#vascular endothelial growth factor
Text
Epithelial thinning in vaginal atrophy related to lowering of calcitonin gene-related protein, vascular endothelial growth factor, and nerve growth factor expressions in a menopausal rat model
Article published in J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 110-116, January-February 2023.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.56499/jppres22.1512_11.1.110
An Nisa Fithri1,2*, Yuyun Yueniwati3, I Wayan Arsana4, Husnul Khotimah5, Wiwit Nurwidyaningtyas6
1Doctoral Program of Medical Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Brawijaya, Indonesia.
2Midwifery Program, Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Kesehatan…

View On WordPress
#calcitonin gene-related protein#menopause#nerve growth factor#ovariectomy model#vaginal atrophy#vascular endothelial growth factor
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitor Market Research, Development, Top Companies, Trends And Growth 2022 To 2029
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitor Market Overview
The Research report on Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibitor contains all relevant information. By providing its clients with accurate data, it provides the market outlook and aids in the making of crucial decisions. The market size, share, dynamics, and forecast for major segments and sub-segments are provided in this report, which combines primary and secondary research. This market research study keeps track of all the latest advancements and changes in the industry. It gives the data regarding the obstacles while establishing the business and guides to overcome the upcoming challenges and obstacles.
Get a Sample copy of the report:
https://pharmaresearchconsulting.com/reports/vascular-endothelial-growth-factor-inhibitor-market-global-growth-trends-and-forecast-2022-2028-by-vaccine-type-monovalent-multivalent-by-application-pneumococcal-disease-influenza-measles-mumps-and-rubella-mmr-by-region
Get in Touch with Us: -
Phone No.+1 (704) 266-3234
Mail to: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Stem Cell Therapy for Peripheral Artery Disease in India

Peripheral artery disease, also known as PAD, affects millions of people globally by restricting blood flow to their limbs. Conventionally, treatment options for PAD include medications, lifestyle changes, angioplasty, and bypass surgery.
However, a promising new treatment is emerging - stem cell therapy. In this article, we'll discuss how stem cell therapy works for PAD, research on its effectiveness, and options to access top-quality treatment at r3stemcell India in New Delhi, India.
What is Peripheral Artery Disease?
Peripheral artery disease, or PAD, occurs when fatty deposits called plaque build up in the arteries that supply blood to the head, organs, and limbs. This narrows the arteries and reduces blood flow.
PAD most commonly affects the arteries in the legs. However, it can impact any peripheral arteries outside of the heart. The classic symptom is calf pain or cramping in the legs and hips while walking, known as intermittent claudication. Other signs include sores on the feet/legs that won't heal or color changes in the skin.
PAD is caused by atherosclerosis, a disease where plaque builds up in the arteries. Risk factors for developing atherosclerosis and PAD include:
Smoking
High blood pressure
High cholesterol
Diabetes
Obesity
Older age
Without treatment, PAD can progress to severe leg pain at rest or non-healing wounds. In rare cases, it may require amputation if blood flow is severely restricted.
How Does Stem Cell Therapy Work for PAD?
Stem cell therapy for PAD aims to regenerate new blood vessels and improve circulation in the affected limbs. It works through the following mechanisms:
Stem cells promote angiogenesis:
Stem cells secrete factors that stimulate the growth of new blood vessels, a process called angiogenesis. They recruit the body's own stem cells to develop new networks that bypass blockages.
Reduced inflammation:
Stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties. They help reduce inflammation in the arteries and vessel walls caused by PAD. This eases blood flow.
Generation of healthy cells:
Some stem cell types can differentiate into endothelial cells, which line the inside of blood vessels. They form new endothelial layers over damaged areas to improve vascular function.
Bypass artery obstructions:
The new blood vessels generated around narrowed or blocked areas provide pathways for blood to flow, bypassing restrictions in the primary arteries. This restores adequate blood flow.
In summary, stem cells repair and regenerate the blood vessel network from within via multiple regenerative mechanisms. When administered via injections, they home in on sites of injury in peripheral arteries and enact healing.
Research on Stem Cell Therapy for PAD
Research into stem cell therapy for PAD is still emerging but shows promise. Here are some key study findings:
A 2021 review found stem cell therapy significantly improved pain-free walking distance in PAD patients compared to conservative treatments alone.
Animal studies show stem cells increase capillary density and blood flow in ischemic limb muscle tissue with minimal side effects.
A 2017 study of 36 patients found adipose-derived stem cell therapy improved ankle-brachial pressure index (a measure of blood flow) and reduced amputation risk.
A Korean trial of 52 participants found bone marrow-derived mononuclear cell therapy increased pain-free walking time by 165% at 6 months follow-up.
No serious adverse events were reported across multiple clinical trials, indicating stem cell therapy for PAD appears safe when administered properly.
While more large-scale human trials are still needed, current research suggests stem cell therapy improves vascular function, reduces symptoms, and helps avoid amputation in PAD patients. Its safety profile also makes it a promising alternative or addition to standard PAD treatments.
Accessing Stem Cell Therapy for PAD in India
For individuals seeking stem cell therapy for peripheral artery disease, r3stemcell India is one of the top centers in the world. Here are some benefits it offers:
Experienced US-board-certified doctors with over 10,000 successful regenerative procedures completed.
State-of-the-art stem cell lab and facilities cleared by DCGI, India's FDA equivalent.
Full evaluation by a medical team prior to developing a customized treatment plan.
Use of autologous (patient's own) stem cells sourced from adipose tissue or bone marrow.
Minimally invasive stem cell injections or intravenous therapies depending on each case.
Affordable all-inclusive packages including accommodation, meals, transportation, and more.
Additional support services like physiotherapy, supplements, and oxygen therapies.
High success rates were reported across multiple conditions treated, including PAD.
For patients who want to access safe and effective stem cell therapy for peripheral artery disease, r3stemcell India is an excellent choice. Consultations can be arranged online or via phone prior to booking treatment.
Conclusion
In summary, peripheral artery disease affects millions worldwide by restricting blood flow to the limbs. While medications, angioplasty, and surgery are standard treatment protocols currently, stem cell therapy shows promise as an innovative option.
Research suggests it improves vascular function, reduces symptoms, increases walking distance and lowers amputation risks for PAD patients. When administered at reputed centers like r3stemcell India, stem cell therapy also appears to be a safe alternative for peripheral artery disease.
With successful clinical studies already conducted and more in progress, stem cell therapy could emerge as an important addition to the PAD treatment paradigm. It offers hope for regenerative healing with minimal long-term reliance on medications. For individuals seeking this promising treatment, r3stemcell India is a suitable choice.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Pigment Epithelial Detachment Market: Analysis, Size, Outlook, and Forecast
Pigment epithelial detachment (PED) is a significant concern in the realm of ophthalmology, impacting vision and quality of life for affected individuals.
Find out more about the report in Pigment epithelial detachment market forecast
As the prevalence of PED continues to rise, the market for treatments and management strategies experiences notable shifts and advancements.
In this comprehensive analysis, we delve into the dynamics of the pigment epithelial detachment market, examining its size, outlook, and forecast.
Understanding Pigment Epithelial Detachment
Pigment epithelial detachment refers to the separation of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) from the underlying Bruch's membrane in the eye.
This condition can arise due to various factors, including age-related macular degeneration (AMD), central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC), and other retinal diseases. PED can lead to vision impairment and distortion, making it a significant concern for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Market Analysis
The pigment epithelial detachment market encompasses a range of diagnostic tools, therapeutic interventions, and supportive care options.
Key players in this market include pharmaceutical companies developing innovative treatments, medical device manufacturers producing imaging technologies, and research institutions driving advancements in understanding PED pathology and management.
Several factors contribute to the growth of the PED market. Firstly, the aging population worldwide leads to a higher prevalence of age-related eye diseases, including AMD, which often manifests with PED.
Additionally, advancements in diagnostic imaging techniques, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fundus autofluorescence (FAF), enable earlier detection and monitoring of PED, driving demand for related products and services.
Therapeutic interventions for PED primarily focus on addressing underlying causes, such as anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) injections for AMD-related PED or laser therapy for CSC-associated PED.
The market for these treatments is dynamic, with ongoing clinical trials exploring novel drugs and interventions aimed at improving outcomes for patients with PED.
Market Size
The pigment epithelial detachment market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by an increased understanding of disease pathology, advances in diagnostic technologies, and the development of targeted therapies.
According to recent market research reports, the global PED market was valued at [insert value] in [insert year], with projections indicating continued expansion in the coming years.
Factors contributing to the market size include the rising prevalence of AMD and other retinal diseases, expanding access to healthcare services in emerging markets, and the introduction of innovative treatment modalities.
Additionally, collaborations between industry stakeholders, academic institutions, and regulatory bodies facilitate the development and commercialization of new products, further fueling market growth.
Market Outlook
The outlook for the pigment epithelial detachment market is promising, driven by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at addressing unmet needs in disease management. Key trends shaping the market outlook include:
Precision Medicine: Advancements in genetic testing and personalized medicine hold promise for tailoring treatment approaches to individual patients, optimizing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Technological Innovations: Continued innovation in diagnostic imaging technologies, such as OCT angiography and adaptive optics, enhances our ability to visualize and characterize PED, enabling more accurate diagnosis and monitoring.
Emerging Therapies: The pipeline of novel therapies for AMD, CSC, and other retinal diseases associated with PED is robust, with several candidates in late-stage clinical development. These therapies aim to improve visual outcomes, reduce treatment burden, and address disease progression more effectively.
Patient-Centric Care: There is a growing emphasis on holistic care approaches that consider the psychosocial impact of PED on patients' lives, incorporating support services such as low vision rehabilitation and patient education initiatives.
Market Forecast
Looking ahead, market forecasts suggest sustained growth in the pigment epithelial detachment market, driven by the convergence of demographic trends, technological advancements, and therapeutic innovations.
Factors influencing the market forecast include regulatory developments, reimbursement landscape changes, and shifts in healthcare delivery models.
Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into diagnostic and therapeutic algorithms holds potential for enhancing efficiency and decision-making in the management of PED.
In conclusion, the pigment epithelial detachment market presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation, driven by an evolving understanding of disease pathology and a commitment to improving patient outcomes.
By leveraging advances in technology, embracing patient-centric care models, and fostering collaboration across the healthcare ecosystem, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of the PED market and contribute to advancing the field of ophthalmology.
In summary, the pigment epithelial detachment market is poised for growth, driven by factors such as an aging population, technological advancements, and therapeutic innovations.
With a focus on precision medicine, technological innovation, patient-centric care, and collaboration, stakeholders can capitalize on emerging opportunities and contribute to improving outcomes for patients with PED.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
IJMS, Vol. 25, Pages 5479: Available Therapeutic Options for Corneal Neovascularization: A Review
Corneal neovascularization can impair vision and result in a poor quality of life. The pathogenesis involves a complex interplay of angiogenic factors, notably vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). This review provides a comprehensive overview of potential therapies for corneal neovascularization, covering tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs), transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) inhibitors, interleukin-1L receptor antagonist (IL-1 Ra), nitric oxide synthase (NOS) isoforms, galectin-3 inhibitors, retinal pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor inhibitors, and surgical treatments. Conventional treatments include anti-VEGF therapy and laser interventions, while emerging therapies such as immunosuppressive drugs (cyclosporine and rapamycin) have been explored. Losartan and decorin are potential antifibrotic agents that mitigate TGF-β-induced fibrosis. Ocular nanosystems are innovative drug-delivery platforms that facilitate the targeted release of therapeutic agents. Gene therapies, such as small interfering #RNA and antisense oligonucleotides, are promising approaches for selectively inhibiting angiogenesis-related gene expression. Aganirsen is efficacious in reducing the corneal neovascularization area without significant adverse effects. These multifaceted approaches underscore the corneal neovascularization management complexity and highlight ideas for enhancing therapeutic outcomes. Furthermore, the importance of combination therapies and the need for further research to develop specific inhibitors while considering their therapeutic efficacy and potential adverse effects are discussed. https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/10/5479?utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=tumblr
0 notes
Text
Wet AMD: Effective Treatment Options
Wet Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is a serious eye condition that requires prompt and effective treatment to prevent vision loss. At Sanjeevan Netralaya, we specialise in Ayurvedic retinal treatments, offering tailored solutions for wet AMD with a remarkable 100% effectiveness rate. In this blog, we'll explore effective treatment options for wet AMD and how our hospital can provide the best care for this condition.
Understanding Wet AMD
Wet AMD is a progressive eye disease characterised by the growth of abnormal blood vessels beneath the retina. These vessels leak fluid and blood, leading to damage to the macula, the part of the retina responsible for central vision. Without treatment, wet AMD can result in severe vision loss and even blindness.
Wet AMD Treatment at Sanjeevan Netralaya
Anti-VEGF Therapy: Our hospital specialises in Anti-VEGF injections, a highly effective treatment for wet AMD. These injections target vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a protein responsible for the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. By blocking VEGF, Anti-VEGF injections help reduce fluid leakage, preserve vision, and prevent further damage to the macula.
Laser Therapy: In some cases, laser therapy may be used to treat wet AMD. Our hospital utilises advanced laser technology to target and seal leaking blood vessels, reducing the risk of vision loss and stabilising the condition.
Combination Therapy: Sanjeevan Netralaya offers combination therapy for wet AMD, combining Anti-VEGF injections with other treatment modalities as needed. This approach allows us to customise treatment plans based on individual patient needs and optimise outcomes.
Regular Monitoring: We provide comprehensive monitoring of wet AMD patients, including regular eye examinations, imaging tests, and vision assessments. This allows us to track disease progression, adjust treatment plans as necessary, and ensure the best possible outcomes for our patients.
Patient-Centric Approach: At Sanjeevan Netralaya, we take a patient-centric approach to wet AMD treatment, focusing on individualised care and support. Our experienced team of eye care professionals works closely with each patient to develop personalised treatment plans tailored to their specific needs and preferences.
Conclusion
Wet AMD is a serious eye condition that requires prompt and effective treatment to preserve vision and prevent vision loss. At Sanjeevan Netralaya, we specialise in Ayurvedic retinal treatments, offering tailored solutions for wet AMD with a remarkable 100% effectiveness rate. If you or a loved one are living with wet AMD, trust Sanjeevan Netralaya for comprehensive care and the best treatment options available.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and learn more about how we can help you manage wet AMD and preserve your vision for years to come.
At Sanjeevan Netralaya we have treated over 6,00,000 + retina patients with 100% effectiveness
#amd#macular degeneration#wet macular degeneration#health & fitness#ayurveda#eyesight#ayurvedic eye treatment#sanjeevan netralaya#eye health#eyes#eye care#ayurvedic treatment#retina
0 notes
Text
Healing from Within: The Promise of Plasma Injections for Knee Joints
Introduction
Knee pain and discomfort are prevalent issues affecting millions worldwide, often stemming from injuries, arthritis, or general wear and tear. Traditional treatments like pain medication, physical therapy, or surgery offer relief to some extent, but emerging therapies are reshaping the landscape of knee joint treatment. Among these innovative approaches, plasma injections hold significant promise, harnessing the body's natural healing mechanisms to address knee joint issues. This article delves into the science behind plasma injections, their potential benefits, and the implications for knee joint health.
Understanding Plasma Injections
Plasma injections, also known as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, involve extracting a patient's blood, processing it to concentrate platelets, and then injecting this plasma-rich solution into the affected knee joint. Platelets play a crucial role in healing, containing growth factors and proteins that stimulate tissue repair and regeneration. By delivering a concentrated dose of these healing factors directly to the site of injury or degeneration, plasma injections aim to enhance the body's innate healing processes.
The Science Behind Plasma Therapy
The therapeutic effects of plasma injections stem from the bioactive molecules present in platelets. These molecules, including growth factors like platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), orchestrate various stages of tissue repair. PDGF promotes cell proliferation and angiogenesis, TGF-β regulates inflammation and tissue remodeling, while VEGF stimulates the growth of new blood vessels, enhancing oxygen and nutrient supply to the injured area. By amplifying these natural healing mechanisms, plasma injections accelerate tissue repair and alleviate knee joint symptoms.
Benefits of Plasma Injections for Knee Joints
Plasma injections offer several advantages over traditional knee joint treatments. Firstly, they are minimally invasive, involving a simple outpatient procedure with little to no downtime. Unlike surgery, which carries inherent risks and requires lengthy rehabilitation, plasma injections pose minimal risk of complications and allow patients to resume their daily activities promptly. Additionally, plasma therapy addresses the underlying cause of knee joint issues by promoting tissue regeneration, rather than merely masking symptoms with pain medication. This holistic approach not only provides symptomatic relief but also fosters long-term joint health and function.
Moreover, plasma injections are well-tolerated by most patients, as they utilize the patient's blood, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions or rejection. This makes plasma therapy a safe and viable option for individuals who may not be suitable candidates for surgery or pharmaceutical interventions. Furthermore, research suggests that plasma injections may yield lasting benefits, with many patients experiencing sustained improvement in knee function and pain relief even months after treatment. This potential for long-term efficacy positions plasma therapy as a promising alternative or adjunct to conventional knee joint treatments.
Implications for Knee Joint Health
The emergence of plasma injections as a viable treatment option holds significant implications for knee joint health and the broader field of regenerative medicine. By harnessing the body's innate healing mechanisms, plasma therapy represents a paradigm shift towards personalized, biologically-driven interventions. As our understanding of regenerative medicine continues to advance, plasma injections may pave the way for the development of novel therapies targeting a range of musculoskeletal conditions beyond knee osteoarthritis, including tendon injuries, ligament tears, and cartilage defects.
Furthermore, the non-invasive nature of plasma injections makes them accessible to a wider population, including elderly individuals or those with pre-existing medical conditions who may be at higher risk for surgical complications. This democratization of healthcare aligns with the broader trend towards patient-centered, minimally invasive treatments that prioritize safety, efficacy, and quality of life. As such, plasma therapy has the potential to revolutionize the management of knee joint disorders, offering patients a safe, effective, and sustainable solution for restoring mobility and alleviating pain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, plasma injections for knee represent a promising frontier in the treatment of knee joint issues, offering a safe, minimally invasive, and biologically driven approach to tissue repair and regeneration. By harnessing the body's natural healing mechanisms, plasma therapy addresses the underlying cause of knee pain and dysfunction, offering long-term benefits beyond symptomatic relief. As research in regenerative medicine continues to evolve, plasma injections may herald a new era of personalized, patient-centered care, transforming the landscape of orthopedic treatments and improving the quality of life for millions worldwide.
0 notes
Text
Comprehensive Overview of Arteriovenous Malformation
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) represent a complex vascular anomaly characterized by abnormal connections between arteries and veins without an intervening capillary bed. These congenital lesions can occur anywhere in the body but are most commonly found in the brain and spinal cord. While many AVMs remain asymptomatic, they have the potential to cause severe neurological deficits or even life-threatening hemorrhages. The management of AVMs poses a significant challenge to healthcare professionals due to their variable clinical presentation and potential complications. This article provides a comprehensive review of the current treatment modalities for AVMs, highlighting their efficacy, limitations, and emerging therapeutic approaches.
Treatment Modalities:
Observation and Conservative Management:
Small, asymptomatic AVMs with low hemorrhage risk may be managed conservatively through regular monitoring with neuroimaging studies.
This approach is particularly suitable for elderly patients or those with comorbidities where the risks associated with invasive treatment outweigh the potential benefits.
Microsurgical Resection:
Surgical resection involves the complete removal of the AVM nidus, aiming to eliminate the risk of hemorrhage.
Advances in microsurgical techniques, such as intraoperative angiography and neuroimaging, have improved surgical outcomes and reduced the risk of postoperative complications.
However, the success of surgical resection depends on the AVM's location, size, and proximity to critical neurological structures. Deep-seated or eloquent area AVMs present a higher surgical risk.
Endovascular Embolization:
Endovascular embolization is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the selective injection of embolic agents into the feeding arteries of the AVM, leading to occlusion and reduction of blood flow.
This technique is often used as an adjunct to surgery or radiosurgery to decrease the AVM size and vascularity, facilitating subsequent treatment modalities.
While endovascular embolization can achieve significant AVM devascularization, complete occlusion may be challenging in complex or high-flow lesions.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS):
SRS delivers a highly focused beam of ionizing radiation to the AVM nidus, inducing vascular endothelial damage and subsequent thrombosis over time.
Unlike conventional surgery, SRS is non-invasive and can be performed as an outpatient procedure, making it an attractive option for patients deemed high-risk for open surgery.
Optimal outcomes with SRS typically require a latency period of 1-3 years for complete AVM obliteration, during which patients remain at risk of hemorrhage.
Patient selection and precise delineation of the target volume are crucial for maximizing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing radiation-related complications.
Combination Therapy:
Some complex AVMs may require a multimodal treatment approach combining microsurgery, endovascular embolization, and radiosurgery to achieve optimal outcomes.
Sequential or staged therapy allows for the gradual reduction of AVM size and vascularity while minimizing the risk of treatment-related complications.
Multidisciplinary collaboration among neurosurgeons, interventional neuroradiologists, and radiation oncologists is essential for individualizing treatment strategies and optimizing patient outcomes.
Future Directions:
Targeted Therapies:
Emerging research aims to identify molecular targets and signaling pathways involved in AVM pathogenesis, paving the way for novel targeted therapeutic agents.
Potential targets include angiogenic factors, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling, and inflammatory mediators implicated in AVM development and progression.
Targeted therapies may offer a more specific and less invasive approach to AVM treatment, potentially reducing the need for conventional surgical or radiological interventions.
Gene Therapy:
Gene therapy holds promise as a potential curative strategy for AVMs by targeting genetic mutations associated with vascular dysplasia and abnormal angiogenesis.
Preclinical studies utilizing viral vectors or gene-editing technologies have shown encouraging results in animal models of AVMs, demonstrating the feasibility and safety of gene-based interventions.
Further research is needed to optimize gene delivery techniques, ensure long-term transgene expression, and evaluate the safety and efficacy of gene therapy in human subjects.
Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering:
Biomaterials and tissue engineering approaches offer innovative solutions for AVM treatment by providing biocompatible scaffolds for vascular reconstruction and targeted drug delivery.
Bioengineered constructs incorporating endothelial cells, growth factors, and extracellular matrix components can promote vascular maturation and stability, facilitating AVM regression and tissue repair.
Clinical translation of biomaterial-based therapies requires rigorous preclinical evaluation and optimization of scaffold design, biocompatibility, and integration with host tissues.
Conclusion:
The management of arteriovenous malformations poses a complex clinical challenge, requiring a multidisciplinary approach and individualized treatment strategies. While conventional modalities such as microsurgical resection, endovascular embolization, and stereotactic radiosurgery remain the mainstays of AVM therapy, ongoing research efforts are focused on developing novel targeted therapies, gene-based interventions, and biomaterials for safer and more effective treatment options. By leveraging advances in molecular biology, imaging technology, and regenerative medicine, the future holds promise for improving outcomes and reducing the morbidity associated with AVMs.

#healthcare#fitness#medical#health & fitness#Alshifa Healthcare services#treatments#Arteriovenous malformation
0 notes
Text
Gene Therapy Treatment Increasing Body's Signal for New Blood Vessel Growth Shows Promise
EXACT Trial Demonstrated Improvements in Exercise Duration, Ischemia, and Decreased Symptoms for Patients with Advanced CAD
Final 12-month data from the EXACT trial demonstrates safety and efficacy results for a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene therapy treatment for patients who have advanced coronary artery disease (CAD). The late-breaking results were presented today at the…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Can COPD be treated with stem cell therapy?
Introduction
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, refers to a group of progressive lung diseases characterized by long-term breathing problems and poor airflow. The two main conditions that fall under the COPD umbrella are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. As the lungs and airways become damaged from environmental pollutants like cigarette smoke, it becomes progressively harder for the lungs to function normally. This often leads to symptoms like shortness of breath, coughing, wheezing, fatigue, and other issues that significantly impact quality of life.
Currently, medication is relied on to treat and manage COPD symptoms, though it does not reverse underlying damage or restore lung function. Other options like pulmonary rehabilitation, oxygen therapy, lung transplantation, and smoking cessation can also help in severe cases. However, there remains an unmet need for an intervention that can repair damaged tissue and regenerate lost lung cells. This has led researchers to explore whether stem cell therapy may hold promise as a treatment for COPD.
What are stem cells?
Stem cells are unique cells in our bodies that can both self-renew and differentiate into specialized cell types. There are different classes of stem cells:
Embryonic stem cells: Derived from embryos within a few days of fertilization, these cells are considered pluripotent, meaning they can become any cell type in the body. However, research on human embryos faces ethical issues.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs): Adult cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to an embryonic stem cell-like state with pluripotency. iPSCs avoid the use of embryos.
Adult (somatic) stem cells: Present in adult tissues like bone marrow, brain, blood, skin, and muscles. They are multipotent, with the ability to become a few specialized cell types.
In the context of COPD, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) hold particular promise. MSCs are multipotent adult stem cells that can differentiate into cells that make up muscles, bones, cartilage, fat, and other connective tissues. They are most commonly derived from bone marrow but can also be found in fat, dental pulp, and umbilical cord blood.
How could stem cells help treat COPD?
Research suggests MSCs may help treat COPD through these mechanisms:
Lung regeneration: MSCs have the potential to differentiate into lung cell types like epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and pneumocytes that form the gas exchange surface in the lungs. This raises hopes that MSCs could help regrow damaged or missing lung tissue.
Immunomodulation: MSCs secrete cytokines and growth factors that reduce inflammation and regulate the immune system. Persistent inflammation driven by the immune response is a major factor in COPD progression.
Angiogenesis: MSCs stimulate the growth of new blood vessels. In COPD, impaired vascularization and oxygen delivery to lung tissues are issues that may be addressed in this manner.
Antifibrotic effects: COPD lungs experience fibrosis or scarring of pulmonary tissue. Studies show MSCs help reduce fibrosis and promote wound healing through matrix remodeling enzymes.
Neurotrophic support: Dysregulation of the pulmonary neuroimmune axis occurs in COPD. MSCs secrete neurotrophins to stabilize the local neural microenvironment in the lungs.
Overall, through their multipotent and immunomodulatory properties, MSCs aim to suppress lung destruction, restore lung function, and mitigate symptoms in COPD through tissue repair and regeneration. Let's explore the evidence behind this stem cell approach.
Clinical trial evidence
A range of small, early-phase safety and proof-of-concept trials have investigated the potential of stem cell therapy in COPD patients so far:
Intravenous infusion: In a phase I trial, 20 COPD patients received two intravenous infusions of autologous bone marrow-derived MSCs a month apart. At six months, significant increases in exercise capacity and health-related quality of life were observed compared to baseline, along with decreased emphysema in high-resolution CT scans. Similar improvements were seen in other studies testing intravenous MSC administration.
Endobronchial transplantation: Another phase I study involving 14 patients delivered autologous bone marrow-derived MSCs via a bronchoscope into the lungs. At three months, lung function and walking distance increased while clinical symptoms decreased relative to before treatment. Endobronchial delivery likely enhances engraftment in the target tissues.
Intratracheal infusions: A trial in 16 COPD patients evaluated fat-derived MSCs administered by bronchoscope through the trachea. Post-treatment, they saw elevated levels of the lung surfactant-associated protein-A and reduced numbers of inflammatory cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, implying a dampened inflammatory reaction alongside potential regeneration.
While the numbers are still low, no significant safety issues have been reported with MSC use in COPD trials thus far. Further evaluation in larger cohorts continues across the world. Platform trials like ONE-BRIDGE are also exploring more variables including factors like donor age, route of administration, and dosage levels.
Real-world examples
R3 Stem Cell is a stem cell bank based in India with facilities for treating patients using autologous adipose stem cell therapy for various conditions. On their site, they discuss indications for which they have seen benefits with COPD patients, including:
Improved breathing patterns and lung capacity parameters like FEV1 and FVC. Following treatment, patients demonstrate measurable gains in pulmonary function parameters.
Reduced exacerbations and fewer hospitalizations. Patients experience far fewer worsenings of respiratory symptoms requiring medication changes or hospital admissions post-treatment.
Enhanced quality of life. Patients note returned abilities to conduct daily chores, perform physical work and exercise, and an overall better feeling of well-being.
Improved breathing comfort and exercise tolerance. Shortness of breath is diminished. Patients find they no longer get breathless from routine movements and can walk longer distances without gasping for air.
Mitigation of chronic lung infections. With strengthened immunity and fewer exacerbation-prompted hospital visits where patients are exposed to illnesses, recurring lung infections tend to attenuate.
Disease stabilization halts further decline. For patients whose lung function was progressively deteriorating each year, treatment allows stabilization preventing additional loss.
These observations provide real-world insight into how adipose stem cell therapy may benefit COPD patients outside the constraints of clinical trials. Of course, larger studies are still vital to fully validate the approach.
Future considerations
While preliminary results are promising, stem cell therapy for COPD remains in the exploratory phase. Questions that still need answers include:
Determining the optimal cell dose and route of administration. More research aims to establish standardized protocols.
Longer-term follow-up data. Currently, most trials only follow patients up to 6-12 months. Longitudinal studies spanning years are essential.
Delineating which COPD subgroups benefit most. Further stratification is important based on disease severity, emphysema presence, exacerbation frequency, and other criteria.
Elucidating the precise mechanisms of action via lung tissue analysis. Further validation of stem cell effects on regeneration, remodeling, and inflammation modulation is underway.
Conducting comparative effectiveness studies. Head-to-head trials against conventionally available COPD treatments will help define the treatment landscape.
Ensuring consistent quality and safety across providers. Optimization of donor screening, cell manufacturing, and administration standards on large cohorts will strengthen the field.
As more long-term safety and efficacy results emerge, stem cell therapy could become an accepted component of COPD management. It holds great potential to improve care for a condition representing a major worldwide health burden. Further clinical advances and research remain on the horizon.
Conclusion
In summary, while definitive conclusions are still being drawn, initial experiments show stem cell therapy may effectively treat COPD symptoms through regenerative and immunomodulating actions. Mesenchymal stem cells administered through various routes seem to help minimize lung injury and enhance recovery by regenerating tissue and counteracting inflammation. Real-world cases also confirm gains in lung function and quality of life following treatment through adipose stem cell therapy. While larger controlled studies are still warranted, early evidence establishes stem cell therapy as a promising avenue worth further exploration for COPD, a progressive and irreversible disease currently lacking an intervention that can reverse the damage. Continued investigation will likely optimize this cell-based approach and bring it closer to becoming part of standardized COPD care pathways.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Navigating Colorectal Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide to Various Treatment Options By the Best Colorectal Surgeon in Surat

Colorectal cancer is a significant health concern, ranking as one of the most common cancers worldwide. Early detection and advancements in medical science have broadened the spectrum of treatment options available for individuals diagnosed with colorectal cancer. In this blog, we will explore various approaches, as shared by the best colorectal surgeons in Surat for managing colorectal cancer, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy.
1. Surgery: The Primary Treatment Option
Surgery is often the primary treatment for colorectal cancer, especially in cases where the tumour is localized. The goal of surgery is to remove the tumour and nearby lymph nodes, preventing the spread of cancer. Different surgical procedures may be employed based on the location and stage of the cancer. For example, a colectomy involves the removal of a portion of the colon, while a rectal resection addresses tumours in the rectum.
2. Chemotherapy: Systemic Treatment for Colorectal Cancer
Chemotherapy utilizes powerful drugs to target and kill cancer cells throughout the body. In colorectal cancer, chemotherapy may be administered before surgery (neoadjuvant) to shrink tumours, after surgery (adjuvant) to eliminate remaining cancer cells, or as the primary treatment for advanced or metastatic cases.Our gastro surgeons in Surat at Vedam Gastro hospital are of the opinion that while chemotherapy can cause side effects, advancements in drug development aim to minimize these effects while maximizing the therapeutic impact.
3. Radiation Therapy: Precision in Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy involves using high doses of radiation to target and destroy cancer cells. In colorectal cancer, radiation therapy is commonly used before surgery to shrink tumours, making them easier to remove. It may also be employed after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. Gastro hospitals in Surat are leveraging the recent developments in radiation therapy techniques, such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), to allow for more precise targeting of cancer cells, reducing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
4. Targeted Therapies: Precision Medicine for Colorectal Cancer
Targeted therapies focus on specific molecules or pathways involved in cancer growth, allowing for more precise and effective treatment. In colorectal cancer, targeted therapies may include drugs that target proteins like EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) or VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor), which play key roles in cancer development. These therapies can be used alone or in combination with other treatments, providing tailored options based on the unique characteristics of the cancer.
5. Immunotherapy: Empowering the Immune System
Immunotherapy harnesses the body’s own immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Colorectal cancer, particularly tumours with specific molecular features, may respond to immunotherapies such as immune checkpoint inhibitors. These drugs release the brakes on the immune system, allowing it to better target and destroy cancer cells. While immunotherapy has shown promise in certain cases, ongoing research aims to expand its applications and enhance its effectiveness in colorectal cancer treatment.
6. Clinical Trials: Advancing Treatment Paradigms
Participation in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to the advancement of colorectal cancer care. Clinical trials explore novel therapies, combinations of existing treatments, and innovative approaches to improve outcomes and reduce side effects. Patients considering clinical trials should consult with their healthcare team to understand the potential benefits and risks associated with participation.
7. Multidisciplinary Approach: Collaborative Care for Optimal Outcomes
Colorectal cancer treatment often involves a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, and other specialists. This collaborative approach ensures that each patient receives comprehensive care tailored to their specific needs. According to our experts, being one of the best colorectal surgeons in Surat, the treatment plans may be adjusted based on the tumour’s characteristics, stage of cancer, and individual patient factors, emphasizing the importance of personalized medicine in colorectal cancer management.
8. Supportive Care: Enhancing Quality of Life
Supportive care is an integral component of colorectal cancer treatment, focusing on improving patients’ quality of life throughout the journey. At Vedam gastro hospital being one of the best stomach hospitals in Surat, we provide supportive care measures including pain management, nutritional support, psychological counselling, and addressing treatment-related side effects. Palliative care, provided in conjunction with cancer-directed therapies, aims to alleviate symptoms and enhance overall well-being.
Conclusion
The landscape of colorectal cancer treatment has evolved significantly, offering a range of options tailored to individual cases. From surgery and chemotherapy to radiation therapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy, patients and healthcare professionals have a diverse toolkit for managing colorectal cancer. Embracing a multidisciplinary approach, staying informed about the latest advancements, and considering clinical trial opportunities are crucial elements in optimizing treatment outcomes.
0 notes
Text
An Overview of the Age Related Macular Degeneration Market: Trends and Insights
The age-related macular degeneration (AMD) market is influenced by various trends and insights that shape its dynamics and growth trajectory.
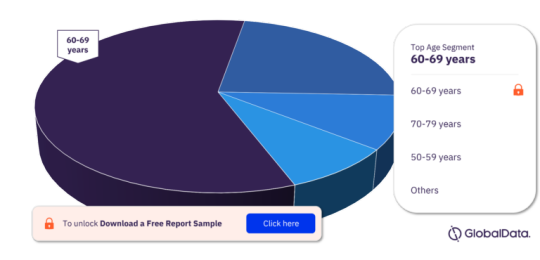
For more age segment insights, download a free report sample
Here's an overview of some key trends and insights in the AMD market:
Prevalence and Demographics: AMD primarily affects older adults, particularly those aged 50 and above. With global aging populations, the prevalence of AMD is increasing steadily. This demographic trend drives demand for AMD treatments and diagnostic solutions.
Advancements in Diagnostic Technologies: Innovations in diagnostic technologies, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fundus autofluorescence imaging, have revolutionized the early detection and monitoring of AMD. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention and management, potentially slowing disease progression and preserving vision.
Treatment Landscape Evolution: The treatment landscape for AMD has evolved significantly over the years. The introduction of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) therapies, such as ranibizumab and aflibercept, has revolutionized the management of neovascular (wet) AMD, leading to improved visual outcomes for patients.
Emerging Therapeutic Approaches: Alongside anti-VEGF therapies, several emerging therapeutic approaches are being explored for AMD treatment. These include novel drug delivery systems, gene therapies, complement inhibitors, and regenerative medicine approaches aimed at addressing various aspects of AMD pathophysiology.
Personalized Medicine: There is a growing emphasis on personalized medicine in AMD treatment, driven by the recognition of inter-individual variability in treatment response and disease progression. Biomarkers, genetic testing, and imaging biomarkers are being investigated to tailor treatment strategies based on individual patient characteristics.
Healthcare Policy and Reimbursement Landscape: Reimbursement policies and healthcare regulations influence access to AMD treatments and diagnostic services. Variations in reimbursement policies across regions can impact market access and adoption rates for innovative therapies.
Patient-Centric Care Models: Patient-centric care models are gaining prominence in AMD management, focusing on holistic patient care, education, and support services. Multidisciplinary care teams comprising ophthalmologists, optometrists, retinal specialists, and allied healthcare professionals play a crucial role in delivering comprehensive care to AMD patients.
Research and Development Investments: Pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, and academic institutions continue to invest heavily in AMD research and development (R&D). Clinical trials are underway to explore novel therapeutic targets, combination therapies, and innovative treatment modalities to address unmet needs in AMD management.
Global Market Expansion: The AMD market is expanding globally, with significant growth opportunities in emerging markets such as Asia-Pacific and Latin America. Rising healthcare expenditure, improving healthcare infrastructure, and increasing awareness of AMD contribute to market growth in these regions.
Collaborations and Partnerships: Collaboration between industry players, research organizations, and healthcare providers is essential for driving innovation and accelerating the development of new AMD therapies and diagnostic solutions. Collaborative efforts facilitate knowledge sharing, resource pooling, and the translation of scientific discoveries into clinical practice.
In summary, the AMD market is characterized by ongoing advancements in diagnostics and therapeutics, a shift towards personalized medicine, and a focus on patient-centric care models. Continued investments in research, collaborations, and global market expansion efforts are expected to shape the future landscape of AMD management.
0 notes
Text
Protecting Vision: Expert Diabetic Retinopathy Care from World Diabetes Centre's Specialist Doctors
Welcome to the World Diabetes Centre, where our team of diabetic retinopathy doctors is committed to safeguarding the vision of individuals living with diabetes. Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye complication that requires specialized care to prevent vision loss and preserve eye health. Let's explore the essential role of our diabetic retinopathy specialist doctors and how they can support you in protecting your vision.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that affects the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage these blood vessels, leading to leakage, swelling, and the growth of abnormal blood vessels. If left untreated, diabetic retinopathy care can cause vision loss and even blindness.
Meet Our Diabetic Retinopathy Specialist Doctors: Leaders in Vision Care
At the World Diabetes Centre, our team includes leading experts in diabetic retinopathy care. Trained in ophthalmology and specialized in the management of retinal diseases associated with diabetes, our diabetic retinopathy specialist doctors possess the knowledge and expertise needed to provide comprehensive care to individuals with diabetic retinopathy.
Comprehensive Care for Diabetic Retinopathy
Our diabetic retinopathy specialist doctors offer a range of services to help manage diabetic retinopathy and protect vision:
Early Detection and Diagnosis: Early detection of diabetic retinopathy is crucial for preventing vision loss. Our specialist doctors use advanced diagnostic techniques, such as retinal imaging and dilated eye exams, to detect signs of retinal damage and intervene promptly.
Treatment Options: Depending on the severity of diabetic retinopathy, treatment options may include laser therapy, intravitreal injections of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) medications, or vitrectomy surgery. Our specialist doctors work closely with patients to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to their individual needs and preferences.
Ongoing Monitoring: Regular eye examinations are essential for monitoring the progression of diabetic retinopathy and assessing the effectiveness of treatment. Our specialist doctors provide ongoing monitoring and adjustments to treatment plans as needed to optimize vision outcomes.
Join Our Community of Diabetes Specialists
If you or a loved one is living with diabetes, regular eye examinations are essential for early detection and treatment of diabetic retinopathy care. At the World Diabetes Centre, our diabetic retinopathy specialist doctors are here to provide expert care and support to help you preserve your vision and enhance your quality of life. Schedule a consultation with one of our specialists today and take the first step towards protecting your vision for years to come.
0 notes