#arduino lora mesh network
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
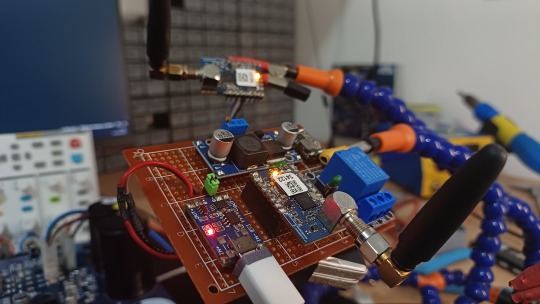
GPIOs do LoRaMesh da Radioenge: Portas digitais
Aprenda como usar as GPIOs do módulo LoRaMesh da Radioenge
As GPIOs do LoRaMesh da Radioenge possibilita que possamos fazer aplicações de automação com um uso reduzido de hardware, dedicando apenas ao circuito de chaveamento (se necessário) e de alimentação. No total temos no LoRaMesh 8 GPIOs sendo todas configuráveis como entrada ou saída digital e duas como leitura analógica. Porém neste post vamos apenas abordar as portas digitais. Por qual motivo…
View On WordPress
#lora mesh arduino#lora mesh chat#lora mesh device#lora mesh library#lora mesh module#lora mesh network#lora mesh network raspberry pi#lora mesh protocol#lora mesh radio#lora mesh range#lora vs lorawan#loramesh#lorawan#lorawan devices#lorawan gateway#lorawan network#mesh lora
0 notes
Link
When the critical infrastructure that so many of us take for granted goes away, how do we organize ourselves and our communities to respond?
If recent ecological disasters have demonstrated anything, it is the inadequacy of existing models and tools to provide efficient allocation of resources, access to emergency communications, and effective coordination of human effort. Few if any solutions exist that are off-grid, affordable, reliable, easily deployed, and openly standardized.
...
disaster.radio is an off-grid, solar-powered, long-range mesh network built on free, open source software and affordable, open hardware.
Designed to be open, distributed, and decentralized, disaster.radio is currently in the prototype/development phase. To learn more about the technologies driving our development, visit the following pages:
Firmware Hardware Software User guides
disaster.radio is a collaborative project between Sudo Mesh and Secure Scuttlebutt, with additional support from the Internet Society and Institute For the Future.
Read more: https://disaster.radio/
#arduino #lora #lorawan #radio #ham #offgrid #solar #mesh #network
youtube
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
IoT Standards & Protocols Guide - Arya College

The essence of IoT is networking that students of information technology college should be followed. In other words, technologies will use in IoT with a set protocol that they will use for communications. In Communication, a protocol is basically a set of rules and guidelines for transferring data. Rules defined for every step and process during communication between two or more computers. Networks must follow certain rules to successfully transmit data.
While working on a project, there are some requirements that must be completed like speed, range, utility, power, discoverability, etc. and a protocol can easily help them find a way to understand and solve the problem. Some of them includes the following:
The List
There are some most popular IoT protocols that the engineers of Top Engineering Colleges in India should know. These are primarily wireless network IoT protocols.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over some short distances ranges from fixed and mobile devices, and building personal area networks (PANs). It invented by Dutch electrical engineer, that is, Jaap Haartsen who is working for telecom vendor Ericsson in 1994. It was originally developed as a wireless alternative to RS-232 data cables.
ZigBee
ZigBee is an IEEE 802.15.4-based specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols that are used by the students of best engineering colleges to create personal area networks. It includes small, low-power digital radios like medical device data collection, home automation, and other low-power low-bandwidth needs, designed for small scale projects which need wireless connection. Hence, ZigBee is a low data rate, low-power, and close proximity wireless ad hoc network.
Z-wave
Z-Wave – a wireless communications protocol used by the students of Top Information Technology Colleges primarily for home automation. It is a mesh network using low-energy radio waves to communicate from appliance to appliance which allows wireless control of residential appliances and other devices like lighting control, thermostats, security systems, windows, locks, swimming pools and garage door openers.
Thread
A very new IP-based IPv6 networking protocols aims at the home automation environment is Thread. It is based on 6LowPAN and also like it; it is not an IoT protocols like Bluetooth or ZigBee. However, it primarily designed as a complement to Wi-Fi and recognises that Wi-Fi is good for many consumer devices with limitations for use in a home automation setup.
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a technology for wireless local area networking with devices according to the IEEE 802.11 standards. The Wi-Fi is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance which prohibits the use of the term Wi-Fi Certified to products that can successfully complete interoperability certification testing.
Devices that can use Wi-Fi technology mainly include personal computers, digital cameras, video-game consoles, smartphones and tablets, smart TVs, digital audio players and modern printers. Wi-Fi compatible devices can connect to the Internet through WLAN and a wireless access point. Such an access point has a range of about 20 meters indoors with a greater range outdoors. Hotspot coverage can be as small as a single room with walls that restricts radio waves, or as large as many square kilometres that is achieved by using multiple overlapping access points.
LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN a media access control protocol mainly used for wide area networks. It designed to enable students of private engineering colleges in India to communicate through low-powered devices with Internet-connected applications over long-range wireless connections. LoRaWAN can be mapped to the second and third layer of the OSI model. It also implemented on top of LoRa or FSK modulation in industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) radio bands.
NFC
Near-field communication is a set of communication protocols that enable students of best engineering colleges in India two electronic devices. One of them is usually a portable device like a smartphone, to establish communication by bringing them within 4cm (1.6 in) of each other.
These devices used in contactless payment systems like to those used in credit cards and electronic ticket smartcards and enable mobile payment to replace/supplement these systems. Sometimes, this referred to as NFC/CTLS (Contactless) or CTLS NFC. NFC used for social networking, for sharing contacts, videos, photos,or files. NFC-enabled devices can act as electronic identity both documents and keycards. NFC also offers a low-speed connection with simple setup that can be used by the students of top btech colleges in India to bootstrap more capable wireless connections.
Cellular
IoT application that requires operation over longer distances can take benefits of GSM/3G/4G cellular communication capabilities. While cellular is clearly capable of sending high quantities of data. Especially for 4G with the expense and also power consumption will be too high for many applications. Also, it can ideal for sensor-based low-bandwidth-data projects that will send very low amounts of data over the Internet. A key product in this area is the SparqEE range of products including the original tiny CELLv1.0 low-cost development board and a series of shield connecting boards for use with the Raspberry Pi and Arduino platforms.
Sigfox
This unique approach in the world of wireless connectivity; where there is no signalling overhead, a compact and optimized protocol; and where objects not attached to the network. So, Sigfox offers a software-based communications solution to the students of top engineering colleges in India. Where all the network and computing complexity managed in the Cloud, rather than on the devices. All that together, it drastically reduces energy consumption and costs of connected devices.
SigFox wireless technology is based on LTN (Low Throughput Network). A wide area network-based technology which supports low data rate communication over larger distances. However, it mainly used for M2M and IoT applications which transmits only few bytes per day.
0 notes
Text
12 уровней IIoT-архитектуры: от периферийных датчиков до аналитики Big Data

Мы уже рассматривали типовую архитектуру систем Internet of Things (IoT). Сегодня поговорим подробнее про уровневую модель передачи и обработки данных от конечных устройств до облачных IoT-платформ, а также приведем примеры наиболее популярных средств обеспечения каждого из уровней этой сложной архитектуры Industrial Internet of Things, включая инструменты Big Data.
Многоуровневый IIoT: 12 слоев архитектуры
В отличие от типовой Big Data системы, работающей по принципу клиент-серверного приложения, модель IIoT-решения гораздо сложнее. Аналогично клиент-серверному принципу, в IIoT-архитектуре можно выделить 2 разных по физическому расположению группы обязательных компонентов: · периферия (Edge) - конечные smart-устройства, расположенные на технологическом оборудовании, за которым осуществляется удаленный мониторинг и управление; · мощные Big Data инструменты, развернутые в центре обработки данных на серверах или в облаке (Backend). Тем не менее, из-за особенностей использования IIoT-решений, связанных с условиями эксплуатации и прикладной специфики, например, экстремальные температуры, вибрации, осадки, большая протяженность каналов передачи данных и пр., в архитектуре Industrial Internet of Things можно выделить целых 12 уровней (слоев) [1]: · физический (Physical Layer), на котором расположены конечные устройства – датчики и сенсоры, камеры и пр. оборудование (таймеры, пьезоэлементы, микрофоны, фотодиоды/транзисторы/резисторы, выключатели, акселерометры, GPS-трекеры, баркод-ридеры и т.д.), собирающее информацию и отправляющее ее дальше, на уровень периферийной обработки данных (Edge Layer). · периферийные вычисления (Edge Layer), который обеспечивает минимальную обработку данных, в частности, преобразования между аналоговым и цифровым представлением информации (АЦП/ЦАП). Как правило, эти функции реализуются с помощью микроконтроллеров Raspberry Pi, Arduino и другие однокристалльные системы – SoC-модули (System-on-a-Chip) - электронные схемы, выполняющая функции целого устройства, в т.ч. беспроводные сети на кристалле (Wireless network-on-chip, WNOC) [2]. Основным требованием к устройствам физического и периферийного уровней является низкое энергопотребление (питание от батарейки), низкая стоимость покупки и эксплуатации (бесперебойная работа без обслуживания от 1 до 10 лет, минимальные затраты на приобретение, установку и обслуживание). Для снижения энергопотребления периферийные устройства обычно имеют четыре режима работы: сон, режим измерения и сбора информации с датчиков, режим связи, передачи и получения информации, а также режим установки и подключения. · Периферейная коммуникация (Local Network Layer), когда данные после первичной обработки отправляются на шлюз (Gateway), который может находиться очень далеко (в пределах нескольких километров). Для надежной передачи данных на дальние расстояния применяются беспроводные динамические самоорганизующиеся сети: одноранговая Ad Hoc и иерархическая Mesh [3]. Обычно для этого используются протоколы ZigBee/Zwave, BLE, LoRa, Proprietary low band, WiFi, Ethernet, CAN, LTE, PLC.

Схема периферийного IIoT-устройства · Шлюз (Gateway Layer), который выполняет ETL-операции (Extract, Transform, Load) — получение, преобразование и сохранение информации с периферийных устройств, обеспечивает важные действия в случае критической ситуации даже без связи с Backend, а также общается с сервером с использованием мобильной беспроводной связи (4G/5G) или проводного доступа в Интернет, отправляя туда обработанную информацию и получая данные конфигурации для конечных устройств. Шлюз необходим в IIoT-решениях, т.к. если Backend будет получать необработанную информацию, это увеличит его мощность и коммуникационные затраты. Кроме того, удаленный Backend-сервер не может гарантировать реакцию в реальном времени для большого количества периферийных устройств, например, камер уличного наблюдения и т.д. · Уровень внешней связи (Wide Network Layer), разделяющий периферию и BackEnd. Здесь используется стандартизированный протокол для IoT-решений IoT – LwM2M (Lightweight M2M, легковесный межмашинный протокол) [4], разработанный для доступа к каждому периферийному устройству. Если периферийное устройство не поддерживает интерфейсы LwM2M, шлюз решит эту проблему, обеспечив связь с периферией. Уровень внешней связи содержит также коммуникационные сервисы и модели ISO, в т.ч. службы балансировки и определения местоположения, основанные на DNS-сервисе, транспортный протокол COAP, протокол шифрования с ключами безопасности и сессией установления соединения DTLS и многие другие компоненты. При этом служба DNS используется в качестве балансировщика нагрузки, периодически генерируя DNS-запрос для получения нового IP-адреса экземпляра уровня безопасности. Помимо LwM2M на уровне внешней связи также используются протоколы PLC, Ethernet, LTE, FOTA/SOTA, Radio. · Уровень безопасности (Security Layer), который обеспечивает аутентификацию, авторизацию, учет и шифрование/дешифрование на основе ролей и разрешений. Как правило, здесь используются средства информационной безопасности от облачных провайдеров, у которых развернуты агрегирующие и анализирующие компоненты IIoT-решений, например, Azure Cloud, AWS R53/IAM/EC2 и т.д. Подробнее про безопасность интернета вещей читайте в наших отдельных статьях об инцидентах cybersecurity и инструментах информационной защиты IoT: криптографических протоколах и защищенных каналах передачи данных. · Уровень внутрисерверной связи (Middleware Layer), обеспечивающий внутреннюю функциональность балансировки нагрузки в облаке, очереди сообщений и передачи потоковой информации на основе микросервисов или PaaS-решений от облачных провайдеров. Компоненты этого слоя должны быть дублированы и автоматически масштабироваться в связи с нестационарным характером передачи данных, чтобы обеспечить асинхронную передачу сообщений с буферизацией и перераспределением нагрузки. Именно на этом уровне работают Big Data брокеры сообщений и управления очередями, такие как Apache Kafka или RabbitMQ. Для быстрой загрузки данных с периферии часто используется платформа обработки событий (сообщений) Apache NiFi или ее упрощенная модификация Apache MiNiFi. · Уровень сбора, обработки и хранения данных (ETL), реализуемый не только в периферийных устройствах и шлюзах, но и в Backend, посредством сбора данных, их агрегации, унификации представления, сохранения для дальнейшего использования, уведомления других сервисов о поступлении новых данных и общего управления жизненным циклом информации, в т. архивирование и уничтожение. Здесь также работают Big Data-средства управления очередями сообщений (Apache Kafka или RabbitMQ) и потоковой загрузки данных (Apache NiFi и MiNiFi). · Big Data аналитика, машинное обучение (Machine Learning, ML) и другие методы искусственного интеллекта (Artificial Intelligence, AI). Инструментальные средства этого уровня наименее стандартизованы и зависят от конкретного случая. Например, для прогнозирования возможных отказов оборудования может использоваться библиотека MLLib фреймворков потоковой Spark или Flink, для генерации OLAP-кубов и сложных SQL-запросов – Spark SQL и FlinkQL соответственно и т.д. Например, здесь мы описывали пример построения сложной Big Data системы для предиктивной аналитики метеозависимого маркетинга на базе Apache Kafka и Spark.

Интеграция Apache Kafka и Spark Streaming для построения предиктивных моделей Machine Learning в IIoT-системе · Уровень уведомлений (Notification layer), сообщающий о наступлении какого-то события, например, в форме письма по электронной почте, СМС-сообщения или телефонного звонка (в крайнем, экстренном случае). Для снижения энергопотребления мобильные приложения переходят в спящий режим, но iOS и Android имеют механизм уведомлений, указывающий на прибытие новых данных. Алгоритмически такое M2P-общение (machine to person) реализуется в виде модели «издатель-подписчик», когда клиентское приложение подписывается на необходимые события и, в случае их наступления, получает информационный сигнал — уведомление. · Уровень представления (Presentation Layer), когда обработанная информация от периферийных устройств презентуется конечному пользователю с помощью UI/UX-интерфейсов на экране компьютерного монитора, планшета или мобильного телефона. Уровень представления также отвечает за обслуживание, конфигурацию и изменения состояния каждого компонента IIoT-системы, позволяя удаленно управлять даже периферийными устройствами. Пока не существует стандартизированных UI/UX-средств для уровня представления IIoT-системы, несмотря на наличие ��еждународных и национальных стандартов, регламентирующих понятия человеко-машинного интерфейса (ГОСТ МЭК 60447-2000, IEC 60447-2015, IEC 60447:1993) [5], широко используемых в SCADA-системах. · Уровень конфигураций (Configuration Layer), обеспечивающий хранилище статусов периферийных устройств (актуальное состояние, новое состояние, которое будет загружено и промежуточный статус, указывающий на процесс обновления состояния). Это необходимо из-за особенностей связи периферии и шлюза с Backend-сервером, т.к. коммуникация конечных устройств с облаком держится не постоянно, а периодическими сеансами, во время которых и происходит отправка и получение данных.

12-уровневая архитектура IIoT-системы Все подробности технической реализации сложных Big Data систем и комплексных IIoT-проектов разбираются на наших практических курсах для менеджеров, архитекторов, инженеров, администраторов, Data Scientist’ов и аналитиков больших данных в лицензированном учебном центре обучения и повышения квалификации ИТ-специалистов в Москве.

Смотреть расписание занятий

Зарегистрироваться на курс Источники 1. https://habr.com/ru/post/455377/ 2. https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Система_на_кристалле 3. https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Беспроводная_ad-hoc-сеть 4. https://itechinfo.ru/content/lightweight-m2m 5. http://docs.cntd.ru/document/gost-r-mek-60447-2000 Read the full article
#BigData#IIoT#InternetofThings#IoT#Kafka#MachineLearning#Spark#архитектура#Большиеданные#интернетвещей#МашинноеОбучение#обработкаданных
0 notes
Text
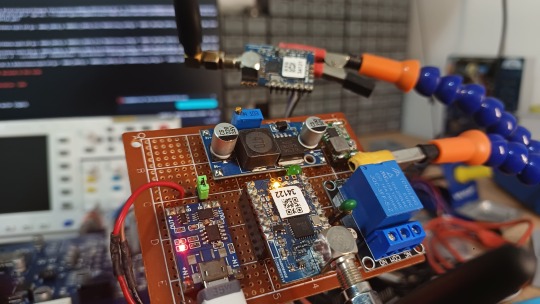
Leitura analógica do LoRaMesh da Radioenge
Aprenda como usar a leitura analógica com o módulo LoRaMesh da Radioenge
A leitura analógica com o LoRaMesh possibilita com que possamos fazer um amplo sistema de sensoriamento remoto sem precisar necessariamente de microcontrolador adicional na parte do slave. Por qual motivo usar a leitura analógica do LoRaMesh da Radioenge? Uma leitura digital em muito dos casos já é mais que o suficiente para saber se algo está ou não funcionando, mas a leitura analógica do…
View On WordPress
#lora mesh arduino#lora mesh chat#lora mesh device#lora mesh library#lora mesh module#lora mesh network#lora mesh network raspberry pi#lora mesh protocol#lora mesh radio#lora mesh range#lora vs lorawan#loramesh#lorawan#lorawan devices#lorawan gateway#lorawan network#mesh lora
0 notes
Text
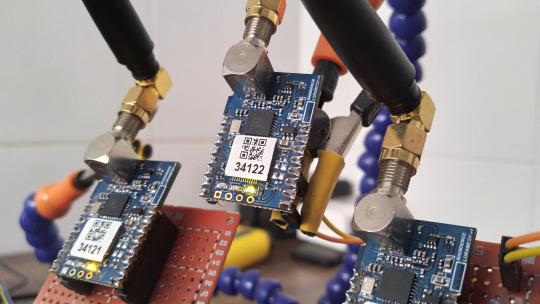
LoRa Mesh da Radioenge Tutorial Completo
LoRa Mesh é uma tecnologia que utiliza a modulação LoRa, porém cada módulo tem a capacidade de atuar como um repetidor que fica repassando a informação até chegar ao destinatário. Clique no link, titulo ou imagem para saber mais.
LoRa Mesh da Radioenge utiliza a tecnologia LoRa porém o grande diferencial deste módulo é a capacidade de se comunicar com outros módulos de modo que a informação saia de ‘A‘ e chegue a ‘J‘ sem se comunicarem de forma direta. Se ‘J‘ estiver fora do alcance de ‘A’, a informação vai percorre todo o “alfabeto”, até chegar ao destino. Caso isso seja confuso para você, ao longo deste post irá…
Ver no WordPress
#alliance lora#arduino lora#arduino lora mesh network#lora agricultura#lora alcance#lora alliance#lora arduino#lora mesh#lora mesh arduino#lora mesh network arduino#lora mesh protocol#lora mesh radio#lora mesh range#lorawan mesh arduino#rede lora mesh
0 notes
Text
IoT protocols every engineer should know about - Arya College

The essence of IoT is networking that students of information technology college should be followed. In other words, technologies will use in IoT with a set protocol that they will use for communications. In Communication, a protocol is basically a set of rules and guidelines for transferring data. Rules defined for every step and process during communication between two or more computers. Networks must follow certain rules to successfully transmit data.
While working on a project, there are some requirements that must be completed like speed, range, utility, power, discoverability, etc. and a protocol can easily help them find a way to understand and solve the problem. Some of them includes the following:
The List
There are some most popular IoT protocols that the engineers of Top Engineering Colleges in India should know. These are primarily wireless network IoT protocols.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over some short distances ranges from fixed and mobile devices, and building personal area networks (PANs). It invented by Dutch electrical engineer, that is, Jaap Haartsen who is working for telecom vendor Ericsson in 1994. It was originally developed as a wireless alternative to RS-232 data cables.
ZigBee
ZigBee is an IEEE 802.15.4-based specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols that are used by the students of best engineering colleges to create personal area networks. It includes small, low-power digital radios like medical device data collection, home automation, and other low-power low-bandwidth needs, designed for small scale projects which need wireless connection. Hence, ZigBee is a low data rate, low-power, and close proximity wireless ad hoc network.
Z-wave
Z-Wave – a wireless communications protocol used by the students of Top Information Technology Colleges primarily for home automation. It is a mesh network using low-energy radio waves to communicate from appliance to appliance which allows wireless control of residential appliances and other devices like lighting control, thermostats, security systems, windows, locks, swimming pools and garage door openers.
Thread
A very new IP-based IPv6 networking protocols aims at the home automation environment is Thread. It is based on 6LowPAN and also like it; it is not an IoT protocols like Bluetooth or ZigBee. However, it primarily designed as a complement to Wi-Fi and recognises that Wi-Fi is good for many consumer devices with limitations for use in a home automation setup.
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a technology for wireless local area networking with devices according to the IEEE 802.11 standards. The Wi-Fi is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance which prohibits the use of the term Wi-Fi Certified to products that can successfully complete interoperability certification testing.
Devices that can use Wi-Fi technology mainly include personal computers, digital cameras, video-game consoles, smartphones and tablets, smart TVs, digital audio players and modern printers. Wi-Fi compatible devices can connect to the Internet through WLAN and a wireless access point. Such an access point has a range of about 20 meters indoors with a greater range outdoors. Hotspot coverage can be as small as a single room with walls that restricts radio waves, or as large as many square kilometres that is achieved by using multiple overlapping access points.
LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN a media access control protocol mainly used for wide area networks. It designed to enable students of private engineering colleges in India to communicate through low-powered devices with Internet-connected applications over long-range wireless connections. LoRaWAN can be mapped to the second and third layer of the OSI model. It also implemented on top of LoRa or FSK modulation in industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) radio bands.
NFC
Near-field communication is a set of communication protocols that enable students of best engineering colleges in India two electronic devices. One of them is usually a portable device like a smartphone, to establish communication by bringing them within 4cm (1.6 in) of each other.
These devices used in contactless payment systems like to those used in credit cards and electronic ticket smartcards and enable mobile payment to replace/supplement these systems. Sometimes, this referred to as NFC/CTLS (Contactless) or CTLS NFC. NFC used for social networking, for sharing contacts, videos, photos,or files. NFC-enabled devices can act as electronic identity both documents and keycards. NFC also offers a low-speed connection with simple setup that can be used by the students of top btech colleges in India to bootstrap more capable wireless connections.
Cellular
IoT application that requires operation over longer distances can take benefits of GSM/3G/4G cellular communication capabilities. While cellular is clearly capable of sending high quantities of data. Especially for 4G with the expense and also power consumption will be too high for many applications. Also, it can ideal for sensor-based low-bandwidth-data projects that will send very low amounts of data over the Internet. A key product in this area is the SparqEE range of products including the original tiny CELLv1.0 low-cost development board and a series of shield connecting boards for use with the Raspberry Pi and Arduino platforms.
Sigfox
This unique approach in the world of wireless connectivity; where there is no signalling overhead, a compact and optimized protocol; and where objects not attached to the network. So, Sigfox offers a software-based communications solution to the students of top engineering colleges in India. Where all the network and computing complexity managed in the Cloud, rather than on the devices. All that together, it drastically reduces energy consumption and costs of connected devices.
SigFox wireless technology is based on LTN (Low Throughput Network). A wide area network-based technology which supports low data rate communication over larger distances. However, it mainly used for M2M and IoT applications which transmits only few bytes per day.
Thanks for Read our blog, you can check out full blog on official Page Arya College, Arya College is one of the Best Engineering College In Jaipur Rajasthan. In This College Many Branches for Engineering you can make great future with us. Arya College Provides Computer Engineering, Electrical Engineering & Electronics Engineering’s Branch for our Engineering students with top companies placements in campus.
0 notes