#Webview App Development
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
0 notes
Text
iWappPress – Best Android App Builder for WordPress
1. iWappPress – Best Android App Builder for WordPress
Why It’s #1: iWappPress (also known as WappPress) is a fast, budget-friendly solution to instantly create an Android app from any WordPress site.
Best For: Bloggers, small businesses, and agencies wanting a quick mobile app.
Key Features:
One-click Android app creation
No coding or technical knowledge required
Custom splash screen, icon, and app layout
AdMob integration for monetization
Supports push notifications (via Firebase)
Very lightweight plugin
2. AppMySite – No-Code Mobile App Builder
Why It’s Great: Powerful and fully featured app builder with WooCommerce and blog support.
Best For: E-commerce, news, and content-driven sites.
Key Features:
Android and iOS apps
Auto-syncs with your WordPress content
WooCommerce support
Drag-and-drop UI customization
Push notifications & AdMob integration
3. AndroApp – Native Android App for WordPress
Why It’s Popular: Designed especially for news, magazine, and content-heavy blogs.
Best For: Publishers and bloggers
Key Features:
Native Android experience
Offline content access
Push notifications
Ad monetization support
Multilingual support
4. Web2App – Android WebView App Template
Why It’s Flexible: Turns your site into a web-based app with native feel and features.
Best For: Developers or users needing more control
Key Features:
Easy WebView integration
Firebase & OneSignal push notifications
AdMob & banner ads support
File upload/download, splash screen, and custom UI
5. MobiLoud – Premium WordPress to App Platform
Why It’s Enterprise-Ready: A done-for-you service with full app publishing support.
Best For: High-traffic sites, enterprises, and WooCommerce stores
Key Features:
Native Android & iOS apps
Full WordPress plugin compatibility
WooCommerce and BuddyPress integration
Custom branding & UI
Full support and maintenance
0 notes
Text
Native Development vs Flutter: Which One Should You Choose?

Introduction
Think about creating two distinct houses for two individuals who desire nearly the same look — one for iOS and one for Android. Now, think of creating one intelligent house that converts to both. That's native app development versus Flutter — and it's a choice that defines mobile app project futures.
Today, with the need for speed, cost-effectiveness, and cross-platform compatibility, mobile development frameworks have changed at a very fast pace. Native development, employing platform-specific programming languages such as Swift for iOS and Kotlin for Android, has been the performance and platform integration gold standard for a long time. But Google-backed frameworks such as Flutter are shaking things up by providing a single codebase to develop apps that can run on several platforms.
This blog delves into the age-old debate between native development and Flutter — breaking down their fundamental differences, strengths, and trade-offs. As a developer, product owner, or technology enthusiast, this article will show you which way may be best for your next project and why this decision is more important than ever.
History and Evolution
The journey of mobile app development began with native technologies, tailored for individual platforms. When Apple launched the iPhone in 2007, developers used Objective-C and later Swift to build iOS apps. Around the same time, Android emerged, with apps written in Java, eventually evolving to Kotlin — Google’s preferred language. These platform-specific tools ensured that apps were tightly integrated with the hardware and software ecosystem, delivering high performance and a smooth user experience.
However, as mobile usage exploded, so did the demand for faster, more cost-effective development. Maintaining two separate codebases for iOS and Android became inefficient for many companies, especially startups and product teams with limited resources. This gave rise to cross-platform frameworks like PhoneGap, Xamarin, and React Native, aiming to simplify development. Each had its pros and cons, but they were steps toward a unified development model.
In 2017, Google introduced Flutter, a revolutionary UI toolkit for building natively compiled applications from a single codebase. Unlike earlier frameworks that relied on WebView or JavaScript bridges, Flutter uses the Dart programming language and a custom rendering engine to produce near-native performance. Its “write once, run anywhere” promise, paired with a rich widget library and hot reload feature, quickly made it a favorite among developers.
On the other hand, native development also evolved, with more robust IDEs (Xcode, Android Studio), improved language features (SwiftUI, Jetpack Compose), and better tooling that made building apps faster and more maintainable. Native development is still the go-to for apps requiring tight integration with device hardware, platform-specific UI/UX, or optimal performance.
As of today, both approaches coexist — each serving different needs. Flutter has matured with strong community support and increasing adoption in enterprise-level projects, while native development remains unmatched in terms of stability and platform consistency for complex applications.
The evolution from native-only to modern cross-platform development represents a major shift in how mobile apps are built, driven by the growing demand for efficiency, maintainability, and faster go-to-market strategies.
Problem Statement
As mobile apps continue to dominate the digital space, businesses are under pressure to deliver seamless, feature-rich experiences across multiple platforms — most commonly Android and iOS. But developing apps for both platforms presents a fundamental challenge: balancing performance, development time, and cost.
Traditionally, native development required companies to build two entirely separate applications — one for Android using Kotlin or Java, and another for iOS using Swift or Objective-C. This approach not only demands two separate development teams, but also doubles the effort when it comes to writing features, fixing bugs, running tests, and deploying updates. As a result, project timelines are longer, development costs are higher, and maintaining feature parity across platforms becomes more difficult.
On the flip side, cross-platform solutions like Flutter offer a compelling alternative by enabling a single codebase to serve both platforms. However, this approach is not without its own concerns. Developers often question whether Flutter can match the performance, stability, and native feel of platform-specific apps. Additionally, accessing certain device features or integrating new platform updates can require writing native code anyway, partially defeating the purpose of going cross-platform.
This presents a key dilemma for developers and product owners:
Should they choose native development for its power and precision, or Flutter for its speed and simplicity?
The problem becomes even more significant for startups and mid-sized companies that must deliver high-quality apps with limited time and budget. They must carefully evaluate trade-offs between performance, scalability, and maintainability — a decision that can greatly influence user satisfaction and business success.
Technology Overview
To understand the differences between native development and Flutter, it's important to first break down what each approach involves — from basic concepts to how they function in real-world development workflows.
Native Development: Platform-Specific Precision
Native development means creating mobile apps using the programming languages and tools officially supported by the operating system:

iOS: Developers use Swift (or the older Objective-C) along with Apple’s Xcode IDE. UI is built using UIKit or the more recent SwiftUI.

Android: Developers use Kotlin (or Java) with Android Studio. UI components are managed using XML or Jetpack Compose, Google’s modern UI toolkit.
Each native app is compiled separately for its target platform, ensuring optimal performance and direct access to platform APIs, animations, sensors, and hardware components. The app naturally follows platform-specific UI/UX conventions, giving users a seamless and familiar experience.
Flutter: Cross-Platform Simplicity with Power
Flutter, developed by Google, is a UI framework that enables developers to build apps for Android, iOS, web, desktop, and more — from a single codebase. Flutter apps are written in Dart, a fast, modern language designed for UI development.

At its core, Flutter does not rely on native UI components. Instead, it uses its own rendering engine (Skia) to paint every pixel on the screen, which allows for:
Full control over UI customization
Consistent design across platforms
Smooth animations and transitions
Flutter’s “hot reload” feature speeds up development by allowing developers to see changes in real time without restarting the app. It also comes with a rich set of pre-built widgets that can be styled and extended, giving teams the flexibility to build complex UIs efficiently.
Integration and Functionality
For platform-specific functionality like camera access, biometrics, or Bluetooth, Flutter uses “platform channels” — a bridge that lets Dart code communicate with native code (Swift/Kotlin). This ensures that Flutter apps can still use native capabilities when needed, albeit with some added complexity.
On the other hand, native apps have first-class access to system APIs, and they typically benefit from earlier support for new OS features introduced by Apple or Google.
In essence, Flutter focuses on developer efficiency and UI flexibility, while native development emphasizes performance and platform integration. Understanding these functional differences helps teams choose the right tool for the right job.
Practical Applications
Both native development and Flutter have proven their value across a wide range of real-world applications. Their adoption depends largely on the nature, complexity, and requirements of the project.
Native Development in Action
Native development is the preferred choice for apps that demand top-tier performance, security, or deep integration with platform features. For example:
Instagram and WhatsApp use native codebases to ensure responsive, feature-rich experiences tailored specifically for Android and iOS.
Banking and fintech apps often choose native development for security reasons and access to low-level device features like biometrics and hardware encryption.
AR/VR applications, games, and apps using advanced hardware (like sensors or GPS-based tracking) are typically built natively to leverage the full capabilities of the device.
These apps require tight control over memory usage, threading, and UI responsiveness — something that native frameworks handle exceptionally well.
Flutter in Real-World Scenarios
Flutter has gained significant traction for apps that prioritize speed to market, visual appeal, and cross-platform consistency. Examples include:
Google Ads and Reflectly (a journaling app) — both built using Flutter, showcasing its capability for building complex, performance-sensitive apps.
Startups and MVPs (Minimum Viable Products) often use Flutter to validate ideas quickly across platforms without the cost of maintaining two separate codebases.
E-commerce and service-based apps benefit from Flutter’s custom UI capabilities, allowing them to maintain a consistent brand identity across Android and iOS.
Additionally, Flutter’s desktop and web support is expanding its application into areas like internal enterprise tools, admin dashboards, and cross-platform business solutions.
Impact Analysis
Flutter significantly reduces development time and cost for companies looking to target multiple platforms simultaneously, while native development provides unmatched performance and reliability for high-end or specialized apps. Ultimately, the impact lies in how closely the technology aligns with the app’s core requirements — whether that’s speed, scalability, or user experience.
Challenges and Limitations
While both native development and Flutter offer powerful tools for building mobile applications, each comes with its own set of challenges and trade-offs.
Native Development: Limitations in Flexibility and Cost
One of the major drawbacks of native development is the need for two separate codebases, which leads to increased development time, higher costs, and duplicated effort. Maintaining feature parity across Android and iOS can become complex, especially for fast-evolving products. Additionally, hiring and retaining separate teams for each platform can strain resources, especially for startups and smaller companies.
Flutter: Gaps in Native Integration and App Size
Despite its advantages, Flutter also faces notable limitations:
Access to platform-specific APIs sometimes requires writing native code using platform channels, which introduces complexity and can reduce productivity.
App size in Flutter tends to be larger compared to native apps, which can be a concern for users in regions with slower internet speeds or limited storage.
Some advanced OS features or new SDK updates may not be immediately available in Flutter, creating a lag in adoption compared to native platforms.
Emerging Solutions
The Flutter team and community continue to address many of these issues through active development, improved plugin support, and tooling enhancements. Meanwhile, native platforms are also evolving to improve developer productivity through tools like SwiftUI and Jetpack Compose, narrowing the gap in development speed and UI flexibility.
Future Outlook
The future of mobile development is increasingly shaped by the need for faster, scalable, and more efficient solutions — and both native development and Flutter are evolving to meet these demands.
On the native side, frameworks like SwiftUI and Jetpack Compose are modernizing the development experience, offering declarative syntax and better performance. These advancements aim to close the productivity gap with cross-platform frameworks while preserving the native advantages of stability and system-level access.
Meanwhile, Flutter is expanding beyond mobile. With support for web, desktop, and embedded systems, it is steadily moving toward becoming a true multi-platform development solution. Its growing ecosystem, increasing corporate adoption, and improved plugin support suggest that Flutter will play a key role in future app development, especially for startups, SMEs, and cross-platform enterprise solutions.
Looking ahead, we can expect a hybrid future — where use cases dictate technology choices. Performance-critical apps may continue to rely on native development, while UI-rich, multi-platform applications will increasingly turn to frameworks like Flutter.
Conclusion
Choosing between native development and Flutter is not about finding a one-size-fits-all solution — it’s about aligning technology with your project’s goals, team capacity, and user expectations. Native development offers unmatched performance, reliability, and tight platform integration, making it ideal for complex, resource-heavy applications. Flutter, on the other hand, empowers teams to move faster with a single codebase, delivering consistent UI and quicker updates across multiple platforms.
As both approaches continue to evolve, developers and decision-makers must evaluate not only the technical capabilities but also the long-term maintainability, scalability, and cost implications. Whether you’re building the next big social app, an enterprise-grade platform, or a startup MVP, understanding these trade-offs will help you make the most strategic and effective decision for your mobile development journey.
0 notes
Text
Xamarin: The Cross-Platform Mobile Development Framework You Should Know
In today’s rapidly evolving mobile app development landscape, businesses and developers are constantly looking for ways to maximize reach while minimizing effort. With multiple mobile operating systems — most notably iOS and Android — developers are often faced with the dilemma of creating separate apps for each platform. Xamarin, a framework powered by Microsoft, has emerged as a robust solution to this problem by enabling developers to build cross-platform mobile applications using a single codebase written in C#. This blog post explores Xamarin in depth — its architecture, features, benefits, limitations, and practical use cases.
What is Xamarin?

Xamarin is an open-source platform for building modern and performant applications for iOS, Android, and Windows with .NET. Originally developed by the team behind Mono and later acquired by Microsoft in 2016, Xamarin integrates with Visual Studio and enables developers to write code in C# or F# that compiles into native code. Unlike hybrid frameworks that rely on WebView components (e.g., Cordova or Ionic), Xamarin offers a more native experience by accessing platform-specific APIs and delivering near-native performance.
Core Components of Xamarin

Xamarin comprises several essential components:
Xamarin.iOS and Xamarin.Android: These are bindings to the iOS and Android SDKs. They allow developers to write platform-specific code in C#.
Xamarin.Forms: A UI toolkit that enables developers to create user interfaces that can be shared across platforms. Xamarin.Forms simplifies UI design by allowing developers to define UIs in XAML and bind them to C# code-behind.
.NET MAUI (Multi-platform App UI): The evolution of Xamarin.Forms, .NET MAUI unifies the development of apps for Android, iOS, macOS, and Windows in a single project.
Mono Runtime: Xamarin uses the Mono runtime, a cross-platform implementation of the .NET Framework, to execute managed code across platforms.
Visual Studio Integration: Xamarin is deeply integrated into Microsoft’s Visual Studio, offering powerful tools for debugging, profiling, and deployment.
Unlock more details here
Why Choose Xamarin?

1. Code Sharing and Reusability
One of the main appeals of Xamarin is its ability to maximize code sharing. Developers can write up to 90% of their codebase in C# and share it across platforms. This reduces development time and cost significantly.
2. Native Performance
Since Xamarin compiles apps into native binaries and provides bindings to native APIs, the resulting applications perform almost as well as those developed using native SDKs.
3. Rich IDE Support
With Microsoft’s backing, Xamarin has deep integration into Visual Studio, one of the most powerful integrated development environments (IDEs). Features such as IntelliSense, debugging, diagnostics, and version control are readily available.
4. Access to Platform-Specific APIs
Xamarin gives developers full access to the platform-specific APIs using C#. You can implement platform-specific functionality without leaving your shared codebase.
5. Strong Community and Ecosystem
With Microsoft’s support and a growing open-source community, Xamarin has extensive documentation, libraries, and third-party tools that simplify mobile development.
Mobile App Development
Framework
0 notes
Text
Navigating the Minefield: Key Mobile App Vulnerabilities and Strategies for Robust Security

In today's digital landscape, mobile applications have become indispensable tools for businesses and individuals alike. From streamlining 1 operations to enhancing customer engagement, the 2 power of mobile apps is undeniable. However, this pervasive adoption also brings forth significant security concerns. As a leading mobile app development company in Sydney, we understand that building a successful app goes beyond functionality and user experience; it necessitates a strong foundation of security. Ignoring potential vulnerabilities can lead to devastating consequences, including data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.
This comprehensive guide delves into the critical mobile app vulnerabilities that developers and businesses must be aware of and outlines effective strategies to safeguard against them. Whether you are looking to hire a mobile app developer in Sydney or are an established enterprise seeking to fortify your existing applications, understanding these risks and implementing robust security measures is paramount.
The Lurking Threats: Understanding Key Mobile App Vulnerabilities
The mobile app ecosystem presents a unique attack surface that malicious actors are constantly trying to exploit. Here are some of the most prevalent vulnerabilities:
1. Insecure Data Storage:
This is a common yet critical vulnerability. Sensitive data, such as user credentials, personal information, API keys, and financial details, should never be stored in plain text on the device. Attackers can gain access to this data through various means, including malware, physical device access, or even backups.
Impact: Data breaches, identity theft, financial fraud, privacy violations.
Example: An e-commerce app storing credit card details in shared preferences without encryption.
2. Weak Server-Side Controls:
Mobile apps heavily rely on backend servers for data and functionality. Weaknesses in server-side security, such as insufficient input validation, insecure APIs, and inadequate authentication mechanisms, can be exploited to compromise the entire system, including the mobile app.
Impact: Data manipulation, unauthorized access, denial of service, server takeover.
Example: An API endpoint that doesn't properly validate user input, allowing attackers to inject malicious code.
3. Insecure Communication:
Data transmitted between the mobile app and the backend server must be protected against eavesdropping and tampering. Failure to implement secure communication protocols like HTTPS can expose sensitive information during transit.
Impact: Man-in-the-middle attacks, data interception, session hijacking.
Example: An app transmitting login credentials over unencrypted HTTP.
4. Insufficient Cryptography:
While encryption is crucial, using weak or improperly implemented cryptographic algorithms and practices can render the encryption ineffective. This includes using outdated algorithms, hardcoding encryption keys, or failing to properly manage keys.
Impact: Data exposure, circumvention of security controls.
Example: An app using a deprecated encryption algorithm with a publicly known vulnerability.
5. Client-Side Injection:
Similar to web application vulnerabilities, mobile apps can be susceptible to client-side injection attacks. This can occur through WebView components, local databases (like SQLite), or even through inter-app communication. Attackers can inject malicious code to manipulate app behavior or gain access to sensitive data.
Impact: Data theft, unauthorized actions, cross-site scripting within the app.
Example: An app using a WebView to display external content without proper sanitization, allowing for JavaScript injection.
6. Binary Exploitation:
Attackers with advanced skills can reverse-engineer and analyze the mobile app's binary code to identify vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities can then be exploited to bypass security controls, inject malicious code, or gain unauthorized access to device resources.
Impact: Code manipulation, privilege escalation, malware injection.
Example: Exploiting a buffer overflow vulnerability in the native code of the app.
7. Third-Party Libraries and SDKs:
Mobile app development often involves integrating third-party libraries and Software Development Kits (SDKs) to expedite development and add functionalities. However, these components can introduce their own vulnerabilities if they are not regularly updated or come from untrusted sources.
Impact: Introduction of known vulnerabilities, malicious code execution.
Example: An outdated advertising SDK with a publicly disclosed security flaw.
8. Improper Session Handling:
Weak session management can allow attackers to hijack user sessions and gain unauthorized access to user accounts and data. This includes using predictable session identifiers, failing to invalidate sessions properly after logout, or storing session tokens insecurely.
Impact: Account takeover, unauthorized access to user data and functionalities.
Example: An app using simple sequential numbers as session identifiers.
9. Lack of Proper Authentication and Authorization:
Robust authentication mechanisms are essential to verify user identities, and proper authorization controls are needed to ensure that users can only access the resources and functionalities they are permitted to. Weaknesses in these areas can lead to unauthorized access and data breaches.
Impact: Account takeover, privilege escalation, unauthorized data access.
Example: An app that doesn't enforce strong password policies or allows users to access administrative functionalities without proper authorization.
10. Sensitive Information Disclosure:
Unintentionally exposing sensitive information through logs, error messages, or other means can provide attackers with valuable insights into the app's internal workings and potential vulnerabilities.
Impact: Information leakage, aiding in further attacks.
Example: An app logging sensitive user data or displaying verbose error messages in production builds.
Fortifying Your Defenses: Strategies to Safeguard Your Mobile App
As a leading app development company in Sydney and home to experienced mobile app developers in Sydney and skilled app developers in Sydney, we advocate for a proactive and layered security approach. Here are crucial strategies to mitigate the aforementioned vulnerabilities:
1. Secure Data Storage Practices:
Encryption: Always encrypt sensitive data at rest using strong, industry-standard encryption algorithms (e.g., AES-256).
Key Management: Implement secure key management practices. Avoid hardcoding keys in the app. Consider using the device's secure hardware (like the Keystore on Android or Secure Enclave on iOS) or secure key management services.
Minimize Storage: Only store essential data locally. For highly sensitive information, rely on secure server-side storage.
2. Robust Server-Side Controls:
Input Validation: Implement rigorous input validation on the server-side to prevent injection attacks and ensure data integrity.
Secure API Design: Design secure APIs with proper authentication (e.g., OAuth 2.0), authorization, and rate limiting.
Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing of your backend infrastructure.
3. Secure Communication Channels:
HTTPS/TLS: Enforce HTTPS (HTTP over TLS/SSL) for all communication between the mobile app and the backend server to encrypt data in transit.
Certificate Pinning: Implement certificate pinning to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks by verifying the server's certificate against a pre-defined set of trusted certificates.
4. Strong Cryptographic Implementation:
Use Strong Algorithms: Employ well-vetted and up-to-date cryptographic algorithms. Avoid using deprecated or known-to-be-weak algorithms.
Proper Key Generation and Management: Generate strong, random keys and implement secure key storage, rotation, and lifecycle management.
Avoid Custom Cryptography: Unless you have specialized expertise, rely on established cryptographic libraries.
5. Client-Side Security Measures:
WebView Security: When using WebView, carefully sanitize any external content and disable unnecessary features like JavaScript execution from untrusted sources.
Secure Local Databases: Encrypt local databases if they store sensitive information. Use parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection.
Secure Inter-App Communication: If your app communicates with other apps, ensure that the communication channels are secure and properly validated.
6. Binary Protection Techniques:
Code Obfuscation: Employ code obfuscation techniques to make it harder for attackers to reverse-engineer the app's code.
Tamper Detection: Implement mechanisms to detect if the app has been tampered with.
Root/Jailbreak Detection: Consider implementing checks to detect if the app is running on a rooted (Android) or jailbroken (iOS) device and implement appropriate security measures.
7. Vigilant Third-Party Library Management:
Source Review: Carefully vet the third-party libraries and SDKs you integrate into your app.
Regular Updates: Keep all third-party components up-to-date to patch known vulnerabilities.
Minimize Dependencies: Only include necessary libraries to reduce the attack surface.
8. Secure Session Management:
Strong Session Identifiers: Use cryptographically strong, random session identifiers.
Session Timeout: Implement appropriate session timeouts.
Secure Storage of Tokens: Store session tokens securely (e.g., in memory or using secure storage mechanisms).
Proper Logout Handling: Invalidate sessions on the server-side when a user logs out.
9. Robust Authentication and Authorization:
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an extra layer of security to user accounts.
Strong Password Policies: Enforce strong password requirements.
Principle of Least Privilege: Grant users only the necessary permissions to perform their tasks.
Regularly Review Permissions: Periodically review and update user roles and permissions.
10. Minimizing Sensitive Information Disclosure:
Disable Debugging in Production: Ensure that debugging features are disabled in production builds.
Limit Logging: Avoid logging sensitive information in production. If logging is necessary, ensure logs are stored securely.
Custom Error Handling: Implement custom error handling to prevent the disclosure of sensitive internal information in error messages.
Partnering for Security: Choosing the Right Development Partner
Selecting the right mobile app development company in Sydney is crucial for building secure and reliable applications. When looking for an app development company in Sydney or a skilled app developer in Sydney, prioritize partners who demonstrate a strong commitment to security best practices throughout the entire development lifecycle. A reputable mobile app developers in Sydney team will integrate security considerations from the initial design phase to post-launch maintenance.
Conclusion: Building a Secure Mobile Future
In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, mobile app security is not a one-time task but an ongoing process. By understanding the key vulnerabilities and implementing robust safeguarding strategies, businesses can build resilient and trustworthy mobile applications. As a leading mobile app development company in Sydney, we are dedicated to helping our clients navigate these challenges and build secure mobile solutions that protect their users and their businesses. Investing in security is not just a cost; it's an investment in the long-term success and reputation of your mobile application.
#mobile app development company in sydney#mobile app developer in sydney#app development company in sydney#app developer in sydney#mobile app developers in sydney
0 notes
Text
Hybrid App Development: Advantages and Disadvantages
Hybrid app development has gained popularity among businesses looking for cost-effective solutions to create mobile applications that run seamlessly across multiple platforms. While hybrid apps offer many benefits, they also come with certain limitations. In this article, we’ll explore the advantages and disadvantages of hybrid app development, helping you determine whether it’s the right choice for your project.
Advantages of Hybrid App Development
1. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Hybrid apps are designed to work on both iOS and Android, eliminating the need for separate codebases. This results in faster development and reduced costs, making them an attractive choice for startups and businesses.
2. Cost-Effective Solution
Since hybrid apps use a single codebase, development costs are significantly lower than native apps. Businesses looking to optimize their budget while maintaining good functionality often turn to hybrid app development.
3. Faster Development & Time-to-Market
Developers can use frameworks like React Native, Flutter, and Ionic to build hybrid apps quickly. This allows businesses to launch their apps faster, gaining a competitive advantage.
4. Easy Maintenance & Updates
Unlike native apps, which require updates for both iOS and Android separately, hybrid apps allow developers to roll out updates universally. This streamlines the maintenance process and ensures users always have access to the latest version.
5. Access to Device Features
Hybrid apps can leverage device capabilities such as camera, GPS, and push notifications using plugins. This ensures they offer functionality similar to native applications.
Disadvantages of Hybrid App Development
1. Performance Limitations
Hybrid apps rely on WebView technology, which can result in slower performance compared to fully native apps. For applications requiring high-speed graphics and animations, hybrid development may not be the best choice.
2. Limited User Experience
Because hybrid apps use a single codebase for multiple platforms, they may lack the smooth, platform-specific UI elements that native apps provide. This can lead to a less intuitive user experience.
3. Dependency on Third-Party Frameworks
Hybrid app development relies on third-party frameworks and libraries, which may become outdated or incompatible with new operating system updates. This could create challenges in app maintenance and stability.
4. Complex Debugging Process
Since hybrid apps function across multiple platforms, debugging can be more challenging compared to native apps. Developers may need additional tools to troubleshoot performance issues.
5. Security Concerns
Hybrid apps may be more vulnerable to security threats because they depend on web technologies. Proper security measures such as data encryption and secure API integrations are necessary to protect user information.
Conclusion
Hybrid app development offers an efficient, cost-effective, and cross-platform solution, making it an excellent choice for businesses looking to reach a wide audience quickly. However, it does come with performance trade-offs and requires careful optimization to ensure a seamless user experience.
For companies seeking expert hybrid app solutions, partnering with a hybrid app development company can help overcome challenges and deliver high-quality mobile applications.
0 notes
Text
React Native App Development: Key Features That Set It Apart from Other Frameworks

When it comes to mobile app development, startups and businesses alike are constantly looking for the most efficient and cost-effective ways to create apps that work seamlessly across both iOS and Android. React Native App Development Companies have been making waves in the industry by offering a framework that enables developers to build apps that provide native performance without the complexities of traditional development. React Native, developed by Facebook, has grown in popularity due to its remarkable ability to build high-performance mobile applications with a single codebase. But what makes React Native stand out from other app development frameworks? Let’s explore the key features that set it apart.
What is React Native?
React Native is an open-source framework that allows developers to build mobile applications for iOS and Android using JavaScript and React. It allows for the creation of applications with a near-native feel, ensuring users get a smooth, high-quality experience. Unlike traditional app development, where separate codebases are needed for iOS and Android, React Native enables developers to write most of the code once and deploy it across multiple platforms. This approach not only saves time but also reduces costs, making it an attractive option for businesses and React Native App Development Companies.
Key Features of React Native That Set It Apart
1. Cross-Platform Compatibility
One of the primary reasons React Native has gained such widespread adoption is its ability to allow developers to write a single codebase for both iOS and Android applications. Traditional native app development requires separate code for iOS (written in Swift or Objective-C) and Android (written in Kotlin or Java), which can be resource-intensive and time-consuming. React Native simplifies this process by allowing developers to create a cross-platform app that works seamlessly on both platforms.
By utilizing a single codebase, businesses can save on development time and costs while also ensuring a more consistent experience for users across different devices. This ability to develop cross-platform apps with a high degree of performance and reliability is one of the standout features of React Native.
2. Native-Like Performance
While there are other cross-platform frameworks, React Native stands out for its ability to deliver near-native performance. Unlike other frameworks that rely on webview-based development (essentially loading the app in a browser window), React Native uses native components. This results in an app that performs more like a traditional native app, offering a better user experience with faster load times and smoother animations.
React Native bridges the gap between web and native apps by using JavaScript to call native code, giving apps the ability to perform complex tasks with speed and efficiency. This makes it a perfect choice for building performance-critical applications such as social media apps, e-commerce platforms, and real-time applications.
3. Reusable Code
Another game-changing feature of React Native is its ability to reuse code across platforms. This means that developers can write the core components of the app once and reuse them across both Android and iOS versions. Although some platform-specific components may require custom code, the majority of the app’s functionality can be shared between platforms, significantly reducing development time.
For businesses looking to launch their app quickly and efficiently, the reusability of code is a major advantage. It not only reduces the overall development time but also ensures that updates and fixes can be applied simultaneously across both platforms, keeping costs down.
4. Hot Reloading
Hot reloading is a unique feature of React Native that allows developers to instantly see changes in the app without having to restart it. This feature significantly speeds up the development process by enabling developers to make real-time changes to the code and instantly test them without waiting for a complete app refresh.
For businesses that want to speed up the development cycle, hot reloading offers a fantastic solution. It allows developers to iterate quickly, implement new features, fix bugs, and optimize performance more efficiently than ever before. This also leads to faster delivery times, which is essential in today’s fast-paced business environment.
5. Rich Ecosystem and Community Support
React Native benefits from a large and active community of developers, as well as extensive documentation and resources. The framework is continuously evolving, with new features and improvements being introduced regularly. The community-driven approach ensures that developers can access a wealth of plugins, libraries, and third-party tools that can speed up development and add new functionalities to the app.
The ecosystem around React Native also includes a wide range of open-source tools and components, which can be integrated into apps to enhance their functionality. The availability of such resources makes React Native an ideal framework for building apps with a rich feature set while keeping development costs manageable.
6. Third-Party Plugin Support
React Native also allows developers to use third-party plugins, both native and JavaScript-based, which can further extend the app’s functionality. For instance, if you need a custom native module for accessing a device’s camera, GPS, or other hardware features, React Native supports the integration of such native modules seamlessly. This flexibility ensures that developers are not restricted in terms of functionality and can easily incorporate advanced features into their apps.
The ability to use third-party plugins enables businesses to keep their apps innovative and feature-rich without having to build everything from scratch, further improving the time-to-market.
7. Cost Efficiency
When it comes to mobile app development, cost efficiency is often a key factor. React Native allows businesses to significantly reduce development costs by eliminating the need for separate development teams for iOS and Android. The ability to share code across platforms reduces both development and maintenance costs, making it a more affordable option for businesses, especially startups.
To understand the costs involved in building a React Native app, businesses can make use of tools like a mobile app cost calculator. These calculators provide a rough estimate of the development costs based on factors like app complexity, required features, and platform choice. By planning ahead and using such tools, businesses can ensure their app development stays within budget.
Why Choose a React Native Development Company?
When it comes to implementing React Native for your business, it’s crucial to work with experienced professionals who can help you navigate the complexities of the framework. A react-native development company can bring valuable expertise to the table, ensuring your app is optimized for performance, scalability, and user experience.
If you're interested in exploring the benefits of React native development services for your business, we encourage you to book an appointment with our team of experts. Book an Appointment
Conclusion
In summary, React Native has proven itself as a powerful and efficient tool for building cross-platform mobile applications. With key features like cross-platform compatibility, native-like performance, reusable code, hot reloading, and third-party plugin support, React Native stands out as a top choice for businesses looking to develop mobile apps. By leveraging the strengths of this framework, startups and established businesses alike can create high-performance apps that save time and money without compromising on quality. Partnering with the right react-native development company can ensure that your app is built with the best practices and the latest tools, setting your business up for success.
0 notes
Text
Website to App: How to Convert Your Online Presence into a Mobile Application

In today’s digital age, having a strong online presence is crucial for business growth. While websites are essential, mobile apps provide a more engaging experience, leading to higher user retention and conversion rates. If you’re looking to expand your reach, converting your website to app is a strategic move. Fortunately, this process is now easier than ever with the help of a web to app converter.
Why Convert Your Website into an App?
With more users accessing the internet via mobile devices, having a dedicated mobile app enhances accessibility and improves the overall user experience. When you turn website into app, you gain several benefits. Apps generally load faster and offer smoother navigation compared to mobile websites. Unlike websites, mobile apps can store data and provide limited functionality even without an internet connection. Apps allow you to send instant notifications to users, increasing engagement and retention. A mobile app provides a cleaner and more customized experience compared to a mobile web browser. Having an app icon on users’ home screens helps reinforce brand recognition and loyalty.
Steps to Turn Your Website into an App
Choose the Right Web to App Converter
The first step in creating a mobile app from your website is selecting a web to app converter. These tools allow you to quickly transform an existing website into an app without requiring extensive coding skills.
Define Your App’s Features
When you make website into app, it’s important to determine what additional features you need. While a webview app mirrors your website’s content, you might want to include features such as push notifications, offline mode, app store monetization, and custom navigation.
Convert Your Website Using a WebView App
A webview app is one of the easiest ways to turn your website into an app. It essentially loads your website inside an app framework while maintaining full functionality. Most web to app converters offer a WebView option, allowing you to quickly create a functional app without major development work.
Test Your App
Before publishing, thoroughly test your app on multiple devices to ensure it works smoothly. You should check for load speed and performance, responsiveness on different screen sizes, compatibility with Android and iOS, and any broken links or features.
Publish Your App on App Stores
Once you’ve tested and refined your app, the next step is to submit it to the Play Store. Be sure to follow the respective app store guidelines, optimize your app description with keywords, and include appealing app screenshots.
Final Thoughts
Converting your website to an app is a powerful way to enhance user engagement, improve brand recognition, and boost customer retention. With the right web to app converter, businesses can quickly create webview app and gain a competitive edge. If you're ready to turn your website into an app, take advantage of these tools today and make your digital presence stronger than ever!
Do not forget to check WebViewGold to effortlessly convert your website into mobile apps.
0 notes
Text
From Concept to Conversion: Mastering Telegram Mini App Ads for Developers

In the rapidly evolving landscape of mobile marketing, Telegram Mini App Ads TMA-ADS.PRO have emerged as a powerful tool for developers seeking to maximize reach and engagement. With Telegram's global user base exceeding 800 million active users, this advertising ecosystem offers unique opportunities that differ significantly from traditional digital advertising channels. This comprehensive guide explores how developers can effectively harness the potential of this platform to drive downloads, engagement, and conversions.
The Developer's Perspective on Telegram's Advertising Environment
Unlike conventional mobile app development which requires separate iOS and Android versions, Telegram Mini Apps operate within the Telegram client itself, creating a distinctive development and advertising paradigm with several key advantages:
Universal compatibility across all devices Telegram supports
Instant loading without app store downloads or installations
Reduced development complexity compared to native applications
Direct access to Telegram's massive user base
Simplified updates without app store review processes
Technical Architecture for Advertising Success
Foundation Elements
Creating Mini Apps optimized for advertising effectiveness requires understanding their technical constraints and advantages:
Telegram Mini App Structure
Size limitations (typically under 10MB)
WebView-based rendering
JavaScript/HTML/CSS foundation
Telegram Bot API integration
Platform-specific UI components
These technical foundations directly impact advertising strategy by influencing:
Loading speed and initial user experience
Feature capabilities that can be highlighted in advertisements
Integration potential with Telegram's native features
Performance consistency across different devices and regions
Development resource requirements and timelines
Performance Optimization for Ad Effectiveness
Advertisements for Mini Apps must emphasize performance advantages, which require:
Efficient code structure minimizing initial load time
Strategic asset loading prioritizing visible elements
Memory management for sustained performance
Battery usage considerations for prolonged engagement
Network efficiency for users with limited connectivity
User Acquisition Strategy Framework
Channel-Specific Targeting
Telegram's ecosystem offers unique targeting opportunities based on:
Channel memberships indicating specific interests
Bot usage patterns revealing user behaviors
Language settings for linguistic targeting
Geographic activity for location-based campaigns
Device characteristics for technical compatibility
Creative Asset Development
Effective advertising assets for Telegram Mini Apps should:
Demonstrate functionality in action through short animations
Highlight platform-specific advantages compared to standalone apps
Showcase integration with existing Telegram workflows
Address potential technical concerns pre-emptively
Emphasize security and privacy advantages
A/B Testing Methodology
Optimizing ad performance requires systematic testing of:
Element: Visuals Variables to Test: Animation vs. Static, Color Schemes, UI Focus Measurement Metrics: CTR, Engagement Time
Element: Messaging Variables to Test: Technical vs. Benefit-Focused, Length, Terminology Measurement Metrics: Conversion Rate, Bounce Rate
Element: Call-to-Action Variables to Test: Phrasing, Placement, Design, Urgency Elements Measurement Metrics: Activation Rate, Time to Action
Element: Targeting Variables to Test: Channel Categories, Geographic Focus, Time of Day Measurement Metrics: CAC, Conversion Quality
Development Workflow for Advertising-Optimized Mini Apps
1. Research and Concept Validation
Before development begins, assess:
Competitor analysis within the Telegram ecosystem
Feature prioritization based on advertising potential
Technical feasibility within platform constraints
User experience flow specifically designed for ad-driven traffic
Performance benchmarks for similar applications
2. Instrumentation for Measurement
Implement comprehensive analytics from day one:
Entry point tracking for attribution accuracy
Event logging for user journey analysis
Conversion funnel visualization
Performance metrics correlation with user behavior
A/B testing infrastructure for continuous optimization
3. Progressive Development Approach
Structure development to support advertising goals:
Focus on core functionality for initial advertising campaigns
Implement rapid iteration cycles based on ad performance data
Prioritize features that demonstrate well in advertising formats
Balance innovation with familiar patterns to reduce learning curves
Develop with variable network conditions in mind
4. QA with Advertising Focus
Test specifically for advertising-related scenarios:
First-time user experience coming directly from ads
Performance under high-volume traffic conditions
Behavior with various entry point parameters
Cross-device consistency of advertised features
Error handling visible to new users
Monetization Models and Ad Strategy Alignment
The advertising approach should align with the Mini App's monetization strategy:
Direct Revenue Models
For applications using direct monetization, advertisements should:
Clearly communicate value proposition before purchase request
Demonstrate premium features without revealing all functionality
Establish trust through transparency about pricing
Highlight security of Telegram's payment infrastructure
Compare value to similar premium applications
Indirect Monetization Approaches
For applications using alternative revenue models, advertisements should focus on:
User acquisition cost relative to lifetime value
Engagement metrics that correlate with monetization potential
Viral coefficient and organic sharing capabilities
Retention indicators predicting long-term value
Community building potential for sustained engagement
Technical Case Study: Gaming Mini App
A developer team created a multiplayer puzzle game as a Telegram Mini App with these technical considerations:
Core Technology Stack: JavaScript with Canvas for rendering, WebSockets for real-time multiplayer
Size Optimization: Procedural generation of puzzles rather than pre-built levels
Performance Focus: Efficient animation techniques and asset management
Telegram Integration: Native sharing for challenge invitations, bot integration for notifications
Their advertising strategy highlighted:
Instant gameplay without installation
Challenge mechanics between Telegram contacts
Performance advantages over similar native applications
Integration with existing Telegram groups and channels
Technical results included:
94% of users completed first puzzle (vs. 72% industry average for installed games)
Average load time of 1.2 seconds (vs. 24+ seconds for app store download)
58% lower development cost compared to dual-platform native development
3.2x higher update frequency due to bypassing app store review processes
Code Implementation Examples
Optimizing First Impressions for Ad Traffic
When users arrive from advertisements, loading perception is critical:
// Progressive loading strategy for ad-driven traffic document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => { // Immediately show interface shell renderApplicationShell();
// Track entry from advertisement const urlParams = new URLSearchParams(window.location.search); const adSource = urlParams.get('utm_source'); const adCampaign = urlParams.get('utm_campaign');
// Log attribution data logAttribution(adSource, adCampaign);
// Prioritize loading visible elements first loadPriorityVisuals().then(() => { // Then load functional components loadFunctionalComponents().then(() => { // Finally load non-critical elements loadBackgroundAssets(); }); }); });
Measuring Advertising Effectiveness
Comprehensive attribution tracking is essential:
// Attribution and conversion tracking function trackConversionFromAd(conversionType, value) { const storage = window.localStorage; const entrySource = storage.getItem('entry_source'); const entryTime = storage.getItem('entry_time'); const currentTime = Date.now();
// Calculate time from ad view to conversion const timeToConversion = currentTime - parseInt(entryTime, 10);
// Send conversion data to analytics sendAnalyticsEvent({ type: 'conversion', source: entrySource, conversionType: conversionType, value: value, timeToConversion: timeToConversion });
// Update conversion rates for this campaign updateCampaignMetrics(entrySource, conversionType, value); }
Optimization Strategies for Different Ad Objectives
Awareness Campaign Optimization
When focusing on maximizing reach and initial engagement:
Emphasize visual appeal and instant understanding
Minimize initial data requirements for loading
Showcase unique functionality in first few seconds
Implement memorable branding elements
Optimize for "wow factor" over depth
Conversion-Focused Campaign Optimization
When prioritizing specific user actions:
Structure direct paths to conversion points
Implement persistent but unobtrusive calls-to-action
Create logical progression toward desired outcomes
Remove unnecessary steps in conversion funnels
Provide clear feedback for each user action
Retention-Centered Campaign Optimization
When focusing on long-term engagement:
Highlight progression systems and ongoing value
Demonstrate social features and community aspects
Showcase content variety and depth
Implement reengagement hooks and notifications
Emphasize regular updates and improvements
Advanced Technical Considerations
Cross-Platform Consistency
Ensure advertising promises match reality across:
Different mobile operating systems
Various Telegram client versions
Desktop versus mobile experiences
Different screen sizes and orientations
Various network connection qualities
Security and Privacy Messaging
Address technical security aspects in advertising:
Data storage approaches and privacy advantages
Authentication security within Telegram's ecosystem
Transaction safety for monetized applications
Transparency about data usage and permissions
Compliance with regional regulations
Performance Monitoring for Ad-Driven Traffic
Implement specialized monitoring for:
Traffic spikes during campaign launches
Geographic performance variations
Device-specific technical issues
Conversion rate anomalies requiring investigation
Load time correlations with bounce rates
Future Technical Trends in Telegram Mini App Advertising
As the platform evolves, developers should prepare for:
1. Enhanced Integration Capabilities
Upcoming API enhancements will likely enable deeper integration with Telegram's native features, creating new advertising angles highlighting seamless experiences.
2. Advanced Targeting Mechanisms
More sophisticated audience segmentation tools will enable developers to create multiple advertising variants optimized for specific user segments.
3. Improved Analytics Infrastructure
Enhanced measurement capabilities will provide more granular insights into user behavior, allowing for more precise optimization of both applications and their advertisements.
4. Expanded Creative Formats
New advertising formats specific to the Telegram ecosystem will offer innovative ways to showcase Mini App functionality beyond current capabilities.
5. AI-Driven Optimization
Machine learning integration will enable automatic optimization of both advertising creative and in-app experiences based on performance data.
Conclusion: The Developer's Roadmap to Success
Telegram Mini App Ads represent a distinctive opportunity for developers to reach users in a less saturated, highly engaged environment. By approaching both development and advertising strategy as interconnected elements of a unified user acquisition system, developers can create more effective campaigns that accurately represent their applications' value propositions.
The technical considerations outlined in this guide provide a framework for creating Mini Apps specifically optimized for advertising effectiveness—combining efficient performance, strategic feature prioritization, and comprehensive measurement to maximize return on advertising investment.
As the Telegram Mini App ecosystem continues to evolve, developers who master these technical aspects of advertising optimization will gain significant advantages in user acquisition efficiency, conversion performance, and ultimately, application success within this rapidly growing platform.
0 notes
Text
Webview Digital is a top mobile app development company in Poland, focused on creating innovative mobile applications for businesses throughout Europe.
0 notes
Text
Top Five Plugins to Create a Mobile App for Your WordPress Site
Wapppress – Best WordPress to Android App Converter
Wapppress is the top-rated plugin for instantly creating Android apps from your WordPress website. It’s perfect for beginners and non-developers, offering a simple 3-step process to generate a mobile app. With features like custom splash screen, app icon, push notifications, and AdMob monetization, Wapppress ensures your app is functional, fast, and aligned with your site’s design. Whether you're running a blog, eCommerce store, or business site, Wapppress offers a quick and cost-effective way to go mobile.
AppMySite – No-Code App Builder AppMySite is a powerful platform that allows users to build Android and iOS apps without any coding. It supports WooCommerce, real-time sync, and in-app purchases. You can preview your app live and publish it to app stores with ease. However, it may require a subscription for full features.
Web2App – Android WebView App Template Web2App is a CodeCanyon plugin that converts your mobile-optimized website into a native Android app. It provides features like navigation menus, pull-to-refresh, and offline support. It’s great for developers seeking more control over app behavior.
WPMobile.App – One-Time Payment App Builder WPMobile.App allows you to create native Android and iOS apps with a one-time payment. It includes push notifications, offline access, and WooCommerce support, making it ideal for long-term projects.
AndroApp – Mobile App for Content Sites AndroApp is suitable for blogs, news, and content-heavy websites. It supports offline reading, monetization, and push notifications. It doesn't support iOS, which may be a limitation for some users.
Conclusion: If you're looking for speed, ease of use, and affordability, Wapppress is the best choice for turning your WordPress site into a mobile app quickly.
0 notes
Text
Step-by-Step Guide to Convert Website into Android App Seamlessly
In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses need to stay connected with their customers through multiple channels. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is by converting your website into an Android app. Not only does this improve user experience, but it also enhances accessibility and engagement. In this step-by-step guide, we will explore how to convert website into android app seamlessly.
Why Convert Website into Android App?
Before diving into the conversion process, it’s important to understand the reasons behind converting a website into an Android app. An Android app offers several advantages, including:
Enhanced User Experience: An app provides a smoother, faster, and more personalized experience compared to a mobile website.
Push Notifications: With an app, you can send real-time updates, promotions, and reminders directly to your users’ devices.
Offline Access: Users can access app content even without an internet connection, which is not always possible with websites.
Better Engagement: An Android app allows for deeper interaction with customers, increasing engagement and customer retention.
Step 1: Assess the Website’s Requirements
The first step in the process of converting your website into an Android app is assessing the website’s functionality and design. You need to determine whether the website is optimized for mobile use and whether all the features can be effectively transferred to an app. If your website has complex functionalities, you might need to consider simplifying them for the mobile experience.
Step 2: Choose the Right Conversion Method
There are multiple methods available to convert website into Android app, and the one you choose will depend on your website’s structure and your budget. The common methods include:
WebView App: This is the simplest way to convert your website into an Android app. It essentially loads your website in a mobile app frame, offering the look and feel of an app without significant development.
Native Android App: If you require additional features like offline capabilities or advanced functionality, building a native Android app from scratch might be the better option. This method requires more time and resources but offers a more custom-tailored experience.
Hybrid App: A hybrid approach uses frameworks like React Native or Flutter, enabling you to write code once and deploy it to both Android and iOS platforms.
Step 3: Develop the Android App
After selecting the right method to convert website into Android app, it’s time for development. For a WebView app, the process involves creating a wrapper for your website and ensuring it functions seamlessly within the app environment. For native or hybrid apps, you will need a development team to code the app based on your requirements.
Some key features to consider during development are:
Responsive Design: Ensure that your app is optimized for all screen sizes, from smartphones to tablets.
User Interface (UI): Focus on a user-friendly UI that replicates the website’s aesthetic while ensuring it’s intuitive and mobile-friendly.
Performance Optimization: Speed is critical for mobile apps, so optimize loading times and minimize lag.
Step 4: Testing the App
Before launching the app, extensive testing is crucial. Test the app across various Android devices to ensure compatibility and usability. You should check for:
Bug-free Functionality: Make sure that all website features are working correctly within the app environment.
User Experience: Ensure that the app is easy to navigate and offers a smooth experience for users.
Security: Implement security measures to protect user data and ensure the app is safe from potential vulnerabilities.
Step 5: Publish the Android App
Once the app is ready, it’s time to publish it on the Google Play Store. You will need a developer account to submit your app. During the submission process, you will need to provide the app’s description, screenshots, and other necessary details. After the app passes the review process, it will be available for download on the Play Store.
Step 6: Promote Your App
Once your app is live, it’s essential to promote it to your audience. Inform your website users about the availability of the Android app through email campaigns, social media, and your website. Encourage them to download and use the app to enjoy enhanced features and benefits.
Conclusion
Converting your website into an Android app can significantly enhance your online presence and improve user engagement. By following this step-by-step guide to convert website into Android app, you can offer a seamless mobile experience to your customers. Whether you opt for a WebView app, native app, or hybrid approach, the key is to focus on delivering a high-quality, user-friendly app. So, start the conversion process today and take your business to the next level!
0 notes
Text
Ionic vs NativeScript-Is Ionic Truly Untouchable or Skipping on NativeScript?

Before we start the debate of Ionic vs Nativescript, let me clear the air of what’s what.
What’s Ionic?
Ionic, a powerful mobile framework that aids you with building native-like-feeling mobile apps with technologies as HTML, CSS & JS. HTML5 SDK that helps you build using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Ionic is focused mainly on the look and feel, and UI interaction of your app. That means we aren’t a replacement for PhoneGap or your favorite JavaScript framework. Is Ionic truly untouchable, or are we skipping on NativeScript?
What’s NativeScript?
NativeScript, an open-source framework for developing apps solely for iOS/Android platforms. In other words, rather than the native-like-feel you get the full experience.
Now that we have set this aside, let’s get into what really sets them apart.
Ionic vs NativeScript
1. Development Speed
2. UI
3. Performance
Development speed
Coding in Ionic is comparatively faster and a lot less tiring. Constructed on top of Angular and built using Apache Cordova, Ionic stands out in hybrid application services, without requiring custom technologies.
However, coding in NativeScript comparatively takes more time. Being a transpiling language, that uses JavaScript, the options seem limited.
UI
When considering performance, Ionic is not suitable for application with complex tasks since it runs on WebView. On the other hand, NativeScript comes off as a one-piece process.
Performance
UI/X has taken over this past few years by storm as we know it. However, both Ionic and NativeScript support them, yet NativeScript comes out top in this due to its seamlessness and rich UI supplement. (Looking to perfect your mobile application UI/X design, check this out)
Ionic comes with UI components for a native-like UI experience. NativeScript uses XML based UI designing and styling through CSS. The component library is built on top of native control for a seamless UI experience compared to that of Ionic.
Ionic vs Native – An overview
What sets them apart?
The key difference is that Ionic requires additional plugins to access system features however, Native doesn’t require this as it has access to the whole API.
Who can benefit from Ionic?
Anyone who is set to develop hybrid mobile apps using CSS, HTML5 or Web platform technology.
Who can benefit from NativeScript?
Anyone who intends to develop an Android or iOS using JavaScript, by sharing the code across platforms.
Wrap up
Wrapping up, I want to make it clear that I am not debating that one is better than the other. To be more precise, when you are in need of creating an application within a limited timeline, that supports both mobile and web browser Ionic should be your means. However, if you want your application to handle complex tasks and your primary goal is performance then opt for NativeScript.
#Ionic#NativeScript#MobileAppDevelopment#HybridApps#UI#Performance#DevelopmentSpeed#WebView#JavaScript#AppDevelopment#MobileFrameworks#Angular#ApacheCordova#NativeExperience#UIComponents#CrossPlatformDevelopment
0 notes
Text
Mobile app development can be costly, much more than a functional website. And as mobile technologies are evolving, experts are trying to figure out ways to reduce this cost. Cross-platform application frameworks are a step towards this motive. Before the introduction of these, businesses had to make different versions of mobile app. A version each for iOS and Android. Hiring experts of two different technologies can be too costly. And not to mention the maintenance cost of each app. React Native and Ionic are two of the popular cross-platform app development platforms going around. In 2020, React native was the most popular mobile app framework used by developers. Ionics was fourth on the list. However, as the two platforms are being continuously improved, the race is still on. Ionics vs React Native has become a hot debate in the developers' community. In this article, I’m going to compare the two in different aspects. I’m not going to be biased, nor am I going to reach a final verdict. The final decision will be yours. So, let's get started! 1. Functionalities React Native and Ionic are two different frameworks, thus they have different functionalities. One has to be proficient in JavaScript as React native apps are developed using JS. The code communicates with the platform, be it iOS or Android, and relays necessary data calls and functions to the native platform API. There’s a JavaScript API that connects with the native platform API via a bridge. This bridge is the reason why React native apps work like native apps. On the other hand, Ionic is based on Cordova that uses a Webview component (UIWebView on iOS and WebView on Android) or a chromeless browser view. The WebView components use an HTML layout engine to render HTML/CSS user interface. Cordova relies on a Javascript-native bridge to ensure communication between the WebView application and the Native platform. This way, the framework can access Native APIs and device features like the camera. 2. Technology Stack As said before, React Native is written in the JavaScript framework. Instead of HTML, the UI pieces are written in JSX. JSX incorporates all the powers of JavaScript and is much more advanced than any other language template. React Native uses both React because both frameworks are open-sourced and products of the same company, Facebook. If we talk about the technology stack of Ionic, you can use Angular, Vue, or even React to build Ionic apps. That makes it a little more flexible than React Native. The latest release of Ionic 4 allows you to use Ionic even with any web development framework. In this regard, developers might consider Ionic a better option -- especially after the recent update. It has opened up a huge amount of flexibility in building Ionic apps. Even web developers can learn and use this framework to develop Ionic apps. 3. Learning Curve The learning curve of different technologies varies greatly. Most people find React Native easy to learn and get started with it in little time. The concepts and way of coding are pretty much the same in React. If you know a bit about React and React Native, you must be aware of the small differences. For example, react has web components like , , while React Native has components that are wrappers around native iOS and Android components. However, if we talk about people who don’t know React, they will have to learn JavaScript and React first. And the learning curve can be quite steep with no React knowledge. On the other hand, Ionic’s tech is flexible. While implementing this framework, developers use JavaScript, CSS, and HTML along with their chosen web framework. It could be Angular, React, Knockout, Vue, or any other compatible framework. So, the learning curve here isn’t as steep as it can be in the case of React Native if you have no knowledge of React. 4. Performance Well, I’ll be honest here. Native apps are great if you are someone keen to give a top-notch performance to your users.
The comparison is between Ionic and React Native, not native apps vs either of them as native apps always exceed the other two. React Native is closer to native apps in terms of performance. And a little ahead of Ionic. React Native uses JavaScript to build native apps, so it has the same look and feel like a native app, and even uses the same building blocks that native apps use. On the other hand, Ionic is a hybrid approach. It doesn’t build native apps and you can encounter performance issues as there are lots of callbacks to the native code. This can also cause a lag. Also, you have to use the Cordova plugin if you want to access native features. One has to deal with performance issues while building UIs. So, if we sum this up, React Native is quite better in terms of performance. 5. Developer Community Community is something we all consider when choosing a certain technology to learn. The more people are involved in it, the faster it grows with time. GitHub stats indicate strong community involvement in both technologies. React Native has over 1900 contributors to the framework, while Ionic has around 330 contributors to the framework. React Native has 78k stars while Ionic has 38k stars. Hence, in terms of community, React Native is far ahead of ionic. But with the recent updates, we can expect Ionic to have greater community involvement in the coming months. P.S. Whatever framework you prefer, we love both! We are a Mobile App Development Company in Dubai with a strong clientele base all across UAE. For the design and development of any kind of app, we’re ready to help. Get in touch for more details.
0 notes
Text
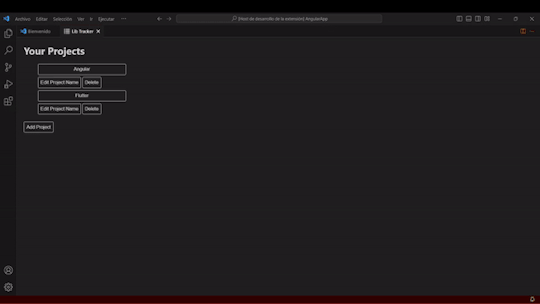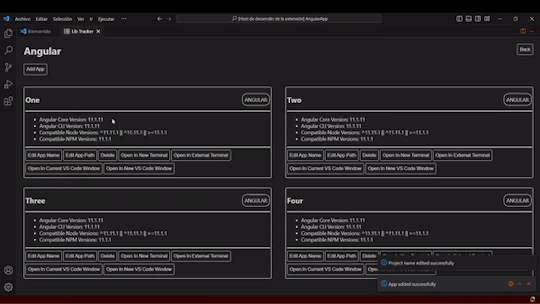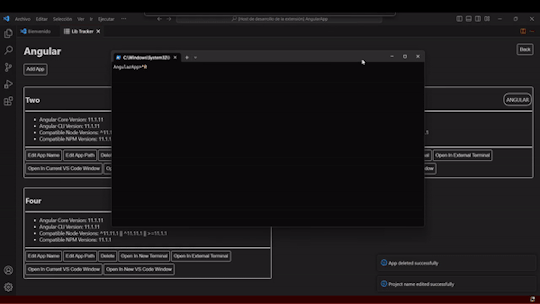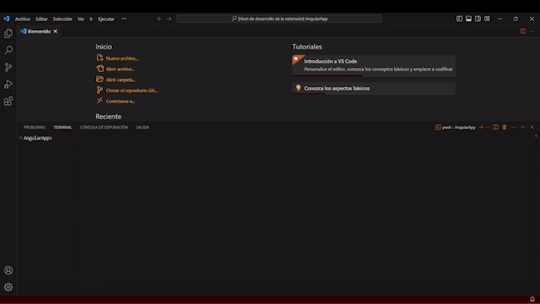
🚧 **LibTracker Development Update**
We've been making solid progress on LibTracker, our lightweight SBOM tool designed to simplify dependency management. Recent updates include:
🔹 Current Progress
Completed CRUD functionality for projects and apps
Enabled opening apps directly in the terminal or VS Code
Added support for Flutter on Android, iOS, and macOS
🔍 Learned So Far
WebView panels don't support alert, confirm, or modals
Panel development resembles a client-server model, where the WebView panel acts as the client, and extension API lives on the "server"
Vanilla JS has proven useful for TDD
Leveraged npm libraries to parse Gradle files for Android support
🎯 Next Steps
Obtain framework and programming language metadata for all apps listed in the popular section
Develop an app dependency page to:
View licenses
Display security vulnerabilities
Enable CRUD on dependencies
(Possibly) Identify unused packages—challenging but potentially achievable with executables
Let us know your thoughts and any insights
0 notes
Text
Why Flutter is the Ideal Choice for Hybrid App Development

In today’s competitive app market, businesses are developing hybrid applications to create versatile applications that work seamlessly across multiple platforms. Flutter has emerged as the leading choice for developers and companies alike. But why is Flutter considered the best platform for hybrid app development? This article explores the advantages of Flutter and why many companies are opting for it to build cross-platform applications.
What is Flutter?
Flutter is an open-source UI software development kit (SDK) created by Google. It allows developers to create natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase. With a growing developer community and continuous updates, Flutter has gained massive popularity for its ability to deliver visually appealing and highly functional hybrid apps.
Advantages of Flutter in Hybrid App Development
1. Single Codebase for Multiple Platforms
One of Flutter’s biggest strengths is its ability to develop apps for both iOS and Android using a single codebase. This eliminates the need for separate development teams for each platform, saving time and resources. By leveraging Flutter’s “write once, run anywhere” approach, developers can ensure consistent performance and appearance across platforms, leading to faster development cycles.
2. Fast Development with Hot Reload
Flutter’s hot reload feature allows developers to instantly see changes made to the code without losing the app's current state. This significantly speeds up the development process by enabling real-time iteration and testing. With quicker debugging and faster adjustments, Flutter helps developers deliver high-quality apps more efficiently.
3. Customizable Widgets for Flexible UI
Flutter offers a rich library of pre-designed and customizable widgets that make UI development both flexible and intuitive. Whether you need a native look or a customized design, Flutter provides the tools to create a smooth user experience. The ease of designing attractive interfaces without compromising functionality gives it a huge edge in hybrid app development.
4. Excellent Performance
Flutter doesn’t rely on WebView components or JavaScript bridges, unlike other hybrid frameworks. Instead, it uses Dart, a modern programming language that compiles native machine code. This ensures Flutter apps perform nearly as well as native apps, offering smooth animations and fast response times that are critical for a good user experience.
5. Vibrant Community and Ecosystem
Another significant benefit of Flutter is its growing community and support ecosystem. The platform is backed by Google, which means continuous improvements, reliable updates, and a plethora of libraries and plugins to extend its functionality. Whether you're a Flutter app development company or a solo developer, the availability of community support can help you overcome challenges during the app creation process.
Why Choose Flutter for Your Next Hybrid App?
Choosing Flutter can provide businesses with cost-effective and future-proof solutions. With access to top-notch tools, reusable code, and superior performance, Flutter app development services offer a reliable path for hybrid apps that don’t compromise on quality. As more industries lean toward hybrid development, Flutter’s versatility makes it the go-to choice.
Conclusion
Flutter stands out as the optimal solution for businesses looking to create high-performance hybrid apps with minimal development costs. From its single codebase and customizable widgets to its excellent performance, it’s no wonder that more companies are turning to Flutter app development services to bring their app ideas to life. As a leading Flutter app development company, investing in this platform ensures you're ready to meet the evolving needs of users in today’s fast-paced digital world.
#flutter app perfromance#flutter performance#flutter app development#flutter architecture#flutter app developers#mobile app development#iphone app development#iphone application development services#flutter app development company#flutter app development services
0 notes