#Geotextile
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
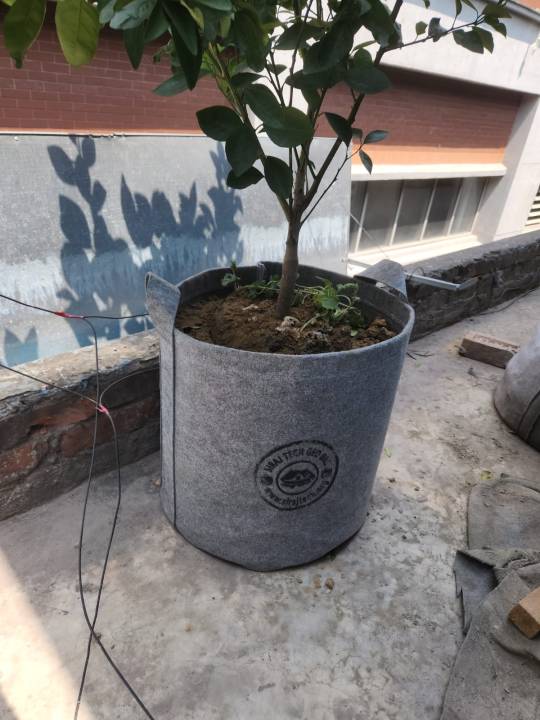
Growing pots for plants | Fabric Pot – Black 500GSM
Growing pots for plants , Fabric Pot এবং জিও পট হলো টিন ও প্লাস্টিক টপের বিকল্প, যা পানিতে সহজে নষ্ট হয় না এবং এটি পরিবেশ বান্ধব হওয়ায় বাড়ির ছাদে ব্যবহার উপযোগী। এতে ছোট বড় সব ধরনের গাছ লাগানো যায়।
আরো জানতে ভিজিট করুন - Geo bag

1 note
·
View note
Text
Build Stronger, Safer Sports Courts with Fibermesh & Geotextile!
Looking to enhance your sports court’s durability, drainage, and long-term performance? Discover how Fibermesh and Geotextile layers make a real difference in synthetic acrylic sports flooring.
✅ Crack prevention ✅ Superior water management ✅ Reinforced base strength
Whether it's a tennis court or a multi-sport facility, these materials are the unsung heroes beneath the surface!
👉 Read more: https://pacecourt.com/fibermesh-and-geotextile-in-sports-flooring/
#Pacecourt#SportsFlooring#Fibermesh#Geotextile#AcrylicCourt#CourtConstruction#DurableCourts#SportsInfraIndia
0 notes
Text
High speed non-woven geotextile is producing short fiber geotextile
0 notes
Text
Maintaining Non-Woven Carpets: Tips for Longevity
Non-woven carpets have become a rather popular choice in homes, commercial spaces, and offices because they are affordable, easy to install, and resist fraying. However, they are like all other flooring options in that you need to care for them properly so that they remain clean, functional, and attractive over time. It does not matter what your carpet is made from — polypropylene, blended fiber, or polyester — you have to follow the correct maintenance practices so that you can extend its lifespan significantly. So, in this blog, we will provide you with some practical tips on maintaining non-woven carpets and ensuring they offer you the best performance and durability.
Understanding the nature of non-woven carpets
This is perhaps the most important factor that you need to be aware of in this particular context. Non-woven carpets are created by bonding fibers with each other using chemicals, solvent treatment, and mechanical heat. As their names would suggest, they are not knitted or woven. These carpets are lightweight and economical, and often they are used in high-traffic areas such as exhibitions, temporary setups, and events. They may be able to resist unraveling and can be maintained easily but since they have porous surfaces they might trap stains and dust quickly if you do not care properly for them.
Vacuuming them regularly
Vacuuming is the most effective way to prevent dirt and dust from being embedded into the fibers of your carpet. For a non-woven carpet, you must vacuum it at least twice a week. In case, you are using them in more high-traffic areas you must vacuum them even more frequently. You can also use a suction-only attachment or vacuum cleaner with adjustable height settings to make sure that you do not end up damaging the fibers. This is especially so when the carpet has a lower pile. In such cases, you can go over the carpet slowly so that you can deep clean it.
Spot cleaning — acting fast with stains
Accidents can and will always happen on your carpet. You might end up spilling coffee, dropping ink, or walking while wearing muddy shoes on it. Immediate spot cleaning is the only way to make sure that these accidents do not end up leaving permanent stains on the carpet. You can always clean the affected area gently by using a clean cloth or a paper towel. You must also never rub it as it might push the stain even deeper into the fibers. The best DIY (do-it-yourself) cleaning solutions here are mild detergent and water.
Avoiding excessive moisture
Non-woven carpets are not designed to absorb huge amounts of water. So, if you use too much water when you are cleaning you can end up weakening the backing layers. This can lead to premature wear — in humid climates you can add mold growth to this as well. In such cases, it is always better to use damp cloths rather than soaking the surface.If you want to clean it deep, use carpet cleaning methods that use less moisture such as dry powder cleaning and encapsulation. In case you use any wet cleaning method, make sure the carpet dries out completely.
Protecting high-traffic areas
If you want your non-woven carpet to last longer you can focus on implementing preventive measures in areas that experience the highest foot traffic. Carpets placed in entryways, seating areas, and hallways are especially vulnerable to wear and tear. In this case, you can try using entrance mats that trap dirt before it gets to the carpet. You can also rearrange the furniture placed on it to distribute the pressure. You can also apply carpet tiles or protective runners atop the carpet to provide it with extra durability.
Periodic deep cleaning
Even if you maintain a non-woven carpet regularly you must deep clean once every 4–6 months as the carpet would benefit significantly from it. This process will remove the embedded dirt, bacteria, and allergens that you might miss during your regular vacuuming. The benefit of hiring professional cleaners for such work is that they will assess the type of your carpet and use the right low-moisture method for it. If you want to do it yourself you should use dry compound or encapsulation products that have been created specifically for synthetic fibers.
Apart from these, you must also mind the furniture that you have placed on the carpet, watch for edge damage or fraying, and store them properly when you are not using them. One of the best steps in this regard is to select a quality product right at the beginning.
0 notes
Text
Significance of BIS Approved Geomembranes and their Applications in Modern Construction
Environmental protection and sustainable development are the most evident problems that the construction sector in general and engineers in particular are confronted with today. In the vast category of materials used in constructions, geomembrane have a great deal to offer towards a vast range of applications ranging from waste containment to dam liners. We would highlight here in this paper the significance of BIS approved geomembrane, the role played by geomembrane manufacturers, and the role played by geotextiles as reinforcing material to geomembranes for application such as dam construction.

What are Geomembranes?
A geomembrane is a man-made, impermeable sheet utilized to prevent water, gases, and liquids from flowing in civil and environmental engineering. They are durable sheets and are typically composed of polymers like high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and polypropylene. Geomembranes are applied on sites where they serve as a containment and shield barrier so that material like toxic waste or water does not seep into the environment.
Why BIS approved Geomembranes are important
BIS approval comes under the reliability and quality of construction and civil engineering materials in India. Geomembranes BIS approved are tested under very stringent testing and efficiency criteria that decide their long term quality, environmental durability, and application for a specific purpose.
After a geomembrane is BIS approved, that would mean that the geomembrane has been tested for the most important properties like:
- Chemical and water impermeability.
- UV resistance to allow exposure to severe outdoor climatic conditions.
- Chemical resistance to inhibit damage through chemical exposure.
To contractors and engineers, using BIS approved geomembranes is using material of the best quality, and they provide efficient and secure solutions for risky infrastructure projects.
Role of Geomembrane Producers
Geomembrane manufacturers are accountable for supply and quality of such vital supplies. They specialize in planning and producing geomembranes of various types, e.g., reinforced, smooth, and textured, based on the needs of a project.
As the technology itself has developed further, geomembrane manufacturer have developed products for a particular use, be it a landfill, a wastewater treatment facility, or dams. Through the development of geomembranes in close coordination with engineers under an exclusive agreement, the manufacturers guarantee that geomembranes made by them bear the specifications of tensile strength, flexibility, and long-term performance.
Apart from the high demand for green solutions, geomembrane manufacturers are also keen on green manufacturing processes and the production of geomembranes with lower environmental impact.
The Supportive Role of Geotextiles
While geomembranes are at the center of impermeable layer construction, they are usually protected by geotextile to ensure overall success in a project. Geotextiles are man-made fibers produced for filtering, reinforcement, or separation of layers in construction works.
Geotextiles, when used in conjunction with geomembranes, provide several benefits including:
1. Separation: Geotextiles provide separation between dissimilar layers of soil and structural support to the foundation.
2. Reinforcement: Geotextiles provide strength and stability to the underlying soil, especially in the event of erosion or water pressure.
3. Filtration: Geotextiles permit free passage of water but filter out finer particles to prevent clogging of drain pipes.
Geomembranes and geotextiles are together a composite material for management of water flow, erosion control, and strengthening of structures for civil engineering purposes.
Application of Geomembranes in Dam Construction: Water Tightness Maintenance
geomembrane for dams possess one of their most significant applications in dam construction. Application of geomembranes by dams is suitable for developing a surface which is water proof so that leakage of water to the maximum extent can be avoided, ensuring stability and safety of the dam.
Geomembranes are even employed for lining dams, ponds, and even lining the interior of dams during construction. Geomembranes are physically and chemically durable and can withstand the aggressive conditions of water storage and prolonged exposure to fluctuating water levels.
Using geomembranes, engineers can:
- Prevention of water seepage: Stability to the dam must be established and the area around it must not be ruined.
- Cost of repair or replacement reduced: Quality barrier equates to reduced cost of repair or replacement.
- Protection against environment: Because they lessen water body contamination in the vicinity, regional environments are protected by geomembranes.
Conclusion
Geomembrane production service and application and BIS compliant geomembranes are part of the essential development activity of the infrastructure today. In dam development by waste dump closure and enviro cover, the product extends maximum protection for water and chemical flow. The product with geomembranes applied along with geotextiles helps to allow engineers and construction builders an opportunity to make activities sustainable and perpetual endeavors.
As expansion and growth of the construction sector occur, the demand for green, quality, and durable materials will increase. BIS-approved geomembranes will facilitate such growth and lead the way in providing required protection and security to infrastructural projects that are needed at an international level.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Buy Geotextile Fabric: Durable & Reliable Solution for Construction | Kttl.

0 notes
Text
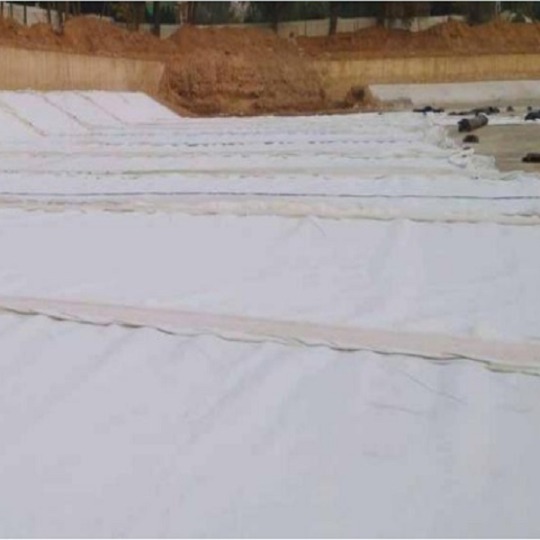

Geotextile is a water-permeable geosynthetic material made of synthetic fibers by needling or weaving. Geotextile is one new material of geosynthetics. The finished product is cloth-like, with a width of 4-6 meters and a length of 50-100 meters. Geotextiles are divided into woven geotextiles and nonwoven geotextiles (filament geotextiles, short-filament geotextiles, filament woven geotextile, and PP woven geotextile).
Geotextile Product Function
Woven Geotextile Fabric are with excellent filtering, drainage, isolation, reinforcement and protection. Characterized by lightweight, high tensile strength, good permeability,high temperature resistance, freeze resistance, aging resistance and corrosion resistance.
Woven Geotextile Fabric Product Features
1. High strength. Sufficient strength and elongation can be maintained in dry and wet conditions because of the application of plastic fiber. 2. Long-term corrosion resistance in soil and water with different PH. 3. Good water permeability due to gaps between the fibers. 4. Good antimicrobial properties. No damage to microorganisms and insects 5. Easy to use. Convenient for transportation, laying and construction due to its light and soft material. 6. Width is 1-9m, mass per unit is 100-1000g/㎡ .
0 notes
Text
The Crucial Role of Geotextiles in Modern Civil Engineering Projects

In the realm of civil engineering, the integration of innovative materials and technologies has become imperative to meet the evolving demands of infrastructure development. Among these advancements, geotextiles have emerged as indispensable components in various civil engineering projects, especially Geotextile in road construction. Singhal Industries Pvt Ltd, a trailblazer in the packaging industry in India, has been at the forefront of providing high-quality geotextiles, catering to the diverse needs of civil engineering ventures across the country.
Geotextiles, essentially permeable fabrics made from synthetic fibers, offer a myriad of benefits in civil engineering applications. Their versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness make them ideal for a wide range of functions, with road construction being a prominent area of utilization.
Understanding Geotextiles in Road Construction:
Enhancing Soil Stability:
Geotextiles play a pivotal role in enhancing soil stability in road construction projects. Placed beneath road surfaces, these fabrics act as reinforcement layers, distributing loads effectively and minimizing the risk of soil erosion and subsidence. By restraining lateral movement of soil particles, geotextiles ensure the longevity and performance of road infrastructure.
Drainage and Filtration:
One of the primary challenges in Geotextile for road construction is managing water accumulation, which can compromise the structural integrity of the road. Geotextiles facilitate efficient drainage by allowing water to permeate through while preventing the ingress of soil particles. This dual functionality not only ensures proper water management but also enhances the overall strength and durability of the road.
Separation of Layers:
In multi-layered road constructions, geotextiles serve as crucial separators between different materials, such as aggregate and soil. By preventing intermixing and providing distinct boundaries between layers, these fabrics prevent the loss of structural integrity and maintain the design specifications of the road, thereby prolonging its service life.
Geotextile GSM and Its Significance:
Geotextile GSM , grams per square meter, denotes the mass per unit area of the fabric and is a critical parameter in determining its performance characteristics. Higher GSM geotextiles generally offer greater strength, durability, and filtration capabilities, making them suitable for applications requiring robust reinforcement and drainage properties, such as road construction in high-traffic areas or areas prone to heavy rainfall.
In conclusion, geotextiles have revolutionized the landscape of civil engineering, particularly in road construction, by offering unparalleled benefits in soil stabilization, drainage, and layer separation. Singhal Industries Pvt Ltd continues to be a trusted provider of high-quality geotextiles, empowering civil engineering projects across India with sustainable and resilient infrastructure solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are the primary benefits of using geotextiles in road construction?
Geotextiles offer enhanced soil stability, efficient drainage, and effective separation between different road layers, thereby improving the overall performance and longevity of the road infrastructure.
2. How do geotextiles contribute to soil stabilization in road construction?
Geotextiles act as reinforcement layers, distributing loads and restraining lateral movement of soil particles, thus minimizing soil erosion and subsidence.
3. What role does geotextile GSM play in road construction?
Geotextile GSM indicates the mass per unit area of the fabric, with higher GSM fabrics offering greater strength, durability, and filtration capabilities, making them suitable for demanding road construction applications.
0 notes
Text
Elevate Civil Engineering with Indonet's Geocomposite Solutions

Unlock the potential of your civil engineering projects with Indonet's innovative geocomposite solutions. From soil reinforcement to effective erosion control, our advanced products are designed to boost durability and performance. Discover how Indonet can transform your construction efforts and take your projects to the next level.
#Indonet#IndonetGroup#geocomposites#saltbarriers#indodrainsaltbarriers#geotextile#indokoncoirgeotextile#geonetmanufacturer#geocell#indokongeocell#dimpleboards#indokondimpleboards
0 notes
Video
youtube
Geosincere Geotextile port construction, coastal protection
1 note
·
View note
Text
Geosynthetics in Geotechnical Engineering: Types and Applications
Introduction Geotechnical engineering is at the core of building a solid foundation for modern infrastructure. However, achieving stability, sustainability, and cost-efficiency in construction can be a challenging task. Enter geosynthetics, a group of engineered materials revolutionizing the field. In this article, we’ll explore the types of geosynthetics and their myriad applications, shedding…

View On WordPress
#erosion control#Geocell#Geofoam#Geogrid#Geomembrane#Geosynthetic Clay Liner#Geosynthetics#Geotechnical engineering#Geotextile#Slope Protection#Sustainability
0 notes
Text

Geo Bag and Geotextile sheet Price in Bangladesh
Geo bag
0 notes
Text
SAMI Layer Pavement Fabrics: Boost Road Durability
SAMI Layer Pavement Fabrics: Boost Road Durability

Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of road construction, innovations like SAMI layer pavement fabrics are transforming the way we approach durability and longevity in infrastructure. This blog post explores the key benefits and applications of SAMI layer fabrics, shedding light on how they play a crucial role in enhancing the resilience of our roads.
Understanding SAMI Layer Pavement Fabrics:

How SAMI Layer Fabrics Boost Road Durability
SAMI layer pavement fabrics strengthen the road in multiple ways:
Crack Prevention
Acting as a barrier, the SAMI fabric inhibits cracks from appearing and spreading across the road surface. This adds years to the pavement life. The bonded fabric intercepts cracks at the surface level preventing downward propagation into the base layers.
Enhanced Structural Stability
The integration of the high-modulus SAMI layer evenly distributes traffic loads over a broader pavement area. This reduces concentrated stresses and deformations leading to pavement failures. The outcome is improved stability and strength.
All-Weather Reliability
SAMI fabrics are engineered using polymers like polyester, polyethylene or glass fibers that can withstand diverse environmental conditions from freezing winters to scorching summers. This makes roads more reliable through changing seasons.
Extended Lifespan
The collective impact of crack prevention, load distribution and weather resistance provided by SAMI layers is a significantly extended road lifespan. The surface maintains integrity for longer periods without requiring repairs and rehab.
Sustainable Construction

Applications of SAMI Layer Pavement Fabrics
Some prominent applications that highlight the benefits of SAMI layers include:
Road Rehabilitation
Applying SAMI fabrics provide an economical overlay solution for rehabilitating aged, damaged road surfaces. The fabric strengthens the existing base while providing a new wearing course.
New Road Construction
Integrating a SAMI layer into new road construction leads to more crack-resistant, durable surfacing that extends the period between overlays.
Preventing Reflective Cracking
SAMI layers serve as effective crack retarders at the interface of old and new pavement sections. This addresses reflective cracking, a common issue in road overlays.
Bridge Deck Protection

In conclusion:
SAMI layer pavement fabrics are a game-changer in the realm of road construction, offering a sustainable and effective solution for enhancing the durability of our infrastructure. As we pave the way to the future, these innovative fabrics prove to be an indispensable asset in creating roads that can withstand the test of time.
#geotextile#pavement#non woven fabrics#woven mesh fabric#pp woven bags#woven#woven fabric manufacturers#fabrics
0 notes
Text
Non-woven geotextiles are an important category of geosynthetics used across a wide range of infrastructure and construction applications. This guide provides a deep dive into what non-wovens are, their types, key properties, manufacturing processes, installation methods, advantages, applications, and more.

Introduction to Non-Woven Geotextiles
Geotextiles refer to permeable, polymeric textile materials used in contact with soil or rock in civil engineering applications. They can be woven or non-woven.
Non-woven geotextiles are made by bonding polymeric fibers together through processes like needle punching, heat bonding or resin bonding. The random arrangement of fibres produces a strong, porous and flexible material.
Geotextiles that are non-woven are better than those that are woven. They are better at filtering, draining, and cushioning, and are easier to install. In addition, they are more budget-friendly. These characteristics make non-wovens ideal for many functions like filtration, drainage, separation, and reinforcement.
Needle Punched Non-Woven Geotextiles
Needle-punched non-wovens are a major type of non-woven geotextile produced by mechanically orienting and entangling fibers. Hundreds of fine needles repeatedly penetrate a fibre web to tangle the fibres into a strong, porous and stable fabric.
Compared to other non-wovens, needle-punched variants have high permeability and drainage capacity along with good puncture resistance. This makes them ideal for filtration and drainage applications.
Types of Needle-Punched Non-Woven Geotextiles
Needle-punched non-wovens can be categorized into three main types based on weight and fiber thickness:
Lightweight Needle Punched Wovens
Made from fine fibres and low fiber weights between 20-100 gsm. Mainly used in applications that do not require high strength.
Medium Weight Needle Punched Non Wovens
Heavier fibers and medium basis weights of 100-250 gsm. Provides moderate strength for functions like separation.
Heavyweight Needle Punched Non-Wovens
Very coarse, thick fibres and high basis weights above 250 gsm. Imparts maximum strength for reinforcement uses.
Selections depend on the target function. Non-woven fabrics can be categorized into lightweight and heavyweight variants.
Key Functions and Applications of Non-Woven Geotextiles
Non-woven geotextiles perform various functions that make them indispensable for major infrastructure and construction projects:
Filtration Applications
The porous structure allows water to pass through while blocking soil particles. This filtration ability is useful in:
Roadway drainage systems
Retaining walls
Landfill drainage
Water treatment plants

Drainage Applications
Nonwovens have high water flow rates in the principal direction. This makes them excellent for drainage purposes like:
Landfill drainage layers
Sports field drainage
Retaining wall and slope drainage
Separation Applications
The fabric physically separates dissimilar materials. Key applications include:
Roadway base and subbase separation
Railroad bed separation
Foundations separation
https://www.aakarperiwal.com/blogs/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/geotextile-500x500-3.webp
Reinforcement Applications
Non-wovens provide reinforcement for additional strength when wrapped around soil. Uses include:
Embankments over soft soils
Retaining walls with stacked blocks
Slopes requiring improved bearing capacity
Erosion Control Applications
The fabric acts as a permeable layer to protect against wind and water erosion while allowing water passage. Some uses are:
Covering slopes along railways and highways
Coastal embankments erosion control
Riverbanks and canal protection
Transportation Applications
Within road construction, non-wovens assist with filtration, separation, drainage and stabilization. Common applications:
Separation between sub-base and subgrade
Filtration in edge drains alongside pavements
Soil stabilization for improved load-bearing
Construction Applications
Foundations and walls drainage
Vapor barriers in concrete slabs
Flooring reinforcement and crack prevention

This demonstrates the versatility of non-woven geotextiles across diverse functions in C&I projects. Their adaptive properties drive widespread adoption.
Key Properties of Non-Woven Geotextiles
Non-woven geotextiles exhibit unique properties derived from their material composition, manufacturing method and overall structure:
Raw Materials
Most non-wovens use polypropylene as the raw material which is cost-effective and provides required properties. High-end variants use polyester or a polypropylene-polyester blend.
Basis Weight
Basis weight is the mass per unit area measured in g/m2. Heavier basis weights produce stronger fabrics with higher puncture resistance. Typical range is from 20 g/m2 to 300 g/m2.
Thickness
Thickness depends on fiber density and varies from 1mm to 15mm. Affects permeability, cushioning ability and separation effectiveness.
Hydraulic Properties
Non-wovens have high water permeability (normal to the plane) and adequate transmissivity. Allows swift drainage while blocking soil passage.
Mechanical Properties
Tensile strength, tear strength, puncture resistance and burst strength are key mechanical properties. Non woven selection depends on the required load capacity.
Endurance Properties
Long-term resistance against environmental exposure, chemicals, microbes and mechanical stresses comes under endurance properties. Requires proper polymer choice.
These characteristics directly impact the effectiveness and lifespan of the non-woven geotextile for its intended function.
Overview of Manufacturing Processes
Non-woven geotextile production involves specialized processes to achieve the desired fiber arrangement and properties:
Web Formation
The first step is creating a uniform web of fibres laid out in overlapping, random orientations using air, mechanical or wet-laid techniques.
Web Bonding
The fiber web undergoes thermal, chemical or mechanical bonding. This interlocks the fibres to impart strength, stability and thickness.
Finishing
Additional treatments enhance properties - for instance, calendering uses heated rollers to achieve smoothness. Fabric edges are trimmed to create rolls.
Testing and Inspection
Extensive testing under certified labs evaluates parameters like strength, permeability, opening size etc. This ensures compliance with specifications.
Keeping manufacturing consistent and monitoring variabilities is vital for non-woven quality assurance. Automation allows scalable production with minimal defects.
Design and Installation Factors for Non-Woven Geotextiles
Proper design, handling and deployment of non-wovens ensures successful project outcomes:

Site Preparation
The installation site must be graded uniformly and cleared of debris/rocks to avoid damage. Burial depth is determined. Subsurface drainage may be added.
Installation Techniques
Non wovens can be unrolled on site and placed loose or tense. Joints are sewn or bonded. Additional layers can be installed to enhance functioning. Fixings like sandbags or pegs may be used.
Seams and Overlaps
Adjoining rolls are overlapped for continuity. End overlaps depend on joint strength. Edges can be sewn, welded, glued or kept loose. Key consideration for soil retention uses.
Design Factors
Careful specifications of geotextile properties like strength, permeability, and opening size based on engineering requirements and testing. Survivability and performance lifetime also key.
Following recommended practices for non-woven deployment optimizes field performance and prevents failures.
Key Benefits and Advantages of Using Non-Woven Geotextiles
Non-woven geotextiles offer numerous benefits that make them advantageous over traditional materials:
Cost-Effectiveness
Made from polypropylene, non-wovens are an affordable alternative to CMP pipe drains or graded aggregates for drainage. Limited overlap joints also reduce the quantity required.
Rapid Drainage Performance
The high porosity provides greater flow capacity compared to sand filters or gravel layers. Useful in applications like retaining walls.
Good Puncture and Burst Resistance
The entangled fibrous structure provides better resistance against punctures during installation compared to woven geotextiles.
Ease of Installation
Flexible, lightweight non-wovens are simpler to install in field conditions compared to rigid materials. No special equipment needed.
Enhanced Properties
Specialized manufacturing processes like calendering and bonding create improved non-wovens with the right balance of filtration, separation, cushioning and strength.
Wider Widths
The ability to produce up to 5m wide rolls compared to just 1m for wovens leads to faster deployment with fewer joints.
These advantages have positioned non-wovens as a material of choice for major construction activities and geotechnical engineering applications.
Applications and Case Studies Demonstrating Non-Woven Geotextiles in Action
Non-woven geotextiles have delivered value across many real-world projects:
Landfill Construction - Needle-punched non-wovens used in leachate collection systems increased design life while reducing clogging through superior filtration compared to gravel layers.
Retaining Wall Drainage - Heat-bonded non-wovens used as wall wraps maintained water drainage and prevented soil washout, keeping 100km of critical rail walls safely stabilized through extreme weather.
Riverbank Protection - Durable non-woven wraps applied on embankments prevented erosion along highly flood-prone rivers through monsoons. Filtered runoff while retaining soil stability.
Roadway Improvement - Calendered non-wovens beneath motorway overpasses provided vital reinforcement to stabilize compressible soil while facilitating drainage and preventing pumping.
Coastal Reinforcement - Wide-width non-wovens encasing sandy coastal cliffs added shear strength and tensile reinforcement. Protected against collapse from rising sea levels and storm surges.
This demonstrates how non-wovens of different compositions can be adapted for specialized needs in infrastructure projects where performance and longevity are critical.
Industry Trends and Ongoing Innovations in Non-Woven Geotextiles
Several interesting trends, developments and innovations are shaping the non-woven geotextiles sector:
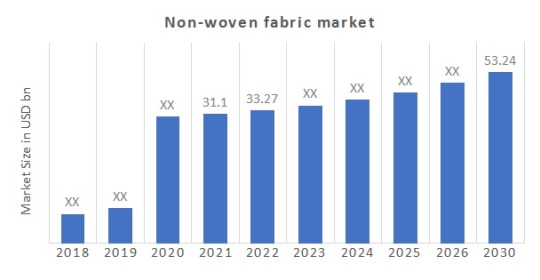
High Growth Potential - The non-wovens market is projected to grow steadily at 6% CAGR driven by major public infrastructure investments and demand from emerging economies.
Raw Material Advances - Enhanced polymers like high-density polypropylene and high-modulus polyester are creating improved non-wovens with greater functionality.
Manufacturing Improvements - Process enhancements and new techniques are allowing more fine-tuned manipulation of fiber properties during production.
Multifunctional Products - Combining non-wovens with drainage nets or reinforcing grids creates single products that provide filtration, separation and reinforcement together.
Application R&D - Ongoing research into novel uses for non-wovens like landfill caps, nuclear waste containment and offshore geotextiles to drive adoption across new domains.
Conclusion
Non-woven geotextiles have become an indispensable resource for civil engineering and infrastructure applications where their high permeability, strength, and versatility can enhance project outcomes and lifespan.
As materials and manufacturing continue evolving, non-wovens are poised to meet more specialized demands. With a thorough understanding of their capabilities, civil engineers can apply these adaptable fabrics for a sustainable future.
0 notes
Text
How roofing felts work to keep your roof secure

It is important to have a properly constructed roof so that your home is protected overall. One element that plays a key role in this particular respect is roofing felts. They are often overlooked, which is surprising when you consider that they act as a necessary protective layer that makes your roof more durable, waterproof, and insulated.
What are roofing felts?
Roofing felts are also referred to as underlayment or tar paper. They can be defined as a protective barrier that is installed within outer roofing materials like tiles or shingles and the roof deck. They are normally made by combining synthetic or natural materials soaked in asphalt so that they have waterproofing properties.
How can they keep your roofs safe?
1. Moisture control and waterproofing
One of the basic functions that roof felts play in securing your roof is in terms of acting as a waterproof barrier. The likes of rain, ice, and snow can get through the outer roofing materials of your home in time. This is especially so when the shingles become loose or damaged. Roofing felts act as an extra defensive layer that prevents moisture infiltration thus lowering the risk of water damage and leaks to the basic structure of your home.
2. Prevention of roof deck damage
The roof deck is normally made of materials such as OSB (oriented strand board) or plywood. It is also immensely vulnerable to moisture damage. If the wood is exposed for a prolonged period to moisture it might rot and become weak. This can lead to structural failures at the worst and costly repairs at the very least. However, if you install roofing felt you can build a buffer that will prevent direct contact between the external elements and the deck thus making sure that the structure of the roof lasts a long time.
3. Enhancement of the roof’s durability
Roofing layers add one more layer of strength to your roof. They do so by distributing weight more evenly over there. Such reinforcement also helps the roof deal well with harsh weather conditions like heavy winds, exposure to UV (ultraviolet) rays, and hail. It also makes sure that the impact of the debris that might fall on the roof is kept to the bare minimum. This, in turn, makes sure that the roof deck is not damaged straight away.
4. Improvement of fire resistance
Certain varieties of roofing felt provide you with greater resistance to fire — this is especially true of synthetic options as well as the ones made using fiberglass as the base. They make sure that in case there is a fire, at least the flames spread slowly, and this provides your home with an additional layer of safety in such serious circumstances. In fact, in a lot of areas you need to use fire-resistant underlayment so that you can meet safety-related rules and regulations. This is yet another reason why roofing felts are such an integral part of fire protection as well.
5. Assistance with maintenance and installation of roofs
Roofing felts provide you with a uniform and smooth surface where you can apply roofing materials such as tiles and shingles. This makes sure that the adhesion is better and also reduces the chances that any shingle would be sealed improperly or unevenly — such issues in turn can lead to leaks later on. Along with that, roofing felts also make it more convenient for you to maintain your roofs. This is because they provide you with the scope for a more organized and cleaner replacement process in case you have to replace the shingles or even repair them for that matter.
Kinds of roofing felt
The most prominent types of roofing felt are organic felts, fiberglass felts, and synthetic underlayment. Organic felts are made from materials such as wood pulp and recycled paper. They are soaked in asphalt so that a waterproofing barrier can be created in this case.
Installing roofing felts and maintaining them
The two most important factors in this particular context are using the right installation techniques and maintaining the roofing felts properly. You need to inspect them regularly as well. The right installation techniques make sure that the roofing felts are the most effective.
Roofing felts are crucial components of all well-constructed roofs as they offer you benefits such as essential waterproofing, fire resistance, durability, and structural support. It does not matter if you are maintaining an existing roof or installing a new one, you should invest in good roofing felts as they keep your home protected from the elements.
0 notes
Text
Geotextile Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Increasing Infrastructure Development and Growing Awareness of Environmental Protection

The global Geotextile Market is estimated to be valued at USD 7.10 billion in 2022 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.6% over the forecast period (2023-2030).
A) Market Overview:
Geotextiles are permeable fabrics that are used in various civil engineering applications, such as filtration, erosion control, reinforcement, and drainage. They are made from synthetic materials, including polyester, polypropylene, and polyethylene, and are widely used in infrastructure development projects, such as roads, railways, airports, and landfills. Geotextiles provide excellent strength, durability, and filtration properties, which make them suitable for various applications in the construction industry.
B) Market Dynamics:
The market is driven by two main factors:
1. Increasing Infrastructure Development: The rapid urbanization and industrialization worldwide have led to a surge in infrastructure development projects. Geotextiles play a crucial role in enhancing the stability and longevity of these infrastructures. They are used in road stabilization, ground improvement, soil erosion control, and environmental protection measures. The growing demand for geotextiles in infrastructure development projects is expected to drive market growth.
2. Growing Awareness of Environmental Protection: Geotextiles offer eco-friendly solutions for various environmental protection measures. They help in preventing soil erosion, managing water drainage, and reducing the impact of pollutants on the environment. With increasing concerns about environmental degradation and regulations promoting sustainable practices, the demand for geotextiles is expected to rise.
C) Market Key Trends:
One key trend observed in the Geotextile Market is the increasing adoption of geosynthetic clay liners (GCLs). GCLs are composite materials that combine geotextiles and bentonite clay to enhance their barrier properties. They are widely used in landfill liners, mining containment, and environmental remediation applications. GCLs offer superior hydraulic performance, chemical resistance, and low permeability, making them an attractive alternative to traditional compacted clay liners.
D) SWOT Analysis:
- Strength: Strong demand for geotextiles in infrastructure development and environmental protection.
- Weakness: Lack of awareness and limited adoption in some regions.
- Opportunity: Growing research and development activities for innovative geotextile products.
- Threats: Intense competition from alternative materials and stringent government regulations.
E) Key Takeaways:
- The global geotextile for market is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 6.6% over the forecast period, due to increasing infrastructure development and the growing awareness of environmental protection.
- Asia-Pacific is projected to be the fastest-growing and dominating region in the geotextile for market, driven by rapid urbanization and infrastructure investment in countries like China and India.
- Key players operating in the global geotextile for market include GSE Holdings Inc., The Dow Chemical Company, Royal Ten Cate Corporate EMEA, Fibertex Nonwovens A/S, Low & Bonar PLC., Huesker Synthetic GmbH, Tenax, CTM GEO Synthetics, Leggett & Platt Incorporated, and Kaytech Engineered Fabrics.
The geotextile for market is poised for significant growth due to the increasing demand for infrastructure development and the need to protect the environment. Geotextiles provide sustainable solutions for various civil engineering applications, making them a vital component of modern construction projects. The market is expected to witness substantial opportunities for innovation and expansion in the coming years.
0 notes