#different types of ethereum tokens
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Expansive World of Altcoins: Exploring the Diversity Beyond Bitcoin

Bitcoin, the original cryptocurrency, has long dominated headlines and market discussions. However, the world of digital currencies is vast and diverse, with thousands of alternative coins, or altcoins, each offering unique features and value propositions. Altcoins encompass a broad range of projects, from utility tokens and stablecoins to meme coins and more. This article delves into the rich ecosystem of altcoins, highlighting their significance, various types, and the innovative projects that make up this vibrant space, including a mention of Sexy Meme Coin.
Understanding Altcoins
The term "altcoin" refers to any cryptocurrency that is not Bitcoin. These coins were developed to address various limitations of Bitcoin or to introduce new features and use cases. Altcoins have proliferated since the creation of Bitcoin in 2009, each aiming to offer something different, whether it be improved transaction speeds, enhanced privacy features, or specific utility within certain ecosystems.
Categories of Altcoins
Utility Tokens: Utility tokens provide users with access to a specific product or service within a blockchain ecosystem. Examples include Ethereum's Ether (ETH), which is used to power applications on the Ethereum network, and Chainlink's LINK, which is used to pay for services on the Chainlink decentralized oracle network.
Stablecoins: Stablecoins are designed to maintain a stable value by being pegged to a reserve of assets, such as fiat currency or commodities. Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC) are popular stablecoins pegged to the US dollar, offering the benefits of cryptocurrency without the volatility.
Security Tokens: Security tokens represent ownership in a real-world asset, such as shares in a company or real estate. They are subject to regulatory oversight and are often seen as a bridge between traditional finance and the blockchain world.
Meme Coins: Meme coins are a playful and often humorous take on cryptocurrency, inspired by internet memes and cultural trends. While they may start as jokes, some have gained significant value and community support. Dogecoin is the most famous example, but many others, like Shiba Inu and Sexy Meme Coin, have also captured the public's imagination.
Privacy Coins: Privacy coins focus on providing enhanced privacy features for transactions. Monero (XMR) and Zcash (ZEC) are notable examples, offering users the ability to transact anonymously and protect their financial privacy.
The Appeal of Altcoins
Altcoins offer several advantages over Bitcoin, including:
Innovation: Many altcoins introduce new technologies and features, driving innovation within the cryptocurrency space. For example, Ethereum introduced smart contracts, enabling decentralized applications (DApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
Specialization: Altcoins often serve specific niches or industries, providing targeted solutions that Bitcoin cannot. For instance, Ripple (XRP) focuses on facilitating cross-border payments, while Filecoin (FIL) aims to create a decentralized storage network.
Investment Opportunities: The diverse range of altcoins presents numerous investment opportunities. Investors can diversify their portfolios by investing in projects with different use cases and growth potentials.
Notable Altcoins in the Market
Ethereum (ETH): Ethereum is the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization and has become the backbone of the DeFi and NFT (Non-Fungible Token) ecosystems. Its smart contract functionality allows developers to create decentralized applications, leading to a thriving ecosystem of financial services, games, and more.
Cardano (ADA): Cardano is a blockchain platform focused on sustainability, scalability, and transparency. It uses a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, which is more energy-efficient than Bitcoin's proof-of-work. Cardano aims to provide a more secure and scalable infrastructure for the development of decentralized applications.
Polkadot (DOT): Polkadot is designed to enable different blockchains to interoperate and share information. Its unique architecture allows for the creation of "parachains," which can operate independently while still benefiting from the security and connectivity of the Polkadot network.
Chainlink (LINK): Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that provides real-world data to smart contracts on the blockchain. This functionality is crucial for the operation of many DeFi applications, making Chainlink a vital component of the blockchain ecosystem.
Sexy Meme Coin: Among the meme coins, Sexy Meme Coin stands out for its combination of humor and innovative tokenomics. It offers a decentralized marketplace where users can buy, sell, and trade memes as NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), rewarding creators for their originality. Learn more about Sexy Meme Coin at Sexy Meme Coin.
The Future of Altcoins
The future of altcoins looks promising, with continuous innovation and increasing adoption across various industries. As blockchain technology evolves, we can expect altcoins to introduce new solutions and disrupt traditional systems. However, the market is also highly competitive, and not all projects will succeed. Investors should conduct thorough research and due diligence before investing in any altcoin.
Conclusion
Altcoins represent a dynamic and diverse segment of the cryptocurrency market. From utility tokens and stablecoins to meme coins and privacy coins, each category offers unique features and potential benefits. Projects like Ethereum, Cardano, Polkadot, and Chainlink are leading the way in innovation, while niche coins like Sexy Meme Coin add a layer of cultural relevance and community engagement. As the cryptocurrency ecosystem continues to grow, altcoins will play a crucial role in shaping the future of digital finance and blockchain technology.
For those interested in the playful and innovative side of the altcoin market, Sexy Meme Coin offers a unique and entertaining platform. Visit Sexy Meme Coin to explore this exciting project and join the community.
107 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Crypto Payments are the Key to Future-Proofing Your Business.
Introduction
In recent years, cryptocurrencies have really been on the radar big time. Big time in ways they're a digital currency that harnesses blockchain technology, which has the potential to completely shake up a lot of different kinds of businesses and transactions. The emergence of cryptocurrencies, especially Bitcoin, has encouraged businesses to think about embracing crypto payments as a way to remain competitive and future-proof their businesses Crypto as an Investment: Volatility and Opportunities
Cryptocurrencies are now a sought-after investment asset, they are extremely volatile. Big swings in crypto prices like Bitcoin and Ethereum have really given investors a chance to do well big time. But of course, that volatility means investors are also risking very big losses, losses like market crashing and real money going up in smoke at the financial winds. In spite of this, most cryptocurrency proponents consider digital currencies a good avenue for diversifying investment portfolios, cognizant of the fact that cryptocurrencies are not stable, long-term assets but speculative investments. For companies, this is a two-edged sword—accepting cryptocurrencies as payment may unlock new revenue streams but companies have to carefully weigh their risk appetite when considering their participation in the world of cryptocurrencies.
Benefits of Acceptance of Crypto Payments
Beyond the risks, moving to accepting different types of cryptocurrency is a win for companies especially those in financial tech. These benefits include:
Lower Transaction Fees: Conventional payment processors and financial intermediaries usually impose high transaction fees. Cryptocurrencies usually have lower transaction fees.
Speedier Transactions: Transactions involving cryptocurrencies are much quicker than traditional banking systems, particularly cross-border payments, where old financial systems take days to clear transactions.
New Customer Bases Access: By embracing cryptocurrency, companies can access a worldwide market of crypto investors and enthusiasts. This gives companies new access to customers who are perhaps excited about making transactions digitally or through decentralized routes.
Improved Security and Fraud Protection: Cryptocurrencies employ encryption and blockchain technology to protect transactions, making it much less likely for fraud or chargebacks to occur.
Challenges and Considerations
Sure, while there are great benefits to adopting cryptocurrency payments for companies, there are also many things to consider and pay attention to. The biggest concern is the built-in price volatility of digital currency, which may lead to unforeseen profits or losses for companies holding crypto assets. To avoid that risk, companies need contingency plans to handle crypto assets and convert them into stable currencies if need be.
Furthermore, the regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies is also developing. Governments across the planet are trying to devise rules and ways to collect taxes on digital money, but some corporations are unsure of their future, because they see rules as unclear and even unstable. Companies should make sure they adapt to local regulations, such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations, in order to avoid a potential legal battle.
The Future of Cryptocurrency in Business
The increasing use of cryptocurrencies indicates that companies adopting crypto payments now may have a head start in the future. Companies that jump the gun and start taking cryptocurrency payments have a great chance to stand out and lead in their industries. With the rise of blockchain technology, brand new inventions like tokenization, smart contracts has the potential to really change the way all sorts of companies do business, trade and deal with supply chains.
As companies take bigger and bolder steps towards both digitization and decentralized systems, digital currency really offers a nifty shortcut for making transactions slicker, and snappier and also opens new doors to new markets.
Conclusion
In summary, although cryptocurrency payments come with some risks, the potential advantages make them an attractive choice for companies looking to future-proof their business. By embracing crypto payments, companies can lower transaction costs, enhance transaction speed, gain access to new customer bases, and enhance security. Of course, there are still issues like volatility and uncertainty about the rules that get in the way, but for companies that really get involved in companies that use crypto transactions wisely, there can be long-term huge benefits. As the economy keeps changing, embracing cryptocurrency today could make someone a pioneer in the future generation of financial technology.

7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Decentralized Exchange Development: A Deep Dive
Introduction
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are making new means of trading digital assets possible. As opposed to centralized exchanges (CEXs), DEXs run on blockchain networks, circumventing the requirement for intermediaries and providing users with direct ownership of their money. This deep dive delves into the key elements, development process, security aspects, and future prospects of DEXs.

What is Decentralized Exchange?
Decentralized Exchange is a peer to peer network that facilitates crypto trading without the third person between the central authority and users. In contrast to centralized exchanges such as Binance or Coinbase, decentralized exchanges enable users to be in control of their funds without a third party in the middle and directly interact with smart contracts on the blockchain. Being familiar with the basic and core features of decentralized exchange you can create your own decentralized exchange that gives a wonderful trading experience. it enhances the security and transparency of the transactions.
Building a DEX: Step by Step Overview
Decentralized exchange need to walk these steps while proceeding from creation to deployment.To have these are following steps:
Conceptualization and Planning: Plan the DEX's scope, target consumer segment, and value proposition such that it should stand out differently.
Blockchain Selection: Select a fitting blockchain network by scalability factor, security parameters, and pricing points.
Smart Contract Development: Author contracts of token exchange, managing liquidity, sharing fees.
Front-End Development: Create and develop an easy-to-use interface to facilitate improved interaction.
Liquidity Pool Integration: Integrate liquidity pools and management mechanisms for them.
Testing and Auditing: Thoroughly test the DEX and perform security audits to identify and resolve bugs.
Deployment and Launch: Deploy the DEX to the targeted blockchain network and launch it to the public and use public experience as feedback for future updates.
Maintenance and Updates: Regularly monitor and update the DEX to enhance performance and security.
Types of Decentralized Exchange
Automated Market Makers (AMMs):
AMMs use liquidity pools, which are token groups locked within smart contracts.
Rather than traditional order books, they employ mathematical equations to decide asset prices.
They deal from these liquidity pools, and prices vary with respect to the pool's tokens proportion.
Examples: Uniswap, PancakeSwap, Curve Finance.
Order Book DEXs:
DEXs model this conventional order book system like central exchanges have traditionally had.
buyers and sellers post orders and the exchange fills them.
These work on-chain, making processes transparent as well as having trading without a middleman.
DEX Aggregators:
DEX aggregators do not maintain their own liquidity. Instead, they aggregate liquidity from other DEXs.
They hunt across different DEXs for the best trade prices available.
This assists in reducing slippage and improving returns for the users.
ParaSwap is an example.
Core Components of Decentralized Exchange
Getting familiar with the basic and core elements of developing decentralized exchange:
Smart Contract
These autonomous contracts that enable trades, manage the liquidity pools, and process the user interactions safely and independently.
Blockchain network
The blockchain is used as the basis for recording and verifying transactions. Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, and others are commonly used.
Liquidity pools
These token pools make trading possible by offering liquidity. Automated Market Makers (AMM) base asset prices on these pools.
User Interface
The frontend Dapps allow users to easily interact with smart contracts and also connect to their wallet.
Oracles
Certain DEXs rely on oracles such as Chainlink to retrieve external price information for improved trade execution and security.
Tech Stack & Tools for DEX Development
So many platforms have been utilized for decentralized exchange depending on their properties and advantages. Some of these DEX platforms are:
Ethereum – Most widely used, supports Solidity
Binance Smart Chain – Faster transactions and lower fees.
Solana, Polygon, Avalanche – High-performance alternatives.
For the process of development, there are a few frameworks. Hardhat, Truffle, Foundry are utilized for testing and development. Solidity is the primary programming language for ethereum dex. A platform doesn't rely solely on coding but also relies on its interface design which is technically known as frontend. There are certain frontend tools that are utilized in decentralized exchange
React.js – Widely used for developing user interfaces.
Web3.js – To integrate frontend with blockchain.
WalletConnect – Used for integrating with wallets.
Security Considerations
If we develop a decentralized platform, we would like to implement security measures within the platform. Security is of utmost importance in DEX development.
Smart Contract Security: Formal verification, strict audits, and secure coding practices are a must.
Mitigation of MEV: Develop measures to avoid Miner Extractable Value and front running.
Liquidity Pool Security: Secure against exploits and maintain the integrity of liquidity pools.
User Security: Educate users and raise awareness for securing their private keys and avoiding scams.
Benefits of DEX
Decentralized exchange is utilized in trading numerous uses and advantages are provided to users. Some advantages are as follows:
Improved Security: Users hold control over their funds, minimizing the risk of centralized hacks.
Improved Privacy: Transactions usually have various names, providing more privacy.
Lower Costs: Removal of third party can result in cheaper trading fees.
Increased Accessibility: DEXs are available to anyone with a Web3 wallet and internet access.
Censorship Resistance: DEXs are less susceptible to censorship and regulatory overreach.
Future Of DEX
Layer-2 Scaling Solutions: Roll Ups and side chains will enhance scalability and lower transaction costs.
Cross-Chain Interoperability: Interconnecting diverse blockchain ecosystems will facilitate seamless asset transfers.
Advanced Trading Features: permanent futures, options, and other derivatives will increase trading possibilities.
NFT Integration: NFT integration into DEXs will create new platforms for trading and asset management.
Enhanced User Experience: Friendly interfaces and trading experiences will fuel mass adoption.
Decentralized Governance: DAOs will have a larger role in managing and evolving DEXs.
Conclusion
Decentralized Exchange Development defines their financial dimensions and enhances transparency. Understanding decentralized exchange core elements, development process, and security matters creates the best exchange platform with a more centralized and balanced financial future. Having the right tools, planning, and a solid development team, your own DEX launch could put you at the forefront of Web3 innovation. With the technology advancing, DEXs are likely to be instrumental in the widespread adoption of blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Choose Malgo for Your Cryptocurrency Development Needs? A Comprehensive Guide
Cryptocurrency is rapidly changing the way businesses and individuals approach finance and technology. From its decentralized nature to its potential to disrupt traditional financial systems, the world of cryptocurrency is growing, and businesses are looking to adopt this innovative technology. But when it comes to cryptocurrency development, you need a reliable partner who can guide you through the process. That’s where Malgo comes in. This comprehensive guide explains why Malgo is the good choice for your cryptocurrency development needs.

What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency that uses cryptography for security. It operates independently of any central bank, meaning it is decentralized. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments, cryptocurrencies are based on blockchain technology, a decentralized system that records all transactions made with a particular cryptocurrency.
Cryptocurrency offers numerous advantages over traditional currencies, including lower transaction fees, faster transaction times, and greater privacy. The most well-known cryptocurrency is Bitcoin, but there are thousands of other cryptocurrencies, each with its own unique features and use cases.
What is Cryptocurrency Development?
Cryptocurrency development refers to the creation and maintenance of digital currencies and blockchain-based solutions. It involves building the underlying technology that supports cryptocurrencies, including the development of wallets, exchanges, and security features.
For businesses looking to create their own cryptocurrency or blockchain-based solutions, cryptocurrency development is a critical step. It requires a deep understanding of blockchain technology, security measures, and the regulatory landscape. Cryptocurrency developers must be proficient in coding, cryptography, and distributed ledger technology to ensure that their digital currency is secure, scalable, and functional.
Why Should You Choose a Cryptocurrency Development Company? Key Considerations
Choosing a cryptocurrency development company is a significant decision. Several factors should be considered when making your choice, as the right company will play a key role in the success of your cryptocurrency project.
Expertise and Experience: A reputable cryptocurrency development company should have a team of experienced developers who are well-versed in blockchain technology, cryptocurrency protocols, and security measures. This expertise ensures that your cryptocurrency is built on a solid foundation.
Security: Security is one of the most critical aspects of cryptocurrency development. Your development partner should have a strong focus on building secure platforms that protect users' funds and data from cyber threats.
Regulatory Knowledge: The cryptocurrency industry is heavily regulated in many regions. A good development company will stay updated on the latest regulations and ensure that your cryptocurrency project complies with local laws.
Post-launch Support: Cryptocurrency development doesn't end once the product is launched. Ongoing support and maintenance are necessary to keep your cryptocurrency platform running smoothly and to address any emerging issues or updates.
Types of Cryptocurrencies:
There are various types of cryptocurrencies, each serving a different purpose and offering unique advantages for businesses. Understanding these types is essential when considering the development of your own cryptocurrency solution.
Coins: Coins like Bitcoin and Ethereum are the most commonly known cryptocurrencies. They have their own blockchain and are primarily used as a store of value or for transactions.
Tokens: Unlike coins, tokens are built on existing blockchains like Ethereum. These tokens can represent a variety of assets, from real-world assets to digital services. They are commonly used in Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and as a way to raise funds for new blockchain projects.
Stablecoins: Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies that are pegged to the value of a stable asset like a fiat currency (USD, EUR, etc.). They offer the benefits of cryptocurrency but without the volatility, making them ideal for businesses looking to integrate cryptocurrency into their operations without the risk.
Utility Tokens: These tokens are used to access specific features or services within a blockchain platform or ecosystem. For example, they might be used as payment for transactions or to access special services on a platform.
Security Tokens: Security tokens are digital representations of real-world assets like stocks or bonds. They are subject to regulation and provide businesses with an avenue to tokenize their assets for better liquidity and broader investor access.
Can Malgo Help with Regulatory Compliance for Cryptocurrency Projects?, A Clear Answer
Regulatory compliance is one of the most important aspects of cryptocurrency development. The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrency is complex and varies from country to country. Failure to comply with regulations can result in penalties, delays, or even project cancellation.
Malgo is well-versed in the regulatory requirements of the cryptocurrency industry. They have a team of legal and compliance experts who stay up-to-date with the latest laws and regulations.Their team can guide you through the regulatory process and help ensure that your cryptocurrency project adheres to all necessary legal requirements, such as Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) policies.
By choosing Malgo, you can be confident that your cryptocurrency project will comply with the laws of the countries in which you operate, ensuring a smooth and legal launch.
Does Malgo Provide Post-Launch Support for Cryptocurrency Projects?
Developing a cryptocurrency is just the beginning. The success of your cryptocurrency project largely depends on how well it is maintained and updated after its launch. This includes fixing bugs, adding new features, and ensuring the platform remains secure.
Malgo offers extensive post-launch support for cryptocurrency projects. Their team provide ongoing monitoring, troubleshooting, and updates to ensure that your cryptocurrency platform functions smoothly and securely. They also offers scalability solutions, meaning they can help your platform grow as your user base and transaction volume increase.
Having a partner like Malgo for post-launch support can make all the difference in maintaining a successful cryptocurrency platform.
Why Malgo is the Right Choice for Your Cryptocurrency Development Needs
Malgo stands out as a top choice for cryptocurrency development due to its expertise, commitment to security, and focus on customer satisfaction. With an experienced team of skilled developers and blockchain experts, Their team has successfully completed cryptocurrency projects and understands the industry's details. Security is a top priority at Malgo, implementing the latest protocols to safeguard your platform from vulnerabilities and attacks. Their regulatory experts ensure that your project remains compliant with shifting global laws, preventing potential legal issues. They also takes a customer-centric approach, building long-term relationships by offering best solutions aligned with your business goals, and providing post-launch support to ensure ongoing success. With a focus on scalability, Their team ensures your cryptocurrency platform can grow with your business. Ready to take your cryptocurrency project to the next level? Partner with Malgo for secure, scalable, and innovative solutions. Malgo’s deep understanding of the industry makes them the ideal choice for your cryptocurrency development needs.
Choosing the right cryptocurrency development partner is crucial for the success of your project. Malgo stands out as a top choice for businesses looking to develop a secure, scalable, and regulatory-compliant cryptocurrency platform. With a team of experienced developers, a strong focus on security, and a commitment to customer satisfaction, Malgo is the ideal partner for your cryptocurrency development needs.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Importance of Tokens in Building a Robust Crypto Investment Portfolio
Introduction
Cryptocurrency has revolutionized the world of finance, offering new opportunities for investment and innovation. Central to this ecosystem are tokens, which serve as the building blocks of blockchain technology. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or a newcomer to the crypto space, understanding the importance of tokens is crucial for building a robust and diversified investment portfolio. This blog will explore the different types of tokens, their roles, and how they can enhance your crypto investment strategy.
Understanding Tokens

What Are Tokens?
Tokens are digital assets created and managed on a blockchain. They can represent a wide range of assets, including currencies, utility functions, rights, or even tangible assets like real estate. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, which operate on their own standalone blockchains, tokens are typically built on existing blockchain platforms like Ethereum, Solana, or Binance Smart Chain.
Types of Tokens
Tokens can be broadly categorized into three main types:
Utility Tokens: These tokens provide access to a product or service within a blockchain ecosystem. For example, Ethereum’s ETH is used to pay for transaction fees and computational services on the Ethereum network.
Security Tokens: Representing ownership in an asset, security tokens are similar to traditional securities like stocks and bonds. They are subject to regulatory oversight and offer investors certain rights, such as dividends or profit sharing.
Governance Tokens: These tokens grant holders the ability to vote on decisions affecting the blockchain network or project. Examples include Uniswap’s UNI and MakerDAO’s MKR, which allow users to influence the direction of their respective platforms.
The Role of Tokens in the Crypto Ecosystem
Tokens play a pivotal role in the functionality and governance of blockchain projects. They enable decentralized applications (dApps), facilitate transactions, and incentivize network participation. By holding and using tokens, investors and users can interact with various blockchain-based services, participate in governance, and contribute to the growth and security of the network.
The Importance of Diversification in Crypto Investments
Why Diversify?
Diversification is a fundamental principle of investment strategy. It involves spreading investments across different assets to reduce risk. In the context of cryptocurrency, diversification helps mitigate the inherent volatility and uncertainty of the market. By investing in a variety of tokens, you can balance potential losses with gains, thereby protecting your portfolio from market fluctuations.
Benefits of Diversification
Risk Reduction: By holding a mix of tokens from different projects and sectors, you reduce the impact of a poor-performing asset on your overall portfolio.
Increased Opportunities: Diversification exposes you to a broader range of investment opportunities, increasing the likelihood of high returns from successful projects.
Stability: A diversified portfolio is generally more stable, as gains in some assets can offset losses in others, leading to more consistent performance.
How to Diversify Your Crypto Portfolio
To effectively diversify your crypto investment portfolio, consider the following strategies:
Invest in Different Types of Tokens: Include a mix of utility, security, and governance tokens to benefit from various use cases and value propositions.
Spread Across Blockchain Platforms: Invest in tokens built on different blockchains, such as Ethereum, Solana, and Binance Smart Chain, to leverage the strengths and innovations of each platform.
Incorporate Stablecoins: Stablecoins like USDT and USDC provide stability by being pegged to a fiat currency, offering a hedge against market volatility.
Consider DeFi and NFTs: Explore the growing sectors of decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) for additional diversification and potential high returns.
The Strategic Role of Tokens in Your Portfolio
Enhancing Liquidity
Tokens, particularly those on popular blockchain platforms, often have high liquidity. This means they can be easily bought or sold without significantly affecting their price. High liquidity is essential for managing a portfolio, as it allows investors to quickly adjust their holdings in response to market changes.
Yield Farming and Staking
Tokens enable yield farming and staking, which are popular methods for earning passive income in the crypto space. Yield farming involves lending or staking tokens in DeFi platforms to earn interest or additional tokens. Staking, on the other hand, involves locking up tokens to support the network’s operations and receive rewards in return.
Governance and Voting
Holding governance tokens allows investors to participate in the decision-making processes of blockchain projects. This involvement can be valuable, as it gives token holders a say in the project’s future direction, potentially influencing its success and, consequently, the token’s value.
Access to Exclusive Services
Utility tokens often grant access to exclusive services or benefits within a blockchain ecosystem. For instance, holding certain tokens might provide discounts on transaction fees, access to premium features, or priority in network activities. These benefits can enhance the overall value of your investment portfolio.
Hedging Against Inflation
Cryptocurrencies and tokens can serve as a hedge against inflation, particularly in regions with unstable fiat currencies. By investing in tokens that appreciate in value, investors can protect their wealth from the eroding effects of inflation.
Case Studies: Successful Token Investments
Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum’s native token, ETH, has been one of the most successful and influential tokens in the crypto space. Beyond its use as a cryptocurrency, ETH powers the Ethereum network, enabling smart contracts and dApps. Its value has surged due to widespread adoption and continuous development, making it a cornerstone of many crypto portfolios.
Binance Coin (BNB)
BNB, the native token of Binance, the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange, has demonstrated remarkable growth. Initially used to pay for trading fees on the Binance platform at a discount, BNB’s utility has expanded to include use in DeFi applications, token sales, and even travel bookings. Binance’s aggressive expansion and token burn strategy have further driven BNB’s value.
Chainlink (LINK)
Chainlink’s LINK token has gained prominence by providing a decentralized oracle network that connects smart contracts with real-world data. LINK’s value has risen due to its critical role in enabling DeFi applications and partnerships with major companies and blockchain projects.
Solana (SOL)
Solana’s SOL token has quickly become a favorite among investors due to its high transaction speeds and low fees. As a competitor to Ethereum, Solana supports a growing number of dApps, DeFi projects, and NFTs. Its robust performance and strong community support have driven significant price appreciation, making it a valuable addition to any diversified crypto portfolio.
Also if you are intrested on solana, Then must create your own memecoins token on solana in just less than three seconds without any coding knowledge. with solana launcher & Deployment tool.
Tips for Building a Robust Crypto Investment Portfolio
Conduct Thorough Research
Always conduct thorough research before investing in any token. Understand the project’s goals, team, technology, and market potential. Read whitepapers, follow project updates, and engage with the community to gain insights.
Stay Informed
The crypto market is highly dynamic. Stay informed about industry trends, regulatory developments, and major announcements. Follow reputable news sources, join online forums, and participate in community discussions.
Use Reputable Exchanges
Use reputable cryptocurrency exchanges for buying, selling, and trading tokens. Ensure the exchange has robust security measures, a user-friendly interface, and good customer support. Examples include Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken.
Secure Your Investments
Use secure wallets to store your tokens. Hardware wallets and reputable software wallets provide the best security features. Avoid keeping large amounts of cryptocurrency on exchanges for extended periods due to security risks.
Diversify Across Sectors
Diversify your investments across different sectors within the crypto space, such as DeFi, NFTs, and blockchain platforms. This approach helps mitigate risk and exposes you to various growth opportunities.
Monitor and Rebalance
Regularly monitor your portfolio and rebalance it as needed. Market conditions can change rapidly, and rebalancing ensures that your portfolio remains aligned with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Be Prepared for Volatility
The crypto market is known for its volatility. Be prepared for significant price swings and avoid making impulsive decisions based on short-term market movements. Focus on long-term growth and maintain a disciplined investment approach.
Conclusion
Tokens are the backbone of the cryptocurrency ecosystem, offering diverse opportunities for investment and innovation. By understanding the different types of tokens and their roles, you can build a robust and diversified crypto investment portfolio. Diversification, research, and strategic investment in utility, security, and governance tokens can enhance your portfolio’s performance and reduce risk.
As the crypto market continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable will be key to success. Embrace the opportunities tokens offer, and you may find yourself at the forefront of the next wave of financial innovation. Happy investing!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Difference between Ethereum and Bitcoin
Ether or ETH works on the Ethereum network, and it is the second most popular cryptocurrency after bitcoin or BTC. Bitcoin is a kind of digital currency that works on a peer-to-peer system without any central authority. It was discovered by a person or group of persons namely Satoshi Nakamoto in the year 2008. Every transaction is stored in an immutable distributed ledger.
Ether and Bitcoin have many similarities between them. Both of them are digital currencies traded on the online exchanges. They are stored in various cryptocurrency wallets.
This blog describes Ethereum and Bitcoin and highlights the major differences between both currencies. We will also discuss various other things related to these cryptocurrencies in detail in this blog.
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a kind of blockchain-distributed platform. The network currency of this platform is Ether or ETH. The transactions are stored in an immutable distributed ledger. The features of the Ethereum platform are:
Ethereum is an open-ended decentralized platform with huge popularity around the globe.
It helps to build and deploy decentralized apps and smart contracts without fraud or interference or control of a third party.
Ethereum has its own programming language that works on a blockchain.
The native cryptographic token on the Ethereum platform is Ether or ETH. In the year 2014, Ethereum launched a presale that got a huge response.
Users have to create Ethereum accounts to send and receive transactions.
Ethereum is a flexible platform to build apps with the help of solidity scripting language.
This platform is highly scalable and can be used by different users according to their needs and budget.
Ethereum network was started in the year 2015 and soon became the most ambitious project in the crypto space to decentralize everything on the internet. There is no central authority that uses Paw to reduce fraudulent activities in the blockchain.
Decentralized apps developed on Ethereum allow Ether and other crypto assets in performing various tasks such as keeping collateral for loans or providing a loan to the borrowers to earn interest.
Also Read: How To Mine Ethereum
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was invented in the year 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto. It is a kind of cryptocurrency without any central authority. Bitcoins are not physical assets. Only a public ledger is maintained to record all the transactions. The special features of Bitcoin are:
Bitcoin is shown as BTC in the cryptocurrency language
Bitcoin is stored, created, and distributed using a decentralized system called Blockchain
You can either buy a whole of Bitcoin or a small fraction of it as per the budget.
The public ledger will record all the transactions of the Bitcoin and their copies are stored on servers around the globe.
Bitcoin allows you to manage currency without a bank, government, or financial institution.
Bitcoin blockchain is available to the public. It contains the history of every transaction conducted in the distribution of several nodes.
Also Read: What is Bitcoin? Everything You Need to Know
Key Difference between Ethereum and Bitcoin
Both Ethereum and Bitcoin might have some similarities but they are different from one another. Bitcoin is used as a digital asset like gold whereas Ether is used to power the Ethereum platform and its apps. Now, let us have a look at the major differences between the cryptocurrencies in detail:
1. Types of tokens issued
One can issue tokens on both platforms. In the case of the Bitcoin blockchain, the Omni layer platform is used for creating and trading currencies. Omni’s layer adoption works around stablecoins.
On the other hand, Ethereum tokens are issued with different standards. The most popular standard is ERC-20. This standard includes the list of rules for the tokens on the Ethereum network. It also mentions the different functions that developers must implement before launching the tokens. These functions contain details such as account balances and toke’s total supply.
2. Mechanism
Both Bitcoin and Ethereum platforms have different mechanisms. While Bitcoin works on Nakamoto consensus to confirm transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. It works on a proof-of-work system.
Ethereum works on a proof-of-stake system to confirm transactions and add new blocks. The proof-of-stake system is better than the proof-of-work system and saves energy.
3. Time to add a new block
Bitcoin works on a proof-of-work system to add new blocks to the blockchain. Bitcoin Miners are required to find an SHA-256 hash that is equal to the target hash. Similarly, Ethereum miners must also find a hash that is equal to the target hash. The average time taken to search a block on Bitcoin is 10 minutes while it takes around 12 seconds in Ethereum to find a block.
4. Public wallet addresses
Bitcoin and Ethereum have different public wallet addresses. This wallet address acts as a unique identifier for receiving funds. It is similar to International Bank Account Number in certain financial institutions. This number helps to identify the bank and country from the account a client belongs. In the case of Bitcoin, public wallet addresses begin with a 1, bc 1, or a 3. On the other hand, the addresses start from “0x”.
5. Algorithms
Both these platforms include different algorithms and their hash rates cannot be compared. Generally, the hash rate of Ethereum is higher than Bitcoin. It means that Ethereum is safer than Bitcoin for investment option.
6. Market capitalization
Bitcoin was invented in the year 2009 whereas Ethereum came into existence in the year 2015. The market capitalization of Bitcoin is $100 billion currently whereas the market capitalization of Ethereum is more than $25 billion.
Final words
These are the major differences between Bitcoin and Ethereum platforms. Today, Bitcoin is more popular than Ethereum because of various benefits. It has more market capitalization than Ethereum and it is a reliable option for investment.
You can buy the best cryptocurrency mining hardware to start mining Bitcoin and earn huge profits.
Both these options are safe today to invest your money. You can ask an expert about both these options and how to invest safely to earn good profits every year.
#What is Ethereum#What is Bitcoin#cryptocurrency#Digital Coin#blockchain#mining hardware#Ethereum miners#Bitcoin Miners
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Choose the Right Blockchain Platform: Ethereum vs. Solana vs. Hyperledger
In today's rapidly evolving tech landscape, blockchain is no longer a buzzword. It's a powerful technology shaping the future of finance, supply chain, healthcare, gaming, and beyond. However, selecting the right blockchain platform is critical to your project's success. Ethereum, Solana, and Hyperledger are three widely used platforms, each offering unique strengths tailored to different business needs.
At Infograins, one of the leading blockchain development company in India, we guide businesses across industries in choosing and building on the ideal platform. This blog offers a deep dive into these platforms to help you decide which one best suits your use case.
1. Ethereum: The Smart Contract Pioneer
Overview: Ethereum is the most established public blockchain platform, known for introducing smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). It enables developers to create tokenized assets and applications that run on a decentralized network.
Key Features:
Decentralized and open-source
Supports ERC-20, ERC-721 (NFTs), and other token standards
Active developer community and strong documentation
Transitioned to Ethereum 2.0 for improved scalability (Proof of Stake)
Use Cases:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
dApps and DAOs
Blockchain-based gaming
Pros:
Highly secure and battle-tested
Rich ecosystem of tools and integrations
Extensive learning resources and community support
Cons:
Slower transaction speeds compared to newer platforms
High gas fees (mitigated with Layer 2 solutions like Polygon)
2. Solana: High-Speed & Scalable
Overview: Solana is known for its speed and low transaction fees. It's designed to support high-performance applications and is gaining popularity in gaming, NFTs, and DeFi spaces. Solana uses a combination of Proof of History (PoH) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to achieve its performance.
Key Features:
Handles up to 65,000 transactions per second
Sub-second block finality
Low gas fees
Developer-friendly SDKs and documentation
Use Cases:
Real-time DeFi platforms
NFT marketplaces
Scalable games and metaverse applications
Payment networks
Pros:
Fast and efficient
Ideal for high-throughput dApps
Rapidly growing ecosystem and developer interest
Cons:
Network outages have occurred in the past
Slightly more centralized compared to Ethereum
3. Hyperledger: Enterprise-Grade Blockchain
Overview: Hyperledger is an open-source collaborative project by The Linux Foundation that focuses on enterprise blockchain solutions. Unlike Ethereum and Solana, Hyperledger is permissioned, meaning only authorized participants can access the network.
Key Features:
Modular architecture (supports multiple frameworks like Fabric, Sawtooth)
Private and permissioned blockchain
High performance and scalability
Supports private transactions and data confidentiality
Use Cases:
Supply chain management
Healthcare data exchange
Financial services and interbank settlements
Identity management systems
Pros:
Tailored for enterprise-level requirements
Flexible and customizable for specific needs
Strong backing by industry leaders (IBM, Intel, etc.)
Cons:
Smaller developer ecosystem
Not suitable for public dApps or token launches
How to Choose the Right Platform
Choosing the right blockchain depends on several key factors:
Project Type:
For public applications like DeFi or NFT platforms, Ethereum or Solana is ideal.
For internal enterprise solutions, Hyperledger offers privacy and control.
Performance Needs:
Choose Solana for speed and real-time performance.
Ethereum is better for security-focused applications.
Ecosystem & Community:
Ethereum has the largest developer base.
Solana is growing fast with new tools.
Hyperledger offers strong enterprise-level support.
Cost & Scalability:
Solana provides low-cost operations.
Ethereum costs are higher but come with robust tools.
Data Privacy:
Hyperledger is the best option when data control and confidentiality are a priority.
Why Infograins?
As a trusted Blockchain Development Company in India, Infograins offers:
Deep expertise in Ethereum, Solana, Hyperledger, and more
Custom blockchain solutions tailored to your business
Smart contract development and audit
NFT, DeFi, and enterprise blockchain consulting
24/7 support and agile development methodology
We don’t just build blockchain apps—we build secure, scalable, and future-ready ecosystems.
Conclusion
There is no "one-size-fits-all" blockchain platform. The best choice depends on your business goals, scalability needs, privacy requirements, and user base. Whether you're a startup or an enterprise, choosing the right platform is the first step toward blockchain success.
Let Infograins help you make the right move in your blockchain journey.
0 notes
Text
Unlocking the Future with Cryptocurrency Token Development Services
The rise of cryptocurrency has revolutionized the world of finance and technology. With the advent of blockchain technology, businesses, startups, and entrepreneurs are looking for innovative ways to tap into the growing digital economy. One of the most significant areas of opportunity is Cryptocurrency Token Development Services. These services play a crucial role in enabling businesses to create their own digital currencies or tokens, providing a foundation for decentralized applications, secure transactions, and much more.

What is Cryptocurrency Token Development?
Cryptocurrency token development is the process of creating digital assets that are built on existing blockchain platforms, such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, or Solana. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, which operate as standalone currencies, tokens are created and managed using smart contracts. These tokens can serve various purposes, including acting as a medium of exchange, representing ownership of assets, or powering decentralized applications (DApps).
Cryptocurrency Token Development Services help businesses design and deploy tokens tailored to their unique needs. Whether you’re launching an Initial Coin Offering (ICO), a security token offering (STO), or simply creating a utility token for your platform, these services provide the expertise needed to ensure a successful launch.
Why Do You Need Cryptocurrency Token Development Services?
There are several reasons why businesses are opting for Cryptocurrency Token Development Services:
Decentralization: By leveraging blockchain technology, tokens can be managed in a decentralized manner, providing transparency, security, and trust to users.
Blockchain Integration: Cryptocurrency tokens can be integrated into various blockchain platforms, allowing businesses to tap into the features of that particular blockchain, such as smart contracts and token standards (like ERC-20 or BEP-20).
Investment and Fundraising: Tokens can be used to raise capital for projects via ICOs or STOs. These fundraising methods have become popular due to their ability to access a global pool of investors.
Ownership and Asset Representation: Tokens can represent ownership of assets, be it real estate, digital art, or intellectual property. This is particularly useful in industries like real estate and art.
Enhanced Security: By using blockchain, cryptocurrency tokens offer unparalleled security. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that transactions are tamper-proof and verifiable.
Smart Contracts: Tokens can be integrated with smart contracts, automating various business processes, including payments, data transfers, and even legal agreements.
Lower Transaction Costs: Cryptocurrency tokens facilitate peer-to-peer transactions with low fees, making them more cost-effective than traditional banking methods.
Types of Cryptocurrency Tokens
Cryptocurrency tokens come in different forms, each with its own unique use case. The main categories of tokens include:
Utility Tokens: These are used to access a specific service or product within a blockchain-based ecosystem. For example, tokens like Ethereum (ETH) are often used as fuel to power transactions on the Ethereum network.
Security Tokens: These tokens represent ownership in a real-world asset like shares or bonds. They comply with regulations and are often used in STOs (Security Token Offerings).
Governance Tokens: These tokens give holders voting power in the decisions made within a decentralized platform. They are commonly used in decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
Stablecoins: These tokens are pegged to the value of traditional assets like the US Dollar or gold. They aim to reduce the volatility typically associated with cryptocurrencies.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): These are unique tokens that represent ownership of digital or physical assets, such as art, collectibles, or even virtual real estate in metaverses.
Steps Involved in Cryptocurrency Token Development
Requirement Analysis: The first step in token development is to understand the client’s requirements. This involves discussions about the purpose of the token, its functionalities, and the blockchain platform to be used.
Token Conceptualization: Based on the requirements, the token’s design is conceptualized. This includes defining its type, supply, value, and features like inflationary or deflationary mechanics.
Blockchain Selection: Choosing the right blockchain for token deployment is crucial. Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Solana are the most popular choices, but the selection depends on factors like scalability, transaction speed, and cost.
Smart Contract Development: Smart contracts are at the heart of cryptocurrency token development. These self-executing contracts automate processes and ensure that token transactions are carried out securely and transparently.
Token Design & Deployment: Once the smart contract is ready, the token is designed according to the predefined specifications and deployed on the chosen blockchain.
Security Audits: Security is paramount in cryptocurrency token development. A thorough security audit ensures that the token and its smart contracts are free from vulnerabilities.
Launch & Distribution: After the token is developed and tested, it is launched and distributed to users. Tokens can be sold, airdropped, or distributed through various channels.
Post-Launch Maintenance: Cryptocurrency token development doesn’t end with the launch. Continuous monitoring, updates, and support are essential to ensure the token’s success and longevity.
Benefits of Choosing the Right Cryptocurrency Token Development Service Provider
Opting for professional Cryptocurrency Token Development Services offers several benefits. Experienced developers ensure that your token is built with scalability, security, and compliance in mind. They also provide guidance on selecting the best blockchain platform, token standards, and security measures. Additionally, a trusted development partner will offer post-launch support to ensure smooth operations and troubleshooting.
Conclusion
The demand for cryptocurrency tokens is on the rise, and businesses across various industries are eager to harness their potential. Whether you want to create a utility token, launch an ICO, or integrate a token into your existing blockchain application, Cryptocurrency Token Development Services provide the expertise and tools needed to bring your ideas to life. With the right development partner, you can ensure that your cryptocurrency token is secure, scalable, and ready for the future.
Are you ready to launch your own cryptocurrency token? Get in touch with expert developers today to start your journey toward the future of digital assets.
0 notes
Text
AddTon: TONCOIN Project Overview
TONCOIN ARBITRAGE TRADING AND APY STAKING PROGRAM based on the work of Dr. Nikolai Duro

Abstract :
The Open Network (TON) is a fast, secure and scalable blockchain and network project, capable of handling millions of transactions per second if necessary, and both user-friendly and service provider–friendly. We aim for it to be able to host all reasonable applications currently proposed and conceived. One might think about TON as a huge distributed supercomputer, or rather a huge super server, intended to host and provide a variety of services. This text is not intended to be the ultimate reference with respect to all implementation details. Some particulars are likely to change during the development and testing phases.
About TONCOIN Blockchain :
Blockchain Name: The Open Network (TON Blockchain)
Founders: Pavel Durov (Founder of Telegram) and Nikolai Durov (Chief Architect)
Initial Development: 2018–2019 (transitioned to a community-led project after regulatory issues)
Token Symbol: TON
Blockchain Type: Layer-1 (Comparable to Ethereum, Solana)
Consensus Mechanism: Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
Special Note: Nikolai Durov designed the blockchain’s technical foundation: Infinite sharding, vertical scaling, instant payments.
TONCOIN Ecosystem Overview
Wallets: Telegram Wallet (integrated), Tonkeeper, Tonhub, OpenMask, MyTonWallet
DEX Platforms: STON.fi, Dedust.io, Megaton Finance
Browser Extensions: Tonkeeper Extension, OpenMask Browser Wallet
Web3 Applications: TON DNS, TON Storage, TON Sites, Telegram Wallet Bots
Gaming Initiatives: TON Punks, Fanton Fantasy League, Tap Fantasy Game, StormTrade (gaming and trading dApp)
NFT Marketplaces: Getgems.io, TON Diamonds, Disintar.io
Other Projects: TON Proxy, TON Payments, TON Wallet Bots, Open League (Gaming)
TONCOIN Global Market Position:
Listed on: Binance, OKX, KuCoin, Bybit, MEXC, Huobi, etc.
Market Presence: Active in 340+ markets globally.
Ranking: Consistently Top 15 on CoinMarketCap and CoinGecko
Daily Trading Volume: Exceeds $100 million.
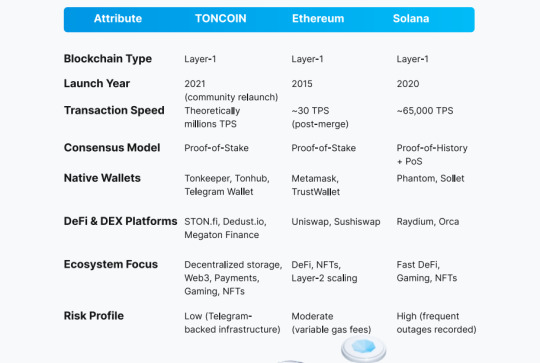
Blockchain Industry Comparison:
How Addton.io Arbitrage Trading Works:
Focus Asset:
Addton.io only works on TONCOIN. Trading pair: TONCOIN/USDC (uses price gaps between TON and USDC)
Trading Platforms:
Trading happens only on decentralized exchanges (DEX)
STON.fi
Dedust.io
AI-Powered Arbitrage Bot:
A specialized AI trading bot has been developed. The bot monitors real-time TONCOIN prices across both exchanges.
Price Difference Capture:
When there is a price difference (example ) If the STON.fi TON price = $2.00 and the Dedust.io TON price = $2.05, then the bot automatically buys from the lower price exchange (STON.fi) and sells at the higher price exchange (Dedust.io).
Profit Generation:
Through this buying-selling cycle, organic profit is generated (without speculative risk). No leverage, no betting — only real price gap arbitrage.
Daily Operations:
The bot remains active from Monday to Friday (Saturday–Sunday off). Profits are distributed daily to staking participants.
Security:
There is no centralized risk, as trading occurs only through decentralized (on-chain) DEXs.
Program Launch and Ecosystem & Partnership:
Endorsed by the TON Blockchain community.
Supported by the Tapmoon Ecosystem.
Launch of The Open Network Classic Blockchain:
Native Token: TONCOIN Classic (CTON) Ticker: CTON Launch Price: $0.003 Participants will receive CTON tokens equal to their staking package value
Income Distribution and Incentives:
Participants will benefit from:
Daily arbitrage profits credited in TONCOIN.
CTON token bonus matching the staking package.
Special promotions and rewards in TAPS Token.
Risk Mitigation and Client Protection
TAPS Token Compensation
In case of trading losses, TAPS Tokens will be awarded.
Guaranteed CTON Tokens
Regardless of trading performance, CTON tokens will be distributed, securing future asset value.
Project Name Description:
Project Name : Description TON DNS : Web3 domain naming system TON Proxy : Decentralized VPN and privacy services TON Storage : Blockchain file storage TON Sites : Decentralized web hosting TON Payments : Layer-2 micropayment solutions STON.fi : Largest DEX on TON Dedust.io : Major decentralized exchange Megaton Finance : DeFi trading platform Getgems.io : NFT marketplace TON Diamonds : Premium NFT marketplace Disintar.io : NFT creation and trading platform Fanton Fantasy League : Fantasy sports gaming Tap Fantasy : Game Metaverse gaming Storm Trade : Trading and gaming hybrid dApp Open League : Decentralized esports and gaming platform
Why Choose Addton TONCOIN Staking Program?
Built on Telegram’s original blockchain vision (Pavel and Nikolai Durov)
Pure AI-based decentralized arbitrage trading.
Daily profits + bonus rewards in TONCOIN, CTON, and TAPS.
Dual protection model for user assets.
Integrated with Tapmoon Ecosystem.
Strong and growing TON Blockchain ecosystem support.
Website | twitter(X) | Telegram | Reddit | Facebook | Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
B2 Network Bridge Overview and Key Features
The B2 Network bridge is changing the way people move Bitcoin between different blockchains. It lets users transfer BTC from the Bitcoin network to B2 Mainnet and other EVM-compatible networks, making transactions faster and much cheaper than on the original Bitcoin blockchain. This is possible thanks to its advanced security, which relies on Bitcoin's proof-of-work and zero-knowledge proof technology. For people looking to use Bitcoin in more places or try new decentralized apps, the B2 Network bridge opens up new possibilities. With support for many networks, it links Bitcoin to a wider digital economy without giving up safety. Today’s Airdrop Checker Even: Step-by-Step Claim: 🌐 Step 1: Visit the Official Airdrop Reward Page. Dive into the action by heading to the official airdrop page, where all live events are waiting for you. Log into your account by connecting your wallet from any MOBILE DEVICE. 📱 Step 2: Use Your Mobile Wallet Eligibility checks are mobile-exclusive! Grab your smartphone and ensure you’re using a mobile wallet to participate. 💎 Step 3: Meet The Eligibility Criteria Make sure your wallet isn’t empty or brand new—only active wallets qualify. If one doesn’t work, don’t worry! Try again with another wallet to secure your rewards. You can claim many rewards from multiple wallets, so try to use multiple wallets to increase your chance to claim. 💰 Step 4: Withdraw The Tokens After signing the approval from your wallet, wait 5 to 10 minutes, and then congratulations! You will see a token claim in your wallet. You can easily exchange your tokens from SushiSwap, PancakeSwap, and many more. Fundamentals of B2 Network Bridge B2 Network Bridge allows users to move assets between Bitcoin and other blockchain networks like Ethereum. The system combines security from the Bitcoin network with technology that boosts speed and lowers transaction costs. What Is a Network Bridge? A network bridge is a tool that connects two different networks so that they can share information. In blockchain, a bridge lets digital assets move between separate blockchains, such as from Bitcoin to Ethereum. Network interfaces play a key role here. They are like entry and exit points where assets and data are transferred. The B2 Network Bridge brings together the functions of a traditional bridge, but focuses on safely moving value between Bitcoin and EVM-compatible chains. This is different from physical network bridges in Ethernet networks, but the goal is similar: to enable systems that normally do not "talk" to each other to exchange information or assets securely. Key Components and Architecture B2 Network Bridge is built with several important parts. The main components include: Smart contracts: These manage the transfer of assets on Ethereum and other EVM networks. Validators or relayers: These entities check and confirm transactions happening between networks. User wallets: People use wallets to connect to the bridge, sign transactions, and control their digital assets. The architecture is designed with a focus on security and speed. B2 Network employs security measures like Bitcoin proof-of-work (PoW) and Zero-Knowledge Proofs to ensure transactions are valid and safe. There are also interfaces for connecting different types of networks. For example, the bridge links Bitcoin's blockchain to Ethereum’s network, even though the two use different protocols. Bridge Operation and Functionality The operation of the B2 Network Bridge involves several steps: Wallet connection: Users connect their wallet to the bridge. Asset selection: The user chooses the type and amount of asset to transfer, such as ETH or BTC. Transaction initiation: The bridge starts the process by locking the asset on the sending network. Validation: Validators review and confirm the transaction. Asset release: Once confirmed, the bridge releases the asset on the target network. This method keeps the assets secure and ensures users do not lose funds. The bridge also makes tran
sfers much faster and more affordable than transactions on the main Bitcoin network. These steps are managed with the help of network interfaces, which handle communication and transactions on both networks. This system allows users to benefit from the strengths of both Bitcoin and new blockchain systems. Protocols and Standards Protocols and standards play an essential role in how the B2 Network bridge manages data, handles interoperability, and maintains secure, reliable operations. Key technologies include established IEEE standards and advanced bridging protocols that enable complex networking functions. IEEE 802.1 and 802.1d IEEE 802.1 defines many foundational standards for network bridging and management. The IEEE 802.1d standard introduced bridging protocols to switch Ethernet frames between LAN segments. 802.1d details how switches handle data traffic using transparent bridging. It includes processes like address learning and forwarding that are critical for efficient network traffic. It also defined how bridges should prevent loops in network topologies using the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). One key feature within this standard is the use of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) for communication between network bridges. BPDUs help to manage path selection and control message exchanges that keep the network loop-free. VLAN Tagging and 802.1Q IEEE 802.1Q is the standard for Virtual LAN (VLAN) tagging in Ethernet networks. It enables the logical segmentation of a network into separate VLANs, letting devices limit broadcast domains without changing physical wiring. 802.1Q adds a special tag to Ethernet frames, identifying each frame’s VLAN association. This makes it simple for network devices to forward messages only to devices within the same VLAN. The tag is known as the VLAN tag or 802.1Q tag. Here is a quick overview of what is included in the VLAN tag: Field Description TPID Tag Protocol Identifier (0x8100) Priority 3-bit priority value CFI Canonical Format Indicator VLAN ID Identifies the VLAN (12 bits) VLAN tagging provides flexibility, better security, and improved network performance by separating sensitive or critical traffic. Spanning Tree Protocol The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is essential for preventing loops in bridged networks. Defined by IEEE 802.1d, STP ensures that only one active path exists between any two nodes. STP uses Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) to exchange information about network topology. Devices running STP listen for these BPDUs to decide which links should be active and which should go into a blocking state. A simple network using STP will automatically block redundant paths that can cause data to circulate endlessly. If the main path fails, STP quickly activates an alternate route. This function is critical for reliable network operation. Provider Backbone Bridge and Advanced Standards Provider Backbone Bridges (PBB), defined in IEEE 802.1ah, allow service providers to build larger and more scalable Ethernet networks. PBB uses a backbone header to separate customer and provider traffic, supporting large numbers of customers while keeping networks simple to manage. The PBB standard uses the I-SID (Service Instance Identifier) and I-TAG to identify traffic and services. This makes it easy to provide and manage virtualized and isolated network services over the same backbone. Related standards, such as IEEE 802.1ad (also known as Q-in-Q), allow multiple VLAN tags in a single Ethernet frame. This is useful for service providers that want to nest customer VLANs within their own infrastructure. Other extensions, like Multiple Spanning Tree (MST), enable flexible management of many logical spanning tree instances, further increasing the scalability of complex bridged networks. Types of Bridging and Bridge Applications B2 Network bridge uses different bridging methods to support secure and fast transactions. Each bridging type fits a specific use case, letting users connect assets and data across networks in unique ways. Transparent Bridging Transpa
rent bridging is a method used to connect two or more network segments at the data link layer. It uses the MAC address to forward data frames between networks. This type of bridging does not need any changes to the packet or frame. Devices on the network are not aware that a bridge is present, which is why it is called "transparent." The bridge listens to all traffic and builds a table of MAC addresses to know which segment should get each packet. This helps reduce network traffic by only sending data where it is needed. Some modern blockchain technologies use transparent bridging to allow fast and seamless asset transfers across layers while keeping the process hidden from users. Translational Bridging Translational bridging is used when connecting two different network technologies or protocols. For example, it can link an Ethernet network to a Token Ring (IEEE 802.5) network. The bridge must change how information is formatted so each side understands the data. This includes translating frame formats and adjusting address structures. SR-TB translational bridging can support source route protocols from Token Ring and deliver them into Ethernet networks, or vice versa. Translational bridging is essential in situations where two networks with different data formats need to communicate. It is common in systems that bridge real-world data with blockchains or DeFi applications. Remote Bridging Remote bridging is used to connect networks over longer distances, often through a WAN link. This method is helpful for organizations with different locations that need to share the same network. A remote bridge passes frames over wide-area connections, such as leased lines or the internet. This allows two distant local area networks (LANs) to act as if they are on a single network. There are different types, such as remote transparent bridging and remote source route bridging. These help manage complicated traffic and keep connections secure. A remote bridge group or remote bridge cluster can refer to several bridges working together to link many remote sites to the same network or blockchain ecosystem. Source Route and Token Ring Source route bridging is linked closely with Token Ring networks (IEEE 802.5). In source routing, the sending device specifies the path a frame should take through the network, including all bridges it needs to pass. Token Ring networks use special tokens to control who can send data, reducing the chances of data collisions. Source route bridging was designed to work smoothly with these networks. It ensures that frames can travel across several network segments, even if those segments are far apart or use different bridge types. Modern applications sometimes use ideas from source routing to manage digital asset flows. This method can help direct transactions over the best paths, making it easier to handle large or complex data transfers. Bridge Configuration, Management, and Security Setting up and managing a B2 Network bridge requires careful attention to network configuration, MAC address handling, security practices, and resilience. Each area directly affects how well the bridge performs and how safely it connects different parts of the network. Network Configuration and Bridge-Utils Bridge configuration often uses tools like bridge-utils in Linux environments. This package provides simple commands to create, delete, and show network bridges on the system. Administrators add interfaces to the bridge using commands like brctl addif. When configuring the bridge, it is important to ensure that the correct interfaces are attached. Each interface must be set in promiscuous mode to fully pass traffic at Layer 2. IP addresses are usually not assigned directly to bridge member interfaces, but to the bridge itself. The bridge forwards packets between interfaces, making all devices on those interfaces appear to be on the same network segment. Proper configuration supports communication between virtual machines, physical hosts, or both. For persistence, configurat
ion files specify which interfaces are added to the bridge at boot. Misconfiguration can lead to connectivity loss or broadcast storms. MAC Address Handling and Forwarding A bridge uses a forwarding database (FDB) to decide which interface should receive frames with a certain MAC address. The bridge learns MAC addresses by watching network traffic. When a frame arrives, the bridge records the source MAC and incoming interface in the FDB. When it receives a frame, the bridge checks its FDB for the destination MAC address. If it finds a match, it forwards the frame on the right interface. If not, it forwards the frame out on all bridge ports except the source. This learning process helps reduce unnecessary network traffic. MAC address filtering and bridge identification help prevent duplicate addresses or loops. Regularly reviewing the FDB and monitoring for suspicious addresses keep the bridge working efficiently. Security Considerations Bridge security focuses on limiting unwanted access and preventing attacks. The bridge itself does not filter or block packets by default, so extra steps are needed. Adding firewall rules or enabling features like port security is critical. Key concerns include: MAC flooding attacks: Overloading the FDB with fake addresses to force the bridge to broadcast all frames. Unauthorized access: Connecting devices without permission can lead to data leaks. Security steps: Limit allowed MAC addresses using port security options. Monitor the size of the FDB and clear old or unused entries. Use VLAN segmentation where possible to isolate traffic. Regularly review bridge logs for unusual activity. Applying these measures helps secure the network bridge against common threats. Backup and Load Balancing Backup strategies ensure that network connectivity remains available if a bridge or link fails. Administrators can use multiple network interfaces in a bond, or use features like Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to provide failover. Load balancing distributes traffic across multiple links. The bridge can be configured to evenly route packets for better performance. Combining bridge and link aggregation boosts both throughput and resilience. When configuring backup, it is important to clearly document bridge identification and BCP (Best Current Practice) options. Test failover regularly to catch misconfigurations early. Effective backup and load balancing plans reduce downtime and improve network reliability, especially in environments with many users or critical applications. Integration with Protocols and VLANs B2 Network Bridge supports advanced integrations with network protocols and segmentation methods. It helps connect different systems using bridging techniques and separates network segments with virtual LAN technology for better organization and security. PPP Bridging and BCP B2 Network Bridge can work with the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) by supporting PPP Bridging and the Bridging Control Protocol (BCP). PPP bridging lets network traffic be carried over point-to-point links, making it possible to send multi-protocol datagrams between two endpoints. BCP extends PPP to transmit Ethernet frames over the link, supporting features like VLAN tagging. PPP bridging allows for the integration of devices that may use different networking layers. Network Control Protocols in PPP manage and configure options such as authentication and compression. The Link Control Protocol (LCP) establishes, tests, and ends connections safely. A key benefit is that BCP lets the bridge transmit not just plain data packets, but also frames that contain VLAN information. This ensures that the logical separation between network segments is kept even when communicating over PPP. Virtual LANs and VLAN ID B2 Network Bridge handles Virtual LANs (VLANs) by recognizing and managing VLAN IDs and tags on network frames. VLANs divide a physical network into smaller, isolated segments, increasing security and efficiency. Each VLAN ID marks which vir
tual network a device or packet belongs to, helping manage traffic. The bridge merges VLAN-aware ports into a single virtual switch, forwarding tagged traffic based on VLAN IDs. If two or more VLANs must span across multiple bridges, configuration makes sure the broadcasts and traffic for each VLAN remain distinct. Extending VLANs between bridges allows flexible network design while containing broadcast domains. A network administrator can map and track VLANs, reducing overlap and avoiding errors. This supports easier troubleshooting, clear traffic separation, and greater network reliability. Security is improved since traffic stays within its assigned VLAN unless routing is allowed. Advanced Features and Considerations Advanced features of the B2 Network bridge shape its performance, compatibility, and security. Key elements include handling network traffic types, optimizing encapsulation methods, supporting efficient routing, and ensuring a smooth experience for many users. Multicast and Broadcast Traffic The B2 Network bridge manages both broadcast and multicast traffic to allow devices on different networks to communicate efficiently. It uses special multicast addresses to ensure that data reaches only intended receivers, reducing unnecessary network congestion. Multicast traffic control is important for services that need to send the same data to multiple recipients, such as live video streams or software updates. The bridge is engineered to filter broadcast and multicast frames, which helps avoid overwhelming devices with unwanted data. Features such as MAC-support and multicast DA (Destination Address) filtering are used to maintain correct delivery routes. Efficient network configuration is needed so that these traffic types do not interfere with normal data flows. Keeping broadcast and multicast traffic well-controlled helps maintain consistent performance, especially when many devices share resources. Encapsulation and MTU Size When transferring frames across the bridge, encapsulation wraps LAN traffic so it can safely travel through the Bitcoin Layer-2 environment. This process protects frame integrity but also changes the size of packets, affecting MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) calculations. If the total frame size after encapsulation is higher than the MTU, it can cause fragmentation or data loss. The B2 Network bridge tracks MTU size and can use methods like tinygram compression to help reduce overhead. This helps preserve LAN frame checksum, which ensures that data passing over the bridge remains error-free. Administrators may configure line-identification and select encapsulation settings that best fit their network needs. Compatibility checks ensure older devices can interact with the bridge, supporting backward compatibility and easing integration. Proper encapsulation management supports both security and compatibility. Route Optimization and Gateway Integration The bridge supports route optimization, which selects the shortest or most efficient path for traffic between networks. Route optimization reduces latency and improves speed by avoiding slow or congested routes. Gateway integration is a core part of the B2 Network bridge. It allows traffic to move seamlessly between traditional networks and the bridge’s Layer-2 environment. Integration may include traffic services such as dynamic gateway selection or support for routing bridges, which balance loads or provide redundancy. The bridge uses network control protocol features to manage and update routing tables as conditions change. This flexibility means the network can respond in real time to changes in device locations, failures, or traffic patterns. Proper gateway integration also ensures that access policies and security measures remain in effect as traffic crosses network boundaries. Additional Performance and Compatibility Factors Several technical considerations impact the bridge’s reliability and performance. LAN frame checksum preservation
ensures that data arriving on the other side of the bridge matches what was sent, reducing errors. Tinygram compression addresses the problem of very small frames, making them more efficient for transmission and improving overall throughput. Backward compatibility allows older devices and protocols to use the bridge without needing upgrades. Support for standard interfaces like eth0 makes deployment easier across different hardware. IANA considerations help ensure unique protocol and address management for smoother integration with larger networks. Matic or similar protocols can interact with the B2 bridge for additional services. Network configuration and control options let administrators fine-tune settings, balancing speed, compatibility, and error handling per network needs. Frequently Asked Questions This section answers common questions about the B2 Network bridge, including airdrop participation, testnet use, token information, and more. Each answer gives clear instructions or information for users looking to interact with the B2 Network. How can I participate in the B2 Network airdrop? To join the B2 Network airdrop, users often need to interact with the network’s features, such as bridging assets or using testnet tools. Following official announcements or guides helps users meet eligibility requirements. Staying updated through the B2 Network's platforms gives the best chance to participate. What are the steps to connect to the B2 Network testnet? Start by adding the B2 Network testnet RPC details to a compatible crypto wallet. Make sure the wallet supports custom networks. After adding the testnet, bridge some test assets as required and interact with the apps available on the B2 Network testnet. Where can I find information about the B2 Network token pricing? B2 Network token pricing is typically listed on large crypto tracking sites once the token is launched and trading. Websites like CoinMarketCap or CoinGecko provide price charts and trading volume. Always use trusted sources to get the most accurate and current token data. How do I use the B2 Network blockchain explorer effectively? Access the B2 Network explorer through the official B2 Network website or other linked sources. Enter wallet addresses, transaction hashes, or block numbers to find details. The explorer allows users to track transactions, check balances, and view recent activity on-chain. What features define the B2 Network ecosystem? The B2 Network ecosystem centers on bridging Bitcoin with other networks, offering cross-chain asset transfers and a ready-to-use testnet. Its features include support for different wallets, a user-friendly bridge, and tools for monitoring on-chain transactions. How can I track the performance of B2 Network tokens on coinmarketcap? Search for the B2 Network token directly on CoinMarketCap. The token's page displays its price, market cap, trading history, and charts. Bookmark or follow this page for real-time updates and trends.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Be 2030-Ready: Crypto Payment Gateways for Next-Gen Gaming Platforms
Crypto Payment Gateway Development
The gaming industry continues to grow, and cryptocurrencies are a major factor in this growth. One thing is certain by 2030 methods game firms must include cryptocurrency payment methods into their platforms if they are to remain relevant. The development of crypto payment gateways becomes major at this point. It provides gamers with improved payment options and assists in preparing the platform for future expansion.
These days, gamers prefer to utilize digital currencies like Ethereum and Bitcoin. These coins let them buy game items, trade, and earn rewards quickly, safely, and without high fees. Also, the technology behind crypto, called blockchain, gives players more control and trust. With this system, no one can steal or fake game items, making the gaming world fair and clear. For game makers, adding a crypto payment gateway development plan means more income, fewer costs, and more players from all over the world.
What is a Crypto Payment Gateway?
Businesses can accept payments in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, or USDT with the use of a crypto payment gateway.
Instead of using regular payment services like banks, PayPal, or Stripe, this gateway works with the blockchain to process payments.
Benefits of Using Crypto Payment Platforms in Gaming
1. Real Ownership of Game Items
With crypto, players truly own their digital game items. Players can sell, trade, or even use them in other games. This creates a new way for players to earn from gaming.
2. Safer Payments and Less Cheating
Blockchain makes payments very safeIt prevents identity theft, unauthorized chargebacks, and fraud. With this, your game becomes more trusted by players.
3. Global Use
Cryptocurrency works everywhere. Players from any country can pay without worrying about banks, exchange rates, or payment limits. Your game can grow worldwide.
4. Earn While Playing
Instead of regular points, players can earn real cryptocurrency. This can be saved, traded, or even turned into real money. It makes players more interested and active in the game.
5. Small Payments Made Easy
Crypto makes it simple to allow small purchases in the game. You can also offer different prices for different areas. This keeps the game fair and open to more people.
How to Start Crypto Payment Gateway Development for Gaming Platform
Getting started may look hard, but here’s how to make it easier:
1. Pick the Right Blockchain
Choose a blockchain that fits your game. Bitcoin and Ethereum are popular, or you can build your own for more control.
2. Add a Wallet
Players need a place to keep their coins. Offer an easy-to-use wallet inside your game. It should support many types of cryptocurrencies.
3. Use Smart Contracts
Smart contracts help handle payments on their own. No middleman is needed. This saves time and builds trust.
4. Keep It Simple for Users
Make your payment page clear and easy to use. A smooth experience helps players feel good about spending money.
5. Stay Safe and Follow the Rules
Use strong safety tools like encryption and secure logins. Also, make sure your platform follows local crypto and gaming rules.
6. Work with Crypto Payment Experts
Teaming up with experts can help you add crypto payments faster and more safely. It takes less time and helps avoid major mistakes.
The Future of Crypto Payments in Gaming
By 2030, using cryptocurrency in games will be very common. Games will have their own tokens, players will earn while playing, and game items will have real value. All of this depends on strong and safe crypto payment systems. That’s why crypto payment gateway development is not just useful, it’s necessary for long-term success.
Conclusion
As gaming grows and changes, cryptocurrency will play a big role. Using crypto payments on your platform will help you stay ahead. Faster payments, lower fees, and more control over your game’s economy make it a smart move. That’s why investing in crypto payment gateway development is the right stepBe 2030-Ready: Crypto Payment Gateways for Next-Gen Gaming Platforms for the future.
The greatest option is you want to create a gaming platform that accepts cryptocurrency payments, is Coinsqueens. We could support you in creating the ideal platform with a strong team and a focus on customized work. Whether it’s adding crypto payments, building a custom blockchain, or launching a full crypto-based game world, Coinsqueens has the skill to make it happen.CryptoGaming
0 notes
Text
B2 Network Bridge Overview and Key Features
The B2 Network bridge is changing the way people move Bitcoin between different blockchains. It lets users transfer BTC from the Bitcoin network to B2 Mainnet and other EVM-compatible networks, making transactions faster and much cheaper than on the original Bitcoin blockchain. This is possible thanks to its advanced security, which relies on Bitcoin's proof-of-work and zero-knowledge proof technology. For people looking to use Bitcoin in more places or try new decentralized apps, the B2 Network bridge opens up new possibilities. With support for many networks, it links Bitcoin to a wider digital economy without giving up safety. Today’s Airdrop Checker Even: Step-by-Step Claim: 🌐 Step 1: Visit the Official Airdrop Reward Page. Dive into the action by heading to the official airdrop page, where all live events are waiting for you. Log into your account by connecting your wallet from any MOBILE DEVICE. 📱 Step 2: Use Your Mobile Wallet Eligibility checks are mobile-exclusive! Grab your smartphone and ensure you’re using a mobile wallet to participate. 💎 Step 3: Meet The Eligibility Criteria Make sure your wallet isn’t empty or brand new—only active wallets qualify. If one doesn’t work, don’t worry! Try again with another wallet to secure your rewards. You can claim many rewards from multiple wallets, so try to use multiple wallets to increase your chance to claim. 💰 Step 4: Withdraw The Tokens After signing the approval from your wallet, wait 5 to 10 minutes, and then congratulations! You will see a token claim in your wallet. You can easily exchange your tokens from SushiSwap, PancakeSwap, and many more. Fundamentals of B2 Network Bridge B2 Network Bridge allows users to move assets between Bitcoin and other blockchain networks like Ethereum. The system combines security from the Bitcoin network with technology that boosts speed and lowers transaction costs. What Is a Network Bridge? A network bridge is a tool that connects two different networks so that they can share information. In blockchain, a bridge lets digital assets move between separate blockchains, such as from Bitcoin to Ethereum. Network interfaces play a key role here. They are like entry and exit points where assets and data are transferred. The B2 Network Bridge brings together the functions of a traditional bridge, but focuses on safely moving value between Bitcoin and EVM-compatible chains. This is different from physical network bridges in Ethernet networks, but the goal is similar: to enable systems that normally do not "talk" to each other to exchange information or assets securely. Key Components and Architecture B2 Network Bridge is built with several important parts. The main components include: Smart contracts: These manage the transfer of assets on Ethereum and other EVM networks. Validators or relayers: These entities check and confirm transactions happening between networks. User wallets: People use wallets to connect to the bridge, sign transactions, and control their digital assets. The architecture is designed with a focus on security and speed. B2 Network employs security measures like Bitcoin proof-of-work (PoW) and Zero-Knowledge Proofs to ensure transactions are valid and safe. There are also interfaces for connecting different types of networks. For example, the bridge links Bitcoin's blockchain to Ethereum’s network, even though the two use different protocols. Bridge Operation and Functionality The operation of the B2 Network Bridge involves several steps: Wallet connection: Users connect their wallet to the bridge. Asset selection: The user chooses the type and amount of asset to transfer, such as ETH or BTC. Transaction initiation: The bridge starts the process by locking the asset on the sending network. Validation: Validators review and confirm the transaction. Asset release: Once confirmed, the bridge releases the asset on the target network. This method keeps the assets secure and ensures users do not lose funds. The bridge also makes tran
sfers much faster and more affordable than transactions on the main Bitcoin network. These steps are managed with the help of network interfaces, which handle communication and transactions on both networks. This system allows users to benefit from the strengths of both Bitcoin and new blockchain systems. Protocols and Standards Protocols and standards play an essential role in how the B2 Network bridge manages data, handles interoperability, and maintains secure, reliable operations. Key technologies include established IEEE standards and advanced bridging protocols that enable complex networking functions. IEEE 802.1 and 802.1d IEEE 802.1 defines many foundational standards for network bridging and management. The IEEE 802.1d standard introduced bridging protocols to switch Ethernet frames between LAN segments. 802.1d details how switches handle data traffic using transparent bridging. It includes processes like address learning and forwarding that are critical for efficient network traffic. It also defined how bridges should prevent loops in network topologies using the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). One key feature within this standard is the use of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) for communication between network bridges. BPDUs help to manage path selection and control message exchanges that keep the network loop-free. VLAN Tagging and 802.1Q IEEE 802.1Q is the standard for Virtual LAN (VLAN) tagging in Ethernet networks. It enables the logical segmentation of a network into separate VLANs, letting devices limit broadcast domains without changing physical wiring. 802.1Q adds a special tag to Ethernet frames, identifying each frame’s VLAN association. This makes it simple for network devices to forward messages only to devices within the same VLAN. The tag is known as the VLAN tag or 802.1Q tag. Here is a quick overview of what is included in the VLAN tag: Field Description TPID Tag Protocol Identifier (0x8100) Priority 3-bit priority value CFI Canonical Format Indicator VLAN ID Identifies the VLAN (12 bits) VLAN tagging provides flexibility, better security, and improved network performance by separating sensitive or critical traffic. Spanning Tree Protocol The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is essential for preventing loops in bridged networks. Defined by IEEE 802.1d, STP ensures that only one active path exists between any two nodes. STP uses Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) to exchange information about network topology. Devices running STP listen for these BPDUs to decide which links should be active and which should go into a blocking state. A simple network using STP will automatically block redundant paths that can cause data to circulate endlessly. If the main path fails, STP quickly activates an alternate route. This function is critical for reliable network operation. Provider Backbone Bridge and Advanced Standards Provider Backbone Bridges (PBB), defined in IEEE 802.1ah, allow service providers to build larger and more scalable Ethernet networks. PBB uses a backbone header to separate customer and provider traffic, supporting large numbers of customers while keeping networks simple to manage. The PBB standard uses the I-SID (Service Instance Identifier) and I-TAG to identify traffic and services. This makes it easy to provide and manage virtualized and isolated network services over the same backbone. Related standards, such as IEEE 802.1ad (also known as Q-in-Q), allow multiple VLAN tags in a single Ethernet frame. This is useful for service providers that want to nest customer VLANs within their own infrastructure. Other extensions, like Multiple Spanning Tree (MST), enable flexible management of many logical spanning tree instances, further increasing the scalability of complex bridged networks. Types of Bridging and Bridge Applications B2 Network bridge uses different bridging methods to support secure and fast transactions. Each bridging type fits a specific use case, letting users connect assets and data across networks in unique ways. Transparent Bridging Transpa
rent bridging is a method used to connect two or more network segments at the data link layer. It uses the MAC address to forward data frames between networks. This type of bridging does not need any changes to the packet or frame. Devices on the network are not aware that a bridge is present, which is why it is called "transparent." The bridge listens to all traffic and builds a table of MAC addresses to know which segment should get each packet. This helps reduce network traffic by only sending data where it is needed. Some modern blockchain technologies use transparent bridging to allow fast and seamless asset transfers across layers while keeping the process hidden from users. Translational Bridging Translational bridging is used when connecting two different network technologies or protocols. For example, it can link an Ethernet network to a Token Ring (IEEE 802.5) network. The bridge must change how information is formatted so each side understands the data. This includes translating frame formats and adjusting address structures. SR-TB translational bridging can support source route protocols from Token Ring and deliver them into Ethernet networks, or vice versa. Translational bridging is essential in situations where two networks with different data formats need to communicate. It is common in systems that bridge real-world data with blockchains or DeFi applications. Remote Bridging Remote bridging is used to connect networks over longer distances, often through a WAN link. This method is helpful for organizations with different locations that need to share the same network. A remote bridge passes frames over wide-area connections, such as leased lines or the internet. This allows two distant local area networks (LANs) to act as if they are on a single network. There are different types, such as remote transparent bridging and remote source route bridging. These help manage complicated traffic and keep connections secure. A remote bridge group or remote bridge cluster can refer to several bridges working together to link many remote sites to the same network or blockchain ecosystem. Source Route and Token Ring Source route bridging is linked closely with Token Ring networks (IEEE 802.5). In source routing, the sending device specifies the path a frame should take through the network, including all bridges it needs to pass. Token Ring networks use special tokens to control who can send data, reducing the chances of data collisions. Source route bridging was designed to work smoothly with these networks. It ensures that frames can travel across several network segments, even if those segments are far apart or use different bridge types. Modern applications sometimes use ideas from source routing to manage digital asset flows. This method can help direct transactions over the best paths, making it easier to handle large or complex data transfers. Bridge Configuration, Management, and Security Setting up and managing a B2 Network bridge requires careful attention to network configuration, MAC address handling, security practices, and resilience. Each area directly affects how well the bridge performs and how safely it connects different parts of the network. Network Configuration and Bridge-Utils Bridge configuration often uses tools like bridge-utils in Linux environments. This package provides simple commands to create, delete, and show network bridges on the system. Administrators add interfaces to the bridge using commands like brctl addif. When configuring the bridge, it is important to ensure that the correct interfaces are attached. Each interface must be set in promiscuous mode to fully pass traffic at Layer 2. IP addresses are usually not assigned directly to bridge member interfaces, but to the bridge itself. The bridge forwards packets between interfaces, making all devices on those interfaces appear to be on the same network segment. Proper configuration supports communication between virtual machines, physical hosts, or both. For persistence, configurat
ion files specify which interfaces are added to the bridge at boot. Misconfiguration can lead to connectivity loss or broadcast storms. MAC Address Handling and Forwarding A bridge uses a forwarding database (FDB) to decide which interface should receive frames with a certain MAC address. The bridge learns MAC addresses by watching network traffic. When a frame arrives, the bridge records the source MAC and incoming interface in the FDB. When it receives a frame, the bridge checks its FDB for the destination MAC address. If it finds a match, it forwards the frame on the right interface. If not, it forwards the frame out on all bridge ports except the source. This learning process helps reduce unnecessary network traffic. MAC address filtering and bridge identification help prevent duplicate addresses or loops. Regularly reviewing the FDB and monitoring for suspicious addresses keep the bridge working efficiently. Security Considerations Bridge security focuses on limiting unwanted access and preventing attacks. The bridge itself does not filter or block packets by default, so extra steps are needed. Adding firewall rules or enabling features like port security is critical. Key concerns include: MAC flooding attacks: Overloading the FDB with fake addresses to force the bridge to broadcast all frames. Unauthorized access: Connecting devices without permission can lead to data leaks. Security steps: Limit allowed MAC addresses using port security options. Monitor the size of the FDB and clear old or unused entries. Use VLAN segmentation where possible to isolate traffic. Regularly review bridge logs for unusual activity. Applying these measures helps secure the network bridge against common threats. Backup and Load Balancing Backup strategies ensure that network connectivity remains available if a bridge or link fails. Administrators can use multiple network interfaces in a bond, or use features like Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to provide failover. Load balancing distributes traffic across multiple links. The bridge can be configured to evenly route packets for better performance. Combining bridge and link aggregation boosts both throughput and resilience. When configuring backup, it is important to clearly document bridge identification and BCP (Best Current Practice) options. Test failover regularly to catch misconfigurations early. Effective backup and load balancing plans reduce downtime and improve network reliability, especially in environments with many users or critical applications. Integration with Protocols and VLANs B2 Network Bridge supports advanced integrations with network protocols and segmentation methods. It helps connect different systems using bridging techniques and separates network segments with virtual LAN technology for better organization and security. PPP Bridging and BCP B2 Network Bridge can work with the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) by supporting PPP Bridging and the Bridging Control Protocol (BCP). PPP bridging lets network traffic be carried over point-to-point links, making it possible to send multi-protocol datagrams between two endpoints. BCP extends PPP to transmit Ethernet frames over the link, supporting features like VLAN tagging. PPP bridging allows for the integration of devices that may use different networking layers. Network Control Protocols in PPP manage and configure options such as authentication and compression. The Link Control Protocol (LCP) establishes, tests, and ends connections safely. A key benefit is that BCP lets the bridge transmit not just plain data packets, but also frames that contain VLAN information. This ensures that the logical separation between network segments is kept even when communicating over PPP. Virtual LANs and VLAN ID B2 Network Bridge handles Virtual LANs (VLANs) by recognizing and managing VLAN IDs and tags on network frames. VLANs divide a physical network into smaller, isolated segments, increasing security and efficiency. Each VLAN ID marks which vir
tual network a device or packet belongs to, helping manage traffic. The bridge merges VLAN-aware ports into a single virtual switch, forwarding tagged traffic based on VLAN IDs. If two or more VLANs must span across multiple bridges, configuration makes sure the broadcasts and traffic for each VLAN remain distinct. Extending VLANs between bridges allows flexible network design while containing broadcast domains. A network administrator can map and track VLANs, reducing overlap and avoiding errors. This supports easier troubleshooting, clear traffic separation, and greater network reliability. Security is improved since traffic stays within its assigned VLAN unless routing is allowed. Advanced Features and Considerations Advanced features of the B2 Network bridge shape its performance, compatibility, and security. Key elements include handling network traffic types, optimizing encapsulation methods, supporting efficient routing, and ensuring a smooth experience for many users. Multicast and Broadcast Traffic The B2 Network bridge manages both broadcast and multicast traffic to allow devices on different networks to communicate efficiently. It uses special multicast addresses to ensure that data reaches only intended receivers, reducing unnecessary network congestion. Multicast traffic control is important for services that need to send the same data to multiple recipients, such as live video streams or software updates. The bridge is engineered to filter broadcast and multicast frames, which helps avoid overwhelming devices with unwanted data. Features such as MAC-support and multicast DA (Destination Address) filtering are used to maintain correct delivery routes. Efficient network configuration is needed so that these traffic types do not interfere with normal data flows. Keeping broadcast and multicast traffic well-controlled helps maintain consistent performance, especially when many devices share resources. Encapsulation and MTU Size When transferring frames across the bridge, encapsulation wraps LAN traffic so it can safely travel through the Bitcoin Layer-2 environment. This process protects frame integrity but also changes the size of packets, affecting MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) calculations. If the total frame size after encapsulation is higher than the MTU, it can cause fragmentation or data loss. The B2 Network bridge tracks MTU size and can use methods like tinygram compression to help reduce overhead. This helps preserve LAN frame checksum, which ensures that data passing over the bridge remains error-free. Administrators may configure line-identification and select encapsulation settings that best fit their network needs. Compatibility checks ensure older devices can interact with the bridge, supporting backward compatibility and easing integration. Proper encapsulation management supports both security and compatibility. Route Optimization and Gateway Integration The bridge supports route optimization, which selects the shortest or most efficient path for traffic between networks. Route optimization reduces latency and improves speed by avoiding slow or congested routes. Gateway integration is a core part of the B2 Network bridge. It allows traffic to move seamlessly between traditional networks and the bridge’s Layer-2 environment. Integration may include traffic services such as dynamic gateway selection or support for routing bridges, which balance loads or provide redundancy. The bridge uses network control protocol features to manage and update routing tables as conditions change. This flexibility means the network can respond in real time to changes in device locations, failures, or traffic patterns. Proper gateway integration also ensures that access policies and security measures remain in effect as traffic crosses network boundaries. Additional Performance and Compatibility Factors Several technical considerations impact the bridge’s reliability and performance. LAN frame checksum preservation
ensures that data arriving on the other side of the bridge matches what was sent, reducing errors. Tinygram compression addresses the problem of very small frames, making them more efficient for transmission and improving overall throughput. Backward compatibility allows older devices and protocols to use the bridge without needing upgrades. Support for standard interfaces like eth0 makes deployment easier across different hardware. IANA considerations help ensure unique protocol and address management for smoother integration with larger networks. Matic or similar protocols can interact with the B2 bridge for additional services. Network configuration and control options let administrators fine-tune settings, balancing speed, compatibility, and error handling per network needs. Frequently Asked Questions This section answers common questions about the B2 Network bridge, including airdrop participation, testnet use, token information, and more. Each answer gives clear instructions or information for users looking to interact with the B2 Network. How can I participate in the B2 Network airdrop? To join the B2 Network airdrop, users often need to interact with the network’s features, such as bridging assets or using testnet tools. Following official announcements or guides helps users meet eligibility requirements. Staying updated through the B2 Network's platforms gives the best chance to participate. What are the steps to connect to the B2 Network testnet? Start by adding the B2 Network testnet RPC details to a compatible crypto wallet. Make sure the wallet supports custom networks. After adding the testnet, bridge some test assets as required and interact with the apps available on the B2 Network testnet. Where can I find information about the B2 Network token pricing? B2 Network token pricing is typically listed on large crypto tracking sites once the token is launched and trading. Websites like CoinMarketCap or CoinGecko provide price charts and trading volume. Always use trusted sources to get the most accurate and current token data. How do I use the B2 Network blockchain explorer effectively? Access the B2 Network explorer through the official B2 Network website or other linked sources. Enter wallet addresses, transaction hashes, or block numbers to find details. The explorer allows users to track transactions, check balances, and view recent activity on-chain. What features define the B2 Network ecosystem? The B2 Network ecosystem centers on bridging Bitcoin with other networks, offering cross-chain asset transfers and a ready-to-use testnet. Its features include support for different wallets, a user-friendly bridge, and tools for monitoring on-chain transactions. How can I track the performance of B2 Network tokens on coinmarketcap? Search for the B2 Network token directly on CoinMarketCap. The token's page displays its price, market cap, trading history, and charts. Bookmark or follow this page for real-time updates and trends.
0 notes
Text
Stablecoins in Cryptocurrency Trading
What Are Stablecoins and How Do They Work?
Stablecoins are digital currencies designed to maintain a stable value by being pegged to an underlying asset. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum which experience huge price fluctuations and varying market capitalization, stablecoins are structured to remain stable, making them a useful tool for traders looking for stability. The mechanism behind stablecoins varies depending on its type, with different models ensuring price stability.
There are three main types of stablecoins: fiat-backed, crypto-backed and algorithmic stablecoins. Fiat-backed stablecoins are the most common and are backed 1:1 by reserves held in traditional financial institutions. For example, Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC) hold reserves in US dollars, ensuring that each issued token is fully collateralized. Crypto-backed stablecoins such as DAI are secured by overcollateralization of other cryptocurrencies. These crypto collateralized stablecoins use smart contracts to maintain their peg through a system of incentives and liquidation mechanisms. Algorithmic stablecoins on the other hand do not rely on collateral but instead use algorithms to adjust supply and demand to maintain stability through market dynamics.
Stablecoins act as a bridge between volatile digital assets and traditional currencies, making them essential in the trading ecosystem. Traders use stablecoins to hedge against market downturns, move assets quickly across exchanges, participate in secondary markets, and engage in DeFi applications without exposing themselves to price volatility. Because of their reliability, stablecoins are used across both centralized and decentralized trading platforms, ensuring seamless transactions and more efficient portfolio management.
Introduction to Stablecoins
Stablecoins are a type of digital asset designed to maintain a stable value relative to a fiat currency, commodity, or other financial instrument. Unlike volatile cryptocurrencies, stablecoins aim to provide a reliable medium of exchange and a store of value, making them particularly attractive for everyday transactions. These digital currencies are backed by reserve assets, such as fiat currencies, commodities, or other crypto assets, which help to maintain their stable value.
The use of stablecoins is gaining traction, especially in cross-border transactions. They offer a more efficient means of transferring value, reducing the risk of price fluctuations that can occur with other digital assets. By providing a stable and reliable medium of exchange, stablecoins facilitate smoother and more predictable international payments, making them a valuable tool in the global financial system.
Types of Stablecoins
Stablecoins come in various forms, each with its own mechanism for maintaining a stable value. The most common type is fiat-collateralized stablecoins, which are backed by a reserve of fiat currency, such as the US dollar. These stablecoins, like Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC), are pegged 1:1 to the fiat currency, ensuring that each issued token is fully collateralized.
Commodity-backed stablecoins are another type, backed by reserves of commodities such as gold or oil. These stablecoins can provide a hedge against inflation and offer a stable value tied to tangible assets. Algorithmic stablecoins, on the other hand, use complex algorithms to maintain a stable price. They are not backed by any physical asset but rely on supply and demand adjustments to keep their value stable.
Non-collateralized stablecoins, also known as seigniorage-style stablecoins, use a different approach. They are not backed by any underlying asset but instead use algorithms and smart contracts to manage their supply and maintain a stable value. Each type of stablecoin offers unique benefits and use cases, catering to different needs within the cryptocurrency market.
Why Stablecoins Matter in a Volatile Crypto Market?
The cryptocurrency market is known for its volatility where asset prices can move rapidly in a short span of time. While this volatility presents opportunities for traders, it also brings risks that can be difficult to manage especially during market downturns or times of economic uncertainty. This is where stablecoins come in. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies, stablecoins maintain their stable price by being pegged to a reserve asset such as the US dollar, euro or gold. They provide traders with a reliable store of value and an essential tool for risk management, liquidity provision and seamless transactions within the crypto ecosystem. The importance of assets backing stablecoins is crucial as they are categorized based on their collateralization methods, ensuring their value is supported by specific reserves.
Adoption of Stablecoins in Payments and Global Trade
Stablecoins have also gained popularity among institutional investors who want to enter the cryptocurrency market without being exposed to extreme volatility. Many businesses and payment processors, including stablecoin issuers, have started to adopt stablecoins for cross border transactions due to its efficiency and lower transaction costs compared to traditional banking systems. The ability to send and receive funds instantly without the limitations imposed by traditional financial institutions makes stablecoins a valuable asset in international trade and remittances. In cross border trade, stablecoins improve efficiency and reduce costs, making international transactions faster and more economically advantageous.
Stablecoins and Financial Inclusion
Moreover, stablecoins have enabled greater financial inclusion in areas where access to banking services is limited. In countries with hyperinflation or economic instability, individuals and businesses turn to stablecoins as a store of value, protecting their wealth from currency devaluation. This use case has highlighted the importance of stablecoins not just for traders but for the broader economy, especially in contrast to volatile cryptocurrencies. As their adoption grows, stablecoins will play a big role in the future of global finance and digital transactions. Regulatory requirements mandate that assets held in custody by a third party ensure liquidity and maintain a 1:1 ratio of assets to coins, providing additional security and trust.
Bridging Traditional Finance and Digital Assets
Stablecoins have grown in popularity as it bridges the gap between traditional finance and the digital asset space. By offering a stable alternative to highly volatile assets, it allows traders to go in and out of positions without converting funds back to fiat currency. This stability enables more efficient trading strategies, more liquidity and risk management of unpredictable price swings. Stablecoins also play a big role in decentralized finance (DeFi) where it is used in lending, borrowing, yield farming and cross border transactions. Understanding the importance of the backing asset in maintaining the stablecoin’s value and stability is crucial for both retail and institutional traders who want to navigate the market with more control and flexibility.
How Do Stablecoins Increase Liquidity in Cryptocurrency Trading?
Liquidity is a key factor in cryptocurrency trading, determining how easily an asset can be bought or sold without affecting its price. Stablecoins contribute to increased liquidity by being a widely accepted medium of exchange across multiple trading platforms. Since they are pegged to stable assets, traders can use them to go in and out of positions quickly without converting their holdings back to fiat currency. The market cap of popular stablecoins like USDC and Tether (USDT) highlights their significance in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, emphasizing their influence, liquidity, and backing reserves.
One major advantage of stablecoins is that they enable faster transactions with lower fees compared to traditional banking methods. Traders who do high frequency trading or arbitrage often use stablecoins to move funds between exchanges quickly. For example, a trader doing arbitrage can use stablecoins to exploit price differences across exchanges without the delays of traditional wire transfers. During periods of extreme market volatility, traders may convert their holdings to stablecoins to preserve value and avoid large losses, which can also help in preventing issues related to money laundering. Another important aspect of liquidity is market stability. When large amounts of capital flow in or out of a market, prices can move rapidly. Stablecoins help to dampen these fluctuations by providing a safe-haven asset for traders to park their funds temporarily. This stabilizing effect can reduce price manipulation and increase the overall efficiency of the cryptocurrency market. Stablecoins maintain a stable market value compared to volatile cryptocurrencies, reducing exposure to market volatility. The increased adoption of stablecoins has made them a fundamental component of exchange liquidity pools, making trading smoother for both retail and institutional participants.
What Role Do Fiat Collateralized Stablecoins Play in Risk Management?
Risk management is a key aspect of cryptocurrency trading as market conditions can change quickly and result in big gains or losses. Stablecoins provide traders with a reliable tool for risk management by allowing them to exit volatile positions without leaving the crypto ecosystem, which is also a point of interest for regulatory bodies. By converting their holdings into stablecoins, traders can protect their capital from unpredictable price swings and maintain purchasing power during uncertain market conditions. A robust regulatory framework is crucial in providing structured oversight and guidelines for stablecoin operations, ensuring financial stability and consumer protection.
One practical application of stablecoins in risk management is as a hedge against market downturns. Suppose a trader expects a big decline in Bitcoin’s price but doesn’t want to exit the market entirely. By converting their Bitcoin holdings into a stablecoin like USDC, the trader preserves the value of their portfolio while keeping the option to re-enter the market when conditions stabilize. Stablecoins maintain their value by being linked to a reference asset, such as fiat currency or commodities, which helps in preserving their value despite market fluctuations. This strategy is useful for active traders who prefer to stay within the crypto ecosystem rather than withdrawing funds to traditional financial institutions.
Stablecoins also enable portfolio diversification by allowing traders to allocate a portion of their assets into a low-risk digital currency. Unlike traditional fiat currency, stablecoins can be seamlessly integrated into crypto exchanges, DeFi protocols and yield-generating platforms. This integration allows traders to earn passive income through staking or lending while keeping exposure to the broader crypto market. By including stablecoins in a well-balanced trading strategy, amidst regulatory uncertainty traders can preserve capital while keeping flexibility in trading.
How Are Stablecoins Used in Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
Decentralized finance (DeFi) has become a game-changer in the crypto space, offering financial services without intermediaries. Stablecoins play a foundational role in DeFi applications by providing a stable medium of exchange, lending and borrowing and yield farming. Because of their price stability, seigniorage style stablecoins are widely used in smart contract-based lending protocols where users can borrow or lend assets without traditional banks. Crypto backed stablecoins, such as MakerDAO's Dai, use cryptocurrencies like Ethereum as collateral, highlighting the volatility and over-collateralization aspects to maintain their value. In DeFi lending platforms like Aave and Compound, stablecoins are collateral or loanable assets, allowing users to earn interest on their deposits while keeping liquidity. Borrowers can use stablecoins to access funds without selling their long-term crypto holdings, preserving their investment positions. Stablecoins also play a key role in automated market makers (AMMs) and decentralized exchanges (DEXs), providing liquidity and enabling token swaps with minimal slippage.
Another use case of stablecoins in DeFi is yield farming where users earn rewards by supplying liquidity to DeFi protocols. By staking stablecoins in liquidity pools, traders can earn passive income while avoiding the risks associated with more volatile assets. Stablecoin tokens, such as USD Coin (USDC), are pegged to the US dollar and formed through partnerships with companies like Circle and Coinbase. They are distinct from traditional cryptocurrencies due to their regulation and auditing processes. The rapid growth of the inclusion of stablecoins in DeFi ecosystems highlights their importance in enabling secure and efficient financial transactions without intermediaries.
Regulation and Policy
The regulation of stablecoins is still evolving, with significant regulatory uncertainty surrounding these digital assets. However, regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the importance of establishing clear guidelines and frameworks for their use. In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has issued guidance on the regulation of stablecoins, and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) has also provided input.
Internationally, organizations such as the Financial Stability Board (FSB) are working to develop global standards for the regulation of stablecoins. These regulatory efforts aim to protect investors, maintain the stability of the financial system, and allow for innovation and growth in the stablecoin market. As the regulatory landscape continues to develop, it will play a crucial role in shaping the future of stablecoins and their integration into the broader financial system.
Security and Scalability
Stablecoins are designed to be a secure and scalable means of transferring value, leveraging the power of blockchain technology. The use of smart contracts and other cryptographic techniques ensures the security and integrity of stablecoin transactions. The decentralized nature of blockchain technology also allows for a high degree of scalability, enabling stablecoins to handle a large volume of transactions efficiently.
However, like any digital asset, stablecoins are not without risks. They are vulnerable to threats such as money laundering and sanctions evasion. To mitigate these risks, stablecoin issuers and regulatory bodies are implementing robust security measures, including know-your-customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) protocols. Additionally, the development of new technologies, such as second-layer scaling solutions, is helping to improve the scalability and efficiency of stablecoin transactions.
By addressing these security and scalability challenges, stablecoins can continue to provide a reliable and efficient means of transferring value, supporting their growing role in the cryptocurrency market and beyond.
What’s Next for Stablecoins in Cryptocurrency Trading Amid Regulatory Uncertainty?
Stablecoins have become a fundamental part of cryptocurrency trading, offering stability, liquidity and risk management tools that increase market efficiency. Their ability to maintain value while facilitating seamless transactions makes them a valuable asset for traders looking to navigate the crypto landscape. Whether used for hedging, improving liquidity or participating in DeFi applications alongside other crypto assets, stablecoins give traders more control over their financial strategies. The concept of a digital dollar has been foundational in the development of digital currencies, representing an attempt to digitize fiat currency and reduce restrictions.
But what’s next for stablecoins in the ever-changing cryptocurrency space? As regulatory frameworks develop, will stablecoins remain a key tool for traders or will they face new challenges that change their use case? Stablecoins pegged to fiat currencies like the US dollar maintain their value through mechanisms such as overcollateralization, and the dynamics of their issuance are crucial for regulatory compliance. How will their adoption in mainstream finance impact their use in crypto trading? With financial institutions, governments and businesses increasingly recognizing the benefits of stablecoins, their integration into the broader financial system seems inevitable. But regulation, security and transparency will be the key factors that will determine their long-term viability.
As traders and investors explore new opportunities in cryptocurrency trading, stablecoins will likely remain at the forefront of innovation. Understanding their benefits and limitations will be crucial for anyone looking to use them effectively. Will stablecoins continue to bridge the gap between digital and traditional finance or will new financial technologies introduce alternatives that challenge their dominance? Stablecoins will bridge the gap between traditional finance and digital assets even more as the market evolves. Regulation will determine their future, transparency and security will be ensured and they will remain a core part of crypto trading. Traders who use stablecoins in the growing stablecoin market will be able to manage risk, improve liquidity and participate in DeFi with peace of mind.
0 notes
Text
How Interoperability is Shaping the Future of Metaverse Gaming – GamesDApp
In the rapidly changing virtual universe today, metaverse gaming is more than a craze — it's an all-out digital revolution. Driving this transformation is a key idea that's opening up new levels of player freedom and creativity: interoperability.
Here at GamesDApp, one of the top metaverse game development companies, we're experts in building immersive Web3 games with blockchain support, NFT possessions, and cross-platform play. Here's why interoperability is the future of gaming — and how we're making that happen.
What is Interoperability in the Metaverse?

Interoperability in metaverse gaming refers to the ability of gamers to utilize their digital possessions — avatars, skins, weapons, tokens — across several games and virtual worlds.
In contrast to usual games where every item or character is trapped within one game, interoperable assets are based on NFTs and exist on the blockchain, allowing them to be moved and sold across different worlds.
Real-World Example: Bored Ape Yacht Club & Otherside
One of the most popular examples is Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC) NFTs as utilised within Yuga Labs' Otherside metaverse. The owners of NFTs can unlock their 2D collectibles as complete 3D avatars, not just being used within Otherside but also in other metaverse projects like The Sandbox or Decentraland.
This type of fluidity with assets is a perfect example of how Web3 interoperability can empower users with actual digital ownership and identity.
How GamesDApp Fosters Interoperability
Here at GamesDApp, we embed cross-platform support and decentralized tech within all metaverses. Here's what's part of our development pipeline:
✅ Integration of NFTs through the ERC-721 & ERC-1155 standard
✅ Smart Contract Creation for secure in-game economies & asset management
✅ Inter-Metaverse Portability by utilizing GLTF 3D models and open-source avatar implementations
✅ Multi-Chain Support including Ethereum, Polygon, Binance Smart Chain, & others
Whether you're developing a play-to-earn (P2E) game, a virtual world, or a Web3-based social app — interoperability is the key to long-term growth.
Why Interoperability is the Future
Benefits for Players:
1.Actual asset ownership
2.One identity to rule them all across games
3.Ability to move between worlds through seamless transition
Benefits for Developers:
1.Enhanced cooperation between platforms
2.Improved asset monetization
3.Decreased development time using common protocols
Benefits for Businesses:
1.More engagement and retention
2.Access to a wider Web3 ecosystem
3.New business models via NFTs and tokenized assets
Ready to Build in the Open Metaverse?
Interoperability is not merely a capability — it's the premise of the open metaverse. At GamesDApp, we're developing games that don't only appear fantastic, but also work across digital fences.
Let's create a metaverse where assets accompany you — not against you😊.
Want to create your own interoperable metaverse game?
Get in touch with GamesDApp today for a complimentary consultation and bring your Web3 game concept to life.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Helium Mining 101: How to Earn HNT with a Helium Hotspot Helium mining is a unique way to earn cryptocurrency (HNT) by supporting a decentralized wireless network. Unlike traditional crypto mining, Helium mining doesn’t require expensive hardware or power-intensive operations. Instead, miners set up Helium Hotspots, which provide coverage for the Helium Network while earning rewards. In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about Helium mining, from setting up a hotspot to maximizing your earnings. 1. What is Helium Mining? Helium mining is the process of running a Helium Hotspot to contribute to The People's Network, a decentralized, blockchain-powered wireless network. Miners earn HNT tokens for providing LongFi coverage, a type of long-range, low-power connectivity used by IoT devices. Why is Helium Mining Different? Unlike Bitcoin or Ethereum mining, Helium mining does not rely on computational power. Instead, it rewards users for offering wireless coverage and data transfer. Eco-friendly – No high energy consumption like Bitcoin mining. Low-cost setup – A hotspot device costs between $300-$1000. Passive income – Once set up, the hotspot works 24/7 to generate HNT. 2. How to Get Started with Helium Mining Step 1: Purchase a Helium Hotspot Miner To mine Helium, you need a Helium-compatible hotspot device. Some of the most popular brands include: Bobcat Miner 300 SenseCAP M1 Rak Wireless V2 Nebra Indoor/Outdoor Hotspot 💡 Ensure that the miner is Helium-approved to avoid scams and unsupported devices. Step 2: Set Up Your Hotspot Once you receive your miner, follow these steps: Download the Helium App (Available on iOS and Android). Create an account and generate a Helium Wallet for storing HNT rewards. Connect your hotspot to Wi-Fi or Ethernet and place it in an elevated position near a window for optimal coverage. Complete the onboarding process in the Helium App. 🚀 Pro Tip: The higher and clearer your hotspot's location, the better its performance! Step 3: Sync with the Helium Blockchain After setup, your miner needs to sync with the Helium blockchain, which can take 24-48 hours. Be patient! 3. How Do You Earn HNT? Helium miners earn HNT in several ways: 1. Providing Network Coverage Your hotspot earns rewards by transmitting data for IoT devices in its coverage area. 2. Participating in Proof-of-Coverage (PoC) Challenges Miners verify each other’s locations through PoC challenges and earn rewards. This system ensures that only legitimate hotspots receive incentives. 3. Relaying Data Packets Whenever devices use your hotspot to send data, you earn small amounts of HNT. 4. Witnessing Other Hotspots Hotspots in the same area validate each other’s activity, generating additional rewards. 📈 More hotspots ≠ More earnings! A balanced number of miners in a given area is optimal. 4. Maximizing Helium Mining Profits To increase HNT earnings, follow these tips: ✅ Optimal Hotspot Placement Position your miner on a rooftop or near a window. Avoid obstructions like buildings or walls. ✅ Upgrade Your Antenna A higher dBi antenna (e.g., 5.8dBi or 8dBi) increases signal range. Choose an omnidirectional antenna for urban areas and directional antennas for rural locations. ✅ Use Ethernet Instead of Wi-Fi A stable wired connection improves reliability. Some miners struggle with weak Wi-Fi signals. ✅ Join the Right Coverage Area Avoid areas too crowded with hotspots, as earnings diminish. Similarly, isolated hotspots may struggle to participate in PoC challenges. 5. How Much Can You Earn with Helium Mining? Earnings vary based on location, competition, and network demand. Here’s an estimate: Coverage TypeHNT Earned (per month)Estimated USD Value (varies with price)Urban, Dense Area5-15 HNT$25 - $75Suburban Area15-50 HNT$75 - $250Ideal High-Placement Area50-100 HNT$250 - $500
💰 Note: HNT prices fluctuate, affecting earnings in USD. 6. Common Issues & Troubleshooting Here are some common problems and solutions: ❌ Low Earnings Improve antenna placement. Reduce interference from walls and obstacles. ❌ Syncing Issues Restart your miner. Ensure a stable internet connection. ❌ No PoC Challenges Check if you are in a too-dense or isolated area. Upgrade to a higher dBi antenna. 7. Is Helium Mining Worth It in 2025? Helium mining is still profitable, but profitability depends on location and competition. While earnings have declined in crowded cities, miners in suburban and rural areas can still earn consistent passive income. Pros of Helium Mining ✅ Low energy consumption ✅ Affordable startup costs ✅ Passive income opportunity Cons of Helium Mining ❌ Earnings depend on location ❌ Initial setup takes time ❌ Hotspot availability may be limited Final Verdict: If you live in an ideal coverage zone, Helium mining can be a profitable side hustle. Conclusion Helium mining is a unique, energy-efficient way to earn cryptocurrency by supporting a decentralized wireless network. Setting up a Helium Hotspot requires minimal investment, and with proper placement and optimization, you can maximize HNT earnings. Are you ready to join the Helium Network revolution? Start mining today! 🚀
0 notes
Text
What steps are involved in defining the core features of a Pump Fun clon
Introduction
In the crypto world that changes day-by-date, Pump fun clone is a first-ever platform that allows the creation and trading of meme coins in a democratic manner. Launched in January 2024 on the Solana Blockchain, Pump.fun allows anyone to create a coin, make it tradable immediately for real money, and never have to provide liquidity. This ease of usage now makes Pump.fun a hub for all meme coin lovers, assisting the launch of over 6 million tokens in its first year alone.

Understanding Pump fun Core Functionalities
Pump.fun is a Solana-based platform that seeks to decentralize the creation and trade of meme coins to actually everyone, including non techs. Users can easily create tokens by defining parameters like the name of the token, symbols, and images by an easy and simple interface. The price of the tokens goes up with their demand and is meant to tease early participation with a fair launch, thus making use of a bonding curve pricing model. Pump.fun is fully integrated with popular wallets on Solana like Phantom and Solflare, where users can handle all their tokens conveniently as securities or savings. With all these attributes put together-Pump.fun-there will be no more questions on being user-friendly, dynamic pricing, and a powerful movement for security.
Essential Features to Incorporate
Token Creation Moduleṣ
The Token Creation Module is one of the very primary features of any DeFi platform that allows users to create their own tokens with minimal effort. The module must facilitate the definition of parameters like the name of the token, its symbol, total supply, and decimal precision. Users must be able to create a token without requiring technical know-how judged beyond what is necessary. With this feature, many types of projects would spring off-across community tokens all the way to utility tokens for a particular application.
"Build Your Pump fun Clone – No Coding Required!
Bonding Curve Integration
Bonding Curve Integration models dynamic pricing on your platform. Bonding curves are mathematical curves that determine the price of tokens according to the supply and demand for them. So, as more tokens are bought, the price goes up; conversely, it goes down when tokens are sold. Continuous liquidity and fair price are assured, giving an incentive for early adoption with a clear valuation model for tokens.
Wallet Integration
Wallet integration is an impetus for important interactions between secure and smooth user experience. Allowing users to connect their wallets to the platform can greatly enhance transactions, bringing tokens management and smart contract interaction within reach. Smooth wallet integration fosters trust among the users while helping onboard easier so that they can easily participate in the DeFi ecosystem.
Technical Considerations
Choosing the Right Blockchain
choose a right, compatible blockchain and development framework and take care of unbearable scalability and security issues when developing a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform. The differences between choosing Ethereum and Solana depend on how such platform requirements vary. Ethereum has a very rich ecosystem and high security but has scalability issues, which gives rise to high gas fees in times of higher usage. Conversely, Solana would be best for high-throughput applications that are particularly spending much due to high-frequency trading because they offer low transaction costs. However, it sometimes gets outages and won't be reliable during those periods.
Development Frameworks
When it comes to frameworks for development, we see Hard Hat and Truffle emerge as the much-famed tools for testing and deploying Ethereum-based projects. For the Solana blockchain, Anchor actually provides a set of tools aimed at facilitating smart contract development and deployment. The framework that should be chosen is dependent on the architecture and the very specific needs of the project.
Ensuring Scalability and Security
Scalability assurance involves deployment of Layer Two solutions like rollups or sidechains, which work to relieve pressure on the main blockchain, thus lowering transaction fees and increasing throughput. Smart contracts have to be optimized for efficiency to reduce
as cost and possible vulnerabilities. Moreover, decentralized consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Stake make security better while keeping in check scalability.
User Experience and Interface Design
A user-friendly design in a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform will need some consideration for simple intuitive navigation, responsive interfaces, and effective onboarding of new users. Intuitive navigation can be achieved through clear and consistent labels, logical organization of content, and effective visual design elements for guiding their experience as a whole . A mobile-first approach is an optimization of the platform by making sure it's ideal for smaller screens until one scale goes bigger and gives priority to the must-have features and flexible layouts for seamless reach across screen sizes. Adding interactive tutorials and then contextual help cues would guide new users through essential usability in otherwise-damaged batches, promoting engagement and retention through step-by-step guidance through key features and workflows.
Security Process
KYC/AML Procedures
DeFi platforms are supplementing their efforts to combat money laundering and other criminal financial activities, i.e., terrorist financing by employing Know Your Customer(KYC) and Anti-money Laundering measures. Such measures include verifying a user's identity and monitoring entered transactions for any suspicious behavior. For example, some platforms may ask users for a government-issued personal ID and allow users to perform facial recognition while entering the platform. Moreover, transaction monitoring systems would detect unusual patterns realized through transactions that could be indicators of money laundering. The Office of Foreign Assets Control under the U.S. Treasury has mandated that DeFi platforms comply with such acts as sanction compliance and the reporting of suspicious activities as part of AML regulations.
Secure Transactions and Data Encryption
User data becomes completely confidential and integral. Like other modern-day financial platforms, these DeFi applications tend to adopt high-end encryption techniques in the protection of sensitive data. For instance, homomorphic encryption permits computation on encrypted data without decrypting it, thus ensuring privacy in the process. The use of secure transaction protocols such as in-transport layer security (TLS) for data transmission and multi- signature wallets in transaction approvals also enhances security.
Conclusion:
Core Features, Depending on Innovation, in Platform Development, while we discuss how to define core features for a Create a pump fun clone it is crucial to acknowledge each component's significant role in building a successful platform. From token creation modules to bonding curve integration or wallet connectivity and user dashboards, these are no longer features but distractions more than anything else that comes in handy when securing user engagement, market competitiveness, and operational efficiency. Thus, on an integrative note, platforms must use these features in an established framework of ease so that the users in focused areas can relate to it easily.
0 notes