#VMware ESXi installation guide
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
5 Tips to Install ESXi on a Mini PC
5 Tips to Install ESXi on a Mini PC @vexpert #homelab #minipc #vmwarecommunities #VMwareESXiInstallationGuide #ESXiOnMiniPCTips #NetworkAdapterCompatibilityForESXi #CustomizingESXiSystemMediaSize #CommunityNetworkDriverForESXi #CustomizingESXiISO
I have been having a lot of fun lately playing around with various Mini PCs in the home lab and finding options for running various hypervisors. I currently run VMware vSphere in the lab environment so installing ESXi on Mini PCs is a natural choice. However, if you are looking to utilize the VMware vSphere hypervisor, ESXi, on mini PC hardware for a micro-server design that is power efficient,…

View On WordPress
#Avoiding vSAN on mini PCs#Community Network Driver for ESXi#Customizing ESXi systemMediaSize#ESXi host configuration for compact systems#ESXi on mini PC tips#Network adapter compatibility for ESXi#Optimal ESXi performance on mini PCs#Step-by-step ESXi setup#Tailoring ESXi ISO for mini PCs#VMware ESXi installation guide
0 notes
Text
How Do You Secure Your Server from Malicious ESX Scripts?
Securing your server from malicious ESX scripts is essential in ensuring the safety and integrity of your data and services. ESX (Elastic Sky X) is a virtualization platform often used in server environments, enabling multiple virtual machines to run on a single host. While ESX provides great flexibility and efficiency, it can also be vulnerable to attacks, particularly through malicious scripts. These scripts, if not properly managed, can compromise the security of your server, lead to data breaches, or disrupt the smooth operation of your virtualized environment.
Here’s a detailed guide on how to secure your server from malicious esx scripts:

Keep Your System Updated
The first and most crucial step in securing your server is to keep your ESX host and all its components up to date. VMware frequently releases patches and updates to address security vulnerabilities, performance improvements, and bug fixes. Regularly check for updates and ensure that all patches are applied promptly. Neglecting these updates can leave your server open to exploitation from attackers using known vulnerabilities.
Use Secure Configurations
Another key to securing your ESX environment is ensuring that your server is configured securely. This includes configuring the ESXi firewall, disabling unnecessary services, and following VMware’s security best practices. By turning off unnecessary services, you limit the number of potential attack vectors. VMware provides a comprehensive security guide that outlines recommended configurations for hardening your ESX installation. Follow these guidelines to ensure your system is as secure as possible.
Enable ESX Host Firewall
The ESX firewall acts as a barrier between your server and any potential intrusions from malicious actors. Ensure that the firewall is configured properly to block unnecessary ports and only allow trusted traffic. Additionally, you can configure the firewall to log suspicious activity, providing valuable information in case of a security breach. Regularly review firewall logs to spot any unusual activity.
Control User Access and Privileges
One of the most common ways attackers gain access to ESX servers is through compromised user accounts or excessive privileges. Implement the principle of least privilege (POLP) by ensuring that users and administrators only have access to the resources they need. Limit access to critical system components and ensure that users cannot execute scripts unless absolutely necessary. Use role-based access controls (RBAC) to assign permissions based on job responsibilities. Moreover, regularly audit user accounts and remove any unused or inactive accounts to minimize potential vulnerabilities.
Monitor and Analyze Logs
Effective logging and monitoring are essential for identifying and responding to malicious activity quickly. Set up centralized logging for all ESX hosts and monitor these logs regularly for signs of abnormal behavior, such as unauthorized access attempts, failed login attempts, or unusual script executions. VMware vRealize Log Insight can help you manage and analyze logs efficiently, enabling you to spot malicious activity in real-time. Promptly investigate and address any suspicious log entries.
Scan for Malicious Scripts
Malicious ESX scripts are often introduced by attackers who exploit vulnerabilities in your environment. To prevent such threats, regularly scan your ESX server for suspicious scripts or files. Automated malware detection tools and anti-virus software can help detect and quarantine malicious files before they can cause damage. Ensure that any scripts running on your server are from trusted sources, and review them periodically to ensure they haven’t been tampered with.
Use Secure Boot and Trusted Execution
Secure boot is an essential security feature that prevents unauthorized firmware, bootloaders, and other malicious code from loading during the boot process. Ensure that secure boot is enabled on your ESX host, as it helps protect against rootkits and boot-time malware. Additionally, using trusted execution environments such as Intel TXT (Trusted Execution Technology) or AMD SEV (Secure Encrypted Virtualization) can further protect the integrity of your ESX server and its virtual machines from malicious scripts.
Use Virtual Machine Isolation
In environments where multiple virtual machines (VMs) are running on the same ESX host, it is essential to ensure proper isolation between VMs. This minimizes the risk of an attacker gaining access to other VMs via a compromised script. Configuring virtual machine isolation settings, such as enabling virtual machine lockdown mode and using a separate network for sensitive VMs, will significantly reduce the chance of a malicious script spreading across your environment.
Backup Regularly
Even with all the security measures in place, it’s always a good practice to have a reliable backup strategy in case of a breach. Regularly back up your ESX server and its virtual machines to secure, offsite storage. This ensures that if a malicious script causes system corruption or data loss, you can quickly restore your system to its previous state. Automate your backups and perform regular tests to ensure data integrity.
Conclusion
Securing your ESX server from malicious scripts requires a comprehensive approach that involves proactive monitoring, secure configurations, and regular updates. By following these best practices and maintaining a vigilant stance against potential threats, you can safeguard your virtualized environment from the damaging effects of malicious ESX scripts. Regular auditing, user privilege management, and the use of advanced security features like secure boot and trusted execution environments will further strengthen your defenses and help you maintain a secure, stable ESX server environment.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Beginners Guide - Using Nested ESXi Hosts for a VCF 5.2.1 Home Lab
Attention: Using Nested ESXi (ESXi installed on ESXi) is not supported by VMware (or Broadcom). Use for your personal practices/learnings only. Not to be used for production environments. Part II – Creating an ESXi VM with my settings To use YOUR own ESXi virtual machine for your VCF lab, several details need to be prepared. You can create as well the ESXi VM with two or three virtual disks…
View On WordPress
#Beginner#Cloud Builder#ESXi#Nested#Nested ESXi#Nested SDDC#Nested vSphere#SDDC#VCF#vSAN ESA#vSAN OSA#vSphere 8.0
0 notes
Text
Dell Unity Deploy D-UN-DY-23 Dumps Questions
If you're considering the D-UN-DY-23 Dell Unity Deploy 2023 Exam, you're in for a challenge that's both rigorous and rewarding. Having recently passed this exam, I want to share my experience and provide some tips that might help you on your journey. I found Certspots' Dell Unity Deploy D-UN-DY-23 dumps questions incredibly helpful. These dumps provide a realistic preview of the exam questions and scenarios you might encounter. Studying these Dell Unity Deploy D-UN-DY-23 Dumps Questions allowed me to familiarize myself with the exam format and question types, making it easier to tackle the actual test.
Why the Dell Unity Deploy 2023 Exam?
The D-UN-DY-23 exam is aimed at professionals involved in deploying Dell Unity systems, which are essential for contemporary data management and storage. It evaluates your knowledge and skills in areas such as installation, configuration, and management of these systems. Specifically, the Dell EMC Unity Deploy certification targets individuals looking to advance their careers in the Unity domain. The Dell EMC Unity Deploy 2023 (DCS-IE) exam confirms that candidates have the basic knowledge and demonstrated abilities required to manage Dell Unity storage systems in a production setting, aligning with business needs. It also covers configuration tasks that support ongoing management and basic integration topics.
Familiar with the D-UN-DY-23 Exam Topics
Dell Unity Platform Concepts, Features, and Architecture (10%)
● Describe the Dell Unity platform architecture, features, and functions
● Describe the Dell Unity VSA software defined storage solution
● Identify the Dell Unity XT hardware components
Dell Unity XT and UnityVSA Installation and Service (10%)
● Install and initialize a Dell Unity XT storage system
● Deploy and initialize a Dell UnityVSA system
● Perform key service tasks and identify related resources
● Describe the Dell Unity Platform service functions
Dell Unity XT and UnityVSA System Administration (5%)
● Identify and describe the user interfaces for monitoring and managing the Dell Unity family of storage systems
● Configure the Dell Unity XT support and basic system settings for system administration
Dell Unity XT and UnityVSA Storage Provisioning and Access (25%)
● Describe dynamic and traditional storage pools and how they are provisioned
● Describe dynamic pool expansion, considerations for mixing drive sizes and the rebuild process
● Provision block, file and VMware datastore storage
● Configure host access to block storage resources
● Configure NAS client access to SMB and NFS file storage resources
● Configure VMware ESXi hosts to access VMware datastore storage resources
Storage Efficiency, Scalability, and Performance Features (25%)
● Describe and configure FAST Cache
● Describe and configure File Level Retention
● Describe and configure Data Reduction
● Describe and configure FAST VP
Data Protection and Mobility (25%)
● Describe the Snapshots data protection feature and snapshot creation
● Descibe the Replication data protection feature
● Create synchronous and asynchronous replication sessions for storage resources
Preparation Tips for Dell Unity Deploy D-UN-DY-23 Exam
Study the Exam Objectives: Make sure you are well-versed in all the key topics listed in the exam objectives. The Dell Unity Deploy exam covers a range of topics including installation, configuration, and troubleshooting. Understanding these areas thoroughly is essential.
Hands-On Practice: Practical experience is invaluable. If possible, get hands-on practice with Dell Unity systems. This could be through a lab environment or real-world experience. The more you work with the systems, the better you'll understand the intricacies of deployment and management.
Review Official Documentation: Dell's official documentation and guides are a goldmine of information. They provide in-depth details about the features and functionalities of Dell Unity systems. Reviewing these documents can give you a clearer understanding of what to expect in the exam.
Join Study Groups: Engaging with a study group or forum can provide additional insights and answer any questions you might have. Sharing knowledge and discussing topics with peers can enhance your understanding and provide different perspectives.
Final Thoughts
Passing the D-UN-DY-23 Dell Unity Deploy 2023 Exam was a rewarding achievement. The preparation process, particularly using Certspots D-UN-DY-23 dumps questions, made a significant difference in my study routine. If you're preparing for this exam, I strongly recommend using these resources to help you succeed. With dedicated study and hands-on practice, you can confidently approach and pass the exam.
Good luck on your journey to becoming a certified Dell Unity Deploy professional!
0 notes
Text
Preparing A Lab For Cisco Sd-Wan Eve-Ng Testing
Many options exist for setting up a personal Cisco SD-WAN lab. EVE-NG is your best bet right now, in my opinion. In this guide, you will see how to set up a local environment for testing Cisco's software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) and how to set up EVE-NG on your own machine. The approach includes downloading the required Cisco and EVE-NG images.
Putting in place EVE-NG.
Preparing the pictures for usage on your EVE-NG system.
Making sure you have permission to use the photos.
Installation
EVE-NG can be operated on real hardware or virtualized with a hypervisor like KVM or VMWare. Prerequisites for EVE can be found on this page. NG's the most recent version of VMWare ESXi (version 7) will be used for the installation.
EVE-NG
You may get EVE-NG, which you can download to your computer, on the download page. It's up to you to decide between two options:
All the Way Down to the Community Edition and the Professional and Educational Institution Versions
Both of these swayed me to acquire the ISO for the commercial release:
As of now, this is the latest revision available.
To add or remove connections doesn't necessitate powering down any virtual machines.
You can agree that it is worthwhile to spend the money on a licence to use the professional version. Create a duplicate of the ISO image on the VMware ESXi host's datastore.
The ESXi Server from VMware
How about you use a virtual computer to install EVE-NG?
Networks of Seaports
The EVE-NG VM's eth0 network interface is linked to the host's local area network (LAN) via the LAB port group. Taking use of this allows us to use the EVE-NG GUI and SSH access the server.
EVE-NG is an abbreviation for "Emulated Virtual Environment for Network, Security, and DevOps Professionals." The EVE-NG platform allows you to set up your own virtual labs and conduct vendor-neutral training. You can also choose to validate the solutions, develop the architecture, and build the network. The EVE-NG system can handle the challenges of today's advanced computer networks. Virtual proof of ideas, solutions, and training environments can now be built by enterprises, e-learning providers and centres, individuals, and collaborative groups.
This course will teach you how to use EVE-NG to set up your own virtual EVE-NG lab on whatever device you possess. This course will teach you how to design and build your own virtual labs for the purposes of self-study or verification of network design solutions. In this self-paced course, you will learn how to obtain the required EVE-NG Image, install EVE-NG, and obtain the required vendor images. You should test your EVE-NG installation to make sure the photographs have been installed properly before continuing the labs and practical.
0 notes
Text
In this blog post we see how to set up time synchronization of your vSphere ESXi / vCenter using a time server from your local network. If using a Local NTP Server is not an option for you, it’s also okay to go with an Internet-based(Public) time server that takes care of your time zone. It is assumed that your NTP server doesn’t have authentication mechanisms in place, or any kind of access control that restricts NTP clients connectivity. Step 1: Configure NTP Server (Optional) You can choose to use publicly available NTP servers or set one locally in your infrastructure. For local installation and configuration of NTP servers check out the guides in the following links. How To Configure NTP Server on pfSense / OPNsense Configure Chrony NTP Server on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 Install FreeIPA Server on Rocky Linux 9 / AlmaLinux 9 With the NTP server installed and configured you can then proceed to configure your vSphere ESXi environment. Step 2: Enable NTP daemon on ESXi Hosts On each ESXi host we’ll need to start and enable NTP service. This can be performed from vSphere Web Client or from vCenter web console. Option 1: Enable NTP daemon on ESXi using vSphere Web Client Login to your host’s vSphere Web Client and go to Host > Manage > Services. Select NTP daemon and click start. Update the policy as well to start the service with the host. Option 2: Enable NTP daemon on ESXi using vCenter Login to vCenter console and select the host where NTP daemon is to be started. Go to Configure > Services. From a list of services choose NTP Daemon and hit Start. Next click “EDIT STARTUP POLICY” to update how the service lifecycle is managed. Choose Start and stop with the host for automatic startup when the host is started. Step 3: Configure vSphere ESXi / vCenter to use NTP Let’s consider the two configuration scenario for setting NTP server in your VMware vSphere environment. Configure vCenter to use NTP synchronization Login to VMware vCenter server management console – https://vcenter.example.com:5480/. Authenticate using credentials set at the time of installation. From the main menu navigate to Time > Time zone > Edit to set the correct timezone. Set NTP host under Time synchronization settings. Configure ESXi host to use NTP Time You can use either of these methods. Method 1: Using vSphere Web client Select the host, then go to Manage > System > Time & date > Edit NTP Settings Choose the setting to enable NTP and input your NTP server IP. If you haven multiple servers separate the list using comma. When done save the settings by clicking Save. Method 2: Using vCenter web console Login to vCenter, then select ESXi host, Configure > Time Configuration > ADD SERVICE > NETWORK TIME PROTOCOL Provide IP address of NTP server. For multiple servers separate the list with comma. Click “TEST SERVICES” to test NTP service connection. Our ESXi host and vCenter should now be using NTP for time settings. It’s recommended to provide multiple NTP servers to ensure time is at sync at any point in time. Configuring multiple NTP servers provides redundancy in case one of the servers is not reachable.
0 notes
Text
Iso image virtualbox mac os x

#Iso image virtualbox mac os x for free
#Iso image virtualbox mac os x how to
#Iso image virtualbox mac os x mac os x
#Iso image virtualbox mac os x mac os
In our next posts, we will post articles about the macOS Mojave installation. In this article, we have prepared and shared the macOS 10.14 image file for you to use macOS on virtual machines. To install macOS 11 on a virtual machine using the VMware virtualization program, click on the image below to browse our article.Īfter downloading the image file, click on the image below to download Mojave on VMware ESXi. If you have already installed macOS Mojave, open the Mac App Store and download and install this version from Updates. Update (July 26, 2018): macOS High Sierra 10.13.6 Released!Īpple introduced macOS 10.14.6 for developers. The macOS ISO file will not open on Windows! Just create a new virtual machine for macOS and add the ISO file to the virtual machine and then start the installation!Ĭlick the button below to get macOS Mojave 10.14 ISO file to your computer. You will also get ISO Corrupted Error if you try to open it on the Windows operating system after downloading the installation image to your computer. We have tested this ISO file, and it works fine. You can use this ISO file with virtualization programs such as VirtualBox, VMware Workstation. If you want to install macOS 10.13.5, check out our macOS High Sierra Installation article.ĭownload macOS Mojave Image File for VirtualBox, ESXi, and VMware In our previous articles, we have shared with you the macOS High Sierra operating system ISO files. After creating an Apple Developer account, you can download and install this update on your computer by downloading the macOS Developer Beta Access Utility. If you want to download and install macOS Beta on your iMac or MacBook computer, you must have an Apple Developer account. Once you have installed the macOS 10.14 installation image file on a virtual machine, you can start the installation immediately. In this article, we have prepared the ISO file for installing the Mojave operating system using VMware Workstation, Oracle VM VirtualBox, VMware Fusion, or ESXi virtualization programs. If you want to update your system to macOS 10.14, we recommend that you first back up your macOS computer for errors that may occur.
#Iso image virtualbox mac os x mac os
You can follow our blog for new images we release for VirtualBox.Although Mac OS Mojave beta is released, many users have updated their systems. It is a free and powerful x86 and AMD64/Intel64 virtualization product available for most of the operating systems such as Linux, Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, Solaris and ported version for FreeBSD. VirtualBox is the most easiest way to run secondary OS on your primary operating system, If your hardware doesn’t allow you to install any other operating system then VirtualBox comes in hand.
#Iso image virtualbox mac os x how to
We do not install ‘Guest Additions’ in the OS or add any kind of stuff, read our privacy policy. This video guide you how to install Mac OS on VirtualBox with Mac OS ISO Download for Virtualbox.Mac OS ISO. the further detail you can read under review.
#Iso image virtualbox mac os x mac os x
Here you can follow the guide how to attach/configure VDI image with VirtualBox. Download Mac OS X 10.6.3 DMG Snow leopard full V setup is full offline installer setup and bootable ISO Image of MAC OS and compatible with 32 and 64 bit. You can check FAQs for Credentials( Username & Password) for VDI images. At the moment we have plans to offer you 30+ Linux/Unix distributions, we may add more to our list in near future, you can also send us suggestions if we are missing any popular distribution from our list.
#Iso image virtualbox mac os x for free
We offer images for both architectures 32bit and 64bit, you can download for free for both architectures. From here you can download and attach the VDI image to your VirtualBox and use it. We offer open-source (Linux/Unix) virtual machines (VDIs) for VirtualBox, we install and make them ready-to-use VirtualBox images for you.

1 note
·
View note
Text
vSphere Distributed Switch Configuration and Best Practices Guide
vSphere Distributed Switch Configuration and Best Practices Guide - Learn how to create and manage vsphere distributed switches and how they compare to vsphere standard switches #vmwarevsphere #vnetworkdistributedswitches #vmwarenetworking #vsphere
VMware vSphere has many advanced networking features as part of the solution. These allow VIadmins to configure just about any setting they need for their network. By default, the vSphere Standard Switch is the default network configuration that comes “out of the box” with a VMware ESXi host installation and virtual switches. However, there is another kind of switch that has many benefits to your…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Better nreoloutiuon oin mac os vmware

#Better nreoloutiuon oin mac os vmware how to#
#Better nreoloutiuon oin mac os vmware mac os x#
#Better nreoloutiuon oin mac os vmware install#
#Better nreoloutiuon oin mac os vmware Patch#
#Better nreoloutiuon oin mac os vmware how to#
In this article, we have reviewed step by step how to change the screen resolution for the macOS High Sierra 10.13.4 virtual machine installed on Oracle VM software. This time the screen resolution is configured as 2048×1080! As a result, you can easily change the screen size of the VM you use with the value you want. I noticed if you go into displays under settings if you increase the monitor count, you can increase the video memory to a max of 256 MB. If you want to try a different resolution size again, type a different value in the X section and apply the command on the CMD. Re: How to improve GPU card Mac High serria. When I’ve unchecked the Use full resolution for Retina display under VMWare display settings - the icons on the desktop are way too big and t. Thing is - I can’t seem to change my resolution. It is full offline installer standalone setup of VMware Fusion 11 Pro macOS freeload for compatible version of macOS. My host is El Capitan which is running on a MacBook Pro. VMware Fusion 11 Pro freeload macOS New and latest Version for macOS. The display resolution of the High Sierra virtual machine is configured to 1920×1080. Hey, Installed MacOS 10.12 (Sierra) on a VMWare. Now open the VBox program and run the virtual machine. Paste the code into the CMD and press Enter. Then type in the resolution you want to change to the X part of the code and copy the code. Because you are running multiple operating systems on a single server, you can imagine that the.
#Better nreoloutiuon oin mac os vmware mac os x#
Install the Mac OS X as like guest OS installation in VMware Workstation.You can also access Command Prompt (Admin)by pressing the Windows Key + X keys together.Īfter opening the CMD prompt, first, move into the VBox folder. With VMware Server, you run virtual guest operating systems inside a host operating system.
You will be able to select MAC OS as option in VMware Workstation.
Right click on install.cmd file and select run as administrator.
For Windows Select the Windows folder and open it.
and to make it better, on a PC running Windows Read on for more information: Ever since Apple made the move to Intel processors, hackers have been trying hard to modify the x86 version of OS X to run on a PC. Lately, several websites have copied and posted up the text on these pages.
#Better nreoloutiuon oin mac os vmware Patch#
The latest Unlocker is having patch for Windows, Linux, Fusion 4.0 on Snow Leopard and Lion and VMware ESXi 5. This is a System Preferences pane to change screen resolution on your macOS guest. Mac OS X 10.4.8 Tiger x86 VMware Installation Guide.
#Better nreoloutiuon oin mac os vmware install#
I heard there were two options: either I install Mac OS X natively, but the installation discs are awfully picky, or I could use VMWare Workstation on a really powerful. One the VMware Workstation installation is completed If its possible, Id like to use Mac OS X (and all the programs that run on it, like iTunes, Final Cut Pro and Safari, lets say) on a PC, just like I could if I bought a Mac.The size within the guest macOS auto-resizes. Simply grab the corner of the VM window on the host Mac, and grow/shrink the VM window. Then you should be able to redefine your virtual display resolution. The resolution is OK, but graphic tasks are very slo. In the Name the Virtual Machine window, name the virtual machine and virtual machine directory. In my PC is installed an Asus RX580 4GB but the virtual machine runs with a graphic card of 128MB of GPU ram. Select Apple Mac OS X in the Guest operating system section and select macOS 10.14 in the Version section. After it completes, your guest macOS restarts. Running macOS Catalina in Windows10 with VMware 15.5 The system runs perfectly with only one very important problem: the display type. I have tried to install MAC OS X 10.7.1 on VMware Workstation Virtual Machine. This mounts an installer app within the Finder of your guest OS. The below blog explain you how to install MAC OS X 10.7 on VMware Workstation Virtual Machine,there are many methods around and this is one of it.

0 notes
Text
Beginners Guide - Using Nested ESXi Hosts for VCF 5.2.1 Home Lab
Attention: Using Nested ESXi (ESXi installed on ESXi) is not supported by VMware (or Broadcom). Use for your personal practices/learnings only. Not to be used for production environments. Part I – My Network Configuration Everyone’s network at home is different. See my configuration with my explanations hoping it will help you. On my physical ESXi Hosts, my VyOS router is running providing…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Download mac os x vmware image

Download mac os x vmware image mac os x#
Download mac os x vmware image install#
Download mac os x vmware image update#
Download mac os x vmware image iso#
I’m making this guide for those who don’t have access to a Mac and need macOS to either try out for a bit or create a macOS boot loader installer for a AMD hackintosh build.
Download mac os x vmware image install#
This guide will show you the steps to install Sierra on a AMD Ryzen PC using a VMWare Virtual Machine.
Before Starting The Download Kindly Consider Small Amount As A Donation By Paypal To continue This Project Well we are Providing OS X Lion VMWARE image.
Download mac os x vmware image mac os x#
Download Mac OS X Sierra 10.12 Beta version. Download Mac OS X Mountain Lion 10.8.5.MacOS X 10.7 Lion VMWare Image Addeddate 11:54:52. Topics MacOS, MacOS X, Lion, VM Collection opensourcemedia Language Swazi. Buy Premium Before Download To Get Resumable Support & Max Speed Links. Choose the appropriate kernel running 'amd-kernel.cmd' and then change the settings of your VM, ie set the amount of memory, etc. Copy the folder 'OS X Mountain Lion' from the downloaded image in a folder with virtual machines.In this article, we have prepared and shared the macOS 10.14 image file for you to use macOS on virtual machines.There are two different types of OS one is Mac OS X Lion 10.7 ISO, DMG and the other one is OS X mountain lion. To install macOS 11 on the virtual machine using the Oracle VirtualBox virtualization program, you can browse our related article by clicking the image below.Īfter downloading the image file, click on the image below to download Mojave on VMware ESXi. To install macOS 11 on a virtual machine using the VMware virtualization program, click on the image below to browse our article. If you have already installed macOS Mojave, open the Mac App Store and download and install this version from Updates. Update (July 26, 2018): macOS High Sierra 10.13.6 Released!Īpple introduced macOS 10.14.6 for developers.
Download mac os x vmware image iso#
The macOS ISO file will not open on Windows! Just create a new virtual machine for macOS and add the ISO file to the virtual machine and then start the installation!Ĭlick the button below to get macOS Mojave 10.14 ISO file to your computer. You will also get ISO Corrupted Error if you try to open it on the Windows operating system after downloading the installation image to your computer. We have tested this ISO file, and it works fine. You can use this ISO file with virtualization programs such as VirtualBox, VMware Workstation. If you want to install macOS 10.13.5, check out our macOS High Sierra Installation article.ĭownload macOS Mojave Image File for VirtualBox, ESXi, and VMware In our previous articles, we have shared with you the macOS High Sierra operating system ISO files.
Download mac os x vmware image update#
After creating an Apple Developer account, you can download and install this update on your computer by downloading the macOS Developer Beta Access Utility. If you want to download and install macOS Beta on your iMac or MacBook computer, you must have an Apple Developer account. Once you have installed the macOS 10.14 installation image file on a virtual machine, you can start the installation immediately. In this article, we have prepared the ISO file for installing the Mojave operating system using VMware Workstation, Oracle VM VirtualBox, VMware Fusion, or ESXi virtualization programs. If you want to update your system to macOS 10.14, we recommend that you first back up your macOS computer for errors that may occur. Although Mac OS Mojave beta is released, many users have updated their systems.

0 notes
Text
Virtualization is a very old technology but still finds high use, especially in cloud computing. It involves creating software-based or virtual versions of computer resources such as storage, networks, applications, and servers. This makes it possible to partition a single server into multiple virtual instances that run and interact independently. There are mainly two types of virtualization. These are: Type 1/Bare Metal virtualization where the hypervisor is installed directly on top of the physical machine. For example Microsoft Hyper-V, open-source Kernel-based VMs (KVMs), VMware ESXi Type 2/Hosted virtualization where the hypervisor is installed on an existing operating system. For example VMware Workstation and Oracle VirtualBox In this guide, we will discuss how to install and use Vagrant With VirtualBox / KVM on Rocky Linux 9. Vagrant is an open-source tool that can be used to build and manage virtual machine environments in a single workflow. It provides the simplest and easiest command line way to manage virtual environments. This reduces the development environment setup time while increasing the production parity. Vagrant is preferred due to the following features: It is built on top of industry-standard technology and is controlled by a single consistent workflow. It offers simplicity when setting up an environment. It standardizes environments across platforms Virtual machines can easily be provisioned on top of VirtualBox, VMware, AWS, or any other provider. It is a cross-platform tool There are terminologies involved when dealing with Vagrant. These are: Vagrant Box: This is the Vagrant setup unit. just like docker, Vagrant is a self-contained image. This is a packaged Vagrant environment. Vagrant File: This is the configuration file for Vagrant. It contains the configurations used to create a VM. Provider: is the location in which the virtual environment runs, the default option is Virtualbox but can be set to any other tool such as KVM, docker e.t.c Now let’s plunge in and enjoy the awesomeness of this tool! Before you Begin Before we begin, you need a hypervisor installed on your Rocky Linux 9 machine. For this case, we will use KVM or Virtualbox, which can be installed with the aid below; Install and Use KVM Virtualization on Rocky Linux 9 Install and Use VirtualBox on Rocky Linux 9 1. Install Vagrant on Rocky Linux 9 Once a preferred hypervisor has been installed, proceed and install Vagrant on Rocky Linux 9. To achieve this, begin by adding the Vagrant repository to the system. sudo yum install yum-utils sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.releases.hashicorp.com/RHEL/hashicorp.repo Install Vagrant on Rocky Linux 9 with the command: sudo yum install vagrant Dependency Tree: Dependencies resolved. ======================================= Package Arch Version Repo Size ======================================= Installing: vagrant x86_64 2.3.0-1 hashicorp 108 M Transaction Summary ======================================= Install 1 Package Total download size: 108 M Installed size: 257 M Is this ok [y/N]: y 2. Using Vagrant with VirtualBox / KVM on Rocky Linux 9 Once installed, Vagrant can be used to create/provision Virtual Machine on your hypervisor. First, create a working directory for Vagrant and navigate into it: mkdir Vagrant && cd Vagrant Install the Vagrant Libvirt Provider(KVM Only) For KVM, you need to download the Vagrant plugin. First, enable the PowerTools CRB repo: sudo dnf install epel-release sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled crb Install the required build tools: sudo dnf install gcc make perl kernel-devel kernel-headers bzip2 dkms elfutils-libelf-devel sudo yum groupinstall "Development Tools sudo dnf install libvirt-devel Install the Vagrant Libvirt Provider vagrant plugin install vagrant-libvirt ##OR CONFIGURE_ARGS="with-libvirt-include=/usr/include/libvirt with-libvirt-lib=/usr/lib64" vagrant plugin install vagrant-libvirt
Verify the installation with the command: $ vagrant plugin list vagrant-libvirt (0.10.1, global) Configure and Initialize the VM Now download a Vagrant box file for the desired VM and set the provider. For example Ubuntu 20.04 ##For VirtualBox vagrant box add generic/ubuntu2004 --provider=virtualbox ##For KVM vagrant box add generic/ubuntu2004 --provider=libvirt Sample Output: ==> box: Loading metadata for box 'generic/ubuntu2004' box: URL: https://vagrantcloud.com/generic/ubuntu2004 ==> box: Adding box 'generic/ubuntu2004' (v4.1.6) for provider: libvirt box: Downloading: https://vagrantcloud.com/generic/boxes/ubuntu2004/versions/4.1.6/providers/libvirt.box box: Calculating and comparing box checksum... ==> box: Successfully added box 'generic/ubuntu2004' (v4.1.6) for 'libvirt'! Create a Vagrant file for the VM using the init command: $ vagrant init generic/ubuntu2004 A `Vagrantfile` has been placed in this directory. You are now ready to `vagrant up` your first virtual environment! Please read the comments in the Vagrantfile as well as documentation on `vagrantup.com` for more information on using Vagrant. You can view the Vagrantfile: cat Vagrantfile Start the VM with the command: vagrant up Sample Output: Bringing machine 'default' up with 'virtualbox' provider... ==> default: Importing base box 'generic/ubuntu2004'... ==> default: Matching MAC address for NAT networking... ==> default: Checking if box 'generic/ubuntu2004' version '4.1.6' is up to date... ==> default: Setting the name of the VM: Vagrant_default_1660834980416_30148 ..... default: Vagrant insecure key detected. Vagrant will automatically replace default: this with a newly generated keypair for better security. default: default: Inserting generated public key within guest... default: Removing insecure key from the guest if it's present... default: Key inserted! Disconnecting and reconnecting using new SSH key... ==> default: Machine booted and ready! ==> default: Checking for guest additions in VM... After this, you will have the VM created and running on your hypervisor. For VirtualBox For KVM Creating a Custom Vagrantfile It is also possible to create your own Vagrantfiles to run the VMs. This can be done as shown: vim Vagrantfile Add the lines below replacing them appropriately: # -*- mode: ruby -*- # vi: set ft=ruby : ENV['VAGRANT_DEFAULT_PROVIDER'] = 'virtualbox' Vagrant.configure("2") do |config| ##### DEFINE VM ##### config.vm.define "centos01" do |config| config.vm.hostname = "centos7.example.com" config.vm.box = "centos/7" config.vm.box_check_update = true end end Now start the VM with the command: vagrant up SSH into the machine You can ssh to the VM with the Vagrant command below: $ vagrant ssh vagrant@ubuntu2004:~$ You are now set to interact with your VM as preferred. To terminate the session. use CTRL+D or the logout command: $ logout Connection to 192.168.121.125 closed. File shares Synced/shared folders are configured within your Vagrantfile using the config.vm.synced_folderparameter. For example, we can choose to share the local vagrant folder by adding the lines below to the Vagrantfile. Vagrant.configure("2") do |config| # other config here config.vm.synced_folder "/home/rocky9/Vagrant/", "/vagrant" ...... end The first parameter represents the path on the local machine /home/rocky9/Vagrant/ for this case and the second is the path to be created on the guest machine Reload the VM to apply the changes vagrant reload Vagrant will automatically mount /vagrant directory which is synced with the directory containing the Vagrantfile on your host system. This can be verified once you SSH into the VM as shown: $ vagrant ssh $ ls /vagrant/ Vagrantfile To test if you can sync files between the host and guest systems, add a new file in the VM’s vagrant directory: vagrant@vagrant:~$ touch /vagrant/share_test
End the session: $ exit Verify if the file exists in the local vagrant directory: $ ls share_test Vagrantfile Ansible Scripts It is also possible to provision VMS using Ansible playbooks. The Vagrant Ansible provisioner is the tool that allows you to perform all this. You need to have: Ansible installed on your Vagrant host. a recent version of OpenSSH that supports ControlPersist on your Vagrant host. Now you can have the simplest Vagrantfile configuration as shown: Vagrant.configure("2") do |config| # # Run Ansible from the Vagrant Host # config.vm.provision "ansible" do |ansible| ansible.playbook = "playbook.yml" end end More on how to use the Vagrant Ansible provisioner has been covered in the guide below: How To Use Ansible Playbook With Vagrant up 3. Teardown an Environment We have explored how to quickly set up a development environment. It is time we know how to stop, shut down and delete the environment. List the available vagrant boxes with the command: $ vagrant box list centos/7 (libvirt, 2004.01) centos/8 (libvirt, 1905.1) generic/ubuntu2004 (libvirt, 3.0.20) Suspend a VM Suspending a VM stop and save the current running state. The command below can be used to suspend a VM: $ vagrant suspend ==> default: Saving VM state and suspending execution... To resume, you need to issue the command: $ vagrant up Bringing machine 'default' up with 'virtualbox' provider... ==> default: Checking if box 'generic/ubuntu2004' version '4.1.6' is up to date... ==> default: Resuming suspended VM... ==> default: Booting VM... ==> default: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes... default: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2222 default: SSH username: vagrant default: SSH auth method: private key ==> default: Machine booted and ready! ==> default: Machine already provisioned. Run `vagrant provision` or use the `--provision` ==> default: flag to force provisioning. Provisioners marked to run always will still run. The VM resumes with the state where you left off. Halt a VM Halting gracefully shuts down the guest operating system and powers off the VM. The command for this is: $ vagrant halt ==> default: Attempting graceful shutdown of VM... When you power on the VM with the vagrant up command, it takes time to start from a cold boot. Destroy a VM To remove all traces of the VM from your system you use the destroy command. This command will stop/power off the VM, and reclaim the disk space and RAM used. The command used is as shown below: $ vagrant destroy default: Are you sure you want to destroy the 'default' VM? [y/N] y You will be prompted to confirm for the VM to be destroyed. Conclusion That marks the end of this amazing guide on how to use Vagrant With VirtualBox / KVM on Rocky Linux 9. At this point, you should be able to provision and manage a VM on VirtualBox / KVM using Vagrant. I hope this was important to you.
0 notes
Text
Top 5 Server Management Software Tools 2022
A server is a computer that aids in storing, transmitting, and reception of data. In a nutshell, it fulfills the function of providing services. Servers can be anything from computers to software programs to storage devices.
Servers are incredibly sophisticated machines. It necessitates cold rooms, as well as regular updates and maintenance, to function correctly. In the absence of updates and maintenance, a company may encounter several issues that negatively impact its performance.
Several Top Server Management Software Tools 2022 work as a savior to avoid server-related problems. Let’s take a look.
LogicMonitor
LogicMonitor is a network monitoring and management platform delivered as a software-as-a-service (SaaS). It provides a customized and hybrid cloud-based infrastructure to the enterprise. The interface is hosted and accessed via the cloud, but the data collecting takes place on the network. LogicMonitor also works with both Windows and Linux operating systems.
With its installation, LogicMonitor promises an agentless and straightforward system. It automatically scans the network after installation to identify all connected devices, although you can also do it manually.
LogicMonitor comes with a user-friendly dashboard with several pre-built layouts. You can customize these templates as per your unique needs.
LogicMonitor may also create custom notifications and send them out via email and SMS. If virtualization is something you’re interested in, this fantastic tool supports VMware ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-V.
DataDog
Datadog’s main product is a SaaS-based server management service. Although it is a cloud-based solution, it can also monitor apps hosted on-premise. It’s a pleasant surprise to see that it provides APIs, services, over 350 integrations, and compatibility for various network protocols. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), and SSH are examples of network protocols (Secure Shell).
Its user-friendly interface presents data clearly and concisely. Customization, on the other hand, is complex with Datadog. However, with detailed guides and helpful pulldowns, it is possible to do so gradually.
Compared to other server management solutions, Datadog takes a unique approach to reporting. Filtering based on period, time and kind of events, and priority usually provides focused and easy search parameters.
Datadog’s installation is more complicated than LogicMonitor’s. Because it is a cloud-hosted product, the initial setup is relatively straightforward. Later stages, however, will necessitate the installation of additional agents on each host system in your network. A console-based technique employing a terminal is required for ESXi or NetFlow.
Adding new devices to an agent-based system can be a lengthy process. Because it lacks an automatic device detection feature, it must download a unique agent for each device or service.
ManageEngine OpManager
ManageEngine OpManager is a cost-effective alternative for organizations searching for a lightweight suit. It’s package software, not a SaaS, unlike Datadog and LogicMonitor.
This utility requires you to choose a database for storage and a path. It comes with Postgres as the default pathway, but you may upgrade to SQL Server for an additional fee.
For organizations searching for visualization, ManageEngine OpManager is an excellent choice. This technology well supports heavy hitters like VMWare and Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisors. With proper monitoring, it also quickly activates and disables.
Although it offers a variety of pre-configured alerts such as alarms, trap alarms, standard events, and Syslog alarms, the alert setting is a little complicated. ManageEngine Applications Manager Plug-In is a functionality offered as an add-on.
You can personalize the product and purchase additional features based on your needs.
Paessler PRTG Network Monitor
Paessler PRTG Network Monitor is a server management software solution that is both old and popular. With years of experience on the market, it has evolved into one of the most feature-rich platforms. However, it is deployed on-premise and does not have a cloud-based support system.
Paessler requires a Microsoft Windows Server machine, as we know that bundled software has specific requirements. That system should also have at least two CPU cores, three gigabytes of RAM, and 250 gigabytes of storage.
Although Paessler PRTG Network Monitor is hosted locally, it features a web-based interface, which is undoubtedly beneficial. This interface has a lot of features and is easy to use. Its network maps are the best on the market, giving you a thorough and precise picture of how well your network is doing.
Agentless server management is made more accessible with PRTG Network Monitor. It contains an auto-discover feature that populates all of your network’s devices. It can also be done manually by manually adding every device. You’ll need to provide an IP address and the type of device for this.
Progress WhatsUp Gold
Progress Another popular choice that’s been around for a while is WhatsUp Gold. You must purchase a license for each device you own using this software.
WhatsUp Gold is a Windows-based application that must be downloaded and installed locally. However, the installation process is not complicated; you must choose installation paths and grant network access.
Configuration alerts are a breeze with WhatsUp Gold. Its policies are assigned based on three statuses: down, maintenance, or up. However, if you want a lot of customized alerts, this isn’t the way to go. It also lacks a customized alert for reports. However, it provides a detailed examination of the pertinent data. It’s also possible to save it as a Microsoft Excel or Adobe Acrobat file.
Consider your current infrastructure before selecting a competent server management software tool. It would also help ensure that the platform chosen is compatible with all devices. Then they must assess which management elements are required and whether monitoring capabilities are sufficient.
If you own a small business, your needs will differ from those of a large corporation. If you still have questions regarding Top Server Management software tools 2022, don’t hesitate to contact Orion eSolutions. With vast industry experience, we ensure the best delivery and server software tools.
0 notes
Text
Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0

Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0 Crack
Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0 Windows 10
Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0 Download Free Trial
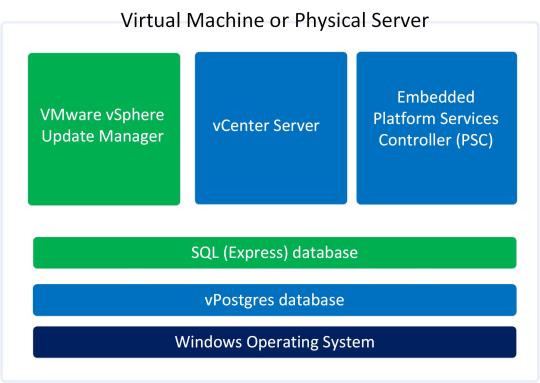
In previous post of this series, we’ve learnt about vCenter Server Architecture, such as its components, services, and Platform Services Controller (PSC). If you’ve missed previous posts of this series, you can find them here.
In this post, we’ll learn installing vCenter Server step-by-step in windows environment. When vCenter Server is installed, following services are also installed with it.
For complete guidance regarding vCenter Server installation and configuration, you can follow VMware vSphere 6.0 Part 2 – vCenter, Alarms and Templates course. In next post, we’ll see how vSphere Web Client works and used for managing and controlling vCenter Server. VMware's vCenter server appliance 6.0 has the same scalability numbers as the windows installable server. It seems that there is no reason to avoid the installation of vCenter appliance again. Buy one Microsoft windows server license less next time.I will not go through an installation guide since there are plenty of these published on the. Click Finish to complete the installation. Installing the VMWARE vCenter Server Appliance 6.0. Double Click the index.html file in the root of the DVD. Ensure pop up blockers to no block the Client Integration Plugin. Select Allow, so the VMware Client Integration Plug-In can access the operating system.
vCenter Server
vSphere Web Client (enables to connect to vCenter Server instance using web browser)
VMware Inventory Service (stores vCenter Server application and inventory data)
vSphere Auto Deploy (support tool that can provision many physical hosts with ESXi software)
vSphere ESXi Dump Collector (configure ESXi to dump the VMkernel memory to a network server, rather than to a disk)
vSphere Syslog Collector (support tool that provides a unified architecture for system and network logging)
vSphere Web Client directly communicates with vCenter Server, and vSphere Client is used to directly communicate with ESXi hosts. vCenter Server provides access to the ESXi hosts via an agent called vpxa.
Minimum Hardware Requirements for vCenter Server
Before installing and configuring vCenter Server, we should consider minimum hardware requirements. Following are the minimum hardware requirements. We’re installing vCenter Server in home-lab environment, so we’ll install it as embedded PSC with 2CPUs and 4GB RAM.
Let’s start the process:
Step 1: Download the vCenter Server ISO from VMware site. After downloading, mount it on CD/DVD drive
Step 2: Open the mounted path and double click the Autorun.exe to start the process.
Step 3: Select vCenter Server for Windows and click Install to begin the installation.
Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0 Crack
Step 4: Windows Installer preparing to install in process, click Next to install vCenter Server 6.0.0
Step 5: Accept the License Agreement and click Next
Step 6: Select Embedded Deployment and click Next
Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0 Windows 10
Step 7: Enter the System Name as FQDN and click Next
Step 8: Select Create New vCenter Single Sign-On domain, enter vCenter Single Sign-On password, Confirm password, Site name, and click Next
Step 9: Select Use Windows Local System Account and click Next
Vmware Vcenter Server 6.0 Download Free Trial
Step 10: Select Use an embedded database (vPostgres) and click Next
Step 11: Verify Configure Ports and click Next
Step 12: Leave Destination Dictionary default and click Next
Step 13: Review your settings and click Install
Step 14: vCenter Server installation process will start now, and will take some time to install.
Step 15: Installation process is completed, click Finish or Launch vSphere Web Client
vCenter Server installation is completed when you click Finish button. When you’ll click on Launch vSphere Web Client, it will launch vSphere Web Client. For complete guidance regarding vCenter Server installation and configuration, you can follow VMware vSphere 6.0 Part 2 – vCenter, Alarms and Templates course. In next post, we’ll see how vSphere Web Client works and used for managing and controlling vCenter Server.
I hope you’ve enjoyed reading this post, if you have any query or suggestion, please feel free to write in comments. Thanks a lot.
Author: Nisar Ahmad
Systems Engineer, double VCP6 (DCV & NV), 5 x vExpert 2017-21, and the owner of My Virtual Journey, with experience in managing a Datacenter environment using VMware and Microsoft Technologies. This blog mainly covers virtualization and cloud technologies but also covers some other technologies such as Cyber Security, Quantum Computing, etc.
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone 6.0 | 14 May 2015 | Build 2716716
Check periodically for additions and updates to these release notes.
What's in the Release Notes
These release notes cover the following topics:
Introduction to Converter Standalone
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone provides an easy-to-use solution to automate the process of creating VMware virtual machines from physical machines (running Windows and Linux), other virtual machine formats, and third-party image formats. Through an intuitive wizard-driven interface and a centralized management console, Converter Standalone can quickly and reliably convert multiple local and remote physical machines without any disruptions or downtime.
Benefits
Convert physical machines running Windows or Linux operating systems to VMware virtual machines quickly and without any disruption or downtime.
Convert third-party image or virtual machine formats such as Parallels Desktop, Symantec Backup Exec System Recovery, Norton Ghost, Acronis, StorageCraft, Microsoft Virtual Server or Virtual PC, and Microsoft Hyper-V Server virtual machines to VMware virtual machines.
Enable centralized management of remote conversions of multiple physical servers or virtual machines simultaneously.
Ensure conversion reliability through quiesced snapshots of the guest operating system on the source machine before data migration.
Enable non-disruptive conversions through hot cloning, with no source server downtime or reboot.
What's New
The VMware vCenter Converter Standalone 6.0 provides:
Support for virtual machine hardware version 11.
Compatibility with vSphere 6.0 and Workstation 11.
Support for additional guest operating systems: Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7, Ubuntu 14, CentOS 6-7, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows 8.1.
Support of pure IPv6 environments.
Proxy mode.
File-level cloning for volumes with ReFS file system.
Support for XFS file system.
Support for predictable network interface names.
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone 6.0 Support Notice
VMware vCenter Converter Standalone 6.0 is the last release of the product to support third-party backup images and virtual machines as sources for conversion. This capability will be discontinued in the next release. If you use this capability, you should start planning your transition. For the full list of the third-party backup images and virtual machines see Interoperability.
Installation Notes
You can download, install, and run VMware vCenter Converter Standalone in English only.
Users with limited rights cannot install Converter Standalone on Windows. You must log in as an administrator to install Converter Standalone.
Platforms
You can install VMware Converter Standalone 6.0 on the following platforms:
Windows Server 2003 R2 SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Vista SP2(32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Server 2008 SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Server 2008 R2 (64-bit)
Windows 7 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows 8 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows 8.1 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Server 2012 (64-bit)
Windows Server 2012 R2 (64-bit)
Interoperability
Converter Standalone 6.0 supports the following sources.
Physical machine running an operating system noted in Supported Guest Operating Systems
VMware Desktop products
Workstation 10.x and 11.0
Fusion 6.x and 7.0
Player 6.x and 7.0
VMware vCenter virtual machines
vSphere 6.0
vSphere 5.5
vSphere 5.1
vSphere 5.0
vSphere 4.1
vSphere 4.0
Third-party backup images and virtual machines - to be discontinued. See Support notice.
Acronis True Image Echo 9.1 and 9.5, and Acronis True Image Home 10 and 11 (.tib)
Symantec Backup Exec System Recovery (formerly LiveState Recovery) 6.5, 7.0, 8.0, and 8.5, and LiveState Recovery 3.0 and 6.0 (.sv2i format only)
Norton Ghost version 10.0, 12.0, and 14.0 (.sv2i format only)
Parallels Desktop 2.5, 3.0, and 4.0 (.pvs and .hdd). Compressed disks are not supported
Parallels Workstation 2.x (.pvs). Compressed disks are not supported. Parallels Virtuozzo Containers are not supported.
StorageCraft ShadowProtect Desktop, ShadowProtect Server, ShadowProtect Small Business Server (SBS), ShadowProtect IT Edition, versions 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.1, and 3.2 (.spf)
The Microsoft VHD format for the following sources:
Microsoft Virtual PC 2004 and Microsoft Virtual PC 2007 (.vmc)
Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 and 2005 R2 (.vmc)
For conditions and limitations about converting Backup Exec System Recovery, ShadowProtect, and Consolidated Backup images, see the VMware vCenter Converter Standalone User's Guide.
Depending on the selected source, you can convert it to the following destinations.
VMware vCenter virtual machines
ESX 4.0 and 4.1
ESXi 4.0, 4.1, 5.0, 5.1, 5.5 and 6.0
vCenter Server 4.0, 4.1, 5.0, 5.1, 5.5 and 6.0
VMware Desktop virtual machines
VMware Workstation 10.x and 11.0
VMware Player 6.x and 7.0
VMware Fusion 6.x and 7.0
Earlier releases of Converter Standalone (versions 3.x, 4.x and 5.x) might not be compatible with VMware vSphere 6.x.
Supported Guest Operating Systems
Converter Standalone 6.0 supports the following guest operating systems:
Windows Server 2003 R2 SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Vista SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Server 2008 SP2 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Server 2008 R2 (64-bit)
Windows 7 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows 8 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows 8.1 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Windows Server 2012 (64-bit)
Windows Server 2012 R2 (64-bit)
CentOS 6.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
CentOS 7.0 (64-bit)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.x (64-bit)
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
Ubuntu 12.04 (32-bit and 64-bit)
Ubuntu 14.x (32-bit and 64-bit)
CAUTION: During cloning of powered on Linux machines, Converter Standalone 6.0 preserves the following source file systems on the destination: ext2, ext3, ext4, reiserfs, vfat, and xfs. All other source file systems are converted into ext3 or ext4 file systems on the destination virtual machine.
For more information about the operating systems supported by Converter Standalone and other system requirements, see the VMware vCenter Converter Standalone User's Guide.
Prior Releases of Converter Standalone
Features from prior releases of Converter Standalone are described in the release notes for each release. To view release notes for prior releases of Converter Standalone, click one of the following links:
Known Issues
The Converter Standalone 6.0 release contains the following known issues:
Installation
If the name of the Converter Standalone installation directory contains non-ASCII characters, you might experience conversion and configuration problems If the name of the Converter Standalone installation directory contains non-ASCII characters, the following issues might occur:
Conversion and configuration of Windows virtual machines might fail with an error message Unable to reconfigure destination virtual machine. In the vmware-converter-worker.log, this error generates a message similar to Error 3 (error restoring key: Unknown error 3 (0x3) (3)) restoring registry key C:ã—ã™ãŸã•ã‹ãn°...dataSKUNKWORKS_FILLER into... .
If you try to convert a Linux physical machine, you might receive an error message in the Convert Machine wizard Unable to obtain hardware information.
You must restart machines that run 64-bit Windows Vista or later before re-installing Converter Standalone If you uninstall Converter Standalone from a 64-bit Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 machine and do not restart it, a subsequent Converter Standalone installation might fail with the following error message: Error 29144. Could not install service Vstor2 MntApi 1.0 Driver (shared). Please reboot and try to install again. Workaround: Restart the Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 machine and try installing Converter Standalone again.
Converter Standalone installer removes Workstation 6.5.x remote agents without notification When you use Workstation 6.5.x to hot-clone a Windows source machine, Workstation deploys a remote Workstation agent on the source. If you choose to leave the remote agent on that source and then install Converter Standalone on the same machine, the Converter Standalone installer uninstalls that agent without any warning messages.
Users with limited rights cannot install Converter Standalone on Windows If you are logged in to Windows as a non-administrator user, the following error message is displayed while the InstallShield is extracting files for Converter Standalone installation: Unable to save file: C:WINDOWSInstaller The system cannot find the path specified. The error is displayed because limited users do not have the required write permissions. Workaround: Select the %TEMP% directory to extract the installation files:
Click OK in the error message. A Save As dialog box appears.
Browse to the Temp folder of the current user (for example, C:Documents and Settings'username'Local SettingsTemp) and click OK.
NOTE: You still need to log in as an administrator to install Converter Standalone.
You cannot install vCenter Converter 4.2.1 on the same machine where you have already installed Converter Standalone 6.0 If you install Converter Standalone 6.0 and then install vCenter Converter 4.2.1 server on the same machine, downloading the vCenter Converter 4.2.1 plug-in from vSphere Client fails. Workaround: First install vCenter Converter 4.2.1 and then install Converter Standalone 6.0.
General
Disk-based cloning of a powered off machine image to a virtual datastore destination might fail You might not be able to perform a disk-based cloning of a powered off machine image to a virtual datastore destination. The conversion might fail at 1% with a message Operation expirienced network error if the size of the source disk is not a number that is a multiple of a MB. Workaround: Use volume-based cloning, if the option is available.
Converter Standalone might display an incorrect version of the Windows operating system Converter Standalone might display incorrect operating system information for running machines or virtual machines with Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 and later.
If the operating system is Windows 8.1, Windows 8 is displayed.
If the operating system is Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012 is displayed.
Workaround: None. Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 work as expected despite the incorrect operating system displayed.
Creation of virtual machine with thick destination disk type of certain size fails on VSAN datastore even if it seems to have enough space If you try to perform disk-based conversion with thick destination disk type of certain size on VSAN datastore, the creation of virtual machine might fail with the following error 'converter.fault.InsufficientManagedDiskSpace', even if it seems to have enough space. Workaround: Change the destination disk type to thin.
If you try to convert a source physical or virtual machine to a managed destination by using thick provisioned disks with large empty spaces on them, the conversion task might fail If you try to perform a disk-based cloning of a physical or virtual machine to a managed destination by using thick provisioned disks with large empty spaces on them, the conversion task might fail with an error message Unable to clone disk source_disk on the virtual machine virtual_machine_name. The following messages appear in the log file:
(03200 warning 'Default') (,0) (NFC ERROR) NfcNetTcpRead: bRead: -1 (03200 warning 'Default') (,0) (NFC ERROR) NfcNet_Recv: requested 264, recevied only 0 bytes (03200 warning 'Default') (,0) (NFC ERROR) NfcFile_Stream: Failed to get message from source (03200 warning 'Default') (,0) (NFC ERROR) NFC_NETWORK_ERROR
The destination ESX server must return an acknowledgement after each processed NFC write request. If the source sends a large block of zeroes that must be written it might take a long time for the ESX to return the acknowledgement. Thus, the Converter assumes that the operation has timed out and closes the connection, no matter that the ESX server is still writing to the target disk.
Workaround: Change the destination disk type to thin.
When converting hosted virtual machines with unpartitioned disks, you might not be able to obtain hardware information about the source When converting hosted virtual machines with unpartitioned disks, you might not be able to obtain hardware information about the source. In such case, the following error messages might appear in the worker log:
(01628 warning 'Default') Partition:Invalid sector magic number.
(01628 warning 'Default') ERROR: Failure during open: Reading disk signature
(01628 error 'Default') (BaseDiskSetComputer::DoOpen) OpenDisks failed, mntapi error: 32.
Workaround: Remove the unpartitioned disks from the conversion job.
A running P2V conversion job fails if you create a new conversion job for the same Windows source machine and use a different port to deploy the Converter Standalone agent If, while running a P2V conversion job, you start creating another conversion job for the same powered on Windows source machine, and specify a port for the connection, Converter Standalone deploys the Converter Standalone agent using the port you specified. If the connection port is different from the one that is being used for the already running conversion job, both jobs fail. The following error message appears in the Job summary tab for the first conversion job: FAILED: A general system error occurred: No connection could be made because the target machine actively refused it. The following error message appears in the Job summary tab for the second conversion job: FAILED: Unable to create a VSS snapshot of the source volume(s). Error code: 2147754774 (0x80042316).
You cannot copy running conversion or configuration jobs If you open the Copy As New wizard for a running configuration or conversion job when the source is a virtual machine or a backup image and you click Next, the wizard displays the error message Unable to obtain hardware information for the selected machine. Workaround: Wait for the job to complete before selecting Copy as New in its pop-up menu.
Linked Cloning of source images greater than 2GB to a network share that does not support large files fails Creating linked clones from source images that are larger than 2GB to a network share that does not support large files (for example, to a Linux SMB share) fails. Converter Standalone does not split the source files into smaller chunks. If the source is larger than the supported file size on the destination, the conversion tasks fails.
Creating a conversion job to convert a standalone VMware source with a VMDK file greater than 2GB from a network share that does not support large files, fails If you select a standalone virtual machine source with VMDK file greater than 2GB residing on a remote network location that does not support large files (for example, Linux SMB share), the following error message appears in the Converter wizard on clicking Next or View source details: Unable to obtain hardware information for the selected machine. Workaround: Map the network shared folder to the machine where Converter Standalone runs, and select the source from there.
Converter Standalone cannot detect the power state of VMware Workstation or other VMware hosted source virtual machines if they are located on a read-only network share If the source machine is a Workstation or another VMware hosted source and is located on a network share with read-only permissions, Converter Standalone cannot detect if the source is powered on or suspended. This might lead to data inconsistency on the destination machine if changes are made to the powered on source virtual machine during conversion. Workarounds:
Verify that the source virtual machine is powered off prior to conversion.
Provide write privileges to the network share where the source virtual machine resides.
Conversion jobs from and to ESX hosts that are not connected to vCenter Servers fail if the number of disks on the source machine is more than nine When converting a source machine that has more than nine disks, conversion fails with the following error in the log file: Error on logout (ignored): Operation timed out SSLStreamImpl::BIORead (3BBA4E8) timed out. The error is due to the limited number of NFC connections that can be established to ESX hosts that are not connected to vCenter Server instances. Workaround: Connect to the destination ESX host through a vCenter Server. In this case, the number of source disks is limited to 27 for ESX and to 23 for ESXi hosts.
Converting source volumes with unrecognized file systems might prevent the destination virtual machines from starting While you are setting up a volume-based cloning task in one of the Converter Standalone wizards, the volume name might be missing in some rows of the Source Volumes tab. This means that Converter Standalone does not recognize the file system on those volumes. The destination virtual machine that is created as a result of such a conversion task might fail to start up. Nevertheless, Converter Standalone copies the source volume data to the destination using block-level copying. Workaround: configure the destination virtual machine after the conversion.
Converting standalone VMware sources with a VMDK file greater than 2GB to a hosted destination that resides on a network share that does not support large files, fails If you select a standalone virtual machine source with VMDK file greater than 2GB and try to convert it to hosted destination residing on a remote network location that does not support large files (for example, Linux SMB or NFS share), the conversion job might fail with one of following error messages:
Unable to connect to the virtual disk
Remote server closed connection after 0 response bytes read
An error occurred during an operation on a virtual disk
If conversion is successful, the following error message related to the VMDK file might appear when you power on the destination virtual machine: Internal Inconsistency errors Workaround:
In the main application window of Converter Standalone, right-click the failed job and select Copy As New...
Go to the Options page and select Data to Copy.
In the Data to Copy pane, select the volumes to copy and click Advanced.
On the Destination layout tab, select Split not pre-allocated or Split pre-allocated as the destination disk type.
Click Next to view a summary of the conversion job.
On the Ready to Complete page, click Finish to resubmit the job.
Converter Standalone is unable to detect the system volume if it resides on a SCSI disk and IDE disks are present in the source machine On source machines with SCSI and IDE disks, Converter is unable to detect the system volume if the system volume resides on a SCSI disk. Converter only checks the first IDE disk in such configurations.
If the hardware configuration of the source machine is modified while the Conversion wizard is open, you need to restart the conversion wizard if you want to view correct source details Source machine details are retrieved per wizard session, as this is a time-consuming process. If some changes occur on the source machine (such as adding memory or hard drives) after this information is retrieved, the Conversion wizard does not show information about the changes. Workaround: Restart the conversion wizard.
Cloning a source that contains file system errors might result in a damaged virtual machine See Cloning a source that contains file system errors may result in a damaged copy (KB 1006689).
Timeout on SSL handshake when converting over a WAN link Converter Standalone does not support conversion over a WAN. When trying to perform a conversion over a WAN link, you might experience an SSL timeout because the timeout for SSL handshakes is two minutes. Workaround:
To avoid the two-minute handshake, perform a conversion to a hosted destination machine (for example, Workstation) in the same LAN.
Copy the temporary virtual machine and send it over the WAN to the remote site. If the intended destination is a Workstation virtual machine, this completes the process.
If the intended destination is ESX, import the Workstation virtual machine to the ESX server.
User Account Control (UAC) prevents installing Converter Standalone agent if you are not using the default Administrator account to connect to a powered on source machine If you are setting up a task to convert a powered on source machine that runs Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows Server 2012, or Windows 8 and you use a non-default Administrator account to log in to the source machine, the following error message might appear when you try to install Converter Standalone agent on the source machine: Insufficient permissions to connect to xxxxxxx. Here xxxxxxx is the IP address of the source machine. This is because Converter Standalone server cannot install Converter Standalone agent when UAC is enabled and you are logged in to the source as non-default Administrator user. Workaround: Disable the UAC on the source machine before you start the Conversion wizard. You can search the Microsoft Web site for procedures on disabling the UAC depending on the source operating system. For Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8, in addition to disabling UAC, you must perform the following steps:
In the Windows Start menu, type gpedit.msc. The Local Group Policy Editor opens.
Navigate to Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options.
Disable the Run all administrators in Admin Approval Mode setting.
Restart.
The Reconfigure Virtual Machine wizard does not display correctly the vDS port group name When you reconfigure a virtual machine that uses dvSwitch and you navigate to the Network interface settings pane, the Network name text box does not display the name of the dvSwitch after the port group name. Only port group is displayed instead.
The reported network transfer rate might not be correct The reported network transfer rate might be higher than the actual one because of the inherent compression used by the network protocol. This does not affect the network throttling.
Adding a virtual machine to a domain might fail if you specify a fully qualified user name When configuring a virtual machine, you might not be able to add the virtual machine to a domain if you use a fully qualified user name (DOMAIN_NAMEUSER_NAME). Workaround: Specify the user name without including the domain name.
Conversion of a physical machine running Microsoft Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 with a BCD manager (Boot Manager for Windows Vista) and later might fail If you try to convert a physical machine with a BCD manager, the P2V conversion might fail in the following cases:
Microsoft Windows Vista or later is installed on the source physical machine, which is a dual-boot machine currently running Microsoft Windows XP or Windows Server 2003.
Microsoft Windows Vista or later is installed as a second operating system on the source physical machine and later is removed, but the BCD manager is left on the source machine.
Workaround 1: In case of a dual-boot machine conversion :
Boot the later version of Windows (Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7).
Perform a physical source conversion.
On the newly created virtual machine, boot a repair CD for the earlier version of Windows (Windows XP or Windows Server 2003).
Remove the BCD manager and revert the operating system to its compatible boot process.
Shut down the virtual machine and reconfigure it by using the Converter Standalone configuration wizard. Now you can boot the machine.
Workaround 2: In case of converting a source machine running Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 with a BCD manager:
On the source machine, boot a repair CD of the corresponding operating system.
Remove the BCD manager and revert the operating system to its compatible boot process.
For more information on how to repair BCD, see the Microsoft knowledge base article Windows no longer starts after you install an earlier version of the Windows operating system in a dual-boot configuration. Submitting a job might fail with The specified parameter was not correct:'info.owner'message If Converter Standalone is installed in a client-server mode and you have connected by using a username, which is the same as the computer name, submitting a job might fail with The specified parameter was not correct:'info.owner' message. Workaround: Connect by using a different user account with administrative rights. You might not be able to convert more than nine disks at once On ESX 3.5 and 4.0, conversion might fail if you try to convert more than nine disks. Workaround: Perform conversion in multiple steps to convert the disks in portions of up to nine. Then, attach all the disks to the target machine.
Windows Sources
If you convert a source machine with Windows 2008 and above operating system, some disk(s) may be offline or read-only If you convert a source machine with Windows 2008 and above operating system, some disk(s) in the destination VM may be offline or read-only. Workaround:
If the disk is offline, in the Disk Management console diskmgmt.msc, right-click the disk and select Online.
If the disk is read-only, run diskpart.exe with administrator's rights, and then run the following commands:
DISKPART> list disk Lists all disks and their status: online/offline.
DISKPART> select disk # Where '#' is the number of disk in offline state.
DISKPART> attribute disk clear readonly
DISKPART> online disk
Repeat steps 2-4 for every offline disk.
DISKPART> exit
Configuration of Windows virtual machines with multiple active partitions might not complete For Windows virtual machines with multiple active partitions, Converter Standalone might not recognize the boot partition and might not be able to complete the reconfiguration of the destination virtual machine. In such cases, after the conversion job is 96-98% complete, the conversion job status changes to Failed and an error message appears. For example: FAILED: Unable to find the system volume, reconfiguration is not possible. In the Worker/Agent log this issue is identified by the following statement: (#### warning 'Default') ERROR: (Mntapi_GetFirstBootDisk) more that *one* active volume found. Current active disk #0, another active disk #1. Workaround 1: Mark all non-boot active partitions on the destination machine as inactive and run configuration on the destination machine.
Boot into Windows Recovery Console on the destination machine.
Run diskpart.exe. The diskpart command prompt appears.
(Optional) To list the available disks, enter list disk.
Enter select disk <disk_number>.
(Optional) To list the partitions on the selected disk, enter list partition.
Enter select partition <partition_number>.
Enter inactive.
Repeat steps 4-7 to mark another partition as inactive.
Power off the destination machine.
Run Converter Standalone and configure the destination machine.
Workaround 2: Mark all non-boot active partitions on the source machine as inactive and attempt to run the conversion again.
On the source machine, run diskpart.exe. The diskpart command prompt appears.
(Optional) To list the available disks, enter list disk.
Enter select disk <disk_number>.
(Optional) To list the partitions on the selected disk, enter list partition.
Enter select partition <partition_number>.
Enter inactive.
Repeat steps 2-6 to mark another partition as inactive.
Run Converter Standalone and start the conversion again.
Conversion of a local powered on source machine fails at 1% If you select This local machine as a conversion source and a Converter Standalone agent from a previous Converter Standalone version is installed on the source machine, the conversion task fails at 1%. The following error message appears in the Status line of the Task progress tab: FAILED: Unable to create a VSS snapshot of the source volume(s). Error code: 127 (0x0000007F). This is because the Converter Standalone installer cannot upgrade previous versions of Converter Standalone agents. Workaround: Manually uninstall Converter Standalone agent from the source machine and create a new conversion task.
Converter Standalone worker process stops responding if you try to copy a configuration job during guest operating system customization If you right-click a running configuration job and select Copy As New while the destination machine is being customized, Converter Standalone worker process stops responding. Workaround: Wait for the configuration job to complete before you copy it.
Subsequent P2V conversions of remote source machines that run 64-bit Windows Vista or later might fail after a successful conversion If you convert successfully a remote source machine that runs 64-bit Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 operating system and then try converting it again, the conversion fails with the error message Converter Standalone Agent installation failed on x.x.x.x Error code: 1603, where x.x.x.x is the IP address of the source machine. This error message might occur if automatic uninstall of remote Converter Standalone agent has been enabled during the first successful conversion. Workaround: Restart the remote source machine and try running the conversion task again.
Converter Standalone does not preserve disabled network adapters during conversion of physical machine sources that run on Windows During P2V conversion of Windows source machines, Converter Standalone does not detect disabled network adapters on the source and does not preserve them on the destination virtual machine. Workaround: On the Options page of the Converter Standalone wizard, click Networks to add network adapters to the destination virtual machine.
Microsoft Windows Vista reboots repeatedly after customization Providing wrong customization information might cause the destination virtual machine to reboot repeatedly if the source operating system is Microsoft Windows Vista. During conversion or configuration, if you choose to customize Microsoft Windows Vista and provide wrong customization information, for example an invalid serial key, the customized destination reboots repeatedly. This is a known issue with Microsoft Windows Vista. Workaround: Make sure that the provided customization information is valid.
Converter Standalone does not support cloning powered on Windows Server 2008 sources with FAT/FAT32 volume file system VSS under Windows Server 2008 does not support FAT/FAT32. Trying to convert a FAT/FAT32 volume causes the conversion task to fail. Workaround: Deselect all FAT/FAT32 volumes on the Options page of the Conversion wizard.
Converter Standalone remote agent does not notify the user about Converter 3.0.x or 4.0.x remote agents that have been installed on the source system during remote hot cloning process If Converter Standalone is converting a remote machine source that already has a remote agent from Converter version 3.0.x or 4.0.x, it uninstalls the old remote agent without issuing a notification or warning message. This prevents older Converter versions from converting this source machine later.
Previous Converter versions cannot convert source machines that have Converter Standalone 6.0 agent installed on them Converter Standalone 6.0 agent is deployed on the source machine during conversion. If Converter Standalone 6.0 agent is not uninstalled after the conversion, older Converter versions cannot deploy their agents on top of the newer Converter Standalone agent version. Therefore, you cannot use previous Converter versions to convert sources that have already been converted with Converter Standalone 6.0. Workaround: Uninstall Converter Standalone 6.0 agent before trying to convert the source with an older Converter version.
Stopping Converter Standalone processes during file-level cloning might cause the machine that runs the Converter Standalone server service to restart During file-level cloning of source systems that run Windows XP or Windows Server 2003, if any of the following Converter Standalone process is forcibly stopped, the machine on which the stopped process was running might automatically reboot.
VMware Converter Standalone Integrated Worker
VMware Converter Standalone Integrated Agent
This behavior is not consistent and depends on the Windows version and patch level.
Workaround: Do not stop any Converter Standalone services on the source machine during file-level cloning. For more information and hot fix, check the Microsoft site Error message when a Delayed Write Failure event is reported in Windows Server 2003: 'Stop 0x00000019 - BAD_POOL_HEADER' or 'Stop 0xCD PAGE_FAULT_BEYOND_END_OF_ALLOCATION'.
Converter Standalone does not change PIC HAL to APIC HAL during conversion of Windows source machines If the source to convert is running a Programmable Interrupt Controller (PIC) HAL, Converter Standalone does not change the PIC HAL to an Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) HAL in the destination virtual machine. As a result, the destination virtual machine might not boot or might fail to perform as expected. To find out which HAL is running, go to Windows Device Manager and select Computer in the list of devices. If it displays Standard PC or Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) PC, you are running a PIC HAL. Workaround: VMware virtual machines are APIC computers. If your source computer is a PIC computer that runs a PIC HAL, you must update the HAL in the destination virtual machine to APIC HAL after the conversion. For more information on configuring the correct HAL, check the Microsoft Web site HAL options after Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 Setup. Note: Microsoft does not support running a PIC HAL on an APIC computer. If your source is an APIC computer running a PIC HAL, you must configure the correct HAL on the source machine before starting the conversion.
Owner name and organization are not displayed properly after customizing the guest operating system After customizing the guest operating system, Unicode characters used for owner name and organization on the Computer Information page do not appear the way they were set in the Conversion or the Configuration wizard. For all Windows operating systems except Windows Vista, customization parameters such as user name and organization must use characters only from the local encoding of the default user profile of the guest. For example, you can use Japanese characters for the user name only on a guest whose default user profile's local encoding is set to Japanese. These restrictions do not apply to Windows Vista guests because Windows Vista uses a UTF-8 encoded XML file to store the Microsoft sysprep parameters. Earlier versions of Windows use the sysprep.inf file, and the Microsoft Windows mini-setup process reads that file in the local encoding only. Workaround: Either avoid Unicode characters when assigning owner name and organization name for the destination virtual machine, or use the workaround described at: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/310441/.
Converter can convert FAT/FAT32 volumes during hot cloning only if the source machine has at least one NTFS volume For source machines running under Windows versions earlier than Windows Server 2008, VSS can take snapshots of FAT/FAT32 volumes only if the source machine has at least one NTFS volume. For all operating systems that support volume-based cloning, you need at least one NTFS volume for VSS to work.
Converter Standalone agent does not start automatically after reboot If the source machine starts up too slowly, Converter Standalone agent might not start automatically after the source machine is restarted. Workaround: Start the Converter Standalone agent manually:
Right-click My Computer and select Manage.
In the Computer Management window, select Services and Applications >Services on the left.
In the list on the right, double-click VMware Converter Standalone Agent.
Click Start to start the process.
Click Apply followed by OK.
The source virtual machine does not have the appropriate drivers The following error message appears in the log file when reconfiguration fails because the appropriate drivers are missing from the source operating system: Unable to find symmpi.sys in the specified CAB files This is usually observed in Windows Server 2003 SP1. Workaround:
Back up the virtual machine created during the failed conversion.
Attach the VMDK file containing the system folder to another Windows Server 2003 virtual machine.
Replace the WINDOWSDriver Cachei386driver.cab file in the destination virtual machine with a version of the driver.cab file that includes the missing driver from the helper virtual machine.
Detach the VMDK file from the helper virtual machine and run the Configure Machine wizard on the destination virtual machine.
Sysprep deletes drive letter mappings during customization If you choose customization options and the destination virtual machine fails at a Please Wait screen after the second sysprep reboot, you need to rerun the conversion task without customization. This issue occurs because of a problem with Microsoft sysprep, which deletes the drive letter mappings, preventing access to certain files.
You cannot import a Windows source with 'signature()' in the boot.ini file You cannot import a Window source with 'signature()' in the boot.ini file. If you import a Windows live source with 'signature()' in the boot.ini file, and try to reconfigure and convert it, the reconfiguration fails and this results in a conversion error. If you try to convert the source without reconfiguration, the conversion succeeds but the destination cannot boot. For more information on 'signature()' go to http://support.microsoft.com/kb/227704.
Linux Sources
Converted SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 machine might not have network connectivity If you convert a SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10 machine, the converted virtual machine might not have network connectivity.
Workaround:
In the /etc/udev/rules.d/30-net_persistent_names.rules.d/30-net_persistent_names.rules file, comment out the lines that start with SUBSYSTEM and contain the old MAC addresses.
Check the /etc/sysconfig/network directory. If there is no ifcfg-eth0 file and there is a file of the form ifcfg-if-mac_address, rename it to ifcfg-eth0.
Restart the network service.
Converted powered on Linux machines cannot start up If you convert a powered on Linux machine that has a non-standard LVM filter saved in the /etc/lvm.conf file, the converted virtual machine might fail to start up. The following error message appears in the virtual machine console: Unable to access resume device (dev//) Workaround: Before the conversion, edit the filter in the lvm.conf file on the source Linux machine to allow all devices. For Red Hat Linux, the default value of the filter is ( 'a/.*/' ).
Linux P2V conversion fails in the beginning with the following error message: 'A general system error occured: <source_server_dns_name>: Connection closed by remote host' If the source machine sshd is configured to allow less than 3 unauthenticated connections, it may sever the converter connection. Workaround: Check MaxStartups in /etc/ssh/sshd_config and ensure it is either commented out or its first number is 3 or higher.
P2V conversions of SLES 9 sources cannot complete, if the root directory is located on an LVM disk When you select to convert a physical SLES 9 source, Converter Standalone cannot complete the conversion if the root directory is located on an LVM disk. After the conversion job is 99% complete, the job status changes to Failed and the following entry is added to the log: FAILED: An error occurred during the conversion: 'Failed to restore original lvm in initrd image: /usr/lib/vmware-converter/restoreLvmInInitrd.sh failed with return code: 1, and message: * Unpacking initrd image /mnt/p2v-src-root//boot/initrd cpio: unsupported cpio format, use newc or crc ERROR: Unable to unpack initrd image /mnt/p2v-src-root//boot/initrd ' Workaround: Convert the LVM disk to a basic disk.
On the Options page of the Conversion wizard, click Data to copy in the options list.
Click Advanced and select the Destination layout tab.
Select the volume that contains the root directory and click To basic.
Virtual machines cloned from SLES 11 SP1 sources to ESX/ESXi managed destinations boot in console mode After the conversion, the destination virtual machine cannot load the GNOME Display Manager and boots in console mode. The following warning message appears: GdmLocalIDisplayFactory: maximum number of X display failures reached: check X server log for errors. Workaround: Recreate the xorg.conf file.
X Server might fail to start in destination virtual machines converted from sources that run Linux When the destination virtual machine starts, X server might fail to start with an error Fatal X server Error. This is due to incompatibility issues between the display driver used in the Linux source and the display adapter of the destination VMware virtual machine. Workarounds:
Install VMware Tools on the destination virtual machine.
configure the X server on the destination virtual machine to change the refresh rate and the display resolution.
Linked cloning of standalone VMware sources to Linux SMB shared destination fails Linked cloning tasks of VMware standalone sources to SMB shared destinations that run on Linux fail with the following error: converter.fault.FileIOFault.
The number of LVM logical volumes per volume group is limited to 12 for powered on Linux sources During the conversion of powered on Linux machines, Converter Standalone converts LVM volume groups into new disks on the destination virtual machine. The number of LVM logical volumes on a source LVM volume group cannot exceed 12. Workaround: Move volumes out of the new disk to other destination disks:
On the Options page of the Conversion wizard, click Data to copy.
From the Data copy type drop-down menu, select Select Volumes to copy and click Advanced.
On the Destination layout tab, select a volume to move and click Move Up or Move Down until it is moved to the destination disk. You can move volumes between disks only if they are not Active /boot or System / volumes.
(Optional) To create a new destination disk, click Add Disk.
By default, the Linux P2V helper virtual machine is powered off when the conversion job finishes Workaround: Manually disable this option in the converter-worker.xml file.
On the machine where Converter Standalone server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware Converter Standalone.
Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and change the powerOffHelperVm flag from true to false.
To restart Converter Standalone worker: Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
Note: Care should be taken when this option is enabled and the helper VM network is configured to use a static IP address. After the conversion, the helper VM retains the statically configured IP because it is still running. Thus any subsequent Linux P2V jobs cannot use the same static IP until this helper VM is powered off, or at least has its network interface disabled. Disabling the powerOffHelperVm flag is useful when the useSourcePasswordInHelperVm Converter Standalone worker flag is enabled. This allows users to log in to the helper virtual machine after conversion.
Source volumes on top of volume managers other than LVM are not recognized during conversion of powered on Linux machines Converter Standalone recognizes only managed source volumes that run on the LVM volume manager. Other volume managers, including but not limited to Veritas Volume Manager (VxVM), are not recognized.
Converter Standalone does not recognize source volumes that reside on Linux Software RAID configurations During cloning of powered on Linux machines, Converter Standalone does not recognize source volumes that are part of a Software RAID configuration (also referred to as multiple disk, or MD, configurations).
By default, Converter Standalone has a 20 minute timeout when waiting for the helper virtual machine to start up during Linux P2V conversion This might cause a Linux P2V conversion task to fail due to connection timeout. Workaround: Extend the timeout period (in milliseconds) by modifying the linuxP2VBootTimeout flag in the converter-worker.xml file.
On the machine where Converter Standalone server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware Converter Standalone.
Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and replace the default value for linuxP2VBootTimeout with the necessary timeout value in milliseconds. Note: The timeout value is measured in milliseconds. To specify the timeout in minutes, multiply the number of minutes by 60000 and use that value.
To restart Converter Standalone worker: Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
Sparse files are not preserved during conversion of powered on source machines that run Linux By default, Converter Standalone does not preserve sparse files on the source machine during Linux P2V conversion. If you have large sparse files on the source, they are created as non-sparse on the destination virtual machine. This renders the used space on the destination file system larger than that on the source machine. This might also cause the conversion task to fail with a timeout error. Workaround: Manually enable preserving sparse files during Linux conversions by modifying the keepsake flag in the converter-worker.xml file.
On the machine where Converter Standalone server runs, browse to the converter-worker.xml file in the following location %ALLUSERSPROFILE%Application DataVMwareVMware Converter Standalone.
Open the converter-worker.xml file in a text editor and change the keepsake flag from false to true.
To restart Converter Standalone worker: Reboot the system or open the Services section in the Microsoft Management Console, find the VMware Converter Worker service and restart it.
Destination virtual machine might not boot if you change the disk controller type while converting a Linux virtual machine In Linux virtual machines, the root device can be defined using the block device name (such as /dev/sda1) in /boot/grub/grub.conf, /boot/grub/menu.lst, or /etc/fstab. If you change the disk controller type while converting the virtual machine, the destination virtual machine might not boot. This is because the root device now has a different name (for example, it might have been changed to /dev/hda1). Workaround: Configure the destination virtual machine manually. At the minimum, change the root device name to reflect its new name in the destination virtual machine. To make your system more robust, use the volume label or UUID instead of the block device name.
During conversion of powered on Linux machines, Converter Standalone does not recognize Linux source volumes if they are mapped directly on a hard disk Workaround: Linux source volumes that are not managed by LVM must be located in a partition so that Converter Standalone can recognize them during cloning of powered on Linux sources.
Linux P2V jobs on ESX 5.0 target hosts fail if the name of the virtual machine is not in ASCII symbols or in the Windows current system locale If the target host is ESX 5.0, the name of the virtual machine must be in ASCII or in the Windows current system locale, otherwise the helper machine cannot be connected and the Linux P2V conversion fails. Workaround: Before the conversion, enter the name of the virtual machine by using ASCII symbols. After the conversion is complete, you can rename the virtual machine.
Third-Party Formats
Virtual machines created from Acronis images that have dynamic volumes do not start up after the conversion Some Acronis True Image images of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, or Windows 7 are not correctly configured and do not start up after the conversion. The problem occurs when the system or the active disk is located on a dynamic volume in the source. Workaround:
Create a new virtual machine using the vSphere Client.
Use the Acronis True Image software to restore the image inside the new virtual machine.
Limitations when converting third-party images You can use Converter Standalone to convert third-party virtual machines, system images, and backup images with the following limitations:
Backups of systems with dynamic disks are not supported (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
All images for the backup of a machine must be in a single folder that contains no other images (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
For incremental images, up to 16 incremental backups are supported (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
Images of systems with logical volumes are not supported if the logical drive is also a system or active volume (only for ShadowProtect sources).
For volume-based cloning of Acronis and StorageCraft, all volumes in the disk before the active and system volumes must be backed up. For example, if a disk has 4 partitions, 1-4, with partition 2 as the active volume and partition 3 as the system volume, the backup must include volumes 1 through 3 (ShadowProtect and Backup Exec System Recovery).
Virtual machines from Macintosh versions of Virtual PC are not supported.
Older versions of VMware products have limited support of newer operating systems. For example, ESX 3.5 does not support Windows 7. The converted source operating system must be supported for the destination VMware platform. For a list of supported systems, see the Guest Operating System Installation Guide.
Separate backup images should be stored in separate folders Storing more than one third-party backup in a single folder results in a failed migration. Workaround: Place each backup in its own folder before using Converter Standalone to convert an image.
SDK Release Notes
Converter Standalone SDK 6.0
The VMware vCenter Converter Standalone API provides language-neutral interfaces to the Converter Standalone server management framework. The Converter Standalone SDK is a ZIP file that contains the following items.
Sample code demonstrating common use cases for programmatically managing Converter Standalone server. The sample code includes Java and C# source code files. See the respective Readme files (readme_java.htm and readme_dotnet.htm ) for information about building and using the samples.
The WSDL that defines the API available on Converter server.
Batch files and shell scripts to automate the process of generating client-side stubs, and for rebuilding the sample applications. For C# developers, the Microsoft Visual Studio project files (.sln) have been included.
Reference documentation, the VMware vCenter Converter Standalone API Reference Guide, which provides language-neutral descriptive information (object type definitions, properties, and method signatures, for example) for the VMware vCenter Converter Standalone API 6.0.
Obtaining the Software
You can obtain the Converter Standalone SDK 6.0 from here.
Supported Platforms
The Converter Standalone 6.0 SDK is tested only on the supported Windows platforms. See Platforms.

0 notes
Text
Download vmware workstation 8.0 無料ダウンロード.VMware Workstation 16.2.1
Download vmware workstation 8.0 無料ダウンロード.Windows用のVMware Workstation Player

VMware vSphere Hypervisor – Install & Configure.Windows用のVMware Workstation Player をダウンロード -
VMware Horizon HTML Access. Check here to skip this screen and always use HTML Access. Click Here to Download VMware Horizon Client. To see the full list of VMware Horizon Clients, click here. For help with VMware Horizon, click here VMware vSphere Hypervisor Download Center. VMware vSphere Hypervisor Download Center. This download center features technical documentation and installation guides to make your use of vSphere Hypervisor a success VMware Workstation, 無料ダウンロード。. VMware Workstation 真のパワーと VMware のワークステーションを使用してデスクトップまたはラップトップ コンピューターの柔軟性を発見します。1 台の PC で同時に複数のオペレーティング システムを実行して 50 % 以上でハードウェアのコストを 4/5(86)
Download vmware workstation 8.0 無料ダウンロード.Download VMware Workstation Free
Functional cookies help us keep track of your past browsing choices so we can improve usability and customize your experience. These cookies enable the website to remember your preferred settings, language preferences, location and other customizable elements such as font or text size Download VMware Workstation General Information on cookies. When you visit our website, we use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience Jul 23, · VMware Customer Connectにログインします。 [製品とアカウント] > [すべての製品] の順に移動します。 VMware vSphere を見つけて、 [ダウンロード コンポーネントの表示] をクリックします。 [バージョンの選択] ドロップダウンから VMware vSphere のバージョンを選択します。 VMware vSphere Hypervisor (ESXi) の
Running the application you need on your computer isn't always as easy as you might think. Yes, a native app may exist for your OS of choice, but if it doesn't or if you need to keep your OS free of clutter, things get complicated.
Getting access to the cloud can also be challenging. This is one reason why I like VMWare Workstation. VMware Workstation is cloud capable and cloud aware. VMware Workstation's operating system support, user experience, feature set and performance will dramatically change the way you work with virtual machines. It's one of the best companion apps for any technical professional as they move to the cloud.
One of the most popular reasons why corporate customers use a virtual machine is to evaluate the next generation operating system. With VMware, you can install, say, Windows 8 and give users access to it, without actually upgrading a specific machine or risking introducing an undesirable user experience into the enterprise. The latest version of VMware Workstation is optimized for running Windows 8 on Windows PCs.
Its Easy Install feature simplifies the task of creating Windows 8 virtual machines. Its Unity mode will intelligently scale windows with Metro applications and multi-touch support will ensure you get the true Windows 8 experience in a virtual machine.
One of the BEST reasons why you'd use VMware Workstation is its new web interface. It allows you to access your virtual machines from a tablet, smart phone, PC or any device with a modern browser. No plugins or special add-ins are necessary.
Now you can power on, off, or suspend your virtual machines and interact with them from almost anywhere. Conclusion: Using a virtual machine on your computer is one of the best ways to use incompatible applications. It also makes it easy to keep your PC free from poorly written apps or apps that don't uninstall cleanly. VMware wrote the book on virtual machines and is one of the BEST ways to accomplish these tasks.
The biggest problems with VMware are that its expensive and complicated to setup and use. Its also a very complicated application to setup and configure. Many consumer users will need to either seek assistance from the help file, printed documentation or support forums to insure that they get the best performance out of the app.
Please note that I've given this app a low usability rating because of its level of complexity. All OSes. All licences. Software Free Download Soft com Home Windows Mac Mobile Blog Search. You can skip this in seconds Click here to continue. Home Windows Internet Remote Tools VMware Workstation Old versions VMware Workstation 8. VMware Workstation 8. VMware Workstation provides a seamless way to access all of the virtual machines you need, regardless of where they are running.
Last update 21 Jun. User rating:. Run a guest OS on your PC with this industry leading Windows app. If you need help or have a question, contact us Would you like to update this product info?
Is there any feedback you would like to provide? Click here. Popular Downloads Macromedia Flash 8 8. MSWLogo 6.
Cool Edit Pro 2. Cheat Engine 6. Counter-Strike 1. C-Free 5. Acoustica MP3 Audio Mixer 2. iFun Screen Recorder is a screen recorder Microsoft Office Service Express your ideas, solve problems, and connect FormatFactory 4. Visual Basic Express Visual Studio Community. Outlook Express 6. NET Framework 4. Horizon 2. Auto-Tune Evo VST 6.
Minecraft 1. Internet Explorer 8 8. Minecraft Beta 1. All popular downloads. All rights reserved. Legal Information Privacy Policy Terms of Service Copyright EULA DMCA Uninstall.
By operating system: All OSes Windows Mac Mobile. By licence: All licences Adware Commercial Demo Data Only Freemium Freeware Open Source Purchase only Shareware. Last updated in: Anytime Last week Last month Last 6 months Last year. JavaScript is required to properly view this page.
0 notes
Text
Vmware fusion 5 download free 無料ダウンロード.vmware fusion 5.0
Vmware fusion 5 download free 無料ダウンロード.Mac – VMware Fusion のダウンロードとインストール

VMware Fusion のダウンロード.無料 vmware fusion をダウンロード - Windows: vmware fusion
Nov 06, · 無料 vmware fusion のダウンロード ソフトウェア UpdateStar - Windows または VMware プレーヤー Linux PC 上の仮想マシンを実行します。この無料のデスクトップ仮想化ソフトウェア アプリケーションを仮想マシンの VMware のワークステーション、VMware Fusion、VMware Server または VMware ESX だけでなく VMware vSphere Hypervisor Download Center. Welcome to the VMware vSphere Hypervisor Download Center! This download center features technical documentation, installation demos and classes to make your use of vSphere Hypervisor a success. Looking for ESXi 4? Download it here Sep 28, · Mac 上に Windows 環境を構築するアプリ「VMware Fusion」のダウンロードとインストール方法を紹介します。 VMware Fusion には、30日間無償のお試し期間が設けられています。その期間を利用して、設定項目や使用感を試してみましょう。 VMware Fusion のダウンロード
Vmware fusion 5 download free 無料ダウンロード.個人ユーザーは無料で利用できるVMware Fusion 12 Player ライセンス発行からダウンロードまでを解説 - プログラミングや副業・フリーランスに関する情報
8/10 (8 点) - Mac VMware Fusionを無料ダウンロード VMware Fusionは複数のオペレーティングシステムを使用するには、ディスクのパーティション分割の設定の操作が必要です. Mac OS Xはおそらく現在存在するオペレーティングシステムの中で最も先進的で使用可能なオペレーティングシステムですが VMware Fusion VMware Fusion delivers the best way to run Windows on the Mac, and the ultimate development and testing tool for building apps to run on any platform. Ready for macOS Big Sur, Fusion 12 supports macOS Catalina and includes Sep 28, · Mac 上に Windows 環境を構築するアプリ「VMware Fusion」のダウンロードとインストール方法を紹介します。 VMware Fusion には、30日間無償のお試し期間が設けられています。その期間を利用して、設定項目や使用感を試してみましょう。 VMware Fusion のダウンロード
Welcome to the VMware vSphere Hypervisor Download Center! This download center features technical documentation, installation demos and classes to make your use of vSphere Hypervisor a success.
Looking for ESXi 4? Download it here. Learn basic tips and tricks for troubleshooting various components of VMware vSphere Hypervisor. VMware vSphere Hypervisor enables single-server partitioning and forms the foundation for a virtualized datacenter. By upgrading to more advanced editions of VMware vSphere , you can build upon this base virtualization layer to obtain centralized management, continuous application availability, and maximum operational efficiency.
VMware vSphere is the most widely deployed enterprise virtualization suite that offers customers:. Please login or create an account to access VMware vSphere Hypervisor license and downloads. View the top articles related to troubleshooting and support for this product. Add keywords to narrow your search. VMware Register to download your Free Product I Have an Account Create an Account. Email Address or Customer Number:. Password :.
Forgot your password? Remember me. Are you a VMware Partner? Yes No. VMware vSphere Hypervisor 5. Top VMware vSphere Hypervisor Resources VMware vSphere 5. Other Resources VMware vSphere Hypervisor Support Discussion Technical Support Documentation Technical Support Guide. How to Buy Build a Dynamic Datacenter with VMware vSphere VMware vSphere Hypervisor enables single-server partitioning and forms the foundation for a virtualized datacenter.
Connect Support View the top articles related to troubleshooting and support for this product. Problem Description VMware vSphere Hypervisor. Or add one of our popular tags:.
Select Your Language.
0 notes