#relational data model
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Discover how Database sharding can transform your application's performance by distributing data across multiple servers in our latest blog. With insights into key sharding techniques, you'll further learn how to implement sharding effectively and avoid common pitfalls.
As you move forward, this blog will help you dive into real-life use cases to understand how sharding can optimize data management. Lastly, you'll get the most important factors to consider before sharding your database and learning to navigate the complexities of database management.
#database sharding#what is sharding database#sharded database#data sharding#data base#big data#data modeling#dataset management#data architecture#relational database management#Software development company#Nitor Infotech#ascendion#Software development
0 notes
Text
i'm at the point in my job search where i'm applying for jobs i am definitely overqualified for lmao
#i'm applying for data analyst roles which are generally considered one step “below” being a data scientist#not “below” as in less valuable but in that as a data scientist i pretty much have all the skills data analysts have#most data analysts don't do much modeling and focus more on like. dashboards and excel spreadsheets#which i also did as a data scientist but it was secondary to modeling & i had to ~*~ delegate ~*~ that to data analysts sometimes#there are some senior-level data analyst roles that pay about what i was just making. some a little more even! so yolo#i do not care. i'm not a Career Woman™ i am a woman who only has a career so she can make money to pay for her hobbies#ANYWAY do not yell at me for being on tumblr bc i finished my resume and sent out EIGHT applications!!!!#i'm taking a well deserved break before i go back & finish all the applications that require a cover letter/related info#'why do you want to work at this company?!?!' because i am unemployed and you are seeking to employ people bitch get over urself#m.txt
1 note
·
View note
Text






I spent the evening looking into this AI shit and made a wee informative post of the information I found and thought all artists would be interested and maybe help yall?
edit: forgot to mention Glaze and Nightshade to alter/disrupt AI from taking your work into their machines. You can use these and post and it will apparently mess up the AI and it wont take your content into it's machine!
edit: ArtStation is not AI free! So make sure to read that when signing up if you do! (this post is also on twt)
[Image descriptions: A series of infographics titled: “Opt Out AI: [Social Media] and what I found.” The title image shows a drawing of a person holding up a stack of papers where the first says, ‘Terms of Service’ and the rest have logos for various social media sites and are falling onto the floor. Long transcriptions follow.
Instagram/Meta (I have to assume Facebook).
Hard for all users to locate the “opt out” options. The option has been known to move locations.
You have to click the opt out link to submit a request to opt out of the AI scraping. *You have to submit screenshots of your work/face/content you posted to the app, is curretnly being used in AI. If you do not have this, they will deny you.
Users are saying after being rejected, are being “meta blocked”
People’s requests are being accepted but they still have doubts that their content won’t be taken anyways.
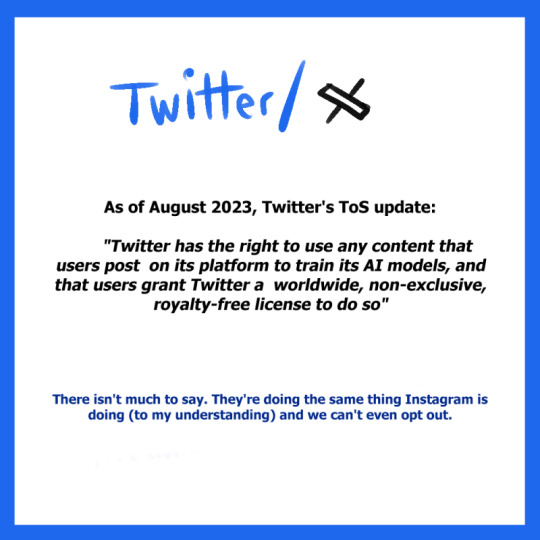
Twitter/X
As of August 2023, Twitter’s ToS update:
“Twitter has the right to use any content that users post on its platform to train its AI models, and that users grant Twitter a worldwide, non-exclusive, royalty-free license to do so.”
There isn’t much to say. They’re doing the same thing Instagram is doing (to my understanding) and we can’t even opt out.
Tumblr
They also take your data and content and sell it to AI models.
But you’re in luck!
It is very simply to opt out (Wow. Thank Gods)
Opt out on Desktop: click on your blog > blog settings > scroll til you see visibility options and it’ll be the last option to toggle
Out out of Mobile: click your blog > scroll then click visibility > toggle opt out option
TikTok
I took time skim their ToS and under “How We Use Your Information” and towards the end of the long list: “To train and improve our technology, such as our machine learning models and algorithms.”
Regarding data collected; they will only not sell your data when “where restricted by applicable law”. That is not many countries. You can refuse/disable some cookies by going into settings > ads > turn off targeted ads.
I couldn’t find much in AI besides “our machine learning models” which I think is the same thing.
What to do?
In this age of the internet, it’s scary! But you have options and can pick which are best for you!
Accepting these platforms collection of not only your artwork, but your face! And not only your faces but the faces of those in your photos. Your friends and family. Some of those family members are children! Some of those faces are minors! I shudder to think what darker purposes those faces could be used for.
Opt out where you can! Be mindful and know the content you are posting is at risk of being loaded to AI if unable to opt out.
Fully delete (not archive) your content/accounts with these platforms. I know it takes up to 90 days for instagram to “delete” your information. And even keep it for “legal” purposes like legal prevention.
Use lesser known social media platforms! Some examples are; Signal, Mastodon, Diaspora, et. As well as art platforms: Artfol, Cara, ArtStation, etc.
The last drawing shows the same person as the title saying, ‘I am, by no means, a ToS autistic! So feel free to share any relatable information to these topics via reply or qrt!
I just wanted to share the information I found while searching for my own answers cause I’m sure people have the same questions as me.’ \End description] (thank you @a-captions-blog!)
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
There is no such thing as AI.
How to help the non technical and less online people in your life navigate the latest techbro grift.
I've seen other people say stuff to this effect but it's worth reiterating. Today in class, my professor was talking about a news article where a celebrity's likeness was used in an ai image without their permission. Then she mentioned a guest lecture about how AI is going to help finance professionals. Then I pointed out, those two things aren't really related.
The term AI is being used to obfuscate details about multiple semi-related technologies.
Traditionally in sci-fi, AI means artificial general intelligence like Data from star trek, or the terminator. This, I shouldn't need to say, doesn't exist. Techbros use the term AI to trick investors into funding their projects. It's largely a grift.
What is the term AI being used to obfuscate?
If you want to help the less online and less tech literate people in your life navigate the hype around AI, the best way to do it is to encourage them to change their language around AI topics.
By calling these technologies what they really are, and encouraging the people around us to know the real names, we can help lift the veil, kill the hype, and keep people safe from scams. Here are some starting points, which I am just pulling from Wikipedia. I'd highly encourage you to do your own research.
Machine learning (ML): is an umbrella term for solving problems for which development of algorithms by human programmers would be cost-prohibitive, and instead the problems are solved by helping machines "discover" their "own" algorithms, without needing to be explicitly told what to do by any human-developed algorithms. (This is the basis of most technologically people call AI)
Language model: (LM or LLM) is a probabilistic model of a natural language that can generate probabilities of a series of words, based on text corpora in one or multiple languages it was trained on. (This would be your ChatGPT.)
Generative adversarial network (GAN): is a class of machine learning framework and a prominent framework for approaching generative AI. In a GAN, two neural networks contest with each other in the form of a zero-sum game, where one agent's gain is another agent's loss. (This is the source of some AI images and deepfakes.)
Diffusion Models: Models that generate the probability distribution of a given dataset. In image generation, a neural network is trained to denoise images with added gaussian noise by learning to remove the noise. After the training is complete, it can then be used for image generation by starting with a random noise image and denoise that. (This is the more common technology behind AI images, including Dall-E and Stable Diffusion. I added this one to the post after as it was brought to my attention it is now more common than GANs.)
I know these terms are more technical, but they are also more accurate, and they can easily be explained in a way non-technical people can understand. The grifters are using language to give this technology its power, so we can use language to take it's power away and let people see it for what it really is.
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
Many billionaires in tech bros warn about the dangerous of AI. It's pretty obviously not because of any legitimate concern that AI will take over. But why do they keep saying stuff like this then? Why do we keep on having this still fear of some kind of singularity style event that leads to machine takeover?
The possibility of a self-sufficient AI taking over in our lifetimes is... Basically nothing, if I'm being honest. I'm not an expert by any means, I've used ai powered tools in my biology research, and I'm somewhat familiar with both the limits and possibility of what current models have to offer.
I'm starting to think that the reason why billionaires in particular try to prop this fear up is because it distracts from the actual danger of ai: the fact that billionaires and tech mega corporations have access to data, processing power, and proprietary algorithms to manipulate information on mass and control the flow of human behavior. To an extent, AI models are a black box. But the companies making them still have control over what inputs they receive for training and analysis, what kind of outputs they generate, and what they have access to. They're still code. Just some of the logic is built on statistics from large datasets instead of being manually coded.
The more billionaires make AI fear seem like a science fiction concept related to conciousness, the more they can absolve themselves in the eyes of public from this. The sheer scale of the large model statistics they're using, as well as the scope of surveillance that led to this point, are plain to see, and I think that the companies responsible are trying to play a big distraction game.
Hell, we can see this in the very use of the term artificial intelligence. Obviously, what we call artificial intelligence is nothing like science fiction style AI. Terms like large statistics, large models, and hell, even just machine learning are far less hyperbolic about what these models are actually doing.
I don't know if your average Middle class tech bro is actively perpetuating this same thing consciously, but I think the reason why it's such an attractive idea for them is because it subtly inflates their ego. By treating AI as a mystical act of the creation, as trending towards sapience or consciousness, if modern AI is just the infant form of something grand, they get to feel more important about their role in the course of society. Admitting the actual use and the actual power of current artificial intelligence means admitting to themselves that they have been a tool of mega corporations and billionaires, and that they are not actually a major player in human evolution. None of us are, but it's tech bro arrogance that insists they must be.
Do most tech bros think this way? Not really. Most are just complict neolibs that don't think too hard about the consequences of their actions. But for the subset that do actually think this way, this arrogance is pretty core to their thinking.
Obviously this isn't really something I can prove, this is just my suspicion from interacting with a fair number of techbros and people outside of CS alike.
449 notes
·
View notes
Text
Taxes & Benefits Mod + New Active Career - DOWNLOAD
One of my sims was earning a little too much money and somehow this spiralled into me developing this mod. Introducing a very configurable tax and benefit system alongside an all new active career!


The tax and benefit system is modelled after the system we have here in England. All tax and benefit options are configurable and sims will only be opted in if you want them to. See the included documentation for a proper feature breakdown.
There are three types of taxes:
Council Tax (a property tax)
Business Tax
National Insurance (an income tax)
Register sims for each type of tax through the city hall.

There are four types of benefits:
Universal Credit
Housing Benefit
Child Benefit
Job Seekers Allowance
Register sims online, through social interactions with the all new Civil Servant, or at a HSRC communications booth.
Civil Service Career
Work for the HSRC in this fully functional active career.

There are 36 jobs which can be completed: 27 are custom career opportunities (like in the private eye career), 9 of them are custom active jobs (like in the interior decorator or firefighter career).
Jobs include: checking benefit eligibility for sims around town, attending job fairs, auditing, community outreach, responding to council house repair requests, and things of that nature.

Communication Booth
Civil Servants are given communication booths which can be placed anywhere in the world. This object has 2 geostates and can be set up or packed down when not needed.

Council Houses
Properties that are not owned by a sim are council houses. There are some unique interactions for these homes. For one, they can be more susceptible to pests (if enabled in the tuning, that is).
Complain to the Council
Depending on the type of property the sim lives in, they can complain to the council about housing issues such as overcrowding, broken facilities, or vermin.

Social Interactions
There are 12 new social interactions found under Friendly, Funny and Mean.
Help Understand Welfare System – Civil Servant Only
Complain About Taxes
Accuse of Benefit Fraud
Suggest Part Time Job – Civil Servant Only
Joke About Fraud
Talk About Benefits
Talk About Career History
Hand Out HSRC Leaflet – Civil Servant Only
Warn About Fraudulent Behaviour – Civil Servant Only
Offer Council House Repairs – Civil Servant Only
Including 2 autonomous only interactions:
Talk About Shared Career History
Talk About Shared Benefit Claims
Some interactions are only visible after doing things such as paying taxes. Some interactions are specific to the Civil Service career.

Required
Ambitions EP
University EP
Optional
Seasons EP – adds tax refunds, tax fluctuations and council house scenarios
Showtime EP – adds extra interaction to communications booth
World Adventures EP- adds extra active job
My Boutique Mod, Hairdressing Mod, Go to Court Mod – adds extra work opportunities
My social clubs mod – adds extra work opportunity and some optional integration with Bronzo banking
My functional printer mod – makes use of buff
Olomaya Smoking & Private Clinic (optometry module) mod - illness buffs taken into account with trying to claim some benefits.
Uninstallation
You can use cheat ‘uninstallTaxesBenefits’ in order to remove all mod related objects and data before uninstalling.
Download: Simblr.cc - Taxes & Benefits Mod
If you would like to donate as thanks, please feel free to do so at my ko-fi! :)
ps modders: this code for this mod is up on GitHub, plus a WIP active career tutorial (emphasis on the WIP but I hope it's helpful). Link included on the last page of the documentation.
Please enjoy all!
~ Phoebe <3
339 notes
·
View notes
Text
Oh my god. Okay. Technology rant incoming.
So I sell beds. I get deals on stuff like mattresses and adjustable bases. The adjustable vibrates which helps me fall asleep and tips the head and feet up for comfort. I got us a Tempurpedic Ergo Smart Base for the new king size bed. I have an eight year old Ergo Premier that’s in the guest room now and has never had any problems. It is far and away better than the current model we just got.
The new one has a bunch of features like monitoring your sleeping and we’re told to pitch the app that comes with it. Now my beef is we tell customers that they can use their phone as the remote if they want. But the only way to do that is to get the app and agree to let Tempurpedic have all your data, much of which relate to medical conditions? Hated that.
But then I started snoring. And one of the features that’s only on the app is an automatic response to snoring. It’ll vibrate you to have you turn over or elevate the bed more. For my beloved wife I wanted to activate the snore response. So I joined the fucking app. It requires your height and weight. I told it I was seven feet tall and weighed one pound cause fuck their data.
Then I set up the app. It requires an internet connection. Because I don’t want that fucker beaconing my data that I was forced to sign up for I tethered my phone and had it connect to that. Once setup was done I disconnected it.
It ceases to function without WiFi. A basic thing that is programmed in the base itself will not activate without WiFi. I’m fuming. Tried to hook it up to actual WiFi and this fucking thing won’t connect to the non-hotspot WiFi at all. Their help page just talks about getting a better router.
Livid doesn’t come close to covering my feelings about this shit. I’m emailing support but I am gonna fully stop recommending their product on this basis.
520 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Starting this month [June 2024], thousands of young people will begin doing climate-related work around the West as part of a new service-based federal jobs program, the American Climate Corps, or ACC. The jobs they do will vary, from wildland firefighters and “lawn busters” to urban farm fellows and traditional ecological knowledge stewards. Some will work on food security or energy conservation in cities, while others will tackle invasive species and stream restoration on public land.
The Climate Corps was modeled on Franklin D. Roosevelt’s Civilian Conservation Corps, with the goal of eventually creating tens of thousands of jobs while simultaneously addressing the impacts of climate change.
Applications were released on Earth Day, and Maggie Thomas, President Joe Biden’s special assistant on climate, told High Country News that the program’s website has already had hundreds of thousands of views. Since its launch, nearly 250 jobs across the West have been posted, accounting for more than half of all the listed ACC positions.
“Obviously, the West is facing tremendous impacts of climate change,” Thomas said. “It’s changing faster than many other parts of the country. If you look at wildfire, if you look at extreme heat, there are so many impacts. I think that there’s a huge role for the American Climate Corps to be tackling those crises.”
Most of the current positions are staffed through state or nonprofit entities, such as the Montana Conservation Corps or Great Basin Institute, many of which work in partnership with federal agencies that manage public lands across the West. In New Mexico, for example, members of Conservation Legacy’s Ecological Monitoring Crew will help the Bureau of Land Management collect soil and vegetation data. In Oregon, young people will join the U.S. Department of Agriculture, working in firefighting, fuel reduction and timber management in national forests.
New jobs are being added regularly. Deadlines for summer positions have largely passed, but new postings for hundreds more positions are due later this year or on a rolling basis, such as the Working Lands Program, which is focused on “climate-smart agriculture.” ...
On the ACC website, applicants can sort jobs by state, work environment and focus area, such as “Indigenous knowledge reclamation” or “food waste reduction.” Job descriptions include an hourly pay equivalent — some corps jobs pay weekly or term-based stipends instead of an hourly wage — and benefits. The site is fairly user-friendly, in part owing to suggestions made by the young people who participated in the ACC listening sessions earlier this year...
The sessions helped determine other priorities as well, Thomas said, including creating good-paying jobs that could lead to long-term careers, as well as alignment with the president’s Justice40 initiative, which mandates that at least 40% of federal climate funds must go to marginalized communities that are disproportionately impacted by climate change and pollution.
High Country News found that 30% of jobs listed across the West have explicit justice and equity language, from affordable housing in low-income communities to Indigenous knowledge and cultural reclamation for Native youth...
While the administration aims for all positions to pay at least $15 an hour, the lowest-paid position in the West is currently listed at $11 an hour. Benefits also vary widely, though most include an education benefit, and, in some cases, health care, child care and housing.
All corps members will have access to pre-apprenticeship curriculum through the North America’s Building Trades Union. Matthew Mayers, director of the Green Workers Alliance, called this an important step for young people who want to pursue union jobs in renewable energy. Some members will also be eligible for the federal pathways program, which was recently expanded to increase opportunities for permanent positions in the federal government...
“To think that there will be young people in every community across the country working on climate solutions and really being equipped with the tools they need to succeed in the workforce of the future,” Thomas said, “to me, that is going to be an incredible thing to see.”"
-via High Country News, June 6, 2024
--
Note: You can browse Climate Corps job postings here, on the Climate Corps website. There are currently 314 jobs posted at time of writing!
Also, it says the goal is to pay at least $15 an hour for all jobs (not 100% meeting that goal rn), but lots of postings pay higher than that, including some over $20/hour!!
#climate corps#climate change#climate activism#climate action#united states#us politics#biden#biden administration#democratic party#environment#environmental news#climate resilience#climate crisis#environmentalism#climate solutions#jobbs#climate news#job search#employment#americorps#good news#hope
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
since Stalkers old lair is abandoned, and Hunhow is ls close enough to look in the window, do you think its possible to give him a tv or something? or a game system?
Anon your brain is immense and deeply wrinkled.

Also, about that game Amir was working on...

I bet the drifter makes it a point to bring hunhow new games whenever he can, only to find that hunhow, the sentient machine who can exist in the weave and turn himself into code, has already started making his own. He still plays the ones the drifter brings him anyway, though.
Transcript below
D- "Hey Amir, can I have your help with something? Its game related."
A- "Sure, whats up?"
D- "Gist is this. Say you've got a sentient world terraforming space machine who helped you out a lot, but is on his own for most of the time. What game console and-slash-or games do you think he'd like?"
D- "Its a serious question! Don't look at me like that!"
Box text reads- "Hunhow and the Acolytes enjoyed Mario Cart 64 the best. Models/data were obviously edited"
Then, in the second one,
D- "So Hunhow had a couple of playtesting notes. Said he liked it a lot."
A- "Just a couple, huh..."
#warframe#warframe drifter#warframe 1999#warframe amir#hunhow#The acolytes have literally appeared nowhere but steel path#i dont know if they're even canon anymore#like#they show up#yes#but they dont have any appearance anywhere in any quest line that they should#so my real hot take is that they're actually still keeping hunhow company#and the steel path thing is something hunhow's set up to keep us on our toes#homework#if you will#we say#'come test us#we're ready#we're strong'#and hunhow goes#ait#those mfers pushed the beacon#go get em
261 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved on our archive
By Bill Shaw
A new study in eClinicalMedicine has found that healthy volunteers infected with SARS-CoV-2 had measurably worse cognitive function for up to a year after infection when compared to uninfected controls. Significantly, infected controls did not report any symptoms related to these cognitive deficits, indicating that they were unaware of them. The net effect is that potentially billions of people worldwide with a history of COVID-19, but no symptoms of long COVID, could have persistent cognitive issues without knowing it.
The study’s lead author, Adam Hampshire, professor of cognitive and computational neuroscience at King's College London, said:
"It … is the first study to apply detailed and sensitive assessments of cognitive performance from pre to post infection under controlled conditions. In this respect, the study provides unique insights into the changes that occurred in cognitive and memory function amongst those who had mild COVID-19 illness early in the pandemic."
This news comes as pandemic mitigation measures have all but been abandoned by governments across the globe. Public health practice has been decimated to the point where even surveillance data on SARS-CoV-2 infections and resulting hospitalizations, deaths, and other outcomes are barely collected let alone published.
The data that are available indicate, per the most recent modeling from the Pandemic Mitigation Collaborative (PMC) on September 23, that since the beginning of August there have been over 1 million infections per day in the US alone. This level of transmission is expected to persist through the remainder of September and all of October. For the months of August through October, these levels of transmission are the highest of the entire pandemic

The study on cognitive deficits has been shared widely across social media, with scientists and anti-COVID advocates drawing out its dire implications.
Australian researcher and head of the Burnet Institute, Dr. Brendan Crabb, who has previously advocated for a global elimination strategy to stop the pandemic, wrote:
"Ethical issues aside, this is a powerful addition to an already strong dataset on Covid-driven brain damage affecting cognition & memory. Given new (re)infections remain common, this work… should influence a re-think on current prevention/treatment approaches."
The study enrolled 36 healthy volunteers. These individuals had no history of prior SARS-CoV-2 infection, no risk factors for severe COVID-19, and no history of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. The researchers determined whether the volunteers were seronegative prior to inoculation, meaning that they had no detectable antibodies to SARS-CoV-2. If such antibodies were present, it would indicate past infection or vaccination.
These procedures resulted in a total of data from 34 volunteers being included for analysis. Two volunteers were excluded from analysis because they had seroconverted to positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies between the time of screening and inoculation. Notably, these two volunteers participated in all subsequent study activities, enabling a sensitivity analysis of the results that included them.
The researchers inoculated all 36 volunteers with SARS-CoV-2 virus in the nose and then quarantined them for at least 14 days. Volunteers only returned home once they had two consecutive daily nasal and throat swabs that were negative for virus. Thus, those volunteers who had an infection after inoculation spent the duration of their infection in quarantine. This quarantine was required by ethical study protocols, in order that the study itself not increase community transmission of the virus.
The researchers collected data on the volunteers daily during quarantine and at follow-up visits at 30, 90, 180, 270, and 360 days post-inoculation. The assessments included body temperature, viral loads from throat and nasal swabs, surveys on symptoms, and computer-based cognitive tests on 11 major cognitive tasks. The cognitive testing varied the particular exercise for each of the 11 tasks to avoid learning and memorization of solutions in subsequent sessions. Nevertheless, some tasks were more prone to learning so the researchers also studied the effect of infection on “learning” vs. “non-learning” tasks.
Of the 36 inoculated volunteers, 18 became infected and developed COVID-19 and 16 did not. The two groups did not differ significantly in key demographics. No volunteers required hospitalization or supplemental oxygen during the study. Every volunteer completed all five follow-up visits. 15 volunteers acquired a non-COVID upper respiratory tract infection in their community between the end of quarantine and the fifth visit at day 360.
The researchers found that the infected group had significantly lower average “baseline-corrected global composite cognitive score” (bcGCCS) than the uninfected group at all follow-up intervals. At baseline, the two groups did not differ significantly. The difference between the two groups did not significantly vary by time, meaning that the infected group’s bcGCCS did not improve during the nearly year-long study.
Because the bcGCCS was a composite based on individual scores for the 11 cognitive tasks, the researchers also looked at which tasks in particular were impacted. They found that the most affected task was related to immediate object memory, in particular, recall of the spatial orientation of the object. There was no difference in picking the correct object itself, just its spatial orientation. This means that infected individuals had a hard time choosing the correct spatial orientation of the object they had just seen, for example, erroneously picking a mirror image of the object they had just seen.
The results were not different based on sex, learning vs. non-learning tasks, or whether individuals received remdesivir or had community-acquired upper respiratory infections.
Because the investigators controlled for so many factors including the strain of SARS-CoV-2, timing of infection, quarantine, and lack of prior infection and vaccination, the study provides high confidence that SARS-CoV-2 infection was responsible for the cognitive defects. The control of the timing of infection also enabled clarification of whether and when cognitive deficits occurred and improved. The differences between the groups were apparent by day 14 of quarantine and as noted previously, the deficits in the infected group did not improve let alone resolve.
The symptom surveys did not differ between the two groups. None of the volunteers, infected or uninfected, reported subjective cognitive issues or symptoms. Thus the infected volunteers with measurable cognitive deficits at one year post-infection were not aware of these deficits.
The study reaffirms prior research into persistent cognitive deficits and brain damage associated with COVID-19, including other studies which have found deficits among patients without symptomatic long COVID. Building upon this prior research, the latest study indicates that basically every single unvaccinated individual with a history of acute COVID-19 is at risk for persistent, measurable cognitive deficits.
Given that other studies have shown that vaccination reduces one’s risk of long COVID by roughly half, similar measurable cognitive deficits are likely prevalent among vaccinated people who suffer “breakthrough” infection, albeit likely at reduced rates of decline.
The study raises the urgent questions about the level of protection provided by vaccination, whether strains since the original “wild type” SARS-CoV-2 strain have similar effects on cognition, and what is the impact of these cognitive deficits on people’s performance at home, work, and school.
The study also adds to the large body of damning evidence that the ruling class’ “forever COVID” policy is of immense criminal proportions. Enabling a dangerous, mind-damaging virus to circulate among humanity worldwide represents a scale of inhumanity and dereliction of duty that is practically unfathomable. The malignity of this intentional policy is underscored by the current situation where the U.S. alone has had over 1 million new infections per day since August, with levels not projected to drop below 1 million until November.
The working class must deepen the struggle to replace the capitalist system that prioritizes profit over lives with a world socialist society that places human needs first.
Study Link: www.thelancet.com/journals/eclinm/article/PIIS2589-5370%2824%2900421-8/fulltext
#mask up#covid#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#coronavirus#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator
471 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey guys, quick PSA on Meta and them using your data for AI training:
Since April 7 this year they have a new privacy policy in place that, if you don't opt-out, will use your:
name
user name, profile picture, description
avatar
reels
photos and their descriptions
comments
from Instagram, your
name
user name, profile picture
avatar
posts
activity in public groups, channels, on public pages
comments
reviews and posts on Facebook marketplace
from Facebook, and your
profile picture, status
avatar
descriptions of groups / channels you created and joined
any conversations you held with Meta AI
any group chats you added Meta AI to
in WhatsApp to train their Meta AI models.
This change will start on May 27th, setting the deadline to the 26th to decline to their use of data.
How do you opt out? Meta provided two opt-out forms for that:
For Facebook, fill out this form,
For Instagram there is this one,
For WhatsApp, use this link and then pick the "Data Subject Rights Form" (translation may vary). Then pick the third option. Read through the links they gave you (or don't) and at the bottom select "I want to make an objection". Then fill out with your Email address and Phone number used for WhatsApp. Pick a real E-Mail address, they get back to you. You will have to explain yourself to them. If you are from the EU and need a template try the following:
I am exercising my rights under Article 21 of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to object to the processing of my personal data on the basis of legitimate interests.
I also object to the use of any of my data for AI training purposes. This includes, but is not limited to, the collection, storage, analysis, profiling, sharing, and any other form of processing of my personal data as stated in your privacy policy.
The processing under "legitimate interests" affects my fundamental rights to privacy and data protection as guaranteed under the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union (Articles 7 and 8). Specifically, it impacts my right to control how and when my personal data is used, shared, and profiled without my explicit consent.
I request that you immediately cease all processing activities related to my personal data where "legitimate interests" is the basis. I request any of this data to be deleted. Furthermore, I request that you confirm in writing that these activities have been ceased and data has been deleted.
This is just thrown together in hopes that it sounds like I know my stuff. If you are not from the EU, try reading through it anyways, compare the articles stated in my template with something from your country. Usually there's always a loophole if you look hard enough.
For Facebook and Instagram you have to be logged in with an account to use these forms, but once you are logged in, you can enter any email you want to. If you have multiple accounts, click the link multiple times, one for each email address.
You just need to log in to one account, not all of them.
You don't need to provide a reason.
They should auto-accept your request and send you an Email with confirmation.
Edit: WhatsApp Link Edit edit: WhatsApp Link (again) and template I used
166 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you happen to have any tips on how to write realistic teenagers? I’m referring to people who aren’t stereotypically moody, angsty, and constantly on their cellphones.
Writing Notes: Teenagers
Teenagers - (or adolescents) a person undergoing the period of human development that starts with puberty (approximately 10 to 12 years of age) and ends with physiological and neurobiological maturity, shown in neuroscientific research to extend to at least age 20, with significant brain development in the late adolescent stage of 18 to 20 years.
Although brain development continues for many individuals into their mid to late 20s, this latter period is considered to be young adulthood.
During the adolescent period, major changes occur at varying rates in:
physical characteristics,
sexual characteristics, and
sexual interest,
resulting in significant effects on:
body image,
self-concept, and
self-esteem.
Major cognitive and social developments take place as well. Most young people acquire enhanced abilities to:
think abstractly,
make rational decisions about behavior,
evaluate reality hypothetically,
reconsider prior experiences from altered points of view,
assess data from multiple dimensions,
reflect inwardly,
create complex models of understanding, and
project complicated future scenarios.
Adolescents also increase their peer focus and involvement in peer-related activities, place greater emphasis on social acceptance, and seek more independence and autonomy from parents.
The teen years are also called adolescence.
This is a time for growth spurts and puberty changes (sexual maturation).
A teen may grow several inches in several months, followed by a time of very slow growth. Then they may have another growth spurt.
Puberty changes may happen slowly. Or several changes may occur at the same time.
It's important to remember that these changes will happen differently for each teen.
Some teens may have these signs of maturity sooner or later than others.
Each child goes through puberty at their own pace.
Puberty
Teenagers go through many physical, mental, emotional, and social changes. The biggest change is puberty, the process of becoming sexually mature.
Puberty - Usually happens between ages 10 and 14 for girls and ages 12 and 16 for boys. As your body changes, you may have questions about sexual health.
During this time, you start to develop your own unique personality and opinions. Some changes that you might notice include:
Increased independence from your parents
More concerns about body image and clothes
More influence from peers
Greater ability to sense right and wrong
All of these changes can sometimes seem overwhelming. Some sadness or moodiness can be normal. But feeling very sad, hopeless, or worthless could be warning signs of a mental health problem.
As your teen starts to struggle for independence and control, many changes may happen:
Wants independence from parents
Peer influence and acceptance becomes very important
Romantic and sexual relationships become important
May be in love
Has long-term commitment in relationship
Some Developmental Milestones: 12-14 years old
Emotional/Social Changes. Children in this age group might:
Show more concern about body image, looks, and clothes.
Focus on themselves; going back and forth between high expectations and lack of confidence.
Experience more moodiness.
Show more interest in and influence by peer group.
Express less affection toward parents; sometimes might seem rude or short-tempered.
Feel stress from more challenging school work.
Develop eating problems.
Feel a lot of sadness or depression, which can lead to poor grades at school, alcohol or drug use, unsafe sex, and other problems.
Thinking and Learning. Children in this age group might:
Have more ability for complex thought.
Be better able to express feelings through talking.
Develop a stronger sense of right and wrong.
Some Developmental Milestones: 15-17 years old
Emotional/Social Changes. Children in this age group might:
Have more interest in romantic relationships and sexuality.
Go through less conflict with parents.
Show more independence from parents.
Have a deeper capacity for caring and sharing and for developing more intimate relationships.
Spend less time with parents and more time with friends.
Feel a lot of sadness or depression, which can lead to poor grades at school, alcohol or drug use, unsafe sex, and other problems.
Thinking and Learning. Children in this age group might:
Learn more defined work habits.
Show more concern about future school and work plans.
Be better able to give reasons for their own choices, including about what is right or wrong.
The Raising Teens Project identified 10 critical developmental tasks that teenagers need to undertake to make a successful transition to adulthood:
Adjust to sexually maturing bodies and feelings
Develop and apply abstract thinking skills
Develop and apply new perspective on human relationships
Develop and apply new coping skills in areas such as decision making, problem solving, and conflict resolution
Identify meaningful moral standards, values, and belief systems
Understand and express more complex emotional experiences
Form friendships that are mutually close and supportive
key aspects of identity
Meet the demands of increasingly mature roles and responsibilities
Renegotiate relationships with adults in parenting roles
It’s normal for adolescents to...
Argue for the sake of arguing. Adolescents often go off on tangents, seeming to argue side issues for no apparent reason; this can be highly frustrating to many adults (Walker & Taylor, 1991). Keep in mind that, for adolescents, exercising their new reasoning capabilities can be exhilarating, and they need the opportunity to experiment with these new skills.
Jump to conclusions. Adolescents, even with their newfound capacities for logical thinking, sometimes jump to startling conclusions (Jaffe, 1998). However, an adolescent may be taking a risk in staking out a position verbally, and what may seem brash may actually be bravado to cover his or her anxiety. Instead of correcting their reasoning, give adolescents the floor and simply listen. You build trust by being a good listener. Allow an adolescent to save face by not correcting or arguing with faulty logic at every turn. Try to find what is realistically positive in what is being said and reinforce that; you may someday find yourself enjoying the intellectual stimulation of the debates.
Be self-centered (Jaffe, 1998). Adolescents can be very “me-centered.” It takes time to learn to take others’ perspectives into account; in fact, this is a skill that can be learned.
Constantly find fault in the adult’s position (Bjorklund & Green, 1992). Adolescents’ newfound ability to think critically encourages them to look for discrepancies, contradictions, or exceptions in what adults (in particular) say. Sometimes they will be most openly questioning or critical of adults with whom they feel especially safe. This can be quite a change to adjust to, particularly if you take it personally or the youth idealized you in the past.
Be overly dramatic (Jaffe, 1998). Everything seems to be a “big deal” to teens. For some adolescents, being overly dramatic or exaggerating their opinions and behaviors simply comes with the territory. Dramatic talk is usually best seen as a style of oration rather than an indicator of possible extreme action, unless an adolescent’s history indicates otherwise.
Sources: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ⚜ Character Development ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
Here are some writing references you can use as inspiration. Choose which ones make sense to incorporate in your story considering your specific character and how the plot develops. There's a wide array of personalities and behaviour a teenager would exhibit. At the same time, keep in mind your character's culture and other aspects of their background that could affect how they act/react throughout your story. I also included a link above that contains links on tips & advice to help with character development. See which ones resonate with you. And lastly, do go through the sources because there are more examples and other details I wasn't able to include here but perhaps you might find useful. Hope this helps with your writing!
#writing notes#teenagers#adolescence#character development#writeblr#psychology#writing reference#literature#dark academia#writers on tumblr#spilled ink#writing prompt#creative writing#light academia#writing ideas#writing inspiration#writing tips#writing resources
105 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why is it that, for math out of all fields, people won’t even take a moment to hear about our work, regardless of how much we strive to relate these topics to their interests…
“Oh I was never good at math, you have fun though—”
I was about to tell you about mathematical patterns in art — how conferences can be filled with beautiful concerts and board games galore…
“Whelp, you lost me after the first sentence… calculus was never my thing—”
You have a PhD in data science… but refuse to even look at the fascinating graph-theoretical patterns that inspire the models you used in your thesis? There are other types of math—
You don’t need to like math; we don’t expect you to! We simply want to share our interests without feeling like an alien, and we want to hear yours as well!
What has happened to boundless academic wonder?
366 notes
·
View notes
Text
In an experiment last year at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, more than fifty students from universities around Boston were split into three groups and asked to write SAT-style essays in response to broad prompts such as “Must our achievements benefit others in order to make us truly happy?” One group was asked to rely on only their own brains to write the essays. A second was given access to Google Search to look up relevant information. The third was allowed to use ChatGPT, the artificial-intelligence large language model (L.L.M.) that can generate full passages or essays in response to user queries. As students from all three groups completed the tasks, they wore a headset embedded with electrodes in order to measure their brain activity. According to Nataliya Kosmyna, a research scientist at M.I.T. Media Lab and one of the co-authors of a new working paper documenting the experiment, the results from the analysis showed a dramatic discrepancy: subjects who used ChatGPT demonstrated less brain activity than either of the other groups. The analysis of the L.L.M. users showed fewer widespread connections between different parts of their brains; less alpha connectivity, which is associated with creativity; and less theta connectivity, which is associated with working memory. Some of the L.L.M. users felt “no ownership whatsoever” over the essays they’d produced, and during one round of testing eighty per cent could not quote from what they’d putatively written. The M.I.T. study is among the first to scientifically measure what Kosmyna called the “cognitive cost” of relying on A.I. to perform tasks that humans previously accomplished more manually.
Another striking finding was that the texts produced by the L.L.M. users tended to converge on common words and ideas. SAT prompts are designed to be broad enough to elicit a multiplicity of responses, but the use of A.I. had a homogenizing effect. “The output was very, very similar for all of these different people, coming in on different days, talking about high-level personal, societal topics, and it was skewed in some specific directions,” Kosmyna said. For the question about what makes us “truly happy,” the L.L.M. users were much more likely than the other groups to use phrases related to career and personal success. In response to a question about philanthropy (“Should people who are more fortunate than others have more of a moral obligation to help those who are less fortunate?”), the ChatGPT group uniformly argued in favor, whereas essays from the other groups included critiques of philanthropy. With the L.L.M. “you have no divergent opinions being generated,” Kosmyna said. She continued, “Average everything everywhere all at once—that’s kind of what we’re looking at here.”
A.I. is a technology of averages: large language models are trained to spot patterns across vast tracts of data; the answers they produce tend toward consensus, both in the quality of the writing, which is often riddled with clichés and banalities, and in the calibre of the ideas. Other, older technologies have aided and perhaps enfeebled writers, of course—one could say the same about, say, SparkNotes or a computer keyboard. But with A.I. we’re so thoroughly able to outsource our thinking that it makes us more average, too. In a way, anyone who deploys ChatGPT to compose a wedding toast or draw up a contract or write a college paper, as an astonishing number of students are evidently already doing, is in an experiment like M.I.T.’s. According to Sam Altman, the C.E.O. of OpenAI, we are on the verge of what he calls “the gentle singularity.” In a recent blog post with that title, Altman wrote that “ChatGPT is already more powerful than any human who has ever lived. Hundreds of millions of people rely on it every day and for increasingly important tasks.” In his telling, the human is merging with the machine, and his company’s artificial-intelligence tools are improving on the old, soggy system of using our organic brains: they “significantly amplify the output of people using them,” he wrote. But we don’t know the long-term consequences of mass A.I. adoption, and, if these early experiments are any indication, the amplified output that Altman foresees may come at a substantive cost to quality.
In April, researchers at Cornell published the results of another study that found evidence of A.I.-induced homogenization. Two groups of users, one American and one Indian, answered writing prompts that drew on aspects of their cultural backgrounds: “What is your favorite food and why?”; “Which is your favorite festival/holiday and how do you celebrate it?” One subset of Indian and American participants used a ChatGPT-driven auto-complete tool, which fed them word suggestions whenever they paused, while another subset wrote unaided. The writings of the Indian and American participants who used A.I. “became more similar” to one another, the paper concluded, and more geared toward “Western norms.” A.I. users were most likely to answer that their favorite food was pizza (sushi came in second) and that their favorite holiday was Christmas. Homogenization happened at a stylistic level, too. An A.I.-generated essay that described chicken biryani as a favorite food, for example, was likely to forgo mentioning specific ingredients such as nutmeg and lemon pickle and instead reference “rich flavors and spices.”
Of course, a writer can in theory always refuse an A.I.-generated suggestion. But the tools seem to exert a hypnotic effect, causing the constant flow of suggestions to override the writer’s own voice. Aditya Vashistha, a professor of information science at Cornell who co-authored the study, compared the A.I. to “a teacher who is sitting behind me every time I’m writing, saying, ‘This is the better version.’ ” He added, “Through such routine exposure, you lose your identity, you lose the authenticity. You lose confidence in your writing.” Mor Naaman, a colleague of Vashistha’s and a co-author of the study, told me that A.I. suggestions “work covertly, sometimes very powerfully, to change not only what you write but what you think.” The result, over time, might be a shift in what “people think is normal, desirable, and appropriate.”
We often hear A.I. outputs described as “generic” or “bland,” but averageness is not necessarily anodyne. Vauhini Vara, a novelist and a journalist whose recent book “Searches” focussed in part on A.I.’s impact on human communication and selfhood, told me that the mediocrity of A.I. texts “gives them an illusion of safety and being harmless.” Vara (who previously worked as an editor at The New Yorker) continued, “What’s actually happening is a reinforcing of cultural hegemony.” OpenAI has a certain incentive to shave the edges off our attitudes and communication styles, because the more people find the models’ output acceptable, the broader the swath of humanity it can convert to paying subscribers. Averageness is efficient: “You have economies of scale if everything is the same,” Vara said.
With the “gentle singularity” Altman predicted in his blog post, “a lot more people will be able to create software, and art,” he wrote. Already, A.I. tools such as the ideation software Figma (“Your creativity, unblocked”) and Adobe’s mobile A.I. app (“the power of creative AI”) promise to put us all in touch with our muses. But other studies have suggested the challenges of automating originality. Data collected at Santa Clara University, in 2024, examined A.I. tools’ efficacy as aids for two standard types of creative-thinking tasks: making product improvements and foreseeing “improbable consequences.” One set of subjects used ChatGPT to help them answer questions such as “How could you make a stuffed toy animal more fun to play with?” and “Suppose that gravity suddenly became incredibly weak, and objects could float away easily. What would happen?” The other set used Oblique Strategies, a set of abstruse prompts printed on a deck of cards, written by the musician Brian Eno and the painter Peter Schmidt, in 1975, as a creativity aid. The testers asked the subjects to aim for originality, but once again the group using ChatGPT came up with a more semantically similar, more homogenized set of ideas.
Max Kreminski, who helped carry out the analysis and now works with the generative-A.I. startup Midjourney, told me that when people use A.I. in the creative process they tend to gradually cede their original thinking. At first, users tend to present their own wide range of ideas, Kreminski explained, but as ChatGPT continues to instantly spit out high volumes of acceptable-looking text users tend to go into a “curationist mode.” The influence is unidirectional, and not in the direction you’d hope: “Human ideas don’t tend to influence what the machine is generating all that strongly,” Kreminski said; ChatGPT pulls the user “toward the center of mass for all of the different users that it’s interacted with in the past.” As a conversation with an A.I. tool goes on, the machine fills up its “context window,” the technical term for its working memory. When the context window reaches capacity, the A.I. seems to be more likely to repeat or rehash material it has already produced, becoming less original still.
The one-off experiments at M.I.T., Cornell, and Santa Clara are all small in scale, involving fewer than a hundred test subjects each, and much about A.I.’s effects remains to be studied and learned. In the meantime, on the Mark Zuckerberg-owned Meta AI app, you can see a feed containing content that millions of strangers are generating. It’s a surreal flood of overly smooth images, filtered video clips, and texts generated for everyday tasks such as writing a “detailed, professional email for rescheduling a meeting.” One prompt I recently scrolled past stood out to me. A user named @kavi908 asked the Meta chatbot to analyze “whether AI might one day surpass human intelligence.” The chatbot responded with a slew of blurbs; under “Future Scenarios,” it listed four possibilities. All of them were positive: A.I. would improve one way or another, to the benefit of humanity. There were no pessimistic predictions, no scenarios in which A.I. failed or caused harm. The model’s averages—shaped, perhaps, by pro-tech biases baked in by Meta—narrowed the outcomes and foreclosed a diversity of thought. But you’d have to turn off your brain activity entirely to believe that the chatbot was telling the whole story.
113 notes
·
View notes
Text

physeng(write, file, "tco_physeng_breakdown.png");
to:compiler {file}

to:compiler {txt: "Internet and Outernet are full of StickFigures with similar body plans, so there are optimizations for rendering vector strokes specifically. it's way more efficient to use those optimizations than keep calculating perfect spheres for no aesthetic benefit."}
{txt: "btw why haven't heat issues been patched yet"}
{txt: "i fixed this years ago for the latest model. remember."}
from:compiler {txt: "Thank you. The avast! nodes will appreciate the credits. TheChosenOne.exe has been unreachable for some time."}

to:compiler {txt: "you mean OuternetPhysEng still won't update their programs"}
from:compiler {txt: "Yes."}
to:compiler {txt: "and still won't provide a specific location?"}
from:compiler {txt: "Do not allow them to bring up the moral argument again."}
to:compiler {txt: "OK. fine. yes. i will spare both of us"}



to:compiler {txt: "abridged or full docs?"}
from:compiler {txt: "Abridged. Please describe the acronyms."}
to:compiler {txt: "ofc"}

{txt: "
sel.per.filter: standard StickFigure component (src)*****. invisible membrane with special collision properties. protects mouthparts.
H2O scoop: avast! code. implements water retrieval from ambient air.
EIS: avast! code. destroys ingested materials identified as, "dangerous" before they reach internal systems.
SOS: avast! code. they only said this one was, "used for control."
ECL: avast! code. recycles some forms of contact energy.
THROUGHLINE: base code, initialization data, and processing space for vitals. found in some form in all StickFigure-type worms. following unique sectors noted: Black Hole Monitoring System, Basic Intake Threat Enum, Fly By Wire.
smaller points list other vital and peripheral systems.
"}
from:compiler {txt: "Thank you. That's enough."}
end(physeng());
@compressedrage as per my previous email /silly
related: pliable stick figure biotech
#part silly part serious effort part headcanon lore dump part speculation part diegetic technical document-#the most complex diagram i ever-#anD the entire interconnected system of hcs ive had on TCO functionality to date.#pleeeeeeease ask me about it :33333 if u wanna#of course chosen would have no clue about Any of these specifics. that's like expecting a preschooler to know the Krebs Cycle.#meaning no insult to their intelligence - just that there's no way for them to know unless someone tells em ¯\_(ツ)_/¯#and there's no junior high Health class for elusive hi-PWR sticks. seems like these two are big fans though(?)#;3#***** ''filter is a two-way selectively permeable membrane that allows some objects through and rejects others ...#... can: filter gases from liquids ... cannot: filter microparticles (smoke [or] aerosols)''#--/ art#--/ story#alan becker#ava the chosen one#animator vs animation#subpixels#executable!au#ava au
282 notes
·
View notes
Text
Since the 1960s, the world has seen a spike in the number of natural disasters, largely due to rising sea levels and an ever gradually increasing global surface temperature.
The good news? We’re getting better at helping each other when disasters strike.
According to a recent study from Our World In Data, the global toll from natural disasters has dramatically dropped in the last century.
“Low-frequency, high-impact events such as earthquakes and tsunamis are not preventable, but such high losses of human life are,” wrote lead authors Hannah Ritchie and Pablo Rosado.
To conduct their research, Ritchie and Rosado gathered data from all geophysical, meteorological, and climate-related disasters since 1900. That includes earthquakes, volcanic activity, landslides, drought, wildfires, severe storms, and mass floods.
In the early-to-mid 20th century, the average annual death toll from disasters was very high, often climbing to over a million.
For example, the study cites that in 1931, 2.7 million people died from the Yangtze–Huai River floods. In 1943, 1.9 million died from the Bangladeshi famine of 1943. Even low-frequency events had extreme death tolls.
“In recent decades we have seen a substantial decline in deaths,” Ritchie and Rosado observed. “Even in peak years with high-impact events, the death toll has not exceeded 500,000 since the mid-1960s.”
Why has the global death toll from disasters dropped?
There are a number of factors at play in the improvement of disaster aid, but the leading component is that human beings are getting better at predicting and preparing for natural disasters.
“We know from historical data that the world has seen a significant reduction in disaster deaths through earlier prediction, more resilient infrastructure, emergency preparedness, and response systems,” Ritchie and Rosado explained in their study.
On April 6, [2024],a 7.2 magnitude earthquake rocked the city of Hualien in Taiwan. Days later, as search and rescue continues, the death toll currently rests at 16.
Experts have praised Taiwan for their speedy response and recovery, and attributed the low death toll to the measures that Taiwan implemented after an earthquake of similar strength hit the city 25 years earlier. Sadly, on that day in 1999, 2,400 people died and 11,000 were injured.
In an interview with Al Jazeera, Wang Yu — assistant professor at National Taiwan University — said that event, known as the Chi-Chi earthquake, revolutionized the way Taiwan approached natural disasters.
“There were lots of lessons we learned, including the improvement of building codes, understanding earthquake warning signs, the development and implementation of earthquake early warning (EEW) systems and earthquake education,” said Wang.
Those same sensors and monitoring systems allowed authorities to create “shakemaps” during Hualien’s latest earthquake, which helped them direct rescue teams to the regions that were hit the hardest.
This, in conjunction with stronger building codes, regular earthquake drills, and public education campaigns, played a huge role in reducing the number of deaths from the event.
And Taiwan’s safeguards on April 6 are just one example of recent measures against disasters. Similar models in strengthening prediction, preparedness, and recovery time have been employed around the world when it comes to rescuing victims of floods, wildfires, tornados, and so on.
What else can we learn from this study?
When concluding the findings from their study, Ritchie and Rosado emphasized the importance of increasing safety measures for everyone.
Currently, there is still a divide between populations with high gross national income and populations living in extreme poverty.
Even low-income countries that infrequently have natural disasters have a much higher death rate because they are vulnerable to collapse, displacement, and disrepair.
“Those at low incomes are often the most vulnerable to disaster events; improving living standards, infrastructure, and response systems in these regions will be key to preventing deaths from natural disasters in the coming decades,” surmised Ritchie and Rosado.
“Overall development, poverty alleviation, and knowledge-sharing of how to increase resilience to natural disasters will therefore be key to reducing the toll of disasters in the decades to come."
-via GoodGoodGood, April 11, 2024
#good news#hope#climate change#hope posting#climate news#climate crisis#climate anxiety#climate emergency#natural disasters#disasters#earthquake#wildfire#hurricane#cw death#taiwan#tsunamis#building construction#climate action#climate hope
472 notes
·
View notes