#xen vps provider
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Link
SSDs and HDDs are two kinds of storage devices that are utilized as the local drive for personal computers. If you are willing to buy personal computers, then you have to determine which one you want for you.
#Cheap XEN VPS#KVM VPS Hosting#Xen cheap VPS#XEN VPS provider#reseller hosting USA#reseller hosting plans#web hosting provider in India#XEN VPS server#VPS India#Cheap VPS Server India#unlimited reseller hosting plans in India#Unlimited Reseller Hosting#Cheap KVM VPS#Cheap Windows VPS#cheap reseller unlimited web hosting#unlimited reseller hosting India#reseller hosting plans USA#best reseller hosting plans#cheap windows VPS hosting#cheap windows VPS server#XEN Virtual Private Server#cheap vps reseller#cheap VPS India#cheap VPS hosting India#cheap VPS Server in India#Cheap VPS Servers#cheap reseller hosting USA#affordable reseller web hosting#cheap reseller web hosting plans#cheap vps reseller hosting
0 notes
Link

Nextraone is one of the top Cheapest Web Hosting Company in India. We Provide Windows Plesk Hosting, Reseller Hosting, Linux cPanel Hosting, Cloud VPS, Dedicated Server, OpenVz VPS and XEN VPS in Affordable Cost.
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Multiple computer operating systems executing on the same computer hardware will provide for you the most efficient Hosting solution you’ve ever experienced.
#share #like #follow #Xen #virtualdedicatedhosting #dedicatedhosting #xenhosting #virtualhosting #vps #hosting
https://whitelabelitsolutions.com/services/managed-servers/vps-servers/xen-vps/
1 note
·
View note
Text
AI in online retail: How is hyper-personalisation driving the sector?
Innovation progresses are enabling retailers to introduce new degrees of customisation, with organizations introducing artificial intelligence (AI)- based hyper-personalisation encounters to tailor and pursue consumer goods shopping directions.
Retail Insight Organization investigates the universe of AI in online retail with Raj Badarinath, marketing and environments VP at US-based omnichannel personalisation stage RichRelevance, to find out how hyper-personalisation is driving the industry.
What is hyper-personalisation? Hyper-personalisation combines ongoing social information with unstructured information from printed information found in item portrayals, ratings and surveys using normal language processing (NLP) to turn into their own tastemaker and caretaker.
Badarinath says: "Clients today anticipate customized encounters, with items and administrations tailored to their individual inclinations. In light of this, hyper-personalisation is knowing and serving your client as an individual, and not part of a harsh, probabilistic fragment. As a result, it makes a 'fragment of one' for every client, by understanding their preferences, inclinations and conduct - inspiring them to find more items and content that will suit their extraordinary taste and providing a useful, charming and absolutely special shopping experience."
What is consumers' opinion about the utilization of hyper-personalisation? According to the most recent 'Unpleasant or Cool' study, by RichRelevant, of the 2,577 respondents across the UK, France and Germany, 80% of UK consumers need transparency from retailers about the utilization of AI.
The investigation additionally discovered that 75% of UK respondents are unfamiliar with AI, 43% worth assets like AI to customize their shopping encounters and 80% of UK respondents believe retailers should unveil assuming they are using AI to market items and outline how they are using the innovation.
Close to 33% of UK consumers said they are willing to share more private information for a superior shopping experience.
How can AI customize online shopping?
Badarinath says: "Online shopping offers a seemingly infinite array of decisions on virtual aisles and it's leaving customers overpowered, less happy with their buys and paradoxically more reluctant to settle on buying choices in spite of the variety.
"The reaction to this lies in personalisation. With the utilization of AI-driven machine learning which investigations customers' way of behaving online, gauging client interests, learning and tailoring proposals for every individual client, hyper-personalisation assists brands and retailers with offering a really engaging and positive experience to consumers.
"Today, online shops are ready to tailor everything from searching for items, auto-ideas, customized route and classifications to the substance of their sites and tailored offers for every client, depending on their requirements and affinities. At the point when it seems like the store was fabricated only for that individual client, this is hyper-personalisation working.
"Hyper-personalisation can't occur without AI, explicitly the licensed Xen AI engine - which utilizes NLP and Machine Learning to all the more likely understand and individualize for every client. Xen AI permits computerized pioneers to convey 'techniques' - the pre-defined choice models for retail-with the certainty that the best methodology among the set will be consequently applied to each choice to make the most customized insight for any customer."
How could hyper-personalisation make a superior client experience? "Each business today, regardless of industry, knows its goods and administrations are becoming quickly commoditised. Competing and winning require separation through noteworthy encounters as the following evolutionary move toward the Experience Economy.
"Clients today have more choices than any other time, as well as the necessary resources to secure anything they could need thanks to online shopping and worldwide conveyances. Shopping has never been so natural - however what customers need is importance: to feel perceived and grasped by their number one brands. All things considered, dependability goes the two different ways, and for somebody to remain faithful to a brand or retailer for quite a long time they need to get something consequently.
"What hyper-personalisation gives in this sense is a better encounter, one that shows clients that they are individuals according to the brand and not simply parts of a segment.
"In offering customers an encounter tailored to their own, self-expressed and implicit necessities, preferences and inclinations, hyper-personalisation brings the shopping experience from unimportant or even dreary to fulfilling and extraordinary. Along these lines, it assists brands and retailers with building consumer steadfastness, while customers are ready to appreciate shopping in conditions, be they online or offline, tailored to them."
0 notes
Text
Working with qemu-img in Linux: This is a brief qemu-img cheatsheet for working with qemu-img command on Linux and Unix systems supporting qemu. I made this qemu-img cheatsheet for my own reference and saw a need to share with you guys. Before working with the qemu-img command to perform any disk operation, It’s good to first understand what qemu is and how it is used in Linux and Virtualization world. What is Qemu? According to the Qemu about page, QEMU is defined as a generic and open source machine emulator and virtualizer. This means that Qemu can be used as machine emulator to run Operating systems and programs for one machine on a different machine. An example is running ARM program on x86 PC. In this case, QEMU can use other hypervisors like Xen or KVM for CPU extensions, to achieve what is commonly referred to as Hardware Assisted Virtualization When QEMU is used as a virtualizer, it executes the guest code directly on the host machine CPU to achieve near narrative performances. QEMU image formats are supported by most VPS cloud provides like Amazon, Digital Ocean, Linode, OVH and many others. What is qemu-img? qemu-img is the command line utility that’s used to convert various file systems used by hypervisors like Xen, KVM, VMware, VirtualBox. qemu-img is used to format guest images, add additional storage devices and network storage e.t.c. The output image format can be imported to VPS cloud providers like Openstack and other providers like Cloudstack. This working with qemu-img cheatsheet will show you a couple examples. How to Install qemu-img in Linux? The qemu-img command is installed by default with the libvirt stack: How to install KVM on RHEL/CentOS 8, Fedora, Arch Linux, CentOS, Ubuntu/Debian, SLES Commonly used qemu-img command options The qemu-img uses the following general syntax: qemu-img subcommand [options] The following list shows common subcommands for working with qemu-img: Subcommand Description create Used to create a new disk image on the file system. check Used to check an existing disk image for errors. convert Used to converts an existing disk image from one format to another. info Used to display information about a disk image. snapshot Used to manage snapshots of an existing disk image. commit Use this to apply changes made to an existing disk image. rebase Used to create a new base image based on an existing disk image. resize Used to increase or decrease the size of an existing disk image. Common options Option Explanation – O output format -f specify disk format Supported disk formats The following image formats are supported : Format Description raw This is the default image format. Can be exported to all other emulators. qcow2 QEMU image format which is most versatile format. vmdk VMware compatible image format cloop Useful only to reuse directly compressed CD-ROM images present e.g in Knoppix CD-ROMs. It is Linux compressed Loop image. Working with qemu-img: Examples Below are some of the examples of working with qemu-img . Create a new disk image with qemu-img create Syntax: qemu-img create -f fmt fname size Create raw disk image of size 10 GB: $ qemu-img create -f raw ubuntu.img 10G Formatting 'ubuntu.img', fmt=raw size=10737418240 $ qemu-img info ubuntu.img image: ubuntu.img file format: raw virtual size: 10G (10737418240 bytes) disk size: 0 Replace raw with qcow2, vdk, vmdk to create such formats. Have a look at below for vmdk: $ qemu-img create -f vmdk ubuntu.vmdk 10G Formatting 'ubuntu.vmdk', fmt=vmdk size=10737418240 compat6=off hwversion=undefined $ qemu-img info ubuntu.vmdk image: ubuntu.vmdk file format: vmdk virtual size: 10G (10737418240 bytes) disk size: 12K cluster_size: 65536 Format specific information: cid: 1484281290 parent cid: 4294967295
create type: monolithicSparse extents: [0]: virtual size: 10737418240 filename: ubuntu.vmdk cluster size: 65536 format: Convert disk image with qemu-img convert Syntax: qemu-img convert -O out_fmt fname out_fname Example: Convert vmdk image to qcow2 $ qemu-img create -f vmdk ~/ubuntu.vmdk 10G Formatting '/home/josepy/ubuntu.vmdk', fmt=vmdk size=10737418240 compat6=off hwversion=undefined $ qemu-img convert -O qcow2 ~/ubuntu.vmdk ~/ubuntu.qcow2 $ qemu-img info ~/ubuntu.qcow2 image: /home/josepy/ubuntu.qcow2 file format: qcow2 virtual size: 10G (10737418240 bytes) disk size: 196K cluster_size: 65536 Format specific information: compat: 1.1 lazy refcounts: false refcount bits: 16 corrupt: false Check for disk with qemu-img check Syntax: qemu-img check -f fmt fname Example: $ qemu-img check ubuntu.vmdk No errors were found on the image. Resize disk image with qemu-img resize WARNING: Before using this command to shrink a disk image, you MUST use file system and partitioning tools inside the VM to reduce allocated file systems and partition sizes accordingly. Failure to do so will result in data loss! Syntax: resize filename [+ | -]size Example: Increase disk image by 3GB $ qemu-img create -f qcow2 ubuntu.qcow2 10G Formatting 'ubuntu.qcow2', fmt=qcow2 size=10737418240 encryption=off cluster_size=65536 lazy_refcounts=off refcount_bits=16 $ qemu-img info ubuntu.qcow2 image: ubuntu.qcow2 file format: qcow2 virtual size: 10G (10737418240 bytes) disk size: 196K cluster_size: 65536 Format specific information: compat: 1.1 lazy refcounts: false refcount bits: 16 corrupt: false $ qemu-img info ubuntu.qcow2 image: ubuntu.qcow2 file format: qcow2 virtual size: 10G (10737418240 bytes) disk size: 196K cluster_size: 65536 Format specific information: compat: 1.1 lazy refcounts: false refcount bits: 16 corrupt: false $ qemu-img resize ubuntu.qcow2 +3G Image resized. $ qemu-img info ubuntu.qcow2 image: ubuntu.qcow2 file format: qcow2 virtual size: 13G (13958643712 bytes) disk size: 200K cluster_size: 65536 Format specific information: compat: 1.1 lazy refcounts: false refcount bits: 16 corrupt: false You should notice that the size was increased from 10GB to 13GB NOTE: After enlarging the disk image, you must use file system and partitioning tools inside the virtual machine to actually begin using the new space. How to extend/increase KVM Virtual Machine (VM) disk size How to extend root filesystem using LVM in Linux Managing snapshots with qemu-img snapshot Snapshots are often used to save virtual machine in a particular state. It is a snapshot of the complete environment in which a VM Guest is running. A snapshot normally includes the state of: memory (RAM) the processor (CPU) devices And all writable disks. In order to use snapshots, your VM Guest must contain at least one writable hard disk image in qcow2 format. This device is usually the first virtual hard disk. Working with qemu-img snapshots is illustrated below. Example: Create of current state of VM with a name ubuntu_fresh $ qemu-img snapshot -c ubuntu_fresh ubuntu.qcow2 To list snapshots of VM , use: $ qemu-img snapshot -l ubuntu.qcow2 Snapshot list: ID TAG VM SIZE DATE VM CLOCK 1 ubuntu_fresh 0 2017-03-06 18:41:21 00:00:00.000 If something breaks in your Virtual machine and you need to restore the state of the saved snapshot, you the id given by command above: $ qemu-img snapshot -a 1 ubuntu.qcow2 To delete snapshot: $ qemu-img snapshot -d 1 ubuntu.qcow2 Rebasing derived images $ qemu-img rebase -b /new/ubuntu.raw ubuntu.qcow2 Install OS to created disk image To install an operating system into your disk image, you need the installation medium such as cdrom or ISO image file.
The installation medium should not be mounted because QEMU accesses the media directly. $ qemu-system-x86_64 \ -m 512\ -hda ~/Desktop/virt/arch.qcow2 \ -cdrom ~/iso/CentOS-7-x86_64-Everything-1611.iso \ -enable-kvm You can specify multiple images: -hda ubuntu.qcow2 -hdb files.img -hdc container.qcow2. ISO image location can be cdrom device, -cdrom dev/cdrom
0 notes
Link
#2usdvps#bestcheapvps#budgetkvmvps#cheapvps#cheapestvps#kvm#kvmvps#losangeles#losangelesvps#netherlands#netherlandsvps
0 notes
Text
Cloud Servers

Cloud servers have become a fast, reliable, and affordable solution to server hosting. They provide a lot of benefits over traditional servers. With the growing popularity of cloud servers, we can now host any type of website on the cloud without having to worry about hardware failures or maintenance. On this page, I will be talking about what cloud hosting is and why you might want to consider getting it as your main source for server hosting.
What are Cloud Servers?
Cloud servers are similar to traditional servers, but they exist in the cloud. The term “cloud” is a catch-all term for a group of virtual machines, which can be located anywhere in the world. In other words, you don’t have to own or operate your own hardware to host your applications.
The biggest advantage of cloud servers is that you don’t need to worry about hardware upgrades or maintenance issues. You just pay for what you use and get it up and running quickly. This can be a huge time saver for businesses that are looking to scale their operations quickly without having to invest heavily in hardware or software infrastructure.
Here are Some of the Benefits of Using a Cloud Server
Cost-efficiency - cloud servers are extremely inexpensive compared to traditional server solutions. You'll pay just pennies per hour for your server space, which makes it very easy to keep your costs down.
Flexibility - Cloud servers are completely flexible, meaning that you can scale up or down as needed without having to worry about anything else. This flexibility helps with scalability issues that arise when running traditional servers on your own.
Security - Since nobody owns your data, you have complete control over what happens with it. If someone hacks into your server and takes over everything, nobody will be able to access the data without your permission.
Performance - Cloud servers offer 24/7 access to thousands of specialized programs that make it possible for you to get the performance you need out of your site while still keeping costs low.
Cloud Server Pricing
There are Two main categories of cost associated with cloud server hosting:
Platform fees - This covers the operating costs for each particular server software package and its associated support options. The price is determined by the size and type of package selected for your application. For example, if you want to host WordPress blogs on your virtual private server (VPS), you'll need to pay extra for additional software packages such as cPanel or Plesk.
Bandwidth costs - This covers the amount of data transferred over your network connection between your web browser and your website's data center. Bandwidth can also be measured against other users on the same network connection if you're sharing resources with them via virtual LANs (VLANs) or private internet access (PIA).
Virtualization and the cloud server
Virtualization is a technique that allows multiple physical servers to run as one logical server. A virtual machine (VM) is a software image that runs directly on top of the hardware of the host machine, without requiring any changes to the underlying hardware. The VM is accessible via a hypervisor such as Xen (XenServer), KVM (KVM), ESXi or VMWare ESXi.
The benefits of virtualization include:
Reduced hardware requirements, as one server can run multiple operating systems simultaneously using virtual machines; this also reduces maintenance costs.
Improved resource utilization, as each VM has its own dedicated CPU, disk and memory resources; this promotes better utilization of resources.
Improved security, as each VM is isolated from other VMs on the same physical server.
Conclusion
The cloud server works by receiving user traffic and providing them with the server resources they are using. The cloud provides a shared environment, allowing users to access files as if it was their own server. As a result, there is less stress placed on the device and more room for users to store their files.
To improve their services, many companies provide cloud servers with their own expertise in maintaining a server. These servers generally come with backup servers in case one fails.
When the cloud is down or under maintenance, backup servers relieve some of the stress put on the main one. The basic idea behind the cloud server is that if one company cannot handle its users, then another company will likely have extra space to use. This allows each provider to focus on their specific services, making the price cheaper and the overall quality of service greater.
#cloud#cloudserver#cloudhosting#cloudhostingproviders#cloudhostingcompanies#cloudserverproviders#cloudservercompanies#server#domain#webhosting#webhostingservices#webhostingcompany#wordpress
0 notes
Link
#Cheap XEN VPS#Cheap VPS Server India#KVM VPS Hosting#xen vps cheap#xen vps provider#xen vps server#VPS India#Cheap KVM VPS#Cheap Windows VPS#cheap windows vps hosting#cheap windows vps server#XEN Virtual Private Server Plans#cheap vps reseller#cheap VPS hosting India#cheap VPS India#cheap VPS Server in India#Cheap VPS Servers#cheap reseller hosting USA#cheap vps reseller hosting#best cheap reseller hosting#top vps provider#fastest vps#xen VPS#best VPS reseller hosting#xen vps hosting#vps net
0 notes
Text
What is cloud hosting, and how does it work? What kinds of websites are suitable for cloud hosting?
Every day, cloud hosting gains popularity. Due to its convenience and flexibility, businesses favour it. It's speedy and trustworthy. Traditional web hosting uses one or more physical servers to host one or more websites.
Nope. Cloud hosting can help your organisation develop in countless ways. First, let's define cloud hosting and why it's better.
Cloud hosting?
Cloud hosting uses several servers to host websites. It uses several servers to balance site load, assure security, and provide reliable infrastructure.
A physical server is divided into virtual cloud servers. These workstations create a website-hosting network. Interconnected cloud structure improves uptime and reduces downtime.
Cloud hosting's infrastructure differs from VPS and dedicated servers. Conventional web hosting centralises all sites on one server.
What websites are cloud-hosted?
Cloud hosting's best feature is the website's security. This makes it a safe platform for hosting websites and apps. All major news outlets, e-commerce sites, and high-traffic websites employ Cloud. The cloud offers organisations everything they need to run websites and apps smoothly.
Some of these websites may demand higher protection for client and payment data. In this instance, they may employ a private cloud. Private clouds are hosted on a dedicated server to prevent third-party incursion.
Cloud hosting is suitable for websites with many visitors and enterprises with large files and data. Cloud hosting's architecture makes it easy to predict traffic spikes, which occur when you have many visitors.
Cloud hosting takes care of load-balancing and assures a virtual server's resources won't be overrun during traffic surges like major sales or popular web content.
It's why Cloud hosting is pricier than VPS or dedicated hosting.
What's cloud hosting?
Virtualization enables cloud hosting. It divides a physical server into cloud servers. These cloud servers constitute a website-hosting network. This effective structure is preferred by enterprises of all sizes worldwide.
Cloud computing uses a cluster of servers. Its benefits include reducing reliance on a single machine by distributing the load. Each computer in cloud hosting has a distinct task based on its memory, hard disc, and processor. Hypervisors run cloud software.
Hypervisors manage software-based computers. Servants. Common hypervisors include Xen, VMware, and Hyper-V.
Cloud hosting specifications:
Cloud resources are scalable.
2. It's hardware-fault-free.
3. It's speedy and reliable.
4. You can upgrade our cloud-based servers whenever you wish.
5. It improves business productivity by reducing worker and customer browser wait times.
Why should your organisation use Cloud hosting?
Cloud hosting helps when your website can't run on shared hosting. It's a common alternative that prevents shared server burden. Cloud hosting lets you enjoy dedicated server benefits without the downsides. Cloud hosting? - Discover!
Here are some advantages of cloud hosting for your company website over traditional hosting:
Availability
Cloud hosting has this benefit. Your firm can always use more resources. You can upgrade RAM and CPU as website traffic increases. Cloud hosting lets you add and delete website resources as needed.
Layoff
Cloud hosting eliminates server failure. When one server fails, the other maintains your website up.
Business continuity
Can you ensure your internal servers won't crash? Is there a plan to get these back online quickly? Answer: cloud hosting. Cloud servers reduce data loss's devastating impact.
Pay-per-use
Cloud server hosting is cost-effective. With cloud hosting, you pay only for the resources you use, so you can control your spending. You can upgrade or downgrade as needed. Cloud hosting is cheaper than VPS server hosting.
Security
Your data is safe and protected 24*7. Cloud hosting's benefits and security go hand-in-hand. When you put your website on Cloud, you avoid hacking, data theft, unauthorised access, and identity theft.
Load-balancing
Since your data is on numerous servers, you'll never lose data. When one server goes down, another takes over, and your site runs 24/7. This balances server load and boosts system speed.
Flexibility
Cloud storage and bandwidth are flexible. It makes scaling the cloud easier. It simplifies application testing and deployment. These apps are easy to install or remove.
Competition
Cloud hosting delivers cost-effective enterprise-class technology, pay-as-you-go services, and cloud business apps. It lowers cloud hosting prices.
Cloud hosting disadvantages?
Public Cloud hosting compromises security and control. Some organisations fear losing control of data and apps outside their boundaries. We think this is a perceptual fallacy and that most Cloud hosting firms offer security levels above what most enterprises can afford.
Unless they operate in a highly regulated environment or store sensitive data, businesses shouldn't worry about losing control or data privacy. In these situations, a private Cloud would help with compliance.
Why is cloud hosting better?
Cloud hosting is more efficient and faster than dedicated servers. Evenly distributed servers make cloud hosting websites more stable. Without load balancing, dedicated servers can't compete with cloud hosting. Dedicated servers can't compete with cloud hosting without hardware load balancing.
Soon, web designers and hosting firms will prefer cloud hosting over dedicated. Web hosting will soon be cloud-based.
Looking for a Cloud Hosting provider?
After deciding to employ cloud hosting, a business owner should make sure the hosting company delivers all the rewards. The host should have enough servers to manage traffic and data transfer. Choosing a Cloud hosting service brings more benefits than difficulties, but you still need a trusted organisation.
0 notes
Text
Online Web Hosting Service Gwalior +91-9599526129
Best Online Web Hosting Service in Gwalior +91-9599526129
The Best Online Web Hosting service in Gwalior has been growing at a fast pace over the past couple of years and there are many Web Hosting providers fighting to gain your business and keep it with them in order to make money off you.
What is web hosting?
A web hosting service is an Internet hosting service that allows individuals and organizations to make their website accessible via the World Wide Web. Web hosts are companies that provide space on a server owned or leased for use by clients, as well as providing Internet connectivity, typically in a data center. They also often provide billing and support services for website owners.
Types of Web Hosting
There are three types of web hosting. The first is known as Shared hosting, and it is provided by a host who offers server space on a shared platform that can be utilized by multiple clients at once. This solution works best for those with sites that do not consume too much bandwidth or have extremely large traffic levels. The next option is Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting, which divides one physical server into multiple virtual servers using virtualization software such as Xen or VMWare.
How to choose a web hosting service provider?
So you’ve decided to start your online business, but where do you get your website hosted? Unless you’re a web developer, you don’t want to be bothered with all of that technical mumbo jumbo. That’s why it makes sense to outsource it to a trusted service provider like Interschool Enterprise. We offer top notch web hosting services at competitive prices. Get in touch today!
What factors need to be considered while buying a web hosting package?
When it comes to buying a web hosting package, here are some factors that you should consider: The amount of bandwidth provided by your host (in terms of megabytes per month). If you have a lot of visitors to your site and they download large files, make sure that your web host can provide enough bandwidth for them. Also keep in mind that bigger sites consume more bandwidth and so do those with high levels of traffic.
How Much Does it Cost to Buy a Domain Name and Set Up Web Hosting?
A domain name and web hosting are a bit like a house and land; it’s hard to buy one without the other. And much like real estate, it all depends on where you live—and what features you want.
Choosing the Best Web Hosting Package in 2019.
Choosing a web hosting provider can be confusing, especially if you’re new to internet marketing. This guide will help you make an informed decision about which web hosting package is best for your needs.
Benefits of Website Hosting.
Best Online Web Hosting Services are becoming increasingly popular, as more and more individuals and businesses begin to use websites on a regular basis. If you're thinking about hosting your website on an online server, be sure to weigh all of your options.
Contact Us
Contact Number.:+91-9599526129
Address:310, 3rd Floor, GTB Tower, Near Silver Estate, University Rd, City Center, Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh 474011
0 notes
Photo

Which the most powerful Linux for Xen VPS?
Many medium-sized organizations are looking for a cost-effective solution that meets their urgent and long-term needs. Some consider that they have outgrown the outsourced basic hosting of their website and email server, others are wary of the cost implications of increasing their internal infrastructure.
An attractive solution is virtual private server hosting (“VPS”).
In recent years, VPS has become increasingly popular, particularly among managed service providers, because of its flexibility and ability to support the most common operating systems and applications in secure virtual servers.
Simply put, a VPS environment has three layers:
The Host or Node is a Linux implementation on the physical server. It defines the virtual server environment and resource management services.
The Guests. Each Guest has a virtual server hosting an OS; and
Virtual Servers themselves are sometimes called domains.
HostSailor offers a broad range of Xen VPS options. Read more about them here, or contact us to discuss your options.
0 notes
Photo

CloudSurph provides Cloud VPS Hosting for small business, KVM XEN deployment & more. We offer VPS for 1 Dollar, Cheap VPS $1 Contact us now.
#CloudVPSHosting#VPS$1PerMonth#WindowsVPSHosting#WindowsCloudHosting#CheapUnmeteredVPS#StorageVPSServers
0 notes
Text
What is KVM VPS?
You probably have seen the word KVM VPS before, but what exactly is VPS and KVM VPS? VPS (Virtual Private Server) is virtual server allows you to host and manage resource-intensive applications and projects without physical server.
With virtualization technologies, a single physical server is able to run one or several virtual machines (VMs). These virtual servers communicate with the host through hypervisor, which acts as a link between cloud and hardware resources.
Each VPS is running on its own Operating System (OS) and have dedicated resources. Therefore, compare to Shared Hosting, VPS ensures several benefits like unrestricted root access and faster loading time.
KVM (Kernel Based Virtualization)
On the other hand, KVM, also known as Kernel-based Virtual Machine is one of the virtualization technologies or hypervisors used by hosting companies to set up VPS. Other open source hypervisors including XEN, vSphere and Microdoft’s Hyper-V.
KVM hypervisor has been around for a decade and it’s build into standard Linux kernel. By that, almost any Linux distribution is ready to act as a hypervisor once it’s installed.
The difference between KVM and other hypervisors is the approach to access the virtualization features of CPU. KVM utilizes a module build inside the operating system kernel while other hypervisors like XEN operates outside the host OS, and other hypervisors emulate the CPU completely.
Advantages of KVM VPS
Why should you choose KVM VPS? The pros is that all applications and use cases for KVM should be very similar to how it would on a dedicated server — as it is independent from the host node. Therefore, you can run Docker, OwnCloud, kernel headers, and many more.
In addition, KVM VPS hosting offers better performance. Generally, providers offering KVM VPS tend to run the host nodes on more powerful host nodes than they would for containers, as the extra overhead that KVM requires to operate efficiently from a host-perspective. Furthermore, certain resources within KVM cannot be oversold easily. This is the main reason why consumers prefer to look for “KVM” when finding a VPS hosting solution.
Typically, most KVM VPS hostings offer a control panel such as Virtualizor to allow you to VNC or HTML5 Console into your server. This is useful if you need to console into your server and find remote access like SSH or RDP inaccessible for any reason. Most VPS providers today allow for custom ISO’s as well, enable you to install your own Operating System.
Overall, we can see why many hosting providers adopt their virtualization platforms with KVM throughout the years, and why consumers tend to prefer it when seeking out a virtual private server.
Thanks for reading!
https://www.casbay.com/blog/tips-sharing/what-is-kvm-vps
0 notes
Text
Best Windows Vps Hosting
While most hosting firms supply VPS Hosting strategies with Linux-based operating systems (OS), some hosts will make use of (or call for) a Windows OS. Having a Windows OS is absolutely vital if your website utilizes ASP or ASP.net (the Linux matching would be PHP). Many organizations will certainly also utilize a Windows VPS for their firm because it plays better with other Windows based systems (i.e. Microsoft Exchange). The hosting strategies themselves have a tendency to be a little bit extra pricey, but you also get added security and support straight from Microsoft (through safety launches), whereas with Linux you at the mercy of an open resource area.
1. GoDaddy Windows VPS
GoDaddy provides both Linux as well as Windows VPS hosting strategies, with the Windows VPS plans beginning at $39.99 each month (we have promo code codes to assist to save!) Because it uses proprietary software, the Windows VPS intends constantly cost a bit extra. Yet Godaddy's features give you the finest bang for your dollar overall: the 'value' plan supplies 2GB of RAM to opt for a monthly bandwidth limit of 2,000 GB. Unless you're running a popular video-sharing website (i.e. Vimeo), that is plenty for one website. The next action up is 'deluxe', which uses 15GB much more storage space, but the RAM and also Bandwidth limitations are specifically the exact same. Most definitely not worth the additional $20 monthly.
Those who are utilizing their VPS Hosting for a whole office might intend to go with the "Ultimate" plan, which offers you 8GB of RAM in addition to 8,000 GB of bandwidth. This strategy goes with $149.99/ month, but considering just how much it can handle is definitely worth it.
The Perks: SSH access (not offered with shared hosting), $150+ in free marketing credit ratings (Google Adwords, Facebook), cost-free SSL certificate, 3 dedicated IP addresses and also FTP access.
2. Myhosting Windows VPS Hosting
Myhosting designed their Windows servers with s since their Windows web servers with Enterprise-level customers in mind. Starting at $39.99/ month, myhosting.com's windows servers are all geared up with Hyper-V Virtualization, which is a type of server optimizer that enables your VPS to operate a lot more effectively as well as handling greater volumes of traffic. Similar to Ultrahosting, myhosting.com offers a 100% uptime guarantee, along with a 2-min phone reaction time assurance. If you're wanting to host your company's website and desire a dependable, responsible VPS strategy, this is an excellent option.
3. 1and1 Windows Hosting
1and1's Windows VPS plans are really comparable to Godaddy's, other than in a few crucial locations. 1and1's starter VPS strategy (with Windows OS) is $19.99 each month (for the 1st term, and afterwards $29.99/ month after that). The distinction is in the specifications: 2GB each month (the very same), 1,000 GB/month bandwidth (50% much less) as well as 50GB of storage space (20GB a lot more!).
One more significant distinction is the control panel. 1and1 uses Parallels Plesk Panels, whereas Godaddy supplies either Plesk or cPanel, depending on your preference/comfort area.
Profits: If you do not assume your website(s) will look at the 1,000 GB Bandwidth limitation, after that this will certainly save you numerous dollars annually. Yet if your start taking on great deals of bandwidth due to traffic or media-rich web content, then Godaddy will be your far better bet.
4. Interserver Windows VPS
You will not discover an extra budget plan pleasant VPS host than Ultrahosting. Why is that? They have a 100% uptime assurance on their network. The Windows VPS intends start at $24.99/ month, that includes 384 MEGABYTES of RAM. While this must be enough for the majority of medium-traffic web sites, if you want more RAM you can increase it for $34.99/ month. Ultrahosting additionally provides complete remote desktop connection in addition to remote reboot.In enhancement to the regular Windows VPS Hosting, there are 2 more Windows VPS options: 1)Windows Xen VPS(open resource virtualization to utilize the server's resources )and 2)Windows Forex VPS (if you're not a day-trader/broker after that you do not require this!).
0 notes
Link
(Via: Lobsters)
“BootHole” vulnerability in the GRUB2 bootloader opens up Windows and Linux devices using Secure Boot to attack. All operating systems using GRUB2 with Secure Boot must release new installers and bootloaders.
Join Eclypsium for a webinar “Managing The Hole In Secure Boot” on August 5th, where CEO Yuriy Bulygin and VP R&D John Loucaides will provide advice on mitigating this vulnerability.
Download the PDF >
Introduction
Eclypsium researchers have discovered a vulnerability — dubbed “BootHole” — in the GRUB2 bootloader utilized by most Linux systems that can be used to gain arbitrary code execution during the boot process, even when Secure Boot is enabled. Attackers exploiting this vulnerability can install persistent and stealthy bootkits or malicious bootloaders that could give them near-total control over the victim device.
The vulnerability affects systems using Secure Boot, even if they are not using GRUB2. Almost all signed versions of GRUB2 are vulnerable, meaning virtually every Linux distribution is affected. In addition, GRUB2 supports other operating systems, kernels and hypervisors such as Xen. The problem also extends to any Windows device that uses Secure Boot with the standard Microsoft Third Party UEFI Certificate Authority. Thus the majority of laptops, desktops, servers and workstations are affected, as well as network appliances and other special purpose equipment used in industrial, healthcare, financial and other industries. This vulnerability makes these devices susceptible to attackers such as the threat actors recently discovered using malicious UEFI bootloaders.
Eclypsium has coordinated the responsible disclosure of this vulnerability with a variety of industry entities, including OS vendors, computer manufacturers, and CERTs. Mitigation will require new bootloaders to be signed and deployed, and vulnerable bootloaders should be revoked to prevent adversaries from using older, vulnerable versions in an attack. This will likely be a long process and take considerable time for organizations to complete patching.
Table of Contents
Background: Secure Boot, GRUB2, and CAs
Secure Boot can be a fairly deep and technical topic. Our goal here is to give a high-level introduction to the key concepts relevant to this research without going into all the granular details. We have included a variety of external links to provide additional information for those interested. Alternatively, you can go straight to the description of the vulnerability itself.
Threats to the Boot Process
The boot process is one of the most fundamentally important aspects of security for any device. It relies on a variety of firmware that controls how a device’s various components and peripherals are initialized and ultimately coordinates the loading of the operating system itself. In general, the earlier code is loaded, the more privileged it is. If this process is compromised, attackers can control how the operating system is loaded and subvert all higher-layer security controls. Recent research has identified ransomware in the wild using malicious EFI bootloaders as a way to take control of machines at the time of boot. Previously threat actors used malware tampering with legacy OS bootloaders including APT41 Rockboot, LockBit, FIN1 Nemesis, MBR-ONI, Petya/NotPetya, and Rovnix.
Additional information on threats to the modern PC boot process is available in the “Bootkits and UEFI Secure Boot” section of the System Firmware training.
UEFI Secure Boot
UEFI Secure Boot was originally developed by the UEFI Forum as a way to protect the boot process from these types of attacks. There are other implementations of secure boot designed for different environments, but UEFI Secure Boot is the standard for PCs and servers. The goal is to prevent malicious code from being introduced into the boot process by cryptographically checking each piece of firmware and software before it is run. Any code not recognized as valid is not executed in the boot process.
Secure Boot uses cryptographic signatures to verify the integrity of each piece of code as it is needed during the boot process. There are two critical databases involved in this process: the Allow DB (db) of approved components and the Disallow DB (dbx) of vulnerable or malicious components, including firmware, drivers, and bootloaders. Access to modify these databases is protected by a Key Exchange Key (KEK), which in turn is verified by a Platform Key (PK). Although the PK is used as a root of trust for updates to the platform, it’s not expressly part of the boot process (but is shown below for reference). It is dbx, db, and KEK that are used to verify the signatures for loaded executables at boot time.
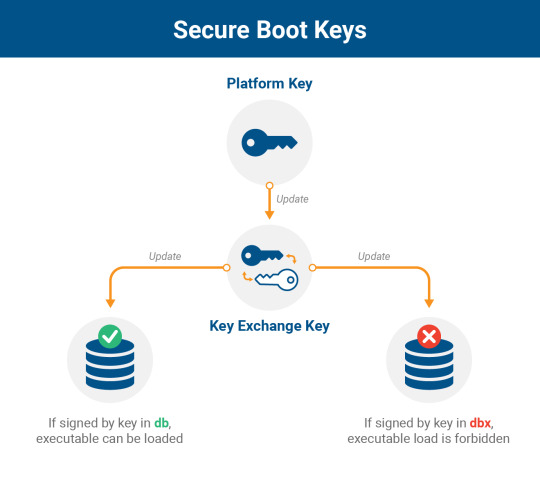
Additional details on the Secure Boot process can be found in this PDF.
Chains of Trust and GRUB2
Next, OEMs must manage a list of who is permitted to sign code trusted by the Secure Boot Database. Instead of having every OEM manage certificates from every possible firmware, driver, or OS provider, Secure Boot allows for the use of a centralized Certificate Authority (CA). Microsoft’s 3rd Party UEFI CA provides the industry standard signing service for Secure Boot. In short, third parties can submit their code to Microsoft, and Microsoft will validate and sign the code with the Microsoft CA. This establishes a chain of trust that only requires OEMs to enroll the Microsoft 3rd Party UEFI CA to their platforms to enable them to boot third-party installation media and operating systems by default when Secure Boot is enabled.
This includes the ability to sign bootloaders from non-Microsoft operating systems such as Linux. In almost every modern Linux distribution, GRUB (the Grand Unified Bootloader) is the bootloader that loads and transfers control to the operating system. In this document, all references to GRUB are intended to refer to GRUB2, which was a complete rewrite from the previous version commonly referred to as “GRUB Legacy.” Starting in 2009, all widely used Linux distributions have transitioned to using GRUB2. GRUB Legacy has been deprecated and is generally only found in older releases.
Due to legal issues arising from license incompatibilities, open-source projects and other third parties build a small application called a “shim,” which contains the vendor’s certificate and code that verifies and runs the bootloader (GRUB2). The vendor’s shim is verified using the Microsoft 3rd Party UEFI CA and then the shim loads and verifies the GRUB2 bootloader using the vendor certificate embedded inside itself.

Additional detail on the role of the Microsoft UEFI CA in the boot process is available here.
Challenges of Secure Boot
As with any technical process, Secure Boot is not without its potential problems. The process involves many pieces of code, and a vulnerability in any one of them presents a single point of failure that could allow an attacker to bypass Secure Boot. Additionally, although UEFI Secure Boot attempts to provide certain integrity guarantees to the boot process, other misconfigurations of the hardware or missing protection features can undermine boot security. One such example is a DMA attack using tools such as PCIe Microblaze. Additionally, as we will show in this blog post, a vulnerability in the boot process that enables arbitrary code execution can allow attackers to control the boot process and operating system, even when secure boot signatures are verified.
Attackers can also use a vulnerable bootloader against the system. For example, if a valid bootloader was found to have a vulnerability, a piece of malware could replace the device’s existing bootloader with the vulnerable version. The bootloader would be allowed by Secure Boot and give the malware complete control over the system and OS. Mitigating this requires very active management of the dbx database used to identify malicious or vulnerable code.

Additionally, updates and fixes to the Secure Boot process can be particularly complex and run the risk of inadvertently breaking machines. The boot process naturally involves a variety of players and components including device OEMs, operating system vendors, and administrators. Given the fundamental nature of the boot process, any sort of problems run a high risk of rendering a device unusable. As a result, updates to Secure Boot are typically slow and require extensive industry testing.
Breaking Secure Boot Through GRUB2
In the course of Eclypsium’s analysis, we have identified a buffer overflow vulnerability in the way that GRUB2 parses content from the GRUB2 config file (grub.cfg). Of note: The GRUB2 config file is a text file and typically is not signed like other files and executables. This vulnerability enables arbitrary code execution within GRUB2 and thus control over the booting of the operating system. As a result, an attacker could modify the contents of the GRUB2 configuration file to ensure that attack code is run before the operating system is loaded. In this way, attackers gain persistence on the device.
Such an attack would require an attacker to have elevated privileges. However, it would provide the attacker with a powerful additional escalation of privilege and persistence on the device, even with Secure Boot enabled and properly performing signature verification on all loaded executables. One of the explicit design goals of Secure Boot is to prevent unauthorized code, even running with administrator privileges, from gaining additional privileges and pre-OS persistence by disabling Secure Boot or otherwise modifying the boot chain.
With the sole exception of one bootable tool vendor who added custom code to perform a signature verification of the grub.cfg config file in addition to the signature verification performed on the GRUB2 executable, all versions of GRUB2 that load commands from an external grub.cfg configuration file are vulnerable. As such, this will require the release of new installers and bootloaders for all versions of Linux. Vendors will need to release new versions of their bootloader shims to be signed by the Microsoft 3rd Party UEFI CA. It is important to note that until all affected versions are added to the dbx revocation list, an attacker would be able to use a vulnerable version of shim and GRUB2 to attack the system. This means that every device that trusts the Microsoft 3rd Party UEFI CA will be vulnerable for that period of time.
In addition to vendors using shims signed by the Microsoft 3rd Party UEFI CA, some OEMs that control both the hardware and the software stack in their devices use their own key that is provisioned into the hardware at the factory to sign GRUB2 directly. They will need to provide updates and revocation of previous vulnerable versions of GRUB2 for these systems as well.
This vulnerability was assigned CVE-2020-10713 “GRUB2: crafted grub.cfg file can lead to arbitrary code execution during boot process” with a CVSS rating of 8.2 (High) / CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:H/UI:N/S:C/C:H/I:H/A:H.
Follow these links to go directly to the Impact and Mitigations sections.
Vulnerability Analysis
The vulnerability is a buffer overflow that occurs in GRUB2 when parsing the grub.cfg file. This configuration file is an external file commonly located in the EFI System Partition and can therefore be modified by an attacker with administrator privileges without altering the integrity of the signed vendor shim and GRUB2 bootloader executables. The buffer overflow allows the attacker to gain arbitrary code execution within the UEFI execution environment, which could be used to run malware, alter the boot process, directly patch the OS kernel, or execute any number of other malicious actions.
To dig a little deeper into the vulnerability itself, we’ll take a closer look at how the code works internally. In order to process commands from the external configuration file, GRUB2 uses flex and bison to generate a parsing engine for a domain-specific language (DSL) from language description files and helper functions.
This is generally considered to be a better approach than manually writing a custom parser for each DSL. However, GRUB2, flex, and bison are all complex software packages with their own design assumptions that can be easy to overlook. And those mismatched design assumptions can result in vulnerable code.
The parser engine generated by flex includes this define as part of the token processing code:
#define YY_DO_BEFORE_ACTION \ yyg->yytext_ptr = yy_bp; \ yyleng = (int) (yy_cp - yy_bp); \ yyg->yy_hold_char = *yy_cp; \ *yy_cp = '\0'; \ if ( yyleng >= YYLMAX ) \ YY_FATAL_ERROR( "token too large, exceeds YYLMAX" ); \ yy_flex_strncpy( yytext, yyg->yytext_ptr, yyleng + 1 , yyscanner); \ yyg->yy_c_buf_p = yy_cp;
In this macro, the generated code detects that it has encountered a token that is too large to fit into flex’s internal parse buffer and calls YY_FATAL_ERROR(), which is a helper function provided by the software that is using the flex-generated parser.
However, the YY_FATAL_ERROR() implementation provided in the GRUB2 software package is:
#define YY_FATAL_ERROR(msg) \ do { \ grub_printf (_("fatal error: %s\n"), _(msg)); \ } while (0)
Rather than halting execution or exiting, it just prints an error to the console and returns to the calling function. Unfortunately, the flex code has been written with the expectation that any calls to YY_FATAL_ERROR() will never return. This results in yy_flex_strncpy() being called and copying the source string from the configuration file into a buffer that is too small to contain it.

Beyond just this specific path, a number of additional places throughout the flex-generated code also expect that any calls to YY_FATAL_ERROR() never return and perform unsafe operations when that expectation is broken. Mismatched assumptions between producers and consumers of an API are a very common source of vulnerabilities.
Ultimately, by providing a configuration file with input tokens that are too long to be handled by the parser, this buffer overflow overwrites critical structures in the heap. These overwritten fields include internal parser structure elements, which can be used as an arbitrary write-what-where primitive to gain arbitrary code execution and hijack the boot process.

Of further note, the UEFI execution environment does not have Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) or Data Execution Prevention (DEP/NX) or other exploit mitigation technologies typically found in modern operating systems, so creating exploits for this kind of vulnerability is significantly easier. The heap is fully executable without the need to build ROP chains.
Finally, rather than being architecture-specific, this vulnerability is in a common code path and was also confirmed using a signed ARM64 version of GRUB2.
Additional Vulnerabilities
There have been a couple of examples of previous vulnerabilities found in GRUB2 that result in arbitrary code execution, but with a much smaller scope.
In April 2019, a vulnerability in how GRUB2 was used by the Kaspersky Rescue Disk was publicly disclosed. In February 2020, more than six months after a fixed version had been released, Microsoft pushed an update to revoke the vulnerable bootloader across all Windows systems by updating the UEFI revocation list (dbx) to block the known-vulnerable Kaspersky bootloader. Unfortunately, this resulted in systems from multiple vendors encountering unexpected errors, including bricked devices, and the update was removed from the update servers.
Additionally, in May 2020, Dmytro Oleksiuk disclosed that certain HPE ProLiant servers contained a version of GRUB2 signed by a HP CA that allows the use of the “insmod” command to load unsigned code. This issue was assigned CVE-2020-7205 and is also embargoed until July 29th.
In response to our initial vulnerability report, additional scrutiny was applied to the GRUB2 code and a number of additional vulnerabilities were discovered by the Canonical security team:
CVE-2020-14308 GRUB2: grub_malloc does not validate allocation size allowing for arithmetic overflow and subsequent heap-based buffer overflow
6.4 (Medium) / CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:H/PR:H/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
CVE-2020-14309 GRUB2: Integer overflow in grub_squash_read_symlink may lead to heap based overflow
5.7 (Medium) / CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:H/PR:H/UI:N/S:U/C:N/I:H/A:H
CVE-2020-14310 GRUB2: Integer overflow read_section_from_string may lead to heap based overflow
5.7 (Medium) / CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:H/PR:H/UI:N/S:U/C:N/I:H/A:H
CVE-2020-14311 GRUB2: Integer overflow in grub_ext2_read_link leads to heap based buffer overflow,
5.7 (Medium) / CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:H/PR:H/UI:N/S:U/C:N/I:H/A:H
CVE-2020-15705 GRUB2: avoid loading unsigned kernels when grub is booted directly under secure boot without shim
6.4 (Medium) /CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:H/PR:H/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
CVE-2020-15706 GRUB2 script: Avoid a use-after-free when redefining a function during execution
6.4 (Medium) /CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:H/PR:H/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
CVE-2020-15707 GRUB2: Integer overflow in initrd size handling.
5.7 (Medium) /CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:H/PR:H/UI:N/S:U/C:N/I:H/A:H
Given the difficulty of this kind of ecosystem-wide update/revocation, there is a strong desire to avoid having to do it again six months later. To that end, a large effort — spanning multiple security teams at Oracle, Red Hat, Canonical, VMware, and Debian — using static analysis tools and manual review helped identify and fix dozens of further vulnerabilities and dangerous operations throughout the codebase that do not yet have individual CVEs assigned.
Impact
Due to a weakness in the way GRUB2 parses its configuration file, an attacker can execute arbitrary code that bypasses signature verification. The Boot Hole vulnerability discovered by Eclypsium can be used to install persistent and stealthy bootkits or malicious bootloaders that operate even when Secure Boot is enabled and functioning correctly. This can ensure attacker code runs before the operating system and can allow the attacker to control how the operating system is loaded, directly patch the operating system, or even direct the bootloader to alternate OS images. It gives the attacker virtually unlimited control over the victim device. Malicious bootloaders have recently been observed in the wild, and this vulnerability would make devices susceptible to these types of threats.
All signed versions of GRUB2 that read commands from an external grub.cfg file are vulnerable, affecting every Linux distribution. To date, more than 80 shims are known to be affected. In addition to Linux systems, any system that uses Secure Boot with the standard Microsoft UEFI CA is vulnerable to this issue. As a result, we believe that the majority of modern systems in use today, including servers and workstations, laptops and desktops, and a large number of Linux-based OT and IoT systems, are potentially affected by these vulnerabilities.
Additionally, any hardware root of trust mechanisms that rely on UEFI Secure Boot could be bypassed as well.
Mitigation
Full mitigation of this issue will require coordinated efforts from a variety of entities: affected open-source projects, Microsoft, and the owners of affected systems, among others. This will include:
Updates to GRUB2 to address the vulnerability.
Linux distributions and other vendors using GRUB2 will need to update their installers, bootloaders, and shims.
New shims will need to be signed by the Microsoft 3rd Party UEFI CA.
Administrators of affected devices will need to update installed versions of operating systems in the field as well as installer images, including disaster recovery media.
Eventually the UEFI revocation list (dbx) needs to be updated in the firmware of each affected system to prevent running this vulnerable code during boot.
On the Coordinated Release Date (CRD) of July 29, we expect to see advisories and/or updates from the following affected parties:
Microsoft
UEFI Security Response Team (USRT)
Oracle
Red Hat (Fedora and RHEL)
Canonical (Ubuntu)
SuSE (SLES and openSUSE)
Debian
Citrix
VMware
Various OEMs
Software vendors, including security software, are also impacted by this vulnerability and will be updating their bootloaders.
… more to be added once we have a full list …
However, full deployment of this revocation process will likely be very slow. UEFI-related updates have had a history of making devices unusable, and vendors will need to be very cautious. If the revocation list (dbx) is updated before a given Linux bootloader and shim are updated, then the operating system will not load. As a result, updates to the revocation list will take place over time to prevent breaking systems that have yet to be updated. There are also edge cases where updating the dbx can be difficult, such as with dual-boot or deprovisioned machines. When any OS is installed or launched, the bootloader and OS need to be updated before the revocation is applied to the system.
Further complicating matters, enterprise disaster recovery processes can run into issues where approved recovery media no longer boots on a system if dbx updates have been applied. In addition when a device swap is needed due to failing hardware, new systems of the same model may have already had dbx updates applied and will fail when attempting to boot previously-installed operating systems. Before dbx updates are pushed out to enterprise fleet systems, recovery and installation media must be updated and verified as well.
Microsoft will be releasing a set of signed dbx updates, which can be applied to systems to block shims that can be used to load the vulnerable versions of GRUB2. Due to the risk of bricking systems or otherwise breaking operational or recovery workflows, these dbx updates will initially be made available for interested parties to manually apply to their systems rather than pushing the revocation entries and applying them automatically. This will allow IT professionals, enthusiasts, and others the opportunity to test the revocation updates on their individual systems and identify any issues before making the revocations mandatory.
Organizations should additionally ensure they have appropriate capabilities for monitoring UEFI bootloaders and firmware and verifying UEFI configurations, including revocation lists, in their systems. Organizations should also test recovery capabilities as updates become available, including the “reset to factory defaults” functionality in the UEFI setup. This will ensure that they can recover devices if a device is negatively impacted by an update. Finally, organizations should be monitoring their systems for threats and ransomware that use vulnerable bootloaders to infect or damage systems.
Recommendations
Right away, start monitoring the contents of the bootloader partition (EFI system partition). This will buy time for the rest of the process and help identify affected systems in your environment. For those who have deployed the Eclypsium solution, you can see this monitoring under the “MBR/Bootloader” component of a device.
Continue to install OS updates as usual across desktops, laptops, servers, and appliances. Attackers can leverage privilege escalation flaws in the OS and applications to take advantage of this vulnerability so preventing them from gaining administrative level access to your systems is critical. Systems are still vulnerable after this, but it is a necessary first step. Once the revocation update is installed later, the old bootloader should stop working. This includes rescue disks, installers, enterprise gold images, virtual machines, or other bootable media.
Test the revocation list update. Be sure to specifically test the same firmware versions and models that are used in the field. It may help to update to the latest firmware first in order to reduce the number of test cases.
To close this vulnerability, you need to deploy the revocation update. Make sure that all bootable media has received OS updates first, roll it out slowly to only a small number of devices at a time, and incorporate lessons learned from testing as part of this process.
Engage with your third-party vendors to validate they are aware of, and are addressing, this issue. They should provide you a response as to its applicability to the services/solutions they provide you as well as their plans for remediation of this high rated vulnerability.
Eclypsium has powershell and bash scripts available which can be used to detect bootloaders that are being revoked by this dbxupdate.
Conclusions
While Secure Boot is easily taken for granted by most users, it is the foundation of security within most devices. Once compromised, attackers can gain virtually complete control over the device, its operating system, and its applications and data. And as this research shows, when problems are found in the boot process, they can have far-reaching effects across many types of devices.
We will update this blog post as more information becomes available, and we encourage users and administrators to closely monitor alerts and notifications from their hardware vendors, the Microsoft MSRC, and any relevant open-source projects. Please join us for a webinar “Managing the Hole in Secure Boot” on August 5th.
References:
Microsoft
UEFI Forum
Debian
Canonical:
Security advisory
KnowledgeBase article
Red Hat
SUSE
Security advisory:
Knowledge Base article:
0 notes
Text
Shared Hosting vs Cloud VPS Hosting in 2020!
In shared hosting, your main node server resources shared with other users. In VPS hosting, have your own virtual resources allocated to your machine that server performance.

Virtualization Since an account is hosted on a shared server, virtualization technology picture. There are many virtualization technologies available VPS viz. Microsoft Hyper-V, VMware, KVM, Xen, Virtuozzo, etc. Performance With the shared hosting, improve website performance, as here work on the physical servers that are connected serial was. However, if your performance demands are limited, and you see the more value in maintenance-then hosting services can attain high ROI. With the virtual synchronization, these hosting service provider offers you performance server performance. You'll surely have more flexibility to configure your application on different servers. This helps the dedicated system, administrator the server running smoothly. If high traffic demands or multiple sites to manage, VPS for such a hassle. Security In the shared hosting plans, websites could affect your web applications performance. risk your system performance and overall impact your performance. Better proper security measure your server performance and keep sharing the devices for interconnections. VPS hosting has more power and control with of the performance, bandwidth and server attribution. Have more flexibility of connection to applications. Ensure your site’s security with more robust safety features that are only available through VPS hosting. If your budget allows, implement better customer support services assist patrons need it. If your business protect personal data, it’s worth considering the upgrade to a VPS. What are they useful for? In Shared Hosting To personalize small businesses that are having low traffic websites that won’t need more new resources. In this hosting, easy for a non-technical person to a shared environment, that's more suitable as not perform any server maintenance. Here the resources are natural to manage that require more technical skills. In VPS Hosting These server-based hostings provide high traffic database driven websites expecting traffic increase. It offers dynamic sites with images, database, or scripts. It is easy to run your game server, trading applications, online applications, SEO applications, etc. Wrapping Up Above mentioned are the Key differences of Shared Hosting and VPS hosting, know and work on for overall server performance at ever subtle needs. If you need more information about SSD KVM VPS Hosting, please as the expert at SSD Cloud.
0 notes