#estonian mythology
Photo

Jüri Arrak (1936-2022)—The Shadow of the Circle of Life [oil, canvas, 2019]
806 notes
·
View notes
Text









estonian mythology: vanemuine
vanemuine is the god of art, music, dance, song, and literature. he is also associated with creativity and artistic expression. vanemuine is said to inspire musicians and poets, and his melodies are said to resonate with creative estonians.
179 notes
·
View notes
Text









myth moodboards: jutta
queen of the birds in estonian mythology
requested by anon
#jutta#estonian mythology#mythology#mythedit#maryanncrimsworth#since you asked to be tagged :D#mine#*#mythmoodboard
231 notes
·
View notes
Text
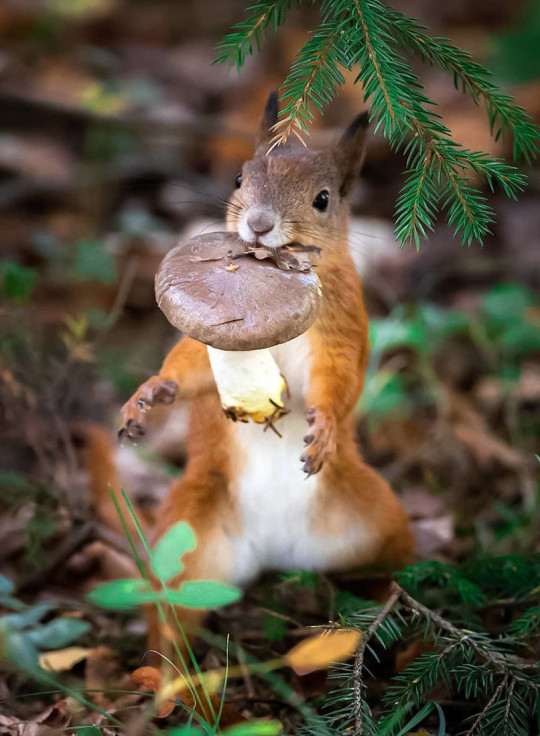

[Photo above by: Ossi Saarinen]
Legends and myths about trees
Forest myths, Estonian traditional beliefs (6)
The world of the Estonians’ ancestors – Metsik, the forest elves
Metsik is the elf of the woodlands. According to ancient Estonian folklore, Metsik were wood elves who lived everywhere there were trees, from coniferous woodlands to shallow swamp forests. When Metsik appears to people, they assume the appearance of a bird, a wild animal, or a beautiful tree. A singing bird who truly is Metsik sings songs that humans can understand. They can also understand the language of the aspen tree that rustles in the wind for that aspen tree is Metsik.
If birdsong is heard, it may be a Metsik singing. People can hear Metsik in an aspen tree that rustles in the wind. Metiks are the guardian spirits of the forest. They do not approve of cutting down trees, bonfires and, above all, waste dumping. When people enter the forest with cruel intentions, Metik misleads them away from their sacred home.

木にまつわる伝説・神話
森の神話・エストニアの民間伝承 (6)
エストニア人の祖先の世界 〜 森の妖精メツィク
メツィクは森の妖精である。古代エストニアの民話によれば、メツィクは針葉樹林から浅い沼沢林まで、木があるところならどこにでも住んでいた森の妖精である。メツィクが人々の前に現れるとき、彼らは鳥や野生の動物、あるいは美しい樹木の姿をとる。本当にメツィクである歌う鳥は、人間が理解できる歌を歌う。また、風にそよぐアスペンの木の言葉を理解することもできる。
鳥のさえずりが聞こえたら、それはメツィクが歌っているのかもしれない。人々は風にそよぐアスペンの木からメツィクの声を聞くことができる。メツィクは森の守護霊である。彼らは木を伐採したり、焚き火をしたり、とりわけゴミを捨てることを認めない。人々が悪意を持って森に入ると、メツィクは彼らを神聖な家から遠ざけるよう惑わす。
#trees#tree legend#tree myth#folklore#mythology#legend#estonian mythology#metsik#forest guardian#forest elf#aspen trees#woodlands#nature#art#forest fairy
192 notes
·
View notes
Text



Yet ANOTHER picrew rendition of a thingy.
This time, it's Vanapagan.
Picrew artists: Doshi, @iamthetwi , and Mano
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
So I was just researching Estonian mythology and

Hmmmmm
#unus annus#lol#thought that was kinda cool#plot twist!#annus is actually death😳#woopsie doopsie#myhtology#markiplier#crankgameplays#estonian mythology#annus
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

Tõnis Grenzstein (Estonian, 1863-1916) - Leviathan at sea
91 notes
·
View notes
Text

Kaljo Põllu.
80 notes
·
View notes
Text

Tempestuous spirits of devastating winds. A raging wind that tears at the land around it with terrible strength.
#BriefBestiary#bestiary#digital art#fantasy#folklore#legend#myth#mythology#estonian folklore#estonian legend#ebajalg#wind spirit#whirlwind#demonic wind#vihur#tuulispask#undead#magic
23 notes
·
View notes
Text








Tallinn, Estonia. 11/2022
#tallinn#estonia#estonian#baltic sea#baltic mythology#baltics#baltic countries#latvia#lituania#eesti#kerli#snow#snowy day#snowy forest#nature#travel#old town#europe#european#northen europe#niguliste#park#memories#the times we had#tartu#parnu#kerli kõiv#ice rink#ice skating
14 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Jüri Arrak (1936-2022) — The Guardian [oil on canvas, 2000]
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
clearing out the drafts of Random Things I've Noticed if you can't tell but here, have another one - this building on the end of aziraphale's row of shops, on the other side of the record shop:

now im fairly certain about two things. first, it's called 'Alf Laylah wa-Laylah' - translated to english from arabic as One Thousand and One Nights. i can't quite tell at this quality if the writing below it is hebrew or yiddish, nor if it's a translation of the text above it (although, as best as i can tell? it isn't? but not sure)

im also not entirely sure on the relevance of the reference - if there is any to be had - to the story compilation that is One Thousand and One Nights, to tell the truth. the immediate thought that springs to mind is how scheherazade tells the king countless folk tales and stories over 1001 nights in order to keep him in suspense of hearing how the stories end - so he essentially stops killing women as revenge for the infidelity of his wife (it's a whole thing), whom he eventually pardons/spares from execution.
all the tales - as well as returns to the 'present' - include debate on philosophies and ethics, and explore various themes and topics, but regardless... my thoughts are somewhat jumping between this, the questions around the reliability of events as presented in s2, the flashbacks and the Lessons, etc. maybe that's not the link to make here, but it's all im coming up with so far.
but back to the building, and the second thing: think that the stars on the bottom half of the building, in the specific configuration they're shown, are the kaheksakand (estonian) / auseklis (latvian) - an eight-pointed star representing fertility and life, the triumph of light over darkness, as well as used as a protection symbol against evil (aptly placed outside the door).
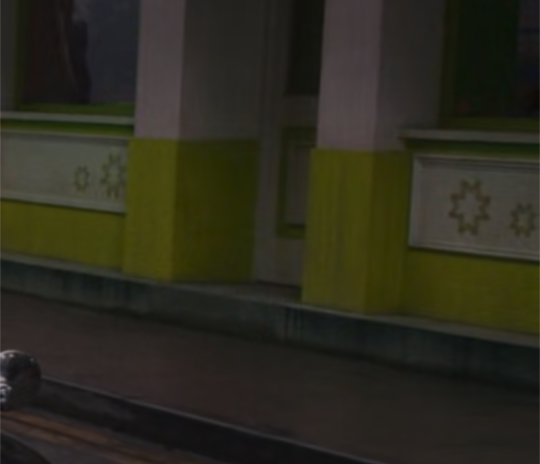

there's a lot to go into re: the symbology behind '8', including its relationship to the concept of balance and harmony, especially in nature. the eight-pointed star in general, not just in the above exact shape, has dozens of cultural, religious, and mythological links (tbh it's probably featured in some capacity in nearly every culture), but i think particularly apt is how it links to venus aka. the morning star.
in the interest of keeping this brief (im sure cleverer people may wish to clarify/develop this more!!!), and keeping on track with where its place may sit in the show, i think it's first of all potentially of interest how this building is lit, given the above. we see the shot of the bentley arriving to whickber street in ep1 at night, and this particular shop (?) front is the most brightly lit... might mean nothing, might mean something:

but when the demons descend in ep5, a good portion of them appear out of the mist from that direction; a green mist (green shop?), reflecting the hell vibes we saw in ep1 etc. that being said, when crowley starts sensing Trouble Is Afoot earlier on, he's looking in all directions and certainly we see some demons behind him (in the direction of the dirty donkey) when he confronts this particular little gang of them, so unless some demons started arriving ahead of schedule, they may not have all come through this building:


but. we know from eric that the lift is broken, and the only other routes are the small lift, one at a time, or the stairs. shax obviously arrives in style, but the other demons? taken the stairs. what if this front is that exit onto earth? but just the back stairwell?
there's so many potentially loose threads to weave in here, and im sure i'll come back to this at some point, but felt it was an interesting design choice nonetheless, even if it ultimately means naff all✨
#good omens#i'll come back to this im sure#props meta#thats probably the most accurate tag for the moment
37 notes
·
View notes
Photo
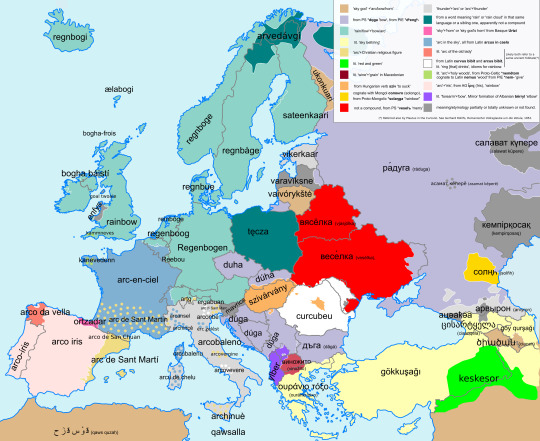
Meaning of the stems of the words for "rainbow" in the languages of Europe.
by u/nickanc
'Rainbow' is typically a compound word in most European languages. Generally, speaking, a part of the word comes from words meaning bow, belt, ring, circle or arc in their respective languages or ancestor languages. The other one varies and is the main concern of this work.
Some incomplete notes on the meanings and the etymologies I gathered while making the map:
'sky god' + 'arc/bow':
Arabic from Quzah, a pre-islamic deity of weather
Maltese from Maltese alla 'god', from Allah, the islamic deity,
Karelian from Ukko, Finnic sky god
Lithuanian from Vaiva, goddess of Baltic mythology
Armenian is uncertain, supposed to derive ultimately from PIE *dyew- 'shine'
from PS *dǫga "bow". they all are not compounds, except maybe for Russian
'rain/flow'+'bow/arc':
Germanic ones but faroese from PG *regnaburô 'rainbow' obvious compound, *burô comes from PIE *bhewgh-
Faroese æla means shower (as in weather), formerly "flow quickly", from PG *ēlaz "eel"
Finnish from Proto-Finnic *satadak "fall, rain"
Irish and Scot Gaelic are compound words in their very language, there are many other interesting Irish words.
'arc of the old lady' and 'circus bibit', 'arcus bibit'. In some ancient folklore tales, that appear in various IE families, various weather phenomena are especially linked with magical or religious figures that assume the form of old ladies. In Italian and Romanian folklore there are the 'giorni della vecchia'/'zilele babelor' that are the days 29th-31st of March, when the cold is expected to return. In Romania an old lady is Baba Dochia that brings forth the spring and various other Babele populate the Romanian folklore; in the Gallo-italic folklore of Italy there is a folklore fog spirit named Borda that is an old lady personifying the fog, Gaelic mythology has its weather old lady Cailleach, the Indian summer is called in German Altweibersommer lit. 'old women's summer'. The rainbow is no exception: Plautus in the Curculio hints at a folktale of an old lady that drinks "like" the rainbow does or maybe is the rainbow itself, hence also other etymologies for rainbow related to expressions like "circus bibit", "arcus bibit", "arcus imbibens" etc.that give etymologies in various languages. Venetian arcombé and Ladin ergabuan come from arcus imbibiens (source), whereas Romanian curcubeu likely from curvus bibit and Neapolitan arcovevere from arcus bibit. Note that expressions containing the rainbow and the old lady or the act of drinking exist in many languages in this map and their dialects, just they are not the common word for rainbow. For example, in Moldovan there is brîul babei that means 'rainbow' (source), Slovenia has the dialectal word pijâvka 'rainbow' from PS *piti 'to drink', while in Spain and Portugal dialectal expressions that are cognates of the Galician one are apparently common, in Czech there is an idiom pije jak duha that means 'drink like a rainbow', i.e. being a drunkard. Ultimately all what I found points to a 1952 article of Gerhard Rohlfs, Romanischer Volksglaube um die Vetula, which however I was not able to find. EDIT: The Hungarian word is linked to the image of drinking the rainbow too, see below.
'thunder'+'arc' or 'arc'+'thunder':
Estonian is apparently cognate with Livonian pit'kiz kor(?) 'rainbow', lit. 'thunder bow', according to this source, though this comment offers more insight on the origin of the word.
Italian arcobaleno where baleno means flash, thunder, apparently from balena, 'whale', due to a popular habit to make many phenomena zoomorphic or anthropomorphic (the map I posted for fog in northern Italy presents a similar case with she-wolves). Alternatively, there is an article supposedly connecting the words of the 4. with arcobaleno: they suggest that, at some stages of the languages and the sociocultural development, the old lady was an old lady of the sea, thus a whale and their witness would be Galician vella 'old lady' which - according to that article - is a word that could mean also whale. The article is aimed ultimately to strengthen the Paleolithic Continuity Theory, so probably there is little to no scientific consensus on it, though at least I hope their examples are not as disputed as their conclusions.
color: teal. from word meaning "rain":
Polish from(?) OCS тѫча 'rain' and cognate with Russian ту́ча 'rain cloud'
Northern Sami related with Northern Sami arvedálki 'rainy weather'
Basque: 'horn of the sky' or 'sky god's horn', from Basque Urtzi
'arc'+figure of Christian religious figure (Saint John, Saint Martin, Saint Mark, Noah, the Virgin). The choice of the figure seems related to the days of these saints (St. Martin is during the Indian summer, related to 4.), though I have not that much experience on the topic to ascertain that. Noah is clearly linked with rain.
color: green. literally 'arc'+'holy woods', from Proto-Celtic *nemētom, cognate to Latin nemus 'wood' from PIE *nem- 'give, take' source, apparently suggesting a sacred role for the rainbow in Celtic traditions.
Curiosity, not sure if or how it is related to 9. and the other words conveying a sacred meaning for rainbow: in southern Italy, the rainbow was superstitiously considered the cause of jaundice, as màlë du uàrchë is jaundice (source]
273 notes
·
View notes
Text

Legends and myths about trees
Forest myths, Estonian traditional beliefs (5)
The world of the Estonians’ ancestors – Magical objects [first part]
White Ship (valge laev) - mythical ship that brings freedom or takes people away to a better land. This myth was born around 1860 when a small sect led by Juhan Leinberg (also known as Prophet Maltsvet) gathered near Tallinn to wait for a white ship to take them away.
Hat of fingernails (küüntest kübar) - makes the bearer (usually Vanatühi) invisible. In Estonian mythology, Vanatühi ("Old empty one", or alternatively, Vanapagan, "Old devil") is a/the devil or god of the underworld, a giant farmer who is more stupid than malevolent. Vanapagan is the ogre character in Estonian versions of the series of internationally known folktales of the stupid ogre.
Letter gloves (kirikindad) – were believed to have protective or magic powers, especially church letter gloves and the gloves that sailors wore. Letter gloves were (are) decorated with special geometric patterns and narrow red stripes; they have many whispers and spells in them because the crafter used to sing while making, dyeing and knitting yarn.
Letter Belt (kirivöö) - the belt had the most ancient and magical patterns of all the craft items, red woven belts and laces were a common item to sacrifice (they were tied to the branches of holy trees). The belt was tied around parts of body that were sick and, pulled tightly around the waist, to protect and give strength to the bearer.
Sacred stones - the last ice age has left a lot of great stones (erratics) in Estonia. Many of them were considered sacred and people came to them to sacrifice silver, blood, red ribbons and coins and ask for welfare and prosperity. Often, the stones have little holes in them, some of them probably used to place the sacrifice in. The meaning and function of the holes is however still disputed; according to a paleoastronomer they may have had a calendary function.
Travelling forests - when people are mean, greedy and cruel, the forests will leave those places. The most stories about travelling forests are found in coastal areas of Estonia.

木にまつわる伝説・神話
森の神話・エストニアの民間伝承 (5)
エストニア人の祖先の世界 〜 魔法のオブジェ(続き)
白船(valge laev)- 自由をもたらし、より良い土地へと人々を連れ去る神話上の船。この神話は1860年頃、ユハン・レインベルグ(預言者マルツヴェトとしても知られる)に率いられた小さな一派がタリン近郊に集まり、自分たちを連れ去ってくれる白い船を待ったことから生まれた。
爪の帽子(küüntest kübar) - 持ち主(通常はヴァナトゥヒ)を見えなくする。エストニア神話では、ヴァナテュヒ(「老いた空っぽの者」、あるいはヴァナパガン、「老いた悪魔」)は冥界の悪魔または神であり、悪意というより愚かな巨大農夫である。ヴァナパガンは、国際的に知られる一連の愚かな鬼の民話のエストニア語版に登場する鬼のキャラクターである。
レター・グローブ(kirikindad)-特に教会便りの手袋や船乗りが身につける手袋には、身を守る力や魔法の力があると信じられていた。レターグ・ローブには特殊な幾何学模様と細い赤い縞模様が施され、糸を作ったり染めたり編んだりするときに職人が歌っていたため、多くのささやきや呪文が込められている。
レター・ベルト(kirivöö)-ベルトは、工芸品の中で最も古く、魔法のような模様をしており、赤い織物のベルトやレースは、生け贄に捧げるための一般的なアイテムだった(聖なる木の枝に結ばれていた)。ベルトは、体の病気の部分に巻かれ、腰の周りにきつく引っ張られ、持ち主を守り、力を与えた。
聖なる石 - 最後の氷河期は、エストニアに多くの巨石(迷子石)を残した。その多くは神聖なものとされ、人々は銀や血、赤いリボンやコインを捧げ、福祉と繁栄を祈願するために訪れた。多くの場合、石には小さな穴が開いており、そのうちのいくつかは生贄を捧げるために使われたものと思われる。古天文学者によれば、穴には暦の機能があったのかもしれない。
旅する森 - 人々が意地悪で、貪欲で、残酷であると、森はその場所を去ってしまう。旅する森にまつわる話は、エストニアの沿岸部に多く見られる。
#trees#forest#tree legend#tree myth#estonian mythology#magical objects#folklore#mythology#legend#nature#art#ural owl
141 notes
·
View notes
Text


yeah, i kinda have a crush on these 2 right now
#the wolf among us#estonian mythology#bigby wolf#vanapagan#fables#fables comic#yes i am crushing hard over these 2
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The variety of descriptions of the devil is something rather peculiar to Polish, German and Estonian trial records. Devils are variously described as German, French or Polish, and within that typology, we have Polish devils who are of aristocratic or peasant origin. The descriptions are mainly concerned with the devils’ style of dress. The most frequent names for devils, according to a collection of trials from Grodzisk, were Jasiek, Jan, and Kuba, followed by Woytech. (...) Hanykowa’s Kuba was dressed fashionably in the German style. (...) In another case, Anna Stelmaszka’s devil was described as pokuśnika po Niemiecku w czerwonej barwie, ‘a temptor in the German style in dressed in red’.
(...) There was also mention of Polish devils, and one may assume that if nationality is not mentioned, then the devil is in fact Polish. Stach, a devil in the Polish style, dressed in green, was neither old nor young, and one of his compatriots, Barbara Konieczna’s devil was dressed as a Polish peasant. Another witch confessed to having a devil named Kuba who was described as dressing in the French style. According to one witch, following her third session of torture, her devil was described as po żydowsku, ‘in the Jewish style’. It was common for devils to be described as dressing in black,green or red, such as a devil named Jarek, who wore green hose, a red hat and black boots. Małgorzata Kupidarzyna’s Jasiek was młody w sukni zielonej i żółtych botach, czapka barankowa, ‘young, in green dress and yellow boots, a lamb fleece hat’.
- Jewish, Noble, German, or Peasant? The Devil in Early Modern Poland by Wanda Wyporska. [Demons, Spirits, Witches Vol. 2 :Christian Demonology And Popular Mythology - Gábor Klaniczay, Éva Pócs (Eds.)]
104 notes
·
View notes