#jvm architecture
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
From 'Write Once, Run Anywhere' to Strong Security: The Java Advantage
Java, a programming language and technology ecosystem, has solidified its place in the digital world as a versatile and powerful tool. With its "Write Once, Run Anywhere" capability and an extensive array of features, Java has been instrumental in diverse domains, from mobile app development to building enterprise-level systems. This blog explores the strengths of Java, including its portability, robustness, vast ecosystem, and the thriving community that supports it. We will also discuss the value of structured training and the role of ACTE Technologies in nurturing your Java skills. By the end of this journey, you'll have a deep appreciation for the enduring excellence of Java and its role in the ever-evolving tech industry.

The Power and Versatility of Java:
1. Portability and Cross-Platform Compatibility:
Java's claim to fame, "Write Once, Run Anywhere," is not just a marketing slogan. It's a fundamental principle of Java that sets it apart. This feature is made possible by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which allows Java code to run on any platform that has a compatible JVM. This portability has been a game-changer, especially in a world where a diverse range of devices and operating systems coexist. Whether it's Windows, macOS, or Linux, Java applications run seamlessly, eliminating compatibility issues and reducing development time and effort.
2. Robust and Secure:
Java's architecture prioritizes robustness and security. It employs strong type checking, automatic memory management (garbage collection), and comprehensive exception handling. These features make Java code less prone to common programming errors and vulnerabilities. For businesses and organizations where system reliability and data security are critical, Java's robustness and built-in security mechanisms make it a go-to choice. Critical systems, such as banking applications, rely on Java to ensure the highest level of protection against errors and threats.
3. Vast Ecosystem:
The Java ecosystem is vast and varied. It includes an extensive library of classes, frameworks, and tools that cater to a wide range of application development needs. Some of the notable components of this ecosystem include:
Java Standard Library: Java's standard library provides a wealth of pre-built classes and utilities for common programming tasks, simplifying development.
Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB): For enterprise-level applications, EJB offers a framework for building scalable, distributed, and transactional components.
JavaServer Pages (JSP) and Servlets: These technologies enable the development of dynamic web applications, making Java a popular choice for web development.
Spring Framework: Spring is a comprehensive framework for building enterprise-level applications, offering features like dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, and more.
Android Development: Java serves as the primary language for developing Android mobile applications, further expanding its reach.
4. Community and Support:
Java's success is not only due to its technical prowess but also its thriving community of developers, enthusiasts, and experts. This community-driven approach ensures that Java remains relevant, up-to-date, and aligned with industry best practices. Developers can find a wealth of resources, forums, and collaborative environments where they can learn, share knowledge, and solve challenges. The community's collective wisdom and problem-solving spirit have contributed to the continuous evolution of Java.

Java's enduring excellence is a testament to its portability, robustness, vast ecosystem, and strong community support. If you're looking to harness the potential of Java and embark on a journey of learning and mastery, consider exploring the Java training programs offered by ACTE Technologies. With dedication and the right resources, you can leverage Java's capabilities and contribute to the ever-evolving tech landscape.
Java has stood the test of time, offering unparalleled portability, robustness, a rich ecosystem, and a vibrant community. Whether you're building enterprise-level applications or dynamic web services, Java remains a reliable choice. ACTE Technologies' structured training can help you unlock the full potential of Java, enabling you to thrive in the dynamic tech industry.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Is Java Secure For Web Applications Today?
Java is considered one of the most secure programming languages for web applications due to its robust architecture, strong memory management, and built-in security features. It runs inside the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which adds an extra layer of abstraction between the application and the underlying hardware, making it harder for malicious code to directly access system resources. Java also offers features like automatic garbage collection, exception handling, and strong type-checking, which reduce the chances of memory leaks and buffer overflow vulnerabilities common issues that can be exploited in other languages.
Additionally, Java provides a comprehensive security API that includes cryptography, authentication, access control, and secure communication. Frameworks like Spring Security further enhance security by enabling features such as role-based access control, CSRF protection, and OAuth2 authentication with minimal configuration. The large and active Java developer community regularly identifies and patches vulnerabilities, ensuring continuous updates and security enhancements.
Because of these features, Java remains a reliable choice for building secure, scalable, and maintainable web applications in enterprise environments.
To understand these principles in-depth, you may explore a full stack Java developer course.
0 notes
Text
Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide

That’s why we’ve created "Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide" to help you get fully prepared and stand out from the competition.
Java remains one of the most widely used programming languages across the tech industry. From building enterprise-grade applications to Android development and cloud-based systems, Java is a powerful, object-oriented language that has stood the test of time. As a result, Java continues to be a core requirement in thousands of job listings globally, and technical interviews often focus heavily on Java fundamentals, coding practices, and real-world problem-solving.
This guide offers a comprehensive breakdown of the most commonly asked Java interview questions, along with expert-level answers that explain not just the what, but the why—helping you build a strong conceptual foundation.
Why This Guide Matters
"Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide" is designed to equip you with the most relevant, up-to-date, and frequently asked questions across various job roles and experience levels. Whether you're a fresher just entering the field or a seasoned Java developer with years of experience, the questions included in this guide cover all the core areas expected in a Java interview.
With structured answers, real-world examples, and technical explanations, this guide helps you understand each topic in depth—so you’re not just memorizing, but truly learning.
Key Topics Covered in This Guide
Here are the primary categories of Java interview questions and answers covered in this ultimate preparation guide:
1. Core Java Basics
These questions test your fundamental knowledge of Java, including syntax, control structures, and data types. Examples include:
What are the main features of Java?
What is the difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM?
Explain the concept of platform independence in Java.
2. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java
As Java is built around the OOP paradigm, interviewers often assess your grasp of these principles:
What is encapsulation, and why is it important?
Explain inheritance with examples.
What is polymorphism, and how is it implemented in Java?
3. Exception Handling
Proper exception handling is critical in robust Java applications. Common questions include:
What is the difference between checked and unchecked exceptions?
How do try, catch, finally, and throw work together?
What is the purpose of custom exceptions?
4. Collections Framework
This is a favorite topic in Java interviews due to its practical importance:
What is the difference between ArrayList and LinkedList?
How does HashMap work internally?
What are the differences between Set, List, and Map?
5. Multithreading and Concurrency
Java supports concurrent programming, and questions in this category test your knowledge of threading concepts:
What is a thread in Java?
Explain the differences between Runnable and Thread.
How do you avoid thread-safety issues in Java applications?
6. Java 8 and Beyond
Modern Java versions introduced features like lambdas, streams, and functional programming:
What are lambda expressions?
How do you use the Stream API in Java 8?
What is the difference between Optional and null?
7. JVM Internals and Memory Management
Senior-level candidates are often expected to understand how Java works under the hood:
How does garbage collection work in Java?
What are the different memory areas in JVM?
How can memory leaks be detected and avoided?
8. Design Patterns and Best Practices
To demonstrate architectural thinking, candidates may be asked:
What is the Singleton pattern and how do you implement it?
Explain the Factory and Observer patterns.
What are SOLID principles in Java programming?
Sample Questions from the Guide
Here are a few samples from "Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide":
1: What is the difference between ‘==’ and .equals() in Java? Ans: == checks reference equality, meaning whether two references point to the same object. .equals() checks logical equality, meaning whether two objects have the same value. For example, two different String objects with the same value will return true using .equals() but false using ==.
2: What is a HashMap, and how does it work internally? Ans: A HashMap stores key-value pairs. It uses a hash function to compute an index where the value should be stored in an array. If multiple keys hash to the same index, Java handles collisions using a linked list or a balanced tree (as of Java 8).
3: How does Java achieve platform independence? Ans: Java code is compiled into bytecode by the Java compiler. This bytecode is platform-independent and can be executed by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which is available on multiple operating systems.
How to Use This Guide for Effective Interview Prep
To get the most out of "Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide", follow these steps:
Study the concepts – Don’t just read the answers; understand the reasoning behind them.
Practice coding – Use platforms like HackerRank, LeetCode, or Codeforces to apply Java in real coding problems.
Mock interviews – Simulate real interview scenarios with peers or mentors to practice verbalizing your thoughts.
Build small projects – Implement real-world solutions to solidify your understanding of Java concepts.
Keep learning – Stay up-to-date with Java updates and community discussions to stay ahead of the curve.
Conclusion
Preparation is key to succeeding in a Java interview, and "Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide" is your all-in-one resource for that journey. By mastering the topics covered in this guide, you'll gain the confidence and knowledge needed to impress your interviewers and secure your desired role in the tech industry.
0 notes
Text
Rethinking the dividing lines between containers and VMs
The technology industry loves to redraw boundary lines with new abstractions, then proclaim that prior approaches are obsolete. It happens in every major arena: application architectures (monoliths vs. microservices), programming languages (JVM languages vs. Swift, Rust, Go), cloud infrastructure (public cloud vs. on-prem), you name it. False dichotomies are good at getting people excited and…
0 notes
Text
🏛️ Day 6 of Java Mastery: Java Architecture: The Blueprint Behind Java's Power 📘 Read blog: https://wp.me/paNbWh-4h #Java #JavaMastery #Day6 #JavaArchitecture #JVM #PlatformIndependent #100DaysOfCode #LearnJava #TechLearning
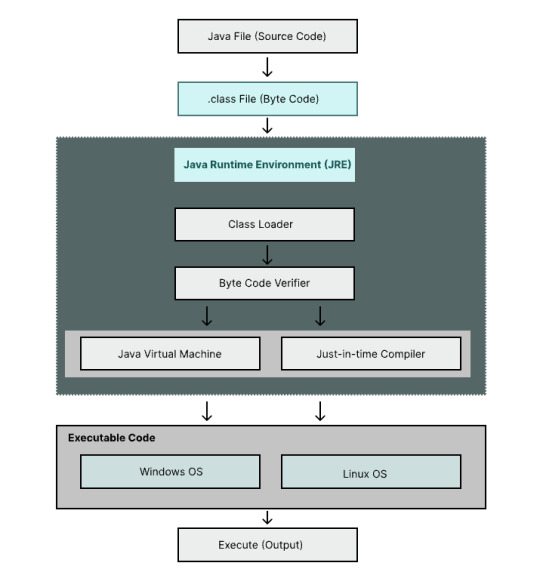
View On WordPress
#app development#architecture of java#backend#beginner#datastructures#execution flow#features of java#frontend#fullstack#fullstackdeveloper#Java#print
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Why Java is Ideal for Enterprise Applications
Start Your Journey with the Best Java Training Institute in Hyderabad
Java continues to dominate the enterprise software development landscape due to its reliability, scalability, and security. For those looking to build a strong foundation in software development, starting with the Best Java Training Institute in Hyderabad provides a clear advantage. With industry-relevant training, hands-on projects, and expert mentorship, learners can gain a deep understanding of Java’s capabilities and applications in the real world.
Platform Independence and Seamless Deployment
Java’s "write once, run anywhere" principle makes it a favorite for enterprise solutions. Applications written in Java can run on any system equipped with the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), regardless of the underlying hardware or operating system. This eliminates compatibility issues and reduces deployment time across platforms. Large enterprises benefit from this flexibility, especially when managing multiple applications across diverse environments.
Scalability to Support Business Growth
Java is inherently scalable, supporting both vertical and horizontal scaling with ease. Whether a company is launching a simple internal tool or a global cloud-based application, Java can handle the load. Its multithreading capabilities and robust memory management ensure applications remain efficient even under heavy traffic and data processing demands.
Advanced Security for Enterprise Standards
Security is a top concern for enterprises, especially those handling sensitive data. Java addresses this with features such as secure class loading, access control, cryptography libraries, and runtime checks. Combined with its strict compile-time checking and exception-handling mechanism, Java minimizes vulnerabilities and ensures a safe execution environment.
Rich Set of Tools, Frameworks, and Libraries
Java offers a comprehensive ecosystem including frameworks like Spring Boot, Hibernate, and Jakarta EE that accelerate development and promote clean, maintainable code. These tools allow developers to focus on business logic while relying on proven, scalable architecture. Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) like IntelliJ IDEA and Eclipse further enhance productivity with debugging, testing, and version control integration.
Large Community and Long-Term Support
Java’s vast global community ensures constant innovation, abundant learning resources, and quick resolution of development issues. Backed by Oracle and supported by many open-source contributors, Java receives regular updates that enhance performance, security, and compatibility—making it a reliable long-term investment for enterprises and developers alike.
Career Opportunities and Professional Growth
Many industries, including finance, healthcare, retail, and government, require Java developers. Proficiency in Java opens doors to roles like backend developer, system architect, Android developer, DevOps engineer, and cloud specialist. Mastering Java equips professionals with versatile skills that remain relevant in a fast-changing tech landscape.
Conclusion: Partner with Monopoly IT Solutions
To build a successful career in Java, hands-on learning and expert guidance are essential. That’s why many professionals choose Monopoly IT Solutions—a trusted name in IT training. With a curriculum designed by industry experts and real-time project experience, Monopoly IT Solutions prepares students for real-world enterprise challenges and long-term success in the tech industry
#programming#java full stack training#java full stack training in hyderabad#java full stack training in kphb#java full stack developer training
0 notes
Text
What to Look for When Hiring Remote Scala Developers

Scala is a popular choice if you as a SaaS business are looking to build scalable, high-performance applications. Regarded for its functional programming potential and seamless integration with Java, Scala is widely implemented in data-intensive applications, distributed systems, and backend development.
However, to identify and hire skilled remote software developers with Scala proficiency can be challenging. An understanding of the needed key skills and qualifications can help you find the right fit. Operating as a SaaS company makes efficiency and scalability vital, which is why the best Scala developers can ensure smooth operations and future-proof applications.
Key Skills and Qualities to Look for When Hiring Remote Scala Developers
Strong knowledge of Scala and functional programming
A Scala developer's proficiency with the language is the most crucial consideration when hiring them. Seek applicants with:
Expertise in Scala's functional programming capabilities, such as higher-order functions and immutability.
Strong knowledge of object-oriented programming (OOP) principles and familiarity with Scala frameworks such as Play, Akka, and Cats.
You might also need to hire backend developers who are adept at integrating Scala with databases and microservices if your project calls for a robust backend architecture.
Experience in distributed systems and big data
Scala is widely used by businesses for large data and distributed computing applications. The ideal developer should be familiar with:
Kafka for real-time data streaming.
Apache Spark, a top framework for large data analysis.
Proficiency in NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB and Cassandra.
Hiring a Scala developer with big data knowledge guarantees effective processing and analytics for SaaS organizations managing massive data volumes.
Ability to operate in a remote work environment
Hiring remotely is challenging since it poses several obstacles. Therefore, remote developers must be able to:
Work independently while still communicating with the team.
Use collaboration technologies like Jira, Slack, and Git for version control.
Maintain productivity while adjusting to distinct time zones.
Employing engineers with excellent communication skills guarantees smooth project management for companies transitioning to a remote workspace.
Knowledge of JVM and Java interoperability
Scala's interoperability with Java is one of its main benefits. Make sure the developer has experience with Java libraries and frameworks and is knowledgeable about JVM internals and performance tuning before employing them. They must be able to work on projects that call for integration between Java and Scala. Businesses switching from Java-based apps to Scala will find this very helpful.
Problem-solving and code optimization skills
Writing clear, effective, and maintainable code is a must for any competent Scala developer. Seek applicants who can:
Optimize and debug code according to best practices.
Refactor current codebases to increase performance.
Possess expertise in continuous integration and test-driven development (TDD).
Conclusion
It takes more than just technical know-how to choose and hire the best Scala developer. Seek out experts who can work remotely, have experience with distributed systems, and have good functional programming abilities. Long-term success will result from hiring developers with the appropriate combination of skills and expertise. Investing in top Scala talent enables SaaS organizations to create high-performing, scalable applications that propel business expansion.
0 notes
Text

Java’s role in high-performance computing (HPC)
Java’s role in High-Performance Computing (HPC) has evolved significantly over the years. While traditionally, languages like C, C++, and Fortran dominated the HPC landscape due to their low-level control over memory and performance, Java has made inroads into this field thanks to various optimizations and frameworks.
Advantages of Java in HPC
Platform Independence — The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) allows Java applications to run on multiple architectures without modification.
Automatic Memory Management — Java’s garbage collection (GC) simplifies memory management, reducing the risk of memory leaks common in manually managed languages.
Multi-threading & Parallelism — Java provides built-in support for multithreading, making it easier to develop parallel applications.
JIT Compilation & Performance Optimizations — Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation helps Java achieve performance close to natively compiled languages.
Big Data & Distributed Computing — Java powers popular big data frameworks like Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, and Flink, which are widely used for distributed HPC tasks.
Challenges of Java in HPC
Garbage Collection Overhead — While automatic memory management is beneficial, GC pauses can introduce latency, making real-time processing challenging.
Lower Native Performance — Even with JIT optimization, Java is generally slower than C or Fortran in numerical and memory-intensive computations.
Lack of Low-Level Control — Java abstracts many hardware-level operations, which can be a disadvantage in fine-tuned HPC applications.
Use Cases of Java in HPC
Big Data Processing — Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark, both written in Java/Scala, enable large-scale data processing.
Financial Computing — Many trading platforms use Java for risk analysis, Monte Carlo simulations, and algorithmic trading.
Bioinformatics — Java-based tools like Apache Mahout and BioJava support genomic and protein structure analysis.
Cloud-Based HPC — Java is widely used in cloud computing frameworks that provide scalable, distributed computing resources.
Java-Based HPC Frameworks & Libraries
Parallel Java (PJ2) — A library designed for parallel computing applications.
Java Grande Forum — A research initiative aimed at improving Java’s suitability for scientific computing.
MPJ Express — A Java implementation of Message Passing Interface (MPI) for distributed computing.
Future of Java in HPC
With ongoing developments like Project Panama (improving native interoperability), Project Valhalla (introducing value types for better memory efficiency), and optimized Garbage Collectors (ZGC, Shenandoah), Java is becoming a more viable option for high-performance computing tasks.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding the Java Virtual Machine (JVM): Internals and Optimization

Introduction
Briefly introduce the JVM and its role in running Java applications.
Highlight why understanding JVM internals is crucial for developers.
Mention key aspects like performance, memory management, and optimizations.
1. JVM Architecture: An Overview
Explain how JVM acts as an abstraction layer between Java code and the underlying hardware.
Key components:
Class Loader: Loads bytecode into memory.
Runtime Memory Areas: Heap, Stack, Method Area, etc.
Execution Engine: Converts bytecode into native code.
Garbage Collector (GC): Manages memory automatically.
2. JVM Memory Management
Heap vs. Stack Memory: What each is used for.
Method Area & Runtime Constant Pool: Storage for metadata and constants.
Garbage Collection (GC) Mechanisms:
Serial, Parallel, CMS, G1, and ZGC collectors.
When and how GC runs.
Tuning GC for performance (using JVM options like -XX:+UseG1GC).
3. Just-In-Time (JIT) Compilation
How JIT compiles frequently used bytecode into native machine code for performance.
Difference between:
Interpreter Mode (slower execution but quick startup).
JIT Compilation (optimizes hot code paths).
JVM optimizations like:
Method Inlining
Loop Unrolling
Escape Analysis
4. JVM Optimization Techniques
Tuning JVM with Command-line Flags
-Xms and -Xmx for memory allocation.
-XX:+PrintGCDetails for monitoring GC.
Profiling and Monitoring Tools
JVisualVM, JConsole, Java Flight Recorder.
Code-level Optimizations
Reducing object creation to avoid excessive GC.
Using efficient data structures (ArrayList vs. LinkedList).
Avoiding memory leaks (proper use of WeakReferences, ThreadLocal).
5. JVM Performance Best Practices
Selecting the right GC algorithm for different workloads.
Analyzing JVM logs to detect performance bottlenecks.
Using Ahead-of-Time (AOT) Compilation (like GraalVM) for even faster execution.
Conclusion
Summarize key takeaways: JVM architecture, memory management, JIT compilation, and optimizations.
Emphasize the importance of tuning JVM settings for different applications.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/core-java-training-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text

Advanced Java Training Institute in Delhi with 100% Placement Assistance
Unlock Your Potential with Advanced Java Training at High Technologies Solutions in Delhi
Are you looking to level up your programming skills and open new career opportunities? High Technologies Solutions offers top-tier Advanced Java Training in Delhi, designed to help you master Java concepts and become a proficient developer. Whether you're aiming for a career in software development, IT consulting, or web development, our comprehensive training program equips you with the knowledge and practical skills required to succeed in today’s competitive job market.
Why Choose High Technologies Solutions?
Expert Trainers Our trainers are highly experienced Java professionals with years of industry expertise. They bring real-world knowledge into the classroom, ensuring you gain valuable insights into the latest Java technologies and frameworks.
Updated Curriculum We stay ahead of the curve with a constantly updated curriculum that reflects the latest trends and technologies in Java. Our Advanced Java Training covers critical topics such as Java 8 features, Hibernate, Spring Framework, JDBC, RESTful web services, and more.
Hands-On Learning Theory is important, but practical experience is what makes you stand out as a developer. Our training focuses on hands-on exercises, coding challenges, and real-world projects to ensure you are ready for the workplace.
Job Assistance At High Technologies Solutions, we don’t just train, we help you launch your career. Our training program includes job placement assistance, resume building, and interview preparation to give you the edge you need when applying for your next role.
Flexible Training Options Whether you’re a working professional or a student, our flexible batch timings ensure you don’t have to compromise on your learning. Choose from weekdays, weekends, or fast-track options to fit your schedule.
What You’ll Learn in Our Advanced Java Course:
Core Java: Understand the fundamentals, including OOP concepts, exception handling, multithreading, and data structures.
Advanced Java Concepts: Master advanced topics like Java 8 features (Streams, Lambda expressions), functional programming, and JVM internals.
Java Frameworks: Get hands-on experience with popular frameworks such as Spring, Hibernate, and Struts.
Web Development with Java: Learn how to develop enterprise-level web applications using Servlets, JSP, and REST APIs.
Database Connectivity: Learn how to connect Java applications with databases using JDBC, JPA, and ORM tools.
Microservices & Cloud: Gain expertise in building scalable, cloud-ready applications with microservices architecture and Spring Boot.
Why Java?
Java remains one of the most popular and versatile programming languages in the world, with a huge demand for skilled developers across industries. From building web applications to mobile apps and enterprise solutions, Java is everywhere. By mastering Advanced Java, you'll position yourself for high-paying jobs, career growth, and a wide array of exciting job opportunities.
Start Your Journey Today!
Are you ready to accelerate your career with the best Advanced Java Training in Delhi? Enroll at High Technologies Solutions today and take the first step toward becoming an expert Java developer.
0 notes
Text
A good understanding of Hadoop Architecture is required to leverage the power of Hadoop. Below are few important practical questions which can be asked to a Senior Experienced Hadoop Developer in an interview. I learned the answers to them during my CCHD (Cloudera Certified Haddop Developer) certification. I hope you will find them useful. This list primarily includes questions related to Hadoop Architecture, MapReduce, Hadoop API and Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). Hadoop is the most popular platform for big data analysis. The Hadoop ecosystem is huge and involves many supporting frameworks and tools to effectively run and manage it. This article focuses on the core of Hadoop concepts and its technique to handle enormous data. Hadoop is a huge ecosystem and referring to a good hadoop book is highly recommended. Below list of hadoop interview questions and answers that may prove useful for beginners and experts alike. These are common set of questions that you may face at big data job interview or a hadoop certification exam (like CCHD). What is a JobTracker in Hadoop? How many instances of JobTracker run on a Hadoop Cluster? JobTracker is the daemon service for submitting and tracking MapReduce jobs in Hadoop. There is only One Job Tracker process run on any hadoop cluster. Job Tracker runs on its own JVM process. In a typical production cluster its run on a separate machine. Each slave node is configured with job tracker node location. The JobTracker is single point of failure for the Hadoop MapReduce service. If it goes down, all running jobs are halted. JobTracker in Hadoop performs following actions(from Hadoop Wiki:) Client applications submit jobs to the Job tracker. The JobTracker talks to the NameNode to determine the location of the data The JobTracker locates TaskTracker nodes with available slots at or near the data The JobTracker submits the work to the chosen TaskTracker nodes. The TaskTracker nodes are monitored. If they do not submit heartbeat signals often enough, they are deemed to have failed and the work is scheduled on a different TaskTracker. A TaskTracker will notify the JobTracker when a task fails. The JobTracker decides what to do then: it may resubmit the job elsewhere, it may mark that specific record as something to avoid, and it may may even blacklist the TaskTracker as unreliable. When the work is completed, the JobTracker updates its status. Client applications can poll the JobTracker for information. How JobTracker schedules a task? The TaskTrackers send out heartbeat messages to the JobTracker, usually every few minutes, to reassure the JobTracker that it is still alive. These message also inform the JobTracker of the number of available slots, so the JobTracker can stay up to date with where in the cluster work can be delegated. When the JobTracker tries to find somewhere to schedule a task within the MapReduce operations, it first looks for an empty slot on the same server that hosts the DataNode containing the data, and if not, it looks for an empty slot on a machine in the same rack. What is a Task Tracker in Hadoop? How many instances of TaskTracker run on a Hadoop Cluster A TaskTracker is a slave node daemon in the cluster that accepts tasks (Map, Reduce and Shuffle operations) from a JobTracker. There is only One Task Tracker process run on any hadoop slave node. Task Tracker runs on its own JVM process. Every TaskTracker is configured with a set of slots, these indicate the number of tasks that it can accept. The TaskTracker starts a separate JVM processes to do the actual work (called as Task Instance) this is to ensure that process failure does not take down the task tracker. The TaskTracker monitors these task instances, capturing the output and exit codes. When the Task instances finish, successfully or not, the task tracker notifies the JobTracker. The TaskTrackers also send out heartbeat messages to the JobTracker, usually every few minutes, to reassure the JobTracker that it is still alive.
These message also inform the JobTracker of the number of available slots, so the JobTracker can stay up to date with where in the cluster work can be delegated. What is a Task instance in Hadoop? Where does it run? Task instances are the actual MapReduce jobs which are run on each slave node. The TaskTracker starts a separate JVM processes to do the actual work (called as Task Instance) this is to ensure that process failure does not take down the task tracker. Each Task Instance runs on its own JVM process. There can be multiple processes of task instance running on a slave node. This is based on the number of slots configured on task tracker. By default a new task instance JVM process is spawned for a task. How many Daemon processes run on a Hadoop system? Hadoop is comprised of five separate daemons. Each of these daemon run in its own JVM. Following 3 Daemons run on Master nodes NameNode - This daemon stores and maintains the metadata for HDFS. Secondary NameNode - Performs housekeeping functions for the NameNode. JobTracker - Manages MapReduce jobs, distributes individual tasks to machines running the Task Tracker. Following 2 Daemons run on each Slave nodes DataNode – Stores actual HDFS data blocks. TaskTracker - Responsible for instantiating and monitoring individual Map and Reduce tasks. What is configuration of a typical slave node on Hadoop cluster? How many JVMs run on a slave node? Single instance of a Task Tracker is run on each Slave node. Task tracker is run as a separate JVM process. Single instance of a DataNode daemon is run on each Slave node. DataNode daemon is run as a separate JVM process. One or Multiple instances of Task Instance is run on each slave node. Each task instance is run as a separate JVM process. The number of Task instances can be controlled by configuration. Typically a high end machine is configured to run more task instances. What is the difference between HDFS and NAS ? The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) is a distributed file system designed to run on commodity hardware. It has many similarities with existing distributed file systems. However, the differences from other distributed file systems are significant. Following are differences between HDFS and NAS In HDFS Data Blocks are distributed across local drives of all machines in a cluster. Whereas in NAS data is stored on dedicated hardware. HDFS is designed to work with MapReduce System, since computation are moved to data. NAS is not suitable for MapReduce since data is stored seperately from the computations. HDFS runs on a cluster of machines and provides redundancy usinga replication protocal. Whereas NAS is provided by a single machine therefore does not provide data redundancy. How NameNode Handles data node failures? NameNode periodically receives a Heartbeat and a Blockreport from each of the DataNodes in the cluster. Receipt of a Heartbeat implies that the DataNode is functioning properly. A Blockreport contains a list of all blocks on a DataNode. When NameNode notices that it has not recieved a hearbeat message from a data node after a certain amount of time, the data node is marked as dead. Since blocks will be under replicated the system begins replicating the blocks that were stored on the dead datanode. The NameNode Orchestrates the replication of data blocks from one datanode to another. The replication data transfer happens directly between datanodes and the data never passes through the namenode. Does MapReduce programming model provide a way for reducers to communicate with each other? In a MapReduce job can a reducer communicate with another reducer? Nope, MapReduce programming model does not allow reducers to communicate with each other. Reducers run in isolation. Can I set the number of reducers to zero? Yes, Setting the number of reducers to zero is a valid configuration in Hadoop. When you set the reducers to zero no reducers will be executed, and the output of each mapper will be stored to a separate file on HDFS.
[This is different from the condition when reducers are set to a number greater than zero and the Mappers output (intermediate data) is written to the Local file system(NOT HDFS) of each mappter slave node.] Where is the Mapper Output (intermediate kay-value data) stored ? The mapper output (intermediate data) is stored on the Local file system (NOT HDFS) of each individual mapper nodes. This is typically a temporary directory location which can be setup in config by the hadoop administrator. The intermediate data is cleaned up after the Hadoop Job completes. What are combiners? When should I use a combiner in my MapReduce Job? Combiners are used to increase the efficiency of a MapReduce program. They are used to aggregate intermediate map output locally on individual mapper outputs. Combiners can help you reduce the amount of data that needs to be transferred across to the reducers. You can use your reducer code as a combiner if the operation performed is commutative and associative. The execution of combiner is not guaranteed, Hadoop may or may not execute a combiner. Also, if required it may execute it more then 1 times. Therefore your MapReduce jobs should not depend on the combiners execution. What is Writable & WritableComparable interface? org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable is a Java interface. Any key or value type in the Hadoop Map-Reduce framework implements this interface. Implementations typically implement a static read(DataInput) method which constructs a new instance, calls readFields(DataInput) and returns the instance. org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable is a Java interface. Any type which is to be used as a key in the Hadoop Map-Reduce framework should implement this interface. WritableComparable objects can be compared to each other using Comparators. What is the Hadoop MapReduce API contract for a key and value Class? The Key must implement the org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable interface. The value must implement the org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable interface. What is a IdentityMapper and IdentityReducer in MapReduce ? org.apache.hadoop.mapred.lib.IdentityMapper Implements the identity function, mapping inputs directly to outputs. If MapReduce programmer do not set the Mapper Class using JobConf.setMapperClass then IdentityMapper.class is used as a default value. org.apache.hadoop.mapred.lib.IdentityReducer Performs no reduction, writing all input values directly to the output. If MapReduce programmer do not set the Reducer Class using JobConf.setReducerClass then IdentityReducer.class is used as a default value. What is the meaning of speculative execution in Hadoop? Why is it important? Speculative execution is a way of coping with individual Machine performance. In large clusters where hundreds or thousands of machines are involved there may be machines which are not performing as fast as others. This may result in delays in a full job due to only one machine not performaing well. To avoid this, speculative execution in hadoop can run multiple copies of same map or reduce task on different slave nodes. The results from first node to finish are used. When is the reducers are started in a MapReduce job? In a MapReduce job reducers do not start executing the reduce method until the all Map jobs have completed. Reducers start copying intermediate key-value pairs from the mappers as soon as they are available. The programmer defined reduce method is called only after all the mappers have finished. If reducers do not start before all mappers finish then why does the progress on MapReduce job shows something like Map(50%) Reduce(10%)? Why reducers progress percentage is displayed when mapper is not finished yet? Reducers start copying intermediate key-value pairs from the mappers as soon as they are available. The progress calculation also takes in account the processing of data transfer which is done by reduce process, therefore the reduce progress starts
showing up as soon as any intermediate key-value pair for a mapper is available to be transferred to reducer. Though the reducer progress is updated still the programmer defined reduce method is called only after all the mappers have finished. What is HDFS ? How it is different from traditional file systems? HDFS, the Hadoop Distributed File System, is responsible for storing huge data on the cluster. This is a distributed file system designed to run on commodity hardware. It has many similarities with existing distributed file systems. However, the differences from other distributed file systems are significant. HDFS is highly fault-tolerant and is designed to be deployed on low-cost hardware. HDFS provides high throughput access to application data and is suitable for applications that have large data sets. HDFS is designed to support very large files. Applications that are compatible with HDFS are those that deal with large data sets. These applications write their data only once but they read it one or more times and require these reads to be satisfied at streaming speeds. HDFS supports write-once-read-many semantics on files. What is HDFS Block size? How is it different from traditional file system block size? In HDFS data is split into blocks and distributed across multiple nodes in the cluster. Each block is typically 64Mb or 128Mb in size. Each block is replicated multiple times. Default is to replicate each block three times. Replicas are stored on different nodes. HDFS utilizes the local file system to store each HDFS block as a separate file. HDFS Block size can not be compared with the traditional file system block size. What is a NameNode? How many instances of NameNode run on a Hadoop Cluster? The NameNode is the centerpiece of an HDFS file system. It keeps the directory tree of all files in the file system, and tracks where across the cluster the file data is kept. It does not store the data of these files itself. There is only One NameNode process run on any hadoop cluster. NameNode runs on its own JVM process. In a typical production cluster its run on a separate machine. The NameNode is a Single Point of Failure for the HDFS Cluster. When the NameNode goes down, the file system goes offline. Client applications talk to the NameNode whenever they wish to locate a file, or when they want to add/copy/move/delete a file. The NameNode responds the successful requests by returning a list of relevant DataNode servers where the data lives. What is a DataNode? How many instances of DataNode run on a Hadoop Cluster? A DataNode stores data in the Hadoop File System HDFS. There is only One DataNode process run on any hadoop slave node. DataNode runs on its own JVM process. On startup, a DataNode connects to the NameNode. DataNode instances can talk to each other, this is mostly during replicating data. How the Client communicates with HDFS? The Client communication to HDFS happens using Hadoop HDFS API. Client applications talk to the NameNode whenever they wish to locate a file, or when they want to add/copy/move/delete a file on HDFS. The NameNode responds the successful requests by returning a list of relevant DataNode servers where the data lives. Client applications can talk directly to a DataNode, once the NameNode has provided the location of the data. How the HDFS Blocks are replicated? HDFS is designed to reliably store very large files across machines in a large cluster. It stores each file as a sequence of blocks; all blocks in a file except the last block are the same size. The blocks of a file are replicated for fault tolerance. The block size and replication factor are configurable per file. An application can specify the number of replicas of a file. The replication factor can be specified at file creation time and can be changed later. Files in HDFS are write-once and have strictly one writer at any time. The NameNode makes all decisions regarding replication of blocks.
HDFS uses rack-aware replica placement policy. In default configuration there are total 3 copies of a datablock on HDFS, 2 copies are stored on datanodes on same rack and 3rd copy on a different rack. Can you think of a questions which is not part of this post? Please don't forget to share it with me in comments section & I will try to include it in the list.
0 notes
Text
Top 5 Programming Languages You Should Learn in 2024

Learning the proper programming languages could make a big difference on your profession. With technology advancing unexpectedly, some programming languages stand out more than others in 2024. Whether you’re just beginning out in coding or looking to upgrade your talents, this listing will help you pick out the quality languages to learn.
Let’s take a look at the top 5 programming languages you should learn in 2024!
1. Python
Why Learn Python?
Python has been one of the maximum popular programming languages for several years—and it’s no longer going anywhere. It’s broadly used in net improvement, records analysis, synthetic intelligence (AI), system learning (ML), and even automation.
Key Advantages:
Easy to Learn: Python is thought for its easy, readable syntax, making it a wonderful choice for novices.
Versatile: Python is used in a extensive form of fields, from facts science to net apps, making it a language with infinite opportunities.
Huge Community: With a massive variety of libraries and frameworks (like Django and Flask), you may without problems locate equipment and help for almost any undertaking.
In 2024, Python will continue to be in high demand, Especially with the increasing focus on AI, statistics technological know-how, and automation.

2. JavaScript
Why Learn JavaScript?
JavaScript is the spine of net improvement. It powers interactivity on web sites, from simple animations to complicated web apps. If you’re looking to build interactive web sites or complete-fledged internet applications, JavaScript is a need to.
Key Advantages:
Universally Used: It’s the maximum widely-used language for internet development. Whether you’re working on the front stop (what users see) or the again give up (server-aspect common sense), JavaScript is vital.
Fast and Dynamic: JavaScript permits for actual-time updates with out fresh the web page, making web apps experience faster and more interactive.
Rich Ecosystem: Tools like React, Angular, and Node.Js make JavaScript even greater powerful, allowing you to construct the whole thing from easy web sites to complex, statistics-pushed applications.
JavaScript's versatility and consistent call for in internet improvement make it a pinnacle language to analyze in 2024.

3. Go (Golang)
Why Learn Go?
Go, additionally called Golang, is a programming language developed with the aid of Google. It's turning into more famous, specially for building fast, reliable, and scalable software program, particularly in cloud computing and microservices.
Key Advantages:
Speed and Performance: Go is known for its lightning-fast typical performance, which makes it incredible for constructing excessive-overall performance applications.
Concurrency Made Easy: Go’s built-in aid for concurrent programming (walking more than one method at the equal time) makes it a pinnacle preference for cloud-based totally programs and services.
Great for Micro services: With its easy syntax and simplicity of use, Go is exceptional for scalable micro services that run easily in cloud environments.
As more agencies adopt cloud computing and micro offerings architectures, Go’s call for is predicted to develop, making it a precious language to research in 2024.
4. Java
Why Learn Java?
Java is one of the most depended on and widely used programming languages, in particular in large-scale enterprise packages, Android app development, and agency structures. Although it's been round for many years, Java nevertheless holds a robust role in 2024.
Key Advantages:
Platform-Independent: Java is thought for its “write once, run everywhere” function. This approach you may run Java programs on any device, as long because it has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Great for Android Development: Java is the official language for Android apps. If you want to become an Android developer, learning Java is a must.
Enterprise Use: Many massive corporations rely upon Java for their backend systems, making it a crucial language in organization software program improvement.
Java’s reliability, balance, and massive surroundings make sure that it remains a top language for corporations and builders alike.

5. Rust
Why Learn Rust?
Rust is a structures programming language designed for safety and overall performance. While it’s more recent than a number of the other languages in this listing, its reputation is rising rapid, especially in areas like game improvement, block chain, and systems programming.
Key Advantages:
Memory Safety: Rust is thought for its interest on memory protection, making sure that your code doesn’t have common bugs like reminiscence leaks or statistics races. This makes it pleasant for universal performance-crucial packages.
Performance: Rust is rather rapid, regularly outperforming different languages like C in positive cases, especially in phrases of memory management.
Growing Demand: Although it’s a surprisingly younger language, Rust is gaining popularity in industries like gaming, cryptocurrency, and even operating systems improvement.
If you’re interested by low-stage programming or walking in industries that require immoderate performance (like block chain or recreation engines), Rust is a exquisite language to research in 2024.
Honorable Mentions
While these five languages are great choices for 2024, there are other languages worth considering depending on your interests:
C#: Great for sport improvement (with Unity) and corporation packages.
Swift: The pass-to language for iOS and macOS app development.
Kotlin: An opportunity to Java for Android improvement, with a greater modern syntax.
Conclusion
Learning a brand new programming language is an funding in your future, and selecting the right one can help you achieve your profession desires. In 2024, Python, JavaScript, Go, Java, and Rust are some of the maximum precious languages to analyze, every supplying unique blessings and opportunities in different tech fields.
Whether you’re inquisitive about internet development, cell apps, sport development, or structures programming, those languages will provide you with the skills you want to live in advance in the ever-evolving tech global. Visit Eloiacs to find more about software development.
So, which one will you learn next?
0 notes
Text
About Java Interview Preparation
Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is a general-purpose programming language intended to let application developers write once, run anywhere (WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need for recompilation. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. Java Language Basics include syntax, data types, and control structures, while core Java concepts cover advanced topics like object-oriented programming, inheritance, and polymorphism. Java is widely used in various sectors, which creates a vast job market for Java developers. They can work in different roles such as Java Developer, Software Developer, Web Developer, Application Developer, EJB Programmer, Software Engineer, Tester, Graphic Designer, among others. They can find opportunities in sectors like IT, E-commerce, Finance, Education, Healthcare, and many more.
0 notes
Text
The Java Full Stack Developer Course: Learn, Build, and Get Placed

Introduction
Overview of Full Stack Development Full stack development encompasses front-end as well as back-end web development. A full stack developer provides both the user's interface and the server-side components of a web application. This role requires expertise in a range of technologies, making developers versatile and capable of handling all aspects of web application development.
Importance of Java in Full Stack Development Java is still a popular choice for full stack development because of its flexibility, trustworthiness, and wide ecosystem. Java's robust backend frameworks and strong community support make it ideal for building enterprise-level applications. Learning Java allows developers to work efficiently on the front end and backend.
What is a Java Full Stack Developer?
Role of a Full Stack Developer A Java full stack developer is skilled at both frontend and backend development with Java technology. They design and develop the entire architecture of a web application, ensuring seamless communication between the user interface and server-side operations.
Core Skills for a Java Full Stack Developer
Key skills include Java programming, knowledge of frontend technologies like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks such as React or Angular. Understanding databases like MySQL and MongoDB, and server-side frameworks like Spring Boot, are essential for backend development.
Why Choose Java for Full Stack Development?
Versatility of Java Java is widely used across industries for building secure, scalable applications. Its cross-platform capabilities make it ideal for full stack development, allowing applications to run seamlessly across various platforms with the help of Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Advantages of Java Java’s object-oriented structure and powerful frameworks, such as Spring Boot and Hibernate, allow developers to build maintainable and scalable applications. Java’s memory management and automatic garbage collection are crucial for handling large-scale applications.
Key Features of the Course
Comprehensive Curriculum The course covers both frontend and backend development. Students learn web technologies, including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and modern frameworks like React or Angular. Additionally, Java-based backend frameworks such as Spring Boot are taught to help students build efficient server-side applications.
Project-Based Learning The course focuses on practical instruction, with students building applications that are practical.Projects like e-commerce sites or social media platforms integrate frontend and backend components, simulating a real-world development environment.
Career Benefits
High Demand for Full Stack Developers Full stack developers are in high demand because of their diverse skill set. With companies looking for developers capable of handling both frontend and backend tasks, Java full stack developers enjoy excellent job prospects and competitive salaries.
Diverse Career Opportunities Graduates can pursue careers as front-end developers, back-end developers, full stack developers, or software engineers. Java’s versatility ensures developers can work on web, mobile, and enterprise applications.
Placement Assistance
Internship and Job Placement Support Many Java full stack courses offer placement assistance to help students secure internships and job opportunities. Internship programs provide industry experience, while job placement support connects graduates with leading companies.
Industry Networking Top institutes often have industry partnerships, offering students access to a network of professionals and hiring managers. This networking can lead to job interviews, career guidance, and mentoring opportunities.
How to Choose the Right Course
Key Considerations When selecting a Java full stack course, consider factors like duration, course structure, and faculty expertise. Look for courses that balance theoretical knowledge with practical experience and offer career counseling and placement support.
Conclusion
A Java Full Stack Developer course teaches the skills required to create whole web applications, including technologies for the frontend and backend. With Java’s continued relevance in the tech industry and the high demand for full stack developers, this course ensures you’re well-prepared for a successful career.
Why Choose GRK Trainings? At GRK Trainings, we offer a comprehensive Java Full Stack Developer course covering Java, Spring Boot, React, and Angular. Our expert instructors provide hands-on learning through real-world projects, and we offer placement assistance to help you launch your career. Enroll today to become a skilled Java Full Stack Developer!
#java full stack developer course#full stack java developer course#java full stack developer course with placement
0 notes
Text
Advantages of Java in Programming Careers

Java is easy to learn. Java was designed to be easy to use and therefore easier to write, compile, debug and learn than other programming languages.
Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It was developed by Sun Microsystems and released in 1995. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java Virtual Machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. This makes it one of the many reasons why Java has become so important in many software development environments.
Java is one of the most popular and versatile programming languages, offering numerous benefits to those pursuing a career in software development. Its platform independence, object-oriented design, and large ecosystem of libraries and frameworks make it ideal for building scalable and secure applications. The widespread use of Java in industries such as finance, healthcare and e-commerce ensures a strong demand for Java developers, leading to a wealth of job opportunities. Additionally, its rich community support and continuous evolution keep Java relevant in a rapidly changing technology landscape, providing developers with long-term career growth and stability.
Learn Java Programming at TCCI Computer Coaching with expert trainers. Master essential concepts and practical skills for real-world applications. Start your coding journey today!
Call us @ +91 98256 18292
Visit us @ https://tccicomputercoaching.wordpress.com/
#TCCI computer coaching institute#best computer classes near me#java programming course ahmedabad#best computer class in Bopal ahmedabad#best computer class in iscon-ambli road-ahmedabad
0 notes