#run a mysql query
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
In our search for vendors that actually run the authorization systems, we found a site called FlyCASS which pitches small airlines a web-based interface to CASS. Intrigued, we noticed every airline had its own login page, such as Air Transport International (8C) being available at /ati. With only a login page exposed, we thought we had hit a dead end. Just to be sure though, we tried a single quote in the username as a SQL injection test, and immediately received a MySQL error: This was a very bad sign, as it seemed the username was directly interpolated into the login SQL query. Sure enough, we had discovered SQL injection and were able to use sqlmap to confirm the issue. Using the username of ' or '1'='1 and password of ') OR MD5('1')=MD5('1, we were able to login to FlyCASS as an administrator of Air Transport International!
Csak hát beszart rovat
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Tableau is Essential in Data Science: Transforming Raw Data into Insights

Data science is all about turning raw data into valuable insights. But numbers and statistics alone don’t tell the full story—they need to be visualized to make sense. That’s where Tableau comes in.
Tableau is a powerful tool that helps data scientists, analysts, and businesses see and understand data better. It simplifies complex datasets, making them interactive and easy to interpret. But with so many tools available, why is Tableau a must-have for data science? Let’s explore.
1. The Importance of Data Visualization in Data Science
Imagine you’re working with millions of data points from customer purchases, social media interactions, or financial transactions. Analyzing raw numbers manually would be overwhelming.
That’s why visualization is crucial in data science:
Identifies trends and patterns – Instead of sifting through spreadsheets, you can quickly spot trends in a visual format.
Makes complex data understandable – Graphs, heatmaps, and dashboards simplify the interpretation of large datasets.
Enhances decision-making – Stakeholders can easily grasp insights and make data-driven decisions faster.
Saves time and effort – Instead of writing lengthy reports, an interactive dashboard tells the story in seconds.
Without tools like Tableau, data science would be limited to experts who can code and run statistical models. With Tableau, insights become accessible to everyone—from data scientists to business executives.
2. Why Tableau Stands Out in Data Science
A. User-Friendly and Requires No Coding
One of the biggest advantages of Tableau is its drag-and-drop interface. Unlike Python or R, which require programming skills, Tableau allows users to create visualizations without writing a single line of code.
Even if you’re a beginner, you can:
✅ Upload data from multiple sources
✅ Create interactive dashboards in minutes
✅ Share insights with teams easily
This no-code approach makes Tableau ideal for both technical and non-technical professionals in data science.
B. Handles Large Datasets Efficiently
Data scientists often work with massive datasets—whether it’s financial transactions, customer behavior, or healthcare records. Traditional tools like Excel struggle with large volumes of data.
Tableau, on the other hand:
Can process millions of rows without slowing down
Optimizes performance using advanced data engine technology
Supports real-time data streaming for up-to-date analysis
This makes it a go-to tool for businesses that need fast, data-driven insights.
C. Connects with Multiple Data Sources
A major challenge in data science is bringing together data from different platforms. Tableau seamlessly integrates with a variety of sources, including:
Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server
Cloud platforms: AWS, Google BigQuery, Snowflake
Spreadsheets and APIs: Excel, Google Sheets, web-based data sources
This flexibility allows data scientists to combine datasets from multiple sources without needing complex SQL queries or scripts.
D. Real-Time Data Analysis
Industries like finance, healthcare, and e-commerce rely on real-time data to make quick decisions. Tableau’s live data connection allows users to:
Track stock market trends as they happen
Monitor website traffic and customer interactions in real time
Detect fraudulent transactions instantly
Instead of waiting for reports to be generated manually, Tableau delivers insights as events unfold.
E. Advanced Analytics Without Complexity
While Tableau is known for its visualizations, it also supports advanced analytics. You can:
Forecast trends based on historical data
Perform clustering and segmentation to identify patterns
Integrate with Python and R for machine learning and predictive modeling
This means data scientists can combine deep analytics with intuitive visualization, making Tableau a versatile tool.
3. How Tableau Helps Data Scientists in Real Life
Tableau has been adopted by the majority of industries to make data science more impactful and accessible. This is applied in the following real-life scenarios:
A. Analytics for Health Care
Tableau is deployed by hospitals and research institutions for the following purposes:
Monitor patient recovery rates and predict outbreaks of diseases
Analyze hospital occupancy and resource allocation
Identify trends in patient demographics and treatment results
B. Finance and Banking
Banks and investment firms rely on Tableau for the following purposes:
✅ Detect fraud by analyzing transaction patterns
✅ Track stock market fluctuations and make informed investment decisions
✅ Assess credit risk and loan performance
C. Marketing and Customer Insights
Companies use Tableau to:
✅ Track customer buying behavior and personalize recommendations
✅ Analyze social media engagement and campaign effectiveness
✅ Optimize ad spend by identifying high-performing channels
D. Retail and Supply Chain Management
Retailers leverage Tableau to:
✅ Forecast product demand and adjust inventory levels
✅ Identify regional sales trends and adjust marketing strategies
✅ Optimize supply chain logistics and reduce delivery delays
These applications show why Tableau is a must-have for data-driven decision-making.
4. Tableau vs. Other Data Visualization Tools
There are many visualization tools available, but Tableau consistently ranks as one of the best. Here’s why:
Tableau vs. Excel – Excel struggles with big data and lacks interactivity; Tableau handles large datasets effortlessly.
Tableau vs. Power BI – Power BI is great for Microsoft users, but Tableau offers more flexibility across different data sources.
Tableau vs. Python (Matplotlib, Seaborn) – Python libraries require coding skills, while Tableau simplifies visualization for all users.
This makes Tableau the go-to tool for both beginners and experienced professionals in data science.
5. Conclusion
Tableau has become an essential tool in data science because it simplifies data visualization, handles large datasets, and integrates seamlessly with various data sources. It enables professionals to analyze, interpret, and present data interactively, making insights accessible to everyone—from data scientists to business leaders.
If you’re looking to build a strong foundation in data science, learning Tableau is a smart career move. Many data science courses now include Tableau as a key skill, as companies increasingly demand professionals who can transform raw data into meaningful insights.
In a world where data is the driving force behind decision-making, Tableau ensures that the insights you uncover are not just accurate—but also clear, impactful, and easy to act upon.
#data science course#top data science course online#top data science institute online#artificial intelligence course#deepseek#tableau
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Taxonomy of Chatbot AI Users
The CEO: doesn't understand how any of this works, but he does understand that it means potential cost-cuts for basic Admin tasks or Customer Service interactions. Typically assumes that we're at the level where C3PO's sapience is achievable, is disproportionately pissed when their LLM of choice shits the bed and tells a customer to [insert a random mySQL function call from an entirely different website here].
The Rubbernecker: asks us if our chatbot service runs offline and we can issue them a demo, is usually under the impression that all chatbots are ChatGPT 4 and that you can ask any model whatsoever to shit out a decent apple crumble recipe. Is amusingly disappointed when the Customer Service bot for a string of dealerships can't return queries concerning recent developments in American politics or booking rates for the Carribbean. Like the CEO, ultimately thinks that computers are now bulky Disney-esque Fairy Godmothers that will one day Solve Everything.
The Griever: probably saw the Black Mirror episode where Imogen Poots clones Domhnal Gleeson, realizes her digital clone of her dead lover is far too perfect, and eventually consigns it to the attic of her picturesque Scottish cottage. Mostly sticks to Character.ai and to self-made clones of lost pets or relatives and is entirely aware that the exercise turns morbid once the bots wander off-of-alignment and invent or hallucinate details that aren't related to the personas being spoofed. Still hasn't stopped, as the 'bots are now digital worry stones ready and waiting to be summoned at the first sign of anxiety.
The Horndog: typically lurks around CrushOn, Dopple or any other variant on would-be "unlocked" LLM services. Never creates a chatbot on their own, but instead ferrets out kink scenarios that fit their exacting needs. All you need is a few saved convos to figure out you're looking at someone who's barely eighteen, lonely, desperately hormonal and clinging onto childlike expectations regarding relationships or sexuality. Insecurities practically seep through the setups that are initiated, and most instances end with you thinking that Goddamn, some of you probably need therapy.
The Fic Writer: has no set platform and oftentimes splits a wider persona across various different services. They're accomplished writers in their own right, and chatbot services tend to come across as more freeform testing grounds for their OCs. If a character is named Kyle, then Kyle exists on Character.ai for all narrative segments, Dopple for all steamy scenes and Tavern AI for anything more casual. The Fic Writer is mostly only curious and has no real need or want to fully subordinate to an AI-powered variant on their own character. Definition material is impeccably-written, the tone is consistent - you can tell this was a crafted experience, and not a spur-of-the-moment thing.
The one problem is that the definition's last update dates back to six months ago. You're witnessing what's left after a curious writer digs deep into a new medium, realizes it isn't the best fit imaginable and then discards it.
The Weeaboo: like the Fic Writer, the Weeaboo spends a lot of time on his definitions. Unlike the Fic Writer, however, the Weeaboo is active. Weeaboo accounts routinely have several hundred chatbots on offer and are the primary purveyors of material for Horndog users. The one hitch in the works is that every single bot that's on offer is a variation on "What if Blorbo from my shows, but [variable]?"
On the one hand, that allows Weeaboos to maximize their content delivery. On the other, it results in chatbot sites routinely being crushed under the weight of Genshin Impact stans all suddenly needing a whole new bot for their tiny, granular adjustment to Gamer Boyfriend Scaramouche's persona.
You're kind of left thinking that in most cases, the characters they fixate on aren't that well-written by the canon developers anyway, and that most of what's on offer is a mass of projections and extrapolations. At this point, why even bother? Just make an OC, man - free your mind! You're tethered to a bottom-of-a-napkin character concept put together by a South-Korean sweatshop team and a good two-thirds of your interest is highly dependent on the Graphics team's effort to flesh out the character's visual identity!
The Literal Kid: you're left scratching your head. They have a single bot on offer, it has no example coversation and the greeting isn't much more than "Hi, I'm [character] from [Anime or Manga Here]!"
The real kicker? This blank-faced nothing-burger is in the Trending lists and has one point two million recorded messages, while literal works of art languish in the lower hundreds of Public posts.
The Stan: this is someone whose only desire, in relation to this tech, is to simulate the act of developing a close friendship or a romantic attachment with real-life people. Most services block and ban posters of IRL bots, but the service isn't entirely automated. Tne end result is that with some timing, you can spot the work of the occasional rare male Swiftie, along with various fans from various Pop Culture music currents. Fake K-Pop Lead Who's Now Your Boyfriend might exist on your portal of choice for all of a day or two at the most, but the use stats for bots of this type tend to balloon insanely quickly.
The Edgelord: they think they're funny for generating a Hitler chatbot on an NSFW portal. Before the banhammer falls, savvier users proceed to abuse and exploit these bots in all the ways possible. Naturally, if someone creates an expy for the poster-child for man's hubris and expects most users to treat them like the person they're based off of, the userbase will relentlessly bowlderize it and post pics on Reddit.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the Cloud Landscape: Unleashing Amazon Web Services (AWS) Potential
In the ever-evolving tech landscape, businesses are in a constant quest for innovation, scalability, and operational optimization. Enter Amazon Web Services (AWS), a robust cloud computing juggernaut offering a versatile suite of services tailored to diverse business requirements. This blog explores the myriad applications of AWS across various sectors, providing a transformative journey through the cloud.

Harnessing Computational Agility with Amazon EC2
Central to the AWS ecosystem is Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), a pivotal player reshaping the cloud computing paradigm. Offering scalable virtual servers, EC2 empowers users to seamlessly run applications and manage computing resources. This adaptability enables businesses to dynamically adjust computational capacity, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Redefining Storage Solutions
AWS addresses the critical need for scalable and secure storage through services such as Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) and Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store). S3 acts as a dependable object storage solution for data backup, archiving, and content distribution. Meanwhile, EBS provides persistent block-level storage designed for EC2 instances, guaranteeing data integrity and accessibility.
Streamlined Database Management: Amazon RDS and DynamoDB
Database management undergoes a transformation with Amazon RDS, simplifying the setup, operation, and scaling of relational databases. Be it MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQL Server, RDS provides a frictionless environment for managing diverse database workloads. For enthusiasts of NoSQL, Amazon DynamoDB steps in as a swift and flexible solution for document and key-value data storage.
Networking Mastery: Amazon VPC and Route 53
AWS empowers users to construct a virtual sanctuary for their resources through Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud). This virtual network facilitates the launch of AWS resources within a user-defined space, enhancing security and control. Simultaneously, Amazon Route 53, a scalable DNS web service, ensures seamless routing of end-user requests to globally distributed endpoints.
Global Content Delivery Excellence with Amazon CloudFront
Amazon CloudFront emerges as a dynamic content delivery network (CDN) service, securely delivering data, videos, applications, and APIs on a global scale. This ensures low latency and high transfer speeds, elevating user experiences across diverse geographical locations.
AI and ML Prowess Unleashed
AWS propels businesses into the future with advanced machine learning and artificial intelligence services. Amazon SageMaker, a fully managed service, enables developers to rapidly build, train, and deploy machine learning models. Additionally, Amazon Rekognition provides sophisticated image and video analysis, supporting applications in facial recognition, object detection, and content moderation.
Big Data Mastery: Amazon Redshift and Athena
For organizations grappling with massive datasets, AWS offers Amazon Redshift, a fully managed data warehouse service. It facilitates the execution of complex queries on large datasets, empowering informed decision-making. Simultaneously, Amazon Athena allows users to analyze data in Amazon S3 using standard SQL queries, unlocking invaluable insights.
In conclusion, Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands as an all-encompassing cloud computing platform, empowering businesses to innovate, scale, and optimize operations. From adaptable compute power and secure storage solutions to cutting-edge AI and ML capabilities, AWS serves as a robust foundation for organizations navigating the digital frontier. Embrace the limitless potential of cloud computing with AWS – where innovation knows no bounds.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Data Engineering Concepts, Tools, and Projects
All the associations in the world have large amounts of data. If not worked upon and anatomized, this data does not amount to anything. Data masterminds are the ones. who make this data pure for consideration. Data Engineering can nominate the process of developing, operating, and maintaining software systems that collect, dissect, and store the association’s data. In modern data analytics, data masterminds produce data channels, which are the structure armature.
How to become a data engineer:
While there is no specific degree requirement for data engineering, a bachelor's or master's degree in computer science, software engineering, information systems, or a related field can provide a solid foundation. Courses in databases, programming, data structures, algorithms, and statistics are particularly beneficial. Data engineers should have strong programming skills. Focus on languages commonly used in data engineering, such as Python, SQL, and Scala. Learn the basics of data manipulation, scripting, and querying databases.
Familiarize yourself with various database systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and NoSQL databases such as MongoDB or Apache Cassandra.Knowledge of data warehousing concepts, including schema design, indexing, and optimization techniques.
Data engineering tools recommendations:
Data Engineering makes sure to use a variety of languages and tools to negotiate its objects. These tools allow data masterminds to apply tasks like creating channels and algorithms in a much easier as well as effective manner.
1. Amazon Redshift: A widely used cloud data warehouse built by Amazon, Redshift is the go-to choice for many teams and businesses. It is a comprehensive tool that enables the setup and scaling of data warehouses, making it incredibly easy to use.
One of the most popular tools used for businesses purpose is Amazon Redshift, which provides a powerful platform for managing large amounts of data. It allows users to quickly analyze complex datasets, build models that can be used for predictive analytics, and create visualizations that make it easier to interpret results. With its scalability and flexibility, Amazon Redshift has become one of the go-to solutions when it comes to data engineering tasks.
2. Big Query: Just like Redshift, Big Query is a cloud data warehouse fully managed by Google. It's especially favored by companies that have experience with the Google Cloud Platform. BigQuery not only can scale but also has robust machine learning features that make data analysis much easier. 3. Tableau: A powerful BI tool, Tableau is the second most popular one from our survey. It helps extract and gather data stored in multiple locations and comes with an intuitive drag-and-drop interface. Tableau makes data across departments readily available for data engineers and managers to create useful dashboards. 4. Looker: An essential BI software, Looker helps visualize data more effectively. Unlike traditional BI tools, Looker has developed a LookML layer, which is a language for explaining data, aggregates, calculations, and relationships in a SQL database. A spectacle is a newly-released tool that assists in deploying the LookML layer, ensuring non-technical personnel have a much simpler time when utilizing company data.
5. Apache Spark: An open-source unified analytics engine, Apache Spark is excellent for processing large data sets. It also offers great distribution and runs easily alongside other distributed computing programs, making it essential for data mining and machine learning. 6. Airflow: With Airflow, programming, and scheduling can be done quickly and accurately, and users can keep an eye on it through the built-in UI. It is the most used workflow solution, as 25% of data teams reported using it. 7. Apache Hive: Another data warehouse project on Apache Hadoop, Hive simplifies data queries and analysis with its SQL-like interface. This language enables MapReduce tasks to be executed on Hadoop and is mainly used for data summarization, analysis, and query. 8. Segment: An efficient and comprehensive tool, Segment assists in collecting and using data from digital properties. It transforms, sends, and archives customer data, and also makes the entire process much more manageable. 9. Snowflake: This cloud data warehouse has become very popular lately due to its capabilities in storing and computing data. Snowflake’s unique shared data architecture allows for a wide range of applications, making it an ideal choice for large-scale data storage, data engineering, and data science. 10. DBT: A command-line tool that uses SQL to transform data, DBT is the perfect choice for data engineers and analysts. DBT streamlines the entire transformation process and is highly praised by many data engineers.
Data Engineering Projects:
Data engineering is an important process for businesses to understand and utilize to gain insights from their data. It involves designing, constructing, maintaining, and troubleshooting databases to ensure they are running optimally. There are many tools available for data engineers to use in their work such as My SQL, SQL server, oracle RDBMS, Open Refine, TRIFACTA, Data Ladder, Keras, Watson, TensorFlow, etc. Each tool has its strengths and weaknesses so it’s important to research each one thoroughly before making recommendations about which ones should be used for specific tasks or projects.
Smart IoT Infrastructure:
As the IoT continues to develop, the measure of data consumed with high haste is growing at an intimidating rate. It creates challenges for companies regarding storehouses, analysis, and visualization.
Data Ingestion:
Data ingestion is moving data from one or further sources to a target point for further preparation and analysis. This target point is generally a data storehouse, a unique database designed for effective reporting.
Data Quality and Testing:
Understand the importance of data quality and testing in data engineering projects. Learn about techniques and tools to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
Streaming Data:
Familiarize yourself with real-time data processing and streaming frameworks like Apache Kafka and Apache Flink. Develop your problem-solving skills through practical exercises and challenges.
Conclusion:
Data engineers are using these tools for building data systems. My SQL, SQL server and Oracle RDBMS involve collecting, storing, managing, transforming, and analyzing large amounts of data to gain insights. Data engineers are responsible for designing efficient solutions that can handle high volumes of data while ensuring accuracy and reliability. They use a variety of technologies including databases, programming languages, machine learning algorithms, and more to create powerful applications that help businesses make better decisions based on their collected data.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
MySQL servers
VCD Studio offers expert MySQL Server management services to ensure your database runs smoothly and efficiently. Our team specializes in optimizing MySQL performance, managing high-availability setups, and providing secure, scalable solutions for businesses of all sizes. From installation and configuration to regular maintenance and performance tuning, we ensure your MySQL environment is reliable and secure. Our proactive monitoring and troubleshooting services minimize downtime and enhance the overall performance of your applications. Whether you need support for complex queries, database optimization, or scaling, VCD Studio’s MySQL expertise ensures your data infrastructure is robust and efficient.
0 notes
Text
DBMS Tutorial for Beginners: Unlocking the Power of Data Management
In this "DBMS Tutorial for Beginners: Unlocking the Power of Data Management," we will explore the fundamental concepts of DBMS, its importance, and how you can get started with managing data effectively.
What is a DBMS?
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a software tool that facilitates the creation, manipulation, and administration of databases. It provides an interface for users to interact with the data stored in a database, allowing them to perform various operations such as querying, updating, and managing data. DBMS can be classified into several types, including:
Hierarchical DBMS: Organizes data in a tree-like structure, where each record has a single parent and can have multiple children.
Network DBMS: Similar to hierarchical DBMS but allows more complex relationships between records, enabling many-to-many relationships.
Relational DBMS (RDBMS): The most widely used type, which organizes data into tables (relations) that can be linked through common fields. Examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
Object-oriented DBMS: Stores data in the form of objects, similar to object-oriented programming concepts.
Why is DBMS Important?
Data Integrity: DBMS ensures the accuracy and consistency of data through constraints and validation rules. This helps maintain data integrity and prevents anomalies.
Data Security: With built-in security features, DBMS allows administrators to control access to data, ensuring that only authorized users can view or modify sensitive information.
Data Redundancy Control: DBMS minimizes data redundancy by storing data in a centralized location, reducing the chances of data duplication and inconsistency.
Efficient Data Management: DBMS provides tools for data manipulation, making it easier for users to retrieve, update, and manage data efficiently.
Backup and Recovery: Most DBMS solutions come with backup and recovery features, ensuring that data can be restored in case of loss or corruption.
Getting Started with DBMS
To begin your journey with DBMS, you’ll need to familiarize yourself with some essential concepts and tools. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Understand Basic Database Concepts
Before diving into DBMS, it’s important to grasp some fundamental database concepts:
Database: A structured collection of data that is stored and accessed electronically.
Table: A collection of related data entries organized in rows and columns. Each table represents a specific entity (e.g., customers, orders).
Record: A single entry in a table, representing a specific instance of the entity.
Field: A specific attribute of a record, represented as a column in a table.
Step 2: Choose a DBMS
There are several DBMS options available, each with its own features and capabilities. For beginners, it’s advisable to start with a user-friendly relational database management system. Some popular choices include:
MySQL: An open-source RDBMS that is widely used for web applications.
PostgreSQL: A powerful open-source RDBMS known for its advanced features and compliance with SQL standards.
SQLite: A lightweight, serverless database that is easy to set up and ideal for small applications.
Step 3: Install the DBMS
Once you’ve chosen a DBMS, follow the installation instructions provided on the official website. Most DBMS solutions offer detailed documentation to guide you through the installation process.
Step 4: Create Your First Database
After installing the DBMS, you can create your first database. Here’s a simple example using MySQL:
Open the MySQL command line or a graphical interface like MySQL Workbench. Run the following command to create a new CREATE DATABASE my_first_database;
Use the database: USE my_first_database;
Step 5: Create Tables
Next, you’ll want to create tables to store your data. Here’s an example of creating a table for storing customer information:
CREATE TABLE customers ( 2 customer_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, 3 first_name VARCHAR(50), 4 last_name VARCHAR(50), 5 email VARCHAR(100), 6 created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP 7);
In this example, we define a table named customers with fields for customer ID, first name, last name, email, and the date the record was created.
Step 6: Insert Data
Now that you have a table, you can insert data into it. Here’s how to add a new customer:
1 INSERT INTO customers (first_name, last_name, email) 2VALUES ('John', 'Doe', '[email protected]');
Query Data
To retrieve data from your table, you can use the SELECT statement. For example, to get all customers:
1 SELECT * FROM customers;
You can also filter results using the WHERE clause:
SELECT * FROM customers WHERE last_name = 'Doe';
Step 8: Update and Delete Data
You can update existing records using the UPDATE statement:
UPDATE customers SET email = '[email protected]' WHERE customer_id = 1;
To delete a record, use the DELETE statement:
DELETE FROM customers WHERE customer_id = 1;
Conclusion
In this "DBMS Tutorial for Beginners: Unlocking the Power of Data Management," we’ve explored the essential concepts of Database Management Systems and how to get started with managing data effectively. By understanding the importance of DBMS, familiarizing yourself with basic database concepts, and learning how to create, manipulate, and query databases, you are well on your way to becoming proficient in data management.
As you continue your journey, consider exploring more advanced topics such as database normalization, indexing, and transaction management. The world of data management is vast and full of opportunities, and mastering DBMS will undoubtedly enhance your skills as a developer or data professional.
With practice and experimentation, you’ll unlock the full potential of DBMS and transform the way you work with data. Happy database management!
0 notes
Text
Live Support Chat Nulled Script 5.1.3

Unlock Real-Time Customer Engagement with Live Support Chat Nulled Script Looking for a powerful, real-time communication solution for your website? The Live Support Chat Nulled Script is the ultimate tool to boost user satisfaction and convert casual visitors into loyal customers. With seamless integration, robust features, and complete customization options, this nulled script gives you the edge of professional-grade live chat without the hefty price tag. What is Live Support Chat Nulled Script? The Live Support Chat Nulled Script is a feature-rich, real-time live chat system designed for businesses, startups, and agencies that want to provide instant customer support. This PHP-based solution is ideal for integrating directly into your website and allows your support team to chat with users, resolve issues, and convert leads — all in real time. Since this is a nulled version, you get complete access to premium features without any licensing restrictions or costs. Why Choose the Live Support Chat Nulled Script? Today’s digital consumers expect immediate responses, and this is where live chat becomes a game-changer. With the Live Support Chat , you’ll provide seamless support, monitor user activity, and increase customer satisfaction. No need to pay extra for live chat services — this nulled solution delivers high-end results for free. Technical Specifications Platform: PHP-based, compatible with all modern browsers Database: MySQL Responsiveness: Fully responsive and mobile-friendly UI Security: Role-based access control, chat encryption support Customization: Easy branding and UI modifications via built-in panel Key Features and Benefits Real-Time Messaging: Engage visitors with real-time conversations to resolve queries instantly. Multi-Agent Support: Allow multiple support agents to assist different users at once. User Monitoring: Track visitor movements, pages visited, and time spent on site. File Sharing: Securely send and receive files during chat sessions. Chat Transcripts: Save and review chat histories for quality and training purposes. Offline Messaging: Capture user inquiries even when your team is offline. Custom Alerts: Notify agents of new visitors, messages, and support tickets in real-time. Who Should Use This Script? The Live Support Chat Nulled Script is perfect for: E-commerce Websites: Help customers instantly with product queries and order assistance. Agencies: Provide immediate consultation and project updates to your clients. SaaS Platforms: Offer technical support without expensive third-party tools. Educational Platforms: Answer student queries and boost engagement. Easy Installation and Setup Guide Download the Live Support Chat Nulled Script from our secure platform. Upload the files to your web hosting account using FTP or cPanel. Configure the database settings by updating the config file. Run the installation wizard to finalize setup. Customize the chat interface to match your website branding. You don’t need to be a developer to get started. With detailed documentation and a user-friendly interface, this nulled script can be set up in minutes. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Is it safe to use the Live Support Chat Nulled Script? Yes, the script is thoroughly scanned and tested for security vulnerabilities. Just ensure your website hosting is secure, and you’re good to go. Can I customize the interface to match my branding? Absolutely! The script includes a built-in customization panel where you can modify colors, fonts, logos, and more. Does it support multiple languages? Yes, the Live Support Chat is fully translation-ready, making it perfect for multilingual support environments. Can I use this script with WordPress? While it's not a native WordPress plugin, it can be easily integrated into any WordPress site using custom pages or widgets. Get More With Our Collection of nulled plugins Why stop at live chat? Explore our vast library of professionally nulled plugins to supercharge your site without spending a dime.
Whether you need SEO tools, backup systems, or security add-ons, we’ve got you covered. Need more advanced tools? Check out UpdraftPlus Premium nulled for hassle-free backups and restoration solutions at zero cost. Final Thoughts The Live Support Chat offers a reliable, scalable, and cost-effective way to provide instant customer service. Whether you’re a small business or a growing enterprise, this script has everything you need to support your users 24/7 — without draining your budget. Download it today and transform your customer experience forever.
0 notes
Text
PHP, LAMP (Linux Apache MySQL PHP)
The LAMP stack — Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP — has been a cornerstone of web development for over two decades. It’s an open-source suite of software components that work together to serve dynamic websites and web applications. Among these, PHP plays a central role, acting as the scripting language responsible for generating dynamic page content. Despite the rise of modern development stacks like MERN or JAMstack, LAMP remains a reliable, accessible, and widely used platform for developers around the world.
What is LAMP?

LAMP is an acronym that stands for:
Linux: The operating system.
Apache: The web server software.
MySQL: The relational database management system.
PHP: The server-side scripting language.
Each component of LAMP is free and open-source, which contributed to its massive adoption in the early 2000s. Even today, LAMP powers a significant portion of the web, including popular platforms like WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla.
PHP: The Dynamic Power of LAMP

PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is the scripting language used in LAMP to process user requests and generate dynamic content. It integrates seamlessly with HTML, making it easy for developers to embed logic within web pages. PHP scripts are executed on the server, and the output is sent to the client’s browser in the form of standard HTML.
PHP supports a vast range of features including form handling, file management, database access, and session tracking. It’s easy to learn for beginners, yet powerful enough to build complex web applications. PHP is constantly evolving, with the latest versions offering improved performance, better error handling, and strong security features.
The Role of Each Component in LAMP

Here’s a breakdown of how each element in the LAMP stack functions together:
1. Linux
Linux acts as the foundation for the LAMP stack. It’s known for its stability, flexibility, and security. Most servers run on some version of Linux because of its ability to handle high volumes of traffic and customizable nature. Common Linux distributions used in LAMP setups include Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian.
2. Apache
Apache is a powerful and flexible open-source web server that handles HTTP requests from users’ browsers. It is responsible for delivering web pages to the client and includes modules for URL rewriting, authentication, and more. Apache can be customized using .htaccess files, making it easy to manage server behavior for specific directories.
3. MySQL
MySQL is a robust relational database management system used to store and manage application data. From user accounts to blog posts, all information can be efficiently queried and updated using SQL (Structured Query Language). PHP and MySQL often work hand in hand, with PHP scripts using MySQL queries to interact with the database.
4. PHP
PHP pulls it all together by connecting the front-end interface with the back-end logic. Whether it’s fetching blog posts from a database or processing user input from a form, PHP makes the content dynamic and personalized. PHP also supports object-oriented programming, error handling, and integration with third-party libraries.
Find Out More About This
Why Developers Still Choose LAMP

Despite the introduction of newer stacks, LAMP remains popular for a few key reasons:
Maturity and Stability: With decades of development, LAMP is well-documented and stable.
Community Support: A large community ensures that developers can find tutorials, tools, and forums for help.
Cost Efficiency: Being open-source, it significantly reduces hosting and licensing costs.
Flexibility: Suitable for projects of all sizes, from small blogs to enterprise-level applications.
Compatibility: Most hosting providers support LAMP out of the box.

PHP and the LAMP stack have stood the test of time in the world of web development. They offer a dependable, efficient, and accessible way to build and maintain dynamic websites. Whether you’re launching a personal blog or developing a business application, the LAMP stack remains a solid choice. As PHP continues to evolve and the ecosystem matures, LAMP proves that reliable technology doesn’t always need to be the newest — sometimes, it just needs to work exceptionally well.
0 notes
Text
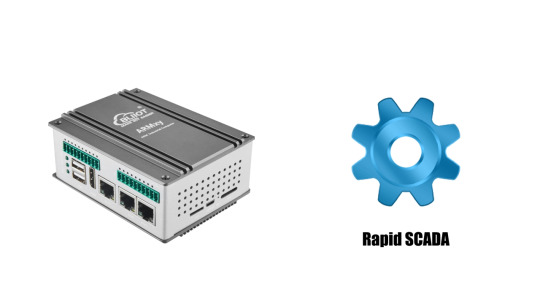
ARMxy Ubuntu Gateway BL370 and Rapid SCADA for Diesel Generator Monitoring System
Case Details
Combining the ARMxy series Ubuntu Gateway BL370 and Rapid SCADA to implement a diesel generator monitoring system is a great choice. This combination offers an efficient, flexible, and scalable monitoring solution. Below are some possible technical solutions and architectural designs:
1. Hardware Platform (ARM Ubuntu Gateway)
The ARM Ubuntu Gateway BL370 running Ubuntu provides powerful computing capabilities and stable support, allowing it to receive sensor data from the diesel generator and perform real-time processing. You can interface with the generator hardware in the following ways:
Digital and Analog Inputs: Connect the sensors of the diesel generator (e.g., temperature, pressure, voltage, current, etc.) through the gateway, often using the MODBUS RTU or TCP protocol to communicate with the SCADA system.
Remote Data Acquisition: The gateway can connect to the remote SCADA system via wireless (Wi-Fi/4G/5G) or wired networks (Ethernet), enabling data transmission and remote control.
2. SCADA System (Rapid SCADA)
Rapid SCADA is an open-source industrial automation platform that works well for monitoring generator operations. It supports a wide range of communication protocols (e.g., Modbus, OPC, SNMP) and integrates smoothly with ARM Ubuntu Gateway BL370.
Main features:
Real-time Monitoring: Display critical parameters like generator status, load, fuel consumption, temperature, pressure, etc.
Data Storage and Historical Queries: Rapid SCADA stores real-time data and allows querying and analysis through a database (like MySQL), generating reports.
Alarming and Event Management: When monitored data exceeds preset thresholds, the system can automatically trigger alarms and log events for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Remote Control: Users can remotely control the generator’s start/stop operations and adjust the load through the SCADA system.
3. System Architecture Example
Sensors and Controllers: Install various sensors (e.g., temperature, pressure, oil level) on the diesel generator, transmitting data to the ARM Ubuntu Gateway BL370 via Modbus RTU/TCP protocol.
Gateway Device (BL370): This gateway runs Ubuntu OS and handles receiving sensor data from the generator and transmitting it to the SCADA system over the network.
SCADA Server: Rapid SCADA runs on a server, processing and displaying data from the gateway, generating real-time data views, alarms, and reports.
User Interface: Users can access the SCADA system through a web interface or desktop client to view the generator's status, historical data, and alarm information.
4. Data Transmission and Protocols
Modbus Protocol: In industrial environments, Modbus is a commonly used protocol for communication between the diesel generator and the SCADA system. Modbus TCP or Modbus RTU can be used, depending on the system design and needs.
MQTT Protocol: For remote communication, MQTT can be used to transmit sensor data, especially when using 4G or wireless networks.
HTTP/HTTPS API: If Rapid SCADA supports it, the gateway can send data to the SCADA system via HTTP or HTTPS APIs.
5. Data Analysis and Prediction
Using historical data accumulated by the SCADA system, deeper data analysis can be conducted. For example, algorithms can predict maintenance needs for the diesel generator or optimize its workload based on performance data, thus reducing downtime.
6. Security Considerations
Data Encryption: To protect data security during communication, it’s recommended to use TLS/SSL encryption protocols.
User Authentication and Access Control: Set proper permissions and roles within the SCADA system to ensure that only authorized users can operate critical equipment.
Summary
Using an ARMxy Ubuntu Gateway BL370 in conjunction with Rapid SCADA to set up generator monitoring system is a flexible and efficient solution. The ARM gateway provides reliable data acquisition and processing capabilities, while Rapid SCADA offers powerful data visualization, alarming, and historical data storage features. Together, they can significantly enhance the monitoring, management, and maintenance of the diesel generator.
0 notes
Text
Google Cloud C4D machine series Compute with AMD Turin

Confidentiality VMs running AMD SEV on C4D machines preview
Google Titanium hardware gives the C4D machine series excellent, reliable, and consistent performance with 5th-generation AMD EPYC (Turin) CPUs.
Google Cloud offers Confidential Compute on AMD N2D, C2D, and C3D machines worldwide. The general-purpose C4D machine series' confidential virtual machines (VMs) with AMD Secure Encrypted Virtualisation (AMD SEV) technology are in preview today and will soon be released.
C4D virtual machines use Titanium and fifth-generation AMD EPYC Turin processors. C4D outperforms C3D by 30% on the anticipated SPECrate2017_int_base benchmark, growing performance with fewer resources and maximising expenditures.
C4D supports web, app, and game servers, AI inference, web serving, video streaming, analytics, and relational and in-memory databases.
C4D can execute 38% more Memorystore for Redis operations and 56% more Cloud SQL for MySQL queries than C3D due to its higher core frequency (up to 4.1 GHz) and improved IPC.
With C4D, AMD EPYC Turin may boost web-serving throughput per vCPU by 80% and enhance branch prediction and L3-cache efficiency.
Features of C4D machines
The C4D machine series has these traits:
Titanium and AMD EPYC Turin power it.
Supports 384 virtual CPUs and 3,024 GB DDR5.
Local Titanium SSDs up to 12,000 GiB are supported.
Preconfigured machines with 2–384 virtual central chips are available.
Future bookings, Spot VMs, and on-demand consumption are supported.
Allows conventional network setup with 100 Gbps bandwidth.
Supports Tier 1 VM networking at 200 Gbps.
For HyperDisk volumes only.
Confidential Virtual Machine AMD SEV support Flexible, resource-based committed use discounts
Supports compact and distributed placement policies.
C4D machine series types
Regular, high-cpu, and high-mem C4D virtual machines have predefined configurations from 2 to 384 vCPUs and up to 3,024 GB of memory.
Build your instance with the C4D machine type -lssd option to use Titanium SSD. Selecting this machine type creates a Titanium SSD-partitioned instance of the required size. Different Titanium SSD volumes cannot be joined.
Custom machines are incompatible with C4D.
Supported C4D VM disc types
It supports only NVMe disc interface and Hyperdisk block storage:
Hyperdisk-steady
Hyperdisk Extreme
Certain system types automatically receive local titanium SSD with the -lssd option.
Persistent Disc is incompatible with C4D.
Disc and capacity limits
A virtual machine (VM) can use a variety of hyperdisks, but their total disc capacity (in TiB) cannot exceed:
For systems under 32 vCPUs, all hyperdisks have 257 TiB.
Different computers with 32 vCPUs or 512 TiB for the hyperdisk
Networking C4D machines
Network interfaces for C4D virtual machines must be gVNIC. C4D can handle 100 Gbps for regular networking and 200 Gbps for per-VM Tier_1 networking.
Make sure your operating system image supports the gVNIC driver before switching to C4D or starting instances. Choose an OS image with “Tier_1 Networking” and “200 Gbps network bandwidth” on the Networking features tab of the OS information table for optimum C4D performance. Although the guest OS lists gve driver version as 1.0.0, these images upgrade the gVNIC driver. If your C4D instance runs an operating system with an outdated gVNIC driver, it may have greater latency or less network bandwidth than it should.
Custom OS images for the C4D machine series allow manual installation of the newest gVNIC driver. C4D instances should use gVNIC driver v1.3.0 or later. Google recommends using the latest gVNIC driver for new features and bug fixes.
#C4Dmachine#AMDSecureEncryptedVirtualization#C4Dvirtualmachines#C4Dmachineseries#Virtualmachines#gVNICdriver#technology#technews#technologynews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
MySQL database courses Coding Bit
MySQL database courses is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) based on Structured Query Language (SQL). It is used to store, manage, and retrieve data for websites and applications. MySQL is known for its speed, reliability, and ease of use, and is widely used with web technologies, especially PHP.
Key Features:
Relational database: Organizes data in tables with rows and columns.
SQL support: Uses SQL for querying and managing data.
Open-source: Free to use under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
Cross-platform: Runs on Windows, Linux, macOS, etc.
Scalable: Suitable for both small and large applications.
Secure: Supports user access control and encryption.
Common Uses:
Websites (e.g., with WordPress, Joomla)
Web apps (e.g., e-commerce, blogs)
Data warehousing
Logging systems 📞 Phone Number: +91 9511803947 📧 Email Address: [email protected]

#MySQL#Database#SQL#RelationalDatabase#MySQLDatabase#SQLQuery#OpenSourceDatabase#DataManagement#MySQLTips
0 notes
Text
Master SQL in 2025: The Only Bootcamp You’ll Ever Need

When it comes to data, one thing is clear—SQL is still king. From business intelligence to data analysis, web development to mobile apps, Structured Query Language (SQL) is everywhere. It’s the language behind the databases that run apps, websites, and software platforms across the world.
If you’re looking to gain practical skills and build a future-proof career in data, there’s one course that stands above the rest: the 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL.
Let’s dive into what makes this bootcamp a must for learners at every level.
Why SQL Still Matters in 2025
In an era filled with cutting-edge tools and no-code platforms, SQL remains an essential skill for:
Data Analysts
Backend Developers
Business Intelligence Specialists
Data Scientists
Digital Marketers
Product Managers
Software Engineers
Why? Because SQL is the universal language for interacting with relational databases. Whether you're working with MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, or Microsoft SQL Server, learning SQL opens the door to querying, analyzing, and interpreting data that powers decision-making.
And let’s not forget—it’s one of the highest-paying skills on the job market today.
Who Is This Bootcamp For?
Whether you’re a complete beginner or someone looking to polish your skills, the 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL is structured to take you through a progressive learning journey. You’ll go from knowing nothing about databases to confidently querying real-world datasets.
This course is perfect for:
✅ Beginners with no prior programming experience ✅ Students preparing for tech interviews ✅ Professionals shifting to data roles ✅ Freelancers and entrepreneurs ✅ Anyone who wants to work with data more effectively
What You’ll Learn: A Roadmap to SQL Mastery
Let’s take a look at some of the key skills and topics covered in this course:
🔹 SQL Fundamentals
What is SQL and why it's important
Understanding databases and tables
Creating and managing database structures
Writing basic SELECT statements
🔹 Filtering & Sorting Data
Using WHERE clauses
Logical operators (AND, OR, NOT)
ORDER BY and LIMIT for controlling output
🔹 Aggregation and Grouping
COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX
GROUP BY and HAVING
Combining aggregate functions with filters
🔹 Advanced SQL Techniques
JOINS: INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, FULL
Subqueries and nested SELECTs
Set operations (UNION, INTERSECT)
Case statements and conditional logic
🔹 Data Cleaning and Manipulation
UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT statements
Handling NULL values
Using built-in functions for data formatting
🔹 Real-World Projects
Practical datasets to work on
Simulated business cases
Query optimization techniques
Hands-On Learning With Real Impact
Many online courses deliver knowledge. Few deliver results.
The 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL does both. The course is filled with hands-on exercises, quizzes, and real-world projects so you actually apply what you learn. You’ll use modern tools like PostgreSQL and pgAdmin to get your hands dirty with real data.
Why This Course Stands Out
There’s no shortage of SQL tutorials out there. But this bootcamp stands out for a few big reasons:
✅ Beginner-Friendly Structure
No coding experience? No problem. The course takes a gentle approach to build your confidence with simple, clear instructions.
✅ Practice-Driven Learning
Learning by doing is at the heart of this course. You’ll write real queries, not just watch someone else do it.
✅ Lifetime Access
Revisit modules anytime you want. Perfect for refreshing your memory before an interview or brushing up on a specific concept.
✅ Constant Updates
SQL evolves. This bootcamp evolves with it—keeping you in sync with current industry standards in 2025.
✅ Community and Support
You won’t be learning alone. With a thriving student community and Q&A forums, support is just a click away.
Career Opportunities After Learning SQL
Mastering SQL can open the door to a wide range of job opportunities. Here are just a few roles you’ll be prepared for:
Data Analyst: Analyze business data and generate insights
Database Administrator: Manage and optimize data infrastructure
Business Intelligence Developer: Build dashboards and reports
Full Stack Developer: Integrate SQL with web and app projects
Digital Marketer: Track user behavior and campaign performance
In fact, companies like Amazon, Google, Netflix, and Facebook all require SQL proficiency in many of their job roles.
And yes—freelancers and solopreneurs can use SQL to analyze marketing campaigns, customer feedback, sales funnels, and more.
Real Testimonials From Learners
Here’s what past students are saying about this bootcamp:
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “I had no experience with SQL before taking this course. Now I’m using it daily at my new job as a data analyst. Worth every minute!” – Sarah L.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “This course is structured so well. It’s fun, clear, and packed with challenges. I even built my own analytics dashboard!” – Jason D.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “The best SQL course I’ve found on the internet—and I’ve tried a few. I was up and running with real queries in just a few hours.” – Meera P.
How to Get Started
You don’t need to enroll in a university or pay thousands for a bootcamp. You can get started today with the 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL and build real skills that make you employable.
Just grab a laptop, follow the course roadmap, and dive into your first database. No fluff. Just real, useful skills.
Tips to Succeed in the SQL Bootcamp
Want to get the most out of your SQL journey? Keep these pro tips in mind:
Practice regularly: SQL is a muscle—use it or lose it.
Do the projects: Apply what you learn to real datasets.
Take notes: Summarize concepts in your own words.
Explore further: Try joining Kaggle or GitHub to explore open datasets.
Ask questions: Engage in course forums or communities for deeper understanding.
Your Future in Data Starts Now
SQL is more than just a skill. It’s a career-launching power tool. With this knowledge, you can transition into tech, level up in your current role, or even start your freelance data business.
And it all begins with one powerful course: 👉 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL
So, what are you waiting for?
Open the door to endless opportunities and unlock the world of data.
0 notes
Text
Build a Strong Backend: Why Web Developers Should Focus on MySQL Early

Introduction
When it comes to web development, most beginners are fascinated by the visual aspects of websites—the buttons, layouts, and animations. But behind every great website lies a powerful backend, and one of the most essential components of this backend is the database. Among the many database management systems out there, MySQL stands out as the most widely used and beginner-friendly option. If you're planning to enroll in a web development course in Yamuna Vihar or web development training in Uttam Nagar, it’s important to understand why you should prioritize learning MySQL early in your journey.
What is MySQL and Why is it So Important?
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system. It is used to store, organize, and retrieve data for web applications. It powers some of the world’s biggest platforms including Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube. For any student taking web designing classes in Yamuna Vihar or web development coaching in Uttam Nagar, learning MySQL is a non-negotiable step.
Why? Because it’s the heart of how web apps interact with data. Whether it’s a login system, product catalog, or a content management system—MySQL is what makes these features function.
Early MySQL Skills = Long-Term Benefits
Students who start learning MySQL early gain a significant advantage:
Better understanding of backend logic
You’ll start understanding how data flows between the front-end and backend, giving you a complete picture of web development.
Stronger foundation for full-stack development
If you're aiming to become a full-stack developer, learning MySQL early prepares you for advanced backend frameworks like Node.js, Django, or Laravel.
Boost your job-readiness
Recruiters and companies look for developers who can handle the full development cycle—especially those with MySQL and database management experience.
If you’re taking a full stack web development course in Yamuna Vihar or searching for the best full stack developer course with placement in Uttam Nagar, you’ll notice MySQL is an integral part of the curriculum.
How MySQL Complements Front-End Skills
Even if your primary interest lies in UI/UX or front-end design, having a grip on MySQL sets you apart. For example:
UI elements like dropdowns or search bars often fetch real-time data from the backend via SQL queries.
Dynamic websites that display user data or product recommendations rely heavily on MySQL databases.
If you're already exploring UI UX free online courses with certificates in Yamuna Vihar or a user interface design course in Uttam Nagar, pairing that with MySQL will make your portfolio completer and more impressive.
Key Concepts You Should Learn in MySQL
Here are some essential MySQL concepts every web developer should master:
Database creation and table structures
SQL queries: SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
Joins and relationships
Data normalization
Indexing for performance optimization
These concepts are often covered thoroughly in a web development training institute in Yamuna Vihar or web development coaching center in Uttam Nagar.
Real-World Applications of MySQL
Whether you're developing an e-commerce website, a social media platform, or a blog, MySQL will help you:
Store user credentials securely
Handle product inventories
Maintain order history
Run analytics on user behavior
Students attending web designing coaching in Yamuna Vihar or web development classes in Uttam Nagar often work on real-time projects that require database connectivity, making MySQL a practical tool rather than just theoretical knowledge.
Conclusion: Start with MySQL to Stay Ahead
Web development is not just about what users see—it's also about how websites work behind the scenes. MySQL teaches you the logic and structure that bring data-driven websites to life. So, if you’re currently enrolled in or planning to join a web designing course in Yamuna Vihar or a web development course in Uttam Nagar, make sure MySQL is at the top of your learning list.
Whether your goal is to become a full stack developer, build your own website, or master UI/UX design, understanding databases like MySQL will take your skills to the next level.
Suggested Links:
Oracle Database Administration
MY SQL Training
PHP Development
#oracle database#MY SQL Training#PHP Development#Web Development course#Wed Designing course in yamuna vihar#Web designing course in uttam nagar
0 notes
Text
Complete PHP Tutorial: Learn PHP from Scratch in 7 Days
Are you looking to learn backend web development and build dynamic websites with real functionality? You’re in the right place. Welcome to the Complete PHP Tutorial: Learn PHP from Scratch in 7 Days — a practical, beginner-friendly guide designed to help you master the fundamentals of PHP in just one week.
PHP, or Hypertext Preprocessor, is one of the most widely used server-side scripting languages on the web. It powers everything from small blogs to large-scale websites like Facebook and WordPress. Learning PHP opens up the door to back-end development, content management systems, and full-stack programming. Whether you're a complete beginner or have some experience with HTML/CSS, this tutorial is structured to help you learn PHP step by step with real-world examples.
Why Learn PHP?
Before diving into the tutorial, let’s understand why PHP is still relevant and worth learning in 2025:
Beginner-friendly: Easy syntax and wide support.
Open-source: Free to use with strong community support.
Cross-platform: Runs on Windows, macOS, Linux, and integrates with most servers.
Database integration: Works seamlessly with MySQL and other databases.
In-demand: Still heavily used in CMS platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal.
If you want to build contact forms, login systems, e-commerce platforms, or data-driven applications, PHP is a great place to start.
Day-by-Day Breakdown: Learn PHP from Scratch in 7 Days
Day 1: Introduction to PHP & Setup
Start by setting up your environment:
Install XAMPP or MAMP to create a local server.
Create your first .php file.
Learn how to embed PHP inside HTML.
Example:
<?php echo "Hello, PHP!"; ?>
What you’ll learn:
How PHP works on the server
Running PHP in your browser
Basic syntax and echo statement
Day 2: Variables, Data Types & Constants
Dive into PHP variables and data types:
$name = "John"; $age = 25; $is_student = true;
Key concepts:
Variable declaration and naming
Data types: String, Integer, Float, Boolean, Array
Constants and predefined variables ($_SERVER, $_GET, $_POST)
Day 3: Operators, Conditions & Control Flow
Learn how to make decisions in PHP:
if ($age > 18) { echo "You are an adult."; } else { echo "You are underage."; }
Topics covered:
Arithmetic, comparison, and logical operators
If-else, switch-case
Nesting conditions and best practices
Day 4: Loops and Arrays
Understand loops to perform repetitive tasks:
$fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"]; foreach ($fruits as $fruit) { echo $fruit. "<br>"; }
Learn about:
for, while, do...while, and foreach loops
Arrays: indexed, associative, and multidimensional
Array functions (count(), array_push(), etc.)
Day 5: Functions & Form Handling
Start writing reusable code and learn how to process user input from forms:
function greet($name) { return "Hello, $name!"; }
Skills you gain:
Defining and calling functions
Passing parameters and returning values
Handling HTML form data with $_POST and $_GET
Form validation and basic security tips
Day 6: Working with Files & Sessions
Build applications that remember users and work with files:
session_start(); $_SESSION["username"] = "admin";
Topics included:
File handling (fopen, fwrite, fread, etc.)
Reading and writing text files
Sessions and cookies
Login system basics using session variables
Day 7: PHP & MySQL – Database Connectivity
On the final day, you’ll connect PHP to a database and build a mini CRUD app:
$conn = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "", "mydatabase");
Learn how to:
Connect PHP to a MySQL database
Create and execute SQL queries
Insert, read, update, and delete (CRUD operations)
Display database data in HTML tables
Bonus Tips for Mastering PHP
Practice by building mini-projects (login form, guest book, blog)
Read official documentation at php.net
Use tools like phpMyAdmin to manage databases visually
Try MVC frameworks like Laravel or CodeIgniter once you're confident with core PHP
What You’ll Be Able to Build After This PHP Tutorial
After following this 7-day PHP tutorial, you’ll be able to:
Create dynamic web pages
Handle form submissions
Work with databases
Manage sessions and users
Understand the logic behind content management systems (CMS)
This gives you the foundation to become a full-stack developer, or even specialize in backend development using PHP and MySQL.
Final Thoughts
Learning PHP doesn’t have to be difficult or time-consuming. With the Complete PHP Tutorial: Learn PHP from Scratch in 7 Days, you’re taking a focused, structured path toward web development success. You’ll learn all the core concepts through clear explanations and hands-on examples that prepare you for real-world projects.
Whether you’re a student, freelancer, or aspiring developer, PHP remains a powerful and valuable skill to add to your web development toolkit.
So open up your code editor, start typing your first <?php ... ?> block, and begin your journey to building dynamic, powerful web applications — one day at a time.

0 notes
Text
The Modern Full Stack Toolkit: What You Really Need
The role of a full stack web developer is more dynamic than ever. With the rapid evolution of technology, staying up-to-date with the latest tools and frameworks is essential. The modern full stack toolkit combines a wide range of technologies, from front-end to back-end development, enabling developers to create robust, efficient, and interactive web applications. Understanding what tools to use is key to building successful web applications, and knowing how to use them simultaneously is equally important.
What Does a Full Stack Web Developer Do?
A full stack web developer is responsible for developing both the client and server sides of web applications. This includes the user interface (UI), as well as the underlying database and server architecture. A typical full stack developer needs to be proficient in various technologies, ranging from HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to server-side languages and databases.
The role requires both a creative and analytical mindset, as developers must consider not only the aesthetic aspects but also performance, scalability, and security. A strong understanding of both front-end and back-end frameworks allows full stack developers to create seamless user experiences while maintaining backend integrity.
Key Components of the Modern Full Stack Toolkit
To excel in this multifaceted role, a full stack web developer needs a toolkit that covers all aspects of development. Here’s a breakdown of the modern tools that developers use simultaneously to build effective web applications:
1. Front-End Development Tools
The front end is everything the user interacts with directly. A good full stack developer must master the following front-end technologies:
HTML5 & CSS3: The building blocks of the web, allowing you to structure content and design the visual layout.
JavaScript: This programming language adds interactivity to your website, allowing for dynamic content and real-time updates.
React.js: A popular front-end JavaScript library developed by Facebook, enabling the creation of responsive, component-based user interfaces.
Vue.js: Another framework for building user interfaces, known for its simplicity and flexibility.
Bootstrap: A front-end framework for developing responsive, mobile-first websites quickly.
2. Back-End Development Tools
The back end of a web application is what powers the user-facing side. It involves handling data storage, user authentication, and communication between the front end and the database. The following tools are essential for the back-end of any modern web application:
Node.js: A JavaScript runtime environment that allows you to run JavaScript on the server side, enabling you to use the same language for both the front end and back end.
Express.js: A minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework that simplifies routing and handling server-side logic.
Django: A high-level Python framework for rapid development of secure and maintainable websites.
Ruby on Rails: A robust framework for building full-featured web applications using Ruby, known for its convention over configuration approach.
3. Databases
No web application is complete without a robust database. A full stack developer should be proficient in working with databases to store and retrieve application data:
MongoDB: A NoSQL database that stores data in JSON-like format, ideal for handling large volumes of unstructured data.
MySQL: A traditional relational database management system (RDBMS) that uses SQL to query data and is well-suited for structured data.
PostgreSQL: An advanced open-source relational database with a focus on extensibility and standards compliance.
4. Version Control
Collaboration is a crucial part of the development process, and version control is a must-have tool for any developer. Git, the most popular version control system, allows developers to track changes in code, collaborate with others, and maintain project histories.
GitHub: A platform that hosts Git repositories, enabling developers to collaborate, share code, and deploy applications easily.
5. DevOps Tools
DevOps tools help manage the infrastructure and deployment pipelines, ensuring continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD). These tools streamline the development process and allow for faster, more reliable releases.
Docker: A containerization platform that allows developers to package applications and their dependencies into a standardized unit for development, testing, and deployment.
Kubernetes: A container orchestration tool that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
6. Testing Tools
To ensure the quality of your application, a full stack web developer must also implement rigorous testing at every stage of the development cycle.
Jest: A JavaScript testing framework for ensuring that your front-end and back-end code works as expected.
Mocha: A feature-rich JavaScript test framework that works well with Node.js applications.
The Importance of Integration and Simultaneous Use
Being proficient in the individual components of full stack development is important, but the real challenge lies in using these tools simultaneously. A full stack web developer must understand how to integrate various front-end and back-end technologies into a cohesive whole.
For example, a full stack web developer working with React.js on the front end might use Node.js and Express on the back end while integrating MongoDB as the database. The developer needs to ensure smooth communication between these components and optimize performance across all layers of the application.
Conclusion
The modern full stack web developer must be equipped with a broad set of tools that spans front-end, back-end, databases, and deployment. The key to success lies not only in mastering individual technologies but in integrating them simultaneously to build seamless, high-performance applications. By leveraging the right tools and frameworks, a full stack web developer can ensure that they stay ahead in the fast-paced world of web development.
0 notes