#Uboot menu dynamic control
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Display and Modification of LVDS Display Interface on AM62x Development Board
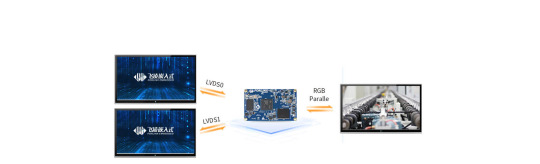
1. LVDS Interface Specification
Forlinx Embedded OK6254-C development board provides 2 x 4-lane LVDS display serial interfaces supporting up to 1.19Gbps per lane; the maximum resolution supported by a single LVDS interface is WUXGA (1920 x 1200@60fps, 162MHz pixel clock).
In addition, the interface supports the following three output modes:
(1) Single-channel LVDS output mode: at this time, only 1 x LVDS interface displays output;
(2) 2x single-channel LVDS (copy) output mode: in this mode, 2 x LVDS display and output the same content;
(3) Dual LVDS output mode: 8-lane data and 2-lane clock form the same display output channel.Forlinx Embedded OK6254-C development board is equipped with dual asynchronous channels (8 data, 2 clocks), supporting 1920x1200@60fps. All signals are by default compatible with Forlinx Embedded's 10.1-inch LVDS screen, with a resolution of 1280x800@60fps.
2. Output Mode Setting
(1) Single LVDS output mode:
We need a single LVDS screen cable. The black port of the cable is connected to the embedded OK6254-C development board, and the white port is connected to the embedded 10.1-inch LVDS display screen. Connection method as shown in the figure below:
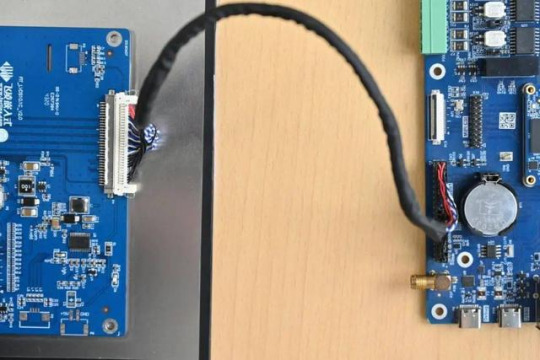
Note that the red line section corresponds to the triangle position, so don't plug it in wrong.

(2) 2x single LVDS (duplicate) output mode:
This mode uses the same connections as the Single LVDS Output Mode. Two white ports link to two 10.1-inch LVDS screens from Forlinx Embedded, and a black port on the right connects to the OK6254-C board's LVDS interface for dual-screen display.
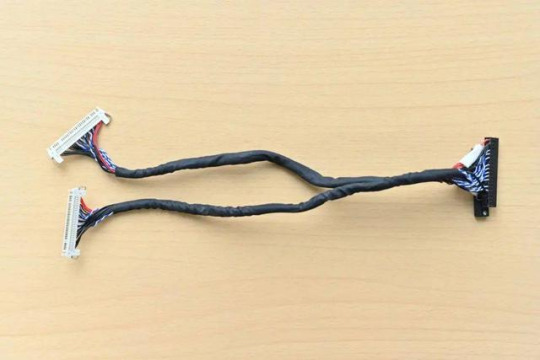
(3) Dual LVDS output mode:
The maximum resolution supported by a single LVDS interface on the OK6254-C development board is WUXGA (1920 x 1200@60fps). To achieve this high-resolution display output, dual LVDS output mode is required.
It is worth noting that the connection between the development board and the screen in this mode is the same as in [Single LVDS Output Mode], but the LVDS cable's and the screen's specifications have been improved.
3. Screen Resolution Changing Method
OK6254-C development board device tree is easy to modify, we need to open the OK6254-C-lvds.dts (single 8-way configuration) and OK6254-C-lvds-dual.dts (dual 8-way configuration) files.
Open OK6254-C-lvds.dts
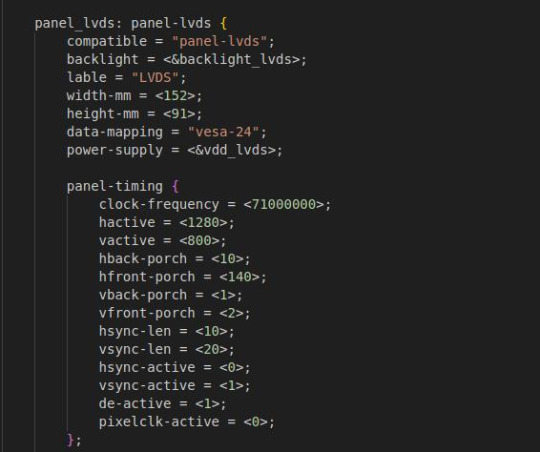
Open OK6254-C-lvds-dual.dts
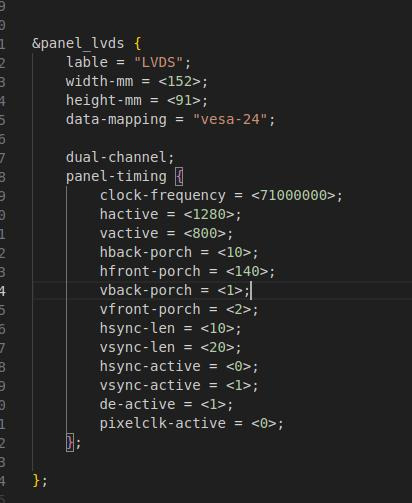
The above figure is the single LVDS and dual LVDS screen resolution information, the default resolution of 1024 * 600, and the maximum resolution support of 1920x1200, you can modify the corresponding parameters according to the Screen User’s Manual.
4. Compilation Configuration
Because we only modified the device tree, we don't need a full compilation. After compiling the kernel, a new Image and multiple device tree files will be generated in the images directory. Here we only need to compile the kernel separately.
(1) Switch directory: cd OK6254-linux-sdk/
(2) Execution environment variables:.. build.sh
(3) Execute the instructions that compile the kernel separately: sudo./build. Sh kernel.
(4) Pack all the device tree files to the development board /boot/ directory and replace them, then sync save and reboot scp images/OK6254-C* [email protected]:/boot/
We have modified the corresponding file. How should we select the screen after replacing it? At present, there are three kinds of screen switching control methods: kernel device tree designation, Uboot menu dynamic control, Forlinx Desktop interface and Uboot menu application. Today, I will briefly introduce the dynamic control of Uboot menu.
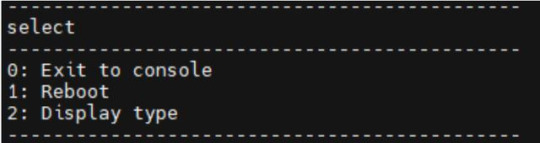
During Uboot, pressing the space bar will take you to the Uboot menu. There are three options in the menu:
Enter 0 to enter the Uboot command line;
Enter 1 to restart Uboot;
Enter 2 to enter the Display Configuration menu.
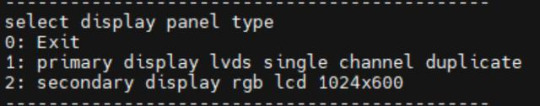
There are three options in the menu:
Enter 0 to return to the previous menu;
Enter 1 will toggle what option 1 displays to configure Screen 1 LVDS; Note: Screen 1 supports single LVDS, dual LVDS, and off (i.e., LVDS off)
Enter 2 to toggle the display of option 2 to configure the Screen 2 LCD. Note: Screen 2 supports 1024 * 600 resolution LCD screen, 800 * 480 resolution LCD screen and off (i.e. RGB off)
When selecting the LVDS screen, we enter 1 to select single 8-channel LVDS or dual 8-channel LVDS.
After selecting the desired configuration, enter 0 to return to the previous menu level. Restart Uboot or enter the command line to start the system, which can make the screen settings take effect. For other resolution screens, please modify the kernel device tree screen parameters according to the screen parameter requirements.
Originally published at www.forlinx.net.
#LVDS Interface#Forlinx Embedded#OK6254C#Screen Resolution Changing Method#Compilation Configuration#Uboot menu dynamic control
0 notes
Text
Forlinx AM62x Development Board Display Program: RGB Display and Modification Methods
Display is one of the most crucial functions of embedded development board, and being able to support a greater variety and higher specifications display interface, means it can cater to a wider range of usage scenarios. Before leaving the factory, each embedded development board undergoes screen debugging. However, during the customer’s project development process, they may encounter compatibility issues when adapting to non-original screens.
Taking the Folinx Embedded AM62x series OK6254-C development board as an example, it features two display interfaces: LVDS and RGB. It can support up to 2 display controllers and simultaneously output two different screens. This article describes in detail the display scheme of the OK6254-C development board - how RGB is displayed and modified.

1. RGB Interface Specification
The embedded OK6254-C development board provides one 24-bit RGB parallel display interface and supports a maximum resolution of WUXGA (1920x1200 @60fps, 165MHz pixels). The 16 bit data interface is led out from the carrier board through the FPC seat, which is suitable for the embedded 7-inch resistance and capacitance touch screen of Forlinx by default, with a resolution of 1024 x600 @ 60 FPS.
If high color detail and realism are required, RGB888 is a better choice. If storage space is limited and there is no high requirement for color representation, then using RGB565 can be considered to save storage resources. At this point, the selection of RGB888 and RGB 565 is involved.
2. Selection and Modification of RGB888 and RGB 565
The modification of OK6254-C device tree is very convenient. We divide the device tree into three parts: kernel device tree, LVDS display device tree and RGB display device tree. To make RGB888 and RGB565 selections and modifications, we need to open the OK6254-C-rgb.dts file as shown below:

In the first red box in the image above, we can modify the RGB display to RGB888 or RGB565, the default is rgb565. The default resolution of the red box at the bottom is 1024*600, which can be modified manually by following the screen manual. The maximum resolution supported is 1920x1200. In addition, the OK6254-C development board also supports 800 * 480 screen resolution, the next step is to introduce the screen selection operation.
Open OK6254-C-rgb-800_480.dts
You can modify the resolution and the screen parameters suitable for the screen in the red box section of the picture below:

(1) Compile:
Because we only modify the device tree, we don't need to compile it all, which is not only time-consuming but also laborious. After compiling the kernel, a new Image and multiple device tree files will be generated in the images directory. Here we only need to compile the kernel separately.
Switch directory: cd OK6254-linux-sdk/
Execute the environment variable:. build.sh
Execute instructions to compile the kernel separately: sudo ./build.sh kernel
Package all the device tree files and replace them in the /boot/ directory of the board, then sync to save and reboot. scp images/OK6254-C* [email protected]:/boot/
Modification is finished here.
(2) Screen Selection Stage:
We have modified the corresponding file. How should we select the screen after replacing it? At present, there are three kinds of screen switching control methods: kernel device tree designation, Uboot menu dynamic control, Forlinx Desktop interface and Uboot menu application. Today, I will briefly introduce the dynamic control of Uboot menu.
During Uboot, pressing the space bar will take you to the Uboot menu. There are three options in the menu:
Enter 0 to enteruboot Commandthe line;
Enter 1 to restart Uboot;
Enter 2 to enter the Display Configuration menu.

There are three options in the menu:
Enter 0 to return to the previous menu;
Enter 1 will toggle what option 1 displays to configure Screen 1 LVDS; Note: Screen 1 supports single LVDS, dual LVDS, and off (i.e., LVDS off)
Enter 2 to toggle the display of option 2 to configure the Screen 2 LCD. Note: Screen 2 supports 1024 * 600 resolution LCD screen, 800 * 480 resolution LCD screen and off (i.e. RGB off)
When selecting the LCD screen, we enter 2 and it's OK.

After selecting the desired configuration, enter 0 to return to the previous menu level. Restart Uboot or enter the command line to start the system, which can make the screen settings take effect. For other resolution screens, please modify the kernel device tree screen parameters according to the screen parameter requirements.
So far, we have finished the introduction of RGB display scheme. Of course, other display interfaces are similar. You can pay attention to the follow-up Application Notes.
Originally published at www.forlinx.net.
#Embedded development board#Display interface#RGB and RGB888#Screen modification#am62x development board
0 notes