#microfinance registration process
Text
Exploring the Benefits of Microfinance Companies
Get Know about Benefits of Microfinance Companies through this video. get the detail of Microfinance Company Registration Process in simple words with Legal Dev. Learn more about Microfinance Companies by visiting our YouTube channel.
0 notes
Text
What is Section 8 Company? Documents, Procedure

A Section 8 Company is a type of nonprofit organization in India, regulated by the Companies Act. Its primary objective is to promote charitable or not-for-profit activities in areas like education, art, science, and social welfare. Unlike other companies, Section 8 companies do not distribute profits among their members and use any surplus for promoting their objectives.
Documents or Details Required for Section 8 Company Registration
To register a Section 8 Company in India, you typically need the following documents and details:
Memorandum of Association (MOA): This document outlines the company's objectives and the scope of its activities.
Articles of Association (AOA): This document defines the company's internal rules and regulations for management and administration.
Declaration by Directors: A declaration by each of the proposed directors stating that they have not been convicted or found guilty of any offense in connection with the promotion, formation, or management of any company.
Affidavits: Affidavits from the directors and subscribers declaring that they are not associated with any other Section 8 company with similar objects.
Address Proof: Address proof for the registered office of the company.
Identity Proof: Identity proof (PAN card) of all directors and subscribers.
Passport-sized Photographs: Passport-sized photographs of all directors and subscribers.
Utility Bills: Utility bills (electricity, water, etc.) or property tax receipt for the registered office address.
Approval from Appropriate Authority: If the proposed name contains any words that require approval from the central government or any authority, then the approval should be obtained.
Which types of Name can be used as the end of Section 8?
The name of a Section 8 Company in India should reflect its objectives and should not resemble the name of any existing company. The name should typically end with words like:
Foundation
Forum
Association
Federation
Chambers
Confederation
Council
Charities
Trust
Society
Organization
Institute
Is Trust, Society and Section 8 Company same?
Trusts, Societies, and Section 8 Companies are different legal entities commonly used for charitable or nonprofit activities in India:
Trust: A trust is a legal arrangement where a trustee holds and manages property for the benefit of beneficiaries. Trusts are governed by the Indian Trusts Act. They are often used for charitable and religious purposes.
Society: A society is formed under the Societies Registration Act. It is a membership-based organization that can be established for promoting literature, science, arts, education, charity, or any other useful purpose. Societies typically have a governing body and members.
Section 8 Company: A Section 8 Company, as per the Companies Act, is a nonprofit organization established for promoting commerce, art, science, sports, education, research, social welfare, religion, charity, protection of the environment, or any other charitable purpose. Unlike trusts and societies, it is a company incorporated under Section 8 of the Companies Act.
While all three serve similar purposes of promoting charitable or nonprofit activities, they differ in their legal structures, formation processes, and regulatory frameworks. The choice between a trust, society, or Section 8 Company depends on the specific requirements and preferences of the individuals or entities involved.
Procedure to Register Section 8 Company
The procedure to register a Section 8 Company in India involves several steps:
1. Name Approval:
Choose a unique and suitable name for the company that complies with naming guidelines.
Apply for name availability through the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) website.
2. Obtain Digital Signatures:
Obtain Digital Signature Certificates (DSC) for all proposed directors. This is required for online filing of documents.
3. Apply for Director Identification Number (DIN):
Directors need to apply for DIN if they don't have one. It can be obtained online from the MCA.
4. Drafting of Memorandum and Articles of Association:
Draft the Memorandum of Association (MOA) and Articles of Association (AOA) detailing the objectives and rules of the company.
5. Declaration by Directors and Subscribers:
Directors and subscribers need to sign a declaration stating that they have not been convicted or found guilty of any offense related to company management.
6. Application for License:
Prepare and file an application for a license under Section 8 with the Regional Director through the MCA.
7. Approval from Regional Director:
The Regional Director reviews the application and may request additional information. If satisfied, they grant the license.
8. Incorporation:
After obtaining the license, submit the incorporation documents including MOA, AOA, and other required details to the Registrar of Companies (RoC) for final incorporation.
9. Registered Office:
Provide proof of the registered office address.
10. Certificate of Incorporation:
Once the RoC verifies the documents, they issue the Certificate of Incorporation, officially establishing the Section 8 Company.
11. PAN and TAN Application:
Apply for the Permanent Account Number (PAN) and Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN) for the Section 8 Company.
Why should I register under section 8, because it is a company?
Registering under Section 8 provides certain advantages for organizations aiming to operate as nonprofit entities with charitable objectives. Here are some reasons why you might choose to register under Section 8:
Legal Recognition: Section 8 registration provides legal recognition to an organization as a nonprofit company. It is a separate legal entity, distinct from its members, which enhances credibility and legitimacy.
Limited Liability: Members of a Section 8 Company have limited liability. This means their personal assets are generally protected from the company's liabilities.
Perpetual Succession: A Section 8 Company enjoys perpetual succession, meaning its existence is not affected by changes in its membership. It continues to exist until it achieves its objectives or is dissolved according to legal provisions.
Tax Exemptions: Section 8 Companies may be eligible for tax exemptions under the Income Tax Act, making it more attractive for donors and contributors.
Fundraising Opportunities: Being a legal entity, Section 8 Companies can easily raise funds through donations, grants, and other fundraising activities to support their charitable purposes.
Greater Credibility: Registration under Section 8 enhances the credibility of the organization, as it is subjected to regulatory oversight and compliance requirements.
Access to Grants and Funding: Many government and non-government organizations prefer to provide grants and funding to registered nonprofit entities, and Section 8 registration facilitates access to such opportunities.
Limited Profit Distribution: Unlike regular companies, Section 8 Companies are restricted in distributing profits to their members. Any surplus generated is utilized for promoting the company's charitable objectives.
How Vakilkaro helps for Section 8 Company Registration?
Expert Guidance: Vakilkaro provides expert legal guidance throughout the Section 8 Company registration process, ensuring accurate documentation and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Efficient Name Approval: Vakilkaro streamlines the name approval process by assisting in the selection of a unique and compliant name, expediting the initial stage of registration.
Online Document Filing: Vakilkaro facilitates the efficient online filing of essential documents, including Memorandum and Articles of Association, Director Identification Number (DIN) application, and more.
License Application Support: Vakilkaro assists in the preparation and filing of the license application under Section 8, navigating the complexities of the approval process with the Regional Director.
Comprehensive Service: From start to finish, Vakilkaro offers end-to-end support, ensuring a smooth and hassle-free Section 8 Company registration experience, allowing clients to focus on their charitable objectives.
#microfinance company#section 8 microfinance company#company registration#section 8 company registration process
0 notes
Text
Comprehensive Guide to NBFC Registration in India: A 2024 Perspective
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) play a crucial role in India’s financial sector by providing services that traditional banks often overlook, such as asset financing, microfinance, and infrastructure lending.
As the Indian economy continues to grow, the demand for NBFCs has surged, making them a lucrative business opportunity.
However, establishing an NBFC in India involves navigating a complex registration process governed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
This blog provides a detailed guide on the NBFC registration process, eligibility criteria, required documents, necessary licenses, and the benefits and challenges of becoming an NBFC in 2024.
Understanding NBFCs: A Quick Overview
Before diving into the registration process of NBFC, it’s important to understand what an NBFC is.
An NBFC is a financial institution that offers various banking services but does not hold a banking license. Unlike traditional banks, NBFCs cannot accept demand deposits, such as savings or current accounts, but they can offer loans, credit facilities, savings schemes, and investment products.
NBFCs are regulated by the RBI under the RBI Act, 1934, and are classified into different categories based on their activities.
Eligibility Criteria for NBFC Registration in 2024
The RBI has set forth stringent eligibility criteria for registering an NBFC to ensure that only credible entities enter this highly regulated space. As of 2024, the key eligibility criteria include:
Minimum Net Owned Fund (NOF): The company must have a minimum NOF of ₹10 crore.
Incorporation: The applicant must be a company registered under the Companies Act, 2013, either as a Private Limited or a Public Limited Company.
Directors’ Expertise: At least one-third of the directors must have relevant experience in finance, particularly in banking, finance, or economic management.
Creditworthiness: The company’s promoters and directors must have a clean credit history, free from any defaults or blacklisting by financial institutions.
Ownership and Control: Foreign investment is allowed in NBFCs under the automatic route, but ownership and control should remain with resident Indian entities.
Documents Required for NBFC Registration
Documentation is a critical part of the NBFC registration process. As of 2024, the following documents are required:
Certificate of Incorporation: Issued by the Registrar of Companies (ROC) under the Companies Act, 2013.
Memorandum of Association (MOA) and Articles of Association (AOA): These documents should clearly state the financial objectives of the company.
Detailed Business Plan: A comprehensive business plan covering at least the next three years, including projected financial statements, market analysis, and growth strategy.
Directors’ and Shareholders’ KYC Documents: This includes Aadhaar, PAN, passport, and photographs.
Net Worth Certificate: Certified by a Chartered Accountant (CA), showing that the company has the required NOF of ₹10 crore.
Credit Reports: Personal credit reports of all directors and shareholders from credit bureaus like CIBIL.
Bank Account Details: Proof of the NOF being deposited in the company's bank account.
Income Tax Returns: The last three years' income tax returns of the directors.
Audited Financial Statements: The company’s balance sheet, profit & loss account, and auditor’s report for the last three years (if applicable).
Step-by-Step NBFC Registration Process in 2024
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the NBFC registration process in 2024:
1. Incorporate the Company
The first step is incorporating a Private or Public Limited Company under the Companies Act, 2013. The company name should reflect its financial nature, as per the naming guidelines provided by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
2. Ensure Compliance with NOF Requirement
Deposit the minimum NOF of ₹10 crore into a bank account under the company’s name. This amount will be locked in until the RBI grants the Certificate of Registration (CoR).
3. Prepare the Necessary Documents
Gather all required documents, including the business plan, NOF certificate, and KYC documents. Make sure all documents are duly signed, notarized, and attested where necessary.
4. Submit the Online Application
Submit the application through the RBI’s COSMOS portal. You’ll need to upload all the required documents electronically and pay the applicable fee.
5. Submit the Physical Copies
Send hard copies of the application and all documents to the regional office of the RBI. Ensure that the documents are submitted in the prescribed format.
6. Respond to RBI’s Queries
During the review process, the RBI may request additional documents or clarifications. Promptly responding to these queries is crucial to avoid delays in the registration process.
7. Receive the Certificate of Registration (CoR)
If the RBI is satisfied with your application, you will receive the Certificate of Registration, allowing you to operate as an NBFC in India. This certificate must be prominently displayed at your place of business.
Licenses and Approvals Required for NBFCs
Apart from the RBI’s Certificate of Registration, certain NBFCs may require additional licenses based on their business activities. These include:
NBFC-MFIs (Microfinance Institutions): Require special approval to offer microfinance services.
NBFC-Factors: Need to register as Factors under the Factoring Regulation Act, 2011.
NBFC-Investment and Credit Companies (NBFC-ICC): May need approvals if they engage in credit activities like issuing credit cards or offering loans against securities.
Benefits of NBFC Registration
Registering as an NBFC offers several advantages:
Wider Market Access: NBFCs can cater to a broader market, including underserved segments like MSMEs and the unbanked population.
Flexible Operations: NBFCs have fewer operational restrictions compared to banks, allowing them to innovate and offer customized financial products.
Growth Potential: With India’s growing economy, NBFCs have significant growth opportunities, especially in lending, asset management, and microfinance.
High Returns: Given the high demand for financial services, especially in rural and semi-urban areas, NBFCs can generate substantial returns on investment.
Challenges in NBFC Registration
While the benefits are significant, there are also challenges:
Stringent Regulatory Compliance: NBFCs must comply with numerous RBI guidelines, including regular audits, reporting, and adherence to capital adequacy norms.
High Capital Requirement: The initial NOF of ₹10 crore and ongoing capital requirements can be a barrier, particularly for small businesses.
Operational Risks: NBFCs face various operational risks, including credit risk, liquidity risk, and market risk, requiring effective risk management strategies.
Competition: The financial sector is highly competitive, with NBFCs competing against banks, fintech companies, and other financial institutions.
Conclusion: The Importance of Professional Guidance
Registering an NBFC in India offers numerous opportunities but comes with its set of challenges. The process involves strict compliance with regulatory requirements, and missing out on any detail can lead to significant delays or rejection of the application.
Therefore, it is crucial to seek professional guidance to navigate the complex registration process efficiently. With expert assistance, you can ensure that your NBFC is set up correctly and is well-positioned to thrive in India’s dynamic financial landscape.
By understanding the updated eligibility, documentation, and procedural requirements, as well as the benefits and challenges of NBFC registration, you can make informed decisions that align with your business goals. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and prepared will be key to your success in the NBFC sector.
Source Link: https://nbfcadvisory.com/comprehensive-guide-nbfc-registration-india-2024-perspective/
0 notes
Text

LAW FAQs
Is it wise to buy just the license of an existing microfinance bank that is closing down?
Acquiring an existing Microfinance Bank (MFB) license can be a viable strategic move, but it comes with significant risks and considerations.
Indeed, acquiring an existing MFB license can be appealing due to factors like:
Ease of entry into the financial sector.
Bypassing the lengthy registration process for new MFBs is a tempting advantage.
Existing infrastructure and customer base
Acquiring established infrastructure and a ready customer base can save time and resources.
It's essential to act cautiously while carefully considering the significant risks and potential challenges.
Understanding the reasons for closure
Thoroughly investigate why the previous owner is shutting down.
Are there underlying financial or regulatory issues?
Uncovering compliance and regulatory issues
Scrutinize the MFB's history for non-compliance penalties, sanctions, or outstanding obligations to regulatory bodies.
Assessing existing financial liabilities
Identify any debts, unpaid obligations, or potential legal liabilities that could be inherited.
Evaluating operational challenges
Significant compliance and financial liabilities can indicate a poor loan portfolio, lack of quality assets, and even reputational damage within the business community. This can also raise concerns with regulatory authorities responsible for approving the acquisition.
Due diligence
Conduct thorough due diligence to assess the extent of these risks.
In some cases, reviving a struggling MFB might be possible if the underlying problems are not compliance-related.
Negotiate warranties and indemnities from the seller to mitigate potential liabilities.
Seek guidance from regulatory bodies like the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) and compliance professionals before making a decision.
Starting fresh: The safer alternative:
Overall, starting a new MFB is often advisable. This approach allows you to:
Build the bank from the ground up to ensure compliance with all regulations.
Avoid inheriting potential hidden issues that could lead to significant financial and reputational damage.
The CBN's launch of an online portal last September for MFB registration has streamlined the previously manual procedure, and made starting a new MFB even more accessible.
#faq hashtag#law hashtag#mfb hashtag#microfinancebank hashtag#nigerianlaw hashtag#aaLawsng hashtag#avielavenantelawpratice hashtag#entrepreneurs
0 notes
Text
Understanding Non Banking Financial Company in India
What is a Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC)?
An NBFC is a company registered under the Companies Act, 2013, that provides financial services but does not hold a banking license. NBFCs operate in various sectors such as loans, asset financing, insurance, leasing, and investments. They are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) under the RBI Act, 1934, but do not offer core banking services like accepting demand deposits from the public or issuing checks.

Key Differences Between NBFCs and Banks
While both banks and NBFCs provide financial services, there are some key differences:
1. Deposit Acceptance: Unlike banks, NBFCs cannot accept demand deposits.
2. Payment and Settlement System: NBFCs are not part of the payment and settlement system and cannot issue checks.
3. Deposit Insurance: Deposits with NBFCs are not insured by the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC), unlike those with banks.
Despite these differences, NBFCs are pivotal in delivering financial services across various sectors.
Types of NBFCs
NBFCs in India are categorized based on their activities and types of deposits accepted. Here are the main categories:
1. Asset Finance Company (AFC): Engages in financing physical assets like machinery, automobiles, and equipment used in productive sectors.
2. Loan Company: Primarily focuses on providing loans and advances that do not involve asset financing.
3. Investment Company: Engages in acquiring securities, such as shares, stocks, and bonds.
4. Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC): Specializes in funding infrastructure projects and requires a minimum Net Owned Fund (NOF) of Rs. 300 Crore.
5. Microfinance Institution (MFI): Provides microloans to individuals or small businesses, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas, with a focus on income generation.
6. Core Investment Company (CIC): Holds a minimum of 90% of its total assets as investments in group companies, with 60% of its equity investments in these companies.
7. Infrastructure Debt Fund (IDF): Facilitates long-term debt flow into infrastructure projects by raising resources through bonds.
8. NBFC-Factors: Engaged in the business of factoring, which involves the sale of receivables to improve cash flow.
9. Mortgage Guarantee Companies (MGC): Provides mortgage guarantee services with at least 90% of assets in guarantee business.
Visit our website for complete details.
Advantages of NBFCs
NBFCs offer several advantages over traditional banks:
1. Diverse Financial Services: NBFCs can engage in various activities such as loans, leasing, hire-purchase, insurance, and investment management, offering a broad range of financial services.
2. Regulatory Flexibility: Although regulated by the RBI, NBFCs enjoy more flexibility than banks, which allows them to cater to niche markets with innovative financial products.
3. Easier Access to Capital: NBFCs can raise funds through various means, including debentures, bonds, and loans. Some NBFCs are also allowed to accept deposits.
4. Faster Loan Processing: NBFCs often have streamlined loan approval processes, resulting in quicker loan disbursals compared to traditional banks.
Foreign Investment in NBFCs
The Indian government allows 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in NBFCs under the automatic route, provided they engage in certain specified financial activities such as asset management, stock broking, financial consultancy, and venture capital. NBFCs with foreign investment must comply with minimum capitalization norms as defined by RBI guidelines, depending on the level of foreign ownership.
Registration Process for NBFCs in India
To operate legally, an NBFC must undergo a registration process with the Reserve Bank of India. Below is a step-by-step guide:
1. Incorporate the Company: Register your company under the Companies Act, 2013, ensuring that the primary objective is engaging in financial activities.
2. Meet the Net Owned Fund (NOF) Requirement: Ensure that the company has a minimum NOF of Rs. 200 Lakhs, primarily in equity shares.
3. Prepare a Detailed Business Plan: Draft a comprehensive business plan, including financial projections and operational strategies.
4. Apply Online: Submit an online application to the RBI through its official portal along with required documents such as the Certificate of Incorporation and business plan.
5. Submit Hard Copies: Send a signed hard copy of the application and supporting documents to the regional RBI office.
6. Board Resolutions: Pass board resolutions confirming adherence to RBI’s Fair Practices Code and affirming that the company will not engage in restricted activities.
7. Director Credentials: Ensure that at least one-third of the company’s directors have a minimum of 10 years of experience in finance.
8. Comply with RBI Norms: Meet any additional compliance requirements such as CIBIL ratings and FDI norms, if applicable.

Conclusion
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) are integral to the financial system in India, providing essential services that extend beyond the reach of traditional banking institutions. By facilitating access to credit, especially in underserved areas, NBFCs contribute significantly to economic development and financial inclusion. With a thorough understanding of regulatory requirements and a clear registration process, businesses can successfully enter the NBFC sector and thrive in India’s growing financial ecosystem.
#Non Banking Financial Company Registration#Non Banking Financial Company In India#Non Banking Financial Company#NBFC Registration
0 notes
Text
Navigating Micro Finance Company Registration: A Step-by-Step Guide
Micro Finance Company Registration: A Comprehensive Guide
In recent years, microfinance has emerged as a vital tool in promoting financial inclusion and supporting economic development, particularly in underserved areas. For those looking to start a microfinance company, understanding the registration process is crucial. This article provides a detailed overview of the steps and requirements involved in Micro Finance Company Registration.
What is a Microfinance Company?
A microfinance company provides financial services to individuals or small businesses that do not have access to traditional banking services. These services often include microloans, savings accounts, and insurance. Microfinance institutions (MFIs) aim to support economic development by providing financial resources to those who need them most, often in developing regions.
Key Benefits of Starting a Microfinance Company
Promotes Financial Inclusion: Provides access to financial services for underserved communities.
Supports Economic Development: Helps small businesses and entrepreneurs grow.
Social Impact: Improves the standard of living for low-income individuals.
Registration Process for a Microfinance Company
1. Understand Regulatory Requirements
Before starting the registration process, familiarise yourself with the regulatory requirements in your country. In India, for instance, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulates microfinance institutions. Ensure you understand the legal framework, including any specific regulations and compliance requirements.
2. Choose the Type of Microfinance Institution
There are several types of microfinance institutions, including:
Microfinance Banks: These are banks that provide microfinance services. They require a banking license from the central bank.
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs): These institutions can also offer microfinance services. They are regulated by the RBI in India.
Cooperative Societies: These are member-owned institutions that provide financial services to their members.
3. Prepare the Required Documents
The registration process typically involves submitting various documents, including:
Business Plan: A detailed plan outlining your business model, target market, and financial projections.
Proof of Identity: Identification documents of the promoters and key management personnel.
Proof of Address: Provide evidence of the address of the company's registered office.
Financial Statements: Bank statements, financial projections, and funding sources.
Incorporation Documents: Company’s Memorandum of Association (MoA) and Articles of Association (AoA) for incorporation as a company.
4. Incorporate Your Company
You need to incorporate your company as per the legal requirements. In India, this involves:
Registering the Company: File for company registration with the Registrar of Companies (RoC).
Obtaining a Director Identification Number (DIN): For the directors of the company.
Acquiring a Certificate of Incorporation: This certifies that your company is legally registered.
5. Apply for a License
For a microfinance company, you need to apply for a license from the relevant regulatory authority. In India, this would be the RBI or the respective state regulatory body, depending on the type of microfinance institution.
Submit Application: Fill out and submit the application form as per the guidelines provided by the regulatory authority.
Undergo Inspection: The regulatory body may inspect your premises and operations.
Receive License: Once approved, you will receive a license to operate as a microfinance institution.
6. Compliance and Reporting
After obtaining the license, ensure you comply with all regulatory requirements. This includes:
Regular Reporting: Submit periodic reports to the regulatory authority.
Adhering to Guidelines: Follow all operational and financial guidelines set by the regulatory body.
Maintaining Records: Keep accurate and up-to-date records of all transactions and operations.
Conclusion
Starting a microfinance company registration involves navigating a complex regulatory environment and meeting specific requirements. By understanding the registration process and complying with all legal obligations, you can establish a successful microfinance institution that contributes to economic development and financial inclusion.
0 notes
Text
What is the process of Section 8 microfinance company registration?
The process of Section 8 microfinance company registration:-
Step 1: Obtain the Digital Signature Certificate (DSC).
To start a corporation, you must apply for the digital signature certificates of the proposed firm's directors. Section 8 corporations file all of their documentation online, and e-forms must be digitally signed. As a result, the designated directors must receive their DSCs from certification agencies.
Step 2: Apply for Name Approval.
The following step is to apply for name approval. The name must indicate that it is a Section 8 company. The company's industrial activity code and object clause must be defined when applying for its name.
Step 3: Submit the SPICe Form (INC-32).
After the name has been approved, the SPICe+ form must be filled out with registration information for the company. It is a simpler proforma for incorporating a business electronically. The details of the form are as follows.
Details of the company
Details of members and subscribers
Application for the Director Identification Number (DIN)
Application for PAN and TAN, including declarations by directors and subscribers.
Declaration and certification by professional
Step 4: File the MoA and AoA under "Finance" Objective
SPICe e-MoA and e-AoA are the related forms that must be completed when applying for company registration.
SPICe e-MoA and e-AoA are the related forms that must be completed when applying for company registration.
The company must draft the MoA and AoA and submit them along with the required documentation.
The Memorandum of Agreement is the foundation upon which the company is founded. It defines the company's constitution, powers, and objectives.
The AoA outlines all of the rules and regulations that govern the company's management.
Step 5: Issue of Incorporation Certificate
Following approval of the paperwork by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, the competent department will issue the PAN, TAN, and Certificate of Incorporation.
0 notes
Text
Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to NBFC Registration and Services in India
In the dynamic landscape of Indian finance, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) play a pivotal role in extending credit, mobilizing savings, and contributing significantly to the financial sector's growth. However, stepping into the realm of NBFCs requires meticulous planning, adherence to regulatory frameworks, and a deep understanding of the market. Whether you're exploring NBFC registration, navigating services, or considering a virtual CFO for your NBFC in India, this guide aims to shed light on these crucial aspects.
Understanding NBFC Registration:
Setting foot into the world of NBFCs necessitates navigating through regulatory requirements and obtaining the requisite approvals. In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) serves as the principal regulatory authority governing NBFCs. The process of NBFC registration involves meticulous scrutiny, compliance, and adherence to regulatory norms prescribed by the RBI.
To kickstart the NBFC registration process, aspiring entrepreneurs need to fulfill certain eligibility criteria, including minimum net owned funds, requisite management experience, and a clean track record. Once the eligibility criteria are met, the application process entails thorough documentation, including a detailed business plan, financial projections, and compliance with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) norms.
Navigating through the intricate maze of NBFC registration demands patience, diligence, and expert guidance to ensure seamless compliance with regulatory mandates.
Exploring NBFC Services in India:
With the regulatory framework in place, NBFCs in India offer a diverse array of services catering to the financial needs of various sectors. From offering loans and advances to facilitating wealth management solutions, NBFCs play a pivotal role in driving financial inclusion and fostering economic growth.
Key services offered by NBFCs in India include:
Retail and Corporate Lending: NBFCs extend credit facilities to both retail and corporate clients, catering to diverse financing needs such as housing loans, vehicle loans, and working capital finance.
Investment Advisory Services: NBFCs provide investment advisory services, guiding clients through investment decisions, portfolio management, and wealth creation strategies.
Asset Management: NBFCs manage investment portfolios, mutual funds, and other financial assets, optimizing returns and mitigating risks for investors.
Microfinance: NBFCs play a pivotal role in microfinance, extending credit facilities to underserved segments of the population, thereby fostering financial inclusion and empowerment.
Leveraging Virtual CFO Services for NBFCs:
In the rapidly evolving landscape of finance, the role of a Chief Financial Officer (CFO) holds paramount importance in driving strategic decision-making, ensuring financial stability, and fostering growth. However, for emerging NBFCs, appointing a full-time CFO might entail substantial costs and resource commitments.
Enter the concept of Virtual CFOs – experienced financial professionals offering strategic guidance, financial management, and compliance expertise on a part-time or project basis. For NBFCs in India, leveraging virtual CFO services presents a viable solution to navigate through financial complexities, streamline operations, and enhance profitability.
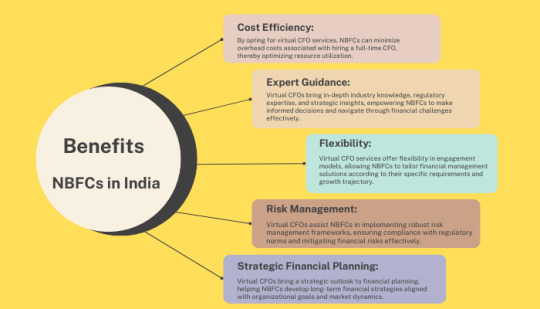
Virtual CFOs for NBFCs offer a plethora of benefits, including:
Cost Efficiency: By opting for virtual CFO services for NBFCs can minimize overhead costs associated with hiring a full-time CFO, thereby optimizing resource utilization.
Expert Guidance: Virtual CFOs bring in-depth industry knowledge, regulatory expertise, and strategic insights, empowering NBFCs to make informed decisions and navigate through financial challenges effectively.
Flexibility: Virtual CFO services offer flexibility in engagement models, allowing NBFCs to tailor financial management solutions according to their specific requirements and growth trajectory.
Risk Management: Virtual CFOs assist NBFCs in implementing robust risk management frameworks, ensuring compliance with regulatory norms and mitigating financial risks effectively.
Conclusion:
In the dynamic landscape of Indian finance, NBFCs serve as catalysts for driving economic growth, fostering financial inclusion, and empowering individuals and businesses. However, venturing into the realm of NBFCs demands meticulous planning, adherence to regulatory frameworks, and leveraging expertise to navigate through financial complexities.
From NBFC registration to exploring diverse services and leveraging virtual CFO solutions, aspiring entrepreneurs and existing players in the NBFC sector need to tread cautiously, armed with knowledge, expertise, and a strategic vision. By embracing innovation, fostering transparency, and adhering to best practices, NBFCs can chart a course towards sustainable growth and contribute significantly to India's burgeoning financial ecosystem.
0 notes
Text
Streamlining Business Operations: A Guide to Various Registrations in Delhi
Welcome to the Company Today blog, your go-to resource for navigating the intricate world of registrations in Delhi. Whether you're a budding entrepreneur, a socially conscious individual looking to establish an NGO, or someone passionate about microfinance, we've got you covered. In this post, we'll delve into the essentials of company, NGO, and microfinance registrations in Delhi, along with insights into business registration.
Company Registration in Delhi:
Starting a business in Delhi? Ensure a solid foundation by understanding the nuances of company registration. At Company Today, we simplify the process, guiding you through the necessary steps to establish and operate your business seamlessly.
Key Points:
Importance of company registration
Step-by-step guide for company registration in Delhi
Compliance and documentation requirements
NGO Registration in Delhi:
For those with a philanthropic spirit, establishing an NGO can be a fulfilling venture. Our blog provides valuable insights into the legalities and procedures involved in NGO registration in Delhi.
Key Points:
Purpose and benefits of NGO registration
Documentation checklist for NGO registration
Compliance with regulatory authorities
Microfinance Registration in Delhi:
Microfinance institutions play a crucial role in empowering communities. Learn about the process of microfinance registration in Delhi and how your efforts can make a meaningful impact on the lives of individuals and small businesses.
Key Points:
Overview of microfinance and its significance
Step-by-step guide to microfinance registration
Regulatory compliance for microfinance institutions
Business Registration in Delhi:
Whether you're a sole proprietor or part of a partnership, understanding the intricacies of business registration is essential. Our blog sheds light on the nuances of registering your business in Delhi.
Key Points:
Types of business structures in Delhi
Registration process for different business entities
Compliance and ongoing requirements for businesses
Conclusion:
Navigating the registration landscape in Delhi doesn't have to be overwhelming. At Company Today, we strive to empower individuals and businesses by providing comprehensive information on company, NGO, microfinance, and business registrations. Stay tuned for more insights and guidance to help you embark on a successful journey.
For personalized assistance and expert advice, contact Company Today, your trusted partner in regulatory compliance and business success.
0 notes
Text
Demystifying NBFC Registration in India
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) have become pivotal players in India's financial sector. They offer a wide range of financial services, catering to the diverse needs of individuals and businesses. Whether you're planning to establish your NBFC or simply seeking to understand the registration process, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the intricacies of NBFC registration in India.
Understanding NBFCs: A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a financial institution that operates without a traditional banking license. Instead, NBFCs provide various financial services, including loans, credit facilities, investment products, and more. They play a vital role in enhancing financial inclusion across the country.
Types of NBFCs: India recognizes several types of NBFCs, each specializing in specific financial services. Some common categories of NBFCs include:
Asset Finance Company (AFC)
Investment Company (IC)
Loan Company (LC)
Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC)
Microfinance Institution (MFI)
Non-Deposit Taking NBFC (ND-NBFC)
Deposit Taking NBFC (D-NBFC)
NBFC Registration Process (In-Depth):
Incorporate Your Company : The journey begins by incorporating a company under the Companies Act, 2013. It's essential to meet the minimum paid-up capital requirement, which varies depending on the type of NBFC you intend to establish.
Minimum Net Owned Fund (NOF) : Ensure that your company fulfills the minimum Net Owned Fund (NOF) requirement as mandated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). This requirement differs for various types of NBFCs.
Prepare the RBI Application : Create a comprehensive application for NBFC registration. This document should provide detailed information about your company's management, business plan, financial projections, and how it complies with RBI regulations.
Assess "Fit and Proper" Criteria : RBI assesses the "fit and proper" status of your company's directors and management to ensure their competence and integrity.
Undergo Due Diligence : RBI conducts thorough background checks on the promoters and directors. They scrutinize financial histories and credibility.
Comply with Prudential Norms : Adhere to prudential norms set by RBI. These norms cover various aspects such as capital adequacy, income recognition, asset classification, and provisioning.
Obtain CIBIL Clearance : Secure a Credit Information Bureau of India Limited (CIBIL) clearance for your company to demonstrate its financial reliability.
Submit Documents to RBI : Submit the application along with all required documents to the Regional Office of the RBI.
On-Site Inspection : RBI may conduct an on-site inspection to verify compliance with regulations and assess your company's operations.
Certificate of Registration : Upon successful evaluation and approval, RBI issues the Certificate of Registration, granting permission to commence NBFC operations.
Conclusion : Starting an NBFC in India is a promising endeavor that demands meticulous planning, unwavering adherence to regulatory norms, and financial stability. The opportunity to provide essential financial services to a diverse customer base makes it a rewarding venture. Seek professional guidance and legal expertise to navigate the complexities of NBFC registration successfully, contributing to the growth and vibrancy of India's financial sector.
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Benefits of Microfinance Companies
Get Know about benefit of Microfinance Companies through this video. get the detail of Microfinance Company Registration Process in simple word with Legal Dev. Learn more about Microfinance Companies by visiting our YouTube Channel.
0 notes
Text
A One-Stop Solution for Microfinance, Money Changer, and Money Transfer Service Registration
Introduction: In today's rapidly evolving financial landscape, it is crucial for businesses to stay ahead of the game by ensuring their compliance with regulatory requirements. If you are looking to establish a microfinance company, become a full-fledged money changer, or offer money transfer services, Estabizz is here to help. With our comprehensive registration services, we make the process seamless, enabling you to focus on what matters most: growing your business. In this article, we will explore how Estabizz can assist you in achieving your goals by obtaining the necessary licenses and registrations for your financial ventures.
Microfinance Company Registration: Microfinance institutions play a vital role in providing financial services to low-income individuals and small businesses. At Estabizz, we understand the complexities of microfinance company registration and provide expert guidance throughout the process. Our team of experienced professionals will assist you in navigating the legal requirements, ensuring that you meet all necessary criteria for registration. With Estabizz by your side, you can confidently launch your microfinance company and make a positive impact in your community.
Full-Fledged Money Changer Registration: Becoming a full-fledged money changer allows you to offer currency exchange services to individuals and businesses. However, obtaining the required registration can be a daunting task. Estabizz offers comprehensive support in the money changer registration process, guiding you through the intricacies and simplifying the procedures. Our experts will help you fulfill the regulatory requirements, including documentation, compliance, and licensing, ensuring that you can operate your money changer business smoothly and securely.
Money Transfer Service Registration: Money transfer services have gained tremendous popularity due to their convenience and efficiency. Whether you are establishing a remittance business or planning to incorporate money transfer services into your existing operations, Estabizz can assist you every step of the way. Our dedicated team will help you navigate the complex landscape of money transfer service registration, ensuring compliance with local regulations. With Estabizz, you can establish a trusted and reliable money transfer service, providing seamless financial solutions to your customers.
Why Choose Estabizz? Estabizz stands out as a trusted partner in the registration process for microfinance companies, full-fledged money changers, and money transfer services. Here are some key reasons to choose Estabizz:
Expertise: Our team comprises experienced professionals with in-depth knowledge of the financial industry and regulatory frameworks.
Tailored Solutions: We understand that every business is unique, and we provide customized solutions to meet your specific requirements.
Streamlined Process: Estabizz simplifies the registration process, saving you time and effort by handling the paperwork and legal formalities on your behalf.
Compliance Assurance: We ensure that your business adheres to all necessary regulations and compliance standards, giving you peace of mind.
Conclusion: Embarking on your journey as a microfinance company, full-fledged money changer, or money transfer service provider requires careful planning and compliance with legal requirements. Estabizz offers comprehensive registration services for these financial ventures, simplifying the process and allowing you to focus on your core business activities. Trust Estabizz to provide expert guidance, ensuring that you fulfill all necessary criteria and launch your financial services with confidence. Start your registration process with Estabizz today and unlock the doors to success in the dynamic financial industry.
0 notes
Text
Complete Guide to Setting Up an NBFC in India
The Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) sector is a critical component of India's financial ecosystem, providing credit and other financial services where traditional banks may not operate. For anyone looking to enter this industry, setting up an NBFC involves understanding various regulatory norms, compliance requirements, and the necessary documentation. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential steps, highlighting the latest updates from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Types of NBFCs in India
Based on Type of Liabilities
Deposit-Accepting NBFCs: These NBFCs accept deposits from the public, similar to banks. However, they are not allowed to issue bank notes or provide checking account facilities.
Non-Deposit-Accepting NBFCs: These NBFCs do not accept deposits from the public but raise funds through other means, such as issuing bonds or debentures.
Based on Size
Systemically Important Non-Deposit Holding Companies (NBFC-NDSI): These are large NBFCs that can pose a significant risk to the financial stability of the system.
Other Non-Deposit Holding Companies (NBFC-ND): These are smaller NBFCs that do not pose a systemic risk.
Based on Activities
Asset Finance Companies (AFCs): These NBFCs primarily engage in financing assets like machinery, vehicles, and equipment.
Loan Companies: These NBFCs offer various types of loans, including personal loans, home loans, education loans, and more.
Investment Companies: These NBFCs invest in securities, such as shares and bonds.
Infrastructure Finance Companies (IFCs): These NBFCs specialize in financing infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and power plants.
Microfinance Institutions (MFIs): These NBFCs provide small loans to low-income individuals and groups, often in rural areas.
Housing Finance Companies (HFCs): These NBFCs primarily focus on providing home loans.
Merchant Banking Companies: These NBFCs offer various financial services, including underwriting, mergers, and acquisitions.
Core Investment Companies (CICs): These NBFCs primarily invest in other companies.
Each type of NBFC is regulated differently based on its risk profile, asset size, and specific focus areas
Regulatory Requirements for NBFC Registration
The RBI has established a robust regulatory framework to ensure the stability and integrity of the NBFC sector. The key requirements for registering an NBFC in India include:
Minimum Net Owned Fund (NOF): The latest RBI guidelines have increased the NOF requirements in a phased manner:
NBFC-ICC, NBFC-MFI, and NBFC-Factors: NOF requirements will increase to ₹10 crore by March 31, 2027. Currently, these companies need to have ₹5 crore (₹2 crore for the North-Eastern region) by 2025.
NBFC-P2P, NBFC-AA, and NBFCs without public funds or customer interfaces continue with an NOF requirement of ₹2 crore
Company Incorporation: The entity must be registered as a Private Limited or Public Limited company under the Companies Act, 2013.
Directors' Experience: At least one director must have relevant experience in the banking or NBFC sector, emphasizing the need for professional expertise in managing NBFC operations
NPA Classification: The RBI has introduced stricter norms for classifying Non-Performing Assets (NPAs). NBFCs must adhere to a 90-day NPA classification norm by March 31, 2026. The phased approach aims to enhance risk management across all NBFC categories
Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process (ICAAP): NBFCs must conduct an internal assessment of their capital needs based on their business risks, aligning with the guidelines set for commercial banks. This requirement encourages better internal risk management techniques for NBFCs
RBI Approval: A detailed application, including the company’s business plan, audited financial statements, and other relevant documents, must be submitted to the RBI for approval.
Key Documents Required for NBFC Setup
Setting up an NBFC involves preparing and submitting a series of essential documents to ensure compliance with regulatory standards. The key documents include:
Incorporation Certificate: Proof that the business is registered as a Private Limited or Public Limited company.
Memorandum of Association (MOA) and Articles of Association (AOA): These outline the company’s objectives and operational guidelines.
Detailed Business Plan: The business plan should include an overview of the NBFC’s strategy, market analysis, and financial projections.
KYC Documents of Directors and Shareholders: Identity and address proofs such as PAN, Aadhaar, and passport copies.
Audited Financial Statements: Financial statements for the past three years, validated by a certified Chartered Accountant.
Net Worth Certificate: A certificate from a CA confirming compliance with NOF requirements.
Bankers’ Report: A report from your banker detailing the company’s account status, creditworthiness, and available funds.
Conclusion
Establishing an NBFC in India is a promising venture that comes with regulatory complexities. The recent updates from the RBI, such as the increased NOF requirements and stricter NPA classifications, reflect the evolving landscape of the financial sector. By understanding the types of NBFCs, meeting the latest regulatory requirements, and preparing the necessary documents, aspiring entrepreneurs can navigate the registration process with confidence.
Consulting with financial experts or regulatory advisors can further streamline the setup process and ensure full compliance, positioning your NBFC for success in India’s dynamic financial market.
Source: https://nbfcadvisory.com/complete-guide-to-setting-up-an-nbfc-in-india/
1 note
·
View note
Text
youtube
Microfinance Company Registration Process
Section 8 Microfinance Company। Microfinance Company Kaise khole। Microfinance Company Registration Process Finance company Kaise banaye।
Contact us- 9828123489- by Vakilkaro For Micro Finance Company Registration: https://vakilkaro.com/microfinance-co...
For Nidhi Company Registration: https://vakilkaro.com/nidhi-company-r...
Today in this video I am explaining the whole process of microfinance section 8 company registration so that people can get knowledge of the topic
Microfinance company registration rules, process, documents, and profit by Adv Satender Saini
Microfinance company registered under section 8 is little restricted by the department however there are some old microfinance companies on sale that can be purchased. In some cases, we also create new microfinance companies, this video contents
0 notes
Photo

MicroFinance Company Registration Process via help of Swarit Advisors
A microfinance company, also known as micro credit, is one of the major types of Non-Banking Finance Companies (NBFCs). It is defined as a company that provides banking services to individuals who are unemployed or individuals who are surviving on low- income. A company must acquire a license to operate as a microfinance company in India.
Visit our Website: MicroFinance Company Registration
#MicroFinance Company Registration#MicroFinance Company Registration in India#MicroFinance Company Registration Process#Online MicroFinance Company Registration#Procedure for MicroFinance Company Registration
0 notes
Text
Section 8 Microfinance Company Registration - Fees, Process, Documents
Section 8 Microfinance Company or Micro-finance Institution (MFI) is a financial organisation that provides credit to people and organisations who are denied access to traditional financial institutions due to poverty, occupation, ethnicity, religion, or nationality.
A Microfinance Company is registered with the Registrar of Companies as per Section 8 of the Indian Companies Act, 2013. Thus, it comes under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
Microfinance companies are the most convenient business to register that can provide unsecured loans without RBI approval at rates upto 26% p.a.
Benefits of Section 8 Microfinance Company:
No RBI Approval required
Can lend Unsecured loan
No Demographic Barrier
Best Rate of Interest
Minimum capital not required
Defaulters can be sued for non-payment
Limited Compliances
Documents required for Section 8 Microfinance Company:
PAN & Aadhar Card of both the directors
Bank Statement with the address of both the directors (not older than 2 months)
Passport Size Photo
Email address & Phone number
Utility Bill of the premises
To know more (click here)

#business#startup#india#business growth#manage business#partnership firm registration#nidhi company registration#private limited company registration in bangalore#private limited company registration in chennai#private limited company registration online#section 8 microfinance company registratioin#microfinance#section 8 registration
0 notes