Photo
CONNECTIONS440




Aviation is an engine of global connectivity and a fundamental tool to achieve the Global Goals. All countries should have access to safe and reliable air transport. The International Civil Aviation Organization works to ensure no country is left behind when it comes to aviation standards. Find out more Thursday’s International Civil Aviation Day here: http://bit.ly/2fZAECW
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our Juno mission has been exploring Jupiter since July 2016 with a special passenger on board: JunoCam, an instrument designed to take spectacular close-up color images of the largest planet in our solar system. From the raw images, citizen scientists have processed a range of beautiful photographs that highlight Jupiter’s features, even turning them into works of art. Below, 10 stunning images JunoCam has given us over the past year.
1. Jovian tempest.

This color-enhanced image of a massive, raging storm in Jupiter’s northern hemisphere was captured by our Juno spacecraft during its ninth close flyby on Oct. 24, 2017. The storm is rotating counter-clockwise with a wide range of cloud altitudes, and the darker clouds are expected to be deeper in the atmosphere than the brightest clouds.
2. A southern stunner.

Jupiter’s southern hemisphere shows off in beautiful detail in this image taken on Oct. 24, 2017. The color-enhanced view captures one of the white ovals in the “String of Pearls,” one of eight massive rotating storms at 40 degrees south latitude on the gas giant planet.
3. Dreaming in color.
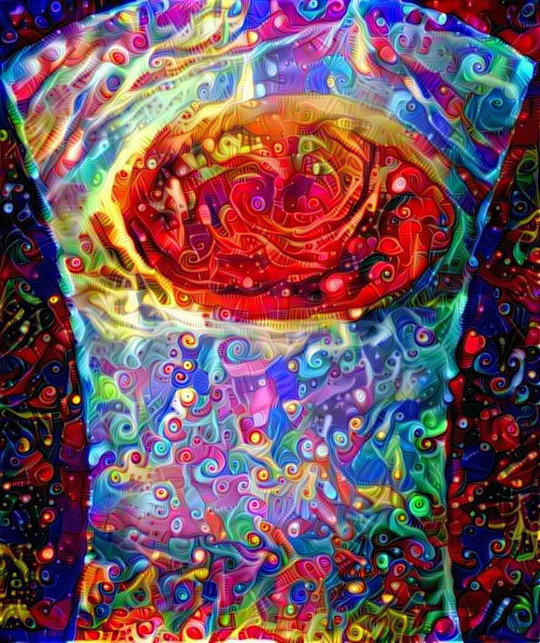

Artist Mik Petter created this unique digital piece using data from the JunoCam. The art form, known as fractals, uses mathematical formulas to create an infinite variety of form, detail, color and light. The original JunoCam image was taken on July 10, 2017.
4. Jovian moon shadow.

Jupiter’s moon Amalthea casts a shadow on the gas giant planet in this image taken on Sept. 1, 2017. The elongated shape of the shadow is a result of both the location of the moon with relation to Jupiter in this image as well as the irregular shape of the moon itself.
5. 95 minutes over Jupiter.

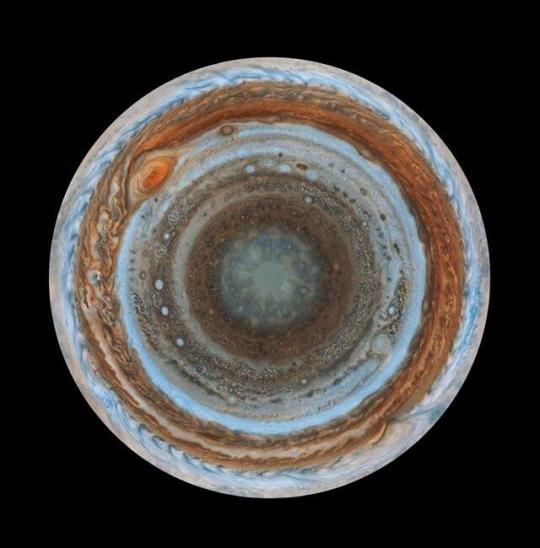
Once every 53 days, Juno swings close to Jupiter, speeding over its clouds. In about two hours, the spacecraft travels from a perch over Jupiter’s north pole through its closest approach (perijove), then passes over the south pole on its way back out. This sequence shows 11 color-enhanced images from Perijove 8 (Sept. 1, 2017) with the south pole on the left (11th image in the sequence) and the north pole on the right (first image in the sequence).
6. Soaring high.
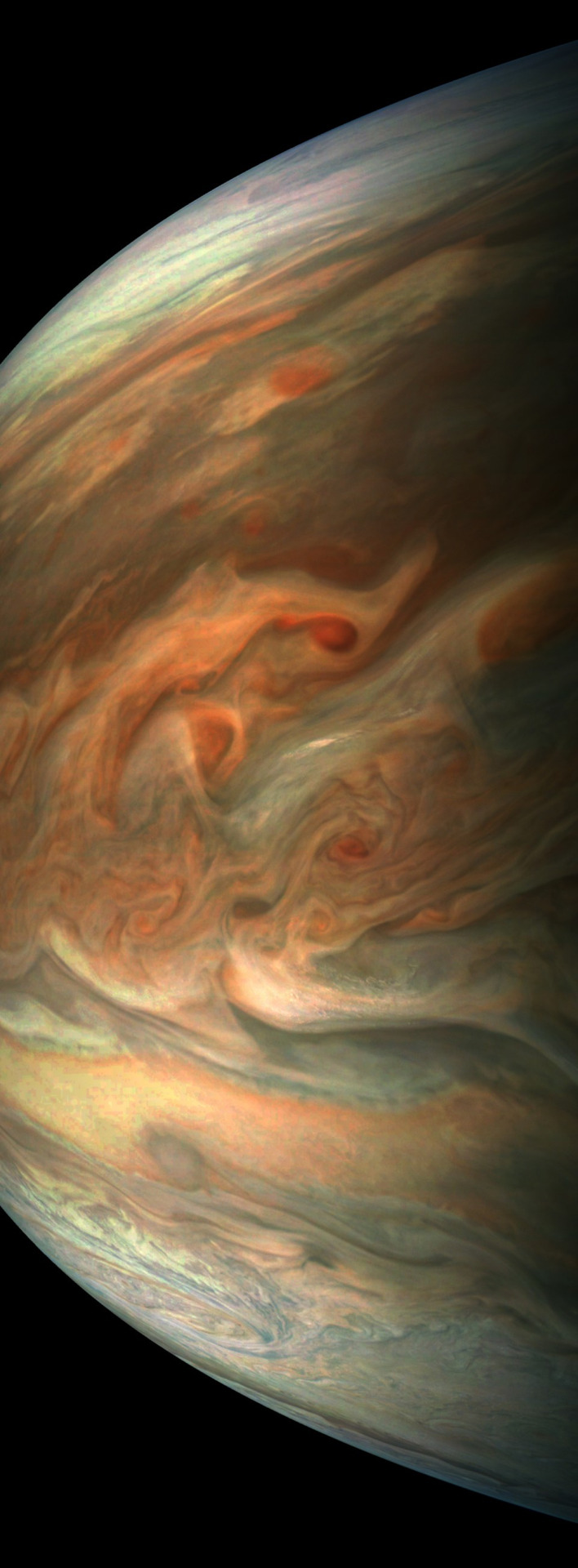

This striking image of Jupiter was taken on Sept. 1, 2017 as Juno performed its eighth flyby. The spacecraft was 4,707 miles (7,576 kilometers) from the tops of the clouds of the planet at a latitude of about -17.4 degrees. Noteworthy: “Whale’s Tail” and “Dan’s Spot.”
7. In true color.
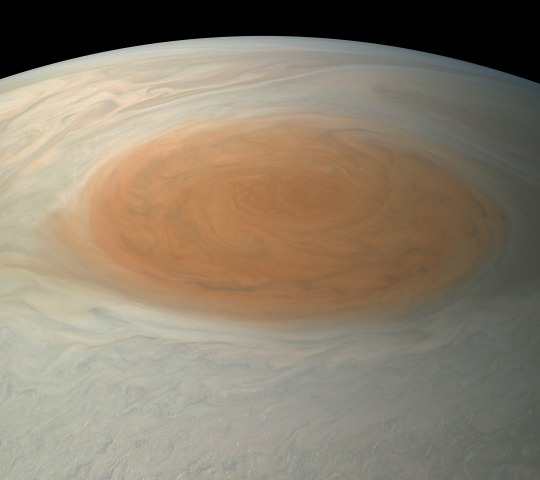

This true-color image offers a natural color rendition of what the Great Red Spot and surrounding areas would look like to human eyes from Juno’s position. The image was taken on July 10, 2017 as the Juno spacecraft performed its seventh close flyby of Jupiter.
8. The ‘face’ of Jupiter.
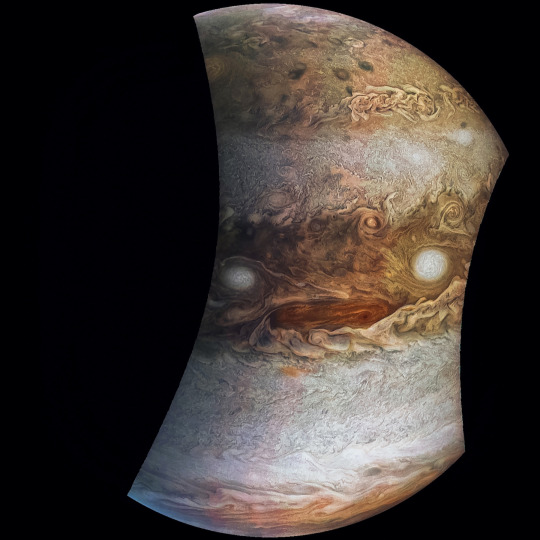
JunoCam images aren’t just for art and science—sometimes they’re created for a good chuckle. This image, processed by citizen scientist Jason Major, is titled “Jovey McJupiterface.” By rotating the image 180 degrees and orienting it from south up, two white oval storms turn into eyeballs, and the “face” of Jupiter is revealed. The original image was taken by the Juno spacecraft on May 19, 2017.
9. Bands of clouds.
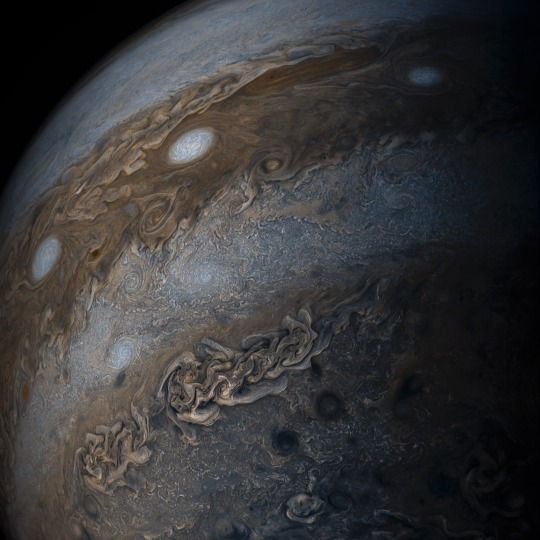

This enhanced-color image of Jupiter’s bands of light and dark clouds was created by citizen scientists Gerald Eichstädt and Seán Doran. Three of the white oval storms known as the “String of Pearls” are visible near the top of the image. Each of the alternating light and dark atmospheric bands in this image is wider than Earth, and each rages around Jupiter at hundreds of miles (kilometers) per hour. The lighter areas are regions where gas is rising, and the darker bands are regions where gas is sinking. Juno captured the image on May 19, 2017.
10. The edge.

This enhanced-color image of a mysterious dark spot on Jupiter seems to reveal a Jovian “galaxy” of swirling storms. Juno captured this image on Feb. 2, 2017 and citizen scientist Roman Tkachenko enhanced the color to bring out the rich detail in the storm and surrounding clouds. Just south of the dark storm is a bright, oval-shaped storm with high, bright, white clouds, reminiscent of a swirling galaxy. As a final touch, he rotated the image 90 degrees, turning the picture into a work of art.
To learn more about the Juno mission at Jupiter, visit: www.nasa.gov/juno.
Follow the Juno mission on Facebook, Instagram and Twitter.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
5K notes
·
View notes
Photo










Front Pages: Japan’s Attack on Pearl Harbour
Above are the front pages from newspapers around the world, these are the headlines and reports that the Allied countries woke up to on December 8th, 1941. With Japan’s attack on Pearl Harbour the US was brought into the war. All eight US battleships stationed at Pearl Harbor were heavily damaged or destroyed and more than 3,500 casualties were suffered, with 68 civilian killed.
Front pages:
The News & Observer, Raleigh N.C. (source)
The New York Times (source)
The Daily Mirror, UK (source)
Manitowoc Herald Times, Wisconsin (source)
The Los Angeles Times (source)
New York World-Telegram (source)
The Observer, UK (source)
Seattle Post Intelligencer (source)
Daily News, New York (source)
992 notes
·
View notes
Link
Check out @MaxCRoser’s Tweet:
0 notes
Photo
Where's the paper industry located, I wonder.

Map of the amount of forest coverage in each US state.
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Black Friday is also Buy Nothing Day, where participants protest consumerism by not purchasing anything for at least 24 hours. People have also been known to stage sit ins, cut up their credit cards, wander around shopping malls as zombies, or host used winter coat exchanges. Source
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Let’s Talk About Food...in Space!
It’s Thanksgiving time…which means you’re probably thinking about food…
Ever wonder what the astronauts living and working on the International Space Station eat during their time 250 miles above the Earth? There’s no microwave, but they get by using other methods.
Here are some fun facts about astronaut food…
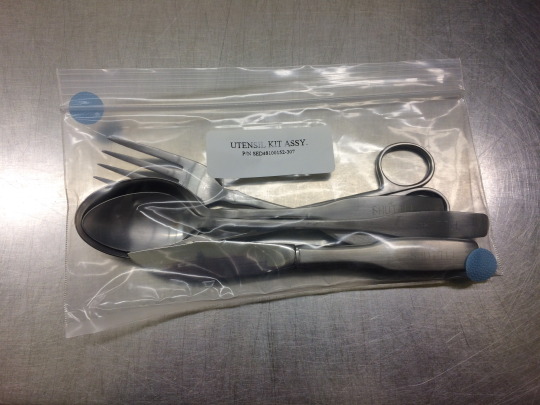
Astronauts are assigned their own set of silverware to use during their mission (they can keep it afterward too). Without a dishwasher in orbit, they use special wipes to sterilize their set between uses, but it’s still better for everyone if they keep track of and use their own! So many sets of silverware were ordered during the space shuttle program that crews on the space station today still use silverware engraved with the word “shuttle” on them! So #retro.

You probably know that astronauts use tortillas instead of bread to avoid crumbs floating everywhere. Rodolfo Neri Vela, a payload specialist from Mexico, who flew on the space shuttle in 1985, introduced tortillas to the space food system. Back then, we would buy fresh tortillas the day before launch to send on the 8-10 day space shuttle missions.

We then learned how to reduce the water activity when formulating tortillas, which coupled with the reduction of oxygen during packaging would prevent the growth of mold and enable them to last for longer shuttle missions. Now, we get tortillas from the military. In August 2017, acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot ate a meal that included tortillas from 2015!

Our food menu is mostly all made from scratch so it can meet the requirements of the nutrition team and ensure astronauts eat enough fruits and vegetables. The space station is stocked with a standard menu that includes a mix of the more than 200 food and drink options available. This ensures lots of variety for the station crews but not too many of each individual item.

The food is packaged into bulk overwrap bags, referred to as BOBs, which are packed into cargo transfer bags for delivery to the space station. Each astronaut also gets to bring nine personalized BOBs for a mission, each containing up to 60 food and drink options so they can include more of their favorites – or choose to send a few specific items for everyone to share on a particular holiday like Thanksgiving. As a result, the crew members often share and swap their food to get more variety. Astronauts also can include any food available at the grocery store as long as it has an 18-month shelf life at room temperature and meets the microbiological requirements.

Fresh fruit and vegetables are a special treat for astronauts, so nearly every cargo resupply mission includes fresh fruit and veggies – and sometimes ice cream!

The Dragon spacecraft has freezers to bring science samples back to Earth. If there is space available on its way to orbit, the ground crew may fill the freezer with small cups of ice cream or ice cream bars.

Some food arrives freeze-dried, and the astronauts rehydrate it by inserting a specific amount of hot or ambient water from a special machine.
Other food comes ready to eat but needs to be reheated, which crew members do on a hot-plate like device. We recently also sent an oven style food warmer to station for the crew to use. And of course, some food like peanuts just get packaged for delivery and are ready to eat as soon as the package is opened!

Our nutritional biochemists have discovered that astronauts who eat more fish in space lost less bone, which is one of the essential problems for astronauts to overcome during extended stays in space. In the limited area aboard the space shuttle, not all crew members loved it when their coworkers ate the (aromatic) fish dishes, but now that the space station is about the size of a six-bedroom house, that’s not really a problem.

Astronauts on station have had the opportunity to grow (and eat!) a modest amount of fresh vegetables since the first lettuce harvest in August 2015, with new crops growing now and more coming soon. Crew members have been experimenting using the Veggie growth chamber, and soon plant research will also occur in the new Advanced Plant Habitat, which is nearly self-sufficient and able to control every aspect of the plant environment!
Growing food in space will be an important component of future deep space missions, and our nutritionists are working with these experiments to ensure they also are nutritious and safe for the crew to eat.
Thanksgiving in Space
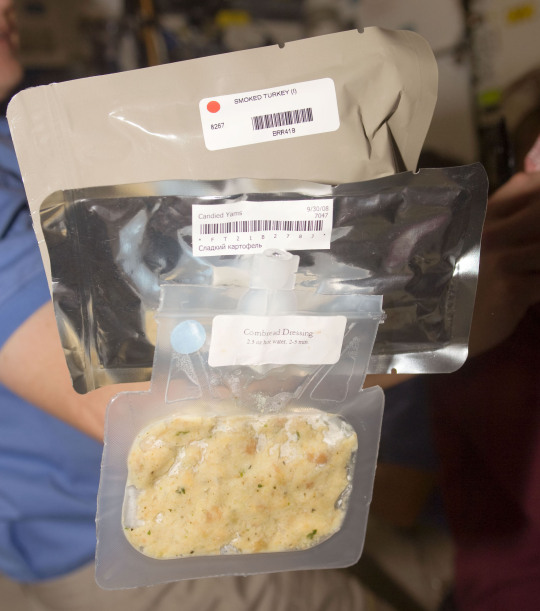
The crew on the space station will enjoy Thanksgiving together. Here’s a look at their holiday menu:
Turkey
Mashed Potatoes
Cornbread Stuffing
Candied Yams
Cran-Apple Dessert
Learn more about growing food on the space station HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
20K notes
·
View notes
Photo






kelimatu, Flores, 11/2017 (Indonesia 9th step in my trip around the world)
395 notes
·
View notes
Text
Solar System: 10 Things to Know This Week
The Living Planet Edition
youtube
Whether it’s crops, forests or phytoplankton blooms in the ocean, our scientists are tracking life on Earth. Just as satellites help researchers study the atmosphere, rainfall and other physical characteristics of the planet, the ever-improving view from above allows them to study Earth’s interconnected life.
1. Life on Earth, From Space

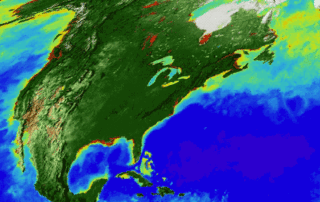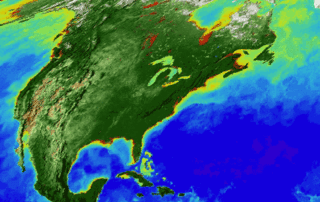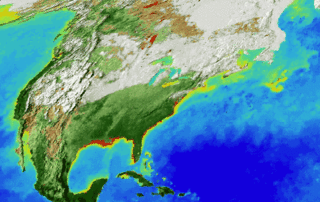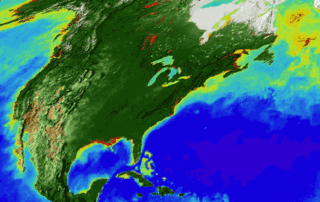
While we (NASA) began monitoring life on land in the 1970s with the Landsat satellites, this fall marks 20 years since we’ve continuously observed all the plant life at the surface of both the land and ocean. The above animation captures the entirety of two decades of observations.
2. Watching the World Breathe
With the right tools, we can see Earth breathe. With early weather satellite data in the 1970s and ‘80s, NASA Goddard scientist Compton Tucker was able to see plants’ greening and die-back from space. He developed a way of comparing satellite data in two wavelengths.
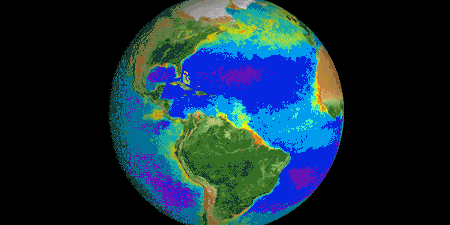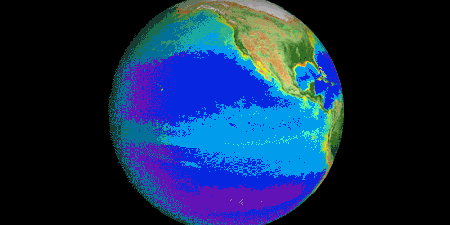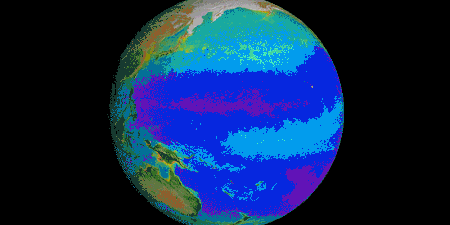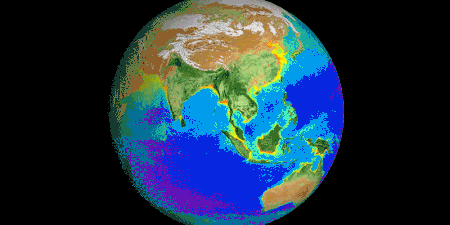
When healthy plants are stocked with chlorophyll and ready to photosynthesize to make food (and absorb carbon dioxide), leaves absorb red light but reflect infrared light back into space. By comparing the ratio of red to infrared light, Tucker and his colleagues could quantify vegetation covering the land.
Expanding the study to the rest of the globe, the scientists could track rainy and dry seasons in Africa, see the springtime blooms in North America, and wildfires scorching forests worldwide.
3. Like Breathing? Thank Earth’s Ocean
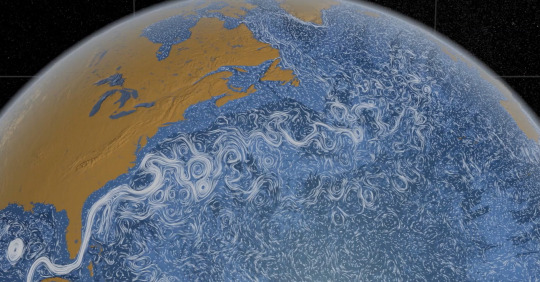
But land is only part of the story. The ocean is home to 95 percent of Earth’s living space, covering 70 percent of the planet and stretching miles deep. At the base of the ocean’s food web is phytoplankton - tiny plants that also undergo photosynthesis to turn nutrients and carbon dioxide into sugar and oxygen. Phytoplankton not only feed the rest of ocean life, they absorb carbon dioxide - and produce about half the oxygen we breathe.

In the Arctic Ocean, an explosion of phytoplankton indicates change. As seasonal sea ice melts, warming waters and more sunlight will trigger a sudden, massive phytoplankton bloom that feeds birds, sea lions and newly-hatched fish. But with warming atmospheric temperatures, that bloom is now happening several weeks earlier - before the animals are in place to take advantage of it.
4. Keeping an Eye on Crops
The “greenness” measurement that scientists use to measure forests and grasslands can also be used to monitor the health of agricultural fields. By the 1980s, food security analysts were approaching NASA to see how satellite images could help with the Famine Early Warning System to identify regions at risk - a partnership that continues today.

With rainfall estimates, vegetation measurements, as well as the recent addition of soil moisture information, our scientists can help organizations like USAID direct emergency help.
The view from space can also help improve agricultural practices. A winery in California, for example, uses individual pixels of Landsat data to determine when to irrigate and how much water to use.
5. Coming Soon to the International Space Station

A laser-based instrument being developed for the International Space Station will provide a unique 3-D view of Earth’s forests. The instrument, called GEDI, will be the first to systematically probe the depths of the forests from space.
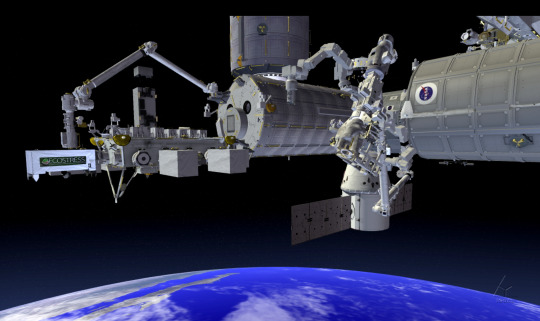
Another ISS instrument in development, ECOSTRESS, will study how effectively plants use water. That knowledge provided on a global scale from space will tell us “which plants are going to live or die in a future world of greater droughts,” said Josh Fisher, a research scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and science lead for ECOSTRESS.
6. Seeing Life, From the Microscopic to Multicellular
Scientists have used our vantage from space to study changes in animal habitats, track disease outbreaks, monitor forests and even help discover a new species. Bacteria, plants, land animals, sea creatures and birds reveal a changing world.
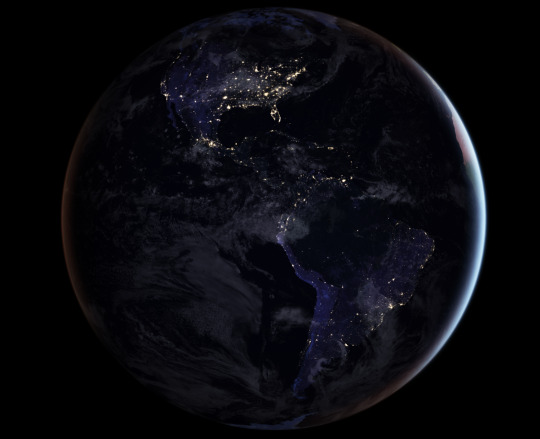
Our Black Marble image provides a unique view of human activity. Looking at trends in our lights at night, scientists can study how cities develop over time, how lighting and activity changes during certain seasons and holidays, and even aid emergency responders during power outages caused by natural disasters.
7. Earth as Analog and Proving Ground
Just as our Mars rovers were tested in Earth’s deserts, the search for life on ocean moons in our solar system is being refined by experiments here. JPL research scientist Morgan Cable looks for life on the moons of Jupiter and Saturn. She cites satellite observations of Arctic and Antarctic ice fields that are informing the planning for a future mission to Europa, an icy moon of Jupiter.

The Earth observations help researchers find ways to date the origin of jumbled, chaotic ice. “When we visit Europa, we want to go to very young places, where material from that ocean is being expressed on the surface,” she explained. “Anywhere like that, the chances of finding biomarkers goes up - if they’re there.”
8. Only One Living Planet
Today, we know of only one living planet: our own. The knowledge and tools NASA developed to study life here are among our greatest assets as we begin the search for life beyond Earth.
There are two main questions: With so many places to look, how can we home in on the places most likely to harbor life? What are the unmistakable signs of life - even if it comes in a form we don’t fully understand? In this early phase of the search, “We have to go with the only kind of life we know,” said Tony del Genio, co-lead of a new NASA interdisciplinary initiative to search for life on other worlds.

So, the focus is on liquid water. Even bacteria around deep-sea vents that don’t need sunlight to live need water. That one necessity rules out many planets that are too close or too far from their stars for water to exist, or too far from us to tell. Our Galileo and Cassini missions revealed that some moons of Jupiter and Saturn are not the dead rocks astronomers had assumed, but appear to have some conditions needed for life beneath icy surfaces.
9. Looking for Life Beyond Our Solar System
In the exoplanet (planets outside our solar system that orbit another star) world, it’s possible to calculate the range of distances for any star where orbiting planets could have liquid water. This is called the star’s habitable zone. Astronomers have already located some habitable-zone planets, and research scientist Andrew Rushby of NASA Ames Research Center is researching ways to refine the search. “An alien would spot three planets in our solar system in the habitable zone [Earth, Mars and Venus],” Rushby said, “but we know that 67 percent of those planets are not inhabited.”

He recently developed a model of Earth’s carbon cycle and combined it with other tools to study which planets in habitable zones would be the best targets to look for life, considering probable tectonic activity and water cycles. He found that larger planets are more likely than smaller ones to have surface temperatures conducive to liquid water. Other exoplanet researchers are looking for rocky worlds, and biosignatures, the chemical signs of life.
10. You Can Learn a Lot from a Dot
When humans start collecting direct images of exoplanets, even the closest ones will appear as only a handful of pixels in the detector - something like the famous “blue dot” image of Earth from Saturn. What can we learn about life on these planets from a single dot?

Stephen Kane of the University of California, Riverside, has come up with a way to answer that question by using our EPIC camera on NOAA’s DSCOVR satellite. “I’m taking these glorious pictures and collapsing them down to a single pixel or handful of pixels,” Kane explained. He runs the light through a noise filter that attempts to simulate the interference expected from an exoplanet mission. By observing how the brightness of Earth changes when mostly land is in view compared with mostly water, Kane reverse-engineers Earth’s rotation rate - something that has yet to be measured directly for exoplanets.
The most universal, most profound question about any unknown world is whether it harbors life. The quest to find life beyond Earth is just beginning, but it will be informed by the study of our own living planet.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Earth’s rotation and Space shuttle launches
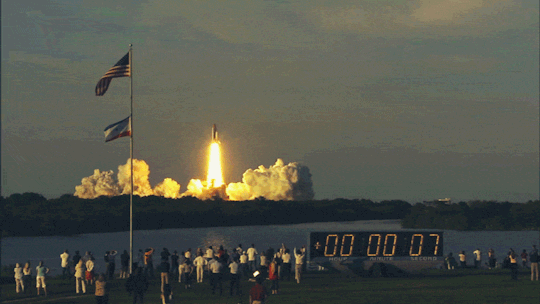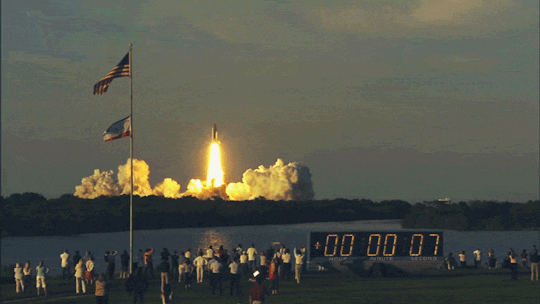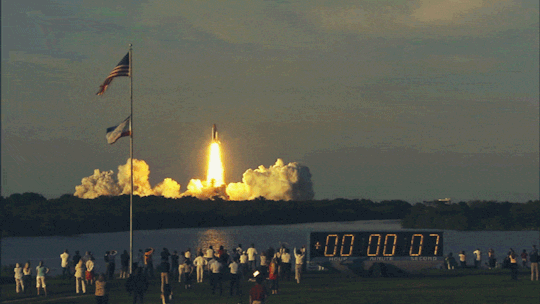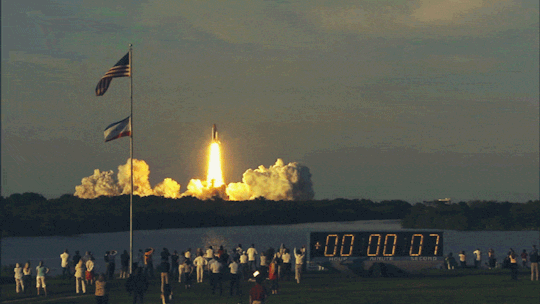
Last week we were talking about wind patterns and how they affect flight time. But it is also worth mentioning that Space shuttles are launched almost at all times from West to East to take advantage of the earth’s rotation
How does earth’s rotation affect shuttles ?
Earth is a spherical body rotating with some angular velocity. And as a result of this, the equator is rotating at a higher velocity than the poles. By launching a space shuttle from the equator you are getting a ‘speed boost’.
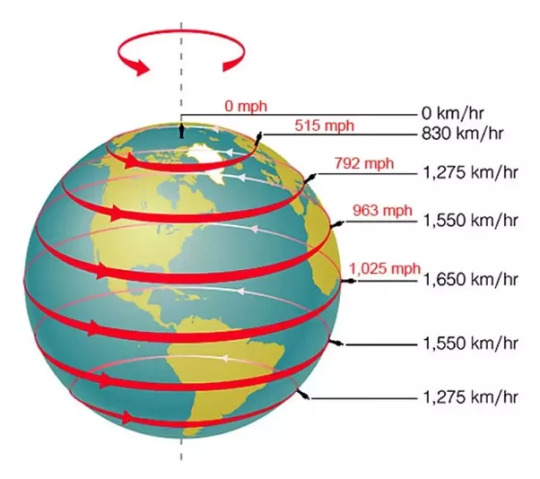
This means that if a shuttle is launched from the pole, it has to accelerate from 0 to 17000mph to reach orbital velocity.
But if a shuttle is launched from the equator, it only needs to accelerate from 1025 to 17000mph. (that 1025mph initial velocity is given by the earth free of charge)
This saves valuable amount of fuel required for propulsion
Polar Orbits
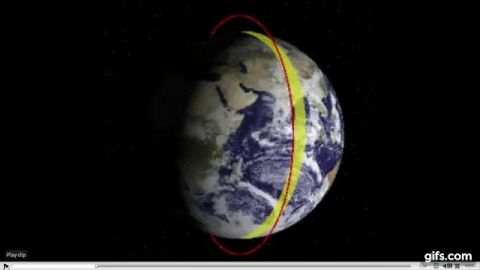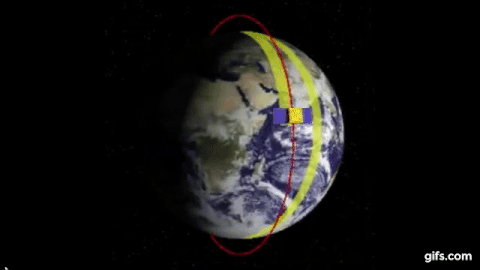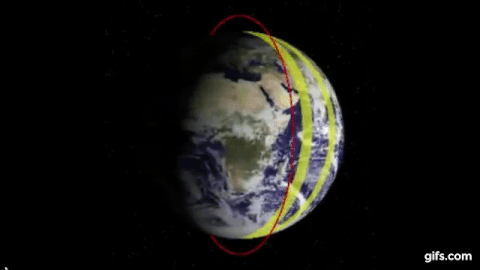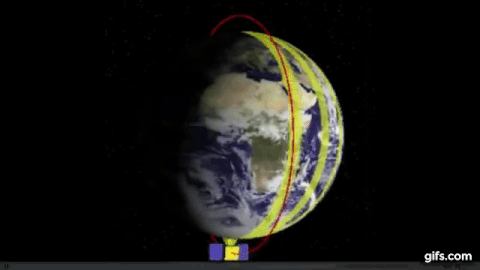
Not all rockets are launched from the west to east and the direction is determined by the purpose of its payload.
The satellites that are used for mapping for instance follow a Polar Orbit i.e they move from north to south or vice versa and therefore during launch they cannot take advantage of the earth’s rotation.
Florida or California

Another characteristic of launching satellites is that the launching stations are generally located near the coast just in case of failure of the launch, the satellite falls in an uninhabited area.
NASA primarily uses Kennedy Space Center, Florida for east-west launches and Vandenberg Base California for polar orbits for the very same reason. ***
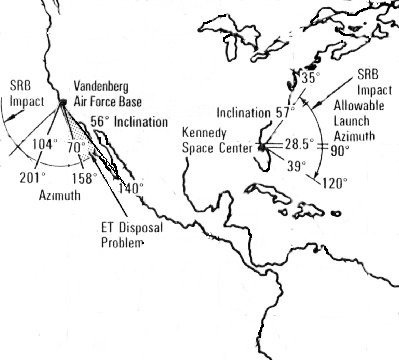
Rocket science is just truly breathtaking.
* How fast are YOU spinning on Earth’s axis right now?
** Also check out about Retrograde motion
*** This statement holds true for most launches.
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo
Ripped from the headlines.
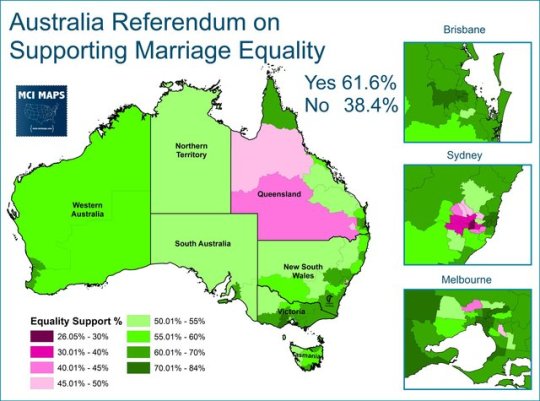
Results of Australian Marriage Equality Postal Vote
2K notes
·
View notes
Link
#AFRICA466, #health, #sleeping sickness disease, Congo
#infections#project zero#neglected tropical diseases#congo#neglected diseases#AFRICA466 health sleeping sickness disease Congo
0 notes
