#dataflows
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The PERFECT Power BI dataflows use case
We get a lot of questions about Power BI dataflows and when to use them. Patrick explores a use case that screams for using … source
0 notes
Text

📊 Why are dataflows important in end-to-end analytics? Dataflows (Gen2) play a key role by helping you: ✅ Prepare consistent data ✅ Stage it in your preferred destination ✅ Reuse it across reports ✅ Easily refresh and update it
They streamline your analytics process from raw data to actionable insights!
💬 How are you using dataflows in your projects?
#PowerBI#Dataflows#DataTransformation#Analytics#MicrosoftFabric#DataPreparation#ETL#Gen2Dataflows#DataEngineering#BI#DataPipeline#TechTips#dax
0 notes
Text
[Fabric] Fast Copy con Dataflows gen2
Cuando pensamos en integración de datos con Fabric está claro que se nos vienen dos herramientas a la mente al instante. Por un lado pipelines y por otro dataflows. Mientras existía Azure Data Factory y PowerBi Dataflows la diferencia era muy clara en audiencia y licencias para elegir una u otra. Ahora que tenemos ambas en Fabric la delimitación de una u otra pasaba por otra parte.
Por buen tiempo, el mercado separó las herramientas como dataflows la simple para transformaciones y pipelines la veloz para mover datos. Este artículo nos cuenta de una nueva característica en Dataflows que podría cambiar esta tendencia.
La distinción principal que separa estas herramientas estaba basado en la experiencia del usuario. Por un lado, expertos en ingeniería de datos preferían utilizar pipelines con actividades de transformaciones robustas d datos puesto que, para movimiento de datos y ejecución de código personalizado, es más veloz. Por otro lado, usuarios varios pueden sentir mucha mayor comodidad con Dataflows puesto que la experiencia de conectarse a datos y transformarlos es muy sencilla y cómoda. Así mismo, Power Query, lenguaje detrás de dataflows, ha probado tener la mayor variedad de conexiones a datos que el mercado ha visto.
Cierto es que cuando el proyecto de datos es complejo o hay cierto volumen de datos involucrado. La tendencia es usar data pipelines. La velocidad es crucial con los datos y los dataflows con sus transformaciones podían ser simples de usar, pero mucho más lentos. Esto hacía simple la decisión de evitarlos. ¿Y si esto cambiara? Si dataflows fuera veloz... ¿la elección sería la misma?
Veamos el contexto de definición de Microsoft:
Con la Fast Copy, puede ingerir terabytes de datos con la experiencia sencilla de flujos de datos (dataflows), pero con el back-end escalable de un copy activity que utiliza pipelines.
Como leemos de su documentación la nueva característica de dataflow podría fortalecer el movimiento de datos que antes frenaba la decisión de utilizarlos. Todo parece muy hermoso aun que siempre hay frenos o limitaciones. Veamos algunas consideraciones.
Origenes de datos permitidos
Fast Copy soporta los siguientes conectores
ADLS Gen2
Blob storage
Azure SQL DB
On-Premises SQL Server
Oracle
Fabric Lakehouse
Fabric Warehouse
PostgreSQL
Snowflake
Requisitos previos
Comencemos con lo que debemos tener para poder utilizar la característica
Debe tener una capacidad de Fabric.
En el caso de los datos de archivos, los archivos están en formato .csv o parquet de al menos 100 MB y se almacenan en una cuenta de Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen2 o de Blob Storage.
En el caso de las bases de datos, incluida la de Azure SQL y PostgreSQL, 5 millones de filas de datos o más en el origen de datos.
En configuración de destino, actualmente, solo se admite lakehouse. Si desea usar otro destino de salida, podemos almacenar provisionalmente la consulta (staging) y hacer referencia a ella más adelante. Más info.
Prueba
Bajo estas consideraciones construimos la siguiente prueba. Para cumplir con las condiciones antes mencionadas, disponemos de un Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 con una tabla con información de vuelos que pesa 1,8Gb y esta constituida por 10 archivos parquet. Creamos una capacidad de Fabric F2 y la asignaciones a un área de trabajo. Creamos un Lakehouse. Para corroborar el funcionamiento creamos dos Dataflows Gen2.
Un dataflow convencional sin FastCopy se vería así:

Podemos reconocer en dos modos la falta de fast copy. Primero porque en el menú de tabla no tenemos la posibilidad de requerir fast copy (debajo de Entable staging) y segundo porque vemos en rojo los "Applied steps" como cuando no tenemos query folding andando. Allí nos avisaría si estamos en presencia de fast copy o intenta hacer query folding:
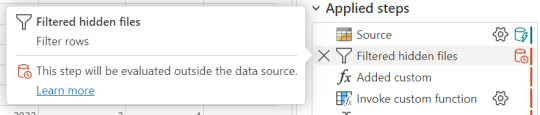
Cuando hace query folding menciona "... evaluated by the datasource."
Activar fast copy
Para activarlo, podemos presenciar el apartado de opciones dentro de la pestaña "Home".
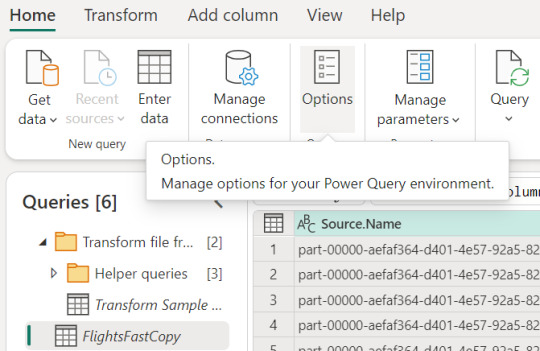
Allí podemos encontrarlo en la opción de escalar o scale:
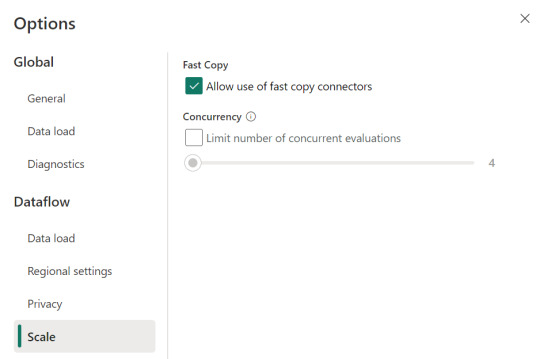
Mientras esa opción esté encendida. El motor intentará utilizar fast copy siempre y cuando la tabla cumpla con las condiciones antes mencionadas. En caso que no las cumpla, por ejemplo la tabla pese menos de 100mb, el fast copy no será efectivo y funcionaría igual que un dataflow convencional.
Aquí tenemos un problema, puesto que la diferencia de tiempos entre una tabla que usa fast copy y una que no puede ser muy grande. Por esta razón, algunos preferiríamos que el dataflow falle si no puede utilizar fast copy en lugar que cambie automaticamente a no usarlo y demorar muchos minutos más. Para exigirle a la tabla que debe usarlo, veremos una opción en click derecho:

Si forzamos requerir fast copy, entonces la tabla devolverá un error en caso que no pueda utilizarlo porque rompa con las condiciones antes mencionadas a temprana etapa de la actualización.
En el apartado derecho de la imagen tambien podemos comprobar que ya no está rojo. Si arceramos el mouse nos aclarará que esta aceptado el fast copy. "Si bien tengo otro detalle que resolver ahi, nos concentremos en el mensaje aclarando que esta correcto. Normalmente reflejaría algo como "...step supports fast copy."
Resultados
Hemos seleccionado exactamente los mismos archivos y ejecutado las mismas exactas transformaciones con dataflows. Veamos resultados.
Ejecución de dataflow sin fast copy:

Ejecución de dataflow con fast copy:

Para validar que tablas de nuestra ejecución usan fast copy. Podemos ingresar a la corrida

En el primer menú podremos ver que en lugar de "Tablas" aparece "Actividades". Ahi el primer síntoma. El segundo es al seleccionar una actividad buscamos en motor y encontramos "CopyActivity". Así validamos que funcionó la característica sobre la tabla.
Como pueden apreciar en este ejemplo, la respuesta de fast copy fue 4 veces más rápida. El incremento de velocidad es notable y la forma de comprobar que se ejecute la característica nos revela que utiliza una actividad de pipeline como el servicio propiamente dicho.
Conclusión
Seguramente esta característica tiene mucho para dar e ir mejorando. No solamente con respecto a los orígenes sino tambien a sus modos. No podemos descargar que también lo probamos contra pipelines y aqui esta la respuesta:
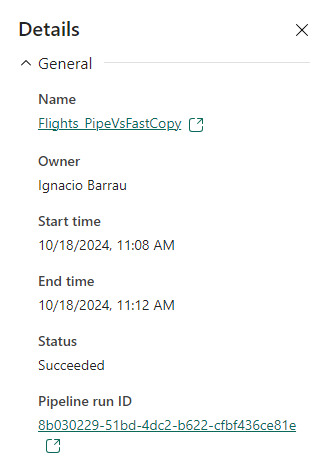
En este ejemplo los Data Pipelines siguen siendo superiores en velocidad puesto que demoró 4 minutos en correr la primera vez y menos la segunda. Aún tiene mucho para darnos y podemos decir que ya está lista para ser productiva con los origenes de datos antes mencionados en las condiciones apropiadas. Antes de terminar existen unas limitaciones a tener en cuenta:
Limitaciones
Se necesita una versión 3000.214.2 o más reciente de un gateway de datos local para soportar Fast Copy.
El gateway VNet no está soportado.
No se admite escribir datos en una tabla existente en Lakehouse.
No se admite un fixed schema.
#fabric#microsoft fabric#fabric training#fabric tips#fabric tutorial#data engineering#dataflows#fabric dataflows#fabric data factory#ladataweb
0 notes
Text
How Can Implementing An Integration Platform As A Service
What is integration platform as a service?
A collection of self-service, cloud-based tools and solutions known as integration platform as a service (iPaaS) are used to combine data from many applications that are housed in various IT environments.
Businesses may create and implement integration processes between the cloud and on-premises data centers, as well as between apps and data housed in public and private clouds, with to integration platform as a service. Software as a service (SaaS) sprawl is a rising issue in contemporary businesses that iPaaS was created to address.
Because SaaS apps are often designed to be simple to install, operate, and deploy, they are a desirable choice for businesses trying to meet certain administrative and commercial requirements. Their simplicity of use, however, also makes it more likely for departments and business teams to purchase SaaS apps in order to satisfy departmental and team demands, which may result in an often complex ecosystem of cloud-based business apps. Approximately 470 SaaS apps are used by contemporary enterprise-sized enterprises, defined as those with 10,000 or more workers.
Prior to iPaaS, businesses used enterprise middleware, bespoke programming, or enterprise application integration (EAI) solutions, such enterprise service bus (ESB) in service-oriented architectures (SOAs), to link applications and business processes.
Although these integration solutions were effective, their development and upkeep were often costly and time-consuming. As the usage of cloud applications, microservices, edge computing, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices increased, they also left businesses vulnerable to data silos where one department within the company lacks insight into another and more general process inefficiencies.
The rising problem of app, data source, and service integration in increasingly complex IT systems (such hybrid cloud and multi-cloud environments) may be solved using iPaaS cloud integration services. By offering solutions like pre-built connections, maps, and transformations, they assist businesses coordinate integration processes and optimize interoperability across diverse systems, therefore addressing corporate integration and data management concerns.
In addition, integration platform as a service(iPaaS) solutions may help with managed file transfers, cloud integration, event stream integration, B2B integration, IoT integration, and other kinds of integration.
Businesses may use iPaaS services to create and manage automated processes with real-time data synchronization that keeps analytics current and data consolidated. They allow teams to expedite security and integration duties. Scaling integration and saving time are made possible by low-code solutions that assist both citizen developers and integration professionals.
Features of iPaaS
For data sharing across IT environments, integration platform as a service(iPaaS) solutions depend on a number of essential integration capabilities and components. iPaaS solutions often include the following characteristics:
Adapters and connectors
Without requiring unique interfaces, iPaaS solutions provide pre-built connectors (or adapters), templates, and business logic that streamline and facilitate interactions across systems and apps.
Development with low-code and no-code
Business users and non-developers may construct and manage integration flows and workflows with the help of several iPaaS solutions, which provide low-code or no-code development environments with user-friendly drag-and-drop interfaces.
Data mapping and transformation
To guarantee data consistency across systems, iPaaS solutions usually provide mapping and data transformation technologies. To provide smooth data compatibility and integration, users may also create custom rules and mappings to change data formats, structures, and values as they travel across apps.
Automation of workflows
By coordinating data flow across many apps, integration platform as a service(iPaaS) streamlines workflow automation and business operations.
Batch and real-time processing
Teams may meet a variety of integration needs since iPaaS systems often provide both batch and real-time data processing capabilities. Additionally, integrations allow for configurable data processing across environments by being scheduled or triggered in response to certain business events or time periods.
Sophisticated analytics and data monitoring
Organizations may monitor the effectiveness of their connections and get real-time insights into data flows, error rates, and bottlenecks that impair system performance by using iPaaS’s powerful monitoring and analytics features.
Use cases for iPaaS
Organizations may more easily handle complicated integration situations without having to spend much in infrastructure or bespoke coding with to iPaaS solutions, which are meant to streamline and speed up the integration process across environments. For a variety of use situations, these functionalities may be helpful for IT integration and data visibility.
Integration between apps
Whether applications are housed in on-premises infrastructure or cloud settings, iPaaS can link them and automate processes across environments.
Integration of data
Regardless of the data source or format, iPaaS’s integrated translators provide smooth data translation, guaranteeing optimal data flow and interoperability.
Microservices and deployments that are containerized
Prominent iPaaS solutions may effectively combine separate microservices, assisting developers in enhancing the scalability and agility of their apps. For more adaptable, portable integration solutions that can be implemented in various IT settings, iPaaS platforms may also provide containerized deployments.
Integration of DevOps
By integrating with DevOps tools and pipelines, iPaaS systems enable continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) of integration processes. This allows integrations to be developed, tested, and deployed without causing performance issues or hiccups.
Business-to-business integration
By offering a unified platform that automates B2B integration processes, integration platform as a service(iPaaS) solutions address B2B integration challenges, including balancing the disparate IT systems and standards of business partners, meeting real-time data processing, monitoring, and adaptability needs, and satisfying data security and compliance requirements.
iPaaS solutions provide smooth interoperability and real-time data transmission by supporting a variety of data formats (X12, EDIFACT, ACH, xml, json), protocols (API, AS2, SFTP, FTPS), and systems. Through strong encryption and governance features, they improve security and compliance. They also provide scalability, ongoing monitoring, and easier flexibility. These characteristics improve the efficiency and manageability of B2B integration.
Oversaw the transmission of files
Managed file transfer solutions that are better equipped to manage contemporary data quantities and formats, file protocols, and security needs are available on iPaaS platforms. Compared to conventional FTP, these technologies provide transfers that are more controlled and secure.
SSH keys for SFTP, SSL/TLS certificates for HTTPS/FTPS, and encryption for both in-transit and at-rest data are all supported by managed file transfers. Managed file transfers further lessen FTP’s high failure rates. Delivery success is increased, visibility is enhanced, automation and scheduling are made possible to satisfy SLAs, interruptions are avoided, and manual labor is decreased.
Machine learning and AI-powered implementations
More intelligent integration automation, such as anomaly detection procedures, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making, may be made possible by integrating AI and machine learning (ML) technology into iPaaS systems. Teams may reduce the amount of human labor needed for intricate integrations by using AI-powered data mapping and transformation.
Improvement of the user experience
With more user-friendly interfaces, more visualization tools, and improved collaboration capabilities, iPaaS’s data, app, and cloud integration features contribute to an improved user experience.
Numerous integration platform as a service(iPaaS) providers, including Oracle, SAP, Microsoft, and IBM, also provide low-code or no-code solutions that enable citizen integrators and non-developers to create, set up, and maintain connections without the need for coding knowledge. Put differently, by giving customers self-service integration capabilities, iPaaS may lessen reliance on IT personnel and speed up integration initiatives.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#IntegrationPlatformAsAService#iPaaS#SaaS#iPaaSsolutions#dataprocessing#dataflows#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#Govindhtech
0 notes
Text
What is Dataflow?
This post is inspired by another post about the Crowd Strike IT disaster and a bunch of people being interested in what I mean by Dataflow. Dataflow is my absolute jam and I'm happy to answer as many questions as you like on it. I even put referential pictures in like I'm writing an article, what fun!
I'll probably split this into multiple parts because it'll be a huge post otherwise but here we go!
A Brief History

Our world is dependent on the flow of data. It exists in almost every aspect of our lives and has done so arguably for hundreds if not thousands of years.
At the end of the day, the flow of data is the flow of knowledge and information. Normally most of us refer to data in the context of computing technology (our phones, PCs, tablets etc) but, if we want to get historical about it, the invention of writing and the invention of the Printing Press were great leaps forward in how we increased the flow of information.
Modern Day IT exists for one reason - To support the flow of data.
Whether it's buying something at a shop, sitting staring at an excel sheet at work, or watching Netflix - All of the technology you interact with is to support the flow of data.
Understanding and managing the flow of data is as important to getting us to where we are right now as when we first learned to control and manage water to provide irrigation for early farming and settlement.
Engineering Rigor
When the majority of us turn on the tap to have a drink or take a shower, we expect water to come out. We trust that the water is clean, and we trust that our homes can receive a steady supply of water.
Most of us trust our central heating (insert boiler joke here) and the plugs/sockets in our homes to provide gas and electricity. The reason we trust all of these flows is because there's been rigorous engineering standards built up over decades and centuries.

For example, Scottish Water will understand every component part that makes up their water pipelines. Those pipes, valves, fitting etc will comply with a national, or in some cases international, standard. These companies have diagrams that clearly map all of this out, mostly because they have to legally but also because it also vital for disaster recovery and other compliance issues.
Modern IT
And this is where modern day IT has problems. I'm not saying that modern day tech is a pile of shit. We all have great phones, our PCs can play good games, but it's one thing to craft well-designed products and another thing entirely to think about they all work together.
Because that is what's happened over the past few decades of IT. Organisations have piled on the latest plug-and-play technology (Software or Hardware) and they've built up complex legacy systems that no one really knows how they all work together. They've lost track of how data flows across their organisation which makes the work of cybersecurity, disaster recovery, compliance and general business transformation teams a nightmare.

Some of these systems are entirely dependent on other systems to operate. But that dependency isn't documented. The vast majority of digital transformation projects fail because they get halfway through and realise they hadn't factored in a system that they thought was nothing but was vital to the organisation running.
And this isn't just for-profit organisations, this is the health services, this is national infrastructure, it's everyone.
There's not yet a single standard that says "This is how organisations should control, manage and govern their flows of data."
Why is that relevant to the companies that were affected by Crowd Strike? Would it have stopped it?
Maybe, maybe not. But considering the global impact, it doesn't look like many organisations were prepared for the possibility of a huge chunk of their IT infrastructure going down.
Understanding dataflows help with the preparation for events like this, so organisations can move to mitigate them, and also the recovery side when they do happen. Organisations need to understand which systems are a priority to get back operational and which can be left.
The problem I'm seeing from a lot of organisations at the moment is that they don't know which systems to recover first, and are losing money and reputation while they fight to get things back online. A lot of them are just winging it.
Conclusion of Part 1
Next time I can totally go into diagramming if any of you are interested in that.
How can any organisation actually map their dataflow and what things need to be considered to do so. It'll come across like common sense, but that's why an actual standard is so desperately needed!
845 notes
·
View notes
Text
very funny watching ppl discover that you can compute associative operations in parallel and acting like it's genius, years after MapReduce
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Challenges of Multi-Cluster Data Flow Management in Apache NiFi | Expert Insights
Explore the key challenges in managing data flows across multiple Apache NiFi clusters. Learn expert strategies for optimizing performance, reliability, and scalability.
0 notes
Text

We’re Hiring: Audiologist
Location: Oman Salary: 350 OMR/Month Free Accommodation + Other Benefits Degree or Diploma in Audiology and 3 years of experience. Dataflow is mandatory
📩 Apply at: [email protected] 📞 +91 85939 85933
🌐 www.mpdservices.co.in
0 notes
Text
Day 4: Ingest and Transform Data in Microsoft Fabric – No-Code and Pro-Code Guide
Ingest and Transform Data in Microsoft Fabric | No-Code and Pro-Code (Day 4) Published: July 5, 2025 🚀 Introduction Now that you’ve created your first Microsoft Fabric workspace, it’s time to bring in some data! In this article, you’ll learn how to ingest data into your Lakehouse or Warehouse and transform it using both no-code (Dataflows Gen2) and pro-code (Notebooks) methods. Whether you’re a…
#ai#azure#cloud#Data transformation#Dataflows Gen2#Fabric ETL#Microsoft Fabric 2025#Microsoft Fabric beginners#Microsoft Fabric data ingestion#Microsoft Fabric tutorial#microsoft-fabric#Power Query Fabric#Real-time Analytics#Spark Notebooks#technology
1 note
·
View note
Text
Getting to play with a quite sizeable dataset at work and I'm very excited
1 note
·
View note
Text
Dataflows end-to-end project (Microsoft Fabric) + Lakehouse + Power BI
10+ hours of FREE Fabric Training: … source
0 notes
Text

🔍 What are Dataflows (Gen 2)? 💬 They are a cloud-based ETL solution designed to create and run scalable data transformation workflows.
📣 Now it’s your turn! How would you define Dataflows Gen 2 in your own words? Drop your answer below 👇
#MicrosoftFabric#Dataflows#ETL#PowerBI#DataEngineering#DataTransformation#CloudData#Gen2#MicrosoftPowerPlatform#DataIntegration
0 notes
Text
If you are a healthcare professional and planning to work abroad in 2025, then it is crucial to understand the dataflow verification process. Whether you’re a doctor, nurse, or allied healthcare worker, understanding the dataflow process for healthcare professionals will save you time, reduce stress, and help you secure your dream role faster. This step-by-step guide breaks down every stage, answers your most searchable questions, and offers practical tips to ensure the dataflow verification process for medical professionals goes smoothly.
Read More: https://elantis.co.in/step-by-step-guide-to-the-dataflow-process-for-healthcare-professionals
1 note
·
View note
Text
Google Cloud Computing Careers in 2024: Trends and Prospects

Cloud Computing Careers
The cloud computing business is predicted to grow rapidly, offering IT experts several Google Cloud Computing Careers opportunities. Despite companies adopting cloud infrastructures, demand for cloud experts is higher than ever. This article highlights 2024’s top cloud computing trends, job openings, and essential skills, certifications, and duties.
Important Developments in Google Cloud Computing Careers
Multi-Cloud/Hybrid Cloud Adoption
Commercial businesses are adopting multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud methods to boost flexibility, decrease risk, and minimize costs. More experts that can manage intricate cloud systems and combine services from many providers are needed as a result of this change.
Pay Attention to Security
Any organisation using cloud services must priorities security due to rising a cyberthreats. Cloud security experts are in demand to protect sensitive data and comply with rules.
The Expansion of Edge Computing
Edge computing is becoming more and more popular. It involves processing data closer to the source rather than in a central data centre. Professionals that install and manage edge computing solutions with proficiency will now have additional responsibilities.
Cloud AI and Machine Learning Growth AI, machine learning, and cloud platforms are changing several industries. For maintaining and creating intelligent apps, cloud experts with ML and AI knowledge are in demand.
Automation together with DevOps
Professionals with infrastructure as code, continuous integration, and continuous deployment skills are in great demand, as automation and DevOps are currently at the heart of every effective cloud operation. Containerization expertise is also in high demand.
Cloud Computing On-Demand Positions
Cloud Solutions Architect
At the request of a single organisation, the cloud solutions architect creates customized cloud solutions while guaranteeing scalability, dependability, and security. Additional prerequisites include proficiency with Google Cloud, Azure, or AWS.
Engineer for Cloud Security
Cloud security experts design safety measures that monitor vulnerabilities and guarantee adherence to industry standards, protecting cloud environments against security breaches.
An engineer for DevOps
With the use of tools like Docker, Kubernetes, and Jenkins for more efficient cloud operations, DevOps engineers close the gap between development and operations teams through process automation, continuous integration, and continuous deployment pipeline management.
Engineer for Cloud Data
Designing, putting into place, and maintaining data processing systems on cloud platforms is the responsibility of cloud data engineers. To ensure prompt data management, they employ ETL, various databases, and big data technologies.
Cloud Engineer AI/ML Cloud Cloud-based machine learning and artificial intelligence models are created and implemented by AI/ML engineers. To create intelligent apps, they make use of technologies like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and cloud-based ML services.
Skills Needed for Google Cloud Computing Careers
Proficiency in Cloud Platforms
Large clouds like Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and Amazon Web Services are crucial. The majority of cloud occupations demand knowledge of their best practices, tools, and services.
Security Proficiency
It is essential to understand the fundamentals of cloud security, IAM, encryption, compliance, etc. AWS Certified Security Specialty and Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) certifications are quite beneficial.
DevOps and Automation Expertise
IaC, containerization, scripting, automation tooling, and IaC are highly desirable. To that end, it is recommended to learn about automation tools, Python, Bash, Terraform, Cloud Formation, Docker, and Kubernetes.
Analysis and Management of Data
Big data technology, data processing, and data storage are necessary for Google Cloud Computing Careers like cloud data engineers and cloud AI/ML engineers.
Database knowledge is crucial: SQL versus NoSQL, pipelines for data.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Exposure to frameworks and methods for machine learning For the cloud AI/ML function, TensorFlow, PyTorch, together with cloud-based ML services like AWS SageMaker, Google AI Platform, would be quite significant.
Top Cloud Computing Certifications for 2024
Associate in Amazon Certified Solutions Architecture
This certification attests to your proficiency in developing and implementing scalable AWS systems. It works well for architects of cloud systems and professionals in general who want to show off their proficiency with AWS.
Expert in Microsoft Azure Solutions Architecture
Because the candidate will have experience planning and executing on Microsoft Azure, it is especially appropriate for individuals who aspire to become outstanding Azure solution architects.
The Professional Cloud Architect from Google
This certification demonstrates your ability to plan, create, and oversee Google Cloud solutions. For individuals that are passionate about GCP specialization, it’s always the best choice.
Professional with Certification in Cloud Security CCSP The CCSP is derived from (ISC)2 and is primarily concerned with cloud security principles and best practices. This implies that it is intended for experts who want to improve their knowledge of cloud security.
Professional DevOps Engineer Certified by AWS
Your proficiency with automation, monitoring, and CI/CD pipeline management on AWS is validated by this certification. For DevOps engineers working in AWS settings, it’s ideal.
Google Cloud Computing Careers many cloud technology jobs. Here are some significant Google Cloud roles:
Cloud engineers develop, manage, and scale high-performance cloud technology. Priorities are IaC, automation, and orchestration.
Experience with Terraform, Kubernetes, Docker, CI/CD pipelines, Python, Go, Java, and GCP.
Cloud architects offer business-specific, scalable, reliable, and inexpensive cloud solutions.
Coordinate cloud plans with stakeholders
Expertise in cloud services, architecture frameworks, microservices, API administration, and problem-solving. Google Cloud Computing Careers Cloud Architect certifications help.
Cloud Developer Duties: Create and manage cloud-based applications. Integrate front-end and back-end components with cloud APIs. Skills: Python, Java, Node.js, cloud-native development, and Google App Engine, Cloud Functions, and Cloud Storage experience.
Data Engineer Design: Data Engineer Design and implement Google Cloud data processing systems. Input, transform, and store analytics and machine learning data. Skills: Data warehousing, ETL, big data tools (Apache Beam, Dataflow, BigQuery), and SQL, Python, or Java programming.
DevOps Engineer Duties: Manage CI/CD pipelines, automate infrastructure provisioning, and optimize deployment on Google Cloud. Knowledge of DevOps, Kubernetes, Jenkins, GitLab, and cloud monitoring and logging tools.
Cloud Security Engineer: Ensure cloud infrastructure and application security. Implement security best practices, analyse risk, and handle events. Skills: Cloud security frameworks, encryption, IAM, network security, and security tools and technologies.
Site dependability Engineer (SRE) Duties: Ensure cloud service dependability, availability, and performance. Set up monitoring, alerting, and incident response. Skills: System administration, Python, Bash scripting, Prometheus, Grafana monitoring, and large-scale distributed system experience.
Cloud Consultant: Provide advice on cloud strategies, migrations, and implementations. Offer best practices and industry standards experience. Communicate well, comprehend cloud services, manage projects, and understand business needs.
Machine Learning Engineer Duties: Create and deploy machine learning models on Google Cloud. Develop scalable AI solutions with data scientists. Python or R expertise, TensorFlow, PyTorch, and cloud ML tools ( AI Platform, AutoML).
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#cloudcomputing#GoogleCloudComputingCareers#cyberthreats#EdgeComputing#cloudsecurity#SensitiveData#edgecomputingsolutions#machinelearning#cloudplatforms#Azure#CloudData#datamanagement#AIML#artificialintelligence#MicrosoftAzure#amazonwebservices#datastorage#devopsengineers#monitoring#DataWarehousing#dataflows#BigQuery#Python#SQL#gitlab#news#TechNews#technology#technologynews#technologytrends
1 note
·
View note
Text
Tumblr’s totally not the place for it but damn I could talk about how to properly map data flow for hours.
Like it’s genuinely exciting non-dystopian digital future stuff when you think how it could help organisations.
It fucking runs circles around businesses crowing about how they’re ’implementing AI’ (they are not).
Would genuinely create a sideblog or something to teach folk but again, tumblr probably not the platform for it.
508 notes
·
View notes