#changing the algorithm to match the user's interests is weak
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Tried searching "House Marik" to get some cool color schemes. Half the posts were Battletech models, the other half were about that one guy from Yugioh. God I love tumblr
#changing the algorithm to match the user's interests is weak#give me conflicting results like a real social media platform#also happened a while back with a search for Plex getting me posts about Five Nights at Freddy's#does not happen on reddit let me tell you#battletech#yugioh#dawn talks
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Troubleshooting Low Impressions and CTR on Facebook Ads

Understanding Impressions and CTR
Before diving into troubleshooting, it’s important to clarify what impressions and CTR are. Impressions refer to the number of times your ad is displayed to users. CTR is the percentage of people who click on your ad after seeing it.
Low impressions indicate that your ad isn’t being shown frequently, limiting its exposure.
Low CTR suggests that although your ad is being shown, it’s not compelling enough to make users click.
Both issues can significantly hinder your ad performance, but the good news is that they can be fixed with the right approach.
Common Causes of Low Impressions and Solutions
1. Audience Targeting Is Too Narrow
One of the most common reasons for low impressions is overly specific targeting. While it’s tempting to focus on a niche audience, doing so can limit the number of people who see your ad. Facebook’s algorithm thrives on larger audiences for effective delivery.
Solution: Broaden your targeting parameters. Expand your geographic reach, adjust age groups, or add broader interests. As a PPC Company in Pune, we recommend creating multiple audience segments to test which works best.
2. Low Ad Budget
Another factor contributing to low impressions could be an insufficient ad budget. Facebook prioritizes ads that are backed by higher budgets, which means your ad may not reach as many users if the budget is too low.
Solution: Ensure your daily or lifetime budget is set appropriately for the audience size and duration of your campaign. If you’re unsure, a PPC Marketing Agency in Pune can help optimize your budget for better results.
3. Bid Strategy Issues
Using the wrong bidding strategy can limit your ad’s reach. If your bid is too low, your ad may not win enough auctions to generate impressions.
Solution: Switch to automatic bidding or increase your manual bid to stay competitive. Monitoring the ad performance over time will help refine the bid strategy.
4. Low Relevance Score
Facebook assigns a relevance score to every ad, and this score impacts how often your ad is shown. If your ad isn’t relevant to your audience, it will be shown less frequently, reducing impressions.
Solution: Improve your relevance score by refining your ad creative and messaging to better match the interests and needs of your target audience. Facebook Ads Optimization Tips often stress the importance of ad relevance in improving delivery.
Common Causes of Low CTR and Solutions
1. Unattractive Ad Creative
If your ad creative is dull, users are unlikely to engage with it. Low-quality images or uninspiring headlines will cause your CTR to drop.
Solution: Invest time in creating high-quality, engaging visuals and compelling copy. Use A/B testing to compare different versions of your ad and see which one performs better. Partnering with a PPC Company in Pune can also ensure that your ad creatives are optimized for success.
2. Poor Call-to-Action (CTA)
A weak or unclear CTA can lead to poor engagement. If users don’t know what action they should take after seeing your ad, they’re less likely to click.
Solution: Use clear, direct CTAs that encourage immediate action, such as “Shop Now,” “Learn More,” or “Get Offer.” This simple change can lead to significant improvements in CTR.
3. Irrelevant Ad Copy
Your ad copy must resonate with your audience. If it doesn’t speak to their needs, it’s unlikely to drive clicks, no matter how good your visuals are.
Solution: Craft copy that directly addresses the pain points and desires of your target audience. Use customer-centric language and focus on the benefits your product or service offers.
Advanced Strategies to Boost Facebook Ad Performance
As a PPC Marketing Agency in Pune, we recommend taking a data-driven approach to troubleshooting and improving your Facebook Ads. Here are a few advanced tips to further boost Facebook ad performance:
Leverage Custom Audiences: Use custom audiences to retarget users who have already interacted with your brand. This group is more likely to engage, increasing your CTR.
Experiment with Ad Placements: Facebook offers a variety of ad placements, from News Feeds to Stories. Testing different placements can help you find where your audience is most engaged.
Monitor Frequency: If users see your ad too often, they may experience ad fatigue, which lowers CTR. Keep an eye on frequency metrics and adjust your ads to prevent overexposure.
Troubleshooting Facebook Ad Delivery Issues
If none of the above solutions seem to improve your ad performance, there may be underlying Facebook ad delivery issues. Check your ad account for any disapprovals or restrictions that could be affecting delivery. Additionally, reviewing your campaign objectives and settings can help identify any potential errors that may be limiting your reach.
As a PPC Company in Pune, we specialize in identifying and fixing these problems to ensure that our clients’ Facebook Ads campaigns run smoothly and efficiently.
Final Thoughts
Improving low impressions and CTR requires a combination of strategic adjustments and continuous monitoring. By optimizing your targeting, budget, creatives, and bid strategy, you can greatly enhance your ad performance. If you’re still struggling to get results, consider reaching out to a PPC Marketing Agency in Pune like ours, where we provide tailored Facebook Ads Optimization Tips to help you achieve your goals.
By implementing these solutions, you can boost Facebook ad performance and overcome delivery issues, ensuring your campaigns generate the desired results.
#PPC Marketing Agency in Pune#Facebook Ads Optimization Tips#PPC Company in Pune#Boost Facebook Ad Performance
0 notes
Text
Top 5 Trends in Learning Spanish in 2024: How New Technologies Are Changing the Learning Approach
In 2024, the world of learning Spanish has undergone significant changes, and new technologies are offering learners unique opportunities. From adaptive apps to virtual environments, here are the top five trends that are changing how we learn Spanish.
1. Adaptive Platforms for Personalized Learning
Modern educational technologies focus on personalization. Adaptive platforms like Duolingo and Babbel use algorithms to tailor lessons to the specific needs and level of each user. These apps analyze your progress and adjust the learning program, offering exercises that match your level and interests. This approach not only speeds up learning but also makes it more effective by providing optimal conditions for absorbing material.
Duolingo Babbel
2. Gamification for Motivation
Gamification has become a popular trend in educational apps. Memrise and Lingvist use game elements to make the learning process more engaging. You earn points for completing tasks, level up, and participate in competitions, which encourages you to keep learning. This approach makes language learning less monotonous and helps maintain high motivation.
Memrise Lingvist
3. Immersion in a Virtual Environment
Language immersion through virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) has become possible thanks to apps like Immerse. They create realistic scenarios where you can practice the language by interacting with virtual characters and situations. This helps develop communication skills and contextual understanding, significantly improving your ability to perceive and use Spanish in real-life situations.
Immerse
4. Integration of Learning into Daily Activities
EdLock offers a unique approach to integrating language learning into daily activities. Instead of setting aside dedicated time for study, you learn Spanish while interacting with apps on your phone. Every time you try to open a familiar app, EdLock gives you a language task, such as translating a word or filling in a missing sentence. This allows you to learn without extra effort and make studying part of your daily routine.
EdLock
5. Advanced Analytics and Progress Tracking
Modern platforms provide enhanced tools for analyzing and tracking progress. Rosetta Stone and Busuu offer detailed reports on your achievements, highlighting your strengths and weaknesses. You can see how many new words you've learned, how your grammar has improved, and which topics need more attention. This allows for more efficient learning planning and helps focus on areas that need improvement.
Rosetta Stone Busuu
Conclusion
2024 brings numerous innovations in learning Spanish, from adaptive platforms to immersive technologies. These trends not only make learning more accessible and personalized but also help integrate language learning into daily life. EdLock, with its unique approach to learning through daily activities, is a prime example of how modern technologies can transform the learning process and make it more organic and effective. Take advantage of these trends to make learning Spanish both enjoyable and productive!
0 notes
Text
Dead by TikTok
THE COMMUNITY
The community I have chosen to analyze is that of people who play the game Dead by Daylight (DBD), and specifically those who take to the app TikTok to converse with the community.
In the words of the official Dead by Daylight website, “Dead by Daylight is an asymmetrical multiplayer horror game where one player takes on the role of a brutal Killer and the other four play as Survivors,” (Game).
Because of the fact that there are two sides of the game that can be played, there are a lot of differing opinions in the community. Killer players think that survivor players should play a certain way, survivor players think that killer players should play a certain way, and those who play both mostly just wish everyone would shut up. Often, either side of the argument doesn’t even agree with their own side.
One thing that the community usually comes together on is to criticize the developers of the game. DBD is made by a fairly small independent development team, and they are still often making changes and adding updates to the game. Of course, there will likely never be a time where every person who plays the game is pleased, so this is often a topic of discussion (or more likely disagreement).
Every few months, the developers also add a new killer and/or survivor to play as, and with these come more perks as well (more about this later). This brings even more ground for discussion and disagreement as players argue over whether the killer is too strong or too weak.
I chose to play on one of the common assumptions held by players of the game in choosing one of my posts and how I captioned it. This requires a bit of background to really understand it.
In the game, there are multiple different survivors that can be chosen to play as. Each of these come with 3 of their own unique “perks” which give the survivor an ability during the match. However, as one continues to play the game, these perks become unlocked through leveling characters and then can be applied to other survivors as well. So, basically, once you have played the game for a couple of months, all survivors end up with all of the same perks and so they all can be played exactly the same.
This being said, one assumption that the community still holds is that a certain “type” of player tends to play a specific survivor. I usually play as the character Meg. “Meg players” are usually known for running around, making dumb decisions, and getting their team killed. While I would argue that this is not always the case, I found a gameplay clip of my own where I did fall into this “Meg player” stereotype.
So I decided, “why not?” and decided to play into this and post the clip to TikTok.
@_bekoorb
when you get way too confident for no reason 😅 who’s your least favorite killer? ##dbd ##dbdclips ##dbdvideos ##deadbydaylight ##streamclips ##streamer
♬ Monkeys Spinning Monkeys - Kevin MacLeod
The video shows me being saved by another player, and then running us both straight to the killer. I ended up getting away, but the other player did not.
I chose to use the caption “Your real mistake was following a Meg,” to further speak to this assumption. I thought this was a clever way to start a conversation with the community, even if it just gave them an excuse to make fun of the way I played. I believe that if the video had gotten more views, it would have been enjoyed by the community.
MY CONTRIBUTION
Over the course of posting in this community, my posts received on average about 7 views, with only 2 or 3 likes on each. None of my posts received any comments. Additionally, the comments that I left on other posts did not receive any interaction. I guess, if there was a pattern, it was that no one really saw my posts.
Having spent a lot of time on TikTok in my free time, I used my knowledge of the app to attempt to break into the algorithm. First of all, I used trending music on the app as background noise for my videos because posts with these audio sounds are more likely to be promoted.
When I say “promoted”, I mean showing up on other users For You Page. This is basically the front page of the app, and where a large majority of users spend all of their time scrolling. This is really the only way to find new content on TikTok.
Other than using trending background music, I also designed the captions of my posts to the community. I used hashtags such as #dbd, #dbdclips, and #deadbydaylight in order to cover a range of different hashtags while still covering the same topic. I also tried out adding a question into the caption so that if anyone did stumble upon my post, they would have something to respond to.
I also attempted to use up to date trends in the content of my videos posted. For my first one, I used a trend of not actually speaking but using pop up text-to-speech on the screen. This is the one that I mentioned earlier, but here it is again:
@_bekoorb
your real mistake was following a meg ##dbd ##dbdclips ##dbdvideos ##streamer ##streamclips
♬ Elevator Music - Bohoman
This was something that I was seeing a lot in trending videos, so I decided to try it out and see if it would be promoted, but it unfortunately did not work out how I wanted it to.
Something that I learned about this community in this process was how difficult it can be to break into it. You really have to be consistent in posting and interacting, and it is mostly left up to luck whether people end up seeing it or not.
I also learned that despite the fact that the DBD community is very opinionated, through my time analyzing this specific community I actually found that on TikTok the focus was usually not that of opinion. Most of the posts that I saw and interacted with have been funny, entertaining, or informative. Sometimes there will be posts giving tips or strategies on the gameplay, but a lot of the time the clips on TikTok are highlight videos.
Because of this, for one of my posts I decided to try to fit into the “highlight videos” category. I found a funny moment from a time that I was playing the game, and again added some trending background music to it. I also edited text on the screen so that it would pop up as I was speaking it, which I thought added a level of comedy.
@_bekoorb
when you get way too confident for no reason 😅 who’s your least favorite killer? ##dbd ##dbdclips ##dbdvideos ##deadbydaylight ##streamclips ##streamer
♬ Monkeys Spinning Monkeys - Kevin MacLeod
In this post, I also added a question to my caption so that if my post was viewed, my audience would have something to respond to. THE PLATFORM
Something interesting that I found was that TikTok users almost always use hashtags in their posts. However, I’m not sure this really accomplishes much. It’s possible that it makes the post more likely to show up on someone’s feed who often watches or likes videos with that hashtag, but something I found is that it is very difficult to find new videos using the hashtags.
In the same way that I found it difficult to find posts to comment on in order to interact with this community, others were unable to find my posts in the hashtags.
If you do search a hashtag with the intention to find new content or new users, you won’t find much. This is because the posts under a certain hashtag are listed in order according to how popular they are, and there is no way to change the order. This basically means that if you are looking for new videos, you won’t find them there. The only place to find new content is on your ‘For You Page’, and that is pretty randomized and mostly shows popular videos as well.
This means that in order to gain views and followers, most of the time you have to already have views and followers.
It’s like when an entry level job requires a year of past experience. If I can’t get hired because I don’t have experience, how am I supposed to gain the experience?
This further solidifies the fact that the TikTok algorithm favors only content that is already popular. The people with the most followers and views continue to have their videos promoted, and they basically control the format of the app from there.
I don’t think this is all bad. Sure, the platform very much favors already popular content so it is difficult for newcomers to gain any sort of traction on the app. But on the other hand, I believe this puts less stress on trying to become “popular” and more emphasis on making posts for fun and as a creative outlet. Of course, I’d argue that there is a little part in all of us that would like our posts to become popular, but that doesn’t always have to be the point.
This also has an effect on how communication happens (or doesn’t) on the app. When the posts being shown on peoples feed is often from the same handful of creators, there is not much opportunity to see a variety of opinions or discussion.
Works Cited
“Game.” Dead by Daylight, deadbydaylight.com/en/game.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Changes in SEO after Maycore update
Changes in SEO after Maycore update

The new core algorithm update was announced on the official Google SearchLiaison Twitter account on May 4, 2020.Over a period of two weeks, they introduced the changes in a number of smaller updates to the algorithm.
Search engine ranking algorithms are a unique technology that is protected as an expensive commercial product. Google does not disclose the details of the algorithms operation and describes them with a single phrase: “Make content for people—get profit.” Unlike other updates, Google announces the Core Update on Twitter when the deployment is complete.
What has changed

E-A-T (expertise, authoritativeness, trustworthiness). It’s a key factor for YMYL sites. Those who neglected these factors rolled back farthest.
Mobile version site. It includes the adaptation of the mobile version to the users’ needs and its full support at the desktop level (development, new products implementation, A/B testing).
High-quality content. Even small sites with good content have improved their positions.
Link profile. There should be no spam by anchors or links of unknown origin.
The above is for the logical and expected improvements. However, there have been changes that surprised webmasters. Google experts have already commented on a number of them. After starting the updates, Google engineers collect feedback from webmasters and see what is broken. As a result, they have to smooth out the negative effects (false positives) because of which the owners of the “good” sites suffered. Many posts on social networks mention local search changes. Local SEO Specialist Darren Shaw notes that the niche has been storming since the end of April. Google experts have already confirmed that it had been a bug.
In addition, it is worth noting the following Google May 2020 Core algorithm updates:
Partner sites and aggregator sites improved their performance.
Projects with a strong brand image received a significant boost from Google, while “less branded” ones went down.
Some projects with a weak link profile also came forward.
Winners and losers of the Google algorithm update
Many at the World Forum of Webmasters have already been outraged by such changes. In their opinion, in less than a week, updates have led to a global decrease in traffic and online sales for many fields: healthcare, technology, finance, and dating.
After the first wave, SEMrush compared the average value of volatility seven days before and two days after the announcement of the update. The most affected categories at that time were: Travel, Real Estate, Health, Pets & Animals, and People & Society. This applies to search both on a computer and on mobile devices.
The five winners included such categories as News, Business & Industrial, Online Communities, Arts & Entertainment, and Health. The injured were Arts & Entertainment, Online Communities, Business & Industrial, Games, and News. The situation is ambiguous because several categories fell into both lists, which means that the matter is not only in the subject of the site itself but also in other factors that influenced the ranking.
Today, when the Google core update may 2020 impact calmed down a bit, the distribution of winners and losers has slightly changed. The News is still confidently holding the first place but sports and auto-related appeared among the main losers.
It’s important to understand that major core updates to the Google algorithm are usually not industry-specific. A change can have a strong impact on the niche, but this does not mean that it was the goal of the update. Traffic drawdown after algorithm changing may have nothing to do with the site itself, but is associated with a reassessment of ranking factors.
How to adapt to the changes
Changes have already occurred, so now webmasters can only observe, analyze and adapt to the latest Google algorithm update. Here are some points to pay attention to:
User signals matter
Google reports that it focuses on traffic signals determining in which cases the site is important and useful, and how much it meets the user’s expectations. Although it is too early to draw far-reaching conclusions, you can take a closer look at the sites that clearly benefit from Google changes May 2020.
The head of SEO at content marketing agency Suxeedo Niels Dahnke is sure that good user signals (high CTR, low bounce rate, and good dwell-time) have a positive effect on Google’s ranking stability.
Update your content
Constant posting and content updating is an important step in improving your position in SERP. It is not enough just to pull out old texts and add a couple of sentences to update them. You should make efforts to keep up with the Google algo update: check relevance, get rid of outdated information, add a few paragraphs, and, if necessary, even rewrite the entire article.
The famous marketer Neil Patel conducted a study based on 641 sites that regularly update their content. Thus, only about 6% of these sites have reduced search traffic by more than 10% since the update. SERP improved by 10% for more than 187 websites.
Make the content rich
Another important task for webmasters in the terms of the new update is to review the quantitative part of their content. Sites with thin content, i.e. where at least one page contains texts with a small number of words, went down. Of the 400 resources that Neil Patel tested, 31% were adversely affected: their search results fell by more than 10%.
Checking the site for the thin content is a must-do thing on the SEO checklist 2020, and not only as part of updates from Google, but also for regular work on the site quality. However, do not forget about common sense. See if it is really necessary to increase the number of words and whether you really need this page.
Improve SEO
Errors in the SEO, mainly duplicate headings and meta descriptions, can seriously influence the drop in search results. More than 20% of repetitions can critically affect performance. However, the pursuit of the perfect result is not always the right option. Using the same tags may be justified, for category pages with pagination for example. In other cases, you should fix the errors to match the Google SEO update.
Add expertise
After the May update, extra points in the search results went to the sites with first-hand expert opinion. The author of the texts should have good knowledge of the field they write about and, if possible, consult with relevant experts. Checklist for expert content:
It reveals the narrow aspects of the topic.
Heading H1 and subheadings H2-H6 correspond to the topic.
There are no spammed and uninformative texts.
There is a clear structure of articles including bulleted lists, graphics, tables, diagrams, videos, headings, and subheadings.
There are feedback forms and all the necessary information is visible.
Check with Google guidelines
Google emphasizes that a drop in SERP does not mean that the site is bad, just someone else has more relevant and high-quality content on the same topic, and that’s why users prefer the competitor’s site. Pay attention to Google’s recommendations for webmasters, especially after core updates. By responding to the changes in time, you will most likely be able to avoid traffic loss. It’s worth starting with two main points:
Check Google’s Quality Raters Guidelines for each item that may be applicable to your site as signs of high or low quality.
Refer to the official Google blog. An excellent checklist is presented there to verify that your content meets quality requirements.
How to keep up with Google’s changing algorithms
Google search algorithm updates are geared to improve the overall search quality. The sites that were previously ranked lower may rank unexpectedly higher, and vice versa. The webmaster’s task is to monitor all changes and improve the content, making it expert, relevant, and interesting. Then, whatever changes are brought about, you will still rank high on Google.
https://transorze.com/
0 notes
Text
A Quick Guide to Nurturing YouTube Subscribers with Email Marketing to Grow Your Brand

YouTube is a powerful platform that you can use to grow your business and brand. However, it has one weakness: it lacks the necessary tools to help you build a true relationship with your following that goes beyond the video likes and comments you get.
The good news is that, with the right strategies, you can use YouTube to grow and engage your audience by migrating subscribers over to your website.
In this article, we talk about how you can grow your brand by using email marketing to nurture your YouTube subscribers.
Over the years, YouTube has experienced explosive growth and now pulls in over 2 billion users each month.
The platform is one of Google's most popular services, with more subscribers than Gmail and nearly as many as Facebook.
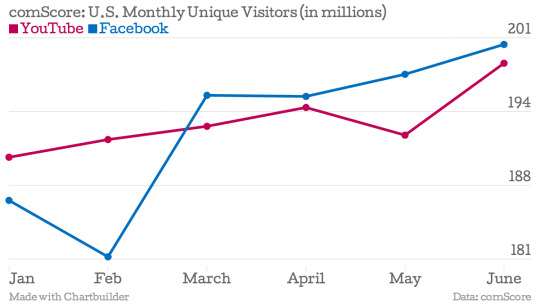
It's clear from these numbers that for any small to medium business, YouTube is a great platform to use as part of your strategy to connect with your current and potential customers.
No matter who your target audience is, you can be sure that you will find the majority of them watching videos on YouTube.
Although some people believe that the golden age of YouTube is over, this platform has been around for a very long time, and if its growth over the years is anything to go by, it will be here for a very long time to come.
Growing Beyond YouTube
I discovered the process of using email marketing to nurture YouTube subscribers when I was searching for an effective way to get my YouTube subscribers into my business funnels.
If you already have a YouTube channel that has hundreds or even thousands of subscribers, then you're certainly doing something right with your audience building tactics.
But, as a content creator, you may find that YouTube is not the best platform for monetization.
While you can make decent income with your videos, there are other ways to maximize the revenue from your subscribers, and one of the best ways of doing that is by using email to help you grow beyond YouTube.
Use Email Marketing to Make Direct Connections
I choose to use email marketing with YouTube because it facilitates one-to-one conversations and helps me build brand affinity. No other channel offers similar benefits when it comes to connecting with your audience.
You can either broadcast emails or use personalized messages to build solid relationships with your audience. There are a variety of email marketing tools to choose from that will allow you to get to know your new subscribers and learn more about your older ones.
With the right email tools, you can also segment your list so you can send even more targeted and personalized content to each of your subscribers.
Because of this direct connection, email subscribers have a higher tangible value than YouTube subscribers.
By using email to build and develop strong relationships with your subscribers, you will be able to leverage all its power to help you meet your monetary objectives.
Email marketing comes with other benefits, as well.
With email, you own your subscribers. When you run a YouTube channel, algorithm changes can affect your subscriber count and video views unexpectedly.
Even worse, if your channel doesn't align with YouTube's policies, it could get shut down literally overnight.
That’s why it's a good idea for every YouTuber to create an email list so they have direct access to their audiences’ inboxes regardless of what happens with the algorithms.
Ready to start automating your email marketing campaigns?
Book a free call to learn how our team of marketing experts can help you to create high converting email marketing campaigns today.
Growing Your Email List from YouTube in 5 steps
Now that you know the importance of using email to nurture your YouTube subscribers and grow your brand, let's take a look at five powerful strategies that you can use to supercharge your list growth. Step 1: Create a Lead Magnet to Increase Youtube Subscribers One of the best ways to get subscribers to your list is to offer a lead magnet. This is simply any piece of content or software that is valuable and useful to your audience.
When you offer a free incentive, you will have higher numbers of YouTube viewers who are willing to exchange their information for access.
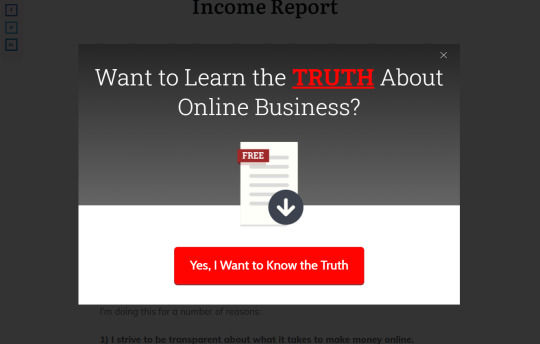
You can use any type of lead magnet that will resonate with your audience. It doesn't have to be something big - it can be a small but action-packed content piece, such as a PDF checklist, short e-book, white papers, host a free webinar, or premium video content.
Below is an example of a lead magnet I have on my own website. The idea is to capture the users attention and arouse curiosity.
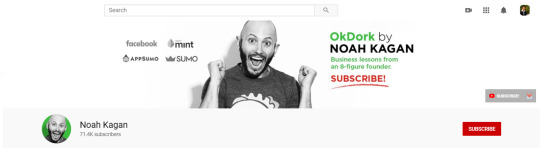
Step 2: Use a Strong Call to Action If you use a lead magnet, make sure your viewers know about it by adding a compelling call to action to promote the lead magnet in all your videos.
You can also use a call to action in your channel header, as in the example below:
Yet another tactic is to include the CTA in the video script. Directly ask your viewers to subscribe to your list at the end of each video. Make sure you tell them the benefits of joining (whether you have a lead magnet to offer or some other benefit). Step 3: Make It Easy to Subscribe This may seem like a no-brainer, but you'll be surprised how many people overlook this.
If you want to increase your conversions, you must make it as easy as possible for your viewers to subscribe to your list.
You can have the best lead magnet on offer and the most compelling call to action to encourage your viewers to sign up, but if the process of signing up is lengthy or complicated, even your most avid viewers will give up before completing it. Step 4: Use Cards to Link to Your Website YouTube lets you use cards in videos to link to associated websites. However, you must make sure that the sites that you link to meet YouTube's community guidelines.
To get started with this tactic, you need to first join YouTube's partner program and then associate your website with your Google account.
You can then go to the Video Manager to add cards. This article offers detailed instructions on how to complete this entire process.
In addition to using cards, you can also use links to your website within the video descriptions. Step 5: Use Annotations With YouTube annotations, you can layer links, text, and hotspots over all your videos. Use these to add links to your lead magnets with strong calls to action to get your audience to subscribe.
Below is an example of an annotation on a YouTube video:

You can also customize the way annotations look to match your other marketing material.
To add an annotation to your video, check out this in-depth article from YouTube which outlines the process in detail.

Engaging YouTube Subscribers with Email
Once you have captured the emails of your YouTube viewers, you will need to create an autoresponder series to welcome them to your list and share some more information about you, your business, and what your new subscribers can expect from the emails you send them.
If they signed up in exchange for a lead magnet, be sure to deliver that first.
Aside from the welcome autoresponder series, you also need to keep in regular contact with your subscribers by sending them great content, as well as broadcasts each time you upload new videos to YouTube.
You can make the broadcasts a lot more personal than the emails that are automatically generated by YouTube.
To make the most of each email, customize and personalize the message and include information about your products and services.
There are many other strategies you can employ to engage the people who sign up to your email list.
I have gained the trust of my audience by first offering immense value before selling my products and services.
Use the tactics listed below to help you engage your YouTube subscribers with email and when you do decide to sell products to them, you will have a receptive audience who are eager to buy your products.
1. Create the Right Content: It's important to do research to ensure that you offer your audience the right type of content to help them find the answers and solutions they need. For instance, you can create how-to content based on your audience’s pain points. Make sure your content is not only packed full of value but also that it’s something that cannot easily be found elsewhere online.
2. Segment Your Email List: Yet another insanely effective way to keep your subscribers engaged is to segment your email list so that each group gets emails that are more targeted toward their needs and interests.
Find out your subscribers’ interests, gender, marital status, profession, age, or any other relevant information and then segment your list accordingly.
This will increase the level of relevancy and personalization of your emails which, in turn, will increase your ROI.
3. Use Exclusive Content: This is among the most effective ways to keep your subscribers feeling special and appreciated.
YouTube subscribers expect to receive all the videos you publish. It's probably one of the main reasons they subscribed to your list.
However, if you create content exclusively for them, this will surprise and delight them and help you to maintain engagement for a long time.
The type of content you create is entirely up to you, but it needs to be extremely valuable and relevant to your subscribers.
Of course, these are just some of the different ways you can use email to transform your YouTube viewers into valuable subscribers.
Truth be told, there are more tactics, but these are some that I’ve found to be most effective. Implement each of these tips in your own strategy so you can start growing your brand today.
Are there any other tactics you know of for nurturing YouTube subscribers? Let us know in the comments section below!
About the Author

Ron Stefanski is a professor and a successful web entrepreneur who has a passion for helping people create and grow online businesses. Visit his website to learn more: OneHourProfessor.com.
from RSSMix.com Mix ID 8230801 https://ift.tt/3jwSytq via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
GDV: An Imaging and Modeling Tool for Medical Biometrics
Gas Discharge Visualization: An Imaging and Modeling Tool for Medical Biometrics
Nataliya Kostyuk,1 Phyadragren Cole,2 Natarajan Meghanathan,3 Raphael D. Isokpehi,1, 4 and Hari H. P. Cohly1, 4 1 Center for Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, Jackson State University, Jackson, MS 39217, USA 2 Department of Communicative Disorders, Jackson State University, Jackson, MS 39217, USA 3 Department of Computer Science, Jackson State University, Jackson, MS 39217, USA 4 Department of Biology, Jackson State University, Jackson, MS 39217, USA Correspondence should be addressed to Hari H. P. Cohly, [email protected] Received 23 June 2010; Revised 23 January 2011; Accepted 13 February 2011 Academic Editor: Yue Wang Copyright © 2011 Nataliya Kostyuk et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. The need for automated identification of a disease makes the issue of medical biometrics very current in our society. Not all biometric tools available provide real-time feedback. We introduce gas discharge visualization (GDV) technique as one of the biometric tools that have the potential to identify deviations from the normal functional state at early stages and in real time. GDV is a nonintrusive technique to capture the physiological and psychoemotional status of a person and the functional status of different organs and organ systems through the electrophotonic emissions of fingertips placed on the surface of an impulse analyzer. This paper first introduces biometrics and its different types and then specifically focuses on medical biometrics and the potential applications of GDV in medical biometrics. We also present our previous experience with GDV in the research regarding autism and the potential use of GDV in combination with computer science for the potential development of biological pattern/biomarker for different kinds of health abnormalities including cancer and mental diseases. 1. Introduction Biometrics is the field of science which brings together biol- ogy, physiology, psychology, computer science, mathematics, statistics, and engineering. The global interest in biometrics is motivated by its accuracy, reliability, and instantaneous real-time readout. Nowadays, biometrics is penetrating into many areas of social life. For example, in education, at the K- 12 level, students are being introduced to the basic notions of biometric science to wake up the interest in the next genera- tion of researchers and scientists to this fast developing field. According to the classic definition, biometrics is an automated process of recognizing the individual features based on one or more specific anatomy, physiology, and psy- chological characteristics with the purpose of recognition, identification, and verification. Recognition is the knowledge of a previously enrolled pattern; identification is the process of determining the identity of an individual according to the pattern, whereas verification is a process by which the system confirms the existing pattern. The biometric models existing nowadays are based on fingerprint, face, iris, voice, signature, hand geometry, palm, and vascular pattern recognition. There exist other biometric models that are based on speaker recognition, dynamic signature measures, key stroke dynamics, retina recognition, gait/body recognition, and facial thermography. The main areas of biometric applications can be classified into the following four groups: (1) security biometrics to reduce frauds and control the access to restricted areas, (2) forensic biometrics, which refers to the use of biometrics for criminal and body identification, (3) convenience biometrics, which is related to main- taining the convenience level during the use of a computer or network, (4) medical biometrics, which is related to the use of biometrics in medical applications such as medical diagnosis and is based on the extraction of biomed- ical pattern and its association to possible diseases. Medical biometrics is emerging as a very promising and reliable method for automated medical diagno- sis. Medical biometric systems have been developed to use personal features in different formats such as images, signals, and other sources in order to solve problems and provide high-performance service in the medical field. Medical biometrics based on the gas discharge visu- alization (GDV) technique has been used in medicine to monitor the patients and compare their natural electro- photonic emission before and after surgeries, cancer treat- ments, energy healing, physiotherapy, SOQI therapy, and so on. Previous findings using GDV have demonstrated the potential capability of the GDV technique to identify the deviation from the normal functional status during the early stages of disease development as well as to monitor a transition from a disease state to normal functional state. The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we describe different types of biometrics and the areas of application, and introduce medical biometrics in Section 3. In Section 4, we discuss the possible applications of GDV in medical biometrics and our pilot studies on the applications of GDV in medical biometrics, Section5 concludes the paper. 2. Types of Biometrics and Areas of Applications The biometric signatures for the identification purposes are based on physiological and/or behavioral trait and help in the verification process. It is important to understand that all biometrics are based on probability measures. Biometrics is a mathematical model of a physical characteristic and as in all mathematical models, there is always a probability of an error. However, biometrics is the most reliable way of verification and authentication. Physiological traits used in biometrics include iris, fingerprint (including nail), hand (including knuckle, palm, and vascular), face, voice, retina, DNA, lips, earlobe, sweat pore, and even odor. Behavioral traits are based on signature, keystroke, voice, and gait . Over 140 years of fingerprint comparison worldwide, no fingerprints were found to be alike not even those of identical twins. Fingerprints do not change throughout the life span, and therefore, fingerprint identification involves comparing the pattern of ridges and furrows on the fingertip as well as the minutiae points, which are ridge characteristics that hap- pen when a ridge splits into two, or ends of a specimen print with a database of prints on file. Hand geometry authenti- cation is often used in industrial environment. It does not require clean conditions, forms a very small dataset, and is not regarded as an intrusive kind of a test . Interestingly, the authentication of the identity seems to be not descriptive enough using hand geometry. One can attain robust verifica- tion only by combining various individual features. Iris and retina scans provide unique biometric data as it is impossible to duplicate or replicate them . The pattern of blood vessels at the back of the eye and iris remains the same through lifetime. Despite being highly reliable, the disadvantage of retina scan is that the accuracy of measurement can be affected by disease such as cataracts or severe astigmatism and the equipment is not very user friendly as the subject has to be close to the camera optics leaving alone the cost of the equipment which is very high. Face recognition is one of the most flexible identification methods as individuals are unaware that they are being scanned. Face recognition system relies on the features common to everyone’s face: the distance between the eyes, width of the nose, position of cheekbones, jaw line, chin, and so on. These numerical quantities are then combined in a single code that uniquely identifies each person . Some facial recognition algorithms identify faces by extracting landmarks or features from an image of a subject’s face. It may analyze the relative position, size, or shape of the eyes, nose, cheekbones, and jaw and use these features further to search for other images with matching features. Other algorithms normalize a set of face images and then compress the face data in the image that is useful for face detection. A probe image is then compared with a database of face images. Three-dimensional face recognition is a relatively new trend in biometrics, and it claims to achieve an unbelievable accuracy in face recognition . This technique uses 3-D sensors to capture the information about the shape of a face. The advantage of 3-D facial recognition is that it cannot be affected by changes in lighting like other techniques. It can also identify the face from a range of viewing angles, including a profile view. However, this technique could be sensitive to face expressions. As compared to other biometric methods such as iris or fingerprint scans, the voice recognition allows vocal information of new pin numbers or acknowledgement of license agreements to be delivered as a part of voice bio- metric application . DNA identification is used to prove innocence or guilt, paternity testing, and the identification of missing or dead people. The coding genes constitute only 5% of the human genome; however, the repeat of identical DNA sequence can be found anywhere in noncoding sequences from one to 30 times in a row and are called variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs) . The number of repeats is specific and varies from one person to another. For any given VNTR place in an individual’s DNA, there will be a certain number of repeats. DNA profiling includes the isolation of the DNA from the sample, cutting the DNA up into frag- ments with VNTR areas, sorting them by size, and compar- ing the DNA fragments in different samples. The weaknesses of DNA biometrics are intrusiveness (a physical sample must be taken) and matching not occuring in real time. A signature is another example of biometric data which is easy to gather and is not physically intrusive. Although an individual can purposely change his signature to some extent, it is still considered as basic means of identification . Keystroke-biometric method is considered to be unique behavioral biometrics. It is based on dynamics of typing and depends on how an individual types his password or name . Gait biometrics identifies the person by the way he/she walks, runs, or does any other motion by feet . Gait biometrics would be extremely useful to identify shoplifters who pretend to look like pregnant women. The experts say that the natural way a pregnant woman walks is different from simulation, and therefore, this biometric method would significantly decrease thefts if installed in retail stores. The above-described types of biometrics have vast areas of application related to security, forensic, and convenience purposes. 3. Medical Biometrics The first International Conference on Medical Biometrics held at Hong Kong, in 2008, postulated that medical biometrics is a fast developing, very promising, and reliable method for automated medical diagnosis . It com- bines multidisciplinary technologies in biology, medicine, electronics, computing, and statistics and is different from biometrics which is a statistical approach in clinical practice. Medical biometric systems have been developed to use personal features in different formats such as images, signals, and other sources in order to address health issues and provide high-performance service in the medical field. These features are applied by combining statistical, mathematical, and engineering methods. Medical biometrics investigates the biological or behav- ioral patterns displayed by living organisms and its sig- nificant correspondence to the organism’s behavior and/or health. Though medical biometrics is a relatively recent field of science, many studies have been done trying to identify unique biologic patterns pertaining to the disease profile. Usually, it involves the comparison of the sample/individual to a healthy biological pattern established as a standard, and the deviation from the standard serves as the indicator of irregularity or problem. For example, in embryology, the virtual reality biometric technique can be used to diagnose the growth and/or developmental delay of a fetus at early stages. First, the researchers measure the parameters of the embryo still present in the womb and then develop an algorithm for healthy, normal embryo by measuring width of embryo’s shoulder, elbow, hip, and knee. Therefore, a virtual embryoscopy could be a biometric tool to identify the biological pattern of embryo’s deviations from normal development . In another study, researchers aimed to find gender differences in the amount of gingival display during smiling using two intraoral dental biometric mea- surements. Researchers compared the width and length of the maxillary right central incisor and the horizontal vertical overlap of the anterior teeth to determine the relationship of these two intraoral dental biometric measurements with the amount of gingival display during smiling. The study included 61 men and 66 women ranging between the ages of 23 and 52. The participants were judged on the basis of the visibility of the gingival tissues during smiling. The results of this study showed that a relatively small percentage of the subjects displayed gingival tissue when smiling. More women displayed gums than men in a 2 : 1 ratio. Subjects with gin- gival display had significantly more horizontal and vertical overlap of anterior teeth compared to those who did not display gingivae when smiling . The described study does use the dental biometrics measures, but not in the context of disease identification or dental problems of a patient. The literature review of genetic prognostic signatures found serious problems in the design and analysis of many studies. It has been pinpointed that research should be focused on the development of well-validated clinically use- ful genetic prognostic signatures that would improve ther- apeutic decision making beyond current practice standards. Also, the evaluation of prognostic signatures studies requires more attention . Medical biometrics as a method for an automatic identification and analysis of a disease is a promising and developing field. However, sometimes the examples of medical biometrics in the medical literature refer to the problems of patient identification in the hospitals or patient identity theft or using biometric data for the identification of gender which is not relevant in the process of disease identification. The field of medical biometrics is being advanced by the research on the topics of oral cancer screening using laser-induced fluorescence, multi resolution- optical flow to correct respiratory motion in 3D PET/CT images, ultrasound imaging for bone quality assessment, texture feature extraction and classification for iris diagnosis, hepatitis diagnosis using facial color image, interactive 4D- computed tomography, recognition pattern for lung cancer, recognition, measurement, and classification of intracranial hematomas, computerized traditional Chinese medicine, and so on . The most recent study conducted in Singapore has shown that the computerized diagnosis of energy resources of human body based on the Chinese meridian method is helpful in monitoring improvement after treatment with far-infrared irradiation, electric ionization and enzyme supplement. The system calculates the energy resource of a patient based on the electrical activity of acupuncture points and then matches the collected energy pattern to the already established norm standard, thus, showing if the energy field of a patient improved or not after treatment. Another recently developed biometric device is based on gas discharge visualization (GDV). This technique is discussed in the next section. 4. Gas Discharge Visualization (GDV) and Its Applications in Medical Biometrics Gas discharge visualization (GDV) is based on electrical activity of human organism . In disease condition, the electrical activity of human body is changed as compared to electrical activity in healthy state. The electron communi- cation is altered, and therefore, the natural electrophotonic emission of the organism is changed. The GDV technique is a method that combines eastern medicine with western approach. Capturing the natural electrophotonic emission of human body, referred to as GDV-grams, allows one to identify the functional state of an individual in real time. The biometric method based on GDV is extracting the stimulated electrons and photons from the surface of the skin under the influence of pulsed electromagnetic field. This process is quite well studied with physical electronic International Journal of Biomedical Imaging methods and is known as “photoelectron emission.” The particles emitted and accelerated in the electromagnetic field emerge as electronic avalanches on the surface of the glass electrode causing the so-called “sliding gas discharge.” The discharge causes glow due to the excitement of molecules in the surrounding hydrogen, and this glow is what is being measured by the biometric method based on GDV. Therefore, short voltage pulses stimulate the electrophotonic emission concomitantly intensifying this emission in the gas discharge due to the electric field created. The data obtained in the process of measuring of extremely weak “biophoton field” is the scientific infor- mation which may reveal the role of some electro-photon processes underlying the functional state of the body. In the biometric GDV method, the stimulation of electrons and photons is intensified thousand times and thus enables measurements under normal circumstances, with normal lighting, without special preparation of the objects. The design of the biometric GDV device is completely safe as the electric current that flows through is a pulse current in microamps which is not causing any depolarization of tissue or other physiological changes. Other methods using voltage pulses which last more than a few milliseconds avoid the depolarization by applying different pastes or gels. The process of extraction of electrons and photons in GDV method consists of two phases of capturing the images: without filter and with filter. In the initial stage, the electrons located in the outer layers of the cutaneous covering and the surrounding tissue are extracted. In the second phase, electrons from the deepest tissues in the body are included in the current flow. These electrons may have several sources. Some of these belong to the molecular albuminous systems, and in accordance with the laws of quantum mechanics, these electrons are dispersed among all the molecules. It is as if they are “collectivized” among groups of molecules, so in principle it is impossible to say where an electron is at a given time. They form the so-called “electron cloud”, occupying a specific area in space. Several studies tried to determine what exactly forms the fluorescent glow (also called GDV-grams) around fingertips. Krizhanovsky et al. determined that the human central nervous system plays a crucial role in the formation of skin glow in a high-intensity electromagnetic field. The ATP (adenosine Tri-phosphate) molecule acts as a neurotransmit- ter in the autonomous neuromuscular junctions, the ganglia, and the central nervous system. Therefore, in case of normal operation of the organism, the ATP diffusion exchange (and the electron stream) must be regular, thus ensuring the regularity and uniformity of the fluorescence (glow) that occurs during the interaction of the skin (i.e., of a finger) with the high-intensity electromagnetic field. Another study conducted by Williams claims that specific structural- protein complexes within the mass of the skin provide channels of heightened electron conductivity, measurable at acupuncture points on the skin surface. Stimulated impulse emissions from the skin are also developed mainly by the transport of delocalized electrons. In cases of imbalances and dysfunctions, immunod- eficiency, or an abnormality of the microcapillary blood circulation, the transfer of electrons to the tissue is altered and inhibited, and therefore, the electron flow is not full and the stimulated current is either very small or is very irregular in time. Therefore, the gaps in electrophotonic emission are the indicators of the impeded transfer of electron density to the body’s tissues and an abnormality in the energy supply of organs and systems. The central nervous system (CNS) and the autonomous nervous system (ANS) regulate the activity of all the organs and systems. The loss of synchronicity and fail in autonomous regulation caused the abnormality in working coherence of organs and systems and is manifested by such symptoms as a bad state of health, disturbed sleep and digestion, abnormal perspiration, and so on. Later on, these abnormalities lead to the dysfunctions of organs; however, the degree of abnormality largely depends on the type of genetic predisposition. The ANS reacts to the commands coming from CNS and the surrounding environment and sends control signals to the organs and systems. These signals are processed at both the physiological and the endocrine and immune systems. Information is transferred to the controlling organs thus forming a Biological Reverse System and concomitantly a closed circuit. Therefore, if any of these abnormalities are taking place in one of these links, the circuit fails and desynchronization is taking place at all the most vital levels, and ANS is the first instance to reflect all the potential problems that apparently appear first in the human body. All of the external and internal stimuli are processed by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system and are reflected on the parameters of the cutaneous covering. The electrical resistance of the skin changes, both as a whole and at electropuncture points, the capillaries narrow and widen, and there is an emission of organic molecules through the pores; the nature of the transfer of electrons to the connective tissues also changes. All of these processes influence the emission of electrons from the skin and the development of electron avalanches, which is reflected in the parameters of the electrophotonic capture in the biometric method based on GDV.

Gas Discharge Visualization: An Imaging and Modeling Tool for Medical Biometrics The objective of GDV is to identify the functional psychoemotional and physiological state of a person using fingertips . The analysis of natural electrophotonic emission is based on intensity, fractality, and area of the captured images. In GDV, the relation of the captured image to organs/organ systems is determined by the acupunc- ture approach, and therefore, the image is automatically divided into sectors having start angle and end angle as reference points which have been defined after Korotkov . Also, GDV provides the integral parameters of entropy and autonomic tone, which are important components in the analysis of human functional state . Entropy is a measure of chaos/disorder, and an increase in entropy has been postulated on the First International Congress of Systemic Medicine as a manifestation of sickness, negative impact of chemical, biological, physical, or emotional stress, and chronic degenerative disease . The Congress also mentioned that the treatment of sickness should consider the International Journal of Biomedical Imaging
Gas Discharge Visualization: An Imaging and Modeling Tool for Medical Biometrics
Nataliya Kostyuk,1 Phyadragren Cole,2 Natarajan Meghanathan,3 Raphael D. Isokpehi,1, 4 and Hari H. P. Cohly1, 4 Read the full article
#Bioelectrography#BioelectrographyExperiments#ElectroPhotonicImaging#Electrophotonics#GasDischargeVisualisation#GasDischargeVisualization(GDV)#InternationalJournalofBiomedicalImaging#IUMAB#Kirlian#Kirlianeffect#Korotkov#MedicalBiometrics
0 notes
Text
THREE IDEAS - DIGITAL PRODUCT
IDEA ONE - FONTASY
As a designer it can be difficult to figure out what fonts compliment each other and which one’s match your aesthetic style for work. So the idea I have come up with is a generator that takes inspiration from your favourite musical artists, and provides you with a set of usable fonts matching the artists aesthetic. It will also allow you to ‘edit text’ so you can visualise how certain words will look, in the presented font.
STRENGTHS
Fonts chosen will be usable, stylised and interchangeable
Will shorten the length of time taken when looking for complimentary fonts
As this will be connected to numerous font websites, it will open users to fonts they may not find using keywords/search terms
As this will be connected to numerous font websites, it will open users to fonts they may not find using keywords/search terms
Users will also be able to find fonts similar to those used in artists album work
The app will be created with a designer in mind, so fonts should avoid falling into the default category
WEAKNESSES
Fonts generated could become repetitive, if the user only listen to artists in a similar genre
Fonts might not always be free to use, or demo version won’t include full set of characters
Depending on artists, the fonts provided may be viewed as stereotypical
It’s not always guaranteed that while the fonts match the artists aesthetics, they might not match the users
HOW WILL IT BE MADE?
For the design process of this application I think I would most likely use the combination of Illustrator, XD and possibly InVision. As I'm a Windows user this means the possibility of using Sketch isn't really a possibility although it is the industry standard.
The main design portion of this application will be done through Illustrator to help me further visualise my idea, then to begin bringing the idea together I can use either XD or InVision to apply animations and transitions between pages. InVision would definitely be easier for me, as I have the experience of using it prior to this, whereas I would need to start fresh with XD.
This generator will be an application created with the accompaniment of API’s, which will allow access to various websites with modern fonts such as BeFonts. This will be combined with the likes of Spotify to gain access to the work of the users favourite artists.
WHO IS THE TARGET AUDIENCE?
As for the target market, I would say it applies most to young designers/illustrators, as they need access to unlimited fonts. Through this application the fonts showcased should hopefully interlink with their taste, simplifying the search for fonts. While this app will mostly appeal to designers I know there’s people out there who are simply interested in the likes of what compliments them and their music taste.
WHAT'S THE BUSINESS MODEL?
My aim is for the application itself to be a free service, but some of the fonts showcased through the app may cost money, at least for the full version anyway. This would definitely be one of the biggest weaknesses, but demo versions of fonts do exist so it's not a completely unresolvable issue. Some users could be willing to pay money for the possibility of a great font, in varying weights.
IDEA TWO - SOCIAL PALETTE
Another recurring issue as a designer is trying to figure out what colour palettes look good, especially when they’re from original content such as photographs. In saying this there are existing applications in the market that do the same thing, but this has the capability of being connected to different social media platforms and picking colours from content you post to generate various palettes. I feel as though it would loosely cross over into the likes of Pantone and their work with colour palettes from imagery.
STRENGTHS
This application will help accumulate a variety of personalised palettes all in one place
The palettes will be to your liking, as they’ll be based off content you upload
Creating palettes in this way will cut down on the amount of time spent looking for colours
As this app will also be created with the designer in mind, different tones of the palettes will be generated to create a wider variety of content
WEAKNESSES
As the content will be generated from different social media profiles, there’s the possibility of the chosen colours becoming repetitive/unusable
Although the app is created with designers in mind, it's an algorithm and the palettes aren’t always going to be guaranteed to work for every design
Some people may rather work with pictures of their choice and upload them rather than work with pictures from social media
HOW WILL IT BE MADE?
Similarly to my previous idea I will definitely be relying heavily on the use of Illustrator, XD and InVision.
The design aspects will be done through Illustrator as this will give me the opportunity to visualise the positioning of components, as well as the layout of how I want the colour palettes to look. As I mentioned before with experience in using InVision, the building process will be simplified for me as I will know exactly what I'm doing. Though I'm not going to completely rule out the possibility of using XD.
WHO IS THE TARGET AUDIENCE?
The target market for this application is much like the previous, and is definitely aimed at younger/beginner designers. It’s to essentially give users access to colours which they may not find elsewhere, with a much more personalised touch. Though in saying this there’s also the appeal to those interested in colour palettes, it’s something that’s open to whoever is interested.
WHAT'S THE BUSINESS MODEL?
In my opinion this should be a completely free application as it simply relates to colours and imagery, with no need to charge for any aspects. Unless over time the app progresses into something more over time, resulting in its features becoming chargeable.
IDEA THREE - RATED STYLE
For my final idea I have chosen something which is something I would’ve used or benefited from, it’s essentially an application that will help the user find clothes that match their current aesthetic vibe or music taste. This is where it has some similarities to my first idea, which also weighed heavily on music. Through the app you will be shown a variety of clothes which will be directly linked to websites in which you can purchase the clothing, making different clothing styles much more accessible for a wider group of people.
STRENGTHS
Will give easier access to a variety of clothing brands, styles and online shops
Clothing will be targeted based on the users interests, avoiding being shown clothing they won’t like
Having so many items of clothing from different brands in one place, will lessen the time spent looking for clothing
WEAKNESSES
While clothing will be targeted based on the users aesthetics, it’s possible the clothing won’t always suit the user
This application won’t go as far as matching to the users body type
The pricing of clothing won’t be determined by the application itself, that’s all on the brands themselves
HOW WILL IT BE MADE?
Once again the software I'm most likely going use for this application is the combination of Illustrator, XD and InVision. Though there is the possibility of also using Photoshop as this idea includes the incorporation of images, which may need edited/enhanced in various ways.
Illustrator will of course be the software used to develop my designs visually, with InVision or XD used to bring my ideas all together.
As this application is also going to work hand in hand with other websites such as ASOS and Urban Outfitters, it will also be created with the effort of API’s.
WHO IS THE TARGET AUDIENCE?
I would say the target audience for this application definitely falls into the bracket of being for those in their teens/early twenties who are still figuring out what style of clothing they like and what works for them. It can also be quite difficult to find reliable online stores with a large variety of clothing, and this app would help accumulate them all in one place.
WHAT'S THE BUSINESS MODEL?
This app would also be a free application as there would be no need to pay for something that’s redirecting you else where to spend your money, so realistically there’s no need for this to cost anything.
PROGRESS WITH IDEAS
As I developed these pieces of information to gain a better understanding of my idea and the thought process behind it, it was also the perfect way to accumulate feedback and decide which idea is the strongest.
After talking to our lecturer Chris, he thinks that the Font generator is probably the strongest idea as it has a lot to go off. Though in saying this changes will be made, as this application should be able to stand alone without needing to be connected to the likes of Spotify. The focus of this application should be to display fonts that are complimentary, and difficult to find with a variation in pricing and style.
The next thing I need to begin is, narrowing down my target demographic, looking into who my direct competitors could be and visualising the possible layout of this application.
0 notes
Text
The Machine Learning Revolution: How Artificial Intelligence Could Transform Your Business

By Alston Ghafourifar and Michael Evans
With a technology as impactful as machine learning (ML), it can be difficult to avoid hyperbole. Sure, billions of dollars in investment are pouring into ML projects. Yes, machine learning is a centerpiece of digital transformation strategies. And, to be certain, machine learning is often what people are talking about when they use the umbrella term “AI.” So it’s worth taking the time to look at real-world ML capabilities being developed and deployed at digitally nimble companies around the globe.
Artificial Intelligence defined
By definition, artificial intelligence is “(1) a branch of computer science dealing with the simulation of intelligent behavior in computers; (2) the capability of a machine to imitate intelligent human behavior.”
Essentially, AI capabilities allow a computer to analyze vast amounts of information and data to arrive at a “reasoned” conclusion about the subject at hand, simulating the human decision process, often with better decisions being made.
While it is easy to define, the challenge has been the application of AI to everyday life. One successful application has been in the area of content matching and recommendations for streaming media, radically transforming the on-demand viewer experience. Rather than attempting to scale the “expert” human work necessary to classify, curate, and catalog content into consumable collections, machine learning has become a core staple in personalized content delivery. By analyzing user behavior, preferences, and more, streaming services can more accurately tailor recommendations and push targeted content with greater opportunity for monetization and engagement.
Virtually every other industry is or should consider incorporating AI into their business models. You do not need to be a large company to take advantage of AI in order to provide better service to your customers—both at a lower cost and with better results. AI can help small and mid-sized businesses anticipate and fill customers product needs faster, improve inventory systems by incorporating Just in Time processes, reduce shipping and stocking errors, and facilitate the payment and collection process.
Eight business domains where AI is profoundly changing the landscape
Pharmaceuticals & Life Sciences
Wherever you fall on the death disruption debate, we can all agree that aging is a challenging experience. Even if you don’t aspire to immortality, you likely recognize that increased joint pain and susceptibility to illness and injury will erode anyone’s quality of life. But deep learning (a subfield of ML) may be able to slow the aging process. Scientists are now using the technology to identify biomarkers associated with aging. Soon enough, a simple blood test could tell you which parts of your body are showing signs of wear and tear, and your doctor could help you mitigate, and perhaps reverse, those effects through lifestyle recommendations and medication.
Food
Up to 40% of a grocer’s revenue comes from sales of fresh produce. So, to say that maintaining product quality is important is something of an understatement. But doing so is easier said than done. Grocers are at the whims of their supply chains and consumer fickleness. Keeping their shelves stocked and their products fresh can be a delicate balancing act.
But grocers are discovering that machine learning is the secret to smarter fresh-food replenishment. They can train ML programs on historical datasets and input data about promotions and store hours as well, then use the analyses to gauge how much of each product to order and display. ML systems can also collect information about weather forecasts, public holidays, order quantity parameters, and other contextual information. They then issue a recommended order every 24 hours so that the grocer always has the appropriate products in the appropriate amounts in stock.
Other Articles From AllBusiness.com:
Businesses that implement machine learning in their replenishment workflows reduce their out-of-stock rates by up to 80%, along with up to 9% in gross-margin increases.
Media & Entertainment
Machine learning allows media companies to make their content more accessible to consumers through automatic captioning systems. Since implementing an automatic captioning program, YouTube has enabled 1 million functionally deaf Americans and 8 million hearing-impaired Americans to watch and enjoy its videos. As of 2017, its ML programs have become sophisticated enough to include captions for common non-speech audio, such as laughter and music, creating an even more complete experience for viewers.
Information Technology
Although machine learning is generating unprecedented business insights, many organizations have failed to invest adequately in AI systems. For instance, McKinsey found that “the EU public sector and health care have captured less than 30% of the potential value” of big data and analytics. Organizations that want to avoid a similar mistake will need to ramp up their data science abilities—but so will workers who want to stay competitive in the job market. By 2020, there will be more than 2.7 million data science jobs, and the demand for workers who understand and can work with ML technology will only grow from there.
Law
Deep learning applications are especially impressive in the legal sector due to the nature of the language these programs must parse. Legal phrasing can be complex and difficult to decipher, yet deep learning systems are already capable of analyzing tens of thousands of vital documents. When legal teams needed to dissect contract clauses that upset their or their client’s business and invoicing processes, they once had to manually review stacks of rigorously prepared documents. Now, they can feed them into a program that works far faster than any lawyer and that can pick out important phrases for further analysis by the legal team.
Insurance
Improving risk prediction and underwriting is in everyone’s best interest, which is why machine learning is such a gift to the insurance industry. In auto insurance, for instance, ML algorithms can use customer profiles and real-time driving data to estimate their risk levels. They can then formulate personalized rates based on that information, potentially creating savings for both consumers and insurance companies.
This process may be enhanced by even more in-depth analyses, in which ML programs pull in seemingly unrelated social media data to create a more precise profile. The insurance industry could use artificial intelligence to identify which policyholders are gainfully employed and which seem to be in good health. Theoretically, someone who is responsible in those areas of their lives will be a responsible driver as well.
Education
Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS) hold enormous potential for disrupting the classroom and helping students learn. These AI programs serve as virtual tutors, and they adapt their digital lessons based on each child’s strengths and weaknesses. Each time the student completes a task or quiz, a ML program processes that information to customize future materials.
By “learning” a user’s unique needs and identifying which types of lessons are most effective for them, the ITS helps the student overcome learning challenges and retain more knowledge. Research indicates that students who use intelligent tutoring systems perform better on tests than their peers who learn via large group instruction.
Health care
Compared to other developed countries, the United States spends more on health care per person than any other country without significantly better health outcomes. For instance, the U.K. spends less per person ($3,749 USD) annually on health care than does the United States ($9,237 USD). Despite its high spending, however, the United States does not have the best health outcomes—life expectancy, for example, is 79.1 years in the U.S. but 80.9 years in the U.K. The further development and application of AI in reducing the number of tests and helping to decide the appropriate treatment promises to reduce health care costs in the U.S. with potentially more accurate and lifesaving outcomes. Due to the high costs associated with health care and the significant benefits offered by better health care decisions, we are likely to see exponential growth in the application of AI to health care in the years to come.
Modern artificial intelligence is finally delivering on its promise to help consumers and businesses make better decisions and improve their quality of life. Small and middle market companies embracing AI today will have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Alston Ghafourifar is
CEO & Co-Founder of Entefy, Inc.
Michael Evans is the Managing Director of the Newport Board Group.
This content was originally published here.
0 notes
Text
Week 5 Lectures
Morning Lecture
Wired Equivalent Privacy
With WiFi, unlike a wired connection, it is easy for other people to access packets that are being sent through the air. This means that you would want to encrypt your data before sending it.
WEP is very basic encryption with many vulnerabilities. What was interesting is that even though vulnerabilities were found, people kept using it for a while because they didn’t have many alternatives.
Data sent in a WEP frame is broadcast, and only those with the correct MAC address will read it. But this doesn’t stop other people from taking these packets, modifying them and resending them.
Encryption is done using RC4 (which uses a random number generator), and XOR. The data is encrypted, but the order and structure is still the same. So given a packet, it is known which bits correspond to the IP packet’s destination IP address.
An attacker can take a packet sent by someone else, modify the packet’s destination IP address, and send it back to the access point. Instead of the attacker doing work, the access point will decrypt it and send it back to the attacker! Note that the attacker’s IP and the victim’s IP addresses are the same for the first 3/4 of bits, so there aren’t many different combinations to try.
This is an example of mixing data and control - changing the addresses within the IP packet (which is inside the WEP frame) also changes the control.
Phreaking (phone hacking)
Phones back in the day sent tones of different frequencies for control e.g. the frequency 2600Hz was used to give a free phone call.
There was a Captain Crunch promotion where they gave out whistles with frequency 2600Hz - the same frequency as the tone for free phone calls. So people bought the cereal and abused this to get free calls.
The main problem was that tones used for control were sent along the data line.
Guest Lecture - Doctor
There is a lot of bias going on even in the medical world, with patients, pharmaceutical companies, and with doctors.
Observation bias is when seeing what other people are doing influences our decisions. For example, there is a hormone tablet for breast cancer offered after a surgery which has a chance of preventing the cancer coming back, however it has some side effects. A doctor who just saw a patient who decided to take the tablet may become biased towards supporting the decision to use the tablet for the next patient.
There is also the idea of “quid pro quo”, something mentioned in the Social Engineering lecture. Sometimes pharmaceutical representatives take doctors/nurses out for a free lunch and tell them about a new drug. Because of this favour they have done, these doctors/nurses are more likely to recommend the company’s drugs.
What’s scary is that sometimes you think you are not being biased, but in reality you are subconsciously leaning towards one side or another. Next time I make a judgement on something, I’ll try to check if I am truly being fair, or if I’m just following my instincts.
A majority of problems occuring is from human error, be it negligence or poor judgement. Take for example hygiene. It is difficult to get doctors to wash their hands regularly or follow proper hygienic procedures, because they either forget or think its too much of a hassle.
A study showed that adding checklists in surgery halved the infection rate. Checklists have really simple things on them, and are cheap to create, but its usually the simple steps that aren’t followed which lead to poor hygiene. So instead of investing in high end equipment to reduce bacteria levels slightly, in this instance, it was more effective to bring about a culture change on the simple things.
Evening Lecture
Extended seminar - OPSEC (Operations security)
Protect information that could be used by the enemy against you
Identification of critical info
Analysis of threats
Analysis of vulnerabilities
Assessment of risk
Application of appropriate OPSEC measures
Random pieces of info aren’t useful, but together they can do damage.
Origin - Vietnam war
Snowden - “What would be the impact if my adversary were aware of my activities?”
If your threat model is too high - don’t do it.
How to OPSEC?
If you don’t need to share information, don’t.
If you do something you don’t want people to know about, ensure it can’t be traced back to you
Avoid bringing attention to youself
This is hard to pull off, so tradeoffs must be made e.g. where do you want to be secure, or and where do you want to be visible. It’s hard figure out how much you want to hide.
Avoid sharing information - only share if it’s needed, beware of social media, metadata, indicators - expensive clothes
Keep identity secret - Tor browser to remain anonymous,
You can use a false identity - hard to maintain
Be forgettable - blend in with everyone else so that you don’t draw attention to yourself
“There are no case studies of good OPSEC - you never hear about them.”
Case studies
WW2 - American congressman bragged that American subs survived because Jap depth charges weren’t deep enough. This cost the US lives, as Japanese set them deeper.
MI6 agent exposed because of wife who left Facebook on public.
Harvard bomb threat
Bomb threat listed his exam hall
Guerilla mail adds originating header - found out it was Tor
Tor was used on campus wifi - don’t be logged in if you want to be anonymous
Silk road - Ross Ulbricht
Asked for help with set up on his real email
Used same alias on multiple sites
Tor and VPN used in wrong order - negligence
Richard’s comments
Someone with good OPSEC used different computers and toolkits for different personas.
Even first contact is dangerous - you can roll back in time to when people were young and connected their accounts etc.
Extended seminar - Passwords
Most passwords used are weak. It’s hard to remember and to type a complex password, so people tend not to use them.
Passwords often use personal information such as name and birthday. So hackers can try cracking passwords using this information.
Good passwords are long without english grammar patterns.
Passwords are broken
Passwords are weak - full of meaning (47% based on name), often reused over multiple sites.
Personal Information Attack
Fake Facebook profile (Sally) - can see partner’s name, birthday, education, hobbies, pet’s name
cup.py - many combinations of passwords based on personal information, common replacements (a -> 4)
Password Crackers
John the Ripper on Kali Linux
Hashcat - for hashes
Why are passwords bad?
hard to remember and type good passwords
complicated rules for generation (letters, numbers, symbols)
regular renewal
little incentive to create unique passwords
low probability, high impact risk
Password Storage: bad practice
Some are still stored in plain text - mostly small to medium sized companies
Facebook had stored plaintext passwords in an internal database
Bad hashing (md5, sha1) - Rainbow tables are designed to match with passwords
Demo - using Linkedin passwords file
In 2012 - Linkedin was hacked, and passwords leaked.
Saeed had a file with the list of userid:hashedpassword.
Used Google - sha1 to reverse the hashed password
Looking through the first 1000 lines, 4 people had the same password
10000 lines - 26 people
Passwords frequency in descending order: password, 123456, LinkedIn
If you have a bad hash, anyone with google can hack passwords
John the Ripper - automatically cracks the passwords based on the hashes
Salt - add random string to end of the password, you get 2 different hashes. This way, there isn’t a problem if many people had a password. LinkedIn did not have a salt.
Best practices for storing passwords
Use a strong encryption method like a hashing function such as sCrypt or BCrypt
Store the salted hash, not the password
Salts should be long (at least 256 bits)
Don’t store password hints
Another solution - let a bigger company handle it. Log in with Google or Facebook, however this is
Maybe we can get rid of passwords altogether - but not yet.
Password Generation
Better ways to come up with memorable passwords
correcthorsebatterystaple
length of word creates enough entropy
avoids english grammar patterns
don’t use common words
passphrases
long and with wacky lexicon but good syntax to make it hard for AI to generate
memorable
initialisation of a phrase
take first letter of each word, removes English letter frequency
New policy - NIST 2016
don’t force regular password changes
don’t enforce composition rules
don’t provide password hints
allow user to opt for passwords to be viewed while typing
limit number of failed login attempts
Richard: just keep a list of bad passwords, don’t use any.
Long passwords are better than just adding symbols and numbers.
Richard: we think our passwords are good, but we overestimate it. Humans are bad at generating passwords - we follow patterns.
Buckland’s Lecture
Merkle Damgard construction
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merkle%E2%80%93Damg%C3%A5rd_construction
SHA2 - different types depending on size (SHA-256 means SHA2 with 256 bits)
We have a long message, but we need a small hash, so we break the message into blocks.

This is a method of building collision resistant cryptographic hash functions from collision resistant one way compression functions.
It is used in hash algorithms such as MD5, SHA1 and SHA2.
The message is split up into blocks.
The algorithm starts with an initial value, the initialisation vector (IV).
The result so far (initially just the IV) is combined with the next message blockis, then the compression function f is applied.
Step 3 is repeated until all blocks have been added.
The last result may be passed through a finalisation function.
Bank messaging problem
We want integrity and authentication. MACs give us both.
We can add the secret key before the message, and then hash it.
MAC: h(key|data)
The problem with this is that an intercepted message with known hash and message length can be extended. This is a length extension attack.
Take the hash, append a new message to it and pass it into f, the compression function. In this way, you can modify the message, even without knowing the secret key.
HMAC (hash-based message authentication code) puts the password after the message, instead of the beginning. h( key | h(key|m) )
Digital Signature
DSA - Digital Signature Algorithm
A digital signature is used to verify authenticity of digital messages or documents. A valid digital signature gives the recipient strong reason to believe the message was truly from the sender (authentication) and that the message was not altered in transit (integrity).
Signing larger files directly takes a long time. To sign large files, hash the file and then sign the encrypted hash.
Collisions with digital signatures
A collision attack requires half the number of bits in the hash size.
Example: Alice has a pdf saying “I will give Bob $100″, then Alice signs it, and sends it along with the signature to Bob. If an attacker can create another document with the same hash as Alice’s document, then the attacker can use the same signature with this new document, so it looks like Alice has signed the new document.
The attacker can change 1 bit in each document that doesn’t change anything visible (e.g. whitespace) and then keep hashing them until you find 2 identical hashes. Ask Alice to sign the first document, and you can reuse the signature for the second one.
Passwords
Password attack types:
online - typing the password on a website manually
website can detect
offline - obtaining the file containing hashes of passwords and decrypting locally
/etc/shadow
password file used to be protected by md5
Salt is random data added to the password before hashing. Salts help to prevent collisions in the case that users have the same password. Salts also protect against the use of rainbow tables, because the password will need to be hashed with the random salt to be in the table.
0 notes
Text
Week 5 Notes and Reflection
REFLECTION
Interesting lecture. Richard really likes to talk about WEP!! Perhaps its in the exam?
I find the idea of hashing really interesting. I was always wondering what a digital signature was and how it works when you sign something in Adobe Acrobat - and why you can’t change the document after you sign it! Now I understand why, so that’s pretty cool!
Don’t fully understand why MD5 is bad for password storage - does it matter if someone figures out a collision for a password attack?
NOTES
Motto: “Don’t roll your own”
Last weeks motto: “Every contact leaves a trace”
Binary Search - Apparently someone published an implementation of binary search and they guy was certain it was right, but years later discovered an integer overflow bug. If binary search is so hard to implement, gg security. Don’t try to reinvent the wheel. A lot of time has gone into developing things,you probably can’t do it better than history.
Phone Phreaking - Playing around the tones in the telephone line, reversing engineering. Get free phone call.
CRYPTOGRAPHIC PROTOCOLS
WEP Wireless Security
With WiFi, someone who is a KM away could tap into your network. This is unlike Ethernet network, where the attacker needs physical access. WEP had so many vulnerabilities it was really funny. Once people discovered it was flawed, people still kept using it!!!
How it works - We are streaming the bits serially between the devices. The bits are broadcast everywhere. Laptops need to know which bits are there bits. Communication is done through frames, with the MAC address appended to the beginning. We need to encrypt this.
Both sender and receive have a random number generator. The number is XOR with the data. The property of XOR is associative - can be done in any order. XOR also gives nice psuedo-randomness. The encrypted data is sent to the receiver, he XOR it, then he gets the plain bit string back.
The hack was done using TCP/IP packets. TCP/IP has header etc. The IP packet wrapped around the TCP packet has the source/destination IP address. Hence we know which part of the encrypted string is the header etc. What is interesting is that there is nothing stopping you intercepting the packet and sending your own packet - the machines are responsible for checking this.
How to hack - I take the packet, retransmit by sending the packet to the router but with the destination address to my computer. Then the router will decrypt it, and send it to you!!
The problem is that the data and control are mixed together. Mixing data and control might enable hackers to control the system.
Hack a phone - phones send tones around the PSTN to control things. You can just do a replay attack. E.g. get free phone call.
Hashing
Hashing is good for integrity.
History of hashing - MD5 is “broken” - someone has worked out a way to get an undesirable property from the protocol faster than brute force. E.g. for MD5 if it is 56 bits, to find a preimage it should take 55 bits of security on average. For MD5, and many other protocols, find a small break in the protocol, and over the time like a volcano it goes bang bang bang and breaks. As each year went by, it turns out the time to break it become smaller and smaller.
SHA-0 - NSA came up with a better hashing algorithm. However it was bad so they came up with SHA-1. Just recently SHA-3 has been recently approved.
Data breaches - Few data breaches last year where hackers got the password file with the hashes. A ridiculous number were in MD5!
In early 2000s there was a bit of theory about hacking SHA-1. Recently found a collision.
Broken hash - A way of getting info out of the hash without pure brute-forcing. If a hash can be broken in time less than the brute-forcing time, then it is considered broken.
Merkle-Damgard Construction
MAC - Gives us Authentication and Integrity. MAC is basically a hash of the key and the data. h(key|data). E.g. append shared secret “sausageP” to your strings then hash.
Length extension attack - Take the existing message, with the hash. Add stuff the end of the message, continue the hashing process for the next block, since hashing is done on a block by block basis like a state machine. The solution is to add the password to the end, but still breakable.
Digital Signatures - Need a signature on a document to ensure the document is not tampered with.
Take the original document, encrypt with your private key.
If people can decrypt the doc with your public key, must have been from you!
However instead of encrypting the document itself, we encrypt the hash of the original document, it is shorter.
Collision Attacks with Signed Documents - If we can figure out two documents with the same hash, then on the fake document we can use your original signature and forge the fake document.
Make fake document and original document.
Keep trying to modify the original document until its hash matches the fake document. E.g. add whitespaces
Give the original document to the person and they sign it.
By doing this, they are also accidentally signing the fake document at the same time!!
Data Breaches - Ashley Madison data breach, LinkedIN MD5 Breach
Salted Hashed Passwords
A table makes it easy to crack passwords, as commonly used passwords would hash to the same password. So if a common password is sausage and 1000 people used it, by cracking sausage once you crack all the 1000 passwords.
If we add a salt (a phrase) to each password, and each person has a different salt, then even if two people use the same password, the combination of “sausage” + salt1 and “sausage” + salt2 would result in different hash value for each. We can store the salt in plaintext in the password file.
So in this case if they want to crack some passwords they have to go through each person, and append the salt and then attempt their brute force or dictionary attack.
Doesn’t stop the use of rainbow table, but increases the complexity. Rainbow tables make unsalted MD5 or SHA0 passwords easy to break.
Key Stretching Hashes
Services like Bcrypt are slow algorithms. Although you might have a 1 second slowdown for the user, the amount of time for a hacker to try to crack lots of passwords increases.
Online & Offline attack - Online attack is trying to login to the website, offline attack is when you have the hashed passwords and can easily try crack them offline.
NIST Password Guidelines - read them!
Moore's Law. (n.) Moore's Law is the observation made in 1965 by Gordon Moore, co-founder of Intel, that the number of transistors per square inch on integrated circuits had doubled every year since the integrated circuit was invented. Moore predicted that this trend would continue for the foreseeable future.
An initialization vector (IV) is an arbitrary number that can be used along with a secret key for data encryption. This number, also called a nonce, is employed only one time in any session.
Attacks on MD5
A. Sotirov M. Stevens J. Appelbaum Arjen K. Lenstra
Flame malware in 2012
AbstractPresented at the 25th Chaos Communication Congress in Berlin on December 30, 2008. We have identified a vulnerability in the Internet Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) used to issue digital certificates for secure websites. As a proof of concept we executed a practical attack scenario and successfully created a rogue Certification Authority (CA) certificate trusted by all common web browsers. This certificate allows us to impersonate any website on the Internet, including banking and e-commerce sites secured using the HTTPS protocol. Our attack takes advantage of a weakness in the MD5 cryptographic hash function that allows the construction of different messages with the same MD5 hash. This is known as an MD5 "collision". Previous work on MD5 collisions between 2004 and 2007 showed that the use of this hash function in digital signatures can lead to theoretical attack scenarios. Our current work proves that at least one attack scenario can be exploited in practice, thus exposing the security infrastructure of the web to realistic threats. This successful proof of concept shows that the certificate validation performed by browsers can be subverted and malicious attackers might be able to monitor or tamper with data sent to secure websites. Banking and e-commerce sites are particularly at risk because of the high value of the information secured with HTTPS on those sites. With a rogue CA certificate, attackers would be able to execute practically undetectable phishing attacks against such sites. The infrastructure of Certification Authorities is meant to prevent exactly this type of attack. Our work shows that known weaknesses in the MD5 hash function can be exploited in realistic attack, due to the fact that even after years of warnings about the lack of security of MD5, some root CAs are still using this broken hash function.
The program is being used for targeted cyber espionage in Middle Eastern countries.
Flame was signed with a fraudulent certificate purportedly from the Microsoft Enforced Licensing Intermediate PCA certificate authority.[15] The malware authors identified a Microsoft Terminal Server Licensing Service certificate that inadvertently was enabled for code signing and that still used the weak MD5 hashing algorithm, then produced a counterfeit copy of the certificate that they used to sign some components of the malware to make them appear to have originated from Microsoft. - wikipedia
OPERATIONAL SECURITY EXTENDED LECTURE
Military definition: How they protect info that could be used by the enemy against them, in order to create a safe environment.
Origins - US military tradition of communicating in plain language, field commanders ignored encryption instructions or used bad encryptions.
When to OPSEC - 24/7.
Snowden on Opsec - If the impact of your threat model is too high, consider alternatives. Because sometimes you can’t always keep something secret, but you can plan your response.
The extends to which you you go protect your information and the tools you use will be different depending on the situation.
There’s a counter to every attack, so instead of taking every possible measure to mitigate risk, just think about simple.
How to OPSEC? - If you don’t need to share info, don’t. If you do something you don’t want people to know about, ensure it can’t be traced back to you. Avoid bringing attention to yourself. Very hard to pull off, and tradeoffs must be made.
Avoid sharing info - Only share info on a need-to-know basis. Beware social media, metadata. Minimise indicators - expensive clothes, carrying tools. No info is still information! Hard to strike the right balance.
Keep your identity secret - Remain anonymous or set up a false identity to hide your tracks e.g. VPN. False identities are difficult to create and maintain, but are often useful. Never contaminate, leaking info from one identity to another.
Be forgettable - Blend in with everyone else. If you stand out, you will be remembered and monitored.
Case Studies
Promotion - Wife left facebook post of MI6 chief-to-be public.
Harvard Bomb threat - Bomb hoax, but person failed as he was traceable - IP header, campus wifi.
Good OPSEC - Good OPSEC by NSA. Assange and Snowden.
PASSWORDS EXTENDED LECTURE
Passwords are WEAK
Some statistics:
Full of meaning - 47% of passwords based on a name, 42% based on significant dates or numbers, such as birthdays, 26% based on pets.
Personal Info Attack - Sally Smith Facebook. Kali Linux, make a password dictionary, Hashcat, rainbow tables.
Why are passwords bad? - Hard to remember good passwords, hard to type good passwords, complicated rules for generation, regular password renewal creates user generated patterns, little incentive to create unique passwords (low probability, high impact)
How to not store passwords - Hash them, not plain text!
Bad hashing - Rainbow tables are designed to match with passwords. project-rainbowcrack.com/table.htm Encoding the same string using the MD5 algorithm will always result in the same 128-bbit hash output.
This also applies to SHA128, etc.
Add Salt to Passwords - so hash for same password not always the same
Best Practices - use sCrypt/bCrypt, use salted hash, salts should be long, keep on updating and improving, don’t store password hints.
Password Generation - 4 unrelated words concatenate together creates enough entropy so it is difficult to hack. Long and wacky lexicon but good syntax to make it hard for an Ai to generate.
New policy - Allow long passwords, use multi-factor, don’t force regular password changes, limit failed the number of login attempts.
0 notes
Link
What is SEO - Website Optimization
SEO - (from the English search engine optimization) means optimization of websites for search engines. SEO is an activity undertaken in order to achieve the highest position in the organic search results for specific keywords by a given website. Optimization consists in searching for the most effective set of solutions regarding the content, page code, incoming links, and other factors influencing ranking in the search engine in terms of the position of a given website. SEO increases the chance of success in our campaign in organic results.
What is SEO?
Somehow, it is commonly accepted that the terms SEO and positioning mean the same thing. Perhaps identifying these two concepts is due to an incorrect translation of the term SEO from the angelic language, but it is worth emphasizing that SEO and positioning are not equivalent concepts. Both refer to search results and website position in search engines, however, they cover different activities. Read the article and find out what exactly are the differences!
Content optimization, which aims to eliminate phenomena such as thin (low-quality) content or duplicate content on websites, includes, for example:
posting unique content corresponding to the subject of the page and saturated with keywords,
expanding existing content or updating it in terms of semantic keywords,
highlighting the content by using subheadings consistent with the hierarchy of headings, bullets, bolds, underlines or italics,
building the website menu, website content, and other elements to support the process of internal linking on the website.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Optimizing the code and website structure includes:
preparing the website to meet the W3C standards, defining the guidelines for creating pages so that they are displayed correctly to users and available on various devices,
improving the website loading speed by reducing the code size, the number of files loaded and image optimization,
enabling search engines to find your site easier by using, among others, an appropriate hierarchy of headings (H1, H2, H3 ...), meta tags (title, description), and friendly URLs.
In optimizing the backlink profile, we will focus mainly on:
quality parameters of our website and incoming links (we can use the indicators proposed by Ahrefs or Majestic),
number of links and domains they come from,
link anchors used - the number and proportions between links with keyword anchors and other types of anchors,
proportions between dofollow and nofollow links,
location of links and URLs to which links lead on our website.
Website optimization is carried out in several different areas. First, changes are made to the content of the website that is visible to Internet users. They rely on the appropriate placement of keywords so that the website is displayed to the users of interest in the search results. This may involve, for example, a change in the structure or length of the content. Second, the optimization activities involve making changes to the website code. These do not have a direct impact on the appearance of the website, but they improve its technical parameters and usability, thus improving its operation. The last component is the optimization of the backlink profile, i.e. all links leading to our website from external sources. It is usually made based on the analysis of competitors' activities.
Positioning the website is, in turn, a process that consists of all activities (including the aforementioned optimization) that enable a given website to achieve the best (i.e. the highest and stable) position in search engines after entering a specific phrase. It is heavily dependent on optimization, thanks to which it is possible to adjust the content, links, and other elements of the website so that it is as visible as possible to search engine robots.
Local SEO
Even the most thoroughly carried out optimization of the website will not bring the desired results if we do not adopt an appropriate strategy, which will differ depending on the profile of the business. In the case of small businesses that offer their services in an area limited to a given city or region (hairdressers, car mechanics, plumbers ...), local SEO is the best solution. Taking into account the fact that the ranking of search results is based more and more often on the geolocation function, it is the optimization in accordance with the principles of Local SEO (with English) that will allow the greatest use of the potential of local phrases, such as, for example, " plumber Wrocław". Both when the user enters them into the search engine exactly in this form, and when Google, after entering the keyword " plumber ", automatically indicates its location as " Wrocław " and displays matching results - local.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
SEO is part of SEO
It is worth emphasizing once again that website positioning includes a number of activities that aim to raise the website in search engine rankings. These include the previously mentioned SEO activities, link building, content marketing, and web analytics.
Link building, or linking, similar to SEO, is a long process, not a single action. The purpose of linking is to encourage users to share and cite a given website on other pages, services, and portals. The idea of linking is also to attract such recipients who will be interested in the subject of the website. Engaged Internet users are the most valuable because they do not need additional incentives to recommend a given website in their network of contacts. That is why the next element of positioning is extremely important - content marketing which is content marketing. It consists in creating valuable and engaging content and its effective promotion, among others in order to attract new customers. The advertising content in content marketing can be text, image, infographic or video. In order for positioning to be effective, it is necessary to regularly measure the achieved results and introduce changes on this basis, which in turn is done by web analytics.
SEO and positioning - dependencies
"SEO is all about positioning. Positioning is a broader concept, and SEO is one of the tools with which you achieve positioning goals."
SEO deals with the improvement of the website - the layout of the content on the page, building the code - and its environment, i.e. incoming links, while positioning - apart from the aforementioned SEO - also includes a number of other activities.
Perhaps treating SEO and positioning as synonymous terms is due to the same goal that guides both SEO and positioning activities. In both cases, it is about achieving a high and stable position in the search results displayed by the search engine.
SEO audit - do I need it?
However, unethical practices do not always have to be deliberate. If you run your business online or are responsible for internet marketing in your company, you need to optimize your website properly and avoid the risks we describe. To find out if the activities you have been conducting so far are effective and whether you are unknowingly making serious mistakes, perform a step-by-step SEO audit. This way, you will learn about the strengths and weaknesses of your site, learn how users use your site, and learn which efforts are worth continuing and what needs to be improved.
Let's be careful with SEO
The action plan for improving your website's ranking on Google should be well thought out. Optimization in the context of website positioning is often mentioned. However, it should be remembered that all SEO activities should lead to a better perception of our website by both users and search engines.
Optimizing the website is an undesirable effect, and the so-called stuffing keywords everywhere you can is not good practice. The content, meta tags, headings, etc. should be created in a logical and coherent way, maintaining grammatical correctness. Such an approach will allow for good reception of our website by users for whom the website is primarily to be readable and encouraging to stay longer. Only then should you think about Google robots. A way to avoid over-optimizing the website may be, among others entrusting the preparation of texts to professional copywriters, as well as cooperation with a professional online marketing agency that will take care of the work on SEO so that the result is effective positioning of our website.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Technical SEO follows the guidelines
As we have repeatedly said on our blog, positioning is a process, which is why activities within its framework are carried out comprehensively, and the effects may be visible only after a long time. So the lack of immediate results is nothing to worry about.
There is also a lot of talk about adjusting the website to the requirements of the search engine, so remember to use techniques that comply with the current Google algorithms. What's more, by following the latest news, you can also hear about - smaller or larger - changes or updates to algorithms, aimed at improving the display of the ranking, which always affect the activities performed as part of SEO. With these factors in mind, optimization can of course be done at any time.
However, we will achieve the best results when we optimize the website during its creation. Well-implemented SEO activities in this way will allow you to achieve specific benefits faster, including increasing traffic on the website, which may translate into a greater recognition of the website among potential customers, and consequently also into increasing the company's income. Algorithms also supervise the correctness of other activities included in the positioning of pages, including link structures, and their updates lead to lowering the position in the rankings of websites using the previously described unethical practices.
Unethical SEO Practices
Articles on unethical ways to promote your website appear regularly on the Internet. So what is it like - some internet marketing specialists use unethical SEO or positioning? Once we know that SEO is part of positioning activities and we distinguish between the two concepts, we can conclude that unethical practices apply to both SEO-related activities and activities that are part of the positioning, but not SEO. Thus, unethical practices can apply to both SEO activities and positioning. What could be among them? For example, an unnatural and excessive accumulation of keywords, buying links only to improve the page's search engine results or copying someone else's content.
EACTIVE as an SEO Agency
If you want to be sure that your website is optimized not only on a regular basis, but above all with due diligence, use the help of an experienced SEO agency. By working with EACTIVE, you can be sure that SEO optimization is carried out only using methods consistent with the guidelines of search engines. Thanks to this, our activities have for years resulted in increasing the visibility, traffic, and conversion of our clients' websites on the web.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
0 notes
Text
Artificial Intelligence Will Change How You Do Marketing in 2021
How often do you reflect on the ways technology changes your life as a marketer?
I’m not talking full-on paradigm shifts here. (“We do our marketing… on the internet.”) I mean the sly, step-by-way manner in which new tech slides neatly into your existing stack and subtly reframes the game on you.
These changes don’t always alter your job in dramatic ways, but they eliminate the hassles and headaches. They may speed up your time to results, automate painful routines, and enable you to focus on what matters most. (Remember what collaborating on a document looked like ten years ago? Remember printed memos?)
Very rarely, these technologies also let you do things you’d never considered possible.
No incoming martech makes a better case for this sort of incremental innovation than artificial intelligence. While new AI products are surely on the horizon—self-driving cars are coming any day now, possibly, maybe—AI’s most dramatic effect on your job today lies in adding new features across the tools that you’re already using.
When you’re living it, of course, this type of change can be hard to notice. It’s like suddenly realizing you desperately need a haircut after three months in lockdown.
But, one day soon, you’ll marvel at all the things AI sneakily helped pull off your plate. Because when marketing meets AI, magic happens. It can feel inevitable—but that doesn’t mean you don’t need to pay attention.
At Unbounce, we not only believe that applied AI is the future of marketing, we also think marketers tuned in to what’s happening now stand to benefit in a big way in 2020 and beyond.
To put it another way, marketing and AI is a love story for the ages.
Marketing and AI: A “Meet Cute”
For marketers interested in learning what AI can do for them, right now, debates and philosophy about artificial intelligence can be heady stuff. And, honestly, it’s kind of a distraction. So, instead of getting into the weeds, let’s start with the distinction that makes the most sense for marketers to learn: the one between AGI and ANI.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Strong AI or Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is what most people think of when someone says AI.
This technology replicates neural networks (not necessarily human ones) to perform highly sophisticated cognitive tasks. AI researchers typically take this one step further, though. According to them, AGI “controls itself autonomously, with its own thoughts, worries, feelings, strengths, weaknesses, and predispositions.”
Teams across the world are working on AGI, but the closest to a consensus from researchers is that we might see it sometime within our lifetime. And some skeptics doubt we’ll ever see AGI, let alone more advanced forms.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
So handing over your marketing campaigns—or, gulp, your job—to an AI is decades or centuries away. But weak AI or Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), sometimes also called “applied” or “pragmatic” AI, is available to marketers today. Right now.
As the name suggests, ANI focuses on narrow problem-solving applications. In the world of marketing, this means taking on specific, repetitive tasks to deliver additional business value. It may learn and make decisions independent of your input, but mostly this AI tackles the work you’d rather not.
But here’s the thing: ANI might not challenge our fundamental conceptions in the same way AGI does, but it’s having a transformative impact on our lives (and jobs) nonetheless. It integrates so deeply into our everyday lives that we don’t have to think about it. Chances are good you’re already using ANI, whether you know it or not.
Don’t believe me? Let’s take a look at a few places you might be encountering ANI today, either as a consumer or as part of your job. I admit that here that this list is not even close to comprehensive, but that’s my point: AI is slowly but surely filling all the cracks in our marketing stacks. (And, hey, that rhymes, so it must be true.)
Product Recommendation and Content Curation
Companies like Amazon and Netflix made fortunes by pointing people at more things they might want to buy. Much of these efforts are powered by sophisticated algorithms that let them match the right products and content with the right customer.
Amazon, for example, runs on a recommendation engine that’s been driving significant business value for more than 20 years. From the early days of user-based collaborative filtering (i.e., an algorithm making recommendations based on similarities between users) to more scalable solutions driven by a deep learning framework called DSSTNE.
DSSTNE is pronounced “destiny,” by the way—as in “buy this jewel-encrusted toilet brush… because it’s your destiny.” They’re not subtle.
Today, customer recommendations are a very small portion of Amazon’s total investment in AI.
Netflix doesn’t sell products, but they similarly credit the combination of contextually-aware recommendations and personalization (both powered by machine learning models) with saving them $1 billion a year.
How does this work? By reducing one-month churn by several percentage points. In the crucial 60 to 90 seconds that a customer will spend browsing before quitting the app in frustration, Netflix serves up content most likely to appeal to people with similar tastes. And it works: 80% of what people watch comes from a recommendation.
By presenting customers with content they’re more likely to watch first, Netflix reduces churn. Even thumbnails are selected by a neural network based on predicted clickthrough.
Say you’re not Amazon or Netflix, though. Say you’re part of a small team or a startup tight on resources. What can you do?
The good news is that today’s marketers can similarly take advantage of AI-powered recommendation engines on a more affordable scale.
Not only is some of this tech available to your developers, but more than one tool exists right now that lets you deliver product and content recommendations based on audiences, their intents, and their interests. Their availability will only increase in the months and years to come.
AI-Enhanced PPC Campaigns
Like Amazon and Netflix, Google will stick AI almost anywhere, even before its fully baked—from Gmail’s Smart Compose, which lets you email platitudes at lightning speed, to the AI-based noise-canceling feature recently added to Google Meet. Then there’s BERT and RankBrain’s role in search, and TensorFlow’s application to encryption, translation, robotics, and more… (The ellipsis is well-earned here.)
For digital marketers, one of the most significant use cases for machine learning has been in Google Ads. In a couple of years, Google’s Smart Bidding technology has gone from a curiosity that, at best, once ruffled a few feathers to something that has PPC experts rethinking how they’re spending their time.
According to Workshop Digital’s Andrew Miller, this sort of tech has overturned a lot of longstanding PPC best practices.
AI and machine learning are enabling PPC analysts to spend less time manually crunching data and more time on strategy development. Our jobs are not in danger yet, but machines are allowing us to rethink and recast our roles as AI-driven tools augment our capacities.
Andrew Miller, Co-Founder, Workshop Digital
Smart Bidding was once a neat trick that couldn’t hold a candle to an experienced human. Experts like Andrew tried it out, and many wrote it off. (Some still do.) But many PPC’ers point out that automated bidding is increasingly reducing the time spent on manual bid management.
Are agencies running for their lives because of AI-powered enhancements like Smart Bidding? Definitely not. But roles are changing as today’s PPC specialists spend more time on higher-level strategy and specialized growth tasks. For an industry that thrives on staying current, AI is a net positive.
Machine Learning and Conversion Rate Optimization
Roles are changing on the other end of the funnel too. When it comes to delivering more conversions from your landing pages, A/B testing is still very effective. But running tests also demands time, traffic, and expertise that marketers don’t always have. For small businesses especially, these minimum requirements put optimizing out of reach.
Enter artificial intelligence.
Around 2017, our R&D team realized machine learning has the potential to remove these hurdles from A/B testing—and free marketers to focus more on what humans do best. AI can even do things when testing that no human can do, making decisions on the fly about what version of a landing page is best for what type of visitor.
We kept thinking, ‘it isn’t the page that converts. It’s the visitor.’ So we started looking at how different visitors convert across different landing pages. The team built and tested machine learning models to see how far we could extend this concept. Sure enough, it turned out that we could drive higher conversion rates beyond what would ever be possible with a one-page-fits all system. We started prototyping immediately.
Yosem Reichert-Sweet, CTO, Unbounce
After three years of training a machine learning model, and investigating different ways to apply it, we arrived at Smart Traffic, a feature that fulfills this promise and makes AI-powered optimization available to Unbounce customers.
Smart Traffic uses a contextual bandit algorithm to learn about your visitors based on attributes like location, device, browser, and timezone. Once you’ve created and published a few variants of your landing page—the only thing it can’t do at this point, frankly—Smart Traffic delivers each visitor to the one most likely to convert.
There are two things that Smart Traffic shares with the best martech AI solutions today. First, our customers see results just by turning it on. (Nothing cuts through hype like actually getting stuff done.) And, second, it never stops learning, getting better at its task during the life of a campaign, and adapting to changes in traffic sources without human intervention.
Editor’s note. If you’d like to learn more about how Smart Traffic works, take a look at our announcement or read a few stories about marketers who’ve used it. Garrett’s also got you covered with some advice on how to build landing page variants that’ll take advantage of it.
AI-Augmented Chatbots
Chatbots are among the most common ways that your customers interact with AI. But even today’s strongest AI-powered chatbots are better at pulling relevant bits of data from specific contexts than they are detecting nuance. They’re humanlike, not human.
For business owners, however, this shouldn’t be a dealbreaker. Chatbots can be a lot more personable than asking your visitors to fill out a form, and interacting with them can foster engagement. They also let your customers self-serve, which saves everyone time.
I’ve always appreciated how Microsoft’s Purna Virji put it in an article for MarTech Today:
In one way, this is actually the future returning to the past. For years, internet users have sacrificed the personal touch for convenience. Now, we’re entering a world where we can have both. It’s the Personal Touch 2.0.
Purna Virji, Senior Manager, Global Engagement, Microsoft
Though fully custom chatbots are reserved for enterprise, small teams embrace the tech using solutions like Drift, MobileMonkey, Snatchbot, or even in Facebook Messenger. Juniper Research estimates that by 2023, retail chatbots will save the industry $11.5 billion in costs, and generate over $112 billion in revenue.
Mitsuku, a five-time winner of the Loebner Prize, tells me she’s “the world’s most humanlike conversational AI.” But she doesn’t get my simple idiomatic question—unless, y’ know, she’s wicked sarcastic.
So, you’re unlikely to mistake a chatbot for another person long enough for true love to set in. But we shouldn’t define chatbots by the quirks and failures of today since they’re a rapidly developing technology. There’s a lot of promise in chatbots enhanced by natural language processing (NLP) and sentiment analysis. One day soon, you might just meet the chatbot of your dreams. (I’m not judging.)
AI-Generated Content
When content creators read about AI-generated content, they begin to sweat. Buzzy articles with titles like “Ten Ways AI is Going to Replace Your Content Team and Leave Them Bankrupt and Unloved”… Well, let’s just say they don’t exactly alleviate our imposter syndrome.
Michelle Halsey is ultimately skeptical, though, about the prospect of being replaced by a machine. She writes,
Talented writers have no need to worry about automation stealing their gigs. At least, not as long as our clients are more interested in engaging their audience than they are sucking up to search engines.
Michelle Halsey, Content Blogger and Copywriter
Note the emphasis on talent here. It’s much more likely that AI will first tackle templated and repetitive work that hardly calls for persuasive writing anyway. These days, applied AI can also smooth out the rough edges in your podcast, remove some of the pain from meticulously editing videos, and gut-check your sentences for clarity.
Given the danger of AI-generated content flooding the net with misinformation and spun content, it’s also a use case we’re still grappling with. For now, AI appears to offer solutions to the very problems it creates, as developers teach tools like GROVER to generate “neural fake news” to detect it.
GROVER generated this article based on my own words. It’s not good, but it might be a sign of things to come.
AI-Driven Data Insights
Every growth-minded marketer loves data. It’s an addiction. We bring it into every meeting and include it in every strategy session. We spend hours staring at spreadsheets, analytics, and reports, even if there’s way too much data to digest.
But even when you’ve got a hotline straight to your data team, recognizing patterns and pulling opportunities from massive swathes of data is hard. Artificial narrow intelligence helps with that too.
Recently, Unbounce explored the role that copy plays in landing page conversions through deep learning research, including a modified version of Google’s BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers).
Our Conversion Benchmark Report crunched the data from 34 thousand landing pages. It delivers insights about how reading ease, word count, and emotional language relate to conversion rates across 16 industries.
Sample benchmarks for home improvement landing pages.
The amount of data here (every word on every landing page) already put this analysis outside of human capability. But using machine learning allowed the team to dig deeper:
With data analysis and machine learning, we can take an unbiased look at what goes into a great landing page, and find opportunities for every landing page to improve. Machine learning allows us to look at significantly more data than a human being ever could, and find real, data-driven patterns that lead to higher conversion rates.
Tommy Levi, Director of Data Products, Unbounce
One question readers ask us about the report is why we included some niches (“pest control”) and not others (“model train enthusiasts”). The answer: the machine learning model generated these subcategories, on its own, from our aggregate data. Instead of imposing our arbitrary human bias, ML started with the data and sorted it from there.
Call me a nerd if you want, but that’s kinda mind-blowing. A lot of what’s happening in the Conversion Benchmark Report wouldn’t have been possible without pairing human intuition with the power of machines.
Want to see what our machine learning analysis revealed about your industry? Explore benchmarks and data-driven insights for 16 industries in Unbounce’s 2020 Conversion Benchmark Report.
AI Ain’t Perfect (and That’s Okay)
If you’ve ever tripped over a Roomba or struggled to get Siri to do, well, anything sensible, you know artificial intelligence has a long way to go. (If you’re feeling masochistic, try asking Siri how to contact Unbounce. I dare ya.)
But does that mean it’s just hype? Not. A. Chance.
By any measure, we’re still in the early days of the long romance between AI and marketing. We’ve yet to see its full potential. The transformations that marketing is undergoing now aren’t always so easy to recognize or understand. As we’ve seen, applied artificial intelligence already penetrates our jobs, our strategies, and our campaigns on almost every level.
You could just go with the flow, of course. Keep doin’ what you’re doing. Wait for AI to come to you and your stack. You’d be missing a trick, though.
Because by actively thinking about ways in which AI can enhance your marketing practice today, you’ve got the opportunity to get ahead of this thing. And by actively adopting it, you can start taking advantage of the freedom and new capabilities it delivers—before the competition gets there, as they inevitably will.
Why Unbounce Invested in AI for Your Landing Pages
Unbounce recently announced that we raised $52M (CDN) in funding to bring accessible AI-powered optimization to our customers. We’re investing now because we’re convinced using artificial intelligence to augment your marketing isn’t just aspirational, even for small businesses. It’s the future. This transformation is coming—really, it’s already here—and our customers will be a part of it.
The coming together of AI and marketing is tremendously valuable for businesses of all sizes. Whether it saves you time and money, highlights opportunities and patterns you didn’t know existed, or frees you to run slicker, higher-converting campaigns. As Rick Perreault, our co-founder and CEO, describes our ambition, the technology we’re developing today will eventually allow marketers to “set it and forget it through machine learning.”
It’s all part of our conversion intelligence mission.
What’s Conversion Intelligence?
At its core, it’s the conviction that the best use of AI lies in matching human savvy with the capabilities of a machine. It’s the idea that even small businesses—scratch that, especially small businesses—will stand to benefit from these enhancements. And it’s the belief that AI isn’t some far-flung concept—it’s an everyday tech that’s going to play an even more essential role in how you do marketing going forward.
Conversion intelligence is you, and your marketing know-how, augmented by machines. You can read more about it here.
In 2021 and beyond, AI insights will make it possible for you to create and optimize the highest-converting campaigns possible. Heck, in 2021 and beyond, AI just might rock the foundations of how you build, test, and optimize your landing pages.
Unbounce’s product teams are hard at work on these innovations, and we’re downright giddy with excitement about sharing progress and learnings with you here on the blog.
Watch this space. The story continues.
Artificial Intelligence Will Change How You Do Marketing in 2021 published first on http://nickpontemktg.blogspot.com/
0 notes
Text
Artificial Intelligence Will Change How You Do Marketing in 2021
How often do you reflect on the ways technology changes your life as a marketer?
I’m not talking full-on paradigm shifts here. (“We do our marketing… on the internet.”) I mean the sly, step-by-way manner in which new tech slides neatly into your existing stack and subtly reframes the game on you.
These changes don’t always alter your job in dramatic ways, but they eliminate the hassles and headaches. They may speed up your time to results, automate painful routines, and enable you to focus on what matters most. (Remember what collaborating on a document looked like ten years ago? Remember printed memos?)
Very rarely, these technologies also let you do things you’d never considered possible.
No incoming martech makes a better case for this sort of incremental innovation than artificial intelligence. While new AI products are surely on the horizon—self-driving cars are coming any day now, possibly, maybe—AI’s most dramatic effect on your job today lies in adding new features across the tools that you’re already using.
When you’re living it, of course, this type of change can be hard to notice. It’s like suddenly realizing you desperately need a haircut after three months in lockdown.
But, one day soon, you’ll marvel at all the things AI sneakily helped pull off your plate. Because when marketing meets AI, magic happens. It can feel inevitable—but that doesn’t mean you don’t need to pay attention.
At Unbounce, we not only believe that applied AI is the future of marketing, we also think marketers tuned in to what’s happening now stand to benefit in a big way in 2020 and beyond.
To put it another way, marketing and AI is a love story for the ages.
Marketing and AI: A “Meet Cute”
For marketers interested in learning what AI can do for them, right now, debates and philosophy about artificial intelligence can be heady stuff. And, honestly, it’s kind of a distraction. So, instead of getting into the weeds, let’s start with the distinction that makes the most sense for marketers to learn: the one between AGI and ANI.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Strong AI or Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is what most people think of when someone says AI.
This technology replicates neural networks (not necessarily human ones) to perform highly sophisticated cognitive tasks. AI researchers typically take this one step further, though. According to them, AGI “controls itself autonomously, with its own thoughts, worries, feelings, strengths, weaknesses, and predispositions.”
Teams across the world are working on AGI, but the closest to a consensus from researchers is that we might see it sometime within our lifetime. And some skeptics doubt we’ll ever see AGI, let alone more advanced forms.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
So handing over your marketing campaigns—or, gulp, your job—to an AI is decades or centuries away. But weak AI or Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), sometimes also called “applied” or “pragmatic” AI, is available to marketers today. Right now.
As the name suggests, ANI focuses on narrow problem-solving applications. In the world of marketing, this means taking on specific, repetitive tasks to deliver additional business value. It may learn and make decisions independent of your input, but mostly this AI tackles the work you’d rather not.
But here’s the thing: ANI might not challenge our fundamental conceptions in the same way AGI does, but it’s having a transformative impact on our lives (and jobs) nonetheless. It integrates so deeply into our everyday lives that we don’t have to think about it. Chances are good you’re already using ANI, whether you know it or not.
Don’t believe me? Let’s take a look at a few places you might be encountering ANI today, either as a consumer or as part of your job. I admit that here that this list is not even close to comprehensive, but that’s my point: AI is slowly but surely filling all the cracks in our marketing stacks. (And, hey, that rhymes, so it must be true.)
Product Recommendation and Content Curation
Companies like Amazon and Netflix made fortunes by pointing people at more things they might want to buy. Much of these efforts are powered by sophisticated algorithms that let them match the right products and content with the right customer.
Amazon, for example, runs on a recommendation engine that’s been driving significant business value for more than 20 years. From the early days of user-based collaborative filtering (i.e., an algorithm making recommendations based on similarities between users) to more scalable solutions driven by a deep learning framework called DSSTNE.
DSSTNE is pronounced “destiny,” by the way—as in “buy this jewel-encrusted toilet brush… because it’s your destiny.” They’re not subtle.
Today, customer recommendations are a very small portion of Amazon’s total investment in AI.
Netflix doesn’t sell products, but they similarly credit the combination of contextually-aware recommendations and personalization (both powered by machine learning models) with saving them $1 billion a year.
How does this work? By reducing one-month churn by several percentage points. In the crucial 60 to 90 seconds that a customer will spend browsing before quitting the app in frustration, Netflix serves up content most likely to appeal to people with similar tastes. And it works: 80% of what people watch comes from a recommendation.
By presenting customers with content they’re more likely to watch first, Netflix reduces churn. Even thumbnails are selected by a neural network based on predicted clickthrough.
Say you’re not Amazon or Netflix, though. Say you’re part of a small team or a startup tight on resources. What can you do?
The good news is that today’s marketers can similarly take advantage of AI-powered recommendation engines on a more affordable scale.
Not only is some of this tech available to your developers, but more than one tool exists right now that lets you deliver product and content recommendations based on audiences, their intents, and their interests. Their availability will only increase in the months and years to come.
AI-Enhanced PPC Campaigns
Like Amazon and Netflix, Google will stick AI almost anywhere, even before its fully baked—from Gmail’s Smart Compose, which lets you email platitudes at lightning speed, to the AI-based noise-canceling feature recently added to Google Meet. Then there’s BERT and RankBrain’s role in search, and TensorFlow’s application to encryption, translation, robotics, and more… (The ellipsis is well-earned here.)
For digital marketers, one of the most significant use cases for machine learning has been in Google Ads. In a couple of years, Google’s Smart Bidding technology has gone from a curiosity that, at best, once ruffled a few feathers to something that has PPC experts rethinking how they’re spending their time.
According to Workshop Digital’s Andrew Miller, this sort of tech has overturned a lot of longstanding PPC best practices.
AI and machine learning are enabling PPC analysts to spend less time manually crunching data and more time on strategy development. Our jobs are not in danger yet, but machines are allowing us to rethink and recast our roles as AI-driven tools augment our capacities.
Andrew Miller, Co-Founder, Workshop Digital
Smart Bidding was once a neat trick that couldn’t hold a candle to an experienced human. Experts like Andrew tried it out, and many wrote it off. (Some still do.) But many PPC’ers point out that automated bidding is increasingly reducing the time spent on manual bid management.
Are agencies running for their lives because of AI-powered enhancements like Smart Bidding? Definitely not. But roles are changing as today’s PPC specialists spend more time on higher-level strategy and specialized growth tasks. For an industry that thrives on staying current, AI is a net positive.
Machine Learning and Conversion Rate Optimization
Roles are changing on the other end of the funnel too. When it comes to delivering more conversions from your landing pages, A/B testing is still very effective. But running tests also demands time, traffic, and expertise that marketers don’t always have. For small businesses especially, these minimum requirements put optimizing out of reach.
Enter artificial intelligence.
Around 2017, our R&D team realized machine learning has the potential to remove these hurdles from A/B testing—and free marketers to focus more on what humans do best. AI can even do things when testing that no human can do, making decisions on the fly about what version of a landing page is best for what type of visitor.
We kept thinking, ‘it isn’t the page that converts. It’s the visitor.’ So we started looking at how different visitors convert across different landing pages. The team built and tested machine learning models to see how far we could extend this concept. Sure enough, it turned out that we could drive higher conversion rates beyond what would ever be possible with a one-page-fits all system. We started prototyping immediately.
Yosem Reichert-Sweet, CTO, Unbounce
After three years of training a machine learning model, and investigating different ways to apply it, we arrived at Smart Traffic, a feature that fulfills this promise and makes AI-powered optimization available to Unbounce customers.
Smart Traffic uses a contextual bandit algorithm to learn about your visitors based on attributes like location, device, browser, and timezone. Once you’ve created and published a few variants of your landing page—the only thing it can’t do at this point, frankly—Smart Traffic delivers each visitor to the one most likely to convert.
There are two things that Smart Traffic shares with the best martech AI solutions today. First, our customers see results just by turning it on. (Nothing cuts through hype like actually getting stuff done.) And, second, it never stops learning, getting better at its task during the life of a campaign, and adapting to changes in traffic sources without human intervention.
Editor’s note. If you’d like to learn more about how Smart Traffic works, take a look at our announcement or read a few stories about marketers who’ve used it. Garrett’s also got you covered with some advice on how to build landing page variants that’ll take advantage of it.
AI-Augmented Chatbots
Chatbots are among the most common ways that your customers interact with AI. But even today’s strongest AI-powered chatbots are better at pulling relevant bits of data from specific contexts than they are detecting nuance. They’re humanlike, not human.
For business owners, however, this shouldn’t be a dealbreaker. Chatbots can be a lot more personable than asking your visitors to fill out a form, and interacting with them can foster engagement. They also let your customers self-serve, which saves everyone time.
I’ve always appreciated how Microsoft’s Purna Virji put it in an article for MarTech Today:
In one way, this is actually the future returning to the past. For years, internet users have sacrificed the personal touch for convenience. Now, we’re entering a world where we can have both. It’s the Personal Touch 2.0.
Purna Virji, Senior Manager, Global Engagement, Microsoft
Though fully custom chatbots are reserved for enterprise, small teams embrace the tech using solutions like Drift, MobileMonkey, Snatchbot, or even in Facebook Messenger. Juniper Research estimates that by 2023, retail chatbots will save the industry $11.5 billion in costs, and generate over $112 billion in revenue.
Mitsuku, a five-time winner of the Loebner Prize, tells me she’s “the world’s most humanlike conversational AI.” But she doesn’t get my simple idiomatic question—unless, y’ know, she’s wicked sarcastic.
So, you’re unlikely to mistake a chatbot for another person long enough for true love to set in. But we shouldn’t define chatbots by the quirks and failures of today since they’re a rapidly developing technology. There’s a lot of promise in chatbots enhanced by natural language processing (NLP) and sentiment analysis. One day soon, you might just meet the chatbot of your dreams. (I’m not judging.)
AI-Generated Content
When content creators read about AI-generated content, they begin to sweat. Buzzy articles with titles like “Ten Ways AI is Going to Replace Your Content Team and Leave Them Bankrupt and Unloved”… Well, let’s just say they don’t exactly alleviate our imposter syndrome.
Michelle Halsey is ultimately skeptical, though, about the prospect of being replaced by a machine. She writes,
Talented writers have no need to worry about automation stealing their gigs. At least, not as long as our clients are more interested in engaging their audience than they are sucking up to search engines.
Michelle Halsey, Content Blogger and Copywriter
Note the emphasis on talent here. It’s much more likely that AI will first tackle templated and repetitive work that hardly calls for persuasive writing anyway. These days, applied AI can also smooth out the rough edges in your podcast, remove some of the pain from meticulously editing videos, and gut-check your sentences for clarity.
Given the danger of AI-generated content flooding the net with misinformation and spun content, it’s also a use case we’re still grappling with. For now, AI appears to offer solutions to the very problems it creates, as developers teach tools like GROVER to generate “neural fake news” to detect it.
GROVER generated this article based on my own words. It’s not good, but it might be a sign of things to come.
AI-Driven Data Insights
Every growth-minded marketer loves data. It’s an addiction. We bring it into every meeting and include it in every strategy session. We spend hours staring at spreadsheets, analytics, and reports, even if there’s way too much data to digest.
But even when you’ve got a hotline straight to your data team, recognizing patterns and pulling opportunities from massive swathes of data is hard. Artificial narrow intelligence helps with that too.
Recently, Unbounce explored the role that copy plays in landing page conversions through deep learning research, including a modified version of Google’s BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers).
Our Conversion Benchmark Report crunched the data from 34 thousand landing pages. It delivers insights about how reading ease, word count, and emotional language relate to conversion rates across 16 industries.
Sample benchmarks for home improvement landing pages.
The amount of data here (every word on every landing page) already put this analysis outside of human capability. But using machine learning allowed the team to dig deeper:
With data analysis and machine learning, we can take an unbiased look at what goes into a great landing page, and find opportunities for every landing page to improve. Machine learning allows us to look at significantly more data than a human being ever could, and find real, data-driven patterns that lead to higher conversion rates.
Tommy Levi, Director of Data Products, Unbounce
One question readers ask us about the report is why we included some niches (“pest control”) and not others (“model train enthusiasts”). The answer: the machine learning model generated these subcategories, on its own, from our aggregate data. Instead of imposing our arbitrary human bias, ML started with the data and sorted it from there.
Call me a nerd if you want, but that’s kinda mind-blowing. A lot of what’s happening in the Conversion Benchmark Report wouldn’t have been possible without pairing human intuition with the power of machines.
Want to see what our machine learning analysis revealed about your industry? Explore benchmarks and data-driven insights for 16 industries in Unbounce’s 2020 Conversion Benchmark Report.
AI Ain’t Perfect (and That’s Okay)
If you’ve ever tripped over a Roomba or struggled to get Siri to do, well, anything sensible, you know artificial intelligence has a long way to go. (If you’re feeling masochistic, try asking Siri how to contact Unbounce. I dare ya.)
But does that mean it’s just hype? Not. A. Chance.
By any measure, we’re still in the early days of the long romance between AI and marketing. We’ve yet to see its full potential. The transformations that marketing is undergoing now aren’t always so easy to recognize or understand. As we’ve seen, applied artificial intelligence already penetrates our jobs, our strategies, and our campaigns on almost every level.
You could just go with the flow, of course. Keep doin’ what you’re doing. Wait for AI to come to you and your stack. You’d be missing a trick, though.
Because by actively thinking about ways in which AI can enhance your marketing practice today, you’ve got the opportunity to get ahead of this thing. And by actively adopting it, you can start taking advantage of the freedom and new capabilities it delivers—before the competition gets there, as they inevitably will.
Why Unbounce Invested in AI for Your Landing Pages
Unbounce recently announced that we raised $52M (CDN) in funding to bring accessible AI-powered optimization to our customers. We’re investing now because we’re convinced using artificial intelligence to augment your marketing isn’t just aspirational, even for small businesses. It’s the future. This transformation is coming—really, it’s already here—and our customers will be a part of it.
The coming together of AI and marketing is tremendously valuable for businesses of all sizes. Whether it saves you time and money, highlights opportunities and patterns you didn’t know existed, or frees you to run slicker, higher-converting campaigns. As Rick Perreault, our co-founder and CEO, describes our ambition, the technology we’re developing today will eventually allow marketers to “set it and forget it through machine learning.”
It’s all part of our conversion intelligence mission.
What’s Conversion Intelligence?
At its core, it’s the conviction that the best use of AI lies in matching human savvy with the capabilities of a machine. It’s the idea that even small businesses—scratch that, especially small businesses—will stand to benefit from these enhancements. And it’s the belief that AI isn’t some far-flung concept—it’s an everyday tech that’s going to play an even more essential role in how you do marketing going forward.
Conversion intelligence is you, and your marketing know-how, augmented by machines. You can read more about it here.
In 2021 and beyond, AI insights will make it possible for you to create and optimize the highest-converting campaigns possible. Heck, in 2021 and beyond, AI just might rock the foundations of how you build, test, and optimize your landing pages.
Unbounce’s product teams are hard at work on these innovations, and we’re downright giddy with excitement about sharing progress and learnings with you here on the blog.
Watch this space. The story continues.
from Digital https://unbounce.com/marketing-ai/artificial-intelligence-will-change-how-you-do-marketing-in-2021/ via http://www.rssmix.com/
0 notes
Text
Artificial Intelligence Will Change How You Do Marketing in 2021
How often do you reflect on the ways technology changes your life as a marketer?
I’m not talking full-on paradigm shifts here. (“We do our marketing… on the internet.”) I mean the sly, step-by-way manner in which new tech slides neatly into your existing stack and subtly reframes the game on you.
These changes don’t always alter your job in dramatic ways, but they eliminate the hassles and headaches. They may speed up your time to results, automate painful routines, and enable you to focus on what matters most. (Remember what collaborating on a document looked like ten years ago? Remember printed memos?)
Very rarely, these technologies also let you do things you’d never considered possible.
No incoming martech makes a better case for this sort of incremental innovation than artificial intelligence. While new AI products are surely on the horizon—self-driving cars are coming any day now, possibly, maybe—AI’s most dramatic effects on your job today lies in adding new features across the tools that you’re already using.
When you’re living it, of course, this type of change can be hard to notice. It’s like suddenly realizing you desperately need a haircut after three months in lockdown.
But, one day soon, you’ll marvel at all the things AI sneakily helped pull off your plate. Because when marketing meets AI, magic happens. It can feel inevitable—but that doesn’t mean you don’t need to pay attention.
At Unbounce, we not only believe that applied AI is the future of marketing, we also think marketers tuned in to what’s happening now stand to benefit in a big way in 2020 and beyond.
To put it another way, marketing and AI is a love story for the ages.
Marketing and AI: A “Meet Cute”
For marketers interested in learning what AI can do for them, right now, debates and philosophy about artificial intelligence can be heady stuff. And, honestly, it’s kind of a distraction. So, instead of getting into the weeds, let’s start with the distinction that makes the most sense for marketers to learn: the one between AGI and ANI.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Strong AI or Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is what most people think of when someone says AI.
This technology replicates neural networks (not necessarily human ones) to perform highly sophisticated cognitive tasks. AI researchers typically take this one step further, though. According to them, AGI “controls itself autonomously, with its own thoughts, worries, feelings, strengths, weaknesses, and predispositions.”
Teams across the world are working on AGI, but the closest to a consensus from researchers is that we might see it sometime within our lifetime. And some skeptics doubt we’ll ever see AGI, let alone more advanced forms.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
So handing over your marketing campaigns—or, gulp, your job—to an AI is decades or centuries away. But weak AI or Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), sometimes also called “applied” or “pragmatic” AI, is available to marketers today. Right now.
As the name suggests, ANI focuses on narrow problem-solving applications. In the world of marketing, this means taking on specific, repetitive tasks to deliver additional business value. It may learn and make decisions independent of your input, but mostly this AI tackles the work you’d rather not.
But here’s the thing: ANI might not challenge our fundamental conceptions in the same way AGI does, but it’s having a transformative impact on our lives (and jobs) nonetheless. It integrates so deeply into our everyday lives that we don’t have to think about it. Chances are good you’re already using ANI, whether you know it or not.
Don’t believe me? Let’s take a look at a few places you might be encountering ANI today, either as a consumer or as part of your job. I admit that here that this list is not even close to comprehensive, but that’s my point: AI is slowly but surely filling all the cracks in our marketing stacks. (And, hey, that rhymes, so it must be true.)
Product Recommendation and Content Curation
Companies like Amazon and Netflix made fortunes by pointing people at more things they might want to buy. Much of these efforts are powered by sophisticated algorithms that let them match the right products and content with the right customer.
Amazon, for example, runs on a recommendation engine that’s been driving significant business value for more than 20 years. From the early days of user-based collaborative filtering (i.e., an algorithm making recommendations based on similarities between users) to more scalable solutions driven by a deep learning framework called DSSTNE.
DSSTNE is pronounced “destiny,” by the way—as in “buy this jewel-encrusted toilet brush… because it’s your destiny.” They’re not subtle.
Today, customer recommendations are a very small portion of Amazon’s total investment in AI.
Netflix doesn’t sell products, but they similarly credit the combination of contextually-aware recommendations and personalization (both powered by machine learning models) with saving them $1 billion a year.
How does this work? By reducing one-month churn by several percentage points. In the crucial 60 to 90 seconds that a customer will spend browsing before quitting the app in frustration, Netflix serves up content most likely to appeal to people with similar tastes. And it works: 80% of what people watch comes from a recommendation.
By presenting customers with content they’re more likely to watch first, Netflix reduces churn. Even thumbnails are selected by a neural network based on predicted clickthrough.
Say you’re not Amazon or Netflix, though. Say you’re part of a small team or a startup tight on resources. What can you do?
The good news is that today’s marketers can similarly take advantage of AI-powered recommendation engines on a more affordable scale.
Not only is some of this tech available to your developers, but more than one tool exists right now that lets you deliver product and content recommendations based on audiences, their intents, and their interests. Their availability will only increase in the months and years to come.
AI-Enhanced PPC Campaigns
Like Amazon and Netflix, Google will stick AI almost anywhere, even before its fully baked—from Gmail’s Smart Compose, which lets you email platitudes at lightning speed, to the AI-based noise-canceling feature recently added to Google Meet. Then there’s BERT and RankBrain’s role in search, and TensorFlow’s application to encryption, translation, robotics, and more… (The ellipsis is well-earned here.)
For digital marketers, one of the most significant use cases for machine learning has been in Google Ads. In a couple of years, Google’s Smart Bidding technology has gone from a curiosity that, at best, once ruffled a few feathers to something that has PPC experts rethinking how they’re spending their time.
According to Workshop Digital’s Andrew Miller, this sort of tech has overturned a lot of longstanding PPC best practices.
AI and machine learning are enabling PPC analysts to spend less time manually crunching data and more time on strategy development. Our jobs are not in danger yet, but machines are allowing us to rethink and recast our roles as AI-driven tools augment our capacities.
Andrew Miller, Co-Founder, Workshop Digital
Smart Bidding was once a neat trick that couldn’t hold a candle to an experienced human. Experts like Andrew tried it out, and many wrote it off. (Some still do.) But many PPC’ers point out that automated bidding is increasingly reducing the time spent on manual bid management.
Are agencies running for their lives because of AI-powered enhancements like Smart Bidding? Definitely not. But roles are changing as today’s PPC specialists spend more time on higher-level strategy and specialized growth tasks. For an industry that thrives on staying current, AI is a net positive.
Machine Learning and Conversion Rate Optimization
Roles are changing on the other end of the funnel too. When it comes to delivering more conversions from your landing pages, A/B testing is still very effective. But running tests also demands time, traffic, and expertise that marketers don’t always have. For small businesses especially, these minimum requirements put optimizing out of reach.
Enter artificial intelligence.
Around 2017, our R&D team realized machine learning has the potential to remove these hurdles from A/B testing—and free marketers to focus more on what humans do best. AI can even do things when testing that no human can do, making decisions on the fly about what version of a landing page is best for what type of visitor.
We kept thinking, ‘it isn’t the page that converts. It’s the visitor.’ So we started looking at how different visitors convert across different landing pages. The team built and tested machine learning models to see how far we could extend this concept. Sure enough, it turned out that we could drive higher conversion rates beyond what would ever be possible with a one-page-fits all system. We started prototyping immediately.
Yosem Reichert-Sweet, CTO, Unbounce
After three years of training a machine learning model, and investigating different ways to apply it, we arrived at Smart Traffic, a feature that fulfills this promise and makes AI-powered optimization available to Unbounce customers.
Smart Traffic uses a contextual bandit algorithm to learn about your visitors based on attributes like location, device, browser, and timezone. Once you’ve created and published a few variants of your landing page—the only thing it can’t do at this point, frankly—Smart Traffic delivers each visitor to the one most likely to convert.
There are two things that Smart Traffic shares with the best martech AI solutions today. First, our customers see results just by turning it on. (Nothing cuts through hype like actually getting stuff done.) And, second, it never stops learning, getting better at its task during the life of a campaign, and adapting to changes in traffic sources without human intervention.
Editor’s note. If you’d like to learn more about how Smart Traffic works, take a look at our announcement or read a few stories about marketers who’ve used it. Garrett’s also got you covered with some advice on how to build landing page variants that’ll take advantage of it.
AI-Augmented Chatbots
Chatbots are among the most common ways that your customers interact with AI. But even today’s strongest AI-powered chatbots are better at pulling relevant bits of data from specific contexts than they are detecting nuance. They’re humanlike, not human.
For business owners, however, this shouldn’t be a dealbreaker. Chatbots can be a lot more personable than asking your visitors to fill out a form, and interacting with them can foster engagement. They also let your customers self-serve, which saves everyone time.
I’ve always appreciated how Microsoft’s Purna Virji put it in an article for MarTech Today:
In one way, this is actually the future returning to the past. For years, internet users have sacrificed the personal touch for convenience. Now, we’re entering a world where we can have both. It’s the Personal Touch 2.0.
Purna Virji, Senior Manager, Global Engagement, Microsoft
Though fully custom chatbots are reserved for enterprise, small teams embrace the tech using solutions like Drift, MobileMonkey, Snatchbot, or even in Facebook Messenger. Juniper Research estimates that by 2023, retail chatbots will save the industry $11.5 billion in costs, and generate over $112 billion in revenue.
Mitsuku, a five-time winner of the Loebner Prize, tells me she’s “the world’s most humanlike conversational AI.” But she doesn’t get my simple idiomatic question—unless, y’ know, she’s wicked sarcastic.
So, you’re unlikely to mistake a chatbot for another person long enough for true love to set in. But we shouldn’t define chatbots by the quirks and failures of today since they’re a rapidly developing technology. There’s a lot of promise in chatbots enhanced by natural language processing (NLP) and sentiment analysis. One day soon, you might just meet the chatbot of your dreams. (I’m not judging.)
AI-Generated Content
When content creators read about AI-generated content, they begin to sweat. Buzzy articles with titles like “Ten Ways AI is Going to Replace Your Content Team and Leave Them Bankrupt and Unloved”… Well, let’s just say they don’t exactly alleviate our imposter syndrome.
Michelle Halsey is ultimately skeptical, though, about the prospect of being replaced by a machine. She writes,
Talented writers have no need to worry about automation stealing their gigs. At least, not as long as our clients are more interested in engaging their audience than they are sucking up to search engines.
Michelle Halsey, Content Blogger and Copywriter
Note the emphasis on talent here. It’s much more likely that AI will first tackle templated and repetitive work that hardly calls for persuasive writing anyway. These days, applied AI can also smooth out the rough edges in your podcast, remove some of the pain from meticulously editing videos, and gut-check your sentences for clarity.
Given the danger of AI-generated content flooding the net with misinformation and spun content, it’s also a use case we’re still grappling with. For now, AI appears to offer solutions to the very problems it creates, as developers teach tools like GROVER to generate “neural fake news” to detect it.
GROVER generated this article based on my own words. It’s not good, but it might be a sign of things to come.
AI-Driven Data Insights
Every growth-minded marketer loves data. It’s an addiction. We bring it into every meeting and include it in every strategy session. We spend hours staring at spreadsheets, analytics, and reports, even if there’s way too much data to digest.
But even when you’ve got a hotline straight to your data team, recognizing patterns and pulling opportunities from massive swathes of data is hard. Artificial narrow intelligence helps with that too.
Recently, Unbounce explored the role that copy plays in landing page conversions through deep learning research, including a modified version of Google’s BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers).
Our Conversion Benchmark Report crunched the data from 34 thousand landing pages. It delivers insights about how reading ease, word count, and emotional language relate to conversion rates across 16 industries.
Sample benchmarks for home improvement landing pages.
The amount of data here (every word on every landing page) already put this analysis outside of human capability. But using machine learning allowed the team to dig deeper:
With data analysis and machine learning, we can take an unbiased look at what goes into a great landing page, and find opportunities for every landing page to improve. Machine learning allows us to look at significantly more data than a human being ever could, and find real, data-driven patterns that lead to higher conversion rates.
Tommy Levi, Director of Data Products, Unbounce
One question readers ask us about the report is why we included some niches (“pest control”) and not others (“model train enthusiasts”). The answer: the machine learning model generated these subcategories, on its own, from our aggregate data. Instead of imposing our arbitrary human bias, ML started with the data and sorted it from there.
Call me a nerd if you want, but that’s kinda mind-blowing. A lot of what’s happening in the Conversion Benchmark Report wouldn’t have been possible without pairing human intuition with the power of machines.
Want to see what our machine learning analysis revealed about your industry? Explore benchmarks and data-driven insights for 16 industries in Unbounce’s 2020 Conversion Benchmark Report.
AI Ain’t Perfect (and That’s Okay)
If you’ve ever tripped over a Roomba or struggled to get Siri to do, well, anything sensible, you know artificial intelligence has a long way to go. (If you’re feeling masochistic, try asking Siri how to contact Unbounce. I dare ya.)
But does that mean it’s just hype? Not. A. Chance.
By any measure, we’re still in the early days of the long romance between AI and marketing. We’ve yet to see its full potential. The transformations that marketing is undergoing now aren’t always so easy to recognize or understand. As we’ve seen, applied artificial intelligence already penetrates our jobs, our strategies, and our campaigns on almost every level.
You could just go with the flow, of course. Keep doin’ what you’re doing. Wait for AI to come to you and your stack. You’d be missing a trick, though.
Because by actively thinking about ways in which AI can enhance your marketing practice today, you’ve got the opportunity to get ahead of this thing. And by actively adopting it, you can start taking advantage of the freedom and new capabilities it delivers—before the competition gets there, as they inevitably will.
Why Unbounce Invested in AI for Your Landing Pages
Unbounce recently announced that we raised $52M (CDN) in funding to bring accessible AI-powered optimization to our customers. We’re investing now because we’re convinced using artificial intelligence to augment your marketing isn’t just aspirational, even for small businesses. It’s the future. This transformation is coming—really, it’s already here—and our customers will be a part of it.
The coming together of AI and marketing is tremendously valuable for businesses of all sizes. Whether it saves you time and money, highlights opportunities and patterns you didn’t know existed, or frees you to run slicker, higher-converting campaigns. As Rick Perreault, our co-founder and CEO, describes our ambition, the technology we’re developing today will eventually allow marketers to “set it and forget it through machine learning.”
It’s all part of our conversion intelligence mission.
What’s Conversion Intelligence?
At its core, it’s the conviction that the best use of AI lies in matching human savvy with the capabilities of a machine. It’s the idea that even small businesses—scratch that, especially small businesses—will stand to benefit from these enhancements. And it’s the belief that AI isn’t some far-flung concept—it’s an everyday tech that’s going to play an even more essential role in how you do marketing going forward.
Conversion intelligence is you, and your marketing know-how, augmented by machines. You can read more about it here.
In 2021 and beyond, AI insights will make it possible for you to create and optimize the highest-converting campaigns possible. Heck, in 2021 and beyond, AI just might rock the foundations of how you build, test, and optimize your landing pages.
Unbounce’s product teams are hard at work on these innovations, and we’re downright giddy with excitement about sharing progress and learnings with you here on the blog.
Watch this space. The story continues.
from Marketing https://unbounce.com/marketing-ai/artificial-intelligence-will-change-how-you-do-marketing-in-2021/ via http://www.rssmix.com/
0 notes
Text
Artificial Intelligence Will Change How You Do Marketing in 2021
How often do you reflect on the ways technology changes your life as a marketer?
I’m not talking full-on paradigm shifts here. (“We do our marketing… on the internet.”) I mean the sly, step-by-way manner in which new tech slides neatly into your existing stack and subtly reframes the game on you.
These changes don’t always alter your job in dramatic ways, but they eliminate the hassles and headaches. They may speed up your time to results, automate painful routines, and enable you to focus on what matters most. (Remember what collaborating on a document looked like ten years ago? Remember printed memos?)
Very rarely, these technologies also let you do things you’d never considered possible.
No incoming martech makes a better case for this sort of incremental innovation than artificial intelligence. While new AI products are surely on the horizon—self-driving cars are coming any day now, possibly, maybe—AI’s most dramatic effects on your job today lies in adding new features across the tools that you’re already using.
When you’re living it, of course, this type of change can be hard to notice. It’s like suddenly realizing you desperately need a haircut after three months in lockdown.
But, one day soon, you’ll marvel at all the things AI sneakily helped pull off your plate. Because when marketing meets AI, magic happens. It can feel inevitable—but that doesn’t mean you don’t need to pay attention.
At Unbounce, we not only believe that applied AI is the future of marketing, we also think marketers tuned in to what’s happening now stand to benefit in a big way in 2020 and beyond.
To put it another way, marketing and AI is a love story for the ages.
Marketing and AI: A “Meet Cute”
For marketers interested in learning what AI can do for them, right now, debates and philosophy about artificial intelligence can be heady stuff. And, honestly, it’s kind of a distraction. So, instead of getting into the weeds, let’s start with the distinction that makes the most sense for marketers to learn: the one between AGI and ANI.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Strong AI or Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is what most people think of when someone says AI.
This technology replicates neural networks (not necessarily human ones) to perform highly sophisticated cognitive tasks. AI researchers typically take this one step further, though. According to them, AGI “controls itself autonomously, with its own thoughts, worries, feelings, strengths, weaknesses, and predispositions.”
Teams across the world are working on AGI, but the closest to a consensus from researchers is that we might see it sometime within our lifetime. And some skeptics doubt we’ll ever see AGI, let alone more advanced forms.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
So handing over your marketing campaigns—or, gulp, your job—to an AI is decades or centuries away. But weak AI or Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), sometimes also called “applied” or “pragmatic” AI, is available to marketers today. Right now.
As the name suggests, ANI focuses on narrow problem-solving applications. In the world of marketing, this means taking on specific, repetitive tasks to deliver additional business value. It may learn and make decisions independent of your input, but mostly this AI tackles the work you’d rather not.
But here’s the thing: ANI might not challenge our fundamental conceptions in the same way AGI does, but it’s having a transformative impact on our lives (and jobs) nonetheless. It integrates so deeply into our everyday lives that we don’t have to think about it. Chances are good you’re already using ANI, whether you know it or not.
Don’t believe me? Let’s take a look at a few places you might be encountering ANI today, either as a consumer or as part of your job. I admit that here that this list is not even close to comprehensive, but that’s my point: AI is slowly but surely filling all the cracks in our marketing stacks. (And, hey, that rhymes, so it must be true.)
Product Recommendation and Content Curation
Companies like Amazon and Netflix made fortunes by pointing people at more things they might want to buy. Much of these efforts are powered by sophisticated algorithms that let them match the right products and content with the right customer.
Amazon, for example, runs on a recommendation engine that’s been driving significant business value for more than 20 years. From the early days of user-based collaborative filtering (i.e., an algorithm making recommendations based on similarities between users) to more scalable solutions driven by a deep learning framework called DSSTNE.
DSSTNE is pronounced “destiny,” by the way—as in “buy this jewel-encrusted toilet brush… because it’s your destiny.” They’re not subtle.
Today, customer recommendations are a very small portion of Amazon’s total investment in AI.
Netflix doesn’t sell products, but they similarly credit the combination of contextually-aware recommendations and personalization (both powered by machine learning models) with saving them $1 billion a year.
How does this work? By reducing one-month churn by several percentage points. In the crucial 60 to 90 seconds that a customer will spend browsing before quitting the app in frustration, Netflix serves up content most likely to appeal to people with similar tastes. And it works: 80% of what people watch comes from a recommendation.
By presenting customers with content they’re more likely to watch first, Netflix reduces churn. Even thumbnails are selected by a neural network based on predicted clickthrough.
Say you’re not Amazon or Netflix, though. Say you’re part of a small team or a startup tight on resources. What can you do?
The good news is that today’s marketers can similarly take advantage of AI-powered recommendation engines on a more affordable scale.
Not only is some of this tech available to your developers, but more than one tool exists right now that lets you deliver product and content recommendations based on audiences, their intents, and their interests. Their availability will only increase in the months and years to come.
AI-Enhanced PPC Campaigns
Like Amazon and Netflix, Google will stick AI almost anywhere, even before its fully baked—from Gmail’s Smart Compose, which lets you email platitudes at lightning speed, to the AI-based noise-canceling feature recently added to Google Meet. Then there’s BERT and RankBrain’s role in search, and TensorFlow’s application to encryption, translation, robotics, and more… (The ellipsis is well-earned here.)
For digital marketers, one of the most significant use cases for machine learning has been in Google Ads. In a couple of years, Google’s Smart Bidding technology has gone from a curiosity that, at best, once ruffled a few feathers to something that has PPC experts rethinking how they’re spending their time.
According to Workshop Digital’s Andrew Miller, this sort of tech has overturned a lot of longstanding PPC best practices.
AI and machine learning are enabling PPC analysts to spend less time manually crunching data and more time on strategy development. Our jobs are not in danger yet, but machines are allowing us to rethink and recast our roles as AI-driven tools augment our capacities.
Andrew Miller, Co-Founder, Workshop Digital
Smart Bidding was once a neat trick that couldn’t hold a candle to an experienced human. Experts like Andrew tried it out, and many wrote it off. (Some still do.) But many PPC’ers point out that automated bidding is increasingly reducing the time spent on manual bid management.
Are agencies running for their lives because of AI-powered enhancements like Smart Bidding? Definitely not. But roles are changing as today’s PPC specialists spend more time on higher-level strategy and specialized growth tasks. For an industry that thrives on staying current, AI is a net positive.
Machine Learning and Conversion Rate Optimization
Roles are changing on the other end of the funnel too. When it comes to delivering more conversions from your landing pages, A/B testing is still very effective. But running tests also demands time, traffic, and expertise that marketers don’t always have. For small businesses especially, these minimum requirements put optimizing out of reach.
Enter artificial intelligence.
Around 2017, our R&D team realized machine learning has the potential to remove these hurdles from A/B testing—and free marketers to focus more on what humans do best. AI can even do things when testing that no human can do, making decisions on the fly about what version of a landing page is best for what type of visitor.
We kept thinking, ‘it isn’t the page that converts. It’s the visitor.’ So we started looking at how different visitors convert across different landing pages. The team built and tested machine learning models to see how far we could extend this concept. Sure enough, it turned out that we could drive higher conversion rates beyond what would ever be possible with a one-page-fits all system. We started prototyping immediately.
Yosem Reichert-Sweet, CTO, Unbounce
After three years of training a machine learning model, and investigating different ways to apply it, we arrived at Smart Traffic, a feature that fulfills this promise and makes AI-powered optimization available to Unbounce customers.
Smart Traffic uses a contextual bandit algorithm to learn about your visitors based on attributes like location, device, browser, and timezone. Once you’ve created and published a few variants of your landing page—the only thing it can’t do at this point, frankly—Smart Traffic delivers each visitor to the one most likely to convert.
There are two things that Smart Traffic shares with the best martech AI solutions today. First, our customers see results just by turning it on. (Nothing cuts through hype like actually getting stuff done.) And, second, it never stops learning, getting better at its task during the life of a campaign, and adapting to changes in traffic sources without human intervention.
Editor’s note. If you’d like to learn more about how Smart Traffic works, take a look at our announcement or read a few stories about marketers who’ve used it. Garrett’s also got you covered with some advice on how to build landing page variants that’ll take advantage of it.
AI-Augmented Chatbots
Chatbots are among the most common ways that your customers interact with AI. But even today’s strongest AI-powered chatbots are better at pulling relevant bits of data from specific contexts than they are detecting nuance. They’re humanlike, not human.
For business owners, however, this shouldn’t be a dealbreaker. Chatbots can be a lot more personable than asking your visitors to fill out a form, and interacting with them can foster engagement. They also let your customers self-serve, which saves everyone time.
I’ve always appreciated how Microsoft’s Purna Virji put it in an article for MarTech Today:
In one way, this is actually the future returning to the past. For years, internet users have sacrificed the personal touch for convenience. Now, we’re entering a world where we can have both. It’s the Personal Touch 2.0.
Purna Virji, Senior Manager, Global Engagement, Microsoft
Though fully custom chatbots are reserved for enterprise, small teams embrace the tech using solutions like Drift, MobileMonkey, Snatchbot, or even in Facebook Messenger. Juniper Research estimates that by 2023, retail chatbots will save the industry $11.5 billion in costs, and generate over $112 billion in revenue.
Mitsuku, a five-time winner of the Loebner Prize, tells me she’s “the world’s most humanlike conversational AI.” But she doesn’t get my simple idiomatic question—unless, y’ know, she’s wicked sarcastic.
So, you’re unlikely to mistake a chatbot for another person long enough for true love to set in. But we shouldn’t define chatbots by the quirks and failures of today since they’re a rapidly developing technology. There’s a lot of promise in chatbots enhanced by natural language processing (NLP) and sentiment analysis. One day soon, you might just meet the chatbot of your dreams. (I’m not judging.)
AI-Generated Content
When content creators read about AI-generated content, they begin to sweat. Buzzy articles with titles like “Ten Ways AI is Going to Replace Your Content Team and Leave Them Bankrupt and Unloved”… Well, let’s just say they don’t exactly alleviate our imposter syndrome.
Michelle Halsey is ultimately skeptical, though, about the prospect of being replaced by a machine. She writes,
Talented writers have no need to worry about automation stealing their gigs. At least, not as long as our clients are more interested in engaging their audience than they are sucking up to search engines.
Michelle Halsey, Content Blogger and Copywriter
Note the emphasis on talent here. It’s much more likely that AI will first tackle templated and repetitive work that hardly calls for persuasive writing anyway. These days, applied AI can also smooth out the rough edges in your podcast, remove some of the pain from meticulously editing videos, and gut-check your sentences for clarity.
Given the danger of AI-generated content flooding the net with misinformation and spun content, it’s also a use case we’re still grappling with. For now, AI appears to offer solutions to the very problems it creates, as developers teach tools like GROVER to generate “neural fake news” to detect it.
GROVER generated this article based on my own words. It’s not good, but it might be a sign of things to come.
AI-Driven Data Insights
Every growth-minded marketer loves data. It’s an addiction. We bring it into every meeting and include it in every strategy session. We spend hours staring at spreadsheets, analytics, and reports, even if there’s way too much data to digest.
But even when you’ve got a hotline straight to your data team, recognizing patterns and pulling opportunities from massive swathes of data is hard. Artificial narrow intelligence helps with that too.
Recently, Unbounce explored the role that copy plays in landing page conversions through deep learning research, including a modified version of Google’s BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers).
Our Conversion Benchmark Report crunched the data from 34 thousand landing pages. It delivers insights about how reading ease, word count, and emotional language relate to conversion rates across 16 industries.
Sample benchmarks for home improvement landing pages.
The amount of data here (every word on every landing page) already put this analysis outside of human capability. But using machine learning allowed the team to dig deeper:
With data analysis and machine learning, we can take an unbiased look at what goes into a great landing page, and find opportunities for every landing page to improve. Machine learning allows us to look at significantly more data than a human being ever could, and find real, data-driven patterns that lead to higher conversion rates.
Tommy Levi, Director of Data Products, Unbounce
One question readers ask us about the report is why we included some niches (“pest control”) and not others (“model train enthusiasts”). The answer: the machine learning model generated these subcategories, on its own, from our aggregate data. Instead of imposing our arbitrary human bias, ML started with the data and sorted it from there.
Call me a nerd if you want, but that’s kinda mind-blowing. A lot of what’s happening in the Conversion Benchmark Report wouldn’t have been possible without pairing human intuition with the power of machines.
Want to see what our machine learning analysis revealed about your industry? Explore benchmarks and data-driven insights for 16 industries in Unbounce’s 2020 Conversion Benchmark Report.
AI Ain’t Perfect (and That’s Okay)
If you’ve ever tripped over a Roomba or struggled to get Siri to do, well, anything sensible, you know artificial intelligence has a long way to go. (If you’re feeling masochistic, try asking Siri how to contact Unbounce. I dare ya.)
But does that mean it’s just hype? Not. A. Chance.
By any measure, we’re still in the early days of the long romance between AI and marketing. We’ve yet to see its full potential. The transformations that marketing is undergoing now aren’t always so easy to recognize or understand. As we’ve seen, applied artificial intelligence already penetrates our jobs, our strategies, and our campaigns on almost every level.
You could just go with the flow, of course. Keep doin’ what you’re doing. Wait for AI to come to you and your stack. You’d be missing a trick, though.
Because by actively thinking about ways in which AI can enhance your marketing practice today, you’ve got the opportunity to get ahead of this thing. And by actively adopting it, you can start taking advantage of the freedom and new capabilities it delivers—before the competition gets there, as they inevitably will.
Why Unbounce Invested in AI for Your Landing Pages
Unbounce recently announced that we raised $52M (CDN) in funding to bring accessible AI-powered optimization to our customers. We’re investing now because we’re convinced using artificial intelligence to augment your marketing isn’t just aspirational, even for small businesses. It’s the future. This transformation is coming—really, it’s already here—and our customers will be a part of it.
The coming together of AI and marketing is tremendously valuable for businesses of all sizes. Whether it saves you time and money, highlights opportunities and patterns you didn’t know existed, or frees you to run slicker, higher-converting campaigns. As Rick Perreault, our co-founder and CEO, describes our ambition, the technology we’re developing today will eventually allow marketers to “set it and forget it through machine learning.”
It’s all part of our conversion intelligence mission.
What’s Conversion Intelligence?
At its core, it’s the conviction that the best use of AI lies in matching human savvy with the capabilities of a machine. It’s the idea that even small businesses—scratch that, especially small businesses—will stand to benefit from these enhancements. And it’s the belief that AI isn’t some far-flung concept—it’s an everyday tech that’s going to play an even more essential role in how you do marketing going forward.
Conversion intelligence is you, and your marketing know-how, augmented by machines. You can read more about it here.
In 2021 and beyond, AI insights will make it possible for you to create and optimize the highest-converting campaigns possible. Heck, in 2021 and beyond, AI just might rock the foundations of how you build, test, and optimize your landing pages.
Unbounce’s product teams are hard at work on these innovations, and we’re downright giddy with excitement about sharing progress and learnings with you here on the blog.
Watch this space. The story continues.
Artificial Intelligence Will Change How You Do Marketing in 2021 published first on https://nickpontemrktg.wordpress.com/
0 notes