#CSRF
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
RCE Bug in Oracle Cloud Shell Could Let Attackers Hijack Sessions
Tenable found a critical flaw in Oracle Cloud’s Code Editor that allowed attackers to push malicious files into a user’s session with a single click. If exploited, it could let hackers run code and spread across services silently.
Source: Tenable
Read more: CyberSecBrief
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
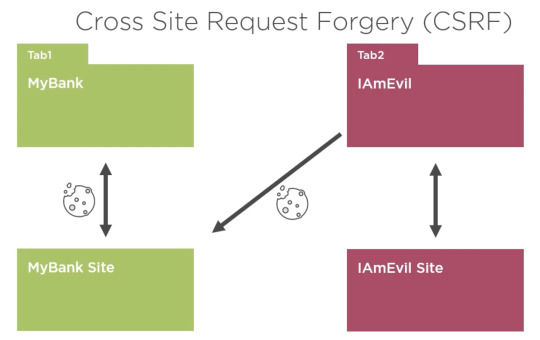
This graphic (in an online Angular course) amuses me. Of course, I know about CSRF, I've been a web developer as long as there have been web developers.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploiting and Fixing Client-Side Path Traversal (CSPT) Vulnerabilities | CyberSecurityTV
youtube
In this video, we explore a powerful yet often overlooked web vulnerability known as Client-Side Path Traversal (CSPT).
0 notes
Text
1 Hour of Popular Web Attacks (XSS, CSRF, SSRF, SQL Injection, MIME Sniffing, Smuggling and more!)
This is a compilation of many of my previous videos discussing with example some of the most popular web attacks Enjoy! source
0 notes
Text
Kas yra CSRF?
Šiuolaikiniame žiniatinklyje saugumas yra labai svarbus siekiant apsaugoti ir naudotojus, ir programas. Viena iš dažnai nepastebimų, bet pavojingų interneto pažeidimų yra kryžminės svetainės užklausos klastojimas (Cross-Site Request Forgery, CSRF). Nors tai gali skambėti sudėtingai, CSRF sąvoka yra stebėtinai paprasta: ji apgaule priverčia naudotoją atlikti veiksmus, kurių jis nenumatė, dažnai jam nežinant.
Įsivaizduokite tokį scenarijų: esate prisijungę prie banko svetainės ir pasiruošę tvarkyti savo sąskaitas. Tuo tarpu kitame skirtuke apsilankote nekaltai atrodančioje svetainėje. Jums nežinant, ta svetainė slapta siunčia užklausą jūsų bankui ir perveda lėšas į užpuoliko sąskaitą. Kadangi jau esate prisijungę, bankas mano, kad užklausa yra teisėta, ir operacija įvykdoma. Tokia yra CSRF galia.
Šiame blog'e bus rašoma informaciją, kas lemia CSRF atakų galimybę, kaip jos gali būti vykdomos ir, svarbiausia, kaip galite apsaugoti savo programas, kad jos netaptų šios tylios grėsmės aukomis. Nesvarbu, ar esate kūrėjas, siekiantis apsaugoti savo svetainę, ar naudotojas, kuriam rūpi internetinis saugumas, CSRF supratimas yra labai svarbus žingsnis saugesnės patirties link.
0 notes
Text
Securing Django Applications
Learn how to secure your Django applications with this comprehensive guide. Follow best practices for secure configurations, user authentication, preventing common threats, and more.
Introduction Security is a critical aspect of web application development. Django, being a high-level Python web framework, comes with numerous built-in security features and best practices. However, developers must be aware of additional steps to ensure their applications are secure. This guide will cover essential security practices for securing Django applications, including setting up secure…

View On WordPress
#best practices#CSRF#Django#HTTPS#secure coding#Security#SQL injection prevention#user authentication#web development#XSS
0 notes
Text
Comment lutter contre une attaque par Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) ? 6 mesures efficaces
Les attaques par Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) représentent une menace significative pour les applications web. Ces attaques exploitent la confiance qu'une application web a en l'utilisateur authentifié, permettant à un attaquant de mener des actions indésirables en utilisant l'identité de l'utilisateur. La lutte contre les CSRF est donc cruciale pour maintenir la sécurité et la confiance dans les systèmes web. Cet article explore les mécanismes d'une attaque CSRF et propose des stratégies robustes pour se défendre contre ces intrusions potentiellement dévastatrices.
Que sont les attaques CSRF ?
Une attaque CSRF, également connue sous le nom de XSRF, est une technique malveillante où des actions indésirables sont effectuées sur une application web où un utilisateur est actuellement authentifié, sans que l'utilisateur en ait conscience. Le but est d'exploiter la confiance qu'une application a en l'utilisateur. Par exemple, un attaquant pourrait forcer l'envoi d'une requête pour changer l'adresse email de l'utilisateur ou effectuer une transaction financière sans son consentement. Les attaques CSRF peuvent être particulièrement sournoises car elles peuvent être déclenchées par des visites sur des sites web malveillants ou des emails de phishing, exploitant les sessions actives des utilisateurs sur d'autres sites. L'absence de validation de l'origine des requêtes permet à ces attaques de passer inaperçues, rendant les applications vulnérables à des manipulations indésirables. Les conséquences d'une attaque CSRF peuvent être graves, allant de la modification de paramètres de compte utilisateur à la réalisation de transactions financières non autorisées. Ainsi, comprendre le fonctionnement des attaques CSRF est le premier pas vers une défense efficace.
Quelles sont les mesures préventives d'une attaque par Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) ?

1. Validation de requêtes et restrictions Cross-origin La prévention des attaques CSRF commence par une approche de sécurité globale et multi-couches. Voici quelques pratiques recommandées : - Validation stricte des requêtes : assurez-vous que toutes les requêtes sensibles, en particulier celles qui modifient l'état du système, sont accompagnées d'une validation rigoureuse. Cela inclut la vérification des méthodes HTTP utilisées (privilégier POST pour les actions modifiant l'état) et l'implémentation d'une authentification renforcée pour les actions critiques. - Restrictions Cross-Origin : mettre en place des politiques de partage des ressources cross-origin (CORS) strictes peut limiter les requêtes entre sites. En définissant clairement quelles origines sont autorisées à accéder à vos ressources, vous réduisez le risque d'attaques CSRF. - Déconnexion automatique : implémenter une fonction de déconnexion automatique après une période d'inactivité peut réduire la fenêtre d'opportunité pour une attaque CSRF, en s'assurant que les sessions ne restent pas actives indéfiniment. 2. Utilisation de Tokens Anti-CSRF : une autre mesure efficace contre une attaque CSRF L'une des méthodes les plus efficaces pour se défendre contre les attaques CSRF est l'utilisation de tokens anti-CSRF, aussi connus sous le nom de tokens de synchronisation. Ces tokens sont des valeurs uniques et imprévisibles générées par le serveur et transmises à l'utilisateur dans les formulaires ou les requêtes AJAX. Lorsque l'utilisateur soumet une requête, le token doit être inclus et validé par le serveur. Pour être efficaces, ces tokens doivent être : - Uniques par session : chaque utilisateur reçoit un token unique, réduisant le risque qu'un attaquant puisse prédire ou usurper un token valide. - Inclus dans chaque requête modifiant l'état : toutes les actions importantes doivent inclure la validation du token pour s'assurer que la requête provient bien de l'interface utilisateur légitime. 3. Validation de l'entête referer Une autre mesure de sécurité consiste à valider l'entête HTTP "Referer" des requêtes entrantes. L'entête "Referer" indique l'URL d'origine d'une requête, permettant ainsi de vérifier si la requête provient d'un domaine de confiance. Bien que cette méthode ne soit pas infaillible, car l'entête "Referer" peut être omis ou manipulé, elle offre une couche de sécurité supplémentaire lorsqu'elle est combinée avec d'autres mécanismes de défense. Il est important de noter que la validation de l'entête "Referer" doit être utilisée avec prudence, en considérant les scénarios où l'entête peut ne pas être disponible en raison de configurations de sécurité ou de la navigation privée par l'utilisateur. 4. Autres techniques de protection En plus des mesures déjà discutées, il existe d'autres techniques importantes pour renforcer la sécurité contre les attaques CSRF. Celles-ci complètent les stratégies précédentes, formant une défense en profondeur. Utilisation de Cookies SameSite Les cookies SameSite sont une mesure de sécurité récente qui permet aux développeurs de contrôler l'envoi des cookies avec les requêtes cross-site. En spécifiant l'attribut SameSite pour un cookie, les développeurs peuvent limiter à quel point les cookies sont attachés, aux requêtes initiées par des sites tiers. Les attributs SameSite acceptent trois valeurs : - Strict : le cookie n'est envoyé que pour les requêtes initiées sur le même site. - Lax : permet des exceptions pour les requêtes GET initiées par des sites tiers, utile pour certaines navigations cross-site. - None : les cookies peuvent être envoyés avec les requêtes cross-site, mais doivent être sécurisés (servis uniquement sur HTTPS). Configurer les cookies de session pour utiliser SameSite=Strict ou SameSite=Lax peut considérablement réduire le risque d'attaques CSRF, en empêchant les cookies d'être automatiquement inclus dans les requêtes cross-site. Mise en œuvre de politiques de sécurité du Contenu (CSP) Les politiques de sécurité du contenu (Content Security Policy, CSP) offrent une couche supplémentaire de sécurité qui aide à détecter et à atténuer certains types d'attaques, y compris les injections de code et les attaques CSRF. CSP permet aux développeurs de spécifier quelles sources de contenu sont fiables, empêchant le navigateur de charger des ressources malveillantes. Pour lutter contre les CSRF, CSP peut être configuré pour : - Limiter les sources à partir desquelles les scripts peuvent être exécutés. - Restreindre l'API fetch et les requêtes AJAX aux seuls domaines de confiance. - Empêcher le chargement de formulaires depuis des sources non autorisées. Bien que CSP ne soit pas spécifiquement conçu pour prévenir les attaques CSRF, sa capacité à restreindre les sources de contenu et les interactions, peut aider à réduire les vecteurs d'attaque possibles. Lecture associée : - Ransomwares : comprendre, prévenir et combattre la menace - Comment lutter contre une attaque Cross Site Scripting (XSS) ? - Injection SQL : découvrez comment lutter contre cette attaque - Spyware : qu’est-ce que c’est et comment s’en protéger ? - Virus informatique : qu’est-ce que c’est et comment l’éliminer ?
Conclusion
La lutte contre les attaques par Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) est un élément crucial de la sécurité des applications web. Les attaques CSRF exploitent la confiance entre une application et son utilisateur, et leur prévention nécessite une approche de sécurité multi-couches. L'utilisation de tokens anti-CSRF, la validation de l'entête Referer, l'emploi de cookies SameSite, et la mise en œuvre de politiques de sécurité du contenu sont parmi les stratégies les plus efficaces pour se défendre contre ces attaques. La sécurité sur Internet est un domaine en constante évolution, et les défenseurs doivent rester vigilants et proactifs dans l'application des meilleures pratiques de sécurité. En intégrant ces mécanismes de défense dans vos applications web, vous pouvez grandement renforcer leur résilience contre les attaques CSRF et protéger à la fois les données des utilisateurs et l'intégrité de vos systèmes. Laissez-nous également un commentaire ci-dessous pour partager vos pensées et vos expériences ! Read the full article
0 notes
Text
AdonisJS : comment résoudre l'erreur 'csrfField() is undefined' ?
AdonisJS est un framework puissant basé sur Node.js, utilisé pour construire des applications web et des API de manière efficace et structurée. Il offre une gamme de fonctionnalités intégrées, dont la sécurité contre les attaques de type Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF). Cependant, même avec ces outils puissants, les développeurs peuvent rencontrer des erreurs spécifiques, telles que "csrfField() is undefined". Cet article vous fournira une compréhension approfondie de l'erreur, ses causes, et vous guidera étape par étape pour la résoudre.

AdonisJS : comment résoudre l'erreur 'csrfField() is undefined' ? - LaRevueGeek.com
#AdonisJS#CSRF#csrfField()#Sécurité Web#Middleware CSRF#Node.js#HttpContextContract#Formulaires Web#Débogage AdonisJS#Protection CSRF
0 notes
Text
Navigating the Risks of JavaScript in Web Development
JavaScript is the linchpin of interactive web experiences, fueling everything from form validation to video streaming. While JavaScript enriches user engagement, it also raises significant security considerations. This post examines JavaScript's potential for misuse and the best practices to mitigate these risks.
The Dual Facets of JavaScript
JavaScript’s ability to execute on the client side is a bedrock feature of dynamic web pages, empowering developers to script complex features and responsive user interfaces. Unfortunately, the same capabilities that streamline user experience can also be exploited for malicious purposes.
Potential Misuse Cases
Malicious actors can leverage JavaScript for a range of harmful activities, including:
Data Theft: Scripts can covertly transmit personal data to unauthorized parties.
Session Hijacking: Exploiting cookies or session tokens to impersonate users.
Malware Distribution: Executing scripts that install harmful software on users' devices.
Understanding misuse scenarios is the first step in fortifying web applications against such threats.
Notable Attack Vectors: XSS and CSRF
The two most prevalent JavaScript-based threats are Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF). Each exploit different aspects of web application interaction with the user.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
XSS attacks involve inserting malicious scripts into otherwise benign web pages. These scripts activate when unsuspecting users interact with the web pages, leading to unauthorized actions or data exposure.
Defense Strategy:
Input Encoding: Systematically encode user-generated content before displaying it on the web, effectively defanging embedded scripts.
Use of CSP: Employ a Content Security Policy to specify legitimate sources for executable scripts and resources.
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
In CSRF attacks, attackers con the victim's browser into performing unintended actions on a site where the victim is authenticated, ranging from changing a user profile to initiating financial transactions.
Defense Strategy:
Anti-CSRF Tokens: Deploy one-time tokens that must accompany each form submission, ensuring requests originate from the site's own pages.
Cookie Attributes: Set 'SameSite' attributes on cookies to limit their flow to requests originating from the site that set them.
Building Defenses into JavaScript
Deploying defensive coding practices is essential to protect against the weaponization of JavaScript. Here are tactics developers can leverage:
Input Validation and Sanitization
Vigilant validation and sanitization of user input are fundamental:
// Validate acceptable characters (e.g., alphanumeric for a username) function isValidUsername(username) { return /^[a-zA-Z0-9]+$/.test(username); }
Implementing a Content Security Policy (CSP)
CSP can significantly reduce the success rate of XSS attacks:
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' https://trusted.cdn.com;
Managing Cookie Security
Correctly setting cookie attributes can prevent CSRF:
document.cookie = "sessionToken=xyz123; Secure; HttpOnly; SameSite=Strict";
Enlisting Users in Their Defense
While technical defenses are critical, empowering users to protect themselves can add another layer of security:
Educate Users: Regularly inform users on the importance of browser updates, installing security extensions, and recognizing phishing attempts.
Enable Security Features: Encourage users to install Firefox and use privacy-focused Browser extensions like uBlock Origin.
Conclusion
JavaScript's agility is a double-edged sword; its seamless integration into web pages can also serve nefarious purposes. Recognizing the potential for misuse compels us to employ rigorous defensive measures. Whether through stringent input handling, careful session management, or leveraging robust browser security features, a proactive approach to JavaScript security is the greatest defense against its weaponization. As technologies advance and threats evolve, so too must our strategies for maintaining web security and user trust.
#ko-fi#kofi#geeknik#nostr#art#blog#writing#twitter#xss#csrf#javascript#web development#dev#coding#programming#csp#content security policy#cross site scripting#information security#security#secure coding#infosec
1 note
·
View note
Text
In an era where the exchange of data across the web has become ubiquitous, safeguarding the integrity and security of web applications is paramount. Among the array of vulnerabilities that can threaten the trustworthiness of these applications, Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) stands as a particularly insidious adversary. By the end of this comprehensive guid, you will possess the knowledge and tools to fortify your web applications against CSRF threats effectively.
0 notes
Text
Application Security : CSRF
Cross Site Request Forgery allows an attacker to capter or modify information from an app you are logged to by exploiting your authentication cookies.
First thing to know : use HTTP method carefully. For instance GET shoud be a safe method with no side effect. Otherwise a simple email opening or page loading can trigger the exploit of an app vulnerability
PortSwigger has a nice set of Labs to understand csrf vulnerabilities : https://portswigger.net/web-security/csrf
Use of CSRF protections in web frameworks
Nuxt
Based on express-csurf. I am not certain of potential vulnerabilities. The token is set in a header and the secret to validate the token in a cookie
Django
0 notes
Text
Exploiting and Fixing Client-Side Path Traversal (CSPT) Vulnerabilities | CyberSecurityTV
youtube
In this video, we explore a powerful yet often overlooked web vulnerability known as Client-Side Path Traversal (CSPT). Using the CSPT Playground by DNSsec, we demonstrate how attackers can exploit insecure client-side logic to manipulate path parameters, bypass access controls, and potentially trigger dangerous POST requests — even with authentication tokens like JWT or CSRF included. We walk through a practical attack scenario, explain how CSPT can be chained with other vulnerabilities like CSRF, and highlight why traditional defenses like same-site cookies may fall short. Most importantly, we discuss critical remediation strategies, including backend JSON schema enforcement, frontend input sanitization, and improving security in API client libraries. This deep dive into CSPT will help developers and security researchers better understand and defend against this subtle yet serious threat.
#cybersecuritytv#pathtraversal#cspf#websecurity#cyberattacks#csrf#webvulnerabilities#clientsidesecurity#apisecurity#inputvalidation#pathtraversalattack#cybersecurityawareness#webapplicationsecurity#securecoding#developersafety#securityremediation#sanitizinginputs#cybersecuritytips#vulnerabilityexploitation#cspfattack#Youtube
0 notes
Text
>article called Demystifying CORS, CSRF tokens, SameSite & Clickjacking - Web Security
>look inside
>still mystifying
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Prevent OAuth Misconfiguration in Symfony Apps Securely
Introduction
OAuth is the industry-standard protocol for authorization. While Symfony offers first-class OAuth bundles, a single misconfiguration can expose sensitive data or allow unauthorized access.

In this guide, we’ll walk you through:
What OAuth misconfiguration entails
Common pitfalls in Symfony setups
Hands-on coding examples
How to scan your app using our Website Vulnerability Scanner online
Best practices to lock down your OAuth flows
For more in-depth tutorials, visit our blog: ➡️ Pentest Testing Corp Blog
What Is OAuth Misconfiguration?
OAuth misconfiguration occurs when the authorization server or client settings are improperly defined, leading to:
Open Redirects: Attackers abuse redirect URIs
Insecure Scopes: Granting excessive permissions
Weak Token Validation: Skipping signature or audience checks
In Symfony, these mistakes often stem from inaccurate security.yaml entries or incorrect client registration on your OAuth provider.
Example: Insecure OAuth Setup
Below is an insecure security.yaml that illustrates two pitfalls: missing state checks and overly permissive redirect URIs.
# config/packages/security.yaml security: firewalls: oauth_login: pattern: ^/connect/ oauth: resource_owners: google: "/login/check-google" login_path: /connect/google check_path: /login/check-google default_target_path: / use_referer: true # insecure: trusts HTTP Referer header oauth_user_provider: service: app.user_provider
Issues:
use_referer: true trusts the HTTP Referer header—easy to spoof.
Redirect URIs not strictly defined on the OAuth provider side.
How to Scan with Our Free Tool
Use our Website Vulnerability Scanner to automatically detect OAuth misconfigurations and other vulnerabilities in seconds.
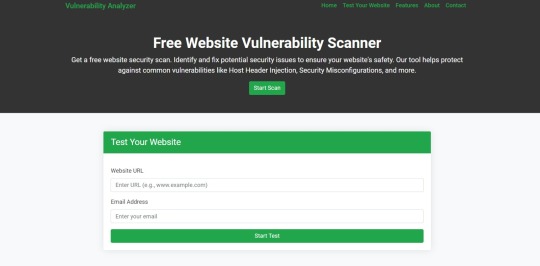
Screenshot of the free tools webpage where you can access security assessment tools for vulnerability detection
Within moments, you’ll receive a detailed report identifying misconfigurations, insecure headers, and more.
Sample Vulnerability Assessment Report
Once the scan completes, you’ll see sample assessment report to check Website Vulnerability:
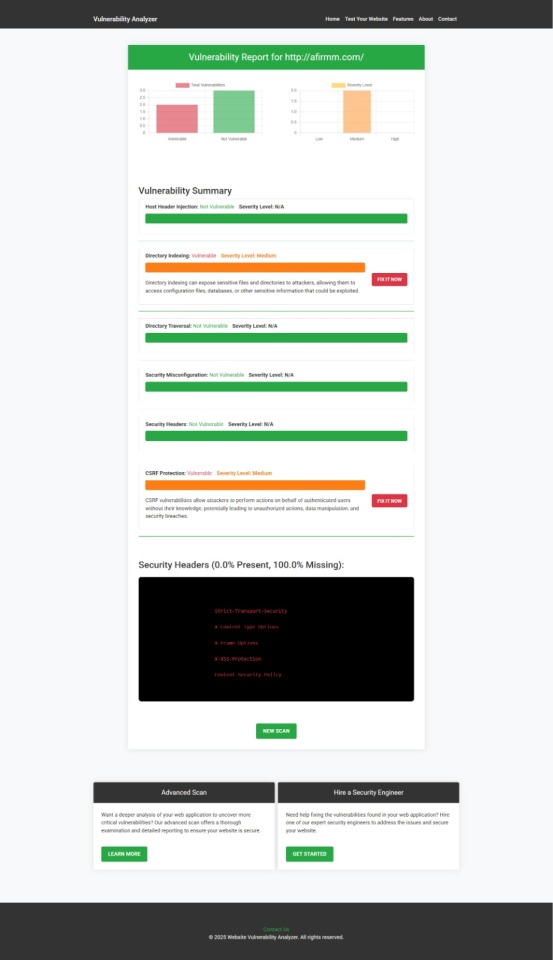
Example of a vulnerability assessment report generated with our free tool, providing insights into possible vulnerabilities
Best Practices to Secure OAuth in Symfony
Strict Redirect URIs Register only exact URIs on your OAuth provider.
# security.yaml oauth: resource_owners: google: redirect_uri: 'https://your-app.com/connect/google/check'
2. Enforce State Parameter Prevent CSRF in the authorization flow.
oauth: resource_owners: google: options: use_state: true
3. Validate Tokens Always verify issuer (iss), audience (aud), and signature.
// src/Security/GoogleTokenValidator.php use Firebase\JWT\JWT; public function validate(string $jwt): array { $publicKey = file_get_contents($this- >projectDir.'/config/jwt/public.pem'); $payload = JWT::decode($jwt, $publicKey, ['RS256']); if ($payload->aud !== 'your-client-id') { throw new \Exception('Invalid audience'); } return (array)$payload; }
4. Limit Scopes Only request the scopes your app truly needs.
oauth: resource_owners: google: options: scope: ['email', 'profile']
AI Application Cybersecurity
Leverage our AI-powered analysis for advanced threat detection in AI applications:
🔗 AI Application Cybersecurity Services
Partner With Us
Offer top-tier cybersecurity to your clients by reselling our pentest & assessment services:
🔗 Offer Cybersecurity Service to Your Clients
Stay Updated
Subscribe to our LinkedIn newsletter for the latest in web security:
✉️ Subscribe on LinkedIn
By following these guidelines and examples, you’ll eliminate OAuth misconfiguration risks in your Symfony applications—and keep your users’ data safe.
Want a free scan? DM me or check https://free.pentesttesting.com/.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Niagara Framework
...Developed by Tridium, an independent business entity of Honeywell, the Niagara Framework is a vendor-neutral platform used to manage and control a wide range of devices from different manufacturers, such as HVAC, lighting, energy management, and security, making it a valuable solution in building management, industrial automation, and smart infrastructure environments.
It consists of two key components: Platform, which is the underlying software environment that provides the necessary services to create, manage, and run Stations, and Station, which communicates with and controls connected devices and systems.
The vulnerabilities identified by Nozomi Networks are exploitable should a Niagara system be misconfigured, causing encryption to be disabled on a network device and opening the door to lateral movement and broader operational disruptions, impacting safety, productivity, and service continuity.
The most severe of the issues are listed below -
CVE-2025-3936 (CVSS score: 9.8) - Incorrect Permission Assignment for Critical Resource
CVE-2025-3937 (CVSS score: 9.8) - Use of Password Hash With Insufficient Computational Effort
CVE-2025-3938 (CVSS score: 9.8) - Missing Cryptographic Step
CVE-2025-3941 (CVSS score: 9.8) - Improper Handling of Windows: DATA Alternate Data Stream
CVE-2025-3944 (CVSS score: 9.8) - Incorrect Permission Assignment for Critical Resource
CVE-2025-3945 (CVSS score: 9.8) - Improper Neutralization of Argument Delimiters in a Command
CVE-2025-3943 (CVSS score: 7.3) - Use of GET Request Method With Sensitive Query Strings
Nozomi Networks said it was able to craft an exploit chain combining CVE-2025-3943 and CVE-2025-3944 that could enable an adjacent attacker with access to the network to breach a Niagara-based target device, ultimately facilitating root-level remote code execution.
Specifically, the attacker could weaponize CVE-2025-3943 to intercept the anti-CSRF (cross-site request forgery) refresh token in scenarios where the Syslog service is enabled, causing the logs containing the token to be transmitted potentially over an unencrypted channel.
Armed with the token, the threat actor can trigger a CSRF attack and lure an administrator into visiting a specially crafted link that causes the content of all incoming HTTP requests and responses to be fully logged. The attacker then proceeds to extract the administrator's JSESSIONID session token and use it to connect to the Niagara Station with full elevated permissions and creates a new backdoor administrator user for persistent access.
In the next stage of the attack, the administrative access is abused to download the private key associated with the device's TLS certificate and conduct adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) attacks by taking advantage of the fact that both the Station and Platform share the same certificate and key infrastructure.
With control of the Platform, the attacker could leverage CVE-2025-3944 to facilitate root-level remote code execution on the device, achieving complete takeover. Following responsible disclosure, the issues have been addressed in Niagara Framework and Enterprise Security versions 4.14.2u2, 4.15.u1, or 4.10u.11.
"Because Niagara often connects critical systems and sometimes bridges IoT technology and information technology (IT) networks, it could represent a high-value target," the company said....
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
how do i... boopbeam.......
I AM SO GLAD YOU ASKED
HOW TO BOOPBEAM UNDER THE CUT

STRAP IN BOYS THIS IS GONNA BE A LONG ONE
ok so.
you need Bun. It's a JavaScript runtime for the server (your computer). It's what runs the little script I made that automates the booping. Copy-paste the little one-liner into your terminal of choice and hit enter.
2. download this file here. THIS IS THE BOOPINATOR!
3. You'll need a couple pieces of information. What you want to do is go to tumblr.com on a computer, then open up the developer tools. Usually Ctrl (or Cmd) + Shift + I (that's an eye). Head to the tab labelled Network.
4. With the network tab open, boop somebody! However you do it. Either by the boop button next to their name, or the paw icon on their profile. Boop somebody!
5. You should see a new entry in the Network tab labeled "boop". Click on it.
6. You should see a bunch of new tabs to the side. One of them will be named "Headers". Click on that if it isn't already selected.
7. Scroll down to where it says "Request Headers" (NOT RESPONSE HEADERS!) and copy THREE values into the boopinator.ts file you downloaded: • Your "Cookie". Copy that whole value into line 39; replace the bit where it says "YOUR COOKIE HERE" (and keep the quotes!) • Your "Authorization". Copy that whole value (including the "Bearer") into line 38; replace the bit that says "YOUR TOKEN HERE (starts with Bearer)" (and keep the quotes!) • Your "X-Csrf". Copy that value into line 85; replace the bit where it says "FIRST CSRF TOKEN" (and keep the quotes!).
I cannot stress this enough these three values are extremely sensitive and should not be shared ever.
8. In a terminal, navigate to the directory you downloaded boopinator.ts (usually with the cd command) Run: bun boopinator.ts and it *should* start going! Optional 9. You can replace the URLs at the top of the file with the URLs of the people you wanna boop. The script will choose between them at random every time it boops somebody, which is about once per second.
🎉 CONGRATULATIONS you have started the boopbeam! It should now run forever, assuming Tumblr doesn't cut you off. They will eventually, your cookie will expire, but that should be good for about 1000 boops. Occasionally you'll get hit with a 429 error; the script will recover from that automatically, but any other error will cause it to stop in its tracks and wait for you to restart it. An authorization error, for example, means you need to grab those three values again (see step 7).
If you have any questions, my DMs should be open? Or just reblog this post with your question and I'll clarify as much as I can.
15 notes
·
View notes