#ajax interview questions and answers pdf
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Interview questions on ajax
The foundations of ASP.NET, server controls, data controls, state management, sessions, cookies, authentication, authorization, and AJAX will all be covered in this article. ajax interview questions. Click here to learn more about it.
0 notes
Text
Portfolio Psd Template

An impressive and informative portfolio is a must these days if you want to stand out from the crowd. Let’s be serious, we all know how important it is to present your work through a professional portfolio. No matter if it’s a photography portfolio, graphic design portfolio, fashion portfolio, resume portfolio or simply architecture portfolio, Flipsnack’s got portfolio ideas for every situation. You might say that is impossible to make a creative portfolio without design skills! This couldn’t be further from the truth. We’ve already done the design thing for you, so all you’ve got to do now is to edit whichever portfolio template you want! So easy, right? Flipsnack offers you hundreds of free online portfolios so you can unleash your creativity and create the best portfolio ever that will definitely catch everyone’s attention! As we’ve said before, it can be any kind of portfolio, we have plenty of everything. Are you a passionate photographer and want to present your beautiful shots that you’ve captured? How about choosing an online photography portfolio from Flipsnack? Or maybe you’re an architect and you’re preparing to present your work to your next possible client. Try an architecture portfolio layout from us in order to impress! Give the world a chance to admire your outstanding work by displaying it in one of our creative graphic designer online portfolios. Are you looking for a job? What a better way to strike at the interview than creating a portfolio in this sense? Pick one of our cv portfolio templates and get that job! And from now on, we also have resume portfolio templates! What are you waiting for? Try these portfolio examples from Flipsnack now! Flipsnack gives you the opportunity to fully customize the entire online portfolio. Pick stunning and professional images from our stock, or simply upload your own photos. Change the background colors, fonts, and graphics to fit your style with our easy to use Flipsnack editor. Create a powerful brand identity with our free online portfolio builder and inspire your audience. Once you’re pleased with the final result, download your portfolio design as PDF, JPG or PNG. And you can also share it with the entire world with just one click. It’s so nice to create stunning portfolios with Flipsnack!

Find & Download Free Graphic Resources for Portfolio Template. 4,000+ Vectors, Stock Photos & PSD files. Free for commercial use High Quality Images.
PSD Website Templates Home › All free resources › Download Photography Portfolio Template Freebie A free porfolio website template suited for pohotgraphers or for those that like to post and show photos from vacations of traveling.
Find & Download Free Graphic Resources for Portfolio Template. 4,000+ Vectors, Stock Photos & PSD files. Free for commercial use High Quality Images.
Jun 20, 2020 Palun is a personal portfolio psd template which is modern, clean, professional, creatinve and presentable. It is suitable for any personal portfolio, for web designers and developers, UI designers or any other person can show his works using this psd template. We have included a documentation file, to guide you through the psd.
Modern Portfolio PSD Theme. Templates & Themes. Portfolio PSD Theme. Templates & Themes. Architecture Icons. GerduKreatip: Agency Portfolio Theme. Templates & Themes. Cuda Single Page Portfolio Template. Templates & Themes. 200 Common People for Architecture. City of Architecture and pattern.
A portfolio is arguably the most crucial asset for any designer. Having an online portfolio should be one of your main priorities. Even though your resume is absolutely important and will be the first thing that employers will look at, your portfolio will be your secret weapon to stand out and show the complexity of the projects you have worked on. Using a template is smart! Too many designers overthink their portfolio and it creates unnecessary stress. Your portfolio is the true value of your job, so make it look fantastic with these free portfolio website design templates!
Unleash The Power of WordPress Ad
Awesome collection of 11,000+ WordPress Themes, including Bootstrap Templates & Design Assets
Business
WordPress
Blog & Magazine
WordPress
Creative Portfolio
WordPress
Ecommerce
WordPress
Landing Page
WordPress
Retail
WordPress
Kards is a modern and clean personal vCard website template. It has many cool features found in premium templates. It has timeline items, stats section, skillbars, working ajax form, frontend form validation, a portfolio section to showcase your works and many more. It looks great on all devices from mobile to desktop. It’s also retina ready so your site will look crisp and sharp on any device. Kards is the ideal template for creating digital personal resume and portfolio website.
Energy offers you severals layouts in order to present yourself and your experiences with simplicity and power thanks the one page template. This template is fully customizable and responsive design for any device.
It is a simple black and white portfolio website built with Bootstrap. It has a clean, minimal design; supports a slider with animated text effect for featured posts; and has awesome portfolio layout to showcase your works in minimal way. It is fully responsive and easy to set up. Whether you are a web developer who want to create professional portfolios or creative professional who wants to build a portfolio on its own you can be greatly benefited by this design templates.
Simple designs to showcase your photos, art, graphics, and other visual content in fully functional, lightbox-style image galleries.
Format is a creative, clean and modern, free website template that you can use for your next portfolio project. If you need a template as a designer, freelancer, agency, web studio, Format is perfect for you! It features pop up video, smooth overlay for portfolio, and animation upon scrolling.
Epitome is a beautifully crafted free resume and personal portfolio website template. It is modern, trendy and features a visually attractive design. An ideal website template for creative professionals and freelancers who want to create an online presence that would stand out from the average. Epitome has all the important elements of an effective resume personal portfolio website template: an awesome fullscreen hero banner, about and qualification section, services, portfolio, testimonial and contact section. Epitome is also mobile and retina ready. It will look great on any devices from mobile to desktop and on any screen resolutions.
Sublime is a Creative HTML5 one-page template designed for creative agencies, studios, digital design, and media agencies or other similar business. The template is a dark theme design with features like fullscreen header/hero section, responsive video lightbox, a nice portfolio section and much more. The template is primarily designed for creative agencies but it is versatile enough to be used for other purposes like a landing page for your startup or business website.
This is a modern and elegant single page HTML5 portfolio template, with a bold feel. Every single detail is carefully designed, in order to enhance user experience. It has a versatile design, which makes it the perfect choice for any kind of projects.
It comes with a very simple and minimalistic concept to make your pictures stand out. This is a clean and creative free responsive portfolio website for photographers who wish to share their incredible stories on stunning gallery style layout. Dropbox free download limit. It is fully compatible with mobile phones, desktop computers and tablets such as iPads.
Venus is a bright and dynamic landing page template for startups. This HTML template is a perfect solution to quickly present your mobile application or to start collecting early interest for an upcoming product launch.
Draco, a free PSD & HTML/CSS resume template. This is perfect for you who are building your resume online. If you’re looking to showcase your portfolio, this is a great template to consider. With its simplistic layout allows visitors to focus on the most important thing — your work. Showcasing your name, picture and bio, the author profile can be displayed on the homepage, which is perfect for telling readers more about yourself, especially if they’re new to your website.
The template is a great solution for photographers, designers and visual artists who need a simple portfolio for showcasing their own work elegantly. Nevada is build on the top of Bootstrap framework and comes with a lightbox gallery feature to make you navigate through the images at full resolution.
Alexis is clean, minimalist, simple and mobile friendly one page Bootstrap portfolio template. It’s lightweight and loads like lightning blot. Alexis is crafted with unmatched possibilities to fit with portfolio site for business firm, freelancers, artists, designers, photographers, creative professionals, and anyone looking for showcasing his high quality work. Alexis Bootstrap portfolio template is an excellent creation, can impress visitors in their first visit. Its interface is fabulous and polished, packed with sequential features which give answer each subconscious questions of potential customers and boost conversion exponentially. Best computer temperature monitor.
This free html5 portfolio template has meaningful interaction with beautiful design flow. So it will help you to impress your user with your portfolio and add more feeling to your works. The serif and sans-serif typography combination with great readability will help the user to understand the contents very well. We used google fonts so you can change these fonts easily anytime. You can customize this template very easily. The HTML, CSS and JavaScript codes are well structured and comment so you can easily modify them.
Architecture Portfolio Template Psd Free
Howdy is a modern & material design vCard / Personal Portfolio template, you can use it to show off yourself to the world in a better way. This template is fully customizable, responsive and bootstrap based. All files and code has been well organized and nicely commented for easy to customize.
MyJourney is a light, fast, responsive HTML/CSS template that can be used for both your personal and client webpage. The clean structure and minimalist design makes it a great choice for your next project. This resource has been created by Pixel Buddha exclusively for GraphicBurger.
The freebie of the day is a bootstrap template that would be a great choice for a startup landing page or any other projects you might consider. This template features a wide/boxed layout toggle and 8 color styles to chose from.
Memphis Design is often found in user interfaces. In fact, it is probably the best way to go with your next project. You could not know the name, you don’t even have to, but I’m sure you’ve seen it before — most likely in modern mobile, web or magazine designs. Discover Roxy, a stylish multi-purpose free Bootstrap template featuring an amazing animated hero section. It has a colorful style and menphis design for digital, business or agency content. The template is multipurpose, so if you like the style, you can use it to represent your art, business, an event, show your portfolio, start a blog, etc.
If you need to showcase your awesome works with elegance and professionalism, then you need to get Architect right away! Architect Free HTML5 Bootstrap Template for Architects and Portfolio Websites. The clean and minimal design along with beautiful typography, big images and smooth animation is ready to entice potential clients. Architect has sticky elements on project details, drop-down menu and off canvas on mobile. Bring your architect business to the next level with Architect!
Today we have for you a developer friendly HTML template with an organized structure that will make a great choice for a portfolio website. Personal is a grid based, ready to use template packed with animations and transitions for a smooth scrolling.
Studorlio is a template for your own personal site. You can have yours running on the cloud in exactly 10 seconds. But first, make sure you have a GitHub account. Ready, set, go!
Today we’d like to share a little decorative effect with you that we’ve encountered on Filippo Bello’s Portfolio, maybe you’ve seen it. It’s a really neat way to add some jazz to background images. The idea is to replicate boxes from a background with the same background image and make these boxes move in perspective towards the viewer. Adding a fitting shadow and some parallax makes all this look quite interesting. Furthermore, we’re employing anime.js, the easy-to-use JavaScript animation library by Julian Garnier.
Drifolio stands for Dribbble Portfolio. There are many designers around me don’t have enough time to setup and manage their own website. For them it could be a great template that needs one time setup. You just need to set your info and dribbble username, that’s all. And after that, whenever you post something on dribbble, it’ll come automatically to your website as well. There’s nothing to do there again. Exclusively crafted for the super lazy designers like me who designed thousand of websites till today but never got a chance to build one himself.
This is a free html code for portfolio layout. It has a beautiful, cool and modern design crafted with elegance in mind. This bootstrap 4 template is ready to give your portfolio website a cool, new look that will surely stand out.
Flat and responsive website template, designed and coded by Maxim Orlov.
An HTML5 minimalistic super-responsive portfolio and blog template. CSS-only hexagon hive gallery!
CVs include information on one’s academic background, including teaching experience, degrees, research, awards, publications, presentations, and other achievements. CVs are thus much longer than resumes, and include more information, particularly related to academic background. Post a link to your CV on sites where you need your personal profile page should be discovered by other users and that provide a lots of information about your professional skills and experience.
Expert is a free one page website template using bootstrap perfect for portfolio, freelancer, agency websites but you can tweak this to suit your needs. This template is responsive and it will look good in all devices. The features are smooth animation upon scrolling, lightbox for video and images, advance owl carousel sliders and many more. Built with the latest technology such as HTML5, CSS3, jQuery, Bootstrap 4 and SCSS.
Elit is an awesome looking onepage free template with a unique portfolio grid layout that is suitable for photographers, freelancers and visual editors that would like to showcase their portfolio online. It has a smooth animation upon the scrolling the page, testimonial slider and an awesome image popup using fancybox.
Create is a free one-page template for portfolio, agency, and freelancers alike of course you can use this to any type of website by tweaking it to suit your needs. The feature includes are lightbox using fancybox, modal video, smooth animation, and testimonial carousel. Build using HTML5, CSS3, jQuery and Bootstrap 4.
This minimalist website design style that the designer is trying to simplify his web interfaces and interactions by deleting unnecessary elements. Minimalism has become an overwhelming trend in current website design. And increasing number of designers have accepted this influential design style and widely used it in their designs. However, as an art of less, designing such minimalist websites does not mean to delete the elements of a website without any restriction. This is best simple, clean and intuitive style of minimalist portfolio website design template for developer and designer.
Clean and minimal design along with necessary content, navigation bar, social media icons, and other important elements make a website more efficient. Here’s another uiCookies free html5 template that is ideal for your next online business, Aside! Aside is a free HTML5 Bootstrap 4 website template perfect for all photography, restaurant, company, individual or agencies portfolios. This template makes it different from previous templates because of the site navigation places on the left side. It features owl carousel and smooth animation on images upon scrolling, mobile off-canvas menu and along with its clean and minimal design.
This is minimalistic, clean and modern template specially designed for all kinds of creators. Made with attention to details, it’s an excellent choice for the presentation of your beautiful portfolio.
Allium is a clean and minimalist porfolio website that allows your reader to focus on your content. It is a beautifully designed, intuitive and attractive, engaging and dynamic, powerful and accessible, gorgeous and flexible free portfolio website. It is specifically developed for creating all types of portfolio websites. Everything you need to build your personal portfolio you can get it through Box.
It is a simple, easy to use, modern and creative portfolio with awesome typography and layout. It is a unique website that delivers amazing imagery for your personal portfolio sites, with a standard two column grid supported by masonry , you’ll always expect a perfect design no matter which device you are on, be it your iPhone, android phone or desktop.
Starting a portfolio page is easy with this modern HTML template due to the features and flat easy going design, large header and clean design. It is responsive, cross-browser compatible. It has a welcoming header on the homepage to impress visitors at the very first sight. Its design is well thought to keep readers focus on content. It has been designed for everybody with or without previous coding experience to effectively and helps to speedily put together polished, professional quality websites without having to so much as peek at a single line of code.
Stylish Portfolio is a one page Bootstrap portfolio theme with off canvas navigation and smooth scrolling through content sections.
It provides a powerful way to showcase your work. It is built with the HTML5 and CSS3 latest technologies, but at the same time make it compatible with older browser versions.
Psd Template Brochure
Avana is a free minimal portfolio HTML template ideal for creative agencies that want to better showcase their own portfolio. The template is built on Bootstrap and takes advantage of Google Fonts and nice appearing animations on scroll. Designed and released by the creative team at Designstub.

0 notes
Text
300+ TOP PROTOTYPE Interview Questions and Answers
Prototype JavaScript Framework Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Prototype? Prototype is a JavaScript framework which is used in dynamic web applications. It is a namespace and a module that is used to manage HTML forms. It is also a JavaScript Library. 2. Who is the developer of Prototype? Sam Stephenson is the developer of Prototype. 3. What are the features of Prototype? The features of Prototype are: Extends DOM elements Powerful Ajax features Does not provide widgets Advanced support for event management It is not a complete application development framework Built-in support for class-style OOP including inheritance 5. What is underscore() method in Prototype String Method? underscore() method: This method is used to converts a String into a series of words separated by an underscore. 6. What is inspect() method in Prototype String Method? inspect() method: This method is used to returns a debug-oriented version of the string. 7. What is empty() method in Prototype Element Method? empty() method is used to check whether the element is empty or not. 8. What is Templates in Prototype? Templates: It is used for formatting group of similar objects. It is also used to produce formatted output for these objects. 9. What are the steps to create the formatted output in Prototype? The steps to create the formatted output are: Step1: Create a template Step2: Defining actual values Step3: Mapping Keys and replacing Values 10. What is include() method in Prototype? include method: This method is used to determine whether the value is included in the range or not. If the value is included, then returns true otherwise returns false.

PROTOTYPE Interview Questions 11. What is $A() method in Prototype? $A() method: This method is used to converts the single argument it receives into an array object. 12. What is $w() method in Prototype? The $w() method is used to splits a string into an array. Here, all whitespace are treated as delimiters. 13. What is AJAX in Prototype? AJAX stands for Asynchronous JavaScript and XML. It is a technique which is used for creating faster, better and more interactive web applications. 14. What is Date.toJSON() in Prototype? The Date.toJSON() method is used to convert the date into a JSON string. 15. What are the ways to construct a Hash instance in Prototype? Two ways to construct a Hash instance are: By using new JavaScript keyword By using $H(Prototype Utility function) 16. What is the use of PeriodicalExecuter object? PeriodicalExecuter object: It is used to execute a function many times after a certain period of time. 17. What is the major advantage of PeriodicalExecuter? The major advantage of PeriodicalExecuter is: PeriodicalExecuter shields you against multiple parallel executions of the callback function. 18. What is the syntax of $R utility function in Prototype? The syntax of $R utility function is: $R(start, end); Example: $R(1, 10).inspect(); 19. What are the AJAX methods available in Prototype? The AJAX methods available in Prototype are: Ajax Options Ajax.PeriodicalUpdater() Ajax.Request() Ajax.Responders() Ajax.Response() Ajax.Updater() 20. Name some callbacks that are not implemented by all browsers? Callbacks that are not implemented by all browsers are: onLoaded onLoading onInteractive onUninitialized 21. What are the methods provided by JSON for Encoding in Prototype? The methods provided by JSON for Encoding are: Number.toJSON() String.toJSON() Array.toJSON() Hash.toJSON() Date.toJSON() Object.toJSON() 22. What are the features of JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)? The features of JSON are: JSON is a lightweight data-interchange format Easy to read and write for humans Easy to parse and generate for machines Based on JavaScript Programming Language Completely language independent 23. What is the use of $H method in Prototype? $H method: This method is used to convert object into enumerable Hash object. Syntax:$H() 24. What will be the output of the following code snippet? var heyObject = {}; .each(function(name, index) { this = index; }, heyObject); heyObject; Output: { foo: 0, Tuto: 1, rial: 2} 25. What is the syntax of pluck() method in Prototype? The syntax of pluck() method is: Iterator.pluck(propertyName); 26. What is the use of isHash() method in Prototype? isHash() method: Returns true if object is an instance of the Hash class, Otherwise returns false. 27. What are the form methods available in Prototype? The form methods available in Prototype are: disable() enable() findFirstElement() focusFirstElement() getElements() getInputs() request() reset() serialize() serializeElements() 28. What is the use of isJSON() method in Prototype? isJSON() method: It is used to check the string is valid JSON with the help of regular expressions. Prototype Interview Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
ajax interview questions
You will learn about the foundations of ASP.NET, server controls, data controls, state management, sessions, cookies, authentication, authorization, and AJAX in this section. interview questions on ajax
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP Sencha Touch Interview Questions and Answers
Sencha Touch Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Sencha Touch? Sencha Touch is an UI (User Interface) JavaScript library. It is written in JavaScript. It is used to build mobile interface quickly and easily. It works on many devices. 2. What are the types of data integrations? The types of data Integrations: AJAX JSONP YQL 3. What is the latest version of Sencha Touch? The latest version of Sencha Touch is 2.4. 4. What are the networks supported by Sencha Touch? Sencha Touch supports following network: HTTP GPS (location-based web services and accelerometer input). 5. What are the languages supported by Sencha Touch? Sencha Touch supports different languages: HTML5 CSS3 Java Script 6. How can we write a hello world program in Sencha Touch? We can write a hello world program by using following codes: Ext.Viewport.add({ xtype: 'panel', html: 'Hello World!' }); 7. What is the stable release version of Sencha Touch? Stable version of Sencha Touch is 2.4.2 and released on June 15, 2015. 8. What are the features of Sencha Touch? The following features of Sencha Touch are: It is easy to setup. It provides adaptive layouts, animations. It provides a set of graphical user interface controls or components. It helps to built-in transitions effects It provides code compatibility of new version with older one. It supports touch event management like: Tap, Double Tap, pinch, Swip and Scrole etc. 9. What are the services of Sencha Touch? Sencha Touch provides various services that are: Comprehensive Services. User Interface (UI) design and development. System architecture specification and review Development Team Mentoring Custom component development etc. 10. What is the difference between jQuery Mobile and Sencha Touch? There are following difference between jQuery and Sencha Touch that are listed table. jQuery Mobile Sencha Touch It supports more than one mobile platform. It supports iOS, Android and Blackberry. It provides UI features with lots of control. It also provides UI features but it is best. It is easy to use. But it is not. It supports only markup and jquery script. But it supports more MVC style application.

Sencha Touch Interview Questions 11. What are the limitations of Sencha Touch? There are following limitations of Sencha Touch that are: It does not have access to the contacts. It does not provide the push notification facility, It is paid for commercial applications. It is not good for hardcore graphics and animations apps such as for gaming apps. 12. What are naming convention in Sencha Touch? In Sencha Touch, naming convention is used to make code more readable and understandable to the other programmers. Following are some naming convention: Name Convention Description Class Name It should start with uppercase letter and followed by camel case E.g. StudentClass. Method Name It should start with lowercase letter and followed by camel case E.g. studentMethod (). Variable Name It should start with lowercase letter and followed by camel case E.g. studentName. Constant Name It should be in uppercase only E.g. COUNT, MAX_VALUE. Property Name It should start with lowercase letter and followed by camel case E.g.enableColumnResize = true. 13. What are events and how to write method in Sencha Touch? In Sencha Touch, Events are something which gets fired when something happens to the class. The following methods of writing events: Built in events using listeners Attaching events later Custom events 14. What are Sencha Touch Layouts and its library? Sencha Touch layouts are a way to arrange an element in to container. It could be horizontal and vertical. The following libraries are: hBox: It allows the element to categories in the horizontal manner. vBox: It allows the element to categories in the vertical manner. Fit : It allows the container to filled with a single panel. Card(TabPanel): It helps to arrange different components in tab fashion. 15. What are the devices supported by Sencha Touch? Android, iOS, Windows, Tizen, Microsoft Surface Pro, RT and BlackBerry devices are supported by Sencha Touch. 16. What are the project structures of Sencha Touch? The project structures of Sencha Touch are given below: src resources CSS files Images JavaScript App Folder Controller Contoller.js Model Model.js Store Store.js View View.js Utils Utils.js app.js HTML files 17. What is data package in Sencha Touch? In Sencha Touch, data package is responsive for carrying of data manipulation either storing or loading the data. It is related to model, store and proxies. 18. How can we write a simple phone profile? We can write a simple phone profile by using following code: Ext.define('Mail.profile.Phone', { extend: 'Ext.app.Profile', config: { name: 'Phone', views: }, isActive: function() { return Ext.os.is('Phone'); } }); 19. What are the devices detection methods in Sencha Touch? In Sencha Touch, device detection methods are given in below table Device Detection method Description Ext.os.is.iPad It will return true if we are using IPad. Ext.os.is.iPhone It will return true if we are using iPhone else it returns false. Ext.os.is.iPod It will return true if we are using iPod. 20. In which language Sencha Touch was written? Sencha Touch was written in Java Script language. 21. What is the difference between Native Apps and Web Apps? There are following difference between Native Apps and Web Apps. Native Apps Web Apps It is easy to access to device features. Any device can access app. Direct access to users through marketplace. Do not need to go through marketplaces. It is high level function capabilities. Do not need to participate in Apple Developer program. It is easier to make available offline. Cannot easily access device features like Motion. 22. Which command is used to create an app in Sencha Touch? In Sencha Touch, “sencha -sdk path/to/touch generate app appName” command is used to create an app. 23. What is Sencha Inspector? Sencha Inspector is a debugging tool that is used to debug any issue in Sencha Code during development. 24. What are the limitations of Sencha Touch? There are following limitation of Sencha Touch: The app does not access device’s camera, contacts and accelerometer. It does not provide the push notifications. Commercial applications are not free. It is not good for hardcore graphics and animations. 25. How can we add CDN link in Sencha Touch? We can add CDN link in Sencha Touch by using following given code: 26. What are the files while installing the project? There are various files while installing the projects: App app.js app.json index.html package.json resources 27. Is Sencha Touch a W3c Standard? Yes, Sencha Touch a W3c Standard. 28. What are the types of layouts in Sencha Touch? There are following types of layouts in Sencha Touch. hBox Vbox Fit Card 29. What is XHR2 in Sencha Touch? In Sencha Touch, XHR2 stands for xmlHttpRequest level 2. It is used to request data from the server. It is also used to configure with Ajax. 30. Who is the developer of Sencha Touch? Sencha is the developer of Sencha Touch. Sencha Touch Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP SYMFONY Interview Questions and Answers
Symfony Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Symfony? Symfony is an open source, web application framework. It is written in PHP and used to design PHP applications. It was first released on18 October, 2005. 2. What is current Stable version of Symfony? Current stable version of Symfony is 3.3.2 and was released on 6 June, 2017. 3. What are the benefits of Symfony? Symfony has various benefits that are listed below: Fast development MVC Pattern Unlimited flexibility Expandable Stable and sustainable Ease of use. 4. Does Symfony use Controller? Yes, Symfony framework use controller. A controller is a PHP function that is used to handle HTTP request and response. The response could be in the form of HTML page, an XML document, an image, a redirect, a 404 error etc. 5. What are the innovations in Symfony2? In Symfony2, some following Innovations are: Symfony2 uses the Dependency Injection pattern. Symfony2 is packaged as Distributions Everything is a Bundle in Symfony2. Symfony2 eases the debugging of your application. Symfony takes Security very seriously 6) How can we install Symfony2? We can install Symfony2 using given following command: In Windows : php -r "readfile('https://symfony.com/installer');" > symfony InLinux and macOS System : sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/bin sudo curl -LsS https://symfony.com/installer -o /usr/local/bin/symfony sudo chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/symfony 7. How can we create controller in Symfony2? In Symfony, we can create controller by extending AbstractActionController class. Example use Zend\Mvc\Controller\AbstractActionController; use Zend\View\Model\ViewModel; class IndexController extends AbstractActionController { public function indexAction() { return new ViewModel(); } } 8. How can we get the request parameters in symfony2? In Symfony, we can get the request parameter using following method: $request = $this->container->get('request'); $name=$request->query->get('name'); 9. When Symfony denies the user access? Symfony denies the user access, when a unauthorized user try to access web application, it throws a 403 HTTP status and error page. 10. In which technology, routing configuration files are written? Routing configuration files are written in the following technology: YAML PHP XML

SYMFONY Interview Questions 11. What is the default routing configuration file in Symfony2 application? Default routing configuration file is: app/config/routing.yml 12. How to create a bundle called AcmeHelloBundle, what command we need to run. Create a bundle called AcmeHelloBundle and run the following command. $ php app/console generate:bundle –namespace=Acme/HelloBundle –format=yml 13. How we can create action in Symfony2 controller? We can create action using following command: public function indexAction() { return $this->render('user/index.html.twig', ); } 14. How can we get current route in Symfony? We can get current route in Symfony using following steps: $request = $this->container->get('request'); $currentRouteName = $request->get('_route'); 15. What is an Environment in Symfony? In Symfony, an environment represents a group of configurations that’s used to run your application. It defines two environments by default: dev (suited for when developing the application locally) prod (optimized for when executing the application on production). 16. What are the Symfony framework applications? There are various Symfony framework applications: Drupal 8 Thelia Dailymotion 17. What are the web servers supported by Symfony? Symfony support various web servers that are given below: WAMP (Windows) LAMP (Linux) XAMP (Multi-platform) MAMP (Macintosh) Nginx (Multi-platform) Microsoft IIS (Windows) PHP built-in development web server (Multi-platform) 18. What is Serializer in Symfony? In Symfony, Serializer is a component that provides an option to convert a PHP object into a specific format such as XMLL, JSON, Binary etc. 19. How to create a request object in Symfony? In Symfony, createFromGlobals() method is used to create a request object in Symfony. 20. What is Twing? Twing is a powerful templating language of Symfony. It performs whitespace control, sandboxing and automatic HTML escaping. 21. Does Symfony framework support component to work with database? No, Symfony does not support component to work with database. 22. What is the syntax of EmailType in Symfony? In Symfony, the following syntax of EmailType is: use Symfony\Component\Form\Extension\Core\Type\EmailType; $builder->add('token', EmailType::class, array( 'data' => 'abcdef', )); 23. What are the form helper functions in Symfony? In Symfony, the form helper functions are given below: Form_start Form_end Textarea Checkbox Input_password_tag etc. 24. What is the syntax to check valid email address? The following syntax is used to check valid email address. use Symfony\Component\Validator\Constraints as Assert; class Student { /** * @Assert\Email( * message = "The email '{{ value }}' is not a valid email.", * checkMX = true * ) */ protected $email; } 25. What is the default port of Symfony? The default port of Symfony is 8000. 26. Which method is used to handle an Ajax request in the server side. The following methods are used to handle an Ajax request in the server side. if ($request->isXmlHttpRequest()) { // Ajax request } else { // Normal request } 27. What is the use of FlashBag? FlashBag is used to hold the data during the page redirections. 28. In which language Symfony was written? Symfony is written in PHP language. 29. What are the cache adapters available in Symfony? In Symfony, the cache adapters available are given below: Array Cache adapter Filesystem Cache adapter PHP Files Cache Adapter APCu Cache Adapter Redis Cache Adapter Symfony PHP Framework Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP FLASK Interview Questions and Answers
Flask Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
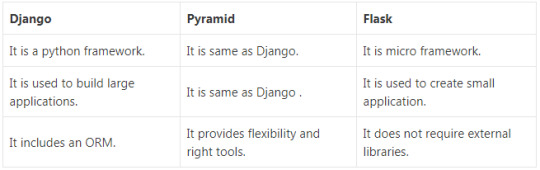
1. What is Flask? Flask is a micro web framework written in Python. It is based on Werkzeug toolkit and Jinja 2 template engine. 2. Who is the developer of Flask? Armin Ronacher is the developer of Flask. 3. What is the stable version of Flask? The stable version of Flask is 0.12.2 and released on 16 May 2017. 4. What are Flask-WTF and its features? It is a template form that is integrated with Flask. It includes various features that are given below. It provides integration with WTF It manages secure form with CSRF token It manages global CSRF protection It provides Internationalization integration It supports recaptcha It handles the file upload that works with Flask uploads 5. What is the benefit of flask? Flask is a part of the micro-framework. It does not require external libraries. It makes the framework light weight, less dependent and less security bugs. 6. What are the differences between Django, Pyramid and Flask? There are following differences between Django, pyramid and Flask:
7. What is the appropriate way to work with Flask script? The appropriate way to work with flask script includes the following steps: Either it should be the import path for our application Or the path to a Python file 8. How can we access sessions in Flask? In Flask, a session allow us to remember information from one request to another. It uses a signed cookie so the user can look at the session contents. We can access session by using the secret key Flask.secret_key in the Flask framework. 9. How can we request database connections in Flask? Flask provides three ways to establish database connection. These are given below. before_request() : It is called before a request and requires no arguments. after_request() : It is called after a request and pass the response that will be sent to the client teardown_request(): It is used when exception is raised and response are not guaranteed. It is called after the response and not allowed to modify the request or their values. 10. What is Flask Sijax? Flask Sijax is a Simple Ajax & jQuery library. It is used to enable Ajax in web applications. It uses JSON to pass data between the server and the browser. 11. How can we get a query string from the Flask? We can get a query string from the flask by using following function. @app.route(‘/data’) def data ( ) : user = request.arg.get (‘user’) 12. How can we create request context in Flask? We can create request context by using following ways. Automatically when the application receives a request OR manually, by calling app.test_request_context (‘/route?param=value) 13. How can we create structure of large Flask application? We can create structure of large Flask application by using following steps: attach to the functions and move them to different files. Use blueprints to assign the views to “categories”. For instance auth, profile, backend, etc. Use the underlying Werkzeug URL map and register functions on there on a central URL. 14. What are the attributes of request objects? There are various attributes of request objects:

15. What are the Mail class methods? There are following Mail class method: send(): It is used to send contents of Message class object. connect(): It is used to opens connection with mail host. send_message(): It is used to sends message object. 16. What are the steps to develop MVC web application in Flask? There are following steps to develop web application: Flask import Flask app = Flask(_name_) @app.route("/") Def hello(): return "Hello World" app.run(debug = True) In this code your, Configuration part will be from flask import Flask app = Flask(_name_) View part will be @app.route("/") Def hello(): return "Hello World" While you model or main part will be app.run(debug = True) 17. What is the extension of Flask? The extension of Flask is .Py. 18. What is the default port of Flask? The default port of Flask is 5000. 19. What is url_for() function in Flask? In Flask, url_for() function is used to build dynamic URL for specific function. 20. What are the HTTP methods in Flask? In Flask, the HTTP methods are given below: GET : It is used to send the data in unencrypted form to the server. HEAD : It is same as GET, but without response body. POST: It is used to send HTML from data to server. Data received by POST method. PUT : It is used to replaces all the current representation uploaded content DELETE : It is used to removes all current reorientation. 21. What is the default route request in Flask? In Flask, GET is the default route request. 22. What are the delimiters used in Jinga2 template? {% … %}: It is used for Statements {{ … }}: It is used for Expressions to print to the template output {# … #}: It is used for Comments not included in the template output # … ## : It is used for Line Statements 23. What is the use redirect() function. Redirect() function is used to display the login page again when a login attempt fails. 24. What are the error codes in Flask? In Flask, the error code is given below: 400 − for Bad Request. 401 − for Unauthenticated. 403 − for Forbidden. 404 − for Not Found. 406 − for Not Acceptable. 415 − for Unsupported Media Type. 429 − Too Many Requests. 25. How can we create a form for file uploading? We can create a form for file uploading by using following code: 26. What are the Mail methods in Flask? In Flask, the Mail methods are given below: send(): It is used to send contents of message class object. connect(): It is used to open connection with mail host. send_message(): It is used to send message object. 27. What are the validators class of WTForms in Flask? In Flask, The validators class of WTForm are listed in below table: Validators class Description DataRequired It is used to check whether input field is empty Email It is used to check whether text in the field follows email ID conventions. IPAddress It is used to validate IP address in input field Length It is used to verify if length of string in input field is in given range NumberRange It is used to validates a number in input field within given range URL It is used to validates URL entered in input field 28. Does Flask support in-built SQlite database? Yes, Flask supports in-built SQlite database. 29. What is ORM? ORM stands for Object Relation Mapping. It is a technique of mapping object parameter. 30. What is WSGI? WSGI stands for Web Server Gateway Interface. It is used to python web application development. 31. What are the popular server that contains WSGI application and Server HTTP? There are many popular server that contains WSGI application and server HTTP: Gunicorn Tornado Gevent Twisted Web Flask Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP AURELIA Interview Questions and Answers
Aurelia Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Aurelia? Aurelia is an open source UI framework which is used for web and mobile app development. This framework is focused on web standards and follows simple conventions. 2. What are the features of Aurelia? There are 5 Features of Aurelia: Components Web Standards Extensible Commercial Support License 3. What are the advantages of Aurelia? Advantages of Aurelia are: It is very clean Easily extensible It is very easy to use It is directed towards web standards 4. What are the component life cycle methods of Aurelia? The component life cycle methods of Aurelia are: constructor() created(owningView, myView) bind(bindingContext, overrideContext) attached() detached() unbind() 5. What is eventAggregator() plugin in Aurelia? The eventAggregator() plugin is used for cross-component communication. This plugin is also used to handle subscribing and publishing to messages or channels inside your app. 6. What are the types of Official Plugins used in Aurelia? Types of Official Plugins used are: i18n() fetch() dialog() animatorCSS() validation() animator-velocity() ui-virtualization() 7. What are the types of Standard Plugins used in Aurelia? Types of Standard Plugins used are: Router() History() eventAggregator() defaultResources() defaultBindingLanguage() 8. What is Throttle in Aurelia? Throttle: It is used to slow down the rate of updating input view-model. 9. What is Debounce in Aurelia? Debounce: It will update the binding after the user has stopped typing. It is almost the same as throttle. 10. Which command is used to install i18n plugin in Aurelia? Command used is: C:\Users\username\Desktop\aureliaApp>jspm install aurelia-i18n

AURELIA Interview Questions 11. What is fetch() plugin in Aurelia? fetch(): This plugin is used for handling HTTP requests. You can also use some other AJAX library. 12. What is i18n() plugin? i18n() Plugin is used for internalization and localization. 13. What is animator-velocity() in Aurelia? animator-velocity(): It is the standard plugin of Aurelia. Here, you can use velocity animation library instead of CSS animations. 14. What is ui-virtualization() in Aurelia? ui-virtualization(): This plugin is a useful library for handling large performance heavy UI tasks. 15. What are the types of data bindings used in Aurelia? There are two types of bindings used in Aurelia are: Simple Binding Two-Way Binding 16. What is the significance of index.html in Aurelia? index.html is deafult page of the app like in most of the HTML based apps. It is a place where scripts and stylesheets are loaded.It looks as under Aurelia System.import('aurelia‐bootstrapper'); We can also configure the programming language selection.Let's adjust our programming language. The default is pointing to TypeScript. However, we will choose ESNext. So we need to change that to So our index.html will now look like Aurelia System.import('aurelia‐bootstrapper'); 17. Explain the components Of Aurelia? Components are main building blocks of Aurelia framework. Simple Component : Each component contains view-model which is written in JavaScript and view, written in HTML. You can see our view-model definition below. This is an ES6 example but you can also use TypeScript. app.js export class MyComponent { header = "This is Header"; content = "This is content"; } We can bind our values to the view as shown in example below. ${header} syntax will bind the defined header value from MyComponent. The same concept is applied for content. app.html ${header} ${content} Aurelia Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP CherryPy Interview Questions and Answers
CherryPy Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is CherryPy? CherryPy is a web framework of Python which provides a friendly interface to the HTTP protocol for Python developers. It is also called a web application library. CherryPy uses Python’s strengths as a dynamic language to model and bind HTTP protocol into an API. It is one of the oldest web frameworks for Python, which provides clean interface and reliable platform. 2. Why we use CherryPy? CherryPy has following strength: Simplicity: It makes less line to code for project development. Open source: CherryPy framework is an open source. Power: It provides powerful tools and plugins which make to develop world-class application. Community Help: It provide full support on different questions and answers by devoted community. Deployment: CherryPy has its own production-ready HTTP server which make cost effective to host application. 3. What are the installation set up for CherryPy? There are various installation set up are available for CherryPy in package form. Using Tarball Using easyinstall Using Subversion 4. What are the basic requirements for CherryPy installation? These are the basic requirement for CherryPy installation: Python with version 2.0 or above CherryPy 3.0 5. What is web server in CherryPy? The web server acts as the gateway to the application which handles all the requests and response. Following command is used to start web server: cherryPy.server.quickstart() 6. What does internal engine in CherryPy? Following activities are performed by internal engine in CherryPy. Creation and management of request and response objects. Controlling and managing the CherryPy objects. 7. Define multithreaded application server? CherryPy provide multithreaded environment to gets and sets a value into the CherryPy namespace. 8. What is CherryPy Toolbox? It is a built-in tool which offers a single interface to call the CherryPy library. This tool is used in three different ways: From configuration settings As a Python decorator or via special _cp_config attribute of a page handler. As a Python callable that can be applied from within any function 9. What is Basic Authentication Tool? The purpose of this tool is to provide basic authentication to application. This tool uses the following arguments: realm users encrypt 10. What is Caching Tool? This tool is used to provide memory caching to CherryPy generated content. This tool uses the following arguments: invalid_methods cache_Class

CherryPy Interview Questions 11. What is Decoding Tool? The purpose of this tool is to decode the incoming request parameters. Following arguments are used in this tool: encoding Default_encoding 12. Define CherryPy Web Services? A web services is a web based components. It helps to exchange data between applications. There are various types of web service available: REST (RESTful) SOAP etc 13. What are the components of CherryPy? CherryPy has the following three components: cherrypy.engine: It controls prcess startup and event handling. cherrypy.server: It controls and configures server (HTTP server). cherrypy.tools: It is like a toolbox that is orthogonal to execute a HTTP request. 14. What is Atom Publication Protocol (APP)? APP is an application level protocol. It allows the publishing and editing of web resources. It also performs set of operations between APP service and user-agent. It uses Atom XML-document format for message unit between APP server and client. 15. What is Kid template? Kid is a simple template engine written in Python. While creating the template for first time, Kid creates a Python module which can be works as a cached version of the template. Kid template includes the name of the template to be processed which is mandatory. 16. What is Cherrypy configuration? The framework comes with its own configuration system allowing you to parameterize the HTTP server. The settings for the configuration can be stored either in a text file with syntax close to the INI format or as a complete Python dictionary. To configure the CherryPy server instance, the developer needs to use the global section of the settings. global_conf = { 'global': { 'server.socket_host': 'localhost', 'server.socket_port': 8080, }, } application_conf = { '/style.css': { 'tools.staticfile.on': True, 'tools.staticfile.filename': os.path.join(_curdir, 'style.css'), } } This could be represented in a file like this: server.socket_host = "localhost" server.socket_port = 8080 tools.staticfile.on = True tools.staticfile.filename = "/full/path/to.style.css" 17. How to applying Ajax to the application? Consider the application which includes a folder named “media” with index.html and Jquery plugin, and a file with AJAX implementation. Let us consider the name of the file as “ajax_app.py” ajax_app.py import cherrypy import webbrowser import os import simplejson import sys MEDIA_DIR = os.path.join(os.path.abspath("."), u"media") class AjaxApp(object): @cherrypy.expose def index(self): return open(os.path.join(MEDIA_DIR, u'index.html')) @cherrypy.expose def submit(self, name): cherrypy.response.headers = 'application/json' return simplejson.dumps(dict(title="Hello, %s" % name)) config = {'/media': {'tools.staticdir.on': True, 'tools.staticdir.dir': MEDIA_DIR,} } def open_page(): webbrowser.open("http://127.0.0.1:8080/") cherrypy.engine.subscribe('start', open_page) cherrypy.tree.mount(AjaxApp(), '/', config=config) cherrypy.engine.start() The class “AjaxApp” redirects to the web page of “index.html”, which is included in the media folder. AJAX with jQuery and cherrypy $(function() { // When the testform is submitted... $("#formtest").submit(function() { // post the form values via AJAX... $.post('/submit', {name: $("#name").val()}, function(data) { // and set the title with the result $("#title").html(data) ; }); return false ; }); });
What's your name?
Name: The function for AJAX is included within tags. 18. What is rest interface through cherrypy? RESTful web service implements each section of CherryPy architecture with the help of the following − Authentication Authorization Structure Encapsulation Error Handling Authentication: Authentication helps in validating the users with whom we are interacting. CherryPy includes tools to handle each authentication method. def authenticate(): if not hasattr(cherrypy.request, 'user') or cherrypy.request.user is None: # cherrypy.request.authorized = False # This only authenticates. Authz must be handled separately. cherrypy.request.unauthorized_reasons = cherrypy.request.authorization_queries = cherrypy.tools.authenticate = cherrypy.Tool('before_handler', authenticate, priority=10) The above function authenticate() will help to validate the existence of the clients or users. The built-in tools help to complete the process in a systematic way. Authorization: Authorization helps in maintaining the sanity of the process via URI. The process also helps in morphing objects by user token leads. def authorize_all(): cherrypy.request.authorized = 'authorize_all' cherrypy.tools.authorize_all = cherrypy.Tool('before_handler', authorize_all, priority=11) def is_authorized(): if not cherrypy.request.authorized: raise cherrypy.HTTPError("403 Forbidden", ','.join(cherrypy.request.unauthorized_reasons)) cherrypy.tools.is_authorized = cherrypy.Tool('before_handler', is_authorized, priority = 49) cherrypy.config.update({ 'tools.is_authorized.on': True, 'tools.authorize_all.on': True }) The built-in tools of authorization help in handling the routines in a systematic way, as mentioned in the previous example. 19. What is Cherrypy web services? A web service is a set of web-based components that helps in the exchange of data between the application or systems which also includes open protocols and standards. It can be published, used and found on the web. 20. What is decoding tool? The purpose of this tool is to decode the incoming request parameters. Arguments This tool uses the following arguments: encoding---- None--- It looks for the content-type header Default_encoding--- "UTF-8"--- Default encoding to be used when none is provided or found. CherryPy Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP DOJO Interview Questions and Answers
Dojo Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Dojo? Dojo is a JavaScript framework, an assembly of utilities written to ease development of client-side web applications. It is a tool for constructing dynamic web user interfaces. 2. What is the basic structure in Dojo? The basic directory structure of the application is very simple and it will evolve later: /index.html - The application entry point. /app - The application module. /app/main.js - The main script for app module. 3. Explain the function of Dojo/ready module? The dojo/ready module has a function that records a callback that will run once the three conditions have met: DOM is ready All outstanding or remaining modules of requested code have completed loading Other registered functions with a higher priority have completed. 4. What are the advantages or benefits of Dojo? Associative arrays Loosely typed variables Regular expressions Objects and classes Highly evolved date, math, and string libraries W3C DOM support in the Dojo 5. What are application support libraries in Dojo? Application support libraries in Dojo consists of I/O package provides routines, e.g., for AJAX binding For drag and drop operations DND package provides routines Useful routines are available for login, animation and storage. 6. What is the point in Dojo? Dojo bases on the HTML and JavaScript Developer has not to use any strange programming language Dojo ups abstraction layer in a higher level Developer has not to reinvent wheel when starting programming project 7. List out some of the Dijit Layout widgets? ContentPane LinkPane Border Container Tab Container Split Container Stack Container Accordion Container 8. Give some components that comes along with Dojo framework. DOJO Tree DOJO Button DOJO Calendar control DOJO Grid DOJO List box and many more.. 10. History of Dojo. Development was started by Alex Russell and Dylan Schiemann in 2004 The first Dojo code was written in Septemper 2004 Nowadays 40 000 downloads and over 40 developers and companies

DOJO Interview Questions 11. Enlist Dijit layout widgets. Border Container Split Container Stack Container Tab Container Content Pane Link Pane 12. What are the condition necessary for a function that record callback? DOM should be ready. All the modules of requested code have completed loading. Higher priority function should be executed first. 13. What are modules in DOJO? In Dojo, Modules are individual codes that can be loaded separately. They are identified using a string that is similar to the file path where the code is defined. Example: my/module/class. 14. Describe Language Libraries in DOJO. It is the wrapper for common idioms which consist of functional programming API’s Syntax: dojo.lang.* Example: dojo.lang.forEach, dojo.lang.map, dojo.lang.assert. 15. Difference between AJAX and DOJO? Ajax is a technology like XML whereas Dojo is a JavaScript framework also the binding techniques in Dojo are under its abstraction layer. 16. Define Widget Toolkit in Dojo? Widget is a user interface object that has a layout. In Dojo widgets are HTML+CSS bound JavaScript. Example: Tabs, Dialogue, Sorting Table etc. 17. Describe Environment Specific Libraries in Dojo? Libraries provide routines for handling the environment. Consist of svg, html, style and dom packages. Provides some methods for arrange HTML document. There are also methods for handling DOM trees and SVG models. Those routines extend existing routines. 18. Write a code for widget in Dojo? dojo.require(?dojo.widget.Editor2?); … 19. Describe Package System in Dojo? Package System includes only needed files. Each JavaScript file can be named as package dojo.provide(dojo.string). 20. Explain Event System in Dojo? Event system notifies when other function is called. Any DOM object can be connected to any function dojo.event.connect(â€idâ€, â€onClickâ€, listenerObj, â€handleOnClickâ€);. 21. Describe Application Support Libraries in Dojo? Application Support Libraries consist of routines where IO package provides routines e.g. for AJAX binding. There is also some useful routines in logging, storage and animation packages 22. Describe Package System in Dojo? Package System includes only needed files. Each JavaScript file can be named as package dojo.provide(dojo.string). 23. What is the difference between JQuery and Dojo? DOJO : Dojo is a JavaScript toolkit or framework Dojo has also got some built in functionality that are proven and well accepted Dojo is HTML and JavaScript based tool kit Dojo might not be as easy to use Dojo provides the features of widget toolkit Dojo requires higher network bandwidth For creating bigger website and application, Dojo is preferred JQUERY : JQuery is a JavaScript library JQuery has built-in plugin, but the plugins might not be verified JQuery supports almost all web languages JQuery is simpler to use compared to DOJO JQuery is customizable and used to create Ajax applications It will work even at low network bandwidth JQuery is perfect for small websites 24. Explain about the language libraries in Dojo? Language libraries in Dojo includes lang.* Wrappers for common idioms Functional programming APIs Dojo Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP GWT Interview Questions and Answers
GWT Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is GWT? Google Web Toolkit (GWT) is a development toolkit for building ajax application using Java. GWT insist on reusable approaches to common web-app tasks such as bookmarking, UI abstraction, cross-browser portability, etc. GWT provides two modes: Development Mode: It allows debugging the Java code of the application directly via the standard Java debugger. Web mode: In this, the application is translated into HTML and JavaScript code. It can be deployed to a web server. 2. What are the components of GWT? GWT Java-to-JavaScript Compiler: It translates all the Java written code into JavaScript.GWT Development Mode: It allows the developers to run the application in development mode, i.e., app run in Java without compiling JavaScript. Development mode allows native mode plug-in called Google Web Toolkit Developer Plug-in. JRE emulation library: GWT includes a library that follows the Java runtime library i.e. java.lang, java.lang.annotation, java.math, java.io, java.sql, java.util etc. GWT Web UI class library: For creating a widget GWT consist of the set of interface and classes. 3. What is a module descriptor in GWT? A module descriptor is a configuration file used to set-up a GWT application. Its file extension is *.gwt.xml, where * is the name of the application and this file should reside in the project's root. 4. What is a GWT module? A GWT module is simply an encapsulation of functionality. It shares some similarities with a Java package but is not similar. 5. How do I enable assertions? The GWT compiler recognizes the -ea flag to generate code for assertions in the compiled JavaScript. Only use assertions for debugging purposes, not production logic because assertions will only work under GWT's development mode. 6. What is the default style name of any GWT widget? By default, the class name for each component is gwt-. For example, the Button widget has a default style of gwt-Button, and similar way TextBox widget has a default style of gwt-TextBox. 7. What is internationalization? Internationalization is changing the language of the text based on the locale. For example, the browser should display the website content in Hindi for a user sitting in India and French for the user accessing the website from France. 8. What is the purpose of Host Page? The most important public resource is host page which is used to invoke actual GWT application. A typical HTML host page for an application might not include any visible HTML body content at all, but it is always expected to include GWT application via a tag. 9. What is RPC? RPC (Remote Procedure Call) helps in client communication with the server. RPC is a process of calling a method from a class; however, in this process, the only difference is that the class is located on a server but not the part of the client program. 10. What is GWT ClientBundle? The ClientBundle interface moves entries from the everything-else category into the cache-forever category. 11. What are the types of panels in GWT? Root Panel: It is the topmost panel where all other widgets are attached to it. Flow Panel: It is the simplest panel which provides a basic HTML layout. HTML Panel: It is enclosed with specified HTML contents. Form Panel: It specifies that any widget declared in this would be wrapped in HTML form element. Scroll Panel: It puts all the content in the scrollable area. Grid: It helps to create an HTML table. Flex Table: It extends HTML table like a GRID, but here we can create a table on demand. 12. What are the Layout Panels? Layout Panels can contain other widgets. These panels control the way widget is displayed on User Interface. Every Panel widget inherits properties from Panel class which in turn inherits properties from Widget class and which in turn inherits properties from UIObject class. 13. Define GWT JSON? JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) is a language-independent format for data. It is similar to XML as XML uses tags JSON uses Object-Literal notation of JavaScript. 14. Define Parsing in GWT XML? To parse the XML, we have to first parse the raw XML text into XML DOM structure. DOM structure helps in the navigation of the data. XML parser is located under XMLParser class. XMLParser class consists of parse(String) static method which is called to parse the XML and return a Document object. 15. Give the nodes created by XML parsing. Element - represents DOM elements, which are specified by tags in XML: . Text - represents the text between the opening and closing tag of an element: Here is some text.. Comment - represents an XML comment: . Attr - represents an attribute of an element: . 16. Enlist the dependencies required for database in GWT Common: hsqldb, Common-lang , log4j . JDO: datanucleus, showfiles, jdo. Hibernate: hibernate. MyBatis: mybatis. 17. Define GWT History Mechanism. History mechanism is similar to the Ajax history implementations such as RSH (Really Simple History). The Basic idea is to track the internal application state in the URL fragment identifier. Main advantages of this mechanism are: It provides browser history reliable. It provides useful feedback to the user. It is bookmarkable, i.e., the user can create a bookmark to the current state and save it or can email it, etc. 18. Define GWT History Tokens. A token is simply a string that the application can parse to return to a particular state. This token will be saved in browser history as a URL fragment (in the location bar, after the "#"), and this fragment is passed back to the application when the user goes back or forward in history or follows a link. 19. How to create the custom widget? Google Web Toolkit offers a variety of ways for creating the custom widgets. The easiest way is to develop composite widgets by grouping existing basic widgets and adding some interaction logic to them. To create a Custom Widget, it has three general concepts which are as follows: Building Composite Widgets. Create the Java Code for the new widget. Wrap JavaScript using JSNI methods. 20. What is JSNI? JSNI (JavaScript Native Interface) is used to solve problems such as when we need to integrate GWT with existing handwritten JavaScript or with a third-party JavaScript library. Occasionally we need to access low-level browser functionality which is not exposed by the GWT class API's. 21. What are the different uses of JSNI? JSNI is a web equivalent of inline assembly code and can use in many ways such as: Implement a Java method directly in JavaScript. Wrap type-safe Java method signatures around existing JavaScript. Call from JavaScript code into Java code and vice-versa. Throw exceptions across Java/JavaScript boundaries. Read and write Java fields from JavaScript. Use development mode to debug both Java source (with a Java debugger) and JavaScript (with a script debugger). 22. What is GWT compiler? GWT compiler is used to convert the client side Java code to JavaScript at the time of building the source file. 23. How many application development mode GWT provide? GWT provides following two modes. Development mode-It allows us to debug the Java code of the application directly with Java debugger. Web mode-In this mode, Java source code is translated into HTML, CSS & JavaScript. It can be deployed to a webserver. GWT Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP Highcharts Interview Questions and Answers
Highcharts Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Highcharts? Highcharts is a JavaScript based charting library. It is used to enhance web applications by adding interactive charting capability. Highcharts supports a wide range of charts. Charts are drawn using SVG in standard browsers. 2. What are the features of Highcharts? Features of Highcharts are: Export Dynamic Zoomablity Free to Use Lightweight External data Text Rotation Multiple axes DateTime support Multitouch Support Simple Configurations Configurable tooltips 3. What are Line Chart? Line Chart is used to draw line or spline based charts. Types of Line Chart: Basic line With data labels Ajax loaded data, clickable points Time series, zoomable Spline with inverted axes Spline with symbols Spline with plot bands Time data with irregular intervals Logarithmic axis 4. What is Angular Gauge? Angular Gauge is used to draw speedometer/gauge type charts. Types of Angular Gauge: Angular Gauge Solid Gauge Clock VU Meter Gauge with dual axes 5. What is Area Charts? Area Chart is used to draw area wise charts. Types of Area Chart: Basic Area Area with negative values Stacked area Percentage area Area with missing points Inverted axes Area-spline Area range Area range and line 6. What are Pie Charts? Pie Chart is used to draw pie based charts. Types of Pie Chart: Basic Pie Pie with Legends Donut Chart Semi circle Donut Pie with drill down Pie chart with gradient Pie chart with monochrome 7. What is Scatter Chart? Scatter Chart is used to draw scattered charts. 8. What is Bubble Chart? Bubble Chart is used to draw bubble based charts. Types of Bubble Chart: Bubbles Chart 3D Bubbles Chart 9. What is Dynamic Chart? Dynamic Chart is used to draw dynamic charts/data based charts where user can modify charts. Types of Dynamic Chart: Spline updating each second Click to add a point 10. What is 3D Chart? 3D Chart is used to draw 3-dimensional charts. Types of 3D Chart: 3D Column 3D Column with null 3D Column with stacking 3D Pie 3D Donut 11. What is Heat Map? Heat Map is used to draw heat map type charts. Types of Heat Map: Heat Map Large Heat Map 12. What is Tree Map? WebGL supported following drawing modes that are listed in table: Tree Map is used to draw tree map type charts. Types of Tree Map: Tree Map Tree Map with Levels Large Tree Map 13. What is Combination Chart? Combination Chart is used to draw mixed charts (bar chart with pie chart). Types of Combination Chart: Column, Line and Pie Dual Axes, Line and Column Multiple Axes Scatter with regression line 14. Define Irregular Time Data? First define an X value (date) for each point which adds data points with irregular intervals. 15. Does High chart run on client side or server side? It runs on client side only irrespective of your server such as PHP, Perl, ASP, ASP.NET, Node.js etc. It is directly loaded from your system. 16. How to integrate flot with angularjs? Since charting involves heavy DOM manipulation, directives are the way to go. Data can be kept in the Controller App.controller('Ctrl', function($scope) { $scope.data = , , ]]; }); And you can create a custom HTML tag1 specifying the model you want to get data from which angular can compile through a directive App.directive('chart', function() { return { restrict: 'E', link: function(scope, elem, attrs) { var data = scope; $.plot(elem, data, {}); elem.show(); } }; }); 17. Proper way to remove all series data from a Highcharts chart? This to remove all chart series, while(chart.series.length > 0) chart.series.remove(true); Highcharts Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP FuelPHP Interview Questions and Answers
FuelPHP Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is FuelPHP Framework? FuelPHP Framework is an open source web application and written in PHP scripting language. It is based on the HMVC (Hierarchical Model View Controller) design pattern. It was released on January 1, 2014 by GitHub repository named FuelPHP. 2. What is the current Stable version of FuelPHPFramework? FuelPHP current Stable version is1.8and released on 9 April 2016. 3. What are the supported template engines inFuelPHPFramework? There are following template engines in FuelPHPFramework: Mustache Markdown Smarty Twig Haml Jade Dwoo Phptal 4. What are the features of FuelPHPFramework? FuelPHPFramework features are: URL routing system Restful implementation HMVC implementation Form Data validation ORM (Object Relational Mapper) Vulnerability protections like XSS, CSRF, SQL Protection and encode output. Caching System 5. What are the minimum requirements for installing FuelPHPFramework? There are the following minimum requirements for installing FuelPHPFuelPHP Framework: PHP Version >= 5.3.3 Mbstringphp extension installed and enabled Mcryptphp extension installed and enabled Fileinfophp extension installed and enabled PHPUnit version 3.7 or greater is required if we want to run unit tests. 6. What are the benefits of HMVC in FuelPHPFramework? In FuelPHPFramework, HMVC benefitsare: Modularization Organization Reusability Extendibility 7. What are the inbuilt security features of FuelPHP Framework? FuelPHPFrameworkprovides inbuilt security features that are: Output encoding CSRF protection XSS filtering Input filtering SQL injection 8. How can we quick installFuelPHP Framework? We can quick install FuelPHP Framework by using some command: Quick installation using Oil from the web. $ curl https://get.fuelphp.com/oil | sh Now that oil is installed, create a blog project in a directory called Sites. $ cd Sites/ $ oil create blog 9. What is the controller in FuelPhp framework? Controller is a class that contains action methods. It is used to manage HTTP client request and respond back. All controllers are stored in the fuel/app/classes/controller/ directory. Example: classController_Employee extends Controller { public function action_home() { echo "FuelPHP-Employee application!"; } public function action_index() { echo "This is the index method of employee controller"; } } There are two methods in the controller. before() action method after() action method. 10. What are the types of Reserved Routes in FuelPHP Framework? In FuelPHP, there are various types of Reserved Routes: root_: The default route when no URI is specified. _403_: It throws an HttpNoAccessException that isn’t caught. _404_: It throws an HttpNotFoundException that isn’t caught. _500_: It throws an HttpServerErrorException that isn’t caught. 11. What is the use of Oil Package in FuelPHPFramework? In FuelPHP, Oil package is used for installation, development and testing of application. 12. What is Presenter and how to create Presenter in FuelPHP Framework? A Presenter is a class that contains the logic. It is needed to generate our view. A Presenter should not do any data manipulation but it can contain database calls or any other retrieval. To create empty Presenters: classPresenter_Index extends Presenter { --- Body -- } 13. How can we get query in FuelPHP Framework? In FuelPHP, we can get query by using following steps: $userQueryToExecute = Model_Article::query() ->select('users') ->where('blocked', '=', 1); echo $userQueryToExecute->get_query(); 14. How can we check Redis server is running or not? We can check Redis server is running or not by using following source code. Try { $redis = \Redis::instance(); } catch(\RedisException $e) { //here error will come } 15. What are the Event methods in FuelPHP Framework? InFuelPHP Framework, events methods are used to application events. Some methods are given below. register(): It allows files to register an object that will be run when the trigger method is called. Example $my_event_code = function() { echo 'my event'; } Event::register('my_event', $my_event_code); unregister(): It allows the files to unregister an object that would be run when the trigger method is called. Example Event::unregister('my_event', $my_event_code); trigger(): It is used to trigger or activate callbacks that are associated through the register method. Example has_events(): It is used to check if a particular registered event has triggers. Example Event::has_events('my_event'); 16. What is Oil? Oil is a FuelPHP tool that used Command line installation method. 17. Who is the developer of FuelPHP? Harro Verton, Jelmer Schreuder, and Dan Horrigan are the developer of Fuel PHP. 18. What is Scaffolding in FuelPHP? In FuelPHP, Scaffolding is a meta-programming method for building database operations. 19. What are the web servers of FuelPHP? There are following web servers of FuelPHP: WAMP (Windows) Microsoft IIS (Windows) LAMP (Linux) MAMP (Macintosh) XAMP (Multi-platform) Nginx (Multi-platform) PHP in-built development web server (Multi-platform) 20. What are controllers? Controllers are responsible for handing each request. It is located at fuel/app/classes/controller/ files. 21. What is the two important method of controller Two important method of controller is: before() and after() 22. How to create a validation objects? Forge() method is used to create a validation objects. Example: $val = Validation::forge(); 23. What are the upload classes in FuelPHP? There are following upload class in FuelPHP. Upload class Description Max_size It is used to set maximum size of the file to be uploaded. ext_whitelist It is used to allow file extensions. ext_blacklist It is used to disallow file extensions. type_blacklist It is used to set disallowed file types. mime_blacklist It is used to set disallowed mime file types. 24. How to handle an Ajax request properly on the server? The following code is used to handle an Ajax request properly on the server. if (Input::is_ajax()) { // Ajax request } else { // Normal request } 25. What are the types of controllers in FuelPHP? In FuelPHP, There are four types of controller: Base controller Template controller Rest controller Hybrid controller 26. What is Query Builder API? Query builder classes provide options to build SQL queries dynamically. Example: $query = DB::select('name') // select `name` $query = DB::select(array('first_name', 'name')) // select 'first_name' as 'name' 27. Does FuelPHP support multiple themes? Yes, FuelPHP support multiple themes. 28. What are the Session methods in FuelPHP? In FuelPHP Session methods are given below table: Session Methods Description set() It is used to assign a session variable. get() It is used to assign a session variable. delete() It is used to retrieve the stored variable from the sessions. create() It is used to create a new session. destroy() It is used to destroy an existing session. 29. What are the predefine events in FuelPHP? In FuelPHP, there are various predefine events: app_created request_created request_started controller_started controller_finished response_created request_finished shutdown 30. Is FuelPHP support Multilingual? Yes, FuelPHP supports Multilingual. FuelPHP Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP XML Interview Questions and Answers
XML Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is XML? XML stands for eXtensible Markup Language XML plays an important role in many different IT systems XML is often used for distributing data over the Internet It is important for all web developers to have a good understanding of XML XML Example : Tove Jani Reminder Don't forget me this weekend! 2. What is a markup language? A markup language is a set of words and symbols for describing the identity of pieces of a document (for example ‘this is a paragraph’, ‘this is a heading’, ‘this is a list’, ‘this is the caption of this figure’, etc). Programs can use this with a style sheet to create output for screen, print, audio, video, Braille, etc. Some markup languages (eg those used in word processors) only describe appearances (’this is italics’, ‘this is bold’), but this method can only be used for display, and is not normally re-usable for anything else. 3. Where should I use XML? Its goal is to enable generic SGML to be served, received, and processed on the Web in the way that is now possible with HTML. XML has been designed for ease of implementation and for interoperability with both SGML and HTML. Despite early attempts, browsers never allowed other SGML, only HTML (although there were plugins), and they allowed it (even encouraged it) to be corrupted or broken, which held development back for over a decade by making it impossible to program for it reliably. XML fixes that by making it compulsory to stick to the rules, and by making the rules much simpler than SGML. But XML is not just for Web pages: in fact it’s very rarely used for Web pages on its own because browsers still don’t provide reliable support for formatting and transforming it. Common uses for XML include: Information identification because you can define your own markup, you can define meaningful names for all your information items. Information storage because XML is portable and non-proprietary, it can be used to store textual information across any platform. Because it is backed by an international standard, it will remain accessible and processable as a data format. Information structure XML can therefore be used to store and identify any kind of (hierarchical) information structure, especially for long, deep, or complex document sets or data sources, making it ideal for an information-management back-end to serving the Web. This is its most common Web application, with a transformation system to serve it as HTML until such time as browsers are able to handle XML consistently. Publishing the original goal of XML as defined in the quotation at the start of this section. Combining the three previous topics (identity, storage, structure) means it is possible to get all the benefits of robust document management and control (with XML) and publish to the Web(as HTML) as well as to paper (as PDF) and to other formats (eg Braille, Audio, etc) from a single source document by using the appropriate stylesheets. Messaging and data transfer XML is also very heavily used for enclosing or encapsulating information in order to pass it between different computing systems which would otherwise be unable to communicate. By providing a lingua franca for data identity and structure, it provides a common envelope for inter-process communication (messaging). Web services Building on all of these, as well as its use in browsers, machine-processable data can be exchanged between consenting systems, where before it was only comprehensible by humans (HTML). Weather services, e-commerce sites, blog newsfeeds, AJaX sites, and thousands of other data-exchange services use XML for data management and transmission, and the web browser for display and interaction. 4. Why is XML such an important development? It removes two constraints which were holding back Web developments: dependence on a single, inflexible document type (HTML) which was being much abused for tasks it was never designed for; the complexity of full SGML, whose syntax allows many powerful but hard-to-program options. XML allows the flexible development of user-defined document types. It provides a robust, non-proprietary, persistent, and verifiable file format for the storage and transmission of text and data both on and off the Web; and it removes the more complex options of SGML, making it easier to program for. 5. Describe the differences between XML and HTML. It’s amazing how many developers claim to be proficient programming with XML, yet do not understand the basic differences between XML and HTML. Anyone with a fundamental grasp of XML should be able describe some of the main differences outlined in the table below. XML: User definable tags Content driven End tags required for well formed documents Quotes required around attributes values Slash required in empty tags HTML: Defined set of tags designed for web display Format driven End tags not required Quotes not required Slash not required 6. Describe the role that XSL can play when dynamically generating HTML pages from a relational database. Even if candidates have never participated in a project involving this type of architecture, they should recognize it as one of the common uses of XML. Querying a database and then formatting the result set so that it can be validated as an XML document allows developers to translate the data into an HTML table using XSLT rules. Consequently, the format of the resulting HTML table can be modified without changing the database query or application code since the document rendering logic is isolated to the XSLT rules. 7. What is SGML? SGML is the Standard Generalized Markup Language (ISO 8879:1986), the international standard for defining descriptions of the structure of different types of electronic document. There is an SGML FAQ from David Megginson at http://math.albany.edu:8800/hm/sgml/cts-faq.htmlFAQ; and Robin Cover’s SGML Web pages are at http://www.oasis-open.org/cover/general.html. For a little light relief, try Joe English’s ‘Not the SGML FAQ’ at http://www.flightlab.com/~joe/sgml/faq-not.txtFAQ. SGML is very large, powerful, and complex. It has been in heavy industrial and commercial use for nearly two decades, and there is a significant body of expertise and software to go with it. XML is a lightweight cut-down version of SGML which keeps enough of its functionality to make it useful but removes all the optional features which made SGML too complex to program for in a Web environment. 8. Aren’t XML, SGML, and HTML all the same thing? Not quite; SGML is the mother tongue, and has been used for describing thousands of different document types in many fields of human activity, from transcriptions of ancient Irish manuscripts to the technical documentation for stealth bombers, and from patients’ clinical records to musical notation. SGML is very large and complex, however, and probably overkill for most common office desktop applications. XML is an abbreviated version of SGML, to make it easier to use over the Web, easier for you to define your own document types, and easier for programmers to write programs to handle them. It omits all the complex and less-used options of SGML in return for the benefits of being easier to write applications for, easier to understand, and more suited to delivery and interoperability over the Web. But it is still SGML, and XML files may still be processed in the same way as any other SGML file (see the question on XML software). HTML is just one of many SGML or XML applications the one most frequently used on the Web. Technical readers may find it more useful to think of XML as being SGML– rather than HTML++. 9. Who is responsible for XML? XML is a project of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), and the development of the specification is supervised by an XML Working Group. A Special Interest Group of co-opted contributors and experts from various fields contributed comments and reviews by email. XML is a public format: it is not a proprietary development of any company, although the membership of the WG and the SIG represented companies as well as research and academic institutions. The v1.0 specification was accepted by the W3C as a Recommendation on Feb 10, 1998. 10. Why is XML such an important development? It removes two constraints which were holding back Web developments: dependence on a single, inflexible document type (HTML) which was being much abused for tasks it was never designed for; the complexity of full question A.4, SGML, whose syntax allows many powerful but hard-to-program options. XML allows the flexible development of user-defined document types. It provides a robust, non-proprietary, persistent, and verifiable file format for the storage and transmission of text and data both on and off the Web; and it removes the more complex options of SGML, making it easier to program for. 11. Give a few examples of types of applications that can benefit from using XML. There are literally thousands of applications that can benefit from XML technologies. The point of this question is not to have the candidate rattle off a laundry list of projects that they have worked on, but, rather, to allow the candidate to explain the rationale for choosing XML by citing a few real world examples. For instance, one appropriate answer is that XML allows content management systems to store documents independently of their format, which thereby reduces data redundancy. Another answer relates to B2B exchanges or supply chain management systems. In these instances, XML provides a mechanism for multiple companies to exchange data according to an agreed upon set of rules. A third common response involves wireless applications that require WML to render data on hand held devices. 12. What is DOM and how does it relate to XML? The Document Object Model (DOM) is an interface specification maintained by the W3C DOM Workgroup that defines an application independent mechanism to access, parse, or update XML data. In simple terms it is a hierarchical model that allows developers to manipulate XML documents easily Any developer that has worked extensively with XML should be able to discuss the concept and use of DOM objects freely. Additionally, it is not unreasonable to expect advanced candidates to thoroughly understand its internal workings and be able to explain how DOM differs from an event-based interface like SAX. 13. What is SOAP and how does it relate to XML? The Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) uses XML to define a protocol for the exchange of information in distributed computing environments. SOAP consists of three components: an envelope, a set of encoding rules, and a convention for representing remote procedure calls. Unless experience with SOAP is a direct requirement for the open position, knowing the specifics of the protocol, or how it can be used in conjunction with HTTP, is not as important as identifying it as a natural application of XML. 14. Why not just carry on extending HTML? HTML was already overburdened with dozens of interesting but incompatible inventions from different manufacturers, because it provides only one way of describing your information. XML allows groups of people or organizations to question C.13, create their own customized markup applications for exchanging information in their domain (music, chemistry, electronics, hill-walking, finance, surfing, petroleum geology, linguistics, cooking, knitting, stellar cartography, history, engineering, rabbit-keeping, question C.19, mathematics, genealogy, etc). HTML is now well beyond the limit of its usefulness as a way of describing information, and while it will continue to play an important role for the content it currently represents, many new applications require a more robust and flexible infrastructure. 15. Why should I use XML? Here are a few reasons for using XML (in no particular order). Not all of these will apply to your own requirements, and you may have additional reasons not mentioned here (if so, please let the editor of the FAQ know!). XML can be used to describe and identify information accurately and unambiguously, in a way that computers can be programmed to ‘understand’ (well, at least manipulate as if they could understand). XML allows documents which are all the same type to be created consistently and without structural errors, because it provides a standardized way of describing, controlling, or allowing/disallowing particular types of document structure. XML provides a robust and durable format for information storage and transmission. Robust because it is based on a proven standard, and can thus be tested and verified; durable because it uses plain-text file formats which will outlast proprietary binary ones. XML provides a common syntax for messaging systems for the exchange of information between applications. Previously, each messaging system had its own format and all were different, which made inter-system messaging unnecessarily messy, complex, and expensive. If everyone uses the same syntax it makes writing these systems much faster and more reliable. XML is free. Not just free of charge (free as in beer) but free of legal encumbrances (free as in speech). It doesn’t belong to anyone, so it can’t be hijacked or pirated. And you don’t have to pay a fee to use it (you can of course choose to use commercial software to deal with it, for lots of good reasons, but you don’t pay for XML itself). XML information can be manipulated programmatically (under machine control), so XML documents can be pieced together from disparate sources, or taken apart and re-used in different ways. They can be converted into almost any other format with no loss of information. XML lets you separate form from content. Your XML file contains your document information (text, data) and identifies its structure: your formatting and other processing needs are identified separately in a style sheet or processing system. The two are combined at output time to apply the required formatting to the text or data identified by its structure (location, position, rank, order, or whatever). 16. Can you walk us through the steps necessary to parse XML documents? Superficially, this is a fairly basic question. However, the point is not to determine whether candidates understand the concept of a parser but rather have them walk through the process of parsing XML documents step-by-step. Determining whether a non-validating or validating parser is needed, choosing the appropriate parser, and handling errors are all important aspects to this process that should be included in the candidate’s response. 17. Give some examples of XML DTDs or schemas that you have worked with. Although XML does not require data to be validated against a DTD, many of the benefits of using the technology are derived from being able to validate XML documents against business or technical architecture rules. Polling for the list of DTDs that developers have worked with provides insight to their general exposure to the technology. The ideal candidate will have knowledge of several of the commonly used DTDs such as FpML, DocBook, HRML, and RDF, as well as experience designing a custom DTD for a particular project where no standard existed. 18. Using XSLT, how would you extract a specific attribute from an element in an XML document? Successful candidates should recognize this as one of the most basic applications of XSLT. If they are not able to construct a reply similar to the example below, they should at least be able to identify the components necessary for this operation: xsl:template to match the appropriate XML element, xsl:value-of to select the attribute value, and the optional xsl:apply-templates to continue processing the document. Extract Attributes from XML Data Example 1. Attribute Value: 19. When constructing an XML DTD, how do you create an external entity reference in an attribute value? Every interview session should have at least one trick question. Although possible when using SGML, XML DTDs don’t support defining external entity references in attribute values. It’s more important for the candidate to respond to this question in a logical way than than the candidate know the somewhat obscure answer. 20. How would you build a search engine for large volumes of XML data? The way candidates answer this question may provide insight into their view of XML data. For those who view XML primarily as a way to denote structure for text files, a common answer is to build a full-text search and handle the data similarly to the way Internet portals handle HTML pages. Others consider XML as a standard way of transferring structured data between disparate systems. These candidates often describe some scheme of importing XML into a relational or object database and relying on the database’s engine for searching. Lastly, candidates that have worked with vendors specializing in this area often say that the best way the handle this situation is to use a third party software package optimized for XML data. 21. What is the difference between XML and C or C++ or Java? C and C++ (and other languages like FORTRAN, or Pascal, or Visual Basic, or Java or hundreds more) are programming languages with which you specify calculations, actions, and decisions to be carried out in order: mod curconfig; XML is a markup specification language with which you can design ways of describing information (text or data), usually for storage, transmission, or processing by a program. It says nothing about what you should do with the data (although your choice of element names may hint at what they are for): Camshaft end bearing retention circlip Ringtown Fasteners Ltd Angle-nosed insertion tool is required for the removal and replacement of this part. On its own, an SGML or XML file (including HTML) doesn’t do anything. It’s a data format which just sits there until you run a program which does something with it. 22. Does XML replace HTML? No. XML itself does not replace HTML. Instead, it provides an alternative which allows you to define your own set of markup elements. HTML is expected to remain in common use for some time to come, and the current version of HTML is in XML syntax. XML is designed to make the writing of DTDs much simpler than with full SGML. (See the question on DTDs for what one is and why you might want one.) 23. Do I have to know HTML or SGML before I learn XML? No, although it’s useful because a lot of XML terminology and practice derives from two decades’ experience of SGML. Be aware that ‘knowing HTML’ is not the same as ‘understanding SGML’. Although HTML was written as an SGML application, browsers ignore most of it (which is why so many useful things don’t work), so just because something is done a certain way in HTML browsers does not mean it’s correct, least of all in XML. 24. What does an XML document actually look like (inside)? The basic structure of XML is similar to other applications of SGML, including HTML. The basic components can be seen in the following examples. An XML document starts with a Prolog: The XML Declaration which specifies that this is an XML document; Optionally a Document Type Declaration which identifies the type of document and says where the Document Type Description (DTD) is stored; The Prolog is followed by the document instance: A root element, which is the outermost (top level) element (start-tag plus end-tag) which encloses everything else: in the examples below the root elements are conversation and titlepage; A structured mix of descriptive or prescriptive elements enclosing the character data content (text), and optionally any attributes (’name=value’ pairs) inside some start-tags. XML documents can be very simple, with straightforward nested markup of your own design: Hello, world! Stop the planet, I want to get off! Or they can be more complicated, with a Schema or question C.11, Document Type Description (DTD) or internal subset (local DTD changes in ), and an arbitrarily complex nested structure: Hello, world! Vitam capias Or they can be anywhere between: a lot will depend on how you want to define your document type (or whose you use) and what it will be used for. Database-generated or program-generated XML documents used in e-commerce is usually unformatted (not for human reading) and may use very long names or values, with multiple redundancy and sometimes no character data content at all, just values in attributes: 25. How does XML handle white-space in my documents? All white-space, including linebreaks, TAB characters, and normal spaces, even between ’structural’ elements where no text can ever appear, is passed by the parser unchanged to the application (browser, formatter, viewer, converter, etc), identifying the context in which the white-space was found (element content, data content, or mixed content, if this information is available to the parser, eg from a DTD or Schema). This means it is the application’s responsibility to decide what to do with such space, not the parser’s: * insignificant white-space between structural elements (space which occurs where only element content is allowed, ie between other elements,where text data never occurs) will get passed to the application (in SGML this white-space gets suppressed, which is why you can put all that extra space in HTML documents and not worry about it) * significant white-space (space which occurs within elements which can contain text and markup mixed together, usually mixed content or PCDATA) will still get passed to the application exactly as under SGML. It is the application’s responsibility to handle it correctly. The parser must inform the application that white-space has occurred in element content, if it can detect it. (Users of SGML will recognize that this information is not in the ESIS, but it is in the Grove.) My title for Chapter 1. text In the example above, the application will receive all the pretty-printing linebreaks, TABs, and spaces between the elements as well as those embedded in the chapter title. It is the function of the application, not the parser, to decide which type of white-space to discard and which to retain. Many XML applications have configurable options to allow programmers or users to control how such white-space is handled. 26. Which parts of an XML document are case-sensitive? All of it, both markup and text. This is significantly different from HTML and most other SGML applications. It was done to allow markup in non-Latin-alphabet languages, and to obviate problems with case-folding in writing systems which are caseless. * Element type names are case-sensitive: you must follow whatever combination of upper- or lower-case you use to define them (either by first usage or in a DTD or Schema). So you can’t say -: upper- and lower-case must match; thus , , and are three different element types; * For well-formed XML documents with no DTD, the first occurrence of an element type name defines the casing; * Attribute names are also case-sensitive, for example the two width attributes in and (if they occurred in the same file) are separate attributes, because of the different case of width and WIDTH; * Attribute values are also case-sensitive. CDATA values (eg Url=”MyFile.SGML”) always have been, but NAME types (ID and IDREF attributes, and token list attributes) are now case-sensitive as well; * All general and parameter entity names (eg A), and your data content (text), are case-sensitive as always. 27. How can I make my existing HTML files work in XML? Either convert them to conform to some new document type (with or without a DTD or Schema) and write a stylesheet to go with them; or edit them to conform to XHTML. It is necessary to convert existing HTML files because XML does not permit end-tag minimisation (missing , etc), unquoted attribute values, and a number of other SGML shortcuts which have been normal in most HTML DTDs. However, many HTML authoring tools already produce almost (but not quite) well-formed XML. You may be able to convert HTML to XHTML using the Dave Raggett’s HTML Tidy program, which can clean up some of the formatting mess left behind by inadequate HTML editors, and even separate out some of the formatting to a stylesheet, but there is usually still some hand-editing to do. 28. Is there an XML version of HTML? Yes, the W3C recommends using XHTML which is ‘a reformulation of HTML 4 in XML 1.0'. This specification defines HTML as an XML application, and provides three DTDs corresponding to the ones defined by HTML 4.* (Strict, Transitional, and Frameset). The semantics of the elements and their attributes are as defined in the W3C Recommendation for HTML 4. These semantics provide the foundation for future extensibility of XHTML. Compatibility with existing HTML browsers is possible by following a small set of guidelines (see the W3C site). 29. If XML is just a subset of SGML, can I use XML files directly with existing SGML tools? Yes, provided you use up-to-date SGML software which knows about the WebSGML Adaptations TC to ISO 8879 (the features needed to support XML, such as the variant form for EMPTY elements; some aspects of the SGML Declaration such as NAMECASE GENERAL NO; multiple attribute token list declarations, etc). An alternative is to use an SGML DTD to let you create a fully-normalised SGML file, but one which does not use empty elements; and then remove the DocType Declaration so it becomes a well-formed DTDless XML file. Most SGML tools now handle XML files well, and provide an option switch between the two standards. 30. Can XML use non-Latin characters? Yes, the XML Specification explicitly says XML uses ISO 10646, the international standard character repertoire which covers most known languages. Unicode is an identical repertoire, and the two standards track each other. The spec says (2.2): ‘All XML processors must accept the UTF-8 and UTF-16 encodings of ISO 10646. There is a Unicode FAQ at http://www.unicode.org/faq/FAQ. UTF-8 is an encoding of Unicode into 8-bit characters: the first 128 are the same as ASCII, and higher-order characters are used to encode anything else from Unicode into sequences of between 2 and 6 bytes. UTF-8 in its single-octet form is therefore the same as ISO 646 IRV (ASCII), so you can continue to use ASCII for English or other languages using the Latin alphabet without diacritics. Note that UTF-8 is incompatible with ISO 8859-1 (ISO Latin-1) after code point 127 decimal (the end of ASCII). UTF-16 is an encoding of Unicode into 16-bit characters, which lets it represent 16 planes. UTF-16 is incompatible with ASCII because it uses two 8-bit bytes per character (four bytes above U+FFFF). 31. What’s a Document Type Definition (DTD) and where do I get one? A DTD is a description in XML Declaration Syntax of a particular type or class of document. It sets out what names are to be used for the different types of element, where they may occur, and how they all fit together. (A question C.16, Schema does the same thing in XML Document Syntax, and allows more extensive data-checking.) For example, if you want a document type to be able to describe Lists which contain Items, the relevant part of your DTD might contain something like this: This defines a list as an element type containing one or more items (that’s the plus sign); and it defines items as element types containing just plain text (Parsed Character Data or PCDATA). Validators read the DTD before they read your document so that they can identify where every element type ought to come and how each relates to the other, so that applications which need to know this in advance (most editors, search engines, navigators, and databases) can set themselves up correctly. The example above lets you create lists like: Chocolate Music Surfingv (The indentation in the example is just for legibility while editing: it is not required by XML.) A DTD provides applications with advance notice of what names and structures can be used in a particular document type. Using a DTD and a validating editor means you can be certain that all documents of that particular type will be constructed and named in a consistent and conformant manner. DTDs are not required for processing the tip in question Bwell-formed documents, but they are needed if you want to take advantage of XML’s special attribute types like the built-in ID/IDREF cross-reference mechanism; or the use of default attribute values; or references to external non-XML files (’Notations’); or if you simply want a check on document validity before processing. There are thousands of DTDs already in existence in all kinds of areas (see the SGML/XML Web pages for pointers). Many of them can be downloaded and used freely; or you can write your own (see the question on creating your own DTD. Old SGML DTDs need to be converted to XML for use with XML systems: read the question on converting SGML DTDs to XML, but most popular SGML DTDs are already available in XML form. The alternatives to a DTD are various forms of question C.16, Schema. These provide more extensive validation features than DTDs, including character data content validation. 32. Does XML let me make up my own tags? No, it lets you make up names for your own element types. If you think tags and elements are the same thing you are already in considerable trouble: read the rest of this question carefully. 33. How do I create my own document type? Document types usually need a formal description, either a DTD or a Schema. Whilst it is possible to process well-formed XML documents without any such description, trying to create them without one is asking for trouble. A DTD or Schema is used with an XML editor or API interface to guide and control the construction of the document, making sure the right elements go in the right places. Creating your own document type therefore begins with an analysis of the class of documents you want to describe: reports, invoices, letters, configuration files, credit-card verification requests, or whatever. Once you have the structure correct, you write code to express this formally, using DTD or Schema syntax. 34. How do I write my own DTD? You need to use the XML Declaration Syntax (very simple: declaration keywords begin with It says that there shall be an element called Shopping-List and that it shall contain elements called Item: there must be at least one Item (that’s the plus sign) but there may be more than one. It also says that the Item element may contain only parsed character data (PCDATA, ie text: no further markup). Because there is no other element which contains Shopping-List, that element is assumed to be the ‘root’ element, which encloses everything else in the document. You can now use it to create an XML file: give your editor the declarations: (assuming you put the DTD in that file). Now your editor will let you create files according to the pattern: Chocolate Sugar Butter It is possible to develop complex and powerful DTDs of great subtlety, but for any significant use you should learn more about document systems analysis and document type design. See for example Developing SGML DTDs: From Text to Model to Markup (Maler and el Andaloussi, 1995): this was written for SGML but perhaps 95% of it applies to XML as well, as XML is much simpler than full SGML see the list of restrictions which shows what has been cut out. Warning Incidentally, a DTD file never has a DOCTYPE Declaration in it: that only occurs in an XML document instance (it’s what references the DTD). And a DTD file also never has an XML Declaration at the top either. Unfortunately there is still software around which inserts one or both of these. 35. Can a root element type be explicitly declared in the DTD? No. This is done in the document’s Document Type Declaration, not in the DTD. 36. I keep hearing about alternatives to DTDs. What’s a Schema? The W3C XML Schema recommendation provides a means of specifying formal data typing and validation of element content in terms of data types, so that document type designers can provide criteria for checking the data content of elements as well as the markup itself. Schemas are written in XML Document Syntax, like XML documents are, avoiding the need for processing software to be able to read XML Declaration Syntax (used for DTDs). There is a separate Schema FAQ at http://www.schemavalid.com. The term ‘vocabulary’ is sometimes used to refer to DTDs and Schemas together. Schemas are aimed at e-commerce, data control, and database-style applications where character data content requires validation and where stricter data control is needed than is possible with DTDs; or where strong data typing is required. They are usually unnecessary for traditional text document publishing applications. Unlike DTDs, Schemas cannot be specified in an XML Document Type Declaration. They can be specified in a Namespace, where Schema-aware software should pick it up, but this is optional: … More commonly, you specify the Schema in your processing software, which should record separately which Schema is used by which XML document instance. In contrast to the complexity of the W3C Schema model, Relax NG is a lightweight, easy-to-use XML schema language devised by James Clark (see http://relaxng.org/) with development hosted by OASIS. It allows similar richness of expression and the use of XML as its syntax, but it provides an additional, simplified, syntax which is easier to use for those accustomed to DTDs. 37. How do I get XML into or out of a database? Ask your database manufacturer: they all provide XML import and export modules to connect XML applications with databases. In some trivial cases there will be a 1:1 match between field names in the database table and element type names in the XML Schema or DTD, but in most cases some programming will be required to establish the desired match. This can usually be stored as a procedure so that subsequent uses are simply commands or calls with the relevant parameters. In less trivial, but still simple, cases, you could export by writing a report routine that formats the output as an XML document, and you could import by writing an XSLT transformation that formatted the XML data as a load file. 38. Can I encode mathematics using XML?Updated Yes, if the document type you use provides for math, and your users’ browsers are capable of rendering it. The mathematics-using community has developed the MathML Recommendation at the W3C, which is a native XML application suitable for embedding in other DTDs and Schemas. It is also possible to make XML fragments from other DTDs, such as ISO 12083 Math, or OpenMath, or one of your own making. Browsers which display math embedded in SGML existed for many years (eg DynaText, Panorama, Multidoc Pro), and mainstream browsers are now rendering MathML. David Carlisle has produced a set of stylesheets for rendering MathML in browsers. It is also possible to use XSLT to convert XML math markup to LATEX for print (PDF) rendering, or to use XSL:FO. Please note that XML is not itself a programming language, so concepts such as arithmetic and if-statements (if-then-else logic) are not meaningful in XML documents. 39. How will XML affect my document links? The linking abilities of XML systems are potentially much more powerful than those of HTML, so you’ll be able to do much more with them. Existing href-style links will remain usable, but the new linking technology is based on the lessons learned in the development of other standards involving hypertext, such as TEI and HyTime, which let you manage bidirectional and multi-way links, as well as links to a whole element or span of text (within your own or other documents) rather than to a single point. These features have been available to SGML users for many years, so there is considerable experience and expertise available in using them. Currently only Mozilla Firefox implements XLink. The XML Linking Specification (XLink) and the XML Extended Pointer Specification (XPointer) documents contain the details. An XLink can be either a URI or a TEI-style Extended Pointer (XPointer), or both. A URI on its own is assumed to be a resource; if an XPointer follows it, it is assumed to be a sub-resource of that URI; an XPointer on its own is assumed to apply to the current document (all exactly as with HTML). An XLink may use one of #, ?, or |. The # and ? mean the same as in HTML applications; the | means the sub-resource can be found by applying the link to the resource, but the method of doing this is left to the application. An XPointer can only follow a #. The TEI Extended Pointer Notation (EPN) is much more powerful than the fragment address on the end of some URIs, as it allows you to specify the location of a link end using the structure of the document as well as (or in addition to) known, fixed points like IDs. For example, the linked second occurrence of the word ‘XPointer’ two paragraphs back could be referred to with the URI (shown here with linebreaks and spaces for clarity: in practice it would of course be all one long string): http://xml.silmaril.ie/faq.xml#ID(hypertext) .child(1,#element,’answer’) .child(2,#element,’para’) .child(1,#element,’link’) This means the first link element within the second paragraph within the answer in the element whose ID is hypertext (this question). Count the objects from the start of this question (which has the ID hypertext) in the XML source: 1. the first child object is the element containing the question(); 2. the second child object is the answer (the element); 3. within this element go to the second paragraph; 4. find the first link element. Eve Maler explained the relationship of XLink and XPointer as follows: XLink governs how you insert links into your XML document, where the link might point to anything (eg a GIF file); XPointer governs the fragment identifier that can go on a URL when you’re linking to an XML document, from anywhere (eg from an HTML file). David Megginson has produced an xpointer function for Emacs/psgml which will deduce an XPointer for any location in an XML document. XML Spy has a similar function. 40. How does XML handle metadata? Because XML lets you define your own markup languages, you can make full use of the extended hypertext features of XML (see the question on Links) to store or link to metadata in any format (eg using ISO 11179, as a Topic Maps Published Subject, with Dublin Core, Warwick Framework, or with Resource Description Framework (RDF), or even Platform for Internet Content Selection (PICS)). There are no predefined elements in XML, because it is an architecture, not an application, so it is not part of XML’s job to specify how or if authors should or should not implement metadata. You are therefore free to use any suitable method. Browser makers may also have their own architectural recommendations or methods to propose. 41. Can I use JavaScript, ActiveX, etc in XML files? This will depend on what facilities your users’ browsers implement. XML is about describing information; scripting languages and languages for embedded functionality are software which enables the information to be manipulated at the user’s end, so these languages do not normally have any place in an XML file itself, but in stylesheets like XSL and CSS where they can be added to generated HTML. XML itself provides a way to define the markup needed to implement scripting languages: as a neutral standard it neither encourages not discourages their use, and does not favour one language over another, so it is possible to use XML markup to store the program code, from where it can be retrieved by (for example) XSLT and re-expressed in a HTML script element. Server-side script embedding, like PHP or ASP, can be used with the relevant server to modify the XML code on the fly, as the document is served, just as they can with HTML. Authors should be aware, however, that embedding server-side scripting may mean the file as stored is not valid XML: it only becomes valid when processed and served, so care must be taken when using validating editors or other software to handle or manage such files. A better solution may be to use an XML serving solution like Cocoon, AxKit, or PropelX. 42. Can I use Java to create or manage XML files? Yes, any programming language can be used to output data from any source in XML format. There is a growing number of front-ends and back-ends for programming environments and data management environments to automate this. Java is just the most popular one at the moment. There is a large body of middleware (APIs) written in Java and other languages for managing data either in XML or with XML input or output. 43. How do I execute or run an XML file? You can’t and you don’t. XML itself is not a programming language, so XML files don’t ‘run’ or ‘execute’. XML is a markup specification language and XML files are just data: they sit there until you run a program which displays them (like a browser) or does some work with them (like a converter which writes the data in another format, or a database which reads the data), or modifies them (like an editor). If you want to view or display an XML file, open it with an XML editor or an question B.3, XML browser. The water is muddied by XSL (both XSLT and XSL:FO) which use XML syntax to implement a declarative programming language. In these cases it is arguable that you can ‘execute’ XML code, by running a processing application like Saxon, which compiles the directives specified in XSLT files into Java bytecode to process XML. 44. How do I control formatting and appearance? In HTML, default styling was built into the browsers because the tagset of HTML was predefined and hardwired into browsers. In XML, where you can define your own tagset, browsers cannot possibly be expected to guess or know in advance what names you are going to use and what they will mean, so you need a stylesheet if you want to display formatted text. Browsers which read XML will accept and use a CSS stylesheet at a minimum, but you can also use the more powerful XSLT stylesheet language to transform your XML into HTMLâ€â€which browsers, of course, already know how to display (and that HTML can still use a CSS stylesheet). This way you get all the document management benefits of using XML, but you don’t have to worry about your readers needing XML smarts in their browsers. 45. How do I use graphics in XML? Graphics have traditionally just been links which happen to have a picture file at the end rather than another piece of text. They can therefore be implemented in any way supported by the XLink and XPointer specifications (see question C.18, ‘How will XML affect my document links?’), including using similar syntax to existing HTML images. They can also be referenced using XML’s built-in NOTATION and ENTITY mechanism in a similar way to standard SGML, as external unparsed entities. However, the SVG specification (see the tip below, by Peter Murray-Rust) lets you use XML markup to draw vector graphics objects directly in your XML file. This provides enormous power for the inclusion of portable graphics, especially interactive or animated sequences, and it is now slowly becoming supported in browsers. The XML linking specifications for external images give you much better control over the traversal and activation of links, so an author can specify, for example, whether or not to have an image appear when the page is loaded, or on a click from the user, or in a separate window, without having to resort to scripting. XML itself doesn’t predicate or restrict graphic file formats: GIF, JPG, TIFF, PNG, CGM, EPS, and SVG at a minimum would seem to make sense; however, vector formats (EPS, SVG) are normally essential for non-photographic images (diagrams). You cannot embed a raw binary graphics file (or any other binary data) directly into an XML file because any bytes happening to resemble markup would get misinterpreted: you must refer to it by linking (see below). It is, however, possible to include a text-encoded transformation of a binary file as a CDATA Marked Section, using something like UUencode with the markup characters ], & and > removed from the map so that they could not occur as an erroneous CDATA termination sequence and be misinterpreted. You could even use simple hexadecimal encoding as used in PostScript. For vector graphics, however, the solution is to use SVG (see the tip below, by Peter Murray-Rust). Sound files are binary objects in the same way that external graphics are, so they can only be referenced externally (using the same techniques as for graphics). Music files written in MusiXML or an XML variant of SMDL could however be embedded in the same way as for SVG. The point about using entities to manage your graphics is that you can keep the list of entity declarations separate from the rest of the document, so you can re-use the names if an image is needed more than once, but only store the physical file specification in a single place. This is available only when using a DTD, not a Schema. 46. How do I include one XML file in another? This works exactly the same as for SGML. First you declare the entity you want to include, and then you reference it by name: …blah blah… &chap1; &chap2; &chap3; &chap4; &chap5; The difference between this method and the one used for including a DTD fragment (see question D.15, ‘How do I include one DTD (or fragment) in another?’) is that this uses an external general (file) entity which is referenced in the same way as for a character entity (with an ampersand). The one thing to make sure of is that the included file must not have an XML or DOCTYPE Declaration on it. If you’ve been using one for editing the fragment, remove it before using the file in this way. Yes, this is a pain in the butt, but if you have lots of inclusions like this, write a script to strip off the declaration (and paste it back on again for editing). 47. What is parsing and how do I do it in XML Parsing is the act of splitting up information into its component parts (schools used to teach this in language classes until the teaching profession collectively caught the anti-grammar disease). ‘Mary feeds Spot’ parses as Subject = Mary, proper noun, nominative case Verb = feeds, transitive, third person singular, present tense Object = Spot, proper noun, accusative case In computing, a parser is a program (or a piece of code or API that you can reference inside your own programs) which analyses files to identify the component parts. All applications that read input have a parser of some kind, otherwise they’d never be able to figure out what the information means. Microsoft Word contains a parser which runs when you open a .doc file and checks that it can identify all the hidden codes. Give it a corrupted file and you’ll get an error message. XML applications are just the same: they contain a parser which reads XML and identifies the function of each the pieces of the document, and it then makes that information available in memory to the rest of the program. While reading an XML file, a parser checks the syntax (pointy brackets, matching quotes, etc) for well-formedness, and reports any violations (reportable errors). The XML Specification lists what these are. Validation is another stage beyond parsing. As the component parts of the program are identified, a validating parser can compare them with the pattern laid down by a DTD or a Schema, to check that they conform. In the process, default values and datatypes (if specified) can be added to the in-memory result of the validation that the validating parser gives to the application. Judy O’Grady The example above parses as: 1. Element person identified with Attribute corpid containing abc123 and Attribute birth containing 1960-02-31 and Attribute gender containing female containing … 2. Element name containing … 3. Element forename containing text ‘Judy’ followed by … 4. Element surname containing text ‘O’Grady’ (and lots of other stuff too). As well as built-in parsers, there are also stand-alone parser-validators, which read an XML file and tell you if they find an error (like missing angle-brackets or quotes, or misplaced markup). This is essential for testing files in isolation before doing something else with them, especially if they have been created by hand without an XML editor, or by an API which may be too deeply embedded elsewhere to allow easy testing. 48. When should I use a CDATA Marked Section? You should almost never need to use CDATA Sections. The CDATA mechanism was designed to let an author quote fragments of text containing markup characters (the open-angle-bracket and the ampersand), for example when documenting XML (this FAQ uses CDATA Sections quite a lot, for obvious reasons). A CDATA Section turns off markup recognition for the duration of the section (it gets turned on again only by the closing sequence of double end-square-brackets and a close-angle-bracket). Consequently, nothing in a CDATA section can ever be recognised as anything to do with markup: it’s just a string of opaque characters, and if you use an XML transformation language like XSLT, any markup characters in it will get turned into their character entity equivalent. If you try, for example, to use: some text with in it. in the expectation that the embedded markup would remain untouched, it won’t: it will just output some text with markup in it. In other words, CDATA Sections cannot preserve the embedded markup as markup. Normally this is exactly what you want because this technique was designed to let people do things like write documentation about markup. It was not designed to allow the passing of little chunks of (possibly invalid) unparsed HTML embedded inside your own XML through to a subsequent processâ€â€because that would risk invalidating the output. As a result you cannot expect to keep markup untouched simply because it looked as if it was safely ‘hidden’ inside a CDATA section: it can’t be used as a magic shield to preserve HTML markup for future use as markup, only as characters. 49. How can I handle embedded HTML in my XML Apart from using CDATA Sections, there are two common occasions when people want to handle embedded HTML inside an XML element: 1. when they have received (possibly poorly-designed) XML from somewhere else which they must find a way to handle; 2. when they have an application which has been explicitly designed to store a string of characters containing < and & character entity references with the objective of turning them back into markup in a later process (eg FreeMind, Atom). Generally, you want to avoid this kind of trick, as it usually indicates that the document structure and design has been insufficiently thought out. However, there are occasions when it becomes unavoidable, so if you really need or want to use embedded HTML markup inside XML, and have it processable later as markup, there are a couple of techniques you may be able to use: * Provide templates for the handling of that markup in your XSLT transformation or whatever software you use which simply replicates what was there, eg 50. What are the special characters in XML For normal text (not markup), there are no special characters: just make sure your document refers to the correct encoding scheme for the language and/or writing system you want to use, and that your computer correctly stores the file using that encoding scheme. See the question on non-Latin characters for a longer explanation. If your keyboard will not allow you to type the characters you want, or if you want to use characters outside the limits of the encoding scheme you have chosen, you can use a symbolic notation called ‘entity referencing’. Entity references can either be numeric, using the decimal or hexadecimal Unicode code point for the character (eg if your keyboard has no Euro symbol (€) you can type €); or they can be character, using an established name which you declare in your DTD (eg ) and then use as € in your document. If you are using a Schema, you must use the numeric form for all except the five below because Schemas have no way to make character entity declarations. If you use XML with no DTD, then these five character entities are assumed to be predeclared, and you can use them without declaring them: The greater-than character (>) ends a start-tag or an end-tag. The double-quote character (”) can be symbolised with this character entity reference when you need to embed a double-quote inside a string which is already double-quoted. The apostrophe or single-quote character (’) can be symbolised with this character entity reference when you need to embed a single-quote or apostrophe inside a string which is already single-quoted. If you are using a DTD then you must declare all the character entities you need to use (if any), including any of the five above that you plan on using (they cease to be predeclared if you use a DTD). If you are using a Schema, you must use the numeric form for all except the five above because Schemas have no way to make character entity declarations. 51. Do I have to change any of my server software to work with XML? The only changes needed are to make sure your server serves up .xml, .css, .dtd, .xsl, and whatever other file types you will use as the correct MIME content (media) types. The details of the settings are specified in RFC 3023. Most new versions of Web server software come preset. If not, all that is needed is to edit the mime-types file (or its equivalent: as a server operator you already know where to do this, right?) and add or edit the relevant lines for the right media types. In some servers (eg Apache), individual content providers or directory owners may also be able to change the MIME types for specific file types from within their own directories by using directives in a .htaccess file. The media types required are: text/xml for XML documents which are ‘readable by casual users’; application/xml for XML documents which are ‘unreadable by casual users’; text/xml-external-parsed-entity for external parsed entities such as document fragments (eg separate chapters which make up a book) subject to the readability distinction of text/xml; application/xml-external-parsed-entity for external parsed entities subject to the readability distinction of application/xml; application/xml-dtd for DTD files and modules, including character entity sets. The RFC has further suggestions for the use of the +xml media type suffix for identifying ancillary files such as XSLT (application/xslt+xml). If you run scripts generating XHTML which you wish to be treated as XML rather than HTML, they may need to be modified to produce the relevant Document Type Declaration as well as the right media type if your application requires them to be validated. 51. I’m trying to understand the XML Spec: why does it have such difficult terminology? For implementation to succeed, the terminology needs to be precise. Design goal eight of the specification tells us that ‘the design of XML shall be formal and concise’. To describe XML, the specification therefore uses formal language drawn from several fields, specifically those of text engineering, international standards and computer science. This is often confusing to people who are unused to these disciplines because they use well-known English words in a specialised sense which can be very different from their common meaningsâ€â€for example: grammar, production, token, or terminal. The specification does not explain these terms because of the other part of the design goal: the specification should be concise. It doesn’t repeat explanations that are available elsewhere: it is assumed you know this and either know the definitions or are capable of finding them. In essence this means that to grok the fullness of the spec, you do need a knowledge of some SGML and computer science, and have some exposure to the language of formal standards. Sloppy terminology in specifications causes misunderstandings and makes it hard to implement consistently, so formal standards have to be phrased in formal terminology. This FAQ is not a formal document, and the astute reader will already have noticed it refers to ‘element names’ where ‘element type names’ is more correct; but the former is more widely understood. 52. Can I still use server-side inclusions? Yes, so long as what they generate ends up as part of an XML-conformant file (ie either valid or just well-formed). Server-side tag-replacers like shtml, PHP, JSP, ASP, Zope, etc store almost-valid files using comments, Processing Instructions, or non-XML markup, which gets replaced at the point of service by text or XML markup (it is unclear why some of these systems use non-HTML/XML markup). There are also some XML-based preprocessors for formats like XVRL (eXtensible Value Resolution Language) which resolve specialised references to external data and output a normalised XML file. 53. Can I (and my authors) still use client-side inclusions? The same rule applies as for server-side inclusions, so you need to ensure that any embedded code which gets passed to a third-party engine (eg calls to SQL, VB, Java, etc) does not contain any characters which might be misinterpreted as XML markup (ie no angle brackets or ampersands). Either use a CDATA marked section to avoid your XML application parsing the embedded code, or use the standard 63. What is the relationship between XML namespaces and the XML 1.0 recommendation? Although the XML 1.0 recommendation anticipated the need for XML namespaces by noting that element type and attribute names should not include colons, it did not actually support XML namespaces. Thus, XML namespaces are layered on top of XML 1.0. In particular, any XML document that uses XML namespaces is a legal XML 1.0 document and can be interpreted as such in the absence of XML namespaces. For example, consider the following document: If this document is processed by a namespace-unaware processor, that processor will see two elements whose names are google:A and google:B. The google:A element has an attribute named xmlns:google and the google:B element has an attribute named google:C. On the other hand, a namespace-aware processor will see two elements with universal names {http://www.google.org}A and {http://www.google.org}B. The {http://www.google.org}A does not have any attributes; instead, it has a namespace declaration that maps the google prefix to the URI http://www.google.org. The {http://www.google.org}B element has an attribute named {http://www.google.org}C. Needless to say, this has led to a certain amount of confusion. One area of confusion is the relationship between XML namespaces and validating XML documents against DTDs. This occurs because the XML namespaces recommendation did not describe how to use XML namespaces with DTDs. Fortunately, a similar situation does not occur with XML schema languages, as all of these support XML namespaces. The other main area of confusion is in recommendations and specifications such as DOM and SAX whose first version predates the XML namespaces recommendation. Although these have since been updated to include XML namespace support, the solutions have not always been pretty due to backwards compatibility requirements. All recommendations in the XML family now support XML namespaces. 64. What is the difference between versions 1.0 and 1.1 of the XML namspaces recommendation? There are only two differences between XML namespaces 1.0 and XML namespaces 1.1: * Version 1.1 adds a way to undeclare prefixes. For more information, see question 4.7. * Version 1.1 uses IRIs (Internationalized Resource Identifiers) instead of URIs. Basically, URIs are restricted to a subset of ASCII characters, while IRIs allow much broader use of Unicode characters. For complete details, see section 9 of Namespaces in XML 1.1. NOTE: As of this writing (February, 2003), Namespaces in XML 1.1 is still a candidate recommendation and not widely used. PART II: DECLARING AND USING XML NAMESPACES 65. How do I declare an XML namespace in an XML document? To declare an XML namespace, you use an attribute whose name has the form: xmlns:prefix –OR– xmlns These attributes are often called xmlns attributes and their value is the name of the XML namespace being declared; this is a URI. The first form of the attribute (xmlns:prefix) declares a prefix to be associated with the XML namespace. The second form (xmlns) declares that the specified namespace is the default XML namespace. For example, the following declares two XML namespaces, named http://www.google.com/ito/addresses and http://www.google.com/ito/servers. The first declaration associates the addr prefix with the http://www.google.com/ito/addresses namespace and the second declaration states that the http://www.google.com/ito/servers namespace is the default XML namespace. NOTE: Technically, xmlns attributes are not attributes at all — they are XML namespace declarations that just happen to look like attributes. Unfortunately, they are not treated consistently by the various XML recommendations, which means that you must be careful when writing an XML application. For example, in the XML Information Set (http://www.w3.org/TR/xml-infoset), xmlns “attributes” do not appear as attribute information items. Instead, they appear as namespace declaration information items. On the other hand, both DOM level 2 and SAX 2.0 treat namespace attributes somewhat ambiguously. In SAX 2.0, an application can instruct the parser to return xmlns “attributes” along with other attributes, or omit them from the list of attributes. Similarly, while DOM level 2 sets namespace information based on xmlns “attributes”, it also forces applications to manually add namespace declarations using the same mechanism the application would use to set any other attributes. 66. Where can I declare an XML namespace? You can declare an XML namespace on any element in an XML document. The namespace is in scope for that element and all its descendants unless it is overridden. 67. Can I use an attribute default in a DTD to declare an XML namespace? Yes. For example, the following uses the FIXED attribute xmlns:google on the A element type to associate the google prefix with the http://www.google.org/ namespace. The effect of this is that both A and B are in the http://www.google.org/ namespace. abc IMPORTANT: You should be very careful about placing XML namespace declarations in external entities (external DTDs), as non-validating parsers are not required to read these. For example, suppose the preceding DTD was placed in an external entity (google.dtd) and that the document was processed by a non-validating parser that did not read google.dtd. This would result in a namespace error because the google prefix was never declared: abc 68. Do the default values of xmlns attributes declared in the DTD apply to the DTD? No. Declaring a default value of an xmlns attribute in the DTD does not declare an XML namespace for the DTD. (In fact, no XML namespace declarations apply to DTDs.) Instead, these defaults (declarations) take effect only when the attribute is instantiated on an element. For example: Read the full article
0 notes