑𝐄𝐄 𝐒𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞: https://www.nextmsc.com/tactile-sensor-market/request-sample
𝐊𝐞𝐲 𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐃𝐫𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐫𝐬
𝙍𝙤𝙗𝙤𝙩𝙞𝙘𝙨 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝘼𝙪𝙩𝙤𝙢𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣: The increasing adoption of robotics in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and service sectors, drives the demand for tactile sensors. These sensors enable robots to perform delicate tasks with precision, enhancing their utility.
𝙃𝙚𝙖𝙡𝙩𝙝𝙘𝙖𝙧𝙚 𝘼𝙥𝙥𝙡𝙞𝙘𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣𝙨: Tactile sensors are crucial in medical devices and prosthetics. They help in developing advanced prosthetic limbs that provide sensory feedback, improving the quality of life for amputees.
𝘾𝙤𝙣𝙨𝙪𝙢𝙚𝙧 𝙀𝙡𝙚𝙘𝙩𝙧𝙤𝙣𝙞𝙘𝙨: The proliferation of touch-enabled devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and wearable technology, boosts the market. Tactile sensors enhance user experience by providing responsive and intuitive interfaces.
𝐌𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐓𝐫𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐬
𝙈𝙞𝙣𝙞𝙖𝙩𝙪𝙧𝙞𝙯𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙄𝙣𝙩𝙚𝙜𝙧𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣: Advances in technology are leading to smaller, more efficient tactile sensors that can be integrated into compact devices without compromising performance.
𝘼𝙧𝙩𝙞𝙛𝙞𝙘𝙞𝙖𝙡 𝙄𝙣𝙩𝙚𝙡𝙡𝙞𝙜𝙚𝙣𝙘𝙚 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙈𝙖𝙘𝙝𝙞𝙣𝙚 𝙇𝙚𝙖𝙧𝙣𝙞𝙣𝙜: The integration of AI and machine learning with tactile sensors is enhancing their capabilities. These technologies enable sensors to learn and adapt, providing more accurate and reliable data.
𝙁𝙡𝙚𝙭𝙞𝙗𝙡𝙚 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙒𝙚𝙖𝙧𝙖𝙗𝙡𝙚 𝙎𝙚𝙣𝙨𝙤𝙧𝙨: The development of flexible and wearable tactile sensors is gaining momentum. These sensors are used in applications ranging from smart clothing to health monitoring systems, providing continuous and real-time data.
𝐀𝐜𝐜𝐞𝐬𝐬 𝐅𝐮𝐥𝐥 𝐑𝐞𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭: https://www.nextmsc.com/report/tactile-sensor-market
𝐎𝐩𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭𝐮𝐧𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐞𝐬
𝙀𝙢𝙚𝙧𝙜𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙈𝙖𝙧𝙠𝙚𝙩𝙨: There is significant growth potential in emerging markets where automation and advanced healthcare technologies are increasingly being adopted.
𝙄𝙣𝙣𝙤𝙫𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙫𝙚 𝘼𝙥𝙥𝙡𝙞𝙘𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙤𝙣𝙨: Continuous research and development are leading to innovative applications for tactile sensors, such as in virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
As technology continues to evolve, tactile sensors will play an increasingly vital role in enhancing the functionality and user experience of various devices and systems.
#tactilesensors#semiconductors#marketresearch#sensortechnologies#smartsensors#markettrends#industrynews
0 notes
Text
Letting robots manipulate cables
For humans, it can be challenging to manipulate thin flexible objects like ropes, wires, or cables. But if these problems are hard for humans, they are nearly impossible for robots. As a cable slides between the fingers, its shape is constantly changing, and the robot’s fingers must be constantly sensing and adjusting the cable’s position and motion.
Standard approaches have used a series of slow and incremental deformations, as well as mechanical fixtures, to get the job done. Recently, a group of researchers from MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) pursued the task from a different angle, in a manner that more closely mimics us humans. The team’s new system uses a pair of soft robotic grippers with high-resolution tactile sensors (and no added mechanical constraints) to successfully manipulate freely moving cables.
One could imagine using a system like this for both industrial and household tasks, to one day enable robots to help us with things like tying knots, wire shaping, or even surgical suturing.
The team’s first step was to build a novel two-fingered gripper. The opposing fingers are lightweight and quick moving, allowing nimble, real-time adjustments of force and position. On the tips of the fingers are vision-based “GelSight” sensors, built from soft rubber with embedded cameras. The gripper is mounted on a robot arm, which can move as part of the control system.
The team’s second step was to create a perception-and-control framework to allow cable manipulation. For perception, they used the GelSight sensors to estimate the pose of the cable between the fingers, and to measure the frictional forces as the cable slides. Two controllers run in parallel: one modulates grip strength, while the other adjusts the gripper pose to keep the cable within the gripper.
When mounted on the arm, the gripper could reliably follow a USB cable starting from a random grasp position. Then, in combination with a second gripper, the robot can move the cable “hand over hand” (as a human would) in order to find the end of the cable. It could also adapt to cables of different materials and thicknesses.
As a further demo of its prowess, the robot performed an action that humans routinely do when plugging earbuds into a cell phone. Starting with a free-floating earbud cable, the robot was able to slide the cable between its fingers, stop when it felt the plug touch its fingers, adjust the plug’s pose, and finally insert the plug into the jack.
“Manipulating soft objects is so common in our daily lives, like cable manipulation, cloth folding, and string knotting,” says Yu She, MIT postdoc and lead author on a new paper about the system. “In many cases, we would like to have robots help humans do this kind of work, especially when the tasks are repetitive, dull, or unsafe.”
String me along
Cable following is challenging for two reasons. First, it requires controlling the “grasp force” (to enable smooth sliding), and the “grasp pose” (to prevent the cable from falling from the gripper’s fingers).
This information is hard to capture from conventional vision systems during continuous manipulation, because it’s usually occluded, expensive to interpret, and sometimes inaccurate.
What’s more, this information can’t be directly observed with just vision sensors, hence the team’s use of tactile sensors. The gripper’s joints are also flexible — protecting them from potential impact.
The algorithms can also be generalized to different cables with various physical properties like material, stiffness, and diameter, and also to those at different speeds.
When comparing different controllers applied to the team’s gripper, their control policy could retain the cable in hand for longer distances than three others. For example, the “open-loop” controller only followed 36 percent of the total length, the gripper easily lost the cable when it curved, and it needed many regrasps to finish the task.
Looking ahead
The team observed that it was difficult to pull the cable back when it reached the edge of the finger, because of the convex surface of the GelSight sensor. Therefore, they hope to improve the finger-sensor shape to enhance the overall performance.
In the future, they plan to study more complex cable manipulation tasks such as cable routing and cable inserting through obstacles, and they want to eventually explore autonomous cable manipulation tasks in the auto industry.
Yu She wrote the paper alongside MIT PhD students Shaoxiong Wang, Siyuan Dong, and Neha Sunil; Alberto Rodriguez, MIT associate professor of mechanical engineering; and Edward Adelson, the John and Dorothy Wilson Professor in the MIT Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences.
Letting robots manipulate cables syndicated from https://osmowaterfilters.blogspot.com/
0 notes
Text
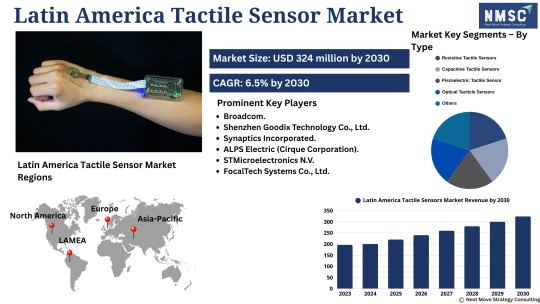
𝗗𝗜𝗗 𝗬𝗢𝗨 𝗞𝗡𝗢𝗪?
𝗟𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗻 𝗔𝗺𝗲𝗿𝗶𝗰𝗮 𝗧𝗮𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗹𝗲 𝗦𝗲𝗻𝘀𝗼𝗿𝘀 𝗠𝗮𝗿𝗸𝗲𝘁 is Heating Up!
𝗗𝗼𝘄𝗻𝗹𝗼𝗮𝗱 𝗙𝗥𝗘𝗘 𝗦𝗮𝗺𝗽𝗹𝗲
The 𝗟𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗻 𝗔𝗺𝗲𝗿𝗶𝗰𝗮 𝗧𝗮𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗹𝗲 𝗦𝗲𝗻𝘀𝗼𝗿𝘀 𝗠𝗮𝗿𝗸𝗲𝘁 is expected to witness robust growth in the coming years — fueled by the surge in automation, robotics, smart prosthetics, and Industry 4.0 adoption across the region.
From robotic surgery in Brazil to automated manufacturing in Mexico, tactile sensors are becoming the backbone of precision, safety, and smart response systems.
𝗞𝗲𝘆 𝗣𝗹𝗮𝘆𝗲𝗿𝘀 : Tekscan Inc., ForceN, Contactile, Sensobright, X-Sensors, Barrett Technology and others.
𝗪𝗵𝘆 𝘀𝗵𝗼𝘂𝗹𝗱 𝗶𝗻𝘃𝗲𝘀𝘁𝗼𝗿𝘀 𝗰𝗮𝗿𝗲?
Latin America is rapidly integrating smart technologies in healthcare, automotive, and industrial automation.
Tactile sensor applications are diversifying — from robotic grippers to smart textiles and wearables.
Governments and private players are heavily investing in digital transformation initiatives.
𝗢𝗽𝗽𝗼𝗿𝘁𝘂𝗻𝗶𝘁𝘆 𝗔𝗹𝗲𝗿𝘁! 𝗔𝗰𝗰𝗲𝘀𝘀 𝗙𝘂𝗹𝗹 𝗥𝗲𝗽𝗼𝗿𝘁 This is a golden window for forward-thinking investors to tap into an underpenetrated but high-potential tech segment.
𝗧𝗵𝗶𝗻𝗸 𝗮𝗵𝗲𝗮𝗱. 𝗜𝗻𝘃𝗲𝘀𝘁 𝘀𝗺𝗮𝗿𝘁 . Be part of the touch technology revolution in Latin America!
#LatinAmerica#TactileSensors#SmartTechnology#TechInvesting#EmergingMarkets#Robotics#Industry40#InvestSmart#DoYouKnow#TechTrends#InvestorAlert
0 notes