#preposition
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Writing Refresher: Prepositional Meanings
The diagram shows the chief prepositions which express spatial meanings.

Most prepositions can be used in several different ways.
Over, for example, is found in:
the sense of position (The picture was over the door),
movement across (They climbed over the wall),
accompanying circumstances (We’ll talk over dinner),
orientation to the speaker (They live over the road), and
other meanings.
Other types of meaning include:
time (e.g. during the night),
cause (e.g. because of the fog),
method (e.g. with a spoon), and
possession (a pianist of talent).
In addition, there are many figurative uses involving prepositions:
He’s in a hole may literally mean what it says, or it may not (R. Quirk, et al., 1985).
A preposition - expresses a relationship of meaning between two parts of a sentence, most often showing how the two parts are related in space or time:
We sat on the bench.
They left at three.
Most of the common prepositions consist of only one word; they have no distinctive ending, and do not vary.
Several prepositions consist of more than one word.
Single-word prepositions include:
about, at, before, by, down, for, from, in, of, on, out, over, round, since, through, to, under, up, with
Multi-word prepositions include:
(two words) ahead of, because of, due to, instead of, near to; (three words) as far as, by means of, in accordance with, in spite of, on behalf of. The words in these prepositions do not vary freely, as they would in other circumstances. In spite of, for example, cannot change to *out spite of or *in spite for.
Source ⚜ More: Prepositional Phrases ⚜ Writing Basics & Refreshers
#writing refresher#writeblr#studyblr#langblr#writing basics#preposition#dark academia#linguistics#language#words#lit#literature#writing prompt#writers on tumblr#poets on tumblr#light academia#grammar#poetry#writing#writing resources#creative writing#writing reference
199 notes
·
View notes
Text
tawa
noun: movement, motion
adjective: moving
verb: to move; to cause an object to move
preposition: to, towards; for, on behalf of; from the perspective of
Examples:
kiwen ni li tawa! ("That rock is moving!")
sina ale o tawa e sijelo sina! ("All of you, move your body!")
o lukin e soweli tawa. ("Watch the moving animals.")
waso li tawa sewi tawa ma anpa lon tenpo lete. ("Birds fly [lit. 'move high'] south [lit. 'toward the low land'] in winter [lit. 'at the cold time'].")
ni li pona tawa mi. ("It's good to me [alt. 'from my perspective'].")
moku li pona mute tawa uta. ("The food tastes really good [lit. 'is very good to the mouth'].")
sitelen pona:

11 notes
·
View notes
Text
If hippos can run faster than humans on land and swim faster than humans in water, the bicycle is the only chance of beating a hippo in a triathlon.

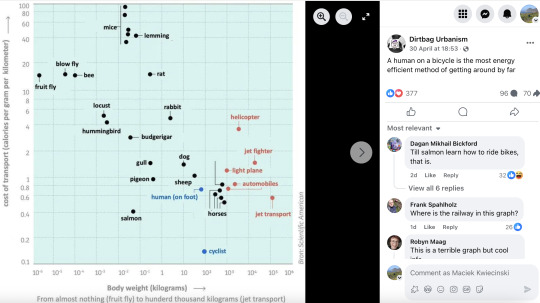

How about a cyclist on an electric bike?
#trolleng#trolledu#trolleng's jokery#joke#jokes#funny#funny jokes for kids#jokes for kids#efl#gerund#gerunds#prepositions#preposition#collocation#collocations#beat somebody in / at something#0 conditional#conditionals#zero conditional#zero conditionals#0 conditionals#cycling#bikes#bike riding#biking#bike#bicycle#biking hacks
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The Visitor"


Quotation marks gone. Got to clarify that Archie is not name checking a Michael Jackson song.

Veronica was Sleeping over AT Betty's often, NOT "Over" Betty. And Reggie no longer has the pet name "Ol' Baby" for Archie.
#Archie Comics#Archie Andrews#Reggie Mantle#Jughead#Gaston#Beat It#Punctuation#Quotation marks#Crunch#Smithers#Chase#Glow#Stan Goldberg#1974#Preposition#Dash
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
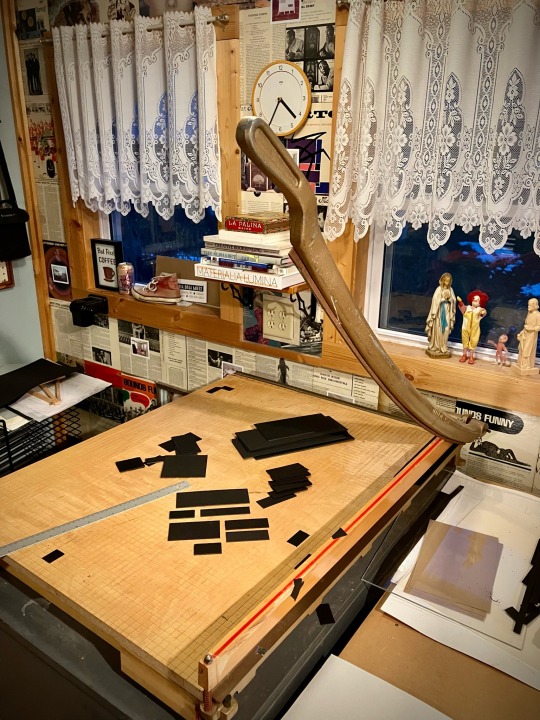




30 Dec 2023, 16:35 | Der Klubhaus
Understanding This Book post-production work: using the beloved 30” paper cutter found on Craigslist for $40 in Sparta, Wisconsin, something like eight years ago to cut down scrap mat board to line the empty California job case belonging to the formerly filthy and disorganized 10 pt Franklin Gothic Italic.
This is what dreams are made of. I generally don’t like ending sentences with a preposition but it feels okay this time.
#utb#letterpress#california job case#metal type#heavy duty#heavydutypress#franklin gothic#understanding#organizing#organizing a mess#Klubhaus#preposition#grammar#dream#dreams
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Preposition Exercise with Answers
Introduction to Prepositions
Prepositions are a fundamental part of English grammar, often small in size but significant in function. They help indicate relationships between other words in a sentence, especially in terms of time, place, direction, and manner. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various types of prepositions, provide examples and exercises, and offer answers to help reinforce your understanding. By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid grasp of prepositions and how to use them correctly.
What Are Prepositions?
Prepositions are words that link nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other words within a sentence. They are typically short words like "in," "at," "on," "by," "with," and "about." A preposition usually indicates the temporal, spatial, or logical relationship of its object to the rest of the sentence.
Importance of Prepositions in English Grammar
Prepositions are essential for conveying the exact meaning of sentences. They can affect the meaning of a sentence entirely, sometimes leading to confusion if used incorrectly. For example, "He is in the house" and "He is on the house" have completely different meanings, with the former indicating that someone is inside and the latter suggesting someone is on the roof.
Common Mistakes When Using Prepositions
One of the most common errors in English grammar is the incorrect use of prepositions. These mistakes can occur due to differences between languages or misunderstanding of preposition rules. For instance, English learners often struggle with choosing the correct preposition for time or place, such as "in" vs. "on" or "at" vs. "in."
Types of Prepositions
Prepositions can be categorized based on their function in a sentence. Understanding these categories will help you use them more effectively.
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time indicate when something happens. Common prepositions of time include "at," "on," "in," and "during."
Examples and Usage
At: Used for precise times (e.g., "at 3 PM").
On: Used for days and dates (e.g., "on Monday," "on the 5th of July").
In: Used for months, years, centuries, and long periods (e.g., "in January," "in 2021").
During: Used for periods or events (e.g., "during the meeting").
Exercises on Prepositions of Time
We will meet ___ 6 PM. (at/on/in)
She was born ___ 1990. (at/on/in)
The concert is ___ Monday. (at/on/in)
He studied ___ the night. (at/on/during)
Prepositions of Place
Prepositions of place indicate where something is located. Common prepositions of place include "in," "on," "at," "above," "below," and "between."
Examples and Usage
In: Used for enclosed spaces (e.g., "in the room").
On: Used for surfaces (e.g., "on the table").
At: Used for specific points (e.g., "at the door").
Above: Higher than a point (e.g., "above the clouds").
Below: Lower than a point (e.g., "below sea level").
Exercises on Prepositions of Place
The keys are ___ the table. (on/in/at)
She is sitting ___ the front row. (in/on/at)
The painting is hanging ___ the fireplace. (above/below/in)
The cat is hiding ___ the bed. (in/under/on)
Prepositions of Direction
Prepositions of direction show the movement towards or away from something. Common prepositions of direction include "to," "from," "into," and "out of."
Examples and Usage
To: Indicates movement towards a specific location (e.g., "She walked to the park").
From: Indicates the starting point of movement (e.g., "He came from the office").
Into: Indicates movement into an enclosed space (e.g., "He went into the room").
Out of: Indicates movement out of an enclosed space (e.g., "She walked out of the house").
Exercises on Prepositions of Direction
He is going ___ the store. (to/from/into)
She came ___ the kitchen. (to/from/out of)
They ran ___ the house. (to/into/out of)
He jumped ___ the pool. (to/into/from)
Prepositions of Manner
Prepositions of manner describe how something happens or is done. Common prepositions of manner include "by," "with," and "like."
Examples and Usage
By: Indicates the method or means (e.g., "She travels by car").
With: Indicates the tool or instrument used (e.g., "He wrote with a pen").
Like: Indicates similarity (e.g., "She sings like an angel").
Exercises on Prepositions of Manner
She solved the puzzle ___ herself. (by/with/like)
He cut the paper ___ scissors. (by/with/like)
They danced ___ grace. (by/with/like)
She painted the picture ___ a brush. (by/with/like)
Prepositions of Agent or Instrument
These prepositions indicate who performed an action or the tool used in performing the action. Examples include "by" and "with."
Examples and Usage
By: Indicates the doer of the action (e.g., "The book was written by J.K. Rowling").
With: Indicates the instrument used (e.g., "The door was opened with a key").
Exercises on Prepositions of Agent or Instrument
The song was sung ___ the choir. (by/with/from)
The cake was baked ___ my grandmother. (by/with/from)
The problem was solved ___ a calculator. (by/with/from)
The letter was delivered ___ the postman. (by/with/from)
Complex Prepositions
Complex prepositions are phrases formed by two or more words that function as a single preposition. Examples include "because of," "in spite of," "on behalf of."
Examples and Usage
Because of: Indicates a reason (e.g., "The game was canceled because of the rain").
In spite of: Indicates contrast (e.g., "In spite of the delay, the project was completed").
On behalf of: Indicates representation (e.g., "She accepted the award on behalf of the team").
Exercises on Complex Prepositions
The event was postponed ___ bad weather. (because of/in spite of/on behalf of)
He spoke ___ his company. (because of/in spite of/on behalf of)
She attended the meeting ___ her illness. (because of/in spite of/on behalf of)
They succeeded ___ the obstacles. (because of/in spite of/on behalf of)
Preposition Exercises
Fill in the Blanks
Complete the following sentences by filling in the blanks with the correct prepositions.
She lives ___ Paris. (at/in/on)
The cat jumped ___ the window. (through/over/into)
He will arrive ___ 10 AM. (at/in/on)
They went ___ a walk. (for/on/in)
Match the Preposition with the Correct Sentence
Match the following prepositions with the correct sentences:
With
She wrote the letter ___ a pen.
At
He is ___ the door.
In
The book is ___ the bag.
On
The vase is ___ the table.
Correct the Sentences
Correct the following sentences by using the appropriate prepositions.
She is waiting at the bus stop. (correct)
The keys are in the table. (correction: on the table)
They arrived on the airport. (correction: at the airport)
He jumped on the pool. (correction: into the pool)
Choose the Correct Preposition
Choose the correct preposition from the options given in brackets.
She is good ___ playing the piano. (in/at/on)
They are interested ___ learning French. (in/on/at)
The picture hangs ___ the wall. (on/in/at)
We arrived ___ the station early. (at/in/on)
Sentence Completion
Complete the following sentences with appropriate prepositions.
She is fond ___ chocolates. (of/in/at)
They are proud ___ their achievements. (of/in/on)
He is responsible ___ the project. (for/of/at)
She succeeded ___ her efforts. (with/in/on)
Answers to Preposition Exercises
Fill in the Blanks - Answers
She lives in Paris.
The cat jumped through the window.
He will arrive at 10 AM.
They went for a walk.
Match the Preposition with the Correct Sentence - Answers
With: She wrote the letter with a pen.
At: He is at the door.
In: The book is in the bag.
On: The vase is on the table.
Correct the Sentences - Answers
She is waiting at the bus stop. (correct)
The keys are on the table.
They arrived at the airport.
He jumped into the pool.
Choose the Correct Preposition - Answers
She is good at playing the piano.
They are interested in learning French.
The picture hangs on the wall.
We arrived at the station early.
Sentence Completion - Answers
She is fond of chocolates.
They are proud of their achievements.
He is responsible for the project.
She succeeded in her efforts.
Read our Article
Commonly Confused Prepositions
In vs. On
In: Used for enclosed spaces or periods of time (e.g., "in the room," "in January").
On: Used for surfaces or specific days/dates (e.g., "on the table," "on Monday").
At vs. In
At: Used for specific points or locations (e.g., "at the door," "at the office").
In: Used for larger areas or enclosed spaces (e.g., "in the city," "in the room").
By vs. With
By: Used to indicate the doer of an action or the method (e.g., "by the author," "by car").
With: Used to indicate the tool used or accompaniment (e.g., "with a pen," "with friends").
Tips for Mastering Prepositions
Practice Regularly
Consistent practice is key to mastering prepositions. Engage in daily exercises, and try using new prepositions in your writing and speech.
Use in Real-Life Situations
Incorporate prepositions into your everyday conversations. This will help reinforce your understanding and improve your fluency.
Learn Through Context
Understanding prepositions within context can make it easier to grasp their usage. Read books, watch movies, or listen to podcasts that use English extensively to see how prepositions are used naturally.
Conclusion
Prepositions may be small, but they play a big role in English grammar. Understanding how to use them correctly can greatly improve your writing and communication skills. Mastering prepositions is essential for clear and accurate communication in English. The Preposition Exercise with Answers provided here serves as a valuable tool for reinforcing your understanding of prepositional usage. By regularly practicing these exercises and reviewing the answers, you can improve your grammatical skills and enhance your proficiency in the language. Remember, consistent practice is key to mastering prepositions and using them effectively in both written and spoken English. Keep honing your skills with exercises and watch your confidence grow!
FAQs
What are the most common prepositions?
Common prepositions include "in," "on," "at," "by," "with," "to," "from," and "about."
How can I avoid mistakes with prepositions?
Regular practice, paying attention to context, and learning the rules for specific prepositions can help you avoid mistakes.
Why are prepositions important in English?
Prepositions are essential for conveying clear and accurate meanings in sentences. They indicate relationships between words and are crucial for fluent communication.
How can I practice prepositions effectively?
Engage in exercises, use them in daily conversations, and immerse yourself in English through reading and listening to improve your preposition usage.
What are some tricky prepositions to watch out for?
Prepositions like "in," "on," "at," and "by" can be tricky due to their various uses. Understanding their specific rules and contexts is key to using them correctly.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Master Prepositions: Exercises and Answers for Fluent English Usage
Introduction to Prepositions
In the realm of English grammar, prepositions play a crucial role in connecting words and phrases, thereby indicating relationships such as time, place, direction, and more. Mastering prepositions is not just about memorization but understanding their contextual usage. This comprehensive guide aims to equip learners with practical exercises and answers to enhance their proficiency in using prepositions effectively.
Understanding Prepositions
What Are Prepositions?
Prepositions are words that link nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other words within a sentence. They provide crucial information about the relationship between elements in context.
Types of Prepositions
1. Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions are single words like in, on, at, to, by, for, with, and about.
2. Compound Prepositions
Compound prepositions consist of two or more words, functioning as a single unit to denote relationships. Examples include because of, in front of, and in spite of.
3. Phrase Prepositions
Phrase prepositions are groups of words that function as single prepositions, such as in addition to, on behalf of, and according to.
4. Participle Prepositions
Participle prepositions end in -ing and often describe how something happens or is done, like during, concerning, and excluding.
Usage of Prepositions
Time
Prepositions such as at, on, in, and during indicate when something happens. For instance, "She arrived at noon."
Place
Prepositions like in, on, at, and under specify where something is located. For example, "The book is on the shelf."
Direction
Prepositions of direction like to, towards, into, and through denote movement towards or away from a place. E.g., "He walked to the park."
Agent/Instrument
Prepositions such as by and with describe how something is done or the means used. For example, "The letter was written by John."
Common Errors with Prepositions
Understanding and avoiding common mistakes is crucial for mastering prepositions:
Misplacement: Incorrect use of prepositions can lead to misunderstandings, such as saying "interested for" instead of "interested in".
Overuse: Using prepositions unnecessarily can clutter sentences and confuse the reader.
Incorrect Choice: Choosing the wrong preposition can alter the meaning of a sentence, e.g., using "on" instead of "at" in time-related contexts.
Preposition Exercises with Answers
Exercise 1: Fill in the Blanks
She is sitting _ the chair.
The cat is hiding _ the bed.
Answers:
on
under
Exercise 2: Multiple Choice Questions
She is going _ the store.
a) to
b) in
c) on
The keys are _ the table.
a) in
b) on
c) at
Answers:
a) to
b) on
Exercise 3: Match the Prepositions
Match the following phrases with suitable prepositions:
_ the morning
_ the car
Answers:
in
in
Advanced Usage and Tips
Idiomatic Expressions
Idiomatic expressions involving prepositions add depth and nuance to language. Examples include at a loss, in the nick of time, and on the verge of.
Phrasal Verbs
Understanding phrasal verbs, which combine verbs with prepositions or adverbs, enhances fluency. Examples include look up to, break down, and run out of.
Tips for Improving Preposition Usage
Read Regularly: Expose yourself to varied texts to observe prepositions in context.
Practice Daily: Incorporate preposition exercises into your daily study routine.
Use Visual Aids: Create flashcards or diagrams to reinforce preposition usage.
Enhance your grammar skills with our Preposition Exercise with Answers for Students. These exercises are designed to help students understand and use prepositions correctly through practical examples and fill-in-the-blank sentences. With included answers, students can easily check their work and focus on areas needing improvement. This resource is perfect for both classroom learning and self-study, making mastering prepositions easy and effective.
Conclusion
Mastering prepositions is pivotal for achieving fluency and accuracy in English. By familiarizing yourself with their types, usages, and common errors, you can navigate language more effectively. Practicing with exercises and understanding nuanced applications will further strengthen your command of prepositions.
Check our other Blogs :-
Master Prepositions: Exercises with Answers for Students
Boost Learning with Engaging GK Questions in Morning Assemblies
Effective Preposition Exercises for Students: Practice with Answers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
lon
noun: truth; life, existence
adjective: real, present; true
verb: is, exists
preposition: is in/at/on [something]; during, in the context of [something]
Examples:
lon a! ("Yes!")
waso li lon. ("There is a bird.")
lon mi li ike mute. ("My life is so bad.")
lon li seme? ("What is life [alt. 'the truth']?")
mi wile e moku lon. ("I want real food.")
jan sitelen li sitelen lon lipu. ("The author [lit. 'text person'] writes on the page.")
soweli pimeja li olin e lape lon tenpo lete. ("The black bear [lit. 'animal'] likes to sleep during winter [lit. 'the cold time'].")
sitelen pona:

6 notes
·
View notes
Text


#birds#bird#duck#ducks#trolleng#trolledu#gerund#prepositions#preposition#gerunds#gerund and prepositions#prepositions activate gerunds
9 notes
·
View notes
Photo

#trolleng#trolledu#speaking#reading#gerund#the gerund#preposition#adverb#prepositions activate gerunds
286K notes
·
View notes
Text
"The Head of the Class"

Moving the question mark to at least partially fill the conspicuously empty word balloon bottom.

Uh-- what Reggie?
Mamsy. Pamsy. I am more familiar with namby, mamby, and pamby.
Namby-pamby [...] originates from the poem Namby Pamby (1725) by Henry Carey. Carey wrote his poem as a satire of Ambrose Philips and published it in his Poems on Several Occasions. Its first publication was Namby Pamby: or, a panegyrick on the new versification address'd to A----- P----, where the A-- P-- implicated Ambrose Philips. Philips had written a series of odes in a new prosody of seven-syllable catalectic trochaic tetrameter and dedicated it to "all ages and characters, from Walpole steerer of the realm, to Miss Pulteney in the nursery." Though once used by Shakespeare in A Midsummer Night's Dream, this 3.5' line became a matter of consternation for more conservative poets, and a matter of mirth for Carey. Carey adopts Philips's choppy line-form for his parody and latches onto the dedication to nurseries to create an apparent nursery rhyme that is, in fact, a grand bit of nonsense and satire mixed.

To. For.

Ivorys. Ivories.

Found some new commas to use.
#Archie Comics#Reggie Mantle#Jughead#Betty Cooper#Veronica Lodge#Mamsy Pamsy#Pie#Pizza#Comma#Punctuation#Spelling#Al Hartley#1969#Word balloon#Preposition#Etymology#Namby-pamby
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
chutœle imoligen day 74:
nede /nɛd/
preposition: over
etymology: from nêtte (above)
0 notes
Text

Golden stars of the Milky Way. Die Milchstrasse. 1908. Cover detail.
Internet Archive
10K notes
·
View notes
