#SELinux & Security
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Red Hat course in Bangalore
About Course
The RHCSA course is designed to provide IT professionals with the skills needed to perform core system administration tasks in Linux environments. With hands-on labs and practical exercises, this course equips learners to deploy, configure, and manage Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) systems effectively. The curriculum prepares candidates to pass the RHCSA certification exam and build a strong foundation for enterprise-level system administration.
RHCSA (Red Hat Certified System Administrator) Online Exam & Certification
What I will learn?
Perform basic system administration.
Manage storage and filesystems.
Secure systems with user management.
We are always ready to help you and answer your questions
Email Us
Bangalore
+91 72044 31703 +91 80959 33365
Hyderabad
+91 77993 51640 +91 90597 64550
#RHCSA Course#Red Hat Certified System Administrator#EX200 Exam Preparation#RHEL System Administration#Linux Hands‑On Labs#SELinux & Security#Storage & LVM#Networking & Firewalls#Container Fundamentals
0 notes
Link
#accesscontrol#auditing#CentOS10#CentOS11#configuration#enforcement#firewall#hardening#Linux#mandatoryaccesscontrol#open-source#permissions#policies#Security#securitycontexts#SELinux#SELinuxmodes#Server#systemadministration#Troubleshooting
0 notes
Text
#hostnextra#linux#technology#linuxserver#ubuntu#linux tutorial#programming#almalinuxserver#selinux#security#firewall
0 notes
Text
Setup and Configuration of Oracle Security
Pfsense, CloudFlare,Meraki Go,Fortigate AP, AWS CloudFront,Cisco Unbrella… Oracle Cloud FW, RedHatEnterprise, SELinux, Nginx reverse Proxy Inclusive To generate SSH security scripts using OpenSSL RSA, you can use the following format: Step 1: Generate the private keyopenssl genrsa -out private.key 2048 This command will generate a private key named “private.key” with a key length of 2048…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
All right, since I bombarded a poor mutual yesterday...
Privacy is not security and security is not privacy. These terms are not interchangeable, but they are intrinsically linked.
While we're at this, anonymity =/= security either. For example, Tor provides the former, but not necessarily the latter, hence using Https is always essential.
It is impossible to have privacy without security, but you can have security without privacy.
A case in point is administrators being able to view any data they want due to their full-access rights to a system. That being said, there are ethics and policies that usually prevent such behavior.
Some general tips:
Operating System: Switch to Linux. Ubuntu and Linux Mint are widely used for a reason. Fedora too. And don't worry! You can keep your current operating system, apps and data. If you're on a Mac computer, you can easily partition your hard drive or SSD by using Disk Utility. If you're on Windows, you can follow this guide.
You want to go a step further? Go with Whonix or Tails. They're Linux distributions as well, but they're both aiming for security, not beauty so the interface might not be ideal for everyone. Many political activists and journalists use them.
You want anonymity? Then you need to familiarize yourself with Tor. Also, Tor and HTTPS and Tor’s weaknesses. When you're using it, don't log in to sites like Google, Facebook, Twitter etc. and make sure to stay away from Java and Javascript, because those things make you traceable.
Alternatives for dealing with censorship? i2p and Freenet.
Is ^ too much? Welp. All right. Let's see. The first step is to degoogle.
Switch to a user-friendly browser like Firefox (or better yet LibreWolf), Brave or Vivaldi. There are plenty of hardened browsers, but they can be overwhelming for a beginner.
Get an ad blocker like Ublock Origin.
Search Engine? StartPage or Duckduckgo. SearXNG too. Like I said degoogle.
Get a PGP encrypted e-mail. Check Protonmail out.
There's also Tutamail that doesn't cover PGP, but uses hybrid encryption that avoids some of the cons of PGP.
Skiff mail is also a decent option.
Use an e-mail aliasing service such as SimpleLogin or AnonAddy.
Check OpenPGP out. Claws Mail is a good e-mail client for Windows and Linux, Thunderbird for Mac OS.
Gpg4win is free and easy to use for anyone that wants to encrypt/decrypt e-mails.
Instead of Whatsapp, Facebook messenger, Telegram etc. use Signal for your encrypted insant messaging, voice and video calls.
Get a metadata cleaner.
Get a firewall like Opensnitch, Portmaster or Netguard which can block Internet for trackers.
Alternatively, go with a private DNS that blocks these trackers. NextDNS is a good paid service. Rethink a good free option.
Replace as many of your applications as you can with FOSS (free and open source) ones. Alternativeto can help you.
Always have automatic updates on. They are annoying af, I know, but they are necessary.
Keep your distance from outdated software.
Always have two-factor authentication (2FA) enabled.
Do not use your administrator account for casual stuff. If you're on Linux, you probably know you can be sudo, but not root.
On Linux distributions use AppArmor, but stay away from random antivirus scanners. Other distributions default to SELinux, which is less suited to a beginner.
Never repeat your passwords. If you can't remember them all, use a password manager like KeePass.
Encrypt your drive.
Honestly, VPNs have their uses and ProtonVPN, Mullvad and Windscribe are decent, but eh. If you don't trust your ISP, why would you trust the VPN provider that claims they don't log you when you can't verify such a thing?
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
Linux VPS Hosting: A Complete Guide
Introduction
Linux VPS (Virtual Private Server) hosting is a powerful and cost-effective solution for businesses, developers, and website owners who need more control, performance, and flexibility than shared hosting can provide. Since Linux is an open-source operating system, it offers stability, security, and customization, making it a preferred choice for VPS environments.
This guide explores Linux VPS hosting, its benefits, how it works, and when to choose it for your projects.
What is Linux VPS Hosting?
A Linux VPS is a virtual server running a Linux-based operating system (such as Ubuntu, CentOS, Debian, or Fedora). It provides dedicated resources (CPU, RAM, storage) within a shared physical server, ensuring better performance and security than shared hosting.
Unlike Windows VPS, Linux VPS is open-source, meaning no licensing fees, lower costs, and greater customization options.
How Does Linux VPS Hosting Work?
Linux VPS hosting uses virtualization technology (such as KVM, OpenVZ, or Xen) to divide a physical server into multiple isolated virtual servers. Each VPS gets:
Dedicated resources (CPU, RAM, disk space) Full root access (complete control over the server) Choice of Linux OS (Ubuntu, CentOS, Debian, etc.) Independent environment (no interference from other users)
Users can install custom software, configure security settings, and optimize performance as needed.
Benefits of Linux VPS Hosting
1. Cost-Effective
No licensing fees (Linux is free and open-source).
More affordable than Windows VPS or dedicated servers.
2. High Performance & Stability
Dedicated resources ensure faster load times.
Linux is known for its reliability and uptime.
3. Enhanced Security
Strong built-in security features (firewalls, SELinux, AppArmor).
Fewer malware threats compared to Windows.
4. Full Root Access & Customization
Install any software (LAMP/LEMP stacks, Docker, Node.js).
Modify server configurations as needed.
5. Scalability
Easily upgrade CPU, RAM, and storage as your website grows.
6. Wide Software Support
Supports popular web hosting tools (Apache, Nginx, MySQL, PHP).
Ideal for hosting WordPress, Magento, and custom apps.
When Should You Choose Linux VPS Hosting?
Linux VPS is ideal for:
Web developers needing a customizable environment. E-commerce sites requiring speed and security. Growing businesses outgrowing shared hosting. Sysadmins & DevOps managing servers and deployments. Hosting multiple websites with high traffic.
Linux VPS vs. Windows VPS vs. Shared Hosting
FeatureShared HostingLinux VPSWindows VPSCostLowModerateHigh (licensing fees)PerformanceLimitedHighHighSecurityBasicStrongModerateControlRestrictedFull (Root)Full (Admin)OS SupportLimitedLinux-basedWindows-onlyBest ForSmall blogsDevelopers, businesses.NET, MSSQL apps
Managed vs. Unmanaged Linux VPS
1. Managed Linux VPS
Hosting provider handles setup, security, updates, and backups. Best for beginners or businesses without IT staff. Examples: Bluehost, Hostinger, A2 Hosting.
2. Unmanaged Linux VPS
Full control but requires technical expertise. Cheaper, ideal for developers and sysadmins. Examples: DigitalOcean, Linode, Vultr.
Top Linux VPS Hosting Providers
ProviderBest ForPricing (Starting)DigitalOceanDevelopers, Cloud VPS$4/monthLinodeHigh-performance apps$5/monthVultrAffordable cloud VPS$2.50/monthBluehostBeginners, WordPress$19.99/monthAWS LightsailScalable cloud hosting$3.50/month
How to Set Up a Linux VPS
Choose a hosting provider (e.g., DigitalOcean, Linode).
Select a Linux OS (Ubuntu, CentOS, Debian).
Configure resources (CPU, RAM, storage).
Connect via SSH (using Terminal or PuTTY).
Install necessary software (Web server, database, security tools).
Deploy your website or application.
Conclusion
Linux VPS hosting is a powerful, flexible, and cost-efficient solution for businesses and developers who need more control than shared hosting but don’t require a full dedicated server. With its high performance, security, and customization options, Linux VPS is an excellent choice for hosting websites, applications, and development projects.
Ready to Upgrade?
If you need better speed, security, and scalability, a Linux VPS is the perfect next step from shared hosting.
0 notes
Text
Application Security in Kubernetes
Running Privileged Applications Safely and Effectively
In modern cloud-native environments, application security is more important than ever. While most applications run securely in isolated containers, there are cases where certain workloads need elevated access—either to the host operating system or the Kubernetes platform itself.
This blog covers what privileged applications are, why they’re sometimes needed, and how to run them securely without compromising your environment.
⚙️ Why Do Some Applications Need Elevated Privileges?
Some containerized applications must interact closely with the underlying system or Kubernetes components. Common examples include:
Monitoring tools that collect system-level metrics
Network management tools like firewalls or VPNs
Storage drivers that require access to the host disk
Legacy applications that require root or admin access
Troubleshooting and debugging tools
These applications break the isolation model that containers are known for, and therefore require stronger security controls.
🛡️ Key Security Considerations
Before granting elevated access, ask these questions:
Is elevated access essential? If not, explore alternatives like APIs or sidecar containers.
What level of access is really required? Avoid giving full system privileges when only partial access is needed.
Is the container image secure? Use lightweight, verified images from trusted sources and remove unnecessary components.
🧰 How to Secure Privileged Applications (Without Code)
There are several built-in features and policies in Kubernetes and OpenShift that help manage privileged workloads safely:
Security policies can enforce which types of applications are allowed to run with elevated access, and where.
User roles and permissions can be configured to control who is allowed to deploy or modify these applications.
Security profiles like SELinux or AppArmor offer additional protection by restricting what privileged applications can do at the operating system level.
Dedicated namespaces can isolate sensitive workloads from the rest of the cluster.
Audit logs and monitoring tools can track privileged actions and alert teams of unusual behavior.
These tools ensure privileged workloads are properly isolated, monitored, and controlled.
✅ Best Practices
Only run privileged applications if there is no safer alternative
Keep them isolated from other workloads
Regularly review and audit your permissions and access controls
Use runtime security tools to detect unusual activity
Keep your container images and host OS patched and up to date
🚧 Risks to Avoid
Allowing unrestricted access can expose your system to:
Accidental or malicious changes to the host OS
Unauthorized access to sensitive data
Security breaches due to vulnerable components
Service disruptions or data loss
By managing privileged workloads carefully, you can avoid these risks and maintain a strong security posture.
🔚 Conclusion
Running applications with elevated privileges is sometimes necessary—but it must be done with strict controls and clear policies. By understanding the risks and using the right security features, you can protect your Kubernetes or OpenShift environment while still meeting application requirements.
Remember: Security should never be an afterthought—especially when elevated access is involved.
For more info, Kindly follow: Hawkstack Technologies
0 notes
Text
Why Linux VPS is the Best Choice for Developers and Businesses in 2025
In 2025, businesses and developers alike are seeking more reliable, scalable, and cost-effective hosting solutions. Whether you’re launching a web app, managing an eCommerce store, or running multiple client websites, choosing the right hosting environment can make a huge difference in performance, security, and scalability.

Among the many options available, Linux VPS (Virtual Private Server) hosting continues to stand out as a top choice. Known for its stability, flexibility, and developer-friendly environment, the Linux VPS server is becoming the backbone of modern digital infrastructure. But what makes it so appealing, especially in 2025? Let’s dive deep into the reasons.
1. Cost-Effective Without Compromising Performance
One of the most attractive features of a Linux VPS is its affordability. Unlike dedicated servers, VPS hosting allows you to get dedicated-like resources at a fraction of the cost. With Linux being open-source, there are no licensing fees, which significantly reduces overall expenses compared to a Windows-based VPS.
Businesses can scale their infrastructure efficiently without burning through their IT budgets, and developers can experiment or deploy projects without worrying about high monthly hosting costs.
2. Superior Performance and Uptime
In 2025, user expectations are higher than ever. Websites and applications need to load fast and be accessible 24/7. A Linux VPS server offers dedicated resources such as CPU, RAM, and SSD storage, ensuring that your applications perform smoothly even during high traffic spikes.
Unlike shared hosting, where resources are distributed among hundreds of users, VPS guarantees that your environment remains isolated. This leads to consistent uptime and fast load times — essential factors for SEO rankings and user experience.
3. Full Root Access for Complete Control
One of the key reasons developers prefer Linux VPS hosting is the root-level access it provides. This level of control allows for full customization of the server environment. Developers can:
Install and configure any software or packages
Modify system files and server settings
Deploy custom applications or scripts
This freedom makes Linux VPS ideal for complex development environments, testing, and production servers. In 2025, when developers need more power and flexibility than ever, having full access is a massive advantage.
4. Security and Privacy
With the increasing number of cyber threats in 2025, securing your server infrastructure is non-negotiable. A Linux VPS server is inherently more secure than shared hosting. You get isolated server resources, making your server less susceptible to attacks caused by neighboring users.
Moreover, Linux as an OS is known for its strong security protocols. Regular updates, strong community support, and customizable firewall configurations ensure your server remains secure. Users can also implement advanced security tools such as Fail2Ban, IPtables, and SELinux for added protection.
5. Scalability for Growing Projects
Whether you’re a startup with growing traffic or a development agency handling multiple client sites, scalability is crucial. A Linux VPS allows you to scale your resources as your needs grow. With just a few clicks (or commands), you can upgrade your server’s RAM, CPU, or storage without affecting your existing configurations or data.
This flexibility makes Linux VPS an ideal choice for businesses aiming to scale in a cost-effective and disruption-free manner.
6. Developer-Friendly Environment
Most developers are familiar with Linux-based environments, especially if they work with tools like Git, Apache, Nginx, Docker, Node.js, and MySQL. A Linux VPS server provides a native environment for these tools, making deployment and server management seamless.
Additionally, Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, CentOS, Debian, and AlmaLinux offer users the choice to work in environments they are most comfortable with.
7. Automation and Scripting Capabilities
In today’s DevOps-driven world, automation is key. Linux VPS servers allow developers to automate tasks using shell scripts, cron jobs, or more advanced tools like Ansible and Puppet. This improves efficiency and helps maintain consistency across deployments.
From automated backups to server monitoring, a Linux VPS environment supports robust automation capabilities that simplify the life of sysadmins and developers alike.
8. Large Community and Documentation
Linux has a massive global community and an abundance of resources. Whether you’re a beginner or an expert, you can find forums, tutorials, GitHub repositories, and documentation to help you resolve issues or improve server performance.
In 2025, this ecosystem is even more valuable. New developers can quickly learn and troubleshoot, while experienced users benefit from the community’s collective knowledge and tools.
Conclusion
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the demand for reliable, scalable, and secure hosting solutions grows stronger. A Linux VPS server offers the perfect balance of performance, control, and affordability, making it the go-to solution for both developers and businesses in 2025.
0 notes
Text
SELinux in AOSP: A Guide to Securing Embedded Android Systems
Introduction
Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is a core security mechanism in the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) that enforces robust access control. Unlike traditional Discretionary Access Control (DAC), which relies on user-based permissions, SELinux uses Mandatory Access Control (MAC) to restrict system interactions based on predefined policies. Android integrated SELinux starting from version 4.3. It runs in either permissive mode, which logs violations, or enforcing mode, which blocks unauthorized actions.

Understanding SELinux policies, labels, and domains is essential for embedded developers working on middleware, HAL, and system daemons in order to secure Android devices. Sensitive system components are protected, unauthorized access is limited, and privilege escalation is avoided with proper SELinux configuration. This blog discusses best practices for creating security policies, how SELinux functions within AOSP, and a real-world example of using SELinux on a binderized HAL. Developers can strengthen embedded systems against exploits and security breaches by becoming proficient with SELinux.
What is SELinux?
With mandatory access control (MAC) policies that limit programs' capabilities beyond conventional discretionary access controls (DAC), SELinux is a security architecture built into the Linux kernel. It guarantees that an application's activities stay contained within predetermined bounds even in the event that it is compromised.
Core Concepts of SELinux
Labels: Every process and object (like files, directories, and ports) in the system is assigned a security label. A key component of SELinux's decision-making process is these labels.
Type Enforcement (TE): The main SELinux mechanism is Type Enforcement (TE), in which policies specify how types (labels) linked to objects and processes can communicate. A process named httpd_t (Apache), for example, can be made to only access files with the label httpd_sys_content_t.
Roles and Users: To manage permissions more precisely, SELinux defines roles and users. Nonetheless, type enforcement continues to be the main focus in many implementations.
SELinux in AOSP
SELinux integration with Android
Google strengthened Android's security by integrating SELinux into the platform starting with version 4.3. SELinux functions in two ways in AOSP:
Permissive Mode: Violators are recorded but not stopped; SELinux rules are not enforced.
Enforcing Mode: SELinux rules are put into effect, and infractions are recorded and prevented. For strong security, Android devices try to run in enforcing mode.
Advantages of SELinux in Android
Privilege escalation is mitigated: SELinux restricts an application's behavior even if it acquires unauthorized privileges, avoiding more widespread system compromises.
Protection Against Malware: By limiting applications' access to private information or system components, SELinux policies can lessen the possible impact of malware.
Enhanced Multi-User Security: SELinux makes sure that user data is kept separate and safe from other users and applications by implementing stringent access controls.
Implementing SELinux in AOSP
Configuring the Linux kernel for SELinux: Make sure the kernel is compiled with SELinux support. This entails turning on particular security module configuration options.
Filesystem Labeling: Give filesystem objects the proper security labels. This can be accomplished by setting default labels in filesystem images or by using tools such as restorecon.
Compilation of Policies: Using tools like checkpolicy, create SELinux policies that are specific to the needs of your system.
Policy Loading: Use tools like load_policy or incorporate the compiled policies into the system's initialization procedure to load them into the kernel.
Writing SELinux Policies
IVI (In-Vehicle Infotainment), ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems), and telematics are among the vital services that Android Automotive OS (AAOS) manages in automotive embedded systems. SELinux policies are necessary to enforce stringent access controls across all system components, especially middleware services, Binderized HALs, and system daemons, in order to ensure security in such a system. In order to make sure that only authorized system components can access and alter vehicle data, we'll map SELinux policy writing to a real-world automotive example below using a binderized HAL.
Determine Types and Domains
Consider a Vehicle HAL (VHAL) in an automotive system, which gives users access to information about the vehicle, including its speed, fuel level, engine status, and door lock condition. The telematics module, navigation app, and IVI system are among the system elements with which the Vehicle HAL service communicates.
The hal_vehicle_t domain is where the Vehicle HAL daemon operates.
vehicle_data_t is the label for vehicle data files.
The ivi_system_t domain is where the IVI system operates.
The telematics_t domain is where the Telematics service functions.
By defining these domains, unauthorized applications are prevented from accessing vital vehicle parameters and controlled access between various system components is ensured.
Tools and Resources
SELinux Notebook: An open-source resource that provides comprehensive insights into SELinux concepts and implementations. GitHub - SELinuxProject/selinux-notebook
NSA's SELinux Implementation Report: An in-depth report detailing the implementation of SELinux as a Linux Security Module. Implementing SELinux as a Linux Security Module
Conclusion
With SELinux included in AOSP, developers can implement strict access controls, isolate processes, and keep sensitive information safe.
Whether you're building embedded Android systems, HAL layers, or automotive and IoT device middleware, SELinux offers a secure framework to ensure system integrity.
For any solution related to SELinux implementation, HAL hardening, or embedded Android security, connect with Silicon Signals at www.siliconsignals.io or email us at [email protected]. 👉 Do follow us on LinkedIn to stay updated on embedded tech insights and innovations.
#linux kernel#androidbsp#linuxdebugging#android#aosp#embeddedtechnology#embeddedsoftware#embeddedsystems#iot development services#selinux#linuxsecurity#aospsecurity
0 notes
Text
Bottlerocket OS: Secure Linux for Containers by AWS
https://techrefreshing.com/bottlerocket-os-secure-linux-for-containers-by-aws/
Bottlerocket OS, AWS’s open-source Linux distribution, is purpose-built for secure and efficient container hosting. With a minimalistic design, robust security features like dm-verity and SELinux, and seamless integration with EKS and ECS, Bottlerocket optimizes containerized workloads. Learn how this lightweight OS reduces attack surfaces, simplifies updates, and enhances performance for modern cloud-native environments.
#BottlerocketOS #AWS #Containers #CloudComputing #Kubernetes #EKS #ECS #Linux #ContainerSecurity #CloudNative #DevOps #OpenSource

0 notes
Text

Comparison of Ubuntu, Debian, and Yocto for IIoT and Edge Computing
In industrial IoT (IIoT) and edge computing scenarios, Ubuntu, Debian, and Yocto Project each have unique advantages. Below is a detailed comparison and recommendations for these three systems:
1. Ubuntu (ARM)
Advantages
Ready-to-use: Provides official ARM images (e.g., Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS) supporting hardware like Raspberry Pi and NVIDIA Jetson, requiring no complex configuration.
Cloud-native support: Built-in tools like MicroK8s, Docker, and Kubernetes, ideal for edge-cloud collaboration.
Long-term support (LTS): 5 years of security updates, meeting industrial stability requirements.
Rich software ecosystem: Access to AI/ML tools (e.g., TensorFlow Lite) and databases (e.g., PostgreSQL ARM-optimized) via APT and Snap Store.
Use Cases
Rapid prototyping: Quick deployment of Python/Node.js applications on edge gateways.
AI edge inference: Running computer vision models (e.g., ROS 2 + Ubuntu) on Jetson devices.
Lightweight K8s clusters: Edge nodes managed by MicroK8s.
Limitations
Higher resource usage (minimum ~512MB RAM), unsuitable for ultra-low-power devices.
2. Debian (ARM)
Advantages
Exceptional stability: Packages undergo rigorous testing, ideal for 24/7 industrial operation.
Lightweight: Minimal installation requires only 128MB RAM; GUI-free versions available.
Long-term support: Up to 10+ years of security updates via Debian LTS (with commercial support).
Hardware compatibility: Supports older or niche ARM chips (e.g., TI Sitara series).
Use Cases
Industrial controllers: PLCs, HMIs, and other devices requiring deterministic responses.
Network edge devices: Firewalls, protocol gateways (e.g., Modbus-to-MQTT).
Critical systems (medical/transport): Compliance with IEC 62304/DO-178C certifications.
Limitations
Older software versions (e.g., default GCC version); newer features require backports.
3. Yocto Project
Advantages
Full customization: Tailor everything from kernel to user space, generating minimal images (<50MB possible).
Real-time extensions: Supports Xenomai/Preempt-RT patches for μs-level latency.
Cross-platform portability: Single recipe set adapts to multiple hardware platforms (e.g., NXP i.MX6 → i.MX8).
Security design: Built-in industrial-grade features like SELinux and dm-verity.
Use Cases
Custom industrial devices: Requires specific kernel configurations or proprietary drivers (e.g., CAN-FD bus support).
High real-time systems: Robotic motion control, CNC machines.
Resource-constrained terminals: Sensor nodes running lightweight stacks (e.g., Zephyr+FreeRTOS hybrid deployment).
Limitations
Steep learning curve (BitBake syntax required); longer development cycles.
4. Comparison Summary
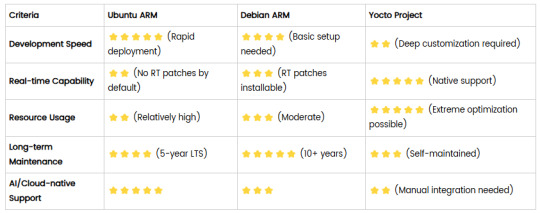
5. Selection Recommendations
Choose Ubuntu ARM: For rapid deployment of edge AI applications (e.g., vision detection on Jetson) or deep integration with public clouds (e.g., AWS IoT Greengrass).
Choose Debian ARM: For mission-critical industrial equipment (e.g., substation monitoring) where stability outweighs feature novelty.
Choose Yocto Project: For custom hardware development (e.g., proprietary industrial boards) or strict real-time/safety certification (e.g., ISO 13849) requirements.
6. Hybrid Architecture Example
Smart factory edge node:
Real-time control layer: RTOS built with Yocto (controlling robotic arms)
Data processing layer: Debian running OPC UA servers
Cloud connectivity layer: Ubuntu Server managing K8s edge clusters
Combining these systems based on specific needs can maximize the efficiency of IIoT edge computing.
0 notes
Text
Master Your IT Career with Gritty Tech’s Linux Administration Online Coaching
If you're serious about breaking into the world of system administration, you're probably already searching for the right Linux administration online coaching. And with good reason—Linux skills are in high demand, especially in today’s cloud-driven, DevOps-powered tech landscape. But here’s the truth: not all online coaching is created equal For More…

At Gritty Tech, we get it. You want coaching that’s practical, flexible, trustworthy, and—most importantly—effective. That’s exactly what we deliver with our Linux administration online coaching.
Why Choose Linux Administration as a Career?
Linux powers over 90% of the world’s cloud infrastructure and supercomputers. It's the backbone of enterprise servers and a staple in everything from cybersecurity to cloud engineering.
Choosing Linux administration online coaching isn’t just about learning commands—it's about building a career in a field that’s:
Highly in demand
Globally recognised
Well-paying
Continuously evolving
So whether you're a fresh graduate, a career switcher, or an IT professional upskilling for future-proof roles—Linux administration online coaching is your gateway to opportunity.
What Makes Gritty Tech Different?
There are hundreds of platforms offering training. So why trust Gritty Tech’s Linux administration online coaching?
Affordable Without Cutting Corners
We believe quality education should be accessible to everyone. Our pricing is transparent and budget-friendly. You can choose between monthly plans, session-wise payments, or full-course fees—whatever works best for your schedule and budget.
Easy Refunds & Tutor Replacements
If something’s not right, we fix it. Our easy refund policy and tutor replacement options ensure your satisfaction. No long emails, no runaround—just real support when you need it.
Experienced Tutors from 110+ Countries
Our tutors aren’t just teachers—they’re seasoned professionals. With a network spanning 110+ countries, you’ll be learning from experts who’ve worked in real Linux environments and know how to prepare you for them.
Flexible Schedules & Personalised Attention
Our Linux administration online coaching is built around you. Whether you’re learning on weekends, after work, or during your lunch break, our tutors accommodate your schedule and learning pace.
What You’ll Learn in Our Linux Administration Online Coaching
Here’s a quick look at what you’ll master:
Linux Fundamentals: Shell, commands, file structures
User & Group Management: Permissions, access control
System Monitoring: Using top, htop, netstat, and more
Package Management: YUM, APT, RPM
Network Configuration: IPs, DNS, firewalls
Scripting Basics: Automate tasks using Bash
Log Management: Reading and troubleshooting logs
System Services: Starting, stopping, and enabling services
Security & Updates: Patching, hardening, SELinux basics
Interview Preparation: Real-world scenarios and mock tests
Every topic in our Linux administration online coaching is hands-on and aligned with industry demands.
Who is This Course For?
Our Linux administration online coaching is for:
Students aiming to land their first IT job
Professionals looking to switch to sysadmin, DevOps, or cloud roles
Freelancers and consultants needing Linux skills for clients
Tech enthusiasts who want to get under the hood of systems
You don’t need a computer science degree. All you need is a willingness to learn—and we’ll take care of the rest.
Real Coaching, Real Results
We’re not here to waste your time with recorded videos and no feedback. Gritty Tech’s Linux administration online coaching means:
One-to-one sessions or small group batches
Live Q&A during sessions
Assignments and projects reviewed by real mentors
Weekly feedback and progress tracking
Your learning isn’t just about watching—it’s about doing, reflecting, and improving.
Value Beyond the Course
Most training platforms end their service once your course is over. Not us.
Post-course support for doubts and interviews
Resume help and job tips from tutors
Community access to other learners and pros
Free resources and updates even after the course ends
When we say we care about your career, we mean it.
Key Benefits and Features at a Glance
Gritty Tech Offers
Flexible Payment
Monthly & Session-wise
Refund Policy
Yes
Tutor Replacement
Yes
Global Tutor Network
110+ Countries
Real-world Learning
Hands-on Labs & Projects
Certification Support
Included
24/7 Support
Via chat/email
Interview Prep
Mock Interviews & Questions
Why Trust Gritty Tech’s Linux Administration Online Coaching?
Our students don’t just finish the course—they build careers. Here's why learners stick with Gritty Tech:
Trusted by thousands globally
Proven track record of success stories
Accessible learning with quality
High-value content, no fluff
If you're investing time and money into learning, you deserve content that keeps you engaged and actually helps you grow. That’s our mission.
10 FAQs About Linux Administration Online Coaching
1. What is Linux administration online coaching?
Linux administration online coaching is a virtual training programme where you learn to manage and maintain Linux systems from expert tutors through live or recorded sessions.
2. How do I choose the best Linux administration online coaching?
Look for a programme like Gritty Tech that offers live interaction, hands-on labs, flexible schedules, tutor support, and post-course help—all while being affordable.
3. What are the prerequisites for Linux administration online coaching?
Basic computer knowledge helps, but you don’t need coding experience. Gritty Tech’s Linux administration online coaching starts from the ground up.
4. How long does it take to complete Linux administration online coaching?
It depends on your pace. Most students complete the course in 6–10 weeks with regular sessions.
5. Will I get a certificate after completing the Linux administration online coaching?
Yes, Gritty Tech provides a certificate upon course completion, which can boost your CV and LinkedIn profile.
6. Can I switch tutors during Linux administration online coaching?
Absolutely. We offer tutor replacement options to ensure you're comfortable and learning effectively.
7. Is Linux administration online coaching suitable for beginners?
Yes. Gritty Tech’s Linux administration online coaching is beginner-friendly and designed to take you from zero to job-ready.
8. Are there any real-world projects in the Linux administration online coaching?
Yes, you’ll work on practical projects like setting up user accounts, configuring firewalls, monitoring system resources, and writing basic scripts.
9. Do you offer flexible payments for Linux administration online coaching?
Yes. You can pay monthly, per session, or in one go—whatever fits your situation.
10. What support is available after Linux administration online coaching ends?
You’ll still have access to tutors for doubt resolution, plus help with job interviews and resume preparation.
Conclusion: Ready to Launch Your Linux Career?
Don’t settle for just any online training. With Gritty Tech’s Linux administration online coaching, you get:
A trusted, practical education built for real-world impact
Experienced mentors who guide you, not just teach
Flexible, affordable plans that work with your life
A clear path to career growth in system administration, DevOps, or cloud
If you’ve been thinking about taking the next step, now is the time.
Start your journey with Gritty Tech’s Linux administration online coaching today. Learn from the best. Learn smart. Learn for your future.
0 notes
Text
Introduction to Radiant Tools APK Looking for a smarter way to monitor, test and tweak your Android device? Radiant Tools APK is the answer to enhance your experience with a small, powerful and easy-to-use app. Designed for developers, gamers and everyday users alike, this tool gives you full control over your phone’s performance, hardware and battery health.
So is Radiant Tools APK worth downloading? Let’s take a look!
Top Features of Radiant Tools APK Latest Version Here are the key features that make this app a must-have for your Android device:
Real-time System Monitor Track CPU, GPU, RAM and battery usage instantly
View temperature to prevent overheating during heavy workloads
Comprehensive Hardware Diagnostics Test your phone’s camera, touchscreen, speakers, sensors and display
Very useful when buying or selling a used phone to confirm its condition
Battery Health Analyzer Check charging speed, charging cycles and battery usage behavior
Find apps that are consuming too much power and extend the life of your device
Network and Connection Tools Measure Wi-Fi signal strength and analyze network speed
Display IP information, DNS details, and more for precise troubleshooting
Authentication and security Detect root status and SELinux settings
Audit app permissions to protect your personal data
Developer-friendly features View logs and error reports for debugging
Ideal for testing apps in real-world environments
Gamer mode Unlock FPS limits for smoother gameplay
Tweak game performance without rooting
Minimalistic widgets Add widgets to show battery level, CPU usage, or temperature on your home screen
User experience and interface Radiant Tools APK comes with a simple interface, free of gimmicks, and focused on getting straight to the point. The app is easy to use, even for beginners, it can browse system information and use various tools conveniently. It is fast, responsive, and most importantly, it is completely ad-free, which is very rare for free apps these days.
Conclusion – Download Radiant Tools APK Free for Android 2025 If you are looking for a powerful, ad-free, multi-purpose tool To better understand and customize your Android device, Radiant Tools APK is the option you should not miss. It is small, practical, and packed with features that will satisfy both techies and everyday users.
0 notes
Text
With RHCA in Infrastructure, You Can…
In the fast-paced world of IT infrastructure, being just certified is no longer enough. Organizations are looking for professionals who can design, secure, automate, and optimize enterprise environments at scale. That’s where the Red Hat Certified Architect (RHCA) in Infrastructure stands out.
If you’ve already earned your RHCE (Red Hat Certified Engineer), the RHCA path elevates your expertise to the next level—proving you can not only implement solutions, but also architect them.
So, with RHCA in Infrastructure, you can...
1. Design Complex, Scalable Systems
RHCA holders are trained to build resilient, high-availability environments using tools like Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Ansible Automation Platform, and Red Hat Satellite. Whether it's an on-premise data center or a hybrid cloud environment, you can design architectures that meet enterprise-grade performance, security, and compliance requirements.
2. Lead IT Automation Initiatives
Automation is the backbone of modern infrastructure. With RHCA, you gain deep knowledge of Ansible at scale, helping organizations reduce manual tasks, enforce consistency, and accelerate deployment times.
3. Implement Enterprise-Grade Security
RHCA training includes expertise in SELinux, identity management, system hardening, and patch management, ensuring infrastructure is not just functional, but also secure by design.
4. Streamline Hybrid Cloud and Edge Deployments
As more organizations adopt Open Hybrid Cloud strategies, RHCA in Infrastructure equips you with the skills to extend your data center across private and public cloud platforms, and even to edge locations—using tools like Red Hat Insights and Red Hat Smart Management.
5. Drive Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Adoption
Modern infrastructure requires repeatable, version-controlled deployments. With RHCA, you’re capable of implementing Infrastructure as Code using Ansible and GitOps practices, bringing DevOps principles to IT operations.
6. Gain Recognition as a Thought Leader
RHCA isn’t just a certification; it’s a validation of expert-level proficiency. It distinguishes you in job markets, helps in career growth, and positions you as a trusted advisor or consultant in the enterprise IT ecosystem.
7. Command Higher Salaries and Strategic Roles
Professionals with RHCA are often considered for senior architect roles, principal engineer, or infrastructure lead positions. Your ability to align technology with business goals makes you a key strategic asset in any organization.
Conclusion
In a world driven by complexity, compliance, and cloud, the RHCA in Infrastructure isn't just about Red Hat—it’s about mastering modern IT. Whether you're looking to lead transformation projects, standardize infrastructure across geographies, or automate operations for efficiency and scale, RHCA puts you in the driver's seat.
So yes, with RHCA in Infrastructure, you can—design smarter, lead confidently, and shape the future of enterprise IT.
For more info kindly check - https://training.hawkstack.com/red-hat-certified-architect/
0 notes
Text
🔄 Automate Linux Administration Tasks with Ansible
Simplify System Management with Powerful Automation
In today’s fast-paced IT environments, managing hundreds—or even thousands—of Linux systems manually is not just inefficient, it's error-prone. This is where automation tools like Ansible come into play. With Ansible, system administrators can automate repetitive tasks, ensure consistency, and drastically reduce the time spent on routine operations.
This blog dives into how Ansible helps automate Linux system administration tasks, even if you're new to automation.
🚀 Why Automate Linux Administration?
Managing Linux systems traditionally involves manual steps: editing configuration files, installing packages, setting up users, and applying security policies. While manageable on one or two servers, it becomes complex and risky when scaled across environments.
The Benefits of Automation:
✅ Consistency: Ensure identical configurations across systems
✅ Speed: Execute tasks on multiple servers in seconds
✅ Reduced Errors: Avoid mistakes common in manual configurations
✅ Auditability: Maintain clear documentation of changes
✅ Scalability: Easily extend tasks across dozens or hundreds of systems
🔧 What Is Ansible?
Ansible is an open-source automation tool used for configuration management, application deployment, and task execution. It’s agentless, uses simple YAML-based playbooks, and connects to systems using SSH.
Unlike other tools, Ansible requires no special software on managed hosts, making it lightweight and easy to adopt.
🛠️ Common Linux Tasks You Can Automate with Ansible
You don’t need to be a scripting expert to automate these routine administrative jobs:
1. User Management
Create or remove users in bulk
Set or reset passwords
Assign users to specific groups
2. Package Management
Install, update, or remove software packages
Ensure required software is always present
3. Service Management
Start, stop, enable, or restart system services
Ensure critical services are always running
4. File and Directory Management
Deploy standard configuration files across systems
Set file permissions and ownership automatically
5. System Updates and Patching
Automate OS updates
Schedule regular patch cycles
6. Security Enforcement
Apply security policies consistently
Ensure firewalls, SELinux, and auditing are configured
7. Disk and Network Configuration
Mount volumes, configure partitions
Manage static IPs, DNS, or hosts files
⚙️ How It Works (In Simple Terms)
You define what needs to be done in a plain-text playbook (no coding required).
Ansible connects to your Linux machines via SSH.
It reads your instructions and performs them in order, ensuring every step completes as expected.
If a system is already in the desired state, Ansible does nothing, which avoids unnecessary changes.
📈 Real-World Use Case: Updating All Servers
Instead of logging into each server individually:
Run one Ansible playbook to update all packages across your fleet.
Reboot servers only if required.
Confirm successful updates with a summary report.
🎯 Who Should Use Ansible?
Linux System Administrators
DevOps Engineers
IT Operations Teams
Security and Compliance Officers
Even beginners can get started with basic tasks and grow into more complex automation.
🚀 Final Thoughts
Automation is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. With Ansible, you can take control of your Linux systems, eliminate repetitive work, and free up time for more strategic tasks. Whether you manage 5 servers or 500, Ansible helps you automate with clarity, consistency, and confidence.
For more info, Kindly follow: Hawkstack Technologies
0 notes
Text
Guide to RK3568 Android Application Porting and System Customization
Application porting on Android devices is an important part of system development. Especially on embedded platforms like RK3568, pre-installing APK, system compilation, and permission management all require specific configurations and optimizations. This guide will provide a detailed introduction on how to complete Android application porting on the RK3568 platform, including key steps such as pre-installing and uninstalling APK and obtaining Root privileges, to help developers quickly adapt and customize the Android system.
Pre-installing Apps on the Android System
1. Adding an APK file: Take dogdog.apk as an example:
Add an Android.mk file under the "dogdog" folder and write the relevant content for the dogdog.apk file.
Add the Android. mk under the dogdog folder and write the dogdog. apk films.

Android.mk writing method:LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir) include $(CLEAR_VARS) LOCAL_MODULE := dogdog LOCAL_SRC_FILES := dogdog.apk LOCAL_MODULE_CLASS := APPS LOCAL_MODULE_SUFFIX := .apk LOCAL_BUILT_MODULE_STEM := package.apk LOCAL_CERTIFICATE := platform LOCAL_DEX_PREOPT := false LOCAL_PRIVILEGED_MODULE := ture include $(BUILD_PREBUILT)

2. Adding an installation configuration
Modify/OK3568-android11-source/device/rockchip/rk356x/ok3568_r/ok3568_r.mk Add dogdog \

Compile again to generate update. img files, which can be flahsed and pre-installed apk normally.
Pre-installing Apps on the Android System
1. Delete the apk file
Delete the doggo file under/OK3568-android11-source/packages/apps/
2.Delete installation configuration
Mod/OK3568-android11-source/device/rockchip/rk356x/ok3568_r/ok3568_r.mk file Delete dogdog \

3.Delete the intermediate files generated by compilation
Delete /Ok3568-android11-source/out/target/product/ok3568_r/system/priv-app/ corresponding files

Compile again to generate the update. img file.
Android Getting Root Privileges
Location of references and test procedures:

1.The user debug version needs to be compiled.
2.Close selinux
Modify the configuration according to the red prompt:
Source code/device/rockchip/common/BoardConfig.mkBOARD_MKBOOTIMG_ARGS := BOARD_PREBUILT_DTBOIMAGE ?= $(TARGET_DEVICE_DIR)/dtbo.img BOARD_ROCKCHIP_VIRTUAL_AB_ENABLE ?= false BOARD_SELINUX_ENFORCING ?= false
false is Close, true is Open.
3. Annotation User Group Permission Detection
Comment the following two lines.
Source code/system/extras/su/su.cppint main(int argc, char** argv) { //uid_t current_uid = getuid(); //if (current_uid != AID_ROOT && current_uid != AID_SHELL) error(1, 0, "not allowed"); // Handle -h and --help. ++argv;
4. Grant root privileges to su files by default
(1)Source code/system/core/libcutils/fs_config.cppstatic const struct fs_path_config android_files[] = { …… // the following two files are INTENTIONALLY set-uid, but they // are NOT included on user builds. { 06755, AID_ROOT, AID_ROOT, 0, "system/xbin/procmem" }, { 06755, AID_ROOT, AID_ROOT, 0, "system/xbin/procmem" }, // the following files have enhanced capabilities and ARE included // in user builds.
(2)Source code/frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cppstatic void DropCapabilitiesBoundingSet(fail_fn_t fail_fn) { /* for (int i = 0; prctl(PR_CAPBSET_READ, i, 0, 0, 0) >= 0; i++) {; if (prctl(PR_CAPBSET_DROP, i, 0, 0, 0) == -1) { if (errno == EINVAL) { ALOGE("prctl(PR_CAPBSET_DROP) failed with EINVAL. Please verify " ''your kernel is compiled with file capabilities support"); } else { fail_fn(CREATE_ERROR("prctl(PR_CAPBSET_DROP, %d) failed: %s", i, strerror(errno))); } } } */ }
(3)Source code/kernel/security/commoncap.cstatic int cap_prctl_drop(unsigned long cap) { struct cred *new; /* if (!ns_capable(current_user_ns(), CAP_SETPCAP)) return -EPERM; if (!cap_valid(cap)) return -EINVAL; */ new = prepare_creds(); if (!new) return -ENOMEM; cap_lower(new->cap_bset, cap); return commit_creds(new); }
5.Complete compilation and flashing.
After compiling and flashing, you can install the RootChecker. apk to detect whether android has obtained root permission. If the prompt is "Root check pass", it indicates that root privileges have been obtained.
0 notes