#difference between static and dynamic website pdf
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
difference between static and dynamic website pdf
Digpoint available website is a new digital website, in this website you will get a lot of computer related information, in this article post the difference between static vs dynamic website difference in hindi is well explained.
static vs dynamic website difference | static vs dynamic website difference in hindi | static vs dynamic pages | difference between static and dynamic website pdf
0 notes
Text
Tokenomics an advance strategy of Wasteinfonet
The Wasteinfonet company, which includes a business model totally different from anything that exists, carried out this challenge through its experts, capitalizes on several years of experience in local industries and communities. Founded in 2019, by Ph.D. Federico Fornicoia with a multidisciplinary team from several different cultures, bringing together the best in value-added IT software and services, Wasteinfonet is strategically positioned in its differentiated approach to global companies and municipalities (cities).

Total Supply
● WIF – TOKEN ISSUED-100,000,000.
● Total Uniswap Listing & Token sales (seed sales/private sale or main sale) 60%
● Team 15%
● Marketing & Bounty 15%
● Estimate Protocol fees 10%
Token Wif Utility
Our token has a fundamental utility, as a vehicle for interconnection between the circuits from where it is produced to where the information arrives. Internally, the team is convinced that a token was never as useful as ours will have, and this is because many crypto projects looked for the utility of their token, without having it and somehow made them have it just for investors to say it is a utility token.

Tokens Strategy
A sales planning will be carried out, which will act jointly with the people in the management of networks and systems. The attractiveness of tokens, everyone will want to buy the tokens because companies will need them to be able to pay the platform that will pay households in that way. Households can be investors and hold them, sell them on the market, or exchange them for some method of payment. But it is intended that they become crypto investors and retain them so
We are a dynamic, young, and totally innovative team, and we have come to introduce really attractive concepts and one of them is that developments in other layers of the platform can be added to the current main development, or changes in the platform, or added annexes that represent a moving and not static structure. Each of our future arms of the platform will be built to the extent that the main one already works according to the criteria determined in an automatic way, although always with central monitoring.
Learn more about the project:
Website : https://wasteinfonet.com Medium : https://wasteinfonet.medium.com Whitepaper : https://wasteinfonet.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/WHITEPAPER-WASTEINFONET-PDF-FILE..pdf Twitter : https://twitter.com/WasteInfonet Telegram : https://t.me/wasteinfonet1
Authorship
BitcoinTalk username : jorina_006
My Bitcointalk Profile Link : https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=2171158
Eth addtess : 0xC36a747dD8123b6A8a01061c3519a50d529EfF70
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
Andy Warhol And His Twelve Faces
Tate unleashes your inner…man during the ongoing Andy Warhol exhibition
Available to see : 12th of March - 15th of November 2020 at Tate Modern
by KLAUDIA KONDRACIUK | 25 OCT 20
The exhibition complements two already existing related events, Andy Warhol Inspired Dining destined for those who wish to enlengthen the experience and stay for… diner, enjoying dishes inspired by the exhibition as well as Members Hours: Andy Warhol, designed for people who value their alone-time spend with the artwork free of the other visitors. Three of them build the full experience of bringing back the memory of Andy Warhol at Tate Modern, the core being today’s topic.
The tittle of the exhibition corresponds with the organisation of the works within the place. Showcasing a lifetime of cultural identity, seen as both an artist and a man, with the latter being predominate, Andy Warhol is humanised in each of the 12 rooms situated at Tate Liverpool. As it is written at Tate Liverpool website of the exhibition: “[..] It draws attention to Warhol’s personal story and how his view of the world shaped his art” (Tate, 2020) and this is truthful to the reality.
Key of the display is the context of a contemporary art maker with the emphasis on personal drives and individual experiences that shape the artistry with theme of art mimicking life.
The rooms are reminiscent to use a form of a narrative, looking back to polyphonic novel, featuring variety of different voices and points of view. Every room unwraps a different chapter of the artist’s biography, narrating the life and artistry of Andrew Warhola in the times of social and cultural shifts, seen at different stages. They provide context of looking at him as a human of change, artist of many genres, political activist, lover, son, American, victim of a shooting, consequently moulding more philosophical, stoic art, achieving the reception of the viewer to be constantly challenged, bombarded by a different image of an individual over and over again. Seeing Warhol in 12 rooms makes an even more generalised division by grouping his life in three stages based on: cultural shift from a Czech ghetto to a new continent, queer identity and existentialism.
Every space creates a moment, achieved by a rather intimate space, in order to meditate over the displayed objects. It shows a dialogue between inclusivity of the public display with an homage to similar spirit of Pop, being a fully realised theme within the exhibition and darkened spaces (see room 6) which arranges a sense of confidentiality. This contrast provides additional dynamic of Room 2, which establishes the relationship of Warhol with his models and the viewers, subconsciously desiring for the same connection.
Execution of Room 2 copies this concept more literally, almost verbally, dedicating to the film Sleep. Made in 22 close-up clips during the spring and autumn of 1963 it examines influence of an oneiric element on the conscious. What function does it have? By showing someone’s act of sleep, something that intimate, the curators of the exhibition deliver quite the awakening. There is fear, desire and uncertainty brought from the world of dreams and implemented into the art. This is what droves an individual to make art. Linking this piece to draw upon those specific to human nature features suggests an everyday man point of view. Self-discovery through love unleash his inner artist even more and connect viewers with the nature of the exhibition, relating to one’s catharsis. At the end of a day, who is not inspired by the ones they love? Human act of creation is seldom dependent on this feeling, having its destructing and creative powers.
Male gaze is also noticeable within the numbers of the early drawings from the 1950s of the men he knew and desired, such as Charles Lisanby, a production designer, whom the artists travelled the world with and work Torso (1977).
The first, lack of predator toxicity, consequently achieving a feeling of curious self-discovery trough lenses of sexuality, emphasising on the interest of establishing queer identity. The later piece was described in the exhibition brochure, available in pdf format to gain additional insight of understating the context more : “This work is based on a Polaroid photograph of the actor and filmmaker Bobby Houston standing on his head. Warhol transforms the intimacy of the original image into a painting, which appears to reference ancient Roman sculpture and erotic photographs. Warhol referred to his paintings depicting male nudes as his ‘landscapes”.
By the use of linearity and synthesis together with care of detail (drawings), Warhol reveals his personal connection with the models within early drawings. Even though the forms are simplified,
the man differ from each other, carrying individualised physical qualities, allowing the viewer to even distinguish some personality traits, such as attachment, feeling of insecurity or pride. Whereas Torso (1977) is an ode to men’s body, reminiscent to Michelangelo’s fascination over what perfection human body is and what potential does it have in the surrounding him world. By the lack of characteristics, the depiction does not objectify man, but celebrates aesthetics of beauty in a Renaissance way.
It is a similar take to what the artist offers in Sleep, where the poet, John Giorno is glorified for his physical beauty, looking back at technique of foreshortening in Andrea Mantegna’s Lamentation of Christ. Both characters are static, however the connotations cannot be more unrelated. Having said that, they relay on analogy of putting the model on a pedestal, what gives an additional layer of analysis to Sleep, sacralising the idea of love. The viewer is meant to make analogies during this exhibition experiment, examining the same context from a different time perspective to notice nuances characteristic to where in his life Warhol is, which leads to a reflection of one’s personal growth.
Selection of different techniques, acrylic paint with screen-print on canvas and a simplified line show the need of experiment within the same subject matter. It allows to experience multidimensionality of different approach to the queer fascination, preventing the project to be realised as featureless.
Art of two different stages in his life, the period of cultural referencing capturing a sense of youth and post-shooting trauma, both still visually stimulating, but in different ways. Rooms 1-6 add a narrative of a world seen trough lenses of an excited and curious artist on the American scene of 1950s-1960s. Making art in the times of forbidden gay love, horror of AIDS, invading the continent since 1960s, loud political manifestations on the streets and racism was not creating a hospitable environment for self-expression. It is still a war, one after another, except for this time, people fight with the system among their country to defeat social constructs. The queer circle composed of poets, dancers, literates, designers and artists united to take a part in rewriting history. Ironically, some of them, including Warhol, became icons, faces of LGBTQ+ America, similarly recognisable to the ones, examined trough lenses of consumerism and social concept of a cult trough the technique of printmaking. This reasoning leads the audience to the room of Pop. Warhol being a prolific illustrator, but constantly driven to challenge himself, turns to advertising imaginary. The artist builds this pop, graphic version of himself, using personal experience to influence his career. Remembering struggles of his family’s emigrant background and poverty, he adapts the memory of eating a provisory version of a soup made of ketchup and salt to revolutionary idea of consumerist art, selling a dream of economic and social progress (Tate, 2020) Faced with criticism, Pop art, had its perfect justification to emerge at this moment in history, just after the time of Utility scheme, providing context for Warhol’s work. Romanticising of liberal accessibility of goods and art for the mass consumer. Although his pop oeuvre shows all of these signs, it also foreshadows a part of him being dominated by the idea of death, which will evoke in pieces like Skulls (1976), Sixty Last Suppers (1986) and Richard Avedon’s photography of Andy Warhol (1969). This pessimistic school of thought was developed because of the incident of the 3rd of June 1968, the writer Valerie Solanas came to the Factory and shot Warhol, damaging his internal organs. Warhol was rushed to hospital and was declared clinically dead, but doctors managed to revive him. (Tate, 2020) The last example takes inspiration form the world of classical art, Leonardo da Vinci, his family kitchen, where the copy was hung and reacts to death of his former lover, Jon Gould. It is a bridge between old and young, the yin and yang perspective on art yet dominated by foreground decadency. Sixty Last Suppers could be seen as a moving portrayal of endless loss, reminiscent of ‘columbarium’, the wall graves found in many cemeteries. (Tate, 2020) Printmaking and copies are very telling in this context. Just like the blurring image of the last copy of Marilyn Monroe, both the image of the 12 apostles and the actress, die becoming a caricature for the sake of the masses.
It is comparable with the recent phenomenon of the aesthetic of a French Girl , (Vogue 2020) generalising and romanticising the visuals of a young woman living in Paris, including a nonchalant look and making it easier to mimic by non-French masses to copy. In result, both of these examples are one nation centred, protecting one’s social appearance such as the idea to fit in. They are both delusional and almost mythical, playing a role in constructing a disappointing in reality expectation such as The American or French Dream. Curation of this piece, just like Pop art uses the tool of nostalgia, taking the viewer back to their adolescence to draw upon positive emotions often associated with one’s years of youth. Warhol dreams five times throughout the exhibition in Sleep, Self-Portrait, Pop period (Campbell’s Soup Cans, 1962), depicting Debbie Harry (1980), who daydreamed that Marilyn Monroe was her real mother and Silver clouds (1966). The not yet mentioned Paintings that float (Tate,2020) reveal the artist need for the audience to engage with his work.
Unconventional sculptures were made to interact with the viewer, bringing the association of waking dream, which could be arranged any way the audience like, becoming the masters of their sleep.
In the context of the exhibition, the chosen pieces help to realise Warhol as a man with secondary look at the artwork itself made for the art’s sake.
The exhibition is based around diversities of 12 rooms, adapting a book narrative, each room represents a chapter in Warhol’s biography and 3 perspectives, which are created by the viewer itself reacting to the way of display, grouping artworks based on the feeling of similarity. The viewer connects the dots, concluding that some pieces even though coming from different rooms, show a level of likeness, although the artworks come from different time periods. For example, audience might reject the chronological order of the works or rooms, because the final result will not be affected.
Instead of disorganising, this natural need of making relation between elements helps to understand that a person (Warhol) is not closing one chapter of their life irreversibly, but the doubt and fear might occur even at the final stage of someone’s life and happiness could be found beyond traumatic experience. Therefore, the exhibition is not quite autonomous, but proves that is well placed since Constellations, also situated at Tate, is using comparable visual vocabulary to examine Walter Benjamin’s theory of the thought image, holding similar concepts to the nature of this review, often build on non-chronological order of events. This narrative discloses new meaning of the context and potential of the exhibition.
According to the statement Curating is an art of storytelling (Kholeif, 2019), the audience feels hospitability to take a part in this experience of self-discovery, no matter what stage of life the viewer happens to be at. Ironically, diversity bring Tate’s audience together, connecting it with the exhibition, using catharsis as a tool of awakening the relatedness to the artist.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Php training course
PHP Course Overview
PHP is a widely-used general-purpose scripting language that is especially suited for Web development and can be embedded into HTML.
PHP can generate the dynamic page content
PHP can create, open, read, write, and close files on the server
PHP can collect form data
PHP can send and receive cookies
PHP can add, delete, modify data in your database
PHP can restrict users to access some pages on your website
PHP can encrypt data
With PHP you are not limited to output HTML. You can output images, PDF files, and even Flash movies. You can also output any text, such as XHTML and XML.
PHP Training Course Prerequisite
HTML
CSS
Javascript
Objectives of the Course
PHP runs on different platforms (Windows, Linux, Unix, Mac OS X, etc.)
PHP is compatible with almost all servers used today (Apache, IIS, etc.)
PHP has support for a wide range of databases
PHP is free. Download it from the official PHP resource: www.php.net
PHP is easy to learn and runs efficiently on the server-side
PHP Training Course Duration
45 Working days, daily 1.30 hours
PHP Training Course Overview
An Introduction to PHP
History of PHP
Versions and Differences between them
Practicality
Power
Installation and configuring Apache and PHP
PHP Basics
Default Syntax
Styles of PHP Tags
Comments in PHP
Output functions in PHP
Datatypes in PHP
Configuration Settings
Error Types
Variables in PHP
Variable Declarations
Variable Scope
PHP’s Superglobal Variables
Variable Variables
Constants in PHP
Magic Constants
Standard Pre-defined Constants
Core Pre-defined Languages
User-defined Constants
Control Structures
Execution Control Statements
Conditional Statements
Looping Statements with Real-time Examples
Functions
Creating Functions
Passing Arguments by Value and Reference
Recursive Functions
Arrays
What is an Array?
How to create an Array
Traversing Arrays
Array Functions
Include Functions
Include, Include_once
Require, Require_once
Regular Expressions
Validating text boxes,emails,phone number,etc
Creating custom regular expressions
Object-Oriented Programming in PHP
Classes, Objects, Fields, Properties, _set(), Constants, Methods
Encapsulation
Inheritance and types
Polymorphism
Constructor and Destructor
Static Class Members, Instance of Keyword, Helper Functions
Object Cloning and Copy
Reflections
PHP with MySQL
What is MySQL
Integration with MySQL
MySQL functions
Gmail Data Grid options
SQL Injection
Uploading and downloading images in Database
Registration and Login forms with validations
Pegging, Sorting,…..
Strings and Regular Expressions
Declarations styles of String Variables
Heredoc style
String Functions
Regular Expression Syntax(POSIX)
PHP’s Regular Expression Functions(POSIX Extended)
Working with the Files and Operating System
File Functions
Open, Create and Delete files
Create Directories and Manipulate them
Information about Hard Disk
Directory Functions
Calculating File, Directory and Disk Sizes
Error and Exception Handling
Error Logging
Configuration Directives
PHP’s Exception Class
Throw New Exception
Custom Exceptions
Date and Time Functions
Authentication
HTTP Authentication
PHP Authentication
Authentication Methodologies
Cookies
Why Cookies
Types of Cookies
How to Create and Access Cookies
Sessions
Session Variables
Creating and Destroying a Session
Retrieving and Setting the Session ID
Encoding and Decoding Session Data
Auto-Login
Recently Viewed Document Index
Web Services
Why Web Services
RSS Syntax
SOAP
How to Access Web Services
XML Integration
What is XML
Create an XML file from PHP with Database records
Reading Information from XML File
MySQL Concepts
Introduction
Storage Engines
Functions
Operators
Constraints
DDL commands
DML Commands
DCL Command
TCL Commands
Views
Joins
Cursors
Indexing
Stored Procedures
Mysql with PHP Programming
Mysql with Sqlserver(Optional)
SPECIAL DELIVERY
Protocols
HTTP Headers and types
Sending Mails using PHP
Email with Attachment
File Uploading and Downloading using Headers
Implementing Chating Applications using PHP
and Ajax
SMS Gateways and sending SMS to Mobiles
Payments gateways and How to Integrate them
With Complete
MVC Architecture
DRUPAL
JOOMLA
Word Press
AJAX
CSS
JQUERY (Introduction and few plugins only)
1 note
·
View note
Text
Egretia - Bring Developers and HTML5 Terminals to the Blockchain World
Egretia Ad Platforms : Distributed Communications and Storage Platform :

As a cross-platform arrangement, HTML5 innovation has been internationally perceived. It covers the Internet, video, promoting and different ventures, with the worldwide market size of many billions dollars
This task participating with Egret Technology, an internationally understood HTML5 technology specialist organization, set up Egretia Blockchain Lab, joining blockchain with HTML5 technology to make the world's first HTML5 blockchain motor and platform, going for applying blockchain to vertical businesses. Bringing Egret technology’s current 200,000 designers and 1 billion portable terminal gadgets into the blockchain world, this undertaking has commonsense and broad criticalness
What is HTML5 Technology?
HTML5 is the most recent form of Hypertext Markup Language, the code that portrays site pages. It's really three sorts of code: HTML, which gives the structure; Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), which deal with introduction; and JavaScript, which gets things going
Utilizing the energy of portable long range informal communication, HTML5 content has been broadly scattered in versatile applications and made altogether new plans of action

What is BlockChain Technology?
A blockchain,originally square chain,is a consistently developing rundown of records, called pieces, which are connected and secured utilizing cryptography.Each square regularly contains a cryptographic hash of the past block,a timestamp and exchange data.By plan, a blockchain is characteristically impervious to adjustment of the information. It is "an open, circulated record that can record exchanges between two gatherings proficiently and in a certain and changeless way".For use as a disseminated record, a blockchain is regularly overseen by a shared system all in all holding fast to a convention for between hub correspondence and approving new squares. Once recorded, the information in any given piece can't be changed retroactively without the adjustment of every single consequent square, which requires agreement of the system dominant part.
Blockchains are secure by plan and embody an appropriated processing framework with high Byzantine adaptation to non-critical failure. Decentralized agreement has along these lines been accomplished with a blockchain.This makes blockchains conceivably appropriate for the chronicle of occasions, medicinal records,and different records administration exercises, for example, character management,transaction preparing, reporting provenance, nourishment traceability or voting.

World's First HTML5 Blockchain Engine and Platform In organization with Egret Technology, the worldwide pioneer in the HTML5 business, Egretia focused on building the world's first HTML5 blockchain motor and platform, joining blockchain technology with demonstrated devices, groups and substance of our accomplices, expecting to bring 200,000 developers and 1 billion mobile devices into the blockchain world.
Building a Decentralized HTML5 User Ecosystem
Fueled by the Egret Engine, HTML5 content has more than 75% promoting infiltration in the HTML5 business, covering in excess of 1 billion mobile devices furthermore, clients. We will join the Egretia blockchain with Egret HTML5 work processes. Utilizing a token system, each player will have a one of a kind ID in diversions controlled by the Egret Engine. This will assemble a strong establishment for a steady client ecosystem.
Creating an Ecosystem With True Token Circulation
In light of the client ecosystem of Egretia, we are dedicated to producing another computerized token that can be utilized as a part of all substance fueled by the Egret Engine: Egreten. • Developers will utilize settled devices + SDKs to rapidly create items that will utilize the Egreten token as installment. • Users can utilize Egreten to purchase in-amusement things, pay for content, and so on. • Users can utilize Egreten to participate in lotteries, rebates, and different advancements on Egretia over the world. • Users can get Egreten as reward through taking an interest in crowdfunding of recreations on Egretia. • Developers and substance distributers can utilize Egreten to promote on the Egretia promoting stage. • Distributors can get Egreten through substance conveyance, promoting, and so forth. • An Egreten computerized wallet is made in light of client's remarkable token travel permit, in request to ensure safe stockpiling of client's virtual resources, products, crowdfunding rewards, platform rewards, and so on.

Egretia key Products and Services
* Blockchain Game Dev Workflow : The world's initially entire HTML5 blockchain motor and improvement unit, will enable engineers to rapidly and productively create blockchain recreations and applications.
* Distributed Communications and Storage Platform : The stage will use the blockchain's hub mode, giving decentralized information correspondences also, capacity arrangements.
* Game Distribution Platform : This platform is our authority Egretia DApp: Players can get Egreten through the application, play HTML5 recreations on this platform , make installments through Egreten. Utilizing the Proof-of-Game (POG) instrument, players can get Egreten remunerates by playing or offering diversions to companions
* Virtual Goods Trading Platform : Utilizing Egreten, all players in Egretia recreations can exchange their virtual products on this platform.
* Egretia Ad Platforms : An exactness promoting framework, in view of blockchain KYC standards, brilliant contracts, and platform computerized tokens.
* Egretia Incubator : Our hatchery bolsters diversion improvement groups and people, making a scaffold amongst players and designers.
Egretia Features
* Egretia Features : We will give Egretia, a self-created, proficient open chain in light of the DPoS (Designated Proof of Stake) agreement component, going for streamlining HTML5 amusement execution. Through the blockchain interface layer, in mix with the Egret motor devices, designers can rapidly make blockchain-based DApps
*Consensus Mechanisms : The Egretia open chain will utilize a DPoS (Delegated Proof of Stake) as accord instrument. The DPoS system is like a board vote, where holders of coins cast a certain number of hubs, utilizing the system for check and accounting. DPoS can essentially diminish the quantity of taking an interest hubs for check also, accounting, it will have the capacity to accomplish agreement confirmation in a moment. The dependability of DPoS component has been checked in BTS, EOS and different undertakings
* High-Performance : Egretia is an open chain with high simultaneous handling power, where execution is advanced for the necessities of the diversion business. It has a quick TPS (Transaction Per Second) rate. Regardless, in blockchain innovation, an "outlandish triangle" exists, implying that adaptability, decentralization, and security can't be accomplished at the same time. Utilizing a DPoS component to significantly build adaptability, in excess of 2000 exchanges every second could be upheld in the underlying test chain. Later on, we will increment the TPS as indicated by business needs.
*Real time parameter adjustment : Egretia can change framework parameters without bifurcation: Instead, Egretia will be ready to change blocktime, blocksize, exchange charge and so forth through voting. Egretia can alter the framework parameters without bifurcation: Instead, Egretia will have the capacity to understand a dynamic change of parameters, for example, blocksize, yield speed, and dealing with charge through voting strategy in view of agreement.
*Convenient and efficient development tools : The demonstrated devices of Egret establishes a strong framework for the Egretia blockchain venture, making blockchain application improvement basic, advantageous and effective.
Lab Core Team
Peter Huang

Dirk Meyer

Yin Ma

Ross Przybylski

Advisors
Lucas Lu

Frank Lee

Yao Yong

Hongfei tian

Egretia website : https://egretia.io/Egretia White-paper: https://egretia.io/static/Egretia_White_Paper_EN_V1.1.pdf
Bitcointalk profile : https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=1583686
youtube
youtube
91 notes
·
View notes
Text
Small Business Video Marketing Ideas That Will Leave You Dumbstruck 2021
It is estimated the 82% share of internet website traffic is video in 2022. However, do you think you're still unsure what you can do to create an effective video for your company?
The promoting company of any type doesn't have to rely on expensive creation studios or revisit your videos for the duration of time. It means that developing your business using video isn't an unrealistic dream. In fact, you can create an important video with the idea that of explainer videos.

Why do private businesses require video advertisements?
Video marketing expands the availability of creative resources and turns B-roll into a treasure trove of brand new advertising concepts that range from traditional to paid.
Testimonial websites: those where your customers guss about you.
There's a reason why people review Amazon studies before deciding what's required in a purchase... The conclusions of the consumer are important. In
However it is true that the typical text snippet will however, in reality, only accomplish very little. When you add video, the customer's testimonials are significantly less slender making them top-to-bottom (and trustworthy!) examinations of the value your company can provide.
No matter if you're B2B or B2C showing issues and arrangements that your company settles on is a that is a cherry on top as a general rule. You may go into depth and create a variety of tributes to an product, or take a broad approach, capturing a single tribute to your many contributions. Whatever approach you decide to take, the footage can help your tributes stand out.
It is possible to use item surveys or share examples from clients of triumph over adversity, or provide an open-ended discussion about your operations. This is applicable to many SMBs that are creative and use donations to support their business. This can lead to businesses on the internet sharing fantastic reviews of their latest product drop.
How do I create an effective business video?
Thinking about creating an effective video for your business? You can produce an online video by yourself or contact a video production firm like the Essence Studio to make a great video for your company.
Tips for business advertising using videos
If you've created some videos to serve as the base of your personal enterprise's marketing, you're ready to discover the best practices to display (and distribute!) these resources throughout an extensive biological system.
Upload video to your website.
Integrating video on your site increases the tenacity of your site. According to studies that are mentioned in Forbes the average person spends 2.6x more time on websites that have video content than with no video. This is great news for small businesses hoping to earn a profit from advertising on their websites; however, it's helpful for sites that are primarily trying to be discovered. In addition, more visible site commitments and longer staying durations further improve SEO.
The videos you embed on your site aren't required to be long-form. Video can be used to showcase recent deals or add spice to the presentation by incorporating interactive development. Create short item demonstrations that last for a few seconds which will aid to build the image of your company.
Create short promos from your longer, drawn-out recordings.
With the help of online services that are accessible to you, basic films can be used to be used for different crowds and stages in just a few minutes. In reality, entrepreneurs who are using these services frequently cut their current film into shorts or ads with the help of natural, adapted formats.
Include video in your email to show off.
Every now and then you'll need a bit of determination to be different in a private way. The addition of video to your emails will increase click-through rates by 300%, according to research stated by Hubspot. This alone should be enough to convince you to integrate an item video to be included in your company's own email advertising system.
Enhance your experience by using your contact structure. Here you can make the watchers segment or psychographic inquiries discover the interests of your customers and broaden your range of information to make your marketing email content more relevant to your audience.
Add recordings and GIFs to your messages using our tool, which integrates the top email platforms such as HubSpot Mailchimp, HubSpot, Campaign Monitor Constant Contact and Keep. Additionally, you can alter the clasp that will be circling for six seconds in your GIF in the email. No more gruelling static screen shots!
Check out other ways to switch leads using video.
Adobe Document Cloud with Google Drive is an integrated bundle of PDF-related services that allows you to accomplish these things open and browse PDFs online using Adobe's web-based, high-quality PDF previewer. Make Adobe PDFs that keep formatting, fonts and layouts.
Chat with your friends about secrets.
If you've crafted your explanations rearranged into short, ad-hoc promotions They're ready to communicate all over the globe. Videos can make a difference between a static social feed from dynamic developments. Even tweets that have video attract a 10x higher number of people to commit than tweets that do not have video.
The independent company video showcase isn't typically an "purchase currently" source of motivation (CTA) with a friendly. The recordings can also provide an opportunity to increase awareness of the brand and to review without selling videos, reels and Stories on Instagram or short video clips on Facebook. The greatest part is that this set of video content takes only a few some time to make move, distribute, and transmit.
Content such as recordings of me preparing morning schedule tips and guides to setting objectives are not necessarily lead-supporting equipment, demonstrating your credibility and expertise as a comprehensive instructor without being too salesy.
People will always have to know what your personal identity is, what your specialization is, the reason you choose to do what you do and the reasons why they need choose your product or service.
Original content by this URL https://medium.com/@essencestudios2d/how-to-small-business-video-marketing-ideas-that-will-leave-you-dumbstruck-44aacb623984
0 notes
Text
Shiny R Markdown


This website is generated using RMarkdown.
RMarkdown is great for creating quick professional looking reports, with embedded R function output with or without the code that created them.
This is an introduction to the basic features of R Markdown, and R Markdown Playground Application as part of the book on Statistical Programming used as a s. Integrating Shiny Apps with R Markdown. A full introduction to shiny app development is beyond the scope of this post, we will cover the basic elements here in order to use the calendar fully. Shiny App Basics. A shiny app consists of two main parts, the UI (User.
R Markdown supports dozens of static and dynamic output formats including HTML, PDF, MS Word, Beamer, HTML5 slides, Tufte-style handouts, books. Shiny, R Markdown, Tidyverse and more. Hosted Services Be our guest, be our guest. Do, share, teach and learn data science. RStudio Public Package Manager. An easy way to access R packages. Let us host your Shiny applications. Professional Enterprise-ready.
You can schedule reports by scheduling the RMarkdown document like you would any R script.
Options include: PDFs, HTML, MS Word, Slides, books, websites (like this one).
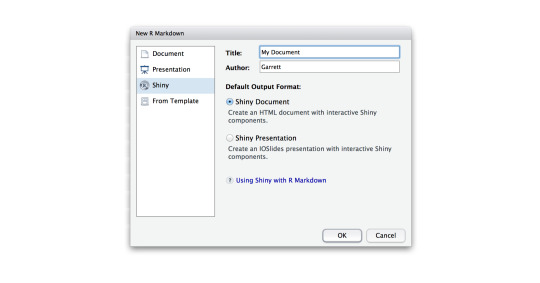
By default, a new RMarkdown document will contain the text below (shown in light gray).
R Markdown
This is an R Markdown document. Markdown is a simple formatting syntax for authoring HTML, PDF, and MS Word documents. For more details on using R Markdown see http://rmarkdown.rstudio.com.
R Shiny Markdown Output
When you click the Knit button a document will be generated that includes both content as well as the output of any embedded R code chunks within the document. You can embed an R code chunk like this:
Including Plots
You can also embed plots. For example:

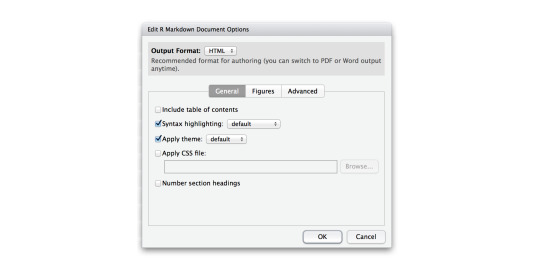
Rmarkdown In Shiny
Note that the echo = FALSE parameter was added to the code chunk to prevent printing of the R code that generated the plot.
Shiny is a web application framework for R, produced by RStudio.
A Shiny app usually has two files, server.R and ui.R. These take care of the web server backend and the HTML frontend, respectivily.
To run a Shiny app you need to have a Shiny server running. RStudio comes with one pre-installed for running your apps locally, but for publishing you will need to install Shiny server or host via shinyapps.io.
Shiny apps use a functionality called reactivity that means that apps can be quick and responsive to changes to inputs. This is one of the best features of Excel, where changing one cell can have consequences throughout the Workbook.
Shiny apps can be tricky to get your head around due to the fact that they have a different work flow from normal R programs. It’s recommended to go through the tutorials online.
A recent development is the ability to put Shiny elements into an RMarkdown document.
These documents, again, need a Shiny server to run, but take advatage of the easy formatting of RMarkdown to present the user interface - server and UI elements sit in the same document.
RMarkdown - supplies the HTML instead of a ui.R file.
Shiny - supplied reactive components within your RMarkdown
An example RMarkdown document with a Shiny element taking care of authentication can be found here.
There are a few options for data presentation using R so an overview is first presented to help you decide which to choose.
NameInteractiveOutputEase of useCostServer needed?ShinyServer-side and client-sideHTMLAdvancedFree for Shiny Server, $9995 for Shiny Server Pro, $9+ a month Shinyapps.ioYesRMarkdownclient-side onlyHTML, PDF, Word, etc.EasyFree, can also publish to a Shiny serverOnly a normal HTML server if you want to host those (e.g. Github Pages lets you host for free)FlexdashboardServer-side and client-sideHTMLEasyFree, can also publish to a Shiny serverIf using Shiny elements, yes
It generally comes down to the amount of interactivity you need in your app. For a full solution where data is updated and processed in real-time, Shiny is your best option. If you just need a nice format for presentation offline, then RMarkdown can produce some very nice looking formats.
Flexdashboard is a bit of both - it is essentially an RMarkdown document that allows Shiny elements to be placed within it.
All the above is further complicated by HTML Widgets - these render in JavaScript that can do a lot of interactivity by itself, so if you can find a JavaScript library that gives you say dropdowns, then you can use that in RMarkdown instead of using Shiny, without hosting a Shiny server.
Shiny
Shiny is a R package by RStudio that lets you run reactive apps on a special Shiny server.
Shiny server
A Shiny server can be installed on a dedicated machine, or it comes bundled with RStudio for local testing. Before you deploy an app online you will need to have a Shiny server available to publish to. At the moment your options are:
Host it yourself on say Google Compute Engine
Publish to https://www.shinyapps.io/
Publish to an RStudio Connect service
Reactive apps
Shiny uses a special approach known as reactive in making its apps. This allows for very responsive applications. A typical Shiny app has two elements - a UI script that is in charge of rendering the HTML front end, and a server script that takes care of which R code is run when elements on the UI change.
RMarkdown
RMarkdown takes a different approach - it renders a special flavour of Markdown into a standard format, which is then in turn rendered into the end product. The end product varies between HTML, PDF, Word etc.
Because the end product has no link with the code made to create it, you can’t call R functions from a final RMarkdown product. However, you can render using JavaScript that can interact with the data on the page in real-time (for HTML apps, it obviously wouldn’t work with a PDF!)
This documentation is written in RMarkdown, as an example.
Flexdashboard
Flexdashboard is a bit of both. You write pages in RMarkdown that can include Shiny elements. If you do incude Shiny elements, then when you publish, flexdashboard uses RMarkdown to create the HTML, and then runs a Shiny server to provide the elements.
Getting Started
The steps required to add Shiny components to a flexdashboard are as follows:
Add runtime: shiny to the options declared at the top of the document (YAML front matter).
Add the (.sidebar) attribute to the first column of the dashboard to make it a host for Shiny input controls (note this step isn’t strictly required, but many Shiny based dashboards will want to do this).
Add Shiny inputs and outputs as appropriate.
When including plots, be sure to wrap them in a call to renderPlot. This is important not only for dynamically responding to changes but also to ensure that they are automatically re-sized when their container changes.
Simple Example
R Markdown Package
Here’s a simple example of a flexdashboard that uses Shiny:
Shiny And R Markdown
Source Code
The first column includes the (.sidebar) attribute and two Shiny input controls; the second column includes the Shiny code required to render the chart based on the inputs.
One important thing to note about this example is the chunk labeled global at the top of the document. The global chunk has special behavior within flexdashboard: it is executed only once within the global environment so that it’s results (e.g. data frames read from disk) can be accessed by all users of a multi-user flexdashboard. Loading your data within a global chunk will result in substantially better startup performance for your users so is highly recommended.

0 notes
Text
Top 14 UX Software For UI/UX Designers
UX Software
UX Softwares is responsible for creating user-centered designs that focus on accumulating requirements. It designs and improves the usefulness and usability of products on part of the end-user.
UI UX software manufactures highly faithful prototype products that allow us to design products for existing users for usability testing. We can use it before starting projects, so it saves lots of money for stakeholders.
How can the best prototype tool be found?
We know that so many different kinds of industries work. Every industry has its target audience and always has a different preference. The software of UX design also agrees with projects. Therefore, the design process is unique for most customers.
Designers always search for the best prototyping tool by-product, choice, and other factors. It depends on the projects and guidelines of its customers. The designer selects advanced instruments most of the time according to a client niche.
UX Wireframing & Prototyping Tools Design
A lot of advanced UI UX design software is available on the market. The best way to give any project a fresh look is by using the right UX software.
We discuss some new, trendy tools that contribute to the stylish development of websites or apps. It helps the websites to look at their organic traffic and to improve it easily.
Adobe XD
Adobe XD allows vector-based user interface tools to create interface-based prototypes and mockups. The UI UX software is renowned for designers who used other products from Adobe.
It comes with a real-time partnership, which offers many UI designers a solution. Another one of the unique design platforms that connect various disciplines is Adobe XD with advanced tools for UI UX designers.
Figma
Figma was the first browser-based interface design software that makes software building for teams simpler. These tools can be used easily because uploading, downloading don’t need to worry.
It allows us to develop design systems with related UI factors that can be used by the entire team. UX software reduces the interference of visual concepts in code and allows us to be flexible and controlled.
Sketch
The sketch is a lightweight UI UX UI software for UI/UX designs based on macOS. It comes with many new features such as infinite zooming, 2x export, and styled vector forms that are suitable for different resolutions to help you achieve professional results.
The 'Export All' column is provided by Sketch to enable designers to easily export PDF, JPG, and PNG files.
MockPlus
As dynamic as any other prototype UX software, MockPlus is as accurate. This software can easily be used because it is free of code, provides a simple drag and drop option, and forms a link to interactive pages and factors.
It has 3000 UI icons and 200 components parallel to Android, iOS, and PC programs, which is an impressive UX software solution. Our teams, group projects, collaborative development, online review, and other features are available.
POP
However, in searching for a practical prototype compatible with our Android device POP POP (PROTOTYPING ON PAPER) is useful. It is a UX design software that is easily used for the development of mobile prototyping from paper to digital prototyping. There is no visual restriction in the app because we have chosen a prototype suitable for a device.
UXPin
UXPin is an absolute UX software wireframing and prototyping. They are equipped with an interface and features that help us to understand a design and create highly interactive wireframes and prototypes.
UI UX designers are able to make design decisions, test usability, count users and their clicks, and submit team results.
It has a dynamic software kit with various design elements and patterns for brilliant scratch designs. We can edit all UXPin images and modify their luminosity, sharpness, contrast, and transparency with convenience.
Proto.io
It makes prototypes very attractive that need to look and feel connected with our mobile apps. This UX design software can be used to test your prototype designs on different devices.
Proto.io has a nice feature in which we increase the application's efficiency. The program includes Dropbox synchronization, Adaptive UI libraries, UI Material Design and Offline mode, and many more features. It is an app for designers to organize fast changes and co-relate easily with other team members.
Zeplin
It is a plugin and Web application adaptable to Sketch and includes in a concerted specification sheet all the characteristics of the selected elements, explaining the handoff between the design and the developer’s teams. It is the best example of UX design software.
Zeplin is effective because it is not necessary to wait until the end of the design process to hand over the developers' contributions. It improves the entire app development process.
Axure
It is the best UI UX wireframing software for websites and applications. it is a zero-coding program.
Axure includes all documentation software needed for the design choices and layouts of documents. The standard edition or pro edition can also be selected as required.
It is the largest application developed for state-of-the-art Prototype solutions and is the best prototype feature of reactive websites and mobile apps.
JustInMind
It's incredible UX prototyping software that allows us to make prototypes for mobile apps and websites better and quicker. JustInMind has a magnificent widget library to enter HTML, video, online widgets, documents, interactive maps, and many more.
UX designers can also add UI library factors for perfectly building master pages. This tool makes it easy for designers to create websites for advanced management and to use apps to boost customers' business.
HotGloo
The powerful UX prototyping software for wireframe uses a wide variety of mobile apps that require a special user interface. The interactive feature of UI UX software design enables one app designer to work together on a single wireframing application project.
Without restricting the browser or operating system, we can work on our wiring project anytime.
Marvel
It turns raw paper sketches into attractive, tappable prototypes that allow designers to demonstrate our approaches to apps and to build up feedback from others.
It works well with.psd files, which are easy to change before you upload. In the background, Marvel maintains the changes in testing times.
It allows designers to import from Sketch, develop prototypes of app interactions, animations, transitions, and advance these prototypes with stakeholders and developers.
Invision
It includes special features like workflow, collaboration, and prototyping of UX software, which transform our static apps into fully interactive prototypes.
Prototypes contain animations, transitions, and actions for Android, iOS and responsive web apps is the most impressive feature of this program. It helps us provide the first-hand navigation experience and convert sales to proposed customers.
Slicy
The product is supplied as resources for our Website or application with reactivated Photoshop cutting and export PSD factors. Policy exports groups of layers individually, giving full freedom to operate, overlap or hide design items.
It focuses entirely on the export of services to GIF, JPG, PNG, and image formats from Photoshop PSD. We know that drag and drop a Photoshop file that exports files automatically makes exporting assets easy.
Conclusion
There is numerous UX software that helps us to create websites or applications in the best possible way. Each design agency or team of designers has its preferences.
It depends most of the time on the project type. Each project has its UX software design preferences. Our designer makes websites and apps more engaging with the latest designs.
We help you if you are new to the company or wish to redesign your website or mobile apps. Call for more information or drop a query.
0 notes
Text
static vs dynamic pages
In Digipoint available website you will find articles in Hindi language related to mobiles and other electronics devices, many computer and other topics like static vs dynamic pages.
static vs dynamic website difference | static vs dynamic website difference in hindi | static vs dynamic pages | difference between static and dynamic website pdf
0 notes
Text
Entrepreneur's guide to getting a profitable website.
Do you remember how websites used to look in the early 2000s? Those of us fortunate enough to have survived the 90’s will agree that websites were once strictly utilitarian. Most of them were awfully boxy and cluttered with information. There were practically no design principles incorporated and the primary function was to display information and do nothing else.
We have come a long way since. Technology has evolved drastically over the last 2 decades. So much so that most trade and transactions now occur in the digital format. Web applications have successfully added ease and extensive connectivity to our lives.
Web development has changed the way the world does business. Today, everything from raw materials to an enhanced investment portfolio can be achieved online. It is a common fact the businesses have been the chief benefactors of the website boom globally. However, not every company understands the fundamental basics of setting out into the digital world.
What are web applications?
If you’ve ever used an online banking service, or messenger or have tried to gather information from the internet, you can be sure that you’ve used a web application. Simply put, a web application is a system that allows users the capability to perform tasks over the internet.
One might wonder if there might be a difference between a website and a web application. A website is simply a static page that does nothing other than displaying information. Whereas, a web application is a dynamic experience, enabling users to interact with the information provided. An uncomplicated way to look at it is that a web application is any website that allows users an interactive and participatory experience.
Web applications can have a variety of avatars. Let's look at a few:
1. Static application
These applications are simple and meet the purpose of displaying information in the form of text, photos, gifs, etc. Static applications have extremely limited interactive capabilities and are not suggested models for businesses. A digital resume or PDF is a good example of a static application.
2. Dynamic applications
These applications are far more technically complex as compared to static applications. They allow users a more robust experience and also permit interaction. Dynamic applications are created using a variety of programming languages like Java, HTML, etc. Most websites used daily are dynamic applications.
3. E-commerce application
These applications allow the purchase and sales of goods online in addition to making digital transactions. E-commerce applications are extremely dynamic and incorporate a variety of technologies that seamlessly integrate to provide users with a hyper-interactive experience.
If you are an aspiring entrepreneur and need a web application developed for your product, you should know that there are a myriad of technologies that can be implemented to help you succeed. These technologies however require subject matter expertise. This is why most successful startups work with web development companies.
0 notes
Text
static vs dynamic website difference in hindi
When it comes to creating a website, there are two broad categories to choose from: static vs dynamic website difference in hindi.Understanding the differences between these two types of websites is crucial in deciding which one is best suited for your needs.
A static website consists of web pages that are fixed and display the same content for every user. These websites are typically created using HTML and CSS, and they are simple and easy to create. However, they offer limited functionality and interactivity, making them less suitable for complex or interactive websites.
Static websites are perfect for small businesses that do not require a lot of interaction with their customers. They are also suitable for personal websites or blogs that do not require frequent updates. Static websites are easy to host, and they load quickly since there is no need to query a database or execute server-side scripts.
On the other hand, dynamic websites are more complex and offer greater interactivity and functionality. They are built using server-side programming languages such as PHP, Python, or Ruby, and their content is generated dynamically based on user input or database queries. This means that dynamic websites can be customized for each user, offering a personalized experience.
Dynamic websites are ideal for large businesses, e-commerce websites, and social networking platforms. They allow for complex functionality such as user registration, login, and content management. Dynamic websites can handle a large amount of data and can be easily scaled to accommodate growing traffic.
Another major static vs dynamic website difference in hindi is how they are maintained and updated. Static websites require manual updates to each individual page, which can be time-consuming and tedious. Dynamic websites, on the other hand, use content management systems (CMS) that allow for easy updates and maintenance. This makes it easy to add new content, change the website's design, and manage user data.
static vs dynamic website difference | static vs dynamic website difference in hindi | static vs dynamic pages | difference between static and dynamic website pdf
0 notes
Link
Many restaurants around the world have been seriously impacted during the Coronavirus pandemic. People are now looking for inventive ways to provide contactless dining to their customers. The contactless menu is an excellent way of reducing social contact while ensuring secure service.While dine-in interaction may be challenging to minimize, there are different methods for minimizing interaction between your clients and staff, such as QR codes based Digital menu. Digital menus could be essential to the success of a pandemic by using QR code menus.

What Is QR Code & How does it Function?
QR codes – short form for Quick Response codes, like bar codes that can be used at a retailer. A QR code menu is a digital menu that uses a generator of online QR code to create a menu. This form of digital menu uses QR codes in its menu embedding PDF/Image. It replaces paperback menus, which raise the risk of transverse contamination.
Customers can scan square QR Code using a cell phone. This allows them to gather information you prefer such as your digital menu or website. The QR code is fast and easy to scan. Most of the smart phones have a QR code scanner built-in. The QR scanner is integrated into the Camera App, for example, on the iPhone. Only direct your back camera to a QR Code and your iPhone will recognize the code automatically. You are then prompted to open the selected destination with a notification.
What are the benefits of the QR menu?
A QR code menu is a must for cafés and restaurants seeking to comply with guidelines on social distances and hygiene.Physical menus are one of the most affected items in a restaurant that are exchanged between customers. By scanning a QR code associated to a digital menu, you can help facilitate social distance and offer your business a touch-less service to its customers.
A QR menu that is easy to set up is a smooth user experience for your customers. As a company, it promotes the acceptance of orders for you and, in turn, allows the management to concentrate on other business needs. We at Trovend provide you a customization of your dine-in and take-out menus with QR-code menus that is interrelated and can accommodate dining-in and take-out customers. The QR code is absolutely dynamic. This means that if you ever upgrade your digital menu, you will never have to reprint your QR code.
How can I access a Digital menu based QR code for my business?
1. Set up Your Digital Menu with Trovend Technology
The QR code menu is endorsed to continue your restaurant service in the new normal environment. The first approach is to find an online QR code generator, which provides encrypted QR codes like Digitalmenu.trovend. Setting up your digital menu with Trovend is easy!
No application required! Your customers can select food without having to download an app directly from your digital menu!
2. Choose Static or Dynamic packages (It is smarter to use dynamic QR codes)
You may now proceed to pick your QR code menu once you have finished filling up the appropriate fields for your QR code menu.
Dynamic QR codes are the best QR code to develop business integration.
3. Creates and checks your QR code.
You can then start generating your QR code after you have chosen the type of QR code that you would like to generate. To ensure scanning of your QR menu, you need to validate your QR code. Since your customers are your restaurant marketer, you need excellent input and perceptions. This means you don't have issues and your business will survive the pandemic.
It is time to update your facilities using QR Codes, if you are reopening the bars and restaurants!
If you'd like to expand your company with a QR code menu, just contact us, please send us a message at any time.
Let us take together small preventive measures to ensure that COVID-19 is not spread in future.
0 notes
Text
QR Codes for Sharing Business Information Securely and Instantly
QR code is a popular term these days. It can be found on any material like flyers, billboards, magazines, newspapers, and more. It has the capability to hold a wide range of information that is quickly readable by using smartphones. Looking at its convenience, these codes have been used across different industries such as retail, logistic, and more. If you’re looking to develop a QR code for your business, consider choosing the best codigo QR generador (QR code generator).
QR codes are of two types viz static and dynamic. Static QR codes can’t be changed once created, which means it contains fixed information. Whereas dynamic codes can be edited even after completion. There is a vast range of generators present on the Internet. You should be careful while choosing the one for you. To crear codigo QR (create QR code), follow these steps.
● Choose the content type from the tabs (URL, email, vCard, message, and more) given at the top of the generator.
● Enter all the fields appear before you after selecting the tab.
● Choose between the type of code that is static and dynamic.
● Customize your QR code. Set a custom color, add a logo, and change the standard shape of your QR code.
● Finally, choose the resolution and download it in .EPS, .PDF, .SVG format.
These are some easy steps, following which, you can generate your QR code. If you’re looking for a free generador de codigos (Code generator), consider using Pageloot. It’s a reliable online website that you can use to generate customized QR codes. This tool has many premium features available for free.
Originally Source:https://bit.ly/31jYdw5
#crear codigo qr (create QR code)#codigo qr generador (QR code generator)#generador de codigos (Code generator)
0 notes
Link
JavaScript is one of the most popular programming languages in the world. I believe it's a great language to be your first programming language ever. We mainly use JavaScript to create websites web applications server-side applications using Node.js but JavaScript is not limited to these things, and it can also be used to create mobile applications using tools like React Native create programs for microcontrollers and the internet of things create smartwatch applications It can basically do anything. It's so popular that everything new that shows up is going to have some kind of JavaScript integration at some point. JavaScript is a programming language that is: high level: it provides abstractions that allow you to ignore the details of the machine where it's running on. It manages memory automatically with a garbage collector, so you can focus on the code instead of managing memory like other languages like C would need, and provides many constructs which allow you to deal with highly powerful variables and objects. dynamic: opposed to static programming languages, a dynamic language executes at runtime many of the things that a static language does at compile time. This has pros and cons, and it gives us powerful features like dynamic typing, late binding, reflection, functional programming, object runtime alteration, closures and much more. Don't worry if those things are unknown to you - you'll know all of those at the end of the course. dynamically typed: a variable does not enforce a type. You can reassign any type to a variable, for example, assigning an integer to a variable that holds a string. loosely typed: as opposed to strong typing, loosely (or weakly) typed languages do not enforce the type of an object, allowing more flexibility but denying us type safety and type checking (something that TypeScript - which builds on top of JavaScript - provides) interpreted: it's commonly known as an interpreted language, which means that it does not need a compilation stage before a program can run, as opposed to C, Java or Go for example. In practice, browsers do compile JavaScript before executing it, for performance reasons, but this is transparent to you: there is no additional step involved. multi-paradigm: the language does not enforce any particular programming paradigm, unlike Java for example, which forces the use of object-oriented programming, or C that forces imperative programming. You can write JavaScript using an object-oriented paradigm, using prototypes and the new (as of ES6) classes syntax. You can write JavaScript in a functional programming style, with its first-class functions, or even in an imperative style (C-like). In case you're wondering, JavaScript has nothing to do with Java, it's a poor name choice but we have to live with it. Update: You can now get a PDF and ePub version of this JavaScript Beginner's Handbook.A little bit of history Created 20 years ago, JavaScript has gone a very long way since its humble beginnings. It was the first scripting language that was supported natively by web browsers, and thanks to this it gained a competitive advantage over any other language and today it's still the only scripting language that we can use to build Web Applications. Other languages exist, but all must compile to JavaScript - or more recently to WebAssembly, but this is another story. In the beginnings, JavaScript was not nearly powerful as it is today, and it was mainly used for fancy animations and the marvel known at the time as Dynamic HTML. With the growing needs that the web platform demanded (and continues to demand), JavaScript had the responsibility to grow as well, to accommodate the needs of one of the most widely used ecosystems of the world. JavaScript is now widely used also outside of the browser. The rise of Node.js in the last few years unlocked backend development, once the domain of Java, Ruby, Python, PHP and more traditional server-side languages. JavaScript is now also the language powering databases and many more applications, and it's even possible to develop embedded applications, mobile apps, TV sets apps and much more. What started as a tiny language inside the browser is now the most popular language in the world. Just JavaScript Sometimes it's hard to separate JavaScript from the features of the environment it is used in. For example, the console.log() line you can find in many code examples is not JavaScript. Instead, it's part of the vast library of APIs provided to us in the browser. In the same way, on the server it can be sometimes hard to separate the JavaScript language features from the APIs provided by Node.js. Is a particular feature provided by React or Vue? Or is it "plain JavaScript", or "vanilla JavaScript" as often called? In this book I talk about JavaScript, the language. Without complicating your learning process with things that are outside of it, and provided by external ecosystems. A brief intro to the syntax of JavaScript In this little introduction I want to tell you about 5 concepts: white space case sensitivity literals identifiers White space JavaScript does not consider white space meaningful. Spaces and line breaks can be added in any fashion you might like, even though this is in theory. In practice, you will most likely keep a well defined style and adhere to what people commonly use, and enforce this using a linter or a style tool such as Prettier. For example, I like to always 2 characters to indent. Case sensitive JavaScript is case sensitive. A variable named something is different from Something. The same goes for any identifier. Literals We define as literal a value that is written in the source code, for example, a number, a string, a boolean or also more advanced constructs, like Object Literals or Array Literals: 5 'Test' true ['a', 'b'] {color: 'red', shape: 'Rectangle'} Identifiers An identifier is a sequence of characters that can be used to identify a variable, a function, an object. It can start with a letter, the dollar sign $ or an underscore _, and it can contain digits. Using Unicode, a letter can be any allowed char, for example, an emoji 😄. Test test TEST _test Test1 $test The dollar sign is commonly used to reference DOM elements. Some names are reserved for JavaScript internal use, and we can't use them as identifiers. Comments are one of the most important part of any program. In any programming language. They are important because they let us annotate the code and add important information that otherwise would not be available to other people (or ourselves) reading the code. In JavaScript, we can write a comment on a single line using //. Everything after // is not considered as code by the JavaScript interpreter. Like this: // a comment true //another comment Another type of comment is a multi-line comment. It starts with /* and ends with */. Everything in between is not considered as code: /* some kind of comment */ Semicolons Every line in a JavaScript program is optionally terminated using semicolons. I said optionally, because the JavaScript interpreter is smart enough to introduce semicolons for you. In most cases, you can omit semicolons altogether from your programs, without even thinking about it. This fact is very controversial. Some developers will always use semicolons, some others will never use semicolons, and you'll always find code that uses semicolons and code that does not. My personal preference is to avoid semicolons, so my examples in the book will not include them. Values A hello string is a value. A number like 12 is a value. hello and 12 are values. string and number are the types of those values. The type is the kind of value, its category. We have many different types in JavaScript, and we'll talk about them in detail later on. Each type has its own characteristics. When we need to have a reference to a value, we assign it to a variable. The variable can have a name, and the value is what's stored in a variable, so we can later access that value through the variable name. Variables A variable is a value assigned to an identifier, so you can reference and use it later in the program. This is because JavaScript is loosely typed, a concept you'll frequently hear about. A variable must be declared before you can use it. We have 2 main ways to declare variables. The first is to use const: const a = 0 The second way is to use let: let a = 0 What's the difference? const defines a constant reference to a value. This means the reference cannot be changed. You cannot reassign a new value to it. Using let you can assign a new value to it. For example, you cannot do this: const a = 0 a = 1 Because you'll get an error: TypeError: Assignment to constant variable.. On the other hand, you can do it using let: let a = 0 a = 1 const does not mean "constant" in the way some other languages like C mean. In particular, it does not mean the value cannot change - it means it cannot be reassigned. If the variable points to an object or an array (we'll see more about objects and arrays later) the content of the object or the array can freely change. Const variables must be initialized at the declaration time: const a = 0 but let values can be initialized later: let a a = 0 You can declare multiple variables at once in the same statement: const a = 1, b = 2 let c = 1, d = 2 But you cannot redeclare the same variable more than one time: let a = 1 let a = 2 or you'd get a "duplicate declaration" error. My advice is to always use const and only use let when you know you'll need to reassign a value to that variable. Why? Because the less power our code has, the better. If we know a value cannot be reassigned, it's one less source for bugs. Now that we saw how to work with const and let, I want to mention var. Until 2015, var was the only way we could declare a variable in JavaScript. Today, a modern codebase will most likely just use const and let. There are some fundamental differences which I detail in this post but if you're just starting out, you might not care about. Just use const and let. Types Variables in JavaScript do not have any type attached. They are untyped. Once you assign a value with some type to a variable, you can later reassign the variable to host a value of any other type, without any issue. In JavaScript we have 2 main kinds of types: primitive types and object types. Primitive types Primitive types are numbers strings booleans symbols And two special types: null and undefined. Object types Any value that's not of a primitive type (a string, a number, a boolean, null or undefined) is an object. Object types have properties and also have methods that can act on those properties. We'll talk more about objects later on. Expressions An expression is a single unit of JavaScript code that the JavaScript engine can evaluate, and return a value. Expressions can vary in complexity. We start from the very simple ones, called primary expressions: 2 0.02 'something' true false this //the current scope undefined i //where i is a variable or a constant Arithmetic expressions are expressions that take a variable and an operator (more on operators soon), and result into a number: 1 / 2 i++ i -= 2 i * 2 String expressions are expressions that result into a string: 'A ' + 'string' Logical expressions make use of logical operators and resolve to a boolean value: a && b a || b !a More advanced expressions involve objects, functions, and arrays, and I'll introduce them later. Operators Operators allow you to get two simple expressions and combine them to form a more complex expression. We can classify operators based on the operands they work with. Some operators work with 1 operand. Most with 2 operands. Just one operator works with 3 operands. In this first introduction to operators, we'll introduce the operators you are most likely familar with: operators with 2 operands. I already introduced one when talking about variables: the assignment operator =. You use = to assign a value to a variable: let b = 2 Let's now introduce another set of binary operators that you already familiar with, from basic math. The addition operator (+) const three = 1 + 2 const four = three + 1 The + operator also serves as string concatenation if you use strings, so pay attention: const three = 1 + 2 three + 1 // 4 'three' + 1 // three1 The subtraction operator (-) const two = 4 - 2 The division operator (/) Returns the quotient of the first operator and the second: const result = 20 / 5 //result === 4 const result = 20 / 7 //result === 2.857142857142857 If you divide by zero, JavaScript does not raise any error but returns the Infinity value (or -Infinity if the value is negative). 1 / 0 //Infinity -1 / 0 //-Infinity The remainder operator (%) The remainder is a very useful calculation in many use cases: const result = 20 % 5 //result === 0 const result = 20 % 7 //result === 6 A reminder by zero is always NaN, a special value that means "Not a Number": 1 % 0 //NaN -1 % 0 //NaN The multiplication operator (*) Multiply two numbers 1 * 2 //2 -1 * 2 //-2 The exponentiation operator (**) Raise the first operand to the power second operand 1 ** 2 //1 2 ** 1 //2 2 ** 2 //4 2 ** 8 //256 8 ** 2 //64 Precedence rules Every complex statement with multiple operators in the same line will introduce precedence problems. Take this example: let a = 1 * 2 + 5 / 2 % 2 The result is 2.5, but why? What operations are executed first, and which need to wait? Some operations have more precedence than the others. The precedence rules are listed in this table: Operator Description * / % multiplication/dividision + - addition/subtraction = assignment Operations on the same level (like + and -) are executed in the order they are found, from left to right. Following these rules, the operation above can be solved in this way: let a = 1 * 2 + 5 / 2 % 2 let a = 2 + 5 / 2 % 2 let a = 2 + 2.5 % 2 let a = 2 + 0.5 let a = 2.5 Comparison operators After assignment and math operators, the third set of operators I want to introduce is conditional operators. You can use the following operators to compare two numbers, or two strings. Comparison operators always returns a boolean, a value that's true or false). Those are disequality comparison operators: < means "less than" <= means "minus than, or equal to" means "greater than" = means "greater than, or equal to" Example: = 1 //true In addition to those, we have 4 equality operators. They accept two values, and return a boolean: === checks for equality !== checks for inequality Note that we also have == and != in JavaScript, but I highly suggest to only use === and !== because they can prevent some subtle problems. Conditionals With the comparison operators in place, we can talk about conditionals. An if statement is used to make the program take a route, or another, depending on the result of an expression evaluation. This is the simplest example, which always executes: if (true) { //do something } on the contrary, this is never executed: if (false) { //do something (? never ?) } The conditional checks the expression you pass to it for true or false value. If you pass a number, that always evaluates to true unless it's 0. If you pass a string, it always evaluates to true unless it's an empty string. Those are general rules of casting types to a boolean. Did you notice the curly braces? That is called a block, and it is used to group a list of different statements. A block can be put wherever you can have a single statement. And if you have a single statement to execute after the conditionals, you can omit the block, and just write the statement: if (true) doSomething() But I always like to use curly braces to be more clear. You can provide a second part to the if statement: else. You attach a statement that is going to be executed if the if condition is false: if (true) { //do something } else { //do something else } Since else accepts a statement, you can nest another if/else statement inside it: if (a === true) { //do something } else if (b === true) { //do something else } else { //fallback } Arrays An array is a collection of elements. Arrays in JavaScript are not a type on their own. Arrays are objects. We can initialize an empty array in these 2 different ways: const a = [] const a = Array() The first is using the array literal syntax. The second uses the Array built-in function. You can pre-fill the array using this syntax: const a = [1, 2, 3] const a = Array.of(1, 2, 3) An array can hold any value, even value of different types: const a = [1, 'Flavio', ['a', 'b']] Since we can add an array into an array, we can create multi-dimensional arrays, which have very useful applications (e.g. a matrix): const matrix = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9] ] matrix[0][0] //1 matrix[2][0] //7 You can access any element of the array by referencing its index, which starts from zero: a[0] //1 a[1] //2 a[2] //3 You can initialize a new array with a set of values using this syntax, which first initializes an array of 12 elements, and fills each element with the 0 number: Array(12).fill(0) You can get the number of elements in the array by checking its length property: const a = [1, 2, 3] a.length //3 Note that you can set the length of the array. If you assign a bigger number than the arrays current capacity, nothing happens. If you assign a smaller number, the array is cut at that position: const a = [1, 2, 3] a //[ 1, 2, 3 ] a.length = 2 a //[ 1, 2 ] How to add an item to an array We can add an element at the end of an array using the push() method: a.push(4) We can add an element at the beginning of an array using the unshift() method: a.unshift(0) a.unshift(-2, -1) How to remove an item from an array We can remove an item from the end of an array using the pop() method: a.pop() We can remove an item from the beginning of an array using the shift() method: a.shift() How to join two or more arrays You can join multiple arrays by using concat(): const a = [1, 2] const b = [3, 4] const c = a.concat(b) //[1,2,3,4] a //[1,2] b //[3,4] You can also use the spread operator (...) in this way: const a = [1, 2] const b = [3, 4] const c = [...a, ...b] c //[1,2,3,4] How to find a specific item in the array You can use the find() method of an array: { //return true or false }) Returns the first item that returns true. Returns undefined if the element is not found. A commonly used syntax is: x.id === my_id) The above line will return the first element in the array that has id === my_id. findIndex() works similarly to find(), but returns the index of the first item that returns true, and if not found, it returns undefined: { //return true or false }) Another method is includes(): a.includes(value) Returns true if a contains value. a.includes(value, i) Returns true if a contains value after the position i. Strings A string is a sequence of characters. It can be also defined as a string literal, which is enclosed in quotes or double quotes: 'A string' "Another string" I personally prefer single quotes all the time, and use double quotes only in HTML to define attributes. You assign a string value to a variable like this: const name = 'Flavio' You can determine the length of a string using the length property of it: 'Flavio'.length //6 const name = 'Flavio' name.length //6 This is an empty string: ''. Its length property is 0: ''.length //0 Two strings can be joined using the + operator: "A " + "string" You can use the + operator to interpolate variables: const name = 'Flavio' "My name is " + name //My name is Flavio Another way to define strings is to use template literals, defined inside backticks. They are especially useful to make multiline strings much simpler. With single or double quotes you can't define a multiline string easily: you'd need to use escaping characters. Once a template literal is opened with the backtick, you just press enter to create a new line, with no special characters, and it's rendered as-is: const string = `Hey this string is awesome!` Template literals are also great because they provide an easy way to interpolate variables and expressions into strings. You do so by using the ${...} syntax: const var = 'test' const string = `something ${var}` //something test inside the ${} you can add anything, even expressions: const string = `something ${1 + 2 + 3}` const string2 = `something ${foo() ? 'x' : 'y'}` Loops Loops are one of the main control structures of JavaScript. With a loop we can automate and repeat indefinitely a block of code, for how many times we want it to run. JavaScript provides many way to iterate through loops. I want to focus on 3 ways: while loops for loops for..of loops while The while loop is the simplest looping structure that JavaScript provides us. We add a condition after the while keyword, and we provide a block that is run until the condition evaluates to true. Example: const list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] let i = 0 while (i < list.length) { console.log(list[i]) //value console.log(i) //index i = i + 1 } You can interrupt a while loop using the break keyword, like this: while (true) { if (somethingIsTrue) break } and if you decide that in the middle of a loop you want to skip the current iteration, you can jump to the next iteration using continue: while (true) { if (somethingIsTrue) continue //do something else } Very similar to while, we have do..while loops. It's basically the same as while, except the condition is evaluated after the code block is executed. This means the block is always executed at least once. Example: const list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] let i = 0 do { console.log(list[i]) //value console.log(i) //index i = i + 1 } while (i < list.length) for The second very important looping structure in JavaScript is the for loop. We use the for keyword and we pass a set of 3 instructions: the initialization, the condition, and the increment part. Example: const list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] for (let i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { console.log(list[i]) //value console.log(i) //index } Just like with while loops, you can interrupt a for loop using break and you can fast forward to the next iteration of a for loop using continue. for...of This loop is relatively recent (introduced in 2015) and it's a simplified version of the for loop: const list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] for (const value of list) { console.log(value) //value } Functions In any moderately complex JavaScript program, everything happens inside functions. Functions are a core, essential part of JavaScript. What is a function? A function is a block of code, self contained. Here's a function declaration: function getData() { // do something } A function can be run any times you want by invoking it, like this: getData() A function can have one or more argument: function getData() { //do something } function getData(color) { //do something } function getData(color, age) { //do something } When we can pass an argument, we invoke the function passing parameters: function getData(color, age) { //do something } getData('green', 24) getData('black') Note that in the second invokation I passed the black string parameter as the color argument, but no age. In this case, age inside the function is undefined. We can check if a value is not undefined using this conditional: function getData(color, age) { //do something if (typeof age !== 'undefined') { //... } } typeof is a unary operator that allows us to check the type of a variable. You can also check in this way: function getData(color, age) { //do something if (age) { //... } } although the conditional will also be true if age is null, 0 or an empty string. You can have default values for parameters, in case they are not passed: function getData(color = 'black', age = 25) { //do something } You can pass any value as a parameter: numbers, strings, booleans, arrays, objects, and also functions. A function has a return value. By default a function returns undefined, unless you add a return keyword with a value: function getData() { // do something return 'hi!' } We can assign this return value to a variable when we invoke the function: function getData() { // do something return 'hi!' } let result = getData() result now holds a string with the the hi! value. You can only return one value. To return multiple values, you can return an object, or an array, like this: function getData() { return ['Flavio', 37] } let [name, age] = getData() Functions can be defined inside other functions: {} dosomething() return 'test' } The nested function cannot be called from the outside of the enclosing function. You can return a function from a function, too. Arrow functions Arrow functions are a recent introduction to JavaScript. They are very often used instead of "regular" functions, the one I described in the previous chapter. You'll find both forms used everywhere. Visually, they allows you to write functions with a shorter syntax, from: function getData() { //... } to { //... } But.. notice that we don't have a name here. Arrow functions are anonymous. We must assign them to a variable. We can assign a regular function to a variable, like this: let getData = function getData() { //... } When we do so, we can remove the name from the function: let getData = function() { //... } and invoke the function using the variable name: let getData = function() { //... } getData() That's the same thing we do with arrow functions: { //... } getData() If the function body contains just a single statement, you can omit the parentheses and write all on a single line: console.log('hi!') Parameters are passed in the parentheses: console.log(param1, param2) If you have one (and just one) parameter, you could omit the parentheses completely: console.log(param) Arrow functions allow you to have an implicit return: values are returned without having to use the return keyword. It works when there is a on-line statement in the function body: 'test' getData() //'test' Like with regular functions, we can have default parameters: You can have default values for parameters, in case they are not passed: { //do something } and we can only return one value. Arrow functions can contain other arrow function, or also regular functions. The are very similar, so you might ask why they were introduced? The big difference with regular functions is when they are used as object methods. This is something we'll soon look into. Objects Any value that's not of a primitive type (a string, a number, a boolean, a symbol, null, or undefined) is an object. Here's how we define an object: const car = { } This is the object literal syntax, which is one of the nicest things in JavaScript. You can also use the new Object syntax: const car = new Object() Another syntax is to use Object.create(): const car = Object.create() You can also initialize an object using the new keyword before a function with a capital letter. This function serves as a constructor for that object. In there, we can initialize the arguments we receive as parameters, to setup the initial state of the object: function Car(brand, model) { this.brand = brand this.model = model } We initialize a new object using const myCar = new Car('Ford', 'Fiesta') myCar.brand //'Ford' myCar.model //'Fiesta' Objects are always passed by reference. If you assign a variable the same value of another, if it's a primitive type like a number or a string, they are passed by value: Take this example: let age = 36 let myAge = age myAge = 37 age //36 const car = { color: 'blue' } const anotherCar = car anotherCar.color = 'yellow' car.color //'yellow' Even arrays or functions are, under the hoods, objects, so it's very important to understand how they work. Object Properties Objects have properties, which are composed by a label associated with a value. The value of a property can be of any type, which means that it can be an array, a function, and it can even be an object, as objects can nest other objects. This is the object literal syntax we saw in the previous chapter: const car = { } We can define a color property in this way: const car = { color: 'blue' } here we have a car object with a property named color, with value blue. Labels can be any string, but beware special characters: if I wanted to include a character not valid as a variable name in the property name, I would have had to use quotes around it: const car = { color: 'blue', 'the color': 'blue' } Invalid variable name characters include spaces, hyphens, and other special characters. As you see, when we have multiple properties, we separate each property with a comma. We can retrieve the value of a property using 2 different syntaxes. The first is dot notation: car.color //'blue' The second (which is the only one we can use for properties with invalid names), is to use square brackets: car['the color'] //'blue' If you access an unexisting property, you'll get the undefined value: car.brand //undefined As said, objects can have nested objects as properties: const car = { brand: { name: 'Ford' }, color: 'blue' } In this example, you can access the brand name using car.brand.name or car['brand']['name'] You can set the value of a property when you define the object. But you can always update it later on: const car = { color: 'blue' } car.color = 'yellow' car['color'] = 'red' And you can also add new properties to an object: car.model = 'Fiesta' car.model //'Fiesta' Given the object const car = { color: 'blue', brand: 'Ford' } you can delete a property from this object using delete car.brand Object Methods I talked about functions in a previous chapter. Functions can be assigned to a function property, and in this case they are called methods. In this example, the start property has a function assigned, and we can invoke it by using the dot syntax we used for properties, with the parentheses at the end: const car = { brand: 'Ford', model: 'Fiesta', start: function() { console.log('Started') } } car.start() Inside a method defined using a function() {} syntax we have access to the object instance by referencing this. In the following example, we have access to the brand and model properties values using this.brand and this.model: const car = { brand: 'Ford', model: 'Fiesta', start: function() { console.log(`Started ${this.brand} ${this.model}`) } } car.start() It's important to note this distinction between regular functions and arrow functions: we don't have access to this if we use an arrow function: { console.log(`Started ${this.brand} ${this.model}`) //not going to work } } car.start() This is because arrow functions are not bound to the object. This is the reason why regular functions are often used as object methods. Methods can accept parameters, like regular functions: const car = { brand: 'Ford', model: 'Fiesta', goTo: function(destination) { console.log(`Going to ${destination}`) } } car.goTo('Rome') Classes We talked about objects, which are one of the most interesting parts of JavaScript. In this chapter we'll go up one level, introducing classes. What are classes? They are a way to define a common pattern for multiple objects. Let's take a person object: const person = { name: 'Flavio' } We can create a class named Person (note the capital P, a convention when using classes), that has a name property: class Person { name } Now from this class, we initialize a flavio object like this: const flavio = new Person() flavio is called an instance of the Person class. We can set the value of the name property: flavio.name = 'Flavio' and we can access it using flavio.name like we do for object properties. Classes can hold properties, like name, and methods. Methods are defined in this way: class Person { hello() { return 'Hello, I am Flavio' } } and we can invoke methods on an instance of the class: class Person { hello() { return 'Hello, I am Flavio' } } const flavio = new Person() flavio.hello() There is a special method called called constructor() that we can use to initialize the class properties when we create a new object instance. It works like this: class Person { constructor(name) { this.name = name } hello() { return 'Hello, I am ' + this.name + '.' } } Note how we use this to access the object instance. Now we can instantiate a new object from the class, passing a string, and when we call hello, we'll get a personalized message: const flavio = new Person('flavio') flavio.hello() //'Hello, I am flavio.' When the object is initialized, the constructor method is called, with any parameters passed. Normally methods are defined on the object instance, not on the class. You can define a method as static to allow it to be executed on the class instead: class Person { static genericHello() { return 'Hello' } } Person.genericHello() //Hello This is very useful, at times. Inheritance A class can extend another class, and objects initialized using that class inherit all the methods of both classes. Suppose we have a class Person: class Person { hello() { return 'Hello, I am a Person' } } We can define a new class Programmer that extends Person: class Programmer extends Person { } Now if we instantiate a new object with class Programmer, it has access to the hello() method: const flavio = new Programmer() flavio.hello() //'Hello, I am a Person' Inside a child class, you can reference the parent class calling super(): class Programmer extends Person { hello() { return super.hello() + '. I am also a programmer.' } } const flavio = new Programmer() flavio.hello() The above program prints Hello, I am a Person. I am also a programmer.. Asynchonous Programming and Callbacks Most of the time, JavaScript code is ran synchronously. This means that a line of code is executed, then the next one is executed, and so on. Everything is as you expect, and how it works in most programming languages. However there are times when you cannot just wait for a line of code to execute. You can't just wait 2 seconds for a big file to load, and halt the program completely. You can't just wait for a network resource to be downloaded, before doing something else. JavaScript solves this problem using callbacks. One of the simplest examples of how to use callbacks is timers. Timers are not part of JavaScript, but they are provided by the browser, and Node.js. Let me talk about one of the timers we have: setTimeout(). The setTimeout() function accepts 2 arguments: a function, and a number. The number is the milliseconds that must pass before the function is ran. Example: { // runs after 2 seconds console.log('inside the function') }, 2000) The function containing the console.log('inside the function') line will be executed after 2 seconds. If you add a console.log('before') prior to the function, and console.log('after') after it: { // runs after 2 seconds console.log('inside the function') }, 2000) console.log('after') You will see this happening in your console: before after inside the function The callback function is executed asynchronously. This is a very common pattern when working with the file system, the network, events, or the DOM in the browser. All of the things I mentioned are not "core" JavaScript, so they are not explained in this handbook, but you'll find lots of examples in my other handbooks available at https://flaviocopes.com. Here's how we can implement callbacks in our code. We define a function that accepts a callback parameter, which is a function. When the code is ready to invoke the callback, we invoke it passing the result: { //do things //do things const result = /* .. */ callback(result) } Code using this function would use it like this: { console.log(result) }) Promises Promises are an alternative way to deal with asynchronous code. As we saw in the previous chapter, with callbacks we'd be passing a function to another function call, that would be called when the function has finished processing. Like this: { console.log(result) }) When the doSomething() code ends, it calls the function received as a a parameter: { //do things //do things const result = /* .. */ callback(result) } The main problems with this approach is that the callback is executed asynchronously, so we don't have a way to do something, and then simply go on with our function. All our code must be nested inside the callback, and if we have to do 2-3 callbacks we enter in what is usually defined "callback hell" with many levels of functions indented into other functions: { console.log(result) }) }) }) Promises are one way to deal with this. Instead of doing: { console.log(result) }) We call a promise-based function in this way: { console.log(result) }) We first call the function, then we have a then() method that is called when the function ends. The indentation does not matter, but you'll often use this style for clarity. It's common to detect errors using a catch() method: { console.log(error) }) Now, to be able to use this syntax, the doSomething() function implementation must be a little bit special. It must use the Promises API. Instead of declaring it as a normal function: { } We declare it as a promise object: const doSomething = new Promise() and we pass a function in the Promise constructor: { }) This function receives 2 parameters. The first is a function we call to resolve the promise, the second a function we call to reject the promise. { }) Resolving a promise means complete it successfully (which results in calling the then() method in who uses it). Rejecting a promise means ending it with an error (which results in calling the catch() method in who uses it). Here's how: { //some code const success = /* ... */ if (success) { resolve('ok') } else { reject('this error occurred') } } ) We can pass a parameter to the resolve and reject functions, of any type we want. Async and Await Async functions are a higher level abstraction over promises. An async function returns a promise, like in this example: resolve('some data'), 2000) }) } Any code that want to use this function will use the async keyword right before the function: const data = await getData() and doing so, any data returned by the promise is going to be assigned to the data variable. In our case, the data is the "some data" string. With one particular caveat: whenever we use the await keyword, we must do so inside a function defined as async. Like this: { const data = await getData() console.log(data) } The Async/await duo allows us to have a cleaner code and a simple mental model to work with asynchronous code. As you can see in the example above, our code looks very simple. Compare it to code using promises, or callback functions. And this is a very simple example, the major benefits will arise when the code is much more complex. As an example, here's how you would get a JSON resource using the Fetch API, and parse it, using promises: response.json()) } getFirstUserData() And here is the same functionality provided using await/async: { // get users list const response = await fetch('/users.json') // parse JSON const users = await response.json() // pick first user const user = users[0] // get user data const userResponse = await fetch(`/users/${user.name}`) // parse JSON const userData = await user.json() return userData } getFirstUserData() Variables scope When I introduced variables, I talked about using const, let, and var. Scope is the set of variables that's visible to a part of the program. In JavaScript we have a global scope, block scope and function scope. If a variable is defined outside of a function or block, it's attached to the global object and it has a global scope, which mean it's available in every part of a program. There is a very important difference between var, let and const declarations. A variable defined as var inside a function is only visible inside that function. Similarly to a function arguments: A variable defined as const or let on the other hand is only visible inside the block where it is defined. A block is a set of instructions grouped into a pair of curly braces, like the ones we can find inside an if statement or a for loop. And a function, too. It's important to understand that a block does not define a new scope for var, but it does for let and const. This has very practical implications. Suppose you define a var variable inside an if conditional in a function function getData() { if (true) { var data = 'some data' console.log(data) } } If you call this function, you'll get some data printed to the console. If you try to move console.log(data) after the if, it still works: function getData() { if (true) { var data = 'some data' } console.log(data) } But if you switch var data to let data: function getData() { if (true) { let data = 'some data' } console.log(data) } You'll get an error: ReferenceError: data is not defined. This is because var is function scoped, and there's a special thing happening here, called hoisting. In short, the var declaration is moved to the top of the closest function by JavaScript, before it runs the code. More or less this is what the function looks like to JS, internally: function getData() { var data if (true) { data = 'some data' } console.log(data) } This is why you can also console.log(data) at the top of a function, even before it's declared, and you'll get undefined as a value for that variable: function getData() { console.log(data) if (true) { var data = 'some data' } } but if you switch to let, you'll get an error ReferenceError: data is not defined, because hoisting does not happen to let declarations. const follows the same rules as let: it's block scoped. It can be tricky at first, but once you realize this difference, then you'll see why var is considered a bad practice nowadays compared to let: they do have less moving parts, and their scope is limited to the block, which also makes them very good as loop variables, because they cease to exist after a loop has ended: function doLoop() { for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++) { console.log(i) } console.log(i) } doLoop() When you exit the loop, i will be a valid variable with value 10. If you switch to let, if you try to console.log(i) will result in an error ReferenceError: i is not defined. Conclusion Thanks a lot for reading this book. I hope it will inspire you to know more about JavaScript. For more on JavaScript, check out my blog flaviocopes.com. Note: You can get a PDF and ePub version of this JavaScript Beginner's Handbook
0 notes
Text
Importing Designer Workflows

Web designers and game designers usually use wholly different toolsets. This is a major restriction in the ability to share knowledge and experience between the widest 2d UX medium and the widest 3d UX medium in the world. Now though, moving forwards with a dedicated design team, this project is challenged with bringing that work from web and app design tools into Unity. The tools aren’t quite ready for that yet, but they are all surprisingly close.
Sketch is one of these UI / UX layout software applications, and happens to be the tool of choice for the studio we are working with. Sketch exports .sketch files that include pngs and incredibly detailed json documents all zipped up. Unity has no import method for this, but a user made plugin has been created to handle Sketch files that had been converted a similar PNG and JSON format (Framer files) and to roughly get those into our Unity editor. My job this week involved cleaning that up.

Why Sketch?
Sketch appears to be one of the top ten or twenty UI/UX specialty apps out there right now. As long as tech platforms keep changing, the tools will likely keep changing too. Other alternatives included Zeplin, InVision, Adobe Experience Design, Framer, and more. Mostly, it is not a loss since it is a common platform, and it is also an advantage since our preferred design studio works closely with it.

Look at all these great (advertised) Sketch designs! Wow-ee! (so cool!)
Why not do it by hand?
Speed and accuracy in moving an artist’s creation from one environment to another creates incredible power for game development. Few games have UI and UX for 2d menu navigation that is comparable to the beauty of many top websites or work apps. Creating this tool not only facilitates more accuracy in one direction though, but in making changes to send back too. An ideal tool would not only show the file in Unity but be able to make changes and save to it in its original format. This reduces the need to communicate, and increases how much both the UX designer and the game developer can do to meet their needs together in the same limited time. It’s especially useful for rapid iteration.
Competitor Framer does many of the same things, and has shared exports.
What filetypes do visual designers use?
Our design studio sent over this list to choose from:
UX files - .sketch/figma, .pdf, .png
UI files - .sketch, .png, .zeplin.io
Animation - .aep, .gif, .mp4 (or any video), .png, and .json lottie files
Most of these are static exports, likely flattened, and fairly standard expectations for dealing with an artist of any type. But the more Unity can read the same tools the artist uses, the more dynamic and accurate their uses can be. Since Sketch files can export to figma and zeplin formats, it makes supporting this filetype a strong choice in the future.
Animation files, like the json lottie ones, will be a different powerful effect later. Understanding how those pieces move from one environment to another though will help set expectations for what is useful in the tool we design too.

Code code code. Version control and open repos!
So what’s working?
So far we’ve added 4x resolution importing to fx-lange’s tool, updated the Unity environment to 2018.1, and fixed the readme for latest tools implementation since Framer and Sketch have both changed a bit in the last two years. Our pull request was submitted, negotiated, and approved, so others will be able to work with UX designers in Sketch a little more easily in the future now too.

Look at that 4x importing in Unity! Dang!
Then what’s next?
Next up is probably taking on Sketch files directly. Currently the Sketch files need a Framer conversion, but this loses dynamic text and a few layers. That kind of access might even mean we could save from Unity back into Sketch files directly. It would let us send files back to our designers with our own tweaks instead of relaying that all by email.

But what if your ending is really... the beginning?
Conclusion
The only big downside is time. Programming a tool like this is a huge investment. It means seamless integration later (comparatively, at least) with great iteration power and sending files back and forth more easily, quickly, and accurately - but it’s a big commitment. If Sketch gets discontinued in the next few years then it’s kind of a bummer to start again, but for now this is a powerful addition that, hopefully, will help this game’s UI/UX stand out from the crowd.
12/2/19
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP DJANGO Interview Questions and Answers
Django Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Django? Django is an open source web framework. It is use to develop web application in python programming language. It makes easier to build better web applications quickly and with less code. It has a tag line – “The Web framework for perfectionists with deadlines”. 2. What does Django mean? Django is named after Django Reinhardt, a gypsy Jazz guitarist from 1930 to 1950. He was known as one of the best guitarist of all time. 3. What are the features available in Django. Features available in Django are Admin Interface (CRUD) Templating Form Handling Internationalization Session, user management, role-based permissions ORM (Object-relational mapping) Testing Framework Fantastic Documentation 4. Which architectural pattern does Django Follow. It follows the MVC (Model View Control) architectural pattern. 5. Describe the architecture of Django. Django is based in MVC architecture. It consist the following components: Models: It describes the database schema and data structure. Views: It is a user interface. The view retrieves data from appropriate models and pass it to the template. Templates: It determines how the user sees it. It describes how the data received from the views should be changed or formated for display on the page. Controller: It specifies the Django framework and URL parsing. 6. Why Django should be used for web-development. It allows to divide code module into logical groups to make it flexible to change. To easy the website administration, it provides auto-generated web admin module. It provides pre-packaged API for common user tasks. It enables to define what should be URL for given function. It enables to separate business logic from the HTML. Everything is written in python programming language. 7. How to create a project in Django. To start a project in Django, use the following command . $django-admin.py startproject javatpoint After execcuting the above command, it will create a project that has following directory structure. javatpoint/ manage.py javatpoint/ __init__.py settings.py urls.py wsgi.py 8. Is Django a high level web framework or low level framework? Django is a high level Python’s web framework which was designed for rapid development and clean realistic design. 9. How we can setup static files in Django. There are three main things required to set up static files in Django. Set STATIC_ROOT in setting.py. run manage.py. Set up a Static Files entry on the Python Anywhere web tab. 10. Which foundation manages Django web framework? Django web framework is managed and maintained by an independent and non- profit organization named DSF (Django Software Foundation).

DJANGO Interview Questions 11. Is Django stable? YES, Django is stable. Many companies like Disqus, Instagram, Pintrest and Mozilla has been using Django for many years. 12. How we can use file based sessions. We have to set the SESSION_ENGINE settings to “django.contrib.sessions.backends.file†to use file based session. 13. What are the inheritance styles in Django. In Django, there are three possible inheritance styles: Abstract base classes- It is used, when we only want parent class to hold information that we don’t want to inherit for each child model. Multi-table Inheritance- It is used, when we are sub-classing an existing model and need each model to have its own database table. Proxy Model- We can use this model, when Python level behavior of the model modifies, without changing the model’s fields. 14. What does the Django field class types? The Django field class types specify: The database column type. The default HTML widget to available while rendering a form field. The minimal validation requirements used in Django admin. Automatic generated forms. 15. What is some typical usage of middlewares in Django? Following are the usage of middlewares in Django: Session management. Use authentication. Cross-site request forgery protection. Content Gzipping, etc. 16. What does Django templates consists of? The template is a simple text file. It can create any text-based format like XML, CSV, HTML, etc. A template contains variables that get replaced with values when the template is evaluated and tags (% tag %) that controls the logic of the template. 17. What command line is used to load data into Django? The command line Django-admin.py loaddata is used to load data into Django. 18. What are the advantages of using Django? Django’s stack is loosely coupled with tight cohesion The Django apps make use of very less code Allows quick development of websites Follows the DRY or the Don’t Repeat Yourself Principle which means, one concept or a piece of data should live in just one place Consistent at low as well as high levels Behaviors are not implicitly assumed, they are rather explicitly specified SQL statements are not executed too many times and are optimized internally Can easily drop into raw SQL whenever required Flexibility while using URL’s 19. How do you connect your Django project to the database? Django comes with a default database which is SQLite. To connect your project to this database, use the following commands: python manage.py migrate (migrate command looks at the INSTALLED_APPS settings and creates database tables accordingly) python manage.py makemigrations (tells Django you have created/ changed your models) python manage.py sqlmigrate (sqlmigrate takes the migration names and returns their SQL) 20. What are ‘templates’? Django’s template layer renders the information to be presented to the user in a designer-friendly format. Using templates, you can generate HTML dynamically. The HTML consists of both static as well as dynamic parts of the content. You can have any number of templates depending on the requirement of your project. It is also fine to have none of them. Django has its own template system called the Django template language (DTL). Regardless of the backend, you can also load and render templates using Django’s standard admin. 21. What is the difference between a Project and an App? An app is basically a Web Application that is created to do something for example, a database of employee records. A project, on the other hand, is a collection of apps of some particular website. Therefore, a single project can consist of ‘n’ number of apps and a single app can be in multiple projects. 22. Briefly explain Django Field Class. ‘Field’ is basically an abstract class that actually represents a column in the database table. The Field class, is in turn, a subclass of RegisterLookupMixin. In Django, these fields are used to create database tables (db_type()) which are used to map Python types to the database using get_prep_value() and vice versa using from_db_value() method. Therefore, fields are fundamental pieces in different Django APIs such as models and querysets. 23. How to do you create a Django project? To create a Django project, cd into the directory where you would like to create your project and type the following command: django-admin startproject xyz NOTE: Here, xyz is the name of the project. You can give any name that you desire. 24. What do you mean by context? Context in Django is a dictionary mapping template variable name given to Python objects. This is the conventional name, but you can give any other name of your choice if you wish to do it. 25. What is the significance of manage.py file in Django? The manage.py file is automatically generated whenever you create a project. This is basically a command-line utility that helps you to interact with your Django project in various ways. It does the same things as django-admin but along with that, it also sets the DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE environment variable in order to point to your project’s settings. Usually, it is better to make use of manage.py rather than the django-admin in case you are working on a single project. 26. Explain the use of ‘migrate’ command in Django? In Django, migrations are used to propagate changes made to the models. The migrate command is basically used to apply or unapply migrations changes made to the models. This command basically synchronizes the current set of models and migrations with the database state. You can use this command with or without parameters. In case you do not specify any parameter, all apps will have all their migrations running. 27. How to view and filter items from the database? In order to view all the items from your database, you can make use of the ‘all()’ function in your interactive shell as follows: XYZ.objects.all() where XYZ is some class that you have created in your models To filter out some element from your database, you either use the get() method or the filter method as follows: XYZ.objects.filter(pk=1) XYZ.objects.get(id=1) 28. Name some companies that make use of Django? Some of the companies that make use of Django are Instagram, DISCUS, Mozilla Firefox, YouTube, Pinterest, Reddit, etc. Django Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes