#i'm so worn out on adaptations much less one of a book series near and dear to me
Text
tbh I'm frankly relieved that the tkc adaptation has stalled. the current state of a lot of TV and movies has left me pretty jaded.
#txt#the kane chronicles#kane chronicles#tkc#rick riordan#i'm real tired of shit after shit after shit#also I'm still scarred from back from the brink last year#i'm so worn out on adaptations much less one of a book series near and dear to me
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
world building cause twn doesn't part 8: nonhumans
this is easily the geekiest part of the series. and it's a Very geeky series. because sapkowski's worldbuilding is waaay more extensive than i have the time, ability, or desire to convey, i'm sticking with races both sentient and important
colour code cause i fucking love colour codes - already happened/introduced, probably s2, important background info, stuff that might be in the prequel, extras
series masterpost
dopplers
dopplers, also known as vexlings, shifters, mimics, doubles, imitators, or pavrats, are a nonhuman race that can take on the appearance of nearly anyone they encounter
before mass migrations of humans, dopplers primarily inhabited the forests and plateaus around the city of novigrad, where they would transform into wolves and pack animals to hunt
their abilities are pretty impressive, dopplers can not only mimic appearance but also voice, personality, skills, behaviours, and knowledge. dopplers can even turn parts of their bodies into pieces of clothing or other objects
however, there are some limitations
dopplers can't transform into someone/thing with dramatically more mass than they have, are burned by silver, and can't drop anything they created (if they did it would kind of turn into a fleshy goop)
we've already met a doppler in twn, this sexy sexy man

BUT
it is important to note that this doppler is a huge deviation from sapkowski's lore. dopplers are pretty much always exceptionally kind and gentle. a lot of times they use their abilities to appear threatening (big teeth, sharp claws etc) because they really don't want to hurt anyone.
when dopplers aren't mimicking another form, they aren't exactly pretty. they're bald, short, have beady yellow eyes, and kinda look like they're made from soft clay
here's the hexer doppler

the most notable doppler is dudu biberveldt, who i mentioned as the halfling dainty biberveldt's fake cousin. dudu's actual name is tellico lunngrevink letorte, but dainty decided to help dudu live in novigrad by adopting him as his fake cousin.
dragons
dragons are fucking awesome. you know it, i know it, and zerrikanians know it. witcher dragons are especially awesome
they are the only being, other than cats, that can naturally harness and absorb the force of chaos
there are multiple subtypes, but most dragons fall into one of four: black dragons, green dragons, red dragons, and white dragons.
black dragons are the largest, and primarily live in swamps and wetlands where they bathe in mud. they have extremely hard scales and don't breathe fire, but an acid that causes burns similar to those from mustard gas.
green dragons (right there) are the most prominent yet smallest species of dragon, mainly living in forested areas and breathe highly flammable chlorine gas.
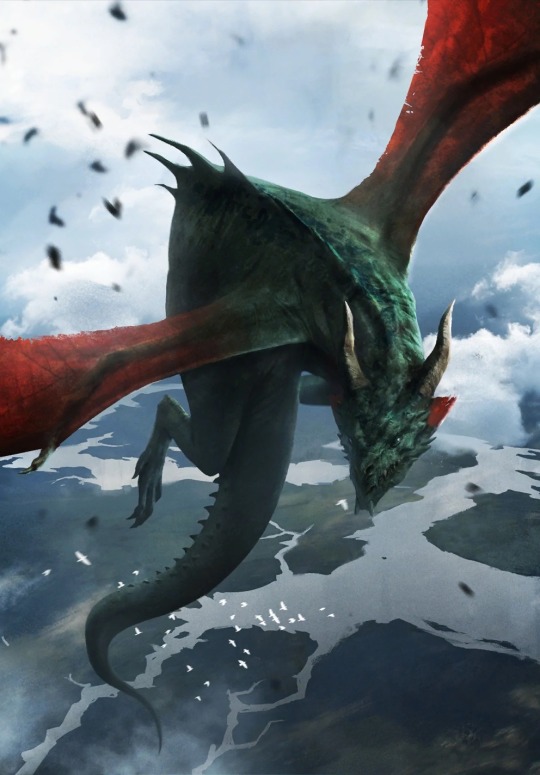

red dragons mainly live in hills and mountain caves and can breathe fire hot enough to melt metal
white dragons are one of the rarest species and live in the far north, and can breathe frost
however, if you watched the witcher netflix as i assume you did, you may remember golden dragons. these dragons are so rare and exceptional that they are not usually included with other species. they breathe steam and fire and can shapeshift into any living being
all dragons communicate through telepathy, although golden dragons can speak when they are in the form of a species that can speak
humans are pretty divided on the topic of dragons, with zerrikanians worshiping them and nordlings hating them.
because they are incredibly intelligent and emotional, witchers (generally) refuse to hunt them
borkh three jackdaws, also known as villentrenmerth, is the only golden dragon we know. there he is right there.

ASSASSINS OF KINGS SPOILERS NEXT TWO BULLET POINTS
the other dragon from twn was a green dragon named myrgtabrakke, borkh's mate. their daughter is named saesenthessis, also known as saskia the dragonslayer (an alias she took to explain her extensive knowledge of dragons) and the virgin of aedirn
because saskia is part golden dragon, she can shapeshift, although is much more limited than her father. she can basically only be a human looking woman with blonde hair or a huge dragon.
cut because this part is getting REALLY long
godlings
ah godlings. i love them so much. they're adorable and precious. they usually look somewhat like a human child, but with blue skin and large amber or green eyes. they don't wear much clothes, their focus is in accessories like jewelry, flowers, or tattoos
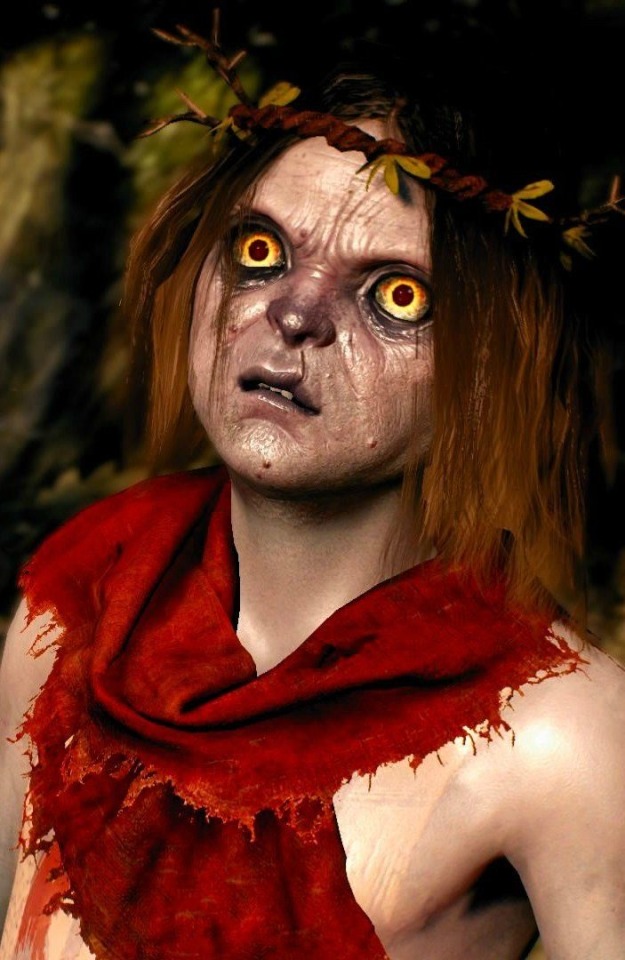

that's johnny, a holding in wild hunt.
godlings are incredibly rare, and are easily confused with young goblins. they primarily live in swamps near drowners, but aren't afraid of them.
they're quite mischievous but kind hearted, many have happy go lucky personalities and love just having fun. i adore godlings. i've said it once and i'll say it again.
higher vampires
definitely the most important group on this list, higher vampires are incredibly powerful and intelligent. they can shapeshift within certain limits, generally either looking like a human or a large terrifying bat. they also have some telepathic abilities - they can basically make you fall asleep and forget stuff
scary wooo
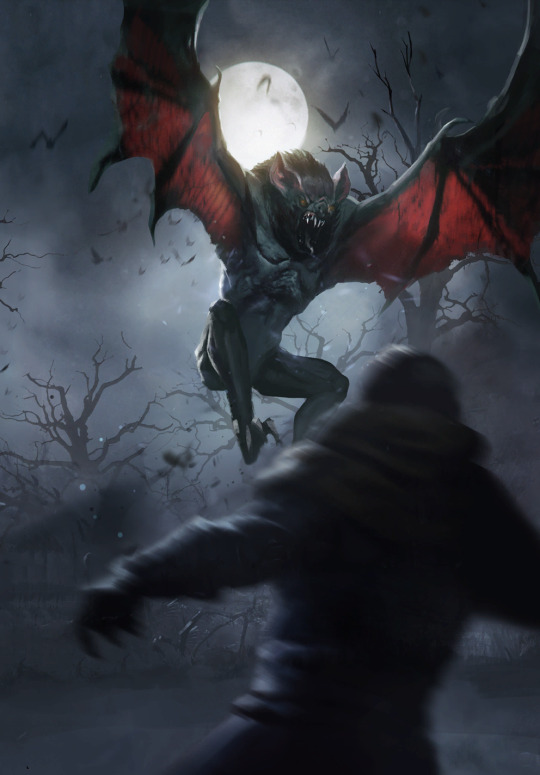

higher vampires do not need to drink blood to survive. some don't drink blood at all. when they do, it's like a human drinking alcohol. on full moons, groups of higher vampires go out partying and get white girl wasted
although all higher vampires have the same basic abilities, each individual has one skill they are exceptional in.
most find humans harmless but annoying, like mosquitos. they don't really like interacting with humans, which works out pretty well as higher vampires can blend in very well, even a witcher's medallion can't detect one
higher vampires also have three distinct cultures, the tdet in the far east, the ammurun across the great sea, and the gharasham in the northern realms
they are really really hard (or impossible, depending on canon) to kill. based on the books, you basically need to disintegrate them. based on the games, only higher vampires can kill other higher vampires, but humans can get close
we only meet one in the books, emiel regis rohellec terzieff-godefroy. he goes by regis for short. regis was an "alcoholic" in his youth, and has since abstained from blood or any other substance. he's incredibly old, by the end of twn season 1 he'd be 425 years old. as for regis' "special ability", he's just kind. he's an incredibly gentle and loving person. that's it. i love him.
merpeople
probably one you're already familiar with! merpeople are intelligent humanoids that inhabit the great sea. mermaids are notably gorgeous, having green hair and tails, and their scales are prized alchemy ingredients
sapkowski's mermaids can breathe above water, but the sun burns their skin so they don't stay at the surface for very long.
merpeople are incredibly powerful, they can summon krakens and the sea-dragon like race of vodyanoy respect their authority
they use their own language that's quite similar to hen llinge, but more lyrical sounding.
nymphs
nymphs are a humanoid race primarily based around nature. they have 5 subspecies, dryads (including hamadryads), leimoniad, naiad, nereid, and oread.
dryads, called eerie wives by humans and aen woedbeanna by elves, are the most prevalent, primarily living in the brokilon forest. some have human skin with olive undertones, but others are green. they usually have dark brown or green hair which is usually worn in dreadlocks (breaking my promise of not being overtly and annoyingly political in this series yet again - the dryads, especially in the netflix adaptation, are classic magical n*gress stereotypes. but more on that later.)
this is a lore-accurate one that i LOVE
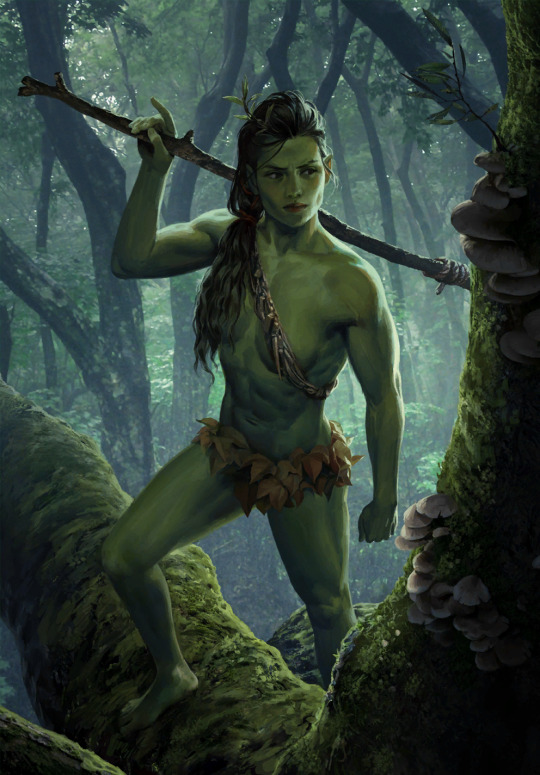

dryads have incredibly strong connections with nature and magic, although it is really rare for a dryad to be a source. dryads are able to draw energy from trees, but rarely do because they don't want to hurt the trees. support dryads and take the bus.
all dryads are women. all of them. they make babies by basically luring men into the forest and doing the adult hokey pokey. also why dryads aren't really a fan of witchers, who don't make the baby butter (i am so sorry)
however, dryads can also turn a girl of another race into one of their own through the use of magic. the water of brokilon has some mutating quality that makes young girls forget their human past and physically turn into dryads, although it is less effective as the girls are older. the dryads tried to do this to ciri, but given that she's a source, nothing happened. generally, this process is done to girls who wander into brokilon, but some dryads will abduct peasants from outside the forest if they need more dryads.
here's twn dryads... yikes
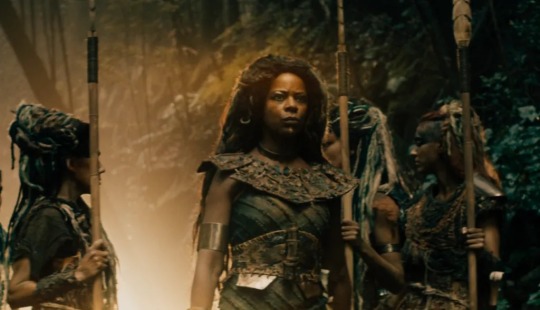
this is where i think the whole racism thing becomes a bit too obvious. "uncivilized" women who live in the forest and have dreadlocks and abduct young girls from "civilized" areas?? in twn they leaned even further into this, having one of the two black women they cast be a dryad and replacing the usual bows and arrows with spears, a less sophisticated weapon. again, this series is about the lore, not the political implications of it, but it is important to keep in mind
dryads are excellent at archery, shooting anyone who comes within 80 metres of the forest. through their connection with nature, they have highly advanced medicine and use glowing fungi as a source of light.
hamadryads are a specific type of dryad that is incredibly connected with her tree. because of this connection they have exceptionally strong magical and healing capabilities, but will also go insane and die if their tree dies.
like merpeople, dryads use a more melodic dialect of hen llinge
leimoniads are a type of nymph that lived exclusively in meadows, but are practically extinct due to wars with humans
naiads, also called rusalki, are nymphs that live in lakes and rivers, although a few live with the dryads in brokilon. naiads are very similar to dryads, although they tend to have very light skin with very dark hair, webbed hands, and can dry out on land
naiads rarely speak common, live in small groups, and have highly developed telepathic abilities
nereids are nymphs that inhabit the great sea, often living closely with merpeople. they usually have blueish skin with either blue or white hair and have some telepathic abilities, though not to the extent of naiads.
oreads are nymphs of the mountains, which, like leimoniads, are nearly extinct due to human conquests.
succubi/incubi
succubi (female) and incubi (male) are creatures which look like incredibly attractive humans but with horns and goat legs. they seduce humans, first in dreams and then physically, using their prey's energy to sustain themselves, often to the point of the human's exhaustion or death
our man eskel has a soft spot for them...
sylvans
sylvans, another race we already met, are exceptionally rare. like, practically extinct. they live mainly in the woodlands of the northern realms and have goat-like faces with yellow eyes, horns, cloven hooves, and tails
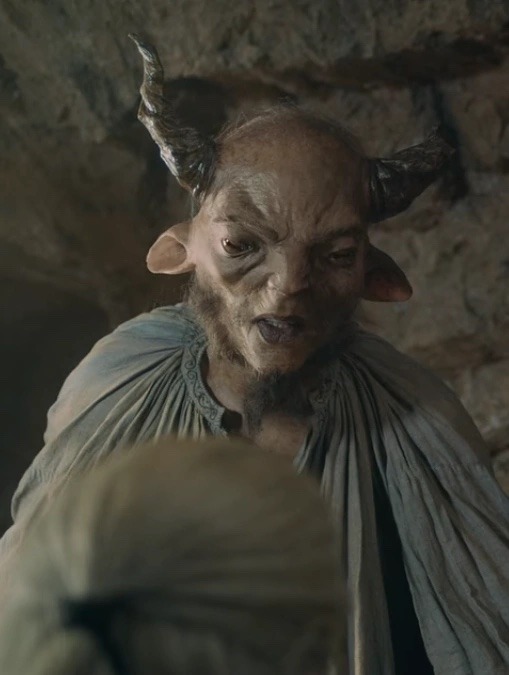

my man torque is quite possibly one of the last sylvans on the continent
they are distantly related to elves, and the two races tend to coexist quite well
generally quite mischievous and merry, highly enjoying pranks and parties. they can use simple spells and are mainly herbivores
sylvans live around 100 years and are highly sought after by dryads for their... ahem... reproductive capabilities
unicorns
yep, we got unicorns! i fucking love unicorns and still kinda think they're real. camels are real and those lumpy fuckers are way weirder than a horse with a spike on its head.
anyways
unicorns are highly advanced beings, they can travel between worlds and use telepathy. they don't really like the "less advanced" races, mostly staying around to observe them. they have distinct societies led by a council of elders and tend to avoid evil
these unicorns are badasses
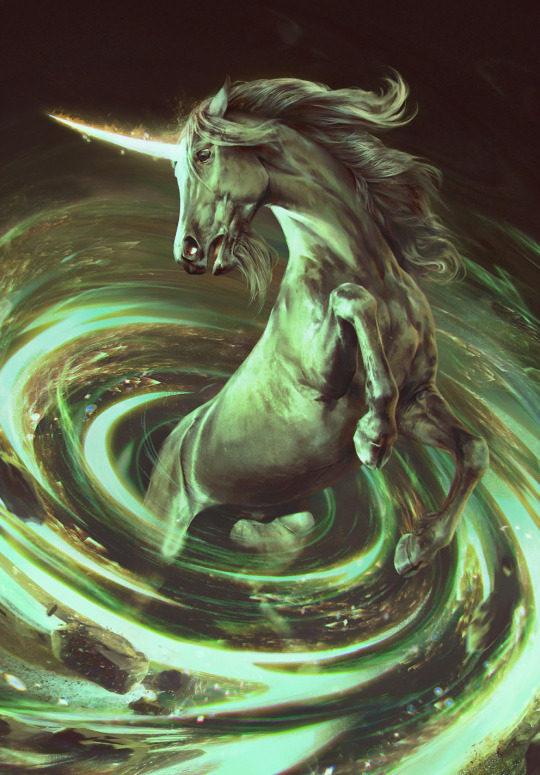

unicorns strongly despise the use of the force but encourage the power of destiny. in the context of pavetta's betrothal feast, a unicorn would not be happy with pavetta's little source hurricane thing, but would encourage geralt to follow the law of surprise
in of the witcher, unicorns are very important because of their world-hopping capabilities. the aen elle, unfortunately, realized this and began enslaving unicorns to help them plunder other worlds. this turned into a massive conflict between the unicorns and elves.
#the witcher#twn#witcher netflix#witcher lore#geralt of rivia#geralt x yennefer x jaskier#geraskier#yennefer x jaskier#wild hunt#yenskier#geraskefer#geralt x jaskier#yennefer of vengerberg#emiel regis rohellec terzieff godefroy#witcher 2#tw3#tw2#lambert#eskel#kaer morhen#mine#gen tag#lore tag#haven't got a fucking queue
161 notes
·
View notes
Note
I really want to create new foods and recipes for one of my worlds, but I have no idea how I would go about doing research for something like that. Do you guys have any resources or advice that might help? To be more specific for this world, most ingredients are incredibly low quality (but they are in abundance) and any imported ingredients are only used for the rich. I was thinking their food would use a lot of seasoning to mask the quality, but I'm not too sure. Thank you!
Feral: We could actually do with a few more specifics to answer this question as fully as you would probably like, but I’ll do the best I can.
First, I’m not sure whether you want to create recipes using real world ingredients that would in fact be cookable to release on your blog as some kind of companion for your audience or you want to conceptualize some recipes to be able to describe taste, texture, etc. If it’s the first option, creating recipes from scratch is pretty difficult. You might want to consider taking some cooking classes to learn techniques, reading cook books for a lesson in combining ingredients, and doing a lot test cooking to nail down the flavor profiles. If you don’t want to go completely chef-y, you could also take recipes and then tweak them by substituting an ingredient or using a slightly different technique (baking instead of broiling, etc). This would also be helpful in the second case. If by "low quality" you mean "low cost," try looking at food preparation that developed in poorer, underprivileged, or minority communities, like American immigrant cuisine and soul food (the original styles, not the bougie, hipster, “elevated” styles).
For example, understanding how immigrant cuisine differs from motherland cuisine can be particularly helpful in determining how your world’s “rich” food can be adapted into “poor” food. In America we often think of corned beef and cabbage as being a traditional Irish food, but in reality, no one in Ireland really eats corned beef and cabbage - it’s a traditional Irish-American food because poor Irish immigrants could not afford the lamb they would have eaten at home (which was more readily available in say rural Ireland than in New York City and therefore at an affordable cost), and they often could not source any bacon or cured pork products because the butchers who would sell to them were often the Jewish immigrant butchers. So, the cheapest cut of cured meat they could get was corned beef and replaced the traditional proteins they would have used at home.
Second, I’m working off the assumption that your world has the same ingredients as we do, but it’s unclear. When you mention creating new foods, that could mean food preparation or it could mean edible plants and animals. If it’s the latter, then the easiest way to do it would be crossing real world things.
So, for example, everyone’s favorite vegetable on your world may be a cross between a cucumber and a lemon (the flesh is cucumber like but grows in segments in a thick skin that wouldn’t be eaten straight but could be zested, and the flavor is like a very watered down citrus). This also gives you the ability to create recipes by using the two ingredients you crossed.
Also, I’m assuming that you’re using actual food rather than powders and extracts (very common in scifi settings where "real" food is incredibly scarce), which I don’t have too many ideas on how to create recipes that way. Firefly has a pretty good method of just obliquely referring to “protein powders in every color” and showing cans of things but only really showing food prepared and being consumed when it is in fact real food provided to the crew as payment.
Finally, seasoning is a good way to hide low quality ingredients, whether it’s a cheap cut of meat or slightly wilted vegetables. Especially sauces. Especially, especially cream sauces (providing that milk of some kind is one of the ingredients generally available). Sauces make spices go further. Also, keep in mind preservation techniques (salting, smoking, drying, pickling); in the real world what has often made something the “cheap” version is that it is preserved and not fresh (with the common exception of salted foods when salt is an expensive import). But those preservation techniques also infuse additional flavors into the food.
And speaking of the real world - have you ever heard that England conquered most of it in search of spices and then decided it wasn’t going to use any of them? Spices were the purview of the very very wealthy for a very long time. The common folk did not have much access to anything they couldn’t grow in their own backyard. So, the working class dishes we commonly associate with England are not particularly spicy. As you’re deciding how the poor disguise the low quality of their food, whether it's less costly trying to appear more costly or slightly less fresh than one would prefer to eat or whatever, keep in mind what they are able to grow in the soil and climate they have (spices are typically tropical while herbs are more often temperate).
A helpful guide in food experimenting:
Cook Smart: How to Maximize Flavor Series
Part 6: Guide to Adding Flavor with Aromatics
Brainstormed: Low quality how? Like, the bakers put sawdust put in bread to save flour low quality? Our teeth are worn down by forty years old because we live in a desert and the sand gets into our food no matter what we do and grinds our molars to nubs? We only get the worst cuts of meat because it’s all we can afford or the best stuff has to be sacrificed or tithed? Salt is expensive because we don’t live near the sea or any salt deposits so trading for it is pricey? There’s been plenty of cheats, circumstances, and shortcuts throughout history that may decrease what we would call the quality of food, and all of those examples really did happen.
Your idea of quality may be a hoity-toity five star restaurant, or an enormous home-cooked fresh meal, or the tastiest dish with all the seasonings on it. Instead of describing the food as low quality, think about what your people would consider high quality. What do they love? What flavors are common, and what’s rarer and therefore richer? How available is plant-based food, meaning are there herbs and fruit trees in everyone’s garden or is agriculture and import the only way of obtaining them? How available is animal-based food, meaning do these people live as herdsfolk and eat a whole sheep every week including the organs or do fishing boats bring in dozens of kinds of seafood or is the entire population practically vegetarian until traders arrive with preserved meats?
Think about where your people are situated geographically to figure out the resources available to them, and their neighboring countries for trade. Also think about how developed your people are. This website is a timeline of food throughout history, and may help you pin down some barebones basics.
Tex: Both Feral and Brainstormed offer excellent advice, and I’ll be reiterating most of that in my own opinion.
Cooking techniques are cumulative skills that reflect a culture’s technological progression. We started with a plain old fire, so cooking food with that meant techniques like spitroasting - with the invention of pottery, we could put things in containers over, on, and even under said fire, which would bring us “new” techniques like broiling, boiling (comestibles in a liquid), roasting, sautéing, searing, and blanching (comestibles scalded in boiling water and then removed into an ice/cold water bath).
These cumulative skills are also exponential, in that most of these adapted techniques can be combined with other skills. Take, for example, a stew. The base ingredients - meats, vegetables, grains - can be cooked with direct heat (e.g. grilling over a fire), then added to a cooking container (e.g. pots of different compositions) with a fat (e.g. oil, butter) to further cook the ingredients until it’s a desired texture (e.g. “spoon tender”).
This would be a “complete” meal by itself, of course - but it’s a cook’s decision to continue on to a stew because… well, because they think it tastes good, and there could be social/cultural reasons to continue expending effort into their food. Adding a liquid - it could be water/milk, but also a composite liquid (more cooking!) such as a broth - and simmering (low indirect heat over an extended period of time) would turn this dish into a stew.
Stews (and soups, the less dense predecessor) are popular in a great deal of cultures for a variety of reasons. For one, it’s relatively easy to make - Medieval European pottage could be tended over a fire throughout the day, portions taken and the dish stretched with minimal fuss. For two, such dishes are filling, with minimal concentration on the type or number of ingredients - the basic recipe is usually water + grain(s) + vegetable(s), and can be dressed up with whatever extra ingredients are on hand. Vegetables are resource-cheap foods, as they can be grown in family/shared gardens, and grains provide the lion’s share of carbohydrates (glucose, necessary for cell function; see: cellular respiration) as well as other things like protein and fats that vegetables are usually unable to provide in significant quantities.
Soup is, in itself, preceded by gruel. Originally, soup was nothing more than something to dip your bread (or other grain-based, dry food) into, and expanded into more than just a glorified sauce. Gruels are liquid + grain, and even simpler than soups or stews. They’re very easy to make, and often invented when a culture experiences their transition to a sedentary society (marked by the shift from hunting/gathering to agriculture). Breads of some sort usually accompany this because someone will figure out indirect heating (our first baking!).
Bread-beers (Ancient History), as a side note, frequently accompany breads and gruels in terms of cooking technique epochs. The Ancient Egyptians had one, Eastern Europe another (Kvass). This is a cousin, sort of, to gruels and breads in terms of technique, and utilizes the introduction of fermentation (another skill! Possibly discovered by accident via “oh this spoiled food didn’t kill me, neat”) from ingredients such as yeast. Alcohol that doesn’t start from a solid base such as bread is the refined version of this technique.
So far, everything I’ve mentioned is made from staple foods. It is the application of technique that creates such a wide variety. There is some degree of social hierarchy when it comes to what techniques are picked by a cook, if only because some of the more refined (a term I use as a concentration of technique, not an indication of quality) ones are costly in terms of time and sometimes also available tools (e.g. it’s simpler to make a bread-beer than vodka, especially if you don’t have a distillation set-up).
Seasoning is… a thorny topic. Most ingredients that get called “seasoning” - especially in the modern, North American sense - are just plants used in lower ratios than others in a dish. Take basil, for example. When it’s used in low proportions, it’s a seasoning (e.g. tomato sauce with basil). When used in high proportions, it’s an ingredient (e.g. pesto).
Now, there’s significant overlap in which plants are called “seasonings” and which are called “herbs”. This would be because plants designated as herbs are frequently prized in cookery as adding aromatic or savoury elements to a dish - too much can be overpowering (e.g. rosemary in small amounts can be delicious, but in large amounts can be too bitter to enjoy), so they’re often relegated as a component towards flavour profiles. Their physical quantity available to a culture does not necessarily designate “high” or “low” quality, merely the ratio that is culturally-accepted in recipes. (E.g. Italy uses basil in many dishes, but does that make either the dishes or the basil low quality? No.)
Herbs, as another side note, are frequently also used in medicine - hence herbal medicine. The medicinal plants wiki is less biased than the herbal medicine one, and offers some greater anthropological context.
Quality in terms of food is… usually more the ratio of preferred to not preferred qualities. In meat, this would mean things like fat, tendons, and gristle. Food, or rather ingredient, quality is a benchmark of how much time needs to be invested in preparing a dish. It takes significantly less time to cook bread when the grains are already hulled (and oftentimes polished), than if you had to go out to the field and do it yourself. Higher quality = higher convenience.
(Despite what Apicius might claim, spoiled food is not actually edible, and is different than purposefully fermented or cultured foods.)
Higher-quality ingredients means time saved, and that time could be allocated toward more complex cooking techniques. This isn’t always true in practice, since something like a cut of meat is better for one type of dish as opposed to another for practicality’s sake (i.e. if you’ve trimmed your meat so much it’s cubed, you’re not going to get a steak out of it). There’s some debate as to the idea of ingredient quantity vs technique complexity, where touted “high quality” foods (e.g. Sachertorte) use few ingredients, and “low quality” foods have many ingredients - usually seasonings, to mask the subpar flavour of something like a cut of meat.
Like Feral said, sauces are a great carrier for flavour, as well as helping to stretch the usable lifespan of an ingredient. A cut of meat ordinarily good for a steak that’s close to expiration might not be a good steak, but it could make for a decent stew or sausage, both of which could have sauces added to them to increase the complexity of the flavour profile. The food timeline which Brainstormed mentioned also has a timeline on sauces, which I think might interest you.
You mention “all the imported food is for the rich”, and I’m curious about that. Feral gave the example of the British upper-class restricting usage of some spices to the wealthier - and thus upper - classes of their society; is that what you’re referencing? What spices are you using as a base for your world, can they be domesticated? (For that matter, do greenhouses and the accompanying opportunistic entrepreneurs also exist? Or just a general opportunistic individual.)
The economic context of spices can’t be readily dismissed - there’s a weighing of amount of resources against amount of diplomatic tensions, so even if there’s an abundant amount of a given product, the providing nation could well make a money-based rude gesture in the direction of their client and increase the prices to artificially restrict supply. (Take tea, for example. Many, many economic wars have been fought over that [Abstract].)
The fluctuations of class-availability can include a factor of a nation’s influence on the global stage, and they could demand a good at a lower price and in large enough quantities to satisfy - at least temporarily - multiple social classes. This often comes at the cost of quality (here, in terms of purity of ingredients) - you can see this with tea, black pepper, olive oil, and many other class-oriented comestible goods (1, 2, 3, 4, 5). I will stress that quality grades aren’t precisely the same for single-source foods and multi-source foods (e.g. sirloin steak vs curry powder), because a drop in single-source quality is more noticeable than multi-source quality due to fewer things to hide an ingredient’s quality behind.
Foods can still be heavily seasoned on both ends of the class spectrum, but there would be differences in local vs foreign (domesticated vs imported), and whether it’s a specialty dish (e.g. foods made for holidays, see: stollen) because infrequently-made dishes on a cultural basis are more likely to have fewer differences in ingredient quality and technique complexity.
There are also some dishes that have artificial class restrictions, because the upper classes have a habit of refusing to eat dishes from the lower classes as a means of social division. This is especially apparent in something like bread (1, 2), but fluctuations of technique complexity and ingredient quality availability can mean that the classifications of bread types can shift (1).
Further Reading
(PDF) Evolution – Culinary Culture – Cooking Technology by Thomas A. Vilgis
History of Cooking by All That Cooking
Feral (again): Modern History has a four part series on food in Medieval England broken down by social class with commentary on how it compares to food today, which may elucidate some of what we’ve been talking about in regards to the culturally variable meaning of “quality” in food.
83 notes
·
View notes