#dataengineercourse
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
SQL Server is quickest way to your Data Analytics journey, says expert
SQL server tools get you through the whole, end-to-end ‘data ecosystem’; where you learn data engineering, data warehousing, and business intelligence all in single platform
Microsoft SQL Server is currently leading the RDBMS market with its tremendously diverse tools and services for data analytics. Whether it’s data management, analysis or reporting, you get all in one package, that too for free.
Given that SQL server provides an end-to-end exposure to the whole data ecosystem, learning SQL server is the quickest path to your data analytics journey..
Note: This career advice is for newbies just starting their analytics journey, as well as for technical geeks who wish to opt for SQL server job roles.
Table of contents
Data Ecosystem and SQL Server Tools
How can SQL Server help me begin a Career in Data Analytics?
Career Tracks to target a job role
Learn SQL Server Tools
Watch Webinar!
Data Ecosystem and SQL Server tools
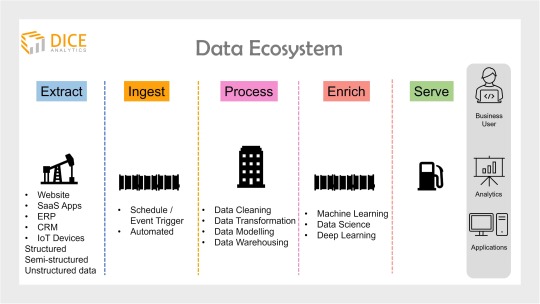
Data ecosystem is the backbone of any organization’s data analytics project.
Simply put, a data ecosystem documents and presents infrastructure and applications for data storage and processing.
Any data ecosystem portrays four to five stages of data, depending on the organization’s objectives.
Starting off, a data expert always needs to collect data from the vast sources of the organization. This includes, website data, SaaS applications, IoT devices, CRM, ERP etc.
Next, all of the data from diverse sources is gathered over a common place through a process called ingestion.
Integrated on a single database, this data needs to be cleaned, transformed and organized into a universal format (data harmonization) to avoid misalignment across the ecosystem.
This process is called data warehousing (aka data engineering).
Optional is to further enrich data using machine learning technology. One of the main data science job roles is to apply predictive analytics at this stage.
Finally, at the last stage, data is analyzed and presented to business users for value driving and decision making. A BI developer or engineer is specialized to handle data visualization at this stage.
SQL Server tools and services offer a low code environment to all of the above steps and therefore quickly and easily helps to build an end-to-end data ecosystem for an organization.
The tools and services can be broadly classified as data management and business intelligence (BI) functionalities.
For data management, SQL Server provides SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS), SQL Server Data Quality Services, and SQL Server Master Data Services.
SQL Server provides SQL Server Data tools for building a database. And for management, deployment, and monitoring the platform has SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) handle data analysis.
SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) are used for reporting and visualization of data.
Earlier known as the R services, the Machine Learning Services came as part of SQL Server suite in 2016 and renamed afterwards.
How can SQL Server help me begin a Career in Data Analytics?
When you learn SQL Server, it exposes you to the complete data ecosystem. This helps you in your career advancement in two ways.
Access to the vast SQL Server jobs
Microsoft SQL Server currently stands at 3rd rank (after Oracle and MySQL) in the world’s most used commercial relational databases. This is because Microsoft offers an intensely feature-rich version of SQL Server for free.
This makes SQL server skills one of the most in-demand across the data analytics ecosystem.
Tip: For newbies, and those with career transitions, if you want to land on an analytics job quickly, learning SQL server tools is a smart idea since the job market is lucrative.
Further, once in, as you move along in your career we recommend growing your skill set and ascending towards more specific job roles, for example, data engineer and BI developer.
Career Tracks to target a job role
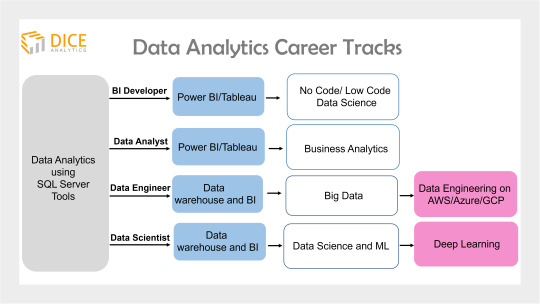
Once you get a grab of the end-to-end data analytics ecosystem, now it’s a step to move forward in your analytics journey.
But why?
Data analytics is a broad field, and carries lucrative job opportunities in the form of various job roles available in the market.
Moreover, given a myriad of job roles, you can opt for a career in the field of your interest.
What are the career tracks when I work with SQL server?
Become a Data Engineer
Once getting to know what data engineering holds, you can now opt for a vendor specific data engineering skills.
For example, Teradata is a market leader in on-premise data warehousing solutions. Learning data engineering on Teradata will offer bright career prospects in the data analytics field.
While SQL Server and Teradata RDBMS have a data architecture built for small scale data, when it comes to data volumes up to petabytes size, these solutions don’t work.
Thus a data engineer can move to learning big data technology that holds even brighter career prospects (read about the blooming big data market forecast).
Become a BI Developer/BI Engineer
This job role narrows to the data visualization, and reporting only. A BI developer is expert in BI tools such as Power BI and Tableau.
As a next step, a BI Developer can also opt for no code/low code Data Science using Knime.
Become an ML Engineer
A Machine Learning engineer uses ML technology to employ predictive analytics and finds out future trends and patterns within data.
The requirement for an ML engineer is to understand how databases and data warehousing works, and needs to build a strong foundation in that.
Next, you can opt for Deep Learning in your career journey for better positions in large enterprises.
Become a Data Analyst
After getting to work with SQL server tools, you can also opt data analyst as your career choice. This requires you to build expertise in BI tools such as Power BI and Tableau.
The next step for career advancement is to learn Business Analytics that deals with business data and marketing analytics.
You might want to view Business Analytics career prospects and salary in Pakistan.
Interested in Learning SQL Server Tools?
Dicecamp offers an 8 weeks course* on Learning SQL Server Tools.
The course covers four tools; SQL Server Integrated Services (SSIS), SQL Server Management Services (SSMS), Azure Cloud, and Power BI.
You will learn:
SQL hands-on
DWH building using SSIS
Data Management using SSMS
AZURE SQL CONFIG, DTU basics
DAX implementation in Power BI
Data visualization in Power BI
Visit complete course outline and registration details here.
*We offer flexible pricing and valuable concessions.
Straight from the Horse’s Mouth!

The instructor of this course is Mr. Abu Bakar Nisar Alvi who’s Pakistan’s celebrated engineer awarded Tamgha e Imtiaz (fourth highest civil rank) for his excellent engineering performance back in 2005.
Mr. Alvi serves as a senior IT consultant at the World Bank with key experience in enabling digital transformation as part of the village service delivery in Indonesia.
Taking two decades of experience and vast work diversity, Mr. Alvi is now associated with Dicecamp as a lead trainer Data Analytics and Visualization.
Webinar: Watch him speaking on ‘Why to Learn SQL Server Tools’ in the latest webinar (LinkedIn Webinar Link).
#dicecamp#datascience#careertest#devops#dataengineercourse#datawarehouse#devopscourse#datawarehousecourse#sqlserver#sql#mysql
1 note
·
View note
Text

Data Engineering Using SQL Server Free Course
Learn SSIS, SSAS, SSRS for data modeling, visualization, and advanced analytics in this Course and Get Certificate.
Link : https://dicecamp.com/data-engineering-using-sql-server-
#dicecamp#datascience#data scientist#dataengineercourse#dataengineering#dataengineer#dataengineeringfreecourse#freecourse
0 notes
Text
SQL and NoSQL: Differences, Use cases and Databases
SQL and NoSQL are counter technologies meant to accomplish the same business goals. The difference mainly exists in the autonomy to ‘explore data deeply’ and ‘ease of scalability’
SQL has existed as a widely accepted industry standard for so long now. Its counterpart; NoSQL, emerged almost 12 years ago when the world needed a disparate system that could process unstructured data as well as comply with increasing storage and power requirements.
The rise of NoSQL almost diminished the decade old SQL paradigm of relational database management system (RDBMS) giving rise to non relational database systems.
Now as we see, SQL didn’t go away, instead its potential to manipulate data in databases is increasingly realized.
In this article, we explore sql and nosql difference, sql vs. nosql use cases, and comparison of databases.
SQL and NoSQL Difference
The differences in SQL and NoSQL exist among four key parameters: Language, Scalability, Structure, and Transaction Processing.
Language
SQL is used to query structured data only. Structured data exists in the form of rows and columns (2D tables) and therefore exert the constraint for a carefully built schema before querying data.
That’s because for data whose structure could not be defined; data from mobile applications, and SAP systems with a lot of varying fields where new fields occur every now and then, SQL fails given its syntax and control flow that works only for table based data.
Apart from the structure constraint on data, SQL has been well nurtured in the past 40 years to offer wide functionality for complex queries, and is secure in usage.
The learning curve of SQL is also short compared to other programming languages (including NoSQL). Moreover, all the variants of SQL including for example SQL server, and MySQL have a great amount of similarity in usage and therefore are easily learnt across the globe.
NoSQL has its own advantages over SQL. It offers the flexibility to query unstructured data (with a dynamic schema not limited to representing data in rows and columns). This means now each type of data could have alternate structure all stored beside each other in a single database.
NoSQL was introduced some 12 years ago with the aim of utilization of unstructured or loosely structured data in database applications.
There’s freedom from rigorous data engineering before the storage to use the data for BI and ML applications. NoSQL offers greater exploration of data in that the raw data is directly fed to the system for storage and after that the BI and ML engineers could build schemas as they like.
The spotlight on NoSQL waned when its users realized it lacked standardization and wide documentation leading to difficulty in carrying out complex queries.
Moreover, NoSQL language varies across databases where each database (MongoDB, Cassandra, etc) have their completely varying versions of noSQL.CategorySQLNoSQLLanguageStructured data onlyStructured and unstructuredScalabilityVerticalHorizontalStructureTable format4 Types incl. columnar formatTransactionsACID complianceCAP theoremSQL vs. NoSQL Difference
Scalability
Scalability is one of the most distinctive features of SQL and NoSQL databases. For the scope of this article, we define scalability as the capacity of a system to process a number of concurrent queries.
The ease of adding and removing processing resources for the purpose of supporting concurrent users determines the effectiveness of scalability.
SQL supports vertical scalability that means new processing resources could be added within the same server. It’s based on the actor model that uses multiple CPU cores. All the processor cores participate in processing over the same data.
NoSQL adopts the horizontal scalability that instead of adding cores to CPU adds new servers in parallel to old ones. It uses a master/slave architecture where a master processor divides data among slave processors.
In essence, horizontal scaling is more desirable due to its ability to divide data across parallel machines. This way it enables faster processing from utilization of all resources in less time. Whereas vertical scaling, although much easier to implement, lacks the kind of linear scalability as in horizontal scaling.
Learn more about differences in horizontal scalability and vertical scalability here.
Structure
SQL databases store data in rows and columns where a column represents a specific data type only. While making these tables some rules are defined to maintain the integrity of data as well as making it efficient for the querying process.
NoSQL databases don’t conform to this tabular structure, and don’t require data engineering such as above. Instead they use other formats that are more flexible to add any kind of data desired. These formats are:
Column-oriented structure: Data resides in columns however these columns support any kind of data type. It results in high dimensional data.
Key-Value structure: Data objects are defined and a unique key is assigned to each object.
Document stores: specifically holds semi-structured data where some of the data is structured, while it may contain other data that has no defined column category.
Graph databases: It uses nodes and relationships to structure data instead of a table or a document. Nodes present data elements while relationships present how they are related to each other.
Learn more about Graph databases in this comprehensive article.
Transaction Processing
As you may be well aware that SQL databases process transactions in such a way as to minimize the erroneous events that might affect the data. For this, it uses the ACID rules. These are the:
Atomicity of a transaction prevents it from getting saved when it’s incomplete. A transaction is either saved when it’s completed only or failed otherwise.
Consistency prevents data from being corrupted by following rules at each step of transactional processing.
Isolation keeps away multiple users to change the same data at same time.
Durability records a transaction once it is made. No roll back can be done after a transaction is saved.
In distributed systems as a copy of data is stored on all distributed nodes through replication the transactional processing is a little different. NoSQL uses the CAP theorem that is specifically designed for successful transaction processing on distributed systems.
Consistency ensures the delivery of latest results where sometimes in case of a node separated from the system due to a network failure might not receive the updated information. An error message must be sent to the user instead of an unlatest value fetched from a node.
Availability, unlike a consistent system, ensures that a transaction is always successful (returning a non-error result) even when there’s network failure.
Partition Tolerance is a phenomenon for uninterruptible system performance in case of a network failure between parallel systems. More than one link is created among nodes such that if a link fails, there are other links that duplicate data to other nodes.
In NoSQL databases, only two properties are fulfilled at a time, that is, either CA, CP, or AP.
Learn more about the CAP theorem with example cases in this insightful article.
SQL vs NoSQL Use Cases
SQL databases are preferred when scalability requirements are not very large. This simply means it won’t support concurrent requests from a large number of users such as those in big data applications.
Big data applications demand storage of huge sized and highly varied data that arrives very frequently on databases. These applications require processing of both structured and unstructured data as well as require high scalability needs.
For big data applications, NoSQL databases have immense use cases and are preferred over SQL based solutions.
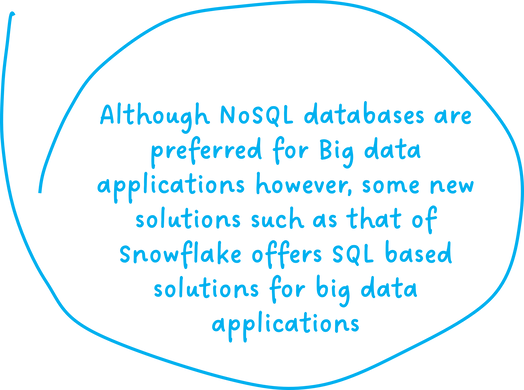
Quite surprisingly, today we see some unique database solutions that leverage the SQL language to query ‘big data’ stored across the distributed systems in the cloud. Examples include Snowflake’s relational database that is scalable as well as capable of storing semi-structured data.
Learn more about Snowflake’s unique approach in this comprehensive article.
Databases
Today the old SQL based databases have started to invent NoSQL like features to compete against the rising technology.
We call it ‘Combined Strength’ that uses the good points of both technologies to enable rich and more flexible database experience.
Today MySQL of Oracle has evolved to support semi-structured data such as JSON and document based files along with support for horizontal scaling
Meanwhile, on the non-relational end, NoSQL databases such as MongoDB also offer relational features such as indexing, aggregation queries, and ACID compliance in its document based data format.
Moreover, the noSQL databases have increasingly adopted a SQL-based syntax for attracting data analysts and data scientists who have extensive SQL experience and limited programing knowhow.
Adding to that, Cassandra has CQL, Spark developed SparkQL, and JIRA developed JQL.
Although the NoSQL databases have a lot to offer through its support for programming languages, building a SQL-like support can empower those with SQL know-how to use the best of their knowledge.
Conclusion
The SQL vs. NoSQL debate has evolved from a clear-cut dichotomy to a more nuanced understanding of their strengths and weaknesses. Modern databases often blend elements of both approaches, offering flexibility and scalability.
Dicecamp's Data Engineering Course Using SQL Server Tools could be a valuable resource for individuals looking to master SQL and its applications in the modern data landscape. By focusing on SQL Server tools, the course likely equips students with practical skills to work with relational databases and potentially explore their integration with NoSQL technologies.
Would you like to learn more about specific SQL Server tools or how they can be used in conjunction with NoSQL databases.
0 notes
Text
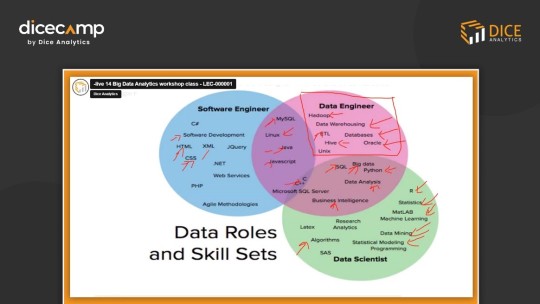
Data Roles & Skill Sets :
The data world offers exciting careers! Here's a breakdown of three key roles:
Software Engineer (Data Focus): Builds and maintains data infrastructure (programming, databases, APIs). Consider Dicecamp's "Backend Development with Python" course.
Data Engineer: Designs and manages data pipelines for analysis (databases, data wrangling tools, cloud platforms). Dicecamp offers a "Data Engineering Fundamentals" course.
Data Scientist: Analyzes data to extract insights and build models (statistics, machine learning, programming). Explore Dicecamp's "Machine Learning with Python" course.
Remember, these are brief descriptions. Check Dicecamp's website for detailed course content!
#dicecamp#datascience#data science course#data scientist#devopscourse#machinelearningcourse#pythoncourse#dataengineercourse#sqlcourse
0 notes