#ibmcertifocation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Cloud Computing | IT Industry | IT Computing Models
Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. The term is generally used to describe data centres available to many users over the Internet.
Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand access to provider-managed suite of both hardware and software resources that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
Cloud computing is a disruptive changing in the IT industry that represents a new model for the IT infrastructure that is different from traditional IT computing models. Cloud computing enables ubiquitous computing, where computing is available anytime and everywhere, using any device, in any location, and in any format.
This new model demands a dynamic and responsive IT infrastructure due to short application lifecycles. To support this model, new development processes, application design, and development tools are required.
Elastic resources: Scale up or down quickly and easily to meet changing demand.
Metered services: Pay only for what you use.
Self-service: Find all the IT resources that you need by using self-service access.
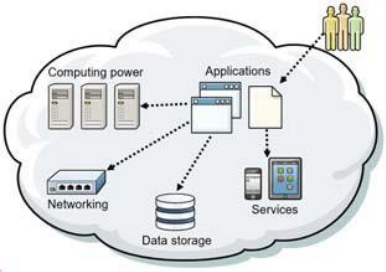
Figure: Cloud Computing
Cloud vendor:
An organization that sells computing infrastructure, software as a service (SaaS) or storage
Top cloud service providers are as follows:
· IBM Cloud
· Amazon Web Services (AWS) Amazon Web Services (AWS)
· Microsoft Azure
· Google Cloud
· Salesforce
· Oracle Cloud
Article 2
Cloud Computing Service Models:
There are three types of cloud service models.
· IAAS (Infrastructure as a Service)
· PAAS (Platform as a Service)
· SAAS (Software as a Service)

Figure: Service models
IAAS:
A cloud provider offers clients pay-as-you-go access to storage, networking, servers, and other computing resources in the cloud.
PAAS:
A cloud provider offers access to a cloud-based development environment in which users can build and deliver applications. The provider supplies and manages the underlying infrastructure.
SAAS:
A cloud provider delivers software and applications through the internet that are ready to be consumed. Users subscribe to the software and access it through the web or vendor application programming interfaces (APIs).
Infrastructure as a Service (IAAS):
Infrastructure as a service is a cloud computing offering in which a vendor provides users access to computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking. IaaS offerings are built on top of a standardized, secure, and scalable infrastructure
Key features:
· Instead of purchasing hardware outright, users pay for IAAS on demand.
· Infrastructure is scalable depending on processing and storage needs.
· Saves enterprises the costs of buying and maintaining their own hardware
· Because data is on the cloud, there is no single point of failure.
· Enables the virtualization of administrative tasks, freeing up time for other work
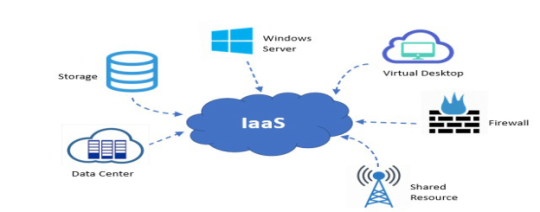
Figure: IAAS
Platform as a Service (PAAS):
Platform as a service (PAAS) is a cloud computing offering that provides users a cloud environment in which they can develop, manage, and deliver applications. In addition to storage and other computing resources, users can use a suite of prebuilt tools to develop, customize and test their own applications.
PAAS also gives the developer an automatic method for scaling. For example, consider a situation where the developer wants more hardware resources that are dedicated to an application (scaling up or vertical scaling) or more instances of the application to handle the load (scaling out or horizontal scaling). PAAS also provides built-in application monitoring. For example, the platform sends notifications to inform developers when their application crashes.
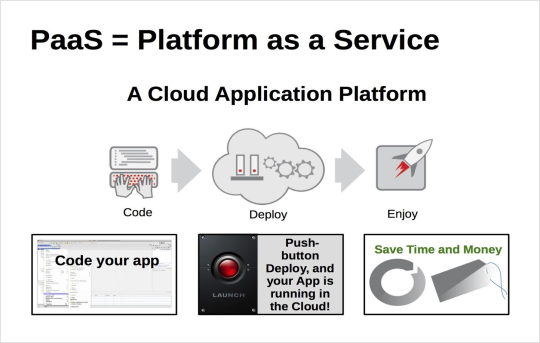
Figure: PAAS
Software as a service (SAAS):
Software as a service is a cloud computing offering that provides users with access to a vendor’s cloud-based software. Users do not install applications on their local devices. Instead, the applications reside on a remote cloud network accessed through the web or an API. Through the application, users can store and analyze data and collaborate on projects.
Key features:
· SAAS vendors provide users with software and applications on a subscription model.
· Users do not have to manage, install, or upgrade software; SAAS providers manage this.
· Data is secure in the cloud; equipment failure does not result in loss of data
· Use of resources can be scaled depending on service needs.
· Applications are accessible from almost any Internet-connected device, from virtually anywhere in the world.
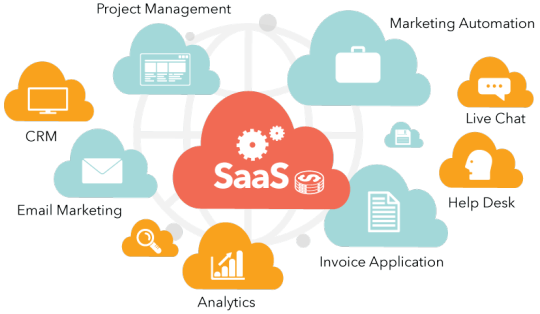
Figure: SAAS
#cloudcomputing#computing#aws#ibm#ibmcertifief#ibmcertifocation#onlinecourses#onlinetraining#training#courses#cloud#technology
13 notes
·
View notes