#aws ec2 instances types
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How to find out AWS EC2 instances type over SSH
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Journey to AWS Proficiency: Unveiling Core Services and Certification Paths
Amazon Web Services, often referred to as AWS, stands at the forefront of cloud technology and has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals leverage the power of the cloud. This blog serves as your comprehensive guide to understanding AWS, exploring its core services, and learning how to master this dynamic platform. From the fundamentals of cloud computing to the hands-on experience of AWS services, we'll cover it all. Additionally, we'll discuss the role of education and training, specifically highlighting the value of ACTE Technologies in nurturing your AWS skills, concluding with a mention of their AWS courses.

The Journey to AWS Proficiency:
1. Basics of Cloud Computing:
Getting Started: Before diving into AWS, it's crucial to understand the fundamentals of cloud computing. Begin by exploring the three primary service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Gain a clear understanding of what cloud computing is and how it's transforming the IT landscape.
Key Concepts: Delve into the key concepts and advantages of cloud computing, such as scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and disaster recovery. Simultaneously, explore the potential challenges and drawbacks to get a comprehensive view of cloud technology.
2. AWS Core Services:
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): Start your AWS journey with Amazon EC2, which provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud. Learn how to create virtual servers, known as instances, and configure them to your specifications. Gain an understanding of the different instance types and how to deploy applications on EC2.
Simple Storage Service (S3): Explore Amazon S3, a secure and scalable storage service. Discover how to create buckets to store data and objects, configure permissions, and access data using a web interface or APIs.
Relational Database Service (RDS): Understand the importance of databases in cloud applications. Amazon RDS simplifies database management and maintenance. Learn how to set up, manage, and optimize RDS instances for your applications. Dive into database engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and more.
3. AWS Certification:
Certification Paths: AWS offers a range of certifications for cloud professionals, from foundational to professional levels. Consider enrolling in certification courses to validate your knowledge and expertise in AWS. AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner, AWS Certified Solutions Architect, and AWS Certified DevOps Engineer are some of the popular certifications to pursue.
Preparation: To prepare for AWS certifications, explore recommended study materials, practice exams, and official AWS training. ACTE Technologies, a reputable training institution, offers AWS certification training programs that can boost your confidence and readiness for the exams.
4. Hands-on Experience:
AWS Free Tier: Register for an AWS account and take advantage of the AWS Free Tier, which offers limited free access to various AWS services for 12 months. Practice creating instances, setting up S3 buckets, and exploring other services within the free tier. This hands-on experience is invaluable in gaining practical skills.
5. Online Courses and Tutorials:
Learning Platforms: Explore online learning platforms like Coursera, edX, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning. These platforms offer a wide range of AWS courses taught by industry experts. They cover various AWS services, architecture, security, and best practices.
Official AWS Resources: AWS provides extensive online documentation, whitepapers, and tutorials. Their website is a goldmine of information for those looking to learn more about specific AWS services and how to use them effectively.
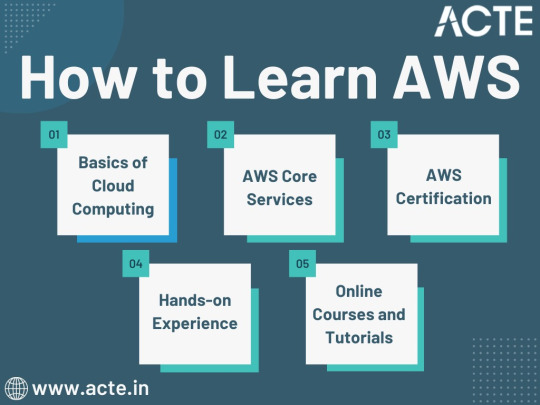
Amazon Web Services (AWS) represents an exciting frontier in the realm of cloud computing. As businesses and individuals increasingly rely on the cloud for innovation and scalability, AWS stands as a pivotal platform. The journey to AWS proficiency involves grasping fundamental cloud concepts, exploring core services, obtaining certifications, and acquiring practical experience. To expedite this process, online courses, tutorials, and structured training from renowned institutions like ACTE Technologies can be invaluable. ACTE Technologies' comprehensive AWS training programs provide hands-on experience, making your quest to master AWS more efficient and positioning you for a successful career in cloud technology.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Future of Intelligent Cloud Computing & Cost Optimization
The Future of Intelligent Cloud Computing & Cost Optimization
In today's competitive digital landscape, businesses face mounting pressure to control cloud expenses while maintaining peak performance. At AI Cloud Insights, we specialize in helping enterprises transform their cloud spending through intelligent optimization strategies.
AI-Powered Cloud Cost Optimization
As cloud adoption accelerates, many organizations struggle with:
Unpredictable monthly bills
Underutilized resources
Complex pricing models across providers
This is where cloud cost optimization becomes critical.
Our team at AI Cloud Insights has identified three pillars of effective cost control:
Visibility - Implementing advanced cloud monitoring tools to track every dollar spent
Strategy - Developing tailored cloud cost optimization services for sustainable savings
AWS Cost Optimization Solutions
Instance Right-Sizing: Stop Paying for Ghost Capacity
Problem: Most businesses overpay for EC2 instances running at <15% utilization.
Our Solution:
AI-driven resizing to optimal instance types
Automated termination of idle instances (saves up to 90%)
How We Help Businesses Save Up to 90% on Cloud Bills
AI Cloud Insights focuses on optimizing costs across four major AWS services:
EC2, RDS, EBS Volumes, and EBS Snapshots.
Our platform delivers intelligent cost-saving opportunities for EC2 and RDS instances, while also identifying optimization potential in EBS Volumes and enabling automated cleanup of unused EBS Snapshots. This ensures efficient resource utilization and significant cost reduction across your cloud infrastructure.
AI CLOUD INSIGHTS
Your Cloud Intervention Starts Here: 📅 Book Your Free Cost Optimization Audit 📞 Or contact our experts today to start saving within your next billing cycle.
Don’t let another month of wasted cloud spending slip by. Your optimized cloud future starts now.
1 note
·
View note
Link
0 notes
Text
AWS cuts prices of some EC2 Nvidia GPU-accelerated instances
AWS has reduced the prices of some of its EC2 Nvidia GPU-accelerated instances to attract more AI workloads while competing with rivals, such as Microsoft and Google, as demand for GPUs and the cost of securing them continues to grow. The instances that are seeing price cuts up to 45% include the P4 (P4d and P4de) and P5 (P5 and P5en) instance types on both On-Demand and Savings Plan options.…
0 notes
Text
AWS 2025: New Features and Changes You Should Know
Discover the key AWS 2025 updates, including new AI tools, instance types, cost-saving features, and security enhancements, plus how startups and enterprises can leverage them for smarter scaling and cloud optimization.
AWS continues to lead the cloud market by rolling out a torrent of new services and enhancements. In this blog, we cover the AWS 2025 updates and AWS new features 2025 that startups and enterprises should watch. You will learn what’s new in AWS 2025, from generative AI to new instance types, and see how the AWS roadmap 2025 is shaping trends in scalability, security, and cost.
We also highlight AWS for startups USA, cost optimization strategies, and AWS security features 2025. Finally, we share a real-world example – a Logiciel case study on optimizing AWS for JobProgress (Leap LLC) – to demonstrate dramatic AWS cost optimization 2025 results and performance gains.
Generative AI and Machine Learning Innovations
AWS is investing heavily in AI/ML, reflecting the trend of AI-powered cloud services. Key highlights include:
Bedrock Data Automation (GA) – Now generally available, this feature automates generation of insights from multimodal content (documents, images, video, audio), helping developers build generative AI applications faster. Bedrock includes over 100 new foundation models, giving startups and enterprises more flexibility and control in deploying AI models.
SageMaker AI Enhancements – SageMaker has new capabilities for large-model training and more third-party model integrations, which streamline AI development while reducing cost and effort. SageMaker is widely adopted to build, train, and deploy models, and these improvements help accelerate AI adoption and cost efficiency.
Conversational AI Tools – AWS’s new tools like Q Developer and Q Business are getting smarter. Q Developer now has an enhanced CLI agent for dynamic code and conversation interaction and can generate documentation, code reviews, and tests in IDEs. Meanwhile, Q Business adds 50+ workflow integrations for automating enterprise tasks.
Hardware for AI – AWS launched faster AI chips. EC2 Trn2 instances (Trainium2-based) deliver faster speed, more memory bandwidth, and higher compute performance for ML training and inference. Also, EC2 P5en instances with high-bandwidth GPUs offer massive networking throughput for deep learning and HPC workloads.
AWS’s 2025 priority on AI is clear from its strategy. The company is even funding AI with a multi-million dollar accelerator program and public-sector research support. For startups, AWS offers cloud credits to experiment with these new AI services. Taken together, the AWS innovations 2025 for startups are vast: from Bedrock and SageMaker enhancements to Q AI assistants, AWS is making generative AI a first-class citizen in the cloud.
Compute, Storage, and Networking Enhancements
AWS continues to expand its core infrastructure with new instance types, chips, and network features:
New EC2 Instances – Several new instance families launched recently
I8g Instances – Storage-optimized instances with next-gen processors and SSDs boost I/O-intensive workloads.
I7ie Instances – Storage-optimized with massive NVMe support and better compute performance.
P5en Instances – Designed for AI/HPC, with ultra-high-speed networking.
Trn2 (Trainium2) Instances – Boosts ML model training with faster compute and memory.
Networking and Zones – AWS is boosting networking and local expansion with advanced adapters and improved VPC tools for securely orchestrating hybrid workflows. Local Zones and Outposts continue expanding in U.S. cities for low-latency edge computing.
Global Infrastructure – AWS is scaling its footprint with new designs for power-efficient data centers. While no new U.S. regions were launched yet, expect continued growth in availability zones and networking capabilities.
Containers, Serverless, and Cloud Services
AWS is also improving its container and serverless offerings, which many startups and microservices architectures rely on:
Kubernetes and Container Management – Enhanced features now auto-encrypt Kubernetes API data and offer Auto Mode for provisioning compute, storage, and networking. EKS Hybrid Nodes let you run Kubernetes on-prem alongside the cloud. These reduce operational overhead and improve governance.
Serverless (Lambda, Fargate, etc.) – Continued refinements in performance and flexibility help developers run code without managing servers. Improvements include faster cold starts and more memory/CPU configurations.
Application Services – Data pipelines are getting streamlined with zero-ETL connections. Event-driven services and secure hybrid integration features have been added. Messaging services now support generative AI capabilities for enhanced customer interactions.
These AWS cloud services 2025 focus on reducing the management burden. Kubernetes is more secure and easier; serverless offerings get performance boosts; and data workflows become more automated. For startups and enterprises alike, this means faster deployments and consistent governance.
Security and Compliance Enhancements
Security is a top focus for AWS in 2025:
Encryption and Protection by Default – Key services now encrypt data automatically. Malware protection is enabled by default. New incident response tools guide organizations through remediation using predefined playbooks.
Secure AI Use – AWS is prioritizing safe AI development. Features include content filters and policy-driven AI guardrails to manage generative outputs responsibly.
Compliance and Identity – AWS continues expanding its certifications and offers stronger access controls and audit features to simplify compliance for U.S.-based organizations.
Cost Optimization and Pricing Changes
Cost control is always critical, especially for startups on tight budgets. AWS 2025 brings both new tools and policy changes:
Reserved Instance / Savings Plan Policy – Effective June 1, 2025, AWS is restricting RIs and Savings Plans to a single end customer’s usage. In practice, this means MSPs and resellers can no longer share one RI/SP across multiple clients. Enterprises should review their commitments: the new policy could require each company (or corporate unit) to manage its own reservations separately. This is a major AWS pricing change 2025 and may impact how large organizations do bulk purchasing.
Spot Instances and Fargate Spot – AWS continues to encourage spot pricing: new visibility tools and deeper discounts (up to 90%) help automate migrating workloads to spot when possible. For example, AWS Batch and SageMaker now integrate Spot more seamlessly.
Cost Management Tools – AWS enhanced Cost Explorer and Budgets in late 2024, adding features like cost anomaly detection powered by ML. Compute Optimizer was updated to support more resource types and provide savings recommendations (rightsizing instances, using Savings Plans, etc.). Startups should leverage these to track their spending.
Case Study: Leap (JobProgress) – Scalable, Cost-Optimized AWS Architecture
To ground these concepts, consider a real success story. Logiciel worked with JobProgress (Leap LLC), a SaaS CRM for contractors, to redesign their AWS architecture for scale and cost efficiency. Here are the highlights:
Scalable AWS Architecture: By adopting microservices on EKS (Kubernetes) and serverless components, Logiciel made the system cloud-native. This change enabled JobProgress to scale from a few users to 15,000+ active users without performance bottlenecks, learn more here logiciel.io. Auto-scaling and container orchestration ensured reliability during traffic spikes.
Cost Reduction: Through an AWS Well-Architected review, Logiciel identified idle resources and oversized instances. They shifted workloads to spot instances and right-sized instances (using AWS Compute Optimizer recommendations). Combined with Savings Plans, these moves cut AWS infrastructure costs by roughly 40%. The savings came without sacrificing uptime – in fact, database queries became faster by using Aurora Serverless and MemoryDB.
Performance Improvement: Logiciel optimized the database layer (introducing Amazon DynamoDB and Aurora) and caching (Redis via MemoryDB), drastically reducing API latency. Network and security were tightened using VPC endpoints and default encryption. The result was snappier performance: page loads and API calls sped up by an estimated 30%, improving user experience.
Outcome: Within five years of launch, JobProgress’s enhanced AWS platform attracted investors and led to an acquisition by Leap (at a multi-million-dollar valuation). (See the full JobProgress (Leap LLC) case study on Logiciel’s site for a deep dive.) This story shows how AWS cost optimization 2025 techniques can directly power business growth: optimized infrastructure enabled rapid scaling while preserving budget.
Looking Ahead: AWS Roadmap 2025 and Future Trends
What’s on the horizon for AWS beyond these immediate changes? While AWS rarely publishes a roadmap, we can anticipate the direction:
More AI Everywhere: Expect deeper AI integration in all services (e.g. AI-driven DevOps, security, analytics). Amazon Q will likely expand to other AWS consoles and new domains (we’ve already seen Q for coding, BI, workflow).
Evolved Compute Hardware: After Graviton4 and Trainium2, keep an eye on GPU/EFA advances and the next Graviton generation. There may also be new specialized chips (e.g. Inferentia3 for edge AI).
Extended Hybrid and Edge: AWS will grow Local Zones in more U.S. metros, plus expand Wavelength for 5G. Outposts and Local Zones might gain additional service support (e.g. RDS on Local Zones). This fits the U.S. emphasis on data sovereignty and low-latency sectors (finance, manufacturing, media).
Serverless and Managed Services: AWS will continue converting more services to serverless or managed models (e.g. RDS Serverless v2 is rolling out, and Fargate improvements are ongoing). Automation features (like AWS Backup support across more services) will simplify operations.
Billing and FinOps Tools: We may see enhancements to cost management – for example, more granular Spot pricing tools or AI-driven spend forecasts. The recent RI/SP policy change hints AWS wants customers to manage commitments more directly; next might come more flexible consumption models.
Conclusion
AWS’s momentum in 2025 is unmistakable. From AI breakthroughs to new instance families and tighter security defaults, the AWS changes 2025 mean faster innovation for businesses. Startups (leveraging AWS Activate) and enterprises (using AWS Partner programs) will both find powerful new tools to cut costs and speed development. By staying current with AWS 2025 updates whether through official news or consultancies like Logiciel organizations can fully exploit the cloud’s promise.
For a concrete example, check out Logiciel’s success stories including the Leap (JobProgress) case study. It’s proof that applying these AWS innovations leads to real-world gains: cost reduction, performance improvement, and business growth. As AWS security features 2025 and new cloud services roll out, the clear strategy is to embrace them proactively. With careful planning and expert guidance, AWS users can harness these changes and stay competitive in the dynamic tech landscape.
0 notes
Text
What Are The Programmatic Commands For EMR Notebooks?

EMR Notebook Programming Commands
Programmatic Amazon EMR Notebook interaction.
How to leverage execution APIs from a script or command line to control EMR notebook executions outside the AWS UI. This lets you list, characterise, halt, and start EMR notebook executions.
The following examples demonstrate these abilities:
AWS CLI: Amazon EMR clusters on Amazon EC2 and EMR Notebooks clusters (EMR on EKS) with notebooks in EMR Studio Workspaces are shown. An Amazon S3 location-based notebook execution sample is also provided. The displayed instructions can list executions by start time or start time and status, halt an ongoing execution, and describe a notebook execution.
Boto3 SDK (Python): Demo.py uses boto3 to interface with EMR notebook execution APIs. The script explains how to initiate a notebook execution, get the execution ID, describe it, list all running instances, and stop it after a short pause. Status updates and execution IDs are shown in this script's output.
Ruby SDK: Sample Ruby code shows notebook execution API calls and Amazon EMR connection setup. Example: describe execution, print information, halt notebook execution, start notebook execution, and get execution ID. Predicted Ruby notebook run outcomes are also shown.
Programmatic command parameters
Important parameters in these programming instructions are:
EditorId: EMR Studio workspace.
relative-path or RelativePath: The notebook file's path to the workspace's home directory. Pathways include my_folder/python3.ipynb and demo_pyspark.ipynb.
execution-engine or ExecutionEngine: EMR cluster ID (j-1234ABCD123) or EMR on EKS endpoint ARN and type to choose engine.
The IAM service role, such as EMR_Notebooks_DefaultRole, is defined.
notebook-params or notebook_params: Allows a notebook to receive multiple parameter values, eliminating the need for multiple copies. Typically, parameters are JSON strings.
The input notebook file's S3 bucket and key are supplied.
The S3 bucket and key where the output notebook will be stored.
notebook-execution-name: Names the performance.
This identifies an execution when describing, halting, or listing.
–from and –status: Status and start time filters for executions.
The console can also access EMR Notebooks as EMR Studio Workspaces, according to documentation. Workspace access and creation require additional IAM role rights. Programmatic execution requires IAM policies like StartNotebookExecution, DescribeNotebookExecution, ListNotebookExecutions, and iam:PassRole. EMR Notebooks clusters (EMR on EKS) require emr-container permissions.
The AWS Region per account maximum is 100 concurrent executions, and executions that last more than 30 days are terminated. Interactive Amazon EMR Serverless apps cannot execute programs.
You can plan or batch EMR notebook runs using AWS Lambda and Amazon CloudWatch Events, or Apache Airflow or Amazon Managed Workflows for Apache Airflow (MWAA).
#EMRNotebooks#EMRNotebookscluster#AWSUI#EMRStudio#AmazonEMR#AmazonEC2#technology#technologynews#technews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
AWS creates EC2 instance types tailored for demanding on-prem workloads
http://securitytc.com/TKSXPx
0 notes
Text
Smart Cloud Cost Optimization: Reducing Expenses Without Sacrificing Performance
As businesses scale their cloud infrastructure, cost optimization becomes a critical priority. Many organizations struggle to balance cost efficiency with performance, security, and scalability. Without a strategic approach, cloud expenses can spiral out of control.
This blog explores key cost optimization strategies to help businesses reduce cloud spending without compromising performance—ensuring an efficient, scalable, and cost-effective cloud environment.
Why Cloud Cost Optimization Matters
Cloud services provide on-demand scalability, but improper management can lead to wasteful spending. Some common cost challenges include:
❌ Overprovisioned resources leading to unnecessary expenses. ❌ Unused or underutilized instances wasting cloud budgets. ❌ Lack of visibility into spending patterns and cost anomalies. ❌ Poorly optimized storage and data transfer costs.
A proactive cost optimization strategy ensures businesses pay only for what they need while maintaining high availability and performance.
Key Strategies for Cloud Cost Optimization
1. Rightsize Compute Resources
One of the biggest sources of cloud waste is overprovisioned instances. Businesses often allocate more CPU, memory, or storage than necessary.
✅ Use auto-scaling to adjust resources dynamically based on demand. ✅ Leverage rightsizing tools (AWS Compute Optimizer, Azure Advisor, Google Cloud Recommender). ✅ Monitor CPU, memory, and network usage to identify underutilized instances.
🔹 Example: Switching from an overprovisioned EC2 instance to a smaller instance type or serverless computing can cut costs significantly.
2. Implement Reserved and Spot Instances
Cloud providers offer discounted pricing models for long-term or flexible workloads:
✔️ Reserved Instances (RIs): Up to 72% savings for predictable workloads (AWS RIs, Azure Reserved VMs). ✔️ Spot Instances: Ideal for batch processing and non-critical workloads at up to 90% discounts. ✔️ Savings Plans: Flexible commitment-based pricing for compute and storage services.
🔹 Example: Running batch jobs on AWS EC2 Spot Instances instead of on-demand instances significantly reduces compute costs.
3. Optimize Storage Costs
Cloud storage costs can escalate quickly if data is not managed properly.
✅ Move infrequently accessed data to low-cost storage tiers (AWS S3 Glacier, Azure Cool Blob Storage). ✅ Implement automated data lifecycle policies to delete or archive unused files. ✅ Use compression and deduplication to reduce storage footprint.
🔹 Example: Instead of storing all logs in premium storage, use tiered storage solutions to balance cost and accessibility.
4. Reduce Data Transfer and Network Costs
Hidden data transfer fees can inflate cloud bills if not monitored.
✅ Minimize inter-region and inter-cloud data transfers to avoid high egress costs. ✅ Use content delivery networks (CDNs) (AWS CloudFront, Azure CDN) to cache frequently accessed data. ✅ Optimize API calls and batch data transfers to reduce unnecessary network usage.
🔹 Example: Hosting a website with AWS CloudFront CDN reduces bandwidth costs by caching content closer to users.
5. Automate Cost Monitoring and Governance
A lack of visibility into cloud spending can lead to uncontrolled costs.
✅ Use cost monitoring tools like AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, and Google Cloud Billing Reports. ✅ Set up budget alerts and automated cost anomaly detection. ✅ Implement tagging policies to track costs by department, project, or application.
🔹 Example: With Salzen Cloud’s automated cost optimization solutions, businesses can track and control cloud expenses effortlessly.
6. Adopt Serverless and Containerization for Efficiency
Traditional VM-based architectures can be cost-intensive compared to modern alternatives.
✅ Use serverless computing (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions) to pay only for execution time. ✅ Adopt containers and Kubernetes for efficient resource allocation. ✅ Scale workloads dynamically using container orchestration tools like Kubernetes.
🔹 Example: Running a serverless API on AWS Lambda eliminates idle costs compared to running a dedicated EC2 instance.
How Salzen Cloud Helps Optimize Cloud Costs
At Salzen Cloud, we offer AI-driven cloud cost optimization solutions to help businesses:
✔️ Automatically detect and eliminate unused cloud resources. ✔️ Optimize compute, storage, and network costs without sacrificing performance. ✔️ Implement real-time cost monitoring and forecasting. ✔️ Apply smart scaling, reserved instance planning, and serverless strategies.
With Salzen Cloud, businesses can maximize cloud efficiency, reduce expenses, and enhance operational performance.
Final Thoughts
Cloud cost optimization is not about cutting resources—it’s about using them wisely. By rightsizing workloads, leveraging reserved instances, optimizing storage, and automating cost governance, businesses can reduce cloud expenses while maintaining high performance and security.
🔹 Looking for smarter cloud cost management? Salzen Cloud helps businesses streamline costs without downtime or performance trade-offs.
🚀 Optimize your cloud costs today with Salzen Cloud!
0 notes
Text
Optimizing GPU Costs for Machine Learning on AWS: Anton R Gordon’s Best Practices

As machine learning (ML) models grow in complexity, GPU acceleration has become essential for training deep learning models efficiently. However, high-performance GPUs come at a cost, and without proper optimization, expenses can quickly spiral out of control.
Anton R Gordon, an AI Architect and Cloud Specialist, has developed a strategic framework to optimize GPU costs on AWS while maintaining model performance. In this article, we explore his best practices for reducing GPU expenses without compromising efficiency.
Understanding GPU Costs in Machine Learning
GPUs play a crucial role in training large-scale ML models, particularly for deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and JAX. However, on-demand GPU instances on AWS can be expensive, especially when running multiple training jobs over extended periods.
Factors Affecting GPU Costs on AWS
Instance Type Selection – Choosing the wrong GPU instance can lead to wasted resources.
Idle GPU Utilization – Paying for GPUs that remain idle results in unnecessary costs.
Storage and Data Transfer – Storing large datasets inefficiently can add hidden expenses.
Inefficient Hyperparameter Tuning – Running suboptimal experiments increases compute time.
Long Training Cycles – Extended training times lead to higher cloud bills.
To optimize GPU spending, Anton R Gordon recommends strategic cost-cutting techniques that still allow teams to leverage AWS’s powerful infrastructure for ML workloads.
Anton R Gordon’s Best Practices for Reducing GPU Costs
1. Selecting the Right GPU Instance Types
AWS offers multiple GPU instances tailored for different workloads. Anton emphasizes the importance of choosing the right instance type based on model complexity and compute needs.
✔ Best Practice:
Use Amazon EC2 P4/P5 Instances for training large-scale deep learning models.
Leverage G5 instances for inference workloads, as they provide a balance of performance and cost.
Opt for Inferentia-based Inf1 instances for low-cost deep learning inference at scale.
“Not all GPU instances are created equal. Choosing the right type ensures cost efficiency without sacrificing performance.” – Anton R Gordon.
2. Leveraging AWS Spot Instances for Non-Critical Workloads
AWS Spot Instances offer up to 90% cost savings compared to On-Demand instances. Anton recommends using them for non-urgent ML training jobs.
✔ Best Practice:
Run batch training jobs on Spot Instances using Amazon SageMaker Managed Spot Training.
Implement checkpointing mechanisms to avoid losing progress if Spot capacity is interrupted.
Use Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling to automatically manage GPU availability.
3. Using Mixed Precision Training for Faster Model Convergence
Mixed precision training, which combines FP16 (half-precision) and FP32 (full-precision) computation, accelerates training while reducing GPU memory usage.
✔ Best Practice:
Enable Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) in TensorFlow, PyTorch, or MXNet.
Reduce memory consumption, allowing larger batch sizes for improved training efficiency.
Lower compute time, leading to faster convergence and reduced GPU costs.
“With mixed precision training, models can train faster and at a fraction of the cost.” – Anton R Gordon.
4. Optimizing Data Pipelines for Efficient GPU Utilization
Poor data loading pipelines can create bottlenecks, causing GPUs to sit idle while waiting for data. Anton emphasizes the need for optimized data pipelines.
✔ Best Practice:
Use Amazon FSx for Lustre to accelerate data access.
Preprocess and cache datasets using Amazon S3 and AWS Data Wrangler.
Implement data parallelism with Dask or PySpark for distributed training.
5. Implementing Auto-Scaling for GPU Workloads
To avoid over-provisioning GPU resources, Anton suggests auto-scaling GPU instances to match workload demands.
✔ Best Practice:
Use AWS Auto Scaling to add or remove GPU instances based on real-time demand.
Utilize SageMaker Multi-Model Endpoint (MME) to run multiple models on fewer GPUs.
Implement Lambda + SageMaker hybrid architectures to use GPUs only when needed.
6. Automating Hyperparameter Tuning with SageMaker
Inefficient hyperparameter tuning leads to excessive GPU usage. Anton recommends automated tuning techniques to optimize model performance with minimal compute overhead.
✔ Best Practice:
Use Amazon SageMaker Hyperparameter Optimization (HPO) to automatically find the best configurations.
Leverage Bayesian optimization and reinforcement learning to minimize trial-and-error runs.
Implement early stopping to halt training when improvement plateaus.
“Automating hyperparameter tuning helps avoid costly brute-force searches for the best model configuration.” – Anton R Gordon.
7. Deploying Models Efficiently with AWS Inferentia
Inference workloads can become cost-prohibitive if GPU instances are used inefficiently. Anton recommends offloading inference to AWS Inferential (Inf1) instances for better price performance.
✔ Best Practice:
Deploy optimized TensorFlow and PyTorch models on AWS Inferentia.
Reduce inference latency while lowering costs by up to 50% compared to GPU-based inference.
Use Amazon SageMaker Neo to optimize models for Inferentia-based inference.
Case Study: Reducing GPU Costs by 60% for an AI Startup
Anton R Gordon successfully implemented these cost-cutting techniques for an AI-driven computer vision startup. The company initially used On-Demand GPU instances for training, leading to unsustainable cloud expenses.
✔ Optimization Strategy:
Switched from On-Demand P3 instances to Spot P4 instances for training.
Enabled mixed precision training, reducing training time by 40%.
Moved inference workloads to AWS Inferentia, cutting costs by 50%.
✔ Results:
60% reduction in overall GPU costs.
Faster model training and deployment with improved scalability.
Increased cost efficiency without sacrificing model accuracy.
Conclusion
GPU optimization is critical for any ML team operating at scale. By following Anton R Gordon’s best practices, organizations can:
✅ Select cost-effective GPU instances for training and inference.
✅ Use Spot Instances to reduce GPU expenses by up to 90%.
✅ Implement mixed precision training for faster model convergence.
✅ Optimize data pipelines and hyperparameter tuning for efficient compute usage.
✅ Deploy models efficiently using AWS Inferentia for cost savings.
“Optimizing GPU costs isn’t just about saving money—it’s about building scalable, efficient ML workflows that deliver business value.” – Anton R Gordon.
By implementing these strategies, companies can reduce their cloud bills, enhance ML efficiency, and maximize ROI on AWS infrastructure.
0 notes
Text
Amazon Web Services (AWS): The Ultimate Guide
Introduction to Amazon Web Services (AWS)

Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the world’s leading cloud computing platform, offering a vast array of services for businesses and developers. Launched by Amazon in 2006, AWS provides on-demand computing, storage, networking, AI, and machine learning services. Its pay-as-you-go model, scalability, security, and global infrastructure have made it a preferred choice for organizations worldwide.
Evolution of AWS
AWS began as an internal Amazon solution to manage IT infrastructure. It launched publicly in 2006 with Simple Storage Service (S3) and Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2). Over time, AWS introduced services like Lambda, DynamoDB, and SageMaker, making it the most comprehensive cloud platform today.
Key Features of AWS
Scalability: AWS scales based on demand.
Flexibility: Supports various computing, storage, and networking options.
Security: Implements encryption, IAM (Identity and Access Management), and industry compliance.
Cost-Effectiveness: Pay-as-you-go pricing optimizes expenses.
Global Reach: Operates in multiple regions worldwide.
Managed Services: Simplifies deployment with services like RDS and Elastic Beanstalk.
AWS Global Infrastructure
AWS has regions across the globe, each with multiple Availability Zones (AZs) ensuring redundancy, disaster recovery, and minimal downtime. Hosting applications closer to users improves performance and compliance.
Core AWS Services

1. Compute Services
EC2: Virtual servers with various instance types.
Lambda: Serverless computing for event-driven applications.
ECS & EKS: Managed container orchestration services.
AWS Batch: Scalable batch computing.
2. Storage Services
S3: Scalable object storage.
EBS: Block storage for EC2 instances.
Glacier: Low-cost archival storage.
Snowball: Large-scale data migration.
3. Database Services
RDS: Managed relational databases.
DynamoDB: NoSQL database for high performance.
Aurora: High-performance relational database.
Redshift: Data warehousing for analytics.
4. Networking & Content Delivery
VPC: Isolated cloud resources.
Direct Connect: Private network connection to AWS.
Route 53: Scalable DNS service.
CloudFront: Content delivery network (CDN).
5. Security & Compliance
IAM: Access control and user management.
AWS Shield: DDoS protection.
WAF: Web application firewall.
Security Hub: Centralized security monitoring.
6. AI & Machine Learning
SageMaker: ML model development and deployment.
Comprehend: Natural language processing (NLP).
Rekognition: Image and video analysis.
Lex: Chatbot development.
7. Analytics & Big Data
Glue: ETL service for data processing.
Kinesis: Real-time data streaming.
Athena: Query service for S3 data.
Lake Formation: Data lake management.
Discover the Full Guide Now to click here
Benefits of AWS
Lower Costs: Eliminates on-premise infrastructure.
Faster Deployment: Pre-built solutions reduce setup time.
Enhanced Security: Advanced security measures protect data.
Business Agility: Quickly adapt to market changes.
Innovation: Access to AI, ML, and analytics tools.
AWS Use Cases
AWS serves industries such as:
E-commerce: Online stores, payment processing.
Finance: Fraud detection, real-time analytics.
Healthcare: Secure medical data storage.
Gaming: Multiplayer hosting, AI-driven interactions.
Media & Entertainment: Streaming, content delivery.
Education: Online learning platforms.
Getting Started with AWS

Sign Up: Create an AWS account.
Use Free Tier: Experiment with AWS services.
Set Up IAM: Secure access control.
Explore AWS Console: Familiarize yourself with the interface.
Deploy an Application: Start with EC2, S3, or RDS.
Best Practices for AWS
Use IAM Policies: Implement role-based access.
Enable MFA: Strengthen security.
Optimize Costs: Use reserved instances and auto-scaling.
Monitor & Log: Utilize CloudWatch for insights.
Backup & Recovery: Implement automated backups.
AWS Certifications & Careers
AWS certifications validate expertise in cloud computing:
Cloud Practitioner
Solutions Architect (Associate & Professional)
Developer (Associate)
SysOps Administrator
DevOps Engineer
Certified professionals can pursue roles like cloud engineer and solutions architect, making AWS a valuable career skill.
0 notes
Text
Managing Multi-Region Deployments in AWS

Introduction
Multi-region deployments in AWS help organizations achieve high availability, disaster recovery, reduced latency, and compliance with regional data regulations. This guide covers best practices, AWS services, and strategies for deploying applications across multiple AWS regions.
1. Why Use Multi-Region Deployments?
✅ High Availability & Fault Tolerance
If one region fails, traffic is automatically routed to another.
✅ Disaster Recovery (DR)
Ensure business continuity with backup and failover strategies.
✅ Low Latency & Performance Optimization
Serve users from the nearest AWS region for faster response times.
✅ Compliance & Data Residency
Meet legal requirements by storing and processing data in specific regions.
2. Key AWS Services for Multi-Region Deployments
🏗 Global Infrastructure
Amazon Route 53 → Global DNS routing for directing traffic
AWS Global Accelerator → Improves network latency across regions
AWS Transit Gateway → Connects VPCs across multiple regions
🗄 Data Storage & Replication
Amazon S3 Cross-Region Replication (CRR) → Automatically replicates S3 objects
Amazon RDS Global Database → Synchronizes databases across regions
DynamoDB Global Tables → Provides multi-region database access
⚡ Compute & Load Balancing
Amazon EC2 & Auto Scaling → Deploy compute instances across regions
AWS Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) → Distributes traffic across regions
AWS Lambda → Run serverless functions in multiple regions
🛡 Security & Compliance
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) → Ensures consistent access controls
AWS Key Management Service (KMS) → Multi-region encryption key management
AWS WAF & Shield → Protects against global security threats
3. Strategies for Multi-Region Deployments
1️⃣ Active-Active Deployment
All regions handle traffic simultaneously, distributing users to the closest region. ✔️ Pros: High availability, low latency ❌ Cons: More complex synchronization, higher costs
Example:
Route 53 with latency-based routing
DynamoDB Global Tables for database synchronization
Multi-region ALB with AWS Global Accelerator
2️⃣ Active-Passive Deployment
One region serves traffic, while a standby region takes over in case of failure. ✔️ Pros: Simplified operations, cost-effective ❌ Cons: Higher failover time
Example:
Route 53 failover routing
RDS Global Database with read replicas
Cross-region S3 replication for backups
3️⃣ Disaster Recovery (DR) Strategy
Backup & Restore: Store backups in a second region and restore if needed
Pilot Light: Replicate minimal infrastructure in another region, scaling up during failover
Warm Standby: Maintain a scaled-down replica, scaling up on failure
Hot Standby (Active-Passive): Fully operational second region, activated only during failure
4. Example: Multi-Region Deployment with AWS Global Accelerator
Step 1: Set Up Compute Instances
Deploy EC2 instances in two AWS regions (e.g., us-east-1, eu-west-1).shaws ec2 run-instances --region us-east-1 --image-id ami-xyz --instance-type t3.micro aws ec2 run-instances --region eu-west-1 --image-id ami-abc --instance-type t3.micro
Step 2: Configure an Auto Scaling Group
shaws autoscaling create-auto-scaling-group --auto-scaling-group-name multi-region-asg \ --launch-template LaunchTemplateId=lt-xyz \ --min-size 1 --max-size 3 \ --vpc-zone-identifier subnet-xyz \ --region us-east-1
Step 3: Use AWS Global Accelerator
shaws globalaccelerator create-accelerator --name MultiRegionAccelerator
Step 4: Set Up Route 53 Latency-Based Routing
shaws route53 change-resource-record-sets --hosted-zone-id Z123456 --change-batch file://route53.json
route53.json example:json{ "Changes": [{ "Action": "UPSERT", "ResourceRecordSet": { "Name": "example.com", "Type": "A", "SetIdentifier": "us-east-1", "Region": "us-east-1", "TTL": 60, "ResourceRecords": [{ "Value": "203.0.113.1" }] } }] }
5. Monitoring & Security Best Practices
✅ AWS CloudTrail & CloudWatch → Monitor activity logs and performance ✅ AWS GuardDuty → Threat detection across regions ✅ AWS KMS Multi-Region Keys → Encrypt data securely in multiple locations ✅ AWS Config → Ensure compliance across global infrastructure
6. Cost Optimization Tips
💰 Use AWS Savings Plans for EC2 & RDS 💰 Optimize Data Transfer Costs with AWS Global Accelerator 💰 Auto Scale Services to Avoid Over-Provisioning 💰 Use S3 Intelligent-Tiering for Cost-Effective Storage
Conclusion
A well-architected multi-region deployment in AWS ensures high availability, disaster recovery, and improved performance for global users. By leveraging AWS Global Accelerator, Route 53, RDS Global Databases, and Auto Scaling, organizations can build resilient applications with seamless failover capabilities.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/aws-training-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
How To Create EMR Notebook In Amazon EMR Studio

How to Make EMR Notebook?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has incorporated Amazon EMR Notebooks into Amazon EMR Studio Workspaces on the new Amazon EMR interface. Integration aims to provide a single environment for notebook creation and massive data processing. However, the new console's “Create Workspace” button usually creates notebooks.
Users must visit the Amazon EMR console at the supplied web URL and complete the previous console's procedures to create an EMR notebook. Users usually select “Notebooks” and “Create notebook” from this interface.
When creating a Notebook, users choose a name and a description. The next critical step is connecting the notebook to an Amazon EMR cluster to run the code.
There are two basic ways users associate clusters:
Select an existing cluster
If an appropriate EMR cluster is already operating, users can click “Choose,” select it from a list, and click “Choose cluster” to confirm. EMR Notebooks have cluster requirements, per documentation. These prerequisites, EMR release versions, and security problems are detailed in specialised sections.
Create a cluster
Users can also “Create a cluster” to have Amazon EMR create a laptop-specific cluster. This method lets users name their clusters. This workflow defaults to the latest supported EMR release version and essential apps like Hadoop, Spark, and Livy, however some configuration variables, such as the Release version and pre-selected apps, may not be modifiable.
Users can customise instance parameters by selecting EC2 Instance and entering the appropriate number of instances. A primary node and core nodes are identified. The instance type determines the maximum number of notebooks that can connect to the cluster, subject to constraints.
The EC2 instance profile and EMR role, which users can choose custom or default roles for, are also defined during cluster setup. Links to more information about these service roles are supplied. An EC2 key pair for cluster instance SSH connections can also be chosen.
Amazon EMR versions 5.30.0 and 6.1.0 and later allow optional but helpful auto-termination. For inactivity, users can click the box to shut down the cluster automatically. Users can specify security groups for the primary instance and notebook client instance, use default security groups, or use custom ones from the cluster's VPC.
Cluster settings and notebook-specific configuration are part of notebook creation. Choose a custom or default AWS Service Role for the notebook client instance. The Amazon S3 Notebook location will store the notebook file. If no bucket or folder exists, Amazon EMR can create one, or users can choose their own. A folder with the Notebook ID and NotebookName and.ipynb extension is created in the S3 location to store the notebook file.
If an encrypted Amazon S3 location is used, the Service role for EMR Notebooks (EMR_Notebooks_DefaultRole) must be set up as a key user for the AWS KMS key used for encryption. To add key users to key policies, see AWS KMS documentation and support pages.
Users can link a Git-based repository to a notebook in Amazon EMR. After selecting “Git repository” and “Choose repository”, pick from the list.
Finally, notebook users can add Tags as key-value pairs. The documentation includes an Important Note about a default tag with the key creatorUserID and the value set to the user's IAM user ID. Users should not change or delete this tag, which is automatically applied for access control, because IAM policies can use it. After configuring all options, clicking “Create Notebook” finishes notebook creation.
Users should note that these instructions are for the old console, while the new console now uses EMR Notebooks as EMR Studio Workspaces. To access existing notebooks as Workspaces or create new ones using the “Create Workspace” option in the new UI, EMR Notebooks users need extra IAM role rights. Users should not change or delete the notebook's default access control tag, which contains the creator's user ID. No notebooks can be created with the Amazon EMR API or CLI.
The thorough construction instructions in some current literature match the console interface, however this transition symbolises AWS's intention to centralise notebook creation in EMR Studio.
#EMRNotebook#AmazonEMRconsole#AmazonEMR#AmazonS3#EMRStudio#AmazonEMRAPI#EC2Instance#technology#technews#technologynews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
AWS Solutions Architect - Associate (SAA-C03) Latest Exam Questions 2025?
As you prepare for the AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate (SAA-C03) exam, effective time management is essential for success. Clearcatnet provides highly effective and up-to-date study materials tailored to help you master key concepts and exam objectives with ease. Our comprehensive resources include real-world scenarios, practice questions, and expert insights to enhance your understanding of AWS architecture. With our structured approach, you can confidently aim for a score above 98% on your first attempt. Invest in your success with Clearcatnet and take the next step in your AWS certification journey!
AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate (SAA-C03) Exam Guide
Understand the Exam Structure
To excel in the AWS SAA-C03 exam, it is essential to understand its domains and weightings:
Design Secure Architectures – 30%
Design Resilient Architectures – 26%
Design High-Performing Architectures – 24%
Design Cost-Optimized Architectures – 20%
Exam Format
Exam Code: SAA-C03
Type: Proctored (Online or Test Center)
Duration: 130 minutes
Total Questions: 65
Passing Score: 70% (700/1000)
Languages Available: English, Japanese, Simplified Chinese, Korean, German, French, Spanish, Portuguese (Brazil), Arabic (Saudi Arabia), Russian, Traditional Chinese, Italian, Indonesian
Study Resources & Renewal
Free Learning Path: Available upon request after Premium Access (Contact Clearcatnet for the link)
Certification Level: Associate
Renewal Requirement: Every 12 months
Prepare strategically with Clearcatnet’s expert-curated materials and maximize your chances of passing on your first attempt!
What measures should be implemented to enable the EC2 instances to obtain the necessary patches?
A) Configure a NAT gateway in a public subnet.
B) Create a custom route table with a route to the NAT gateway for internet traffic and associate it with the private subnets.
C) Assign Elastic IP addresses to the EC2 instances.
D) Create a custom route table with a route to the internet gateway for internet traffic and associate it with the private subnets.
E) Configure a NAT instance in a private subnet.
👉 Correct Answers: A and B
Explanation:To enable private EC2 instances to access the internet without being directly exposed:For Get More Latest Questions and Answers and PDF so Visit:www.clearcatnet.com
#AWS#AWSCertified#AWSCertification#AWSCloud#AWSCommunity#SAAC03#AWSExam#AWSSolutionsArchitect#AWSSAA#AWSAssociate#CloudComputing#CloudCareer#ITCertification#TechLearning#CloudEngineer#StudyTips#ExamPrep#CareerGrowth#LearnAWS#AWSJobs
0 notes
Text
Cloud Cost Optimization: Smart Strategies to Reduce Expenses Without Downtime
Cloud computing provides businesses with scalability and flexibility, but without proper cost management, cloud expenses can quickly spiral out of control. Many organizations overprovision resources, fail to monitor usage, or use inefficient pricing models, leading to unnecessary spending.
To maximize cost efficiency while maintaining performance, businesses need smart cloud cost optimization strategies that minimize expenses without causing downtime or performance issues. In this blog, we’ll explore the best practices and tools for optimizing cloud costs effectively.
Why Cloud Cost Optimization is Essential
Cloud services follow a pay-as-you-go model, meaning companies are charged based on resource usage. However, factors such as unused resources, inefficient storage, and lack of automation can inflate costs. Optimizing cloud expenses helps businesses:
✅ Reduce unnecessary spending without sacrificing performance. ✅ Improve resource efficiency by right-sizing cloud instances. ✅ Prevent unexpected costs through monitoring and budgeting. ✅ Ensure business continuity while optimizing expenses.
1. Right-Sizing Resources for Maximum Efficiency
One of the biggest cost drivers in the cloud is overprovisioning—allocating more CPU, memory, or storage than needed. Right-sizing helps align resources with actual workloads.
🔹 How to Right-Size Cloud Resources
✔ Monitor usage using cloud-native tools like AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or Google Cloud Operations Suite. ✔ Analyze peak and idle times to adjust computing capacity dynamically. ✔ Choose the right instance type based on CPU, RAM, and network requirements.
🔹 Tools for Right-Sizing
AWS Compute Optimizer – Recommends ideal EC2 instance sizes.
Azure Advisor – Suggests ways to optimize VM usage.
Google Cloud Recommender – Provides cost-saving insights for GCP workloads.
2. Use Auto-Scaling to Adjust Resources Dynamically
Auto-scaling helps businesses automatically scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring that you only pay for what you use.
🔹 Key Auto-Scaling Benefits
✔ Reduces costs during low-traffic periods. ✔ Prevents downtime during high-demand spikes. ✔ Optimizes cloud usage without manual intervention.
🔹 Auto-Scaling Tools
AWS Auto Scaling – Adjusts EC2, ECS, and RDS capacity dynamically.
Azure Virtual Machine Scale Sets – Ensures VMs adjust to workload demand.
Google Cloud Autoscaler – Automatically scales VM instances.
3. Leverage Reserved Instances & Spot Instances
Cloud providers offer discounted pricing models to help businesses save costs.
🔹 Reserved Instances (RIs) – Long-Term Savings
✔ Up to 75% savings compared to on-demand pricing. ✔ Best for predictable workloads (e.g., databases, enterprise applications). ✔ Available for AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud with 1- to 3-year commitments.
🔹 Spot Instances – Short-Term Savings
✔ Up to 90% cheaper than regular instances. ✔ Ideal for batch jobs, testing, and non-critical workloads. ✔ Available as AWS Spot Instances, Azure Spot VMs, and Google Preemptible VMs.
4. Optimize Storage Costs
Storage is another major cloud expense, and inefficient storage management can drive up costs significantly.
🔹 Ways to Optimize Cloud Storage
✔ Use lower-cost storage tiers for infrequently accessed data (e.g., AWS S3 Glacier, Azure Archive Storage, Google Coldline). ✔ Enable lifecycle policies to automatically move old data to cheaper storage. ✔ Delete unused snapshots, backups, and logs to free up space.
🔹 Storage Optimization Tools
AWS S3 Intelligent-Tiering – Automatically moves data to lower-cost tiers.
Azure Blob Storage Lifecycle Management – Helps manage storage costs efficiently.
Google Cloud Storage Object Lifecycle – Automates data archival and deletion.
5. Implement Cost Monitoring & Budgeting
Keeping cloud costs under control requires continuous monitoring and real-time alerts to prevent overspending.
🔹 Best Practices for Cloud Cost Monitoring
✔ Set up budgets and alerts for cloud expenses. ✔ Analyze billing reports to track unnecessary charges. ✔ Identify cost spikes and optimize resources accordingly.
🔹 Cost Monitoring Tools
AWS Cost Explorer – Visualizes and forecasts AWS spending.
Azure Cost Management + Billing – Helps monitor and control Azure costs.
Google Cloud Billing Reports – Provides insights into cloud expenses.
6. Use Serverless Computing & Containers
Instead of maintaining always-on cloud servers, businesses can save costs by switching to serverless computing and containerization.
🔹 Serverless Benefits
✔ Pay only for actual execution time (e.g., AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions). ✔ Eliminates idle server costs when no requests are made. ✔ Auto-scales instantly to match demand.
🔹 Containers (Docker & Kubernetes)
✔ Reduces infrastructure costs by running multiple applications efficiently. ✔ Improves resource utilization by eliminating unnecessary VMs. ✔ Speeds up deployments with lightweight, portable containers.
7. Optimize Networking Costs
Cloud providers charge for data transfer and networking usage, which can lead to unexpected costs.
🔹 Cost-Saving Strategies for Networking
✔ Use CDNs (Content Delivery Networks) like AWS CloudFront or Azure CDN to reduce data transfer costs. ✔ Optimize API calls to minimize outbound data usage. ✔ Use VPC peering and private endpoints to lower inter-region traffic costs.
🔹 Networking Optimization Tools
AWS Cost Anomaly Detection – Identifies unusual networking charges.
Azure Traffic Manager – Routes traffic cost-efficiently.
Google Cloud Network Intelligence Center – Helps optimize network traffic.
Conclusion: Reduce Cloud Costs Without Sacrificing Performance
Optimizing cloud costs doesn’t mean cutting resources—it’s about using them efficiently. By leveraging right-sizing, auto-scaling, reserved instances, serverless computing, and storage optimization, businesses like Salzen can reduce expenses while maintaining high performance.
Key Takeaways:
✔ Right-size cloud resources to eliminate overprovisioning. ✔ Enable auto-scaling to match demand dynamically. ✔ Leverage reserved and spot instances for cost-effective computing. ✔ Optimize storage and networking costs with automated policies. ✔ Use serverless computing & containers to improve efficiency.
By following these smart cloud cost optimization strategies, organizations can reduce expenses by 30-50% while ensuring uninterrupted operations.
0 notes