#splunk security
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Why Splunk Is the Go-To Platform for Enterprise Security and Observability
In today’s digital-first world, organizations generate and rely on vast volumes of machine data to run their operations, serve customers, and protect digital assets. As cyber threats grow in complexity and IT environments become more fragmented with cloud, hybrid, and multi-cloud setups, enterprises are under pressure to maintain visibility, ensure compliance, and respond to incidents in real time. Enter Splunk: the platform leading enterprises trust for security, observability, and data-driven decision-making.
Splunk has become synonymous with real-time analytics and intelligent monitoring. Its ability to ingest, index, and correlate data from virtually any source makes it indispensable for enterprises seeking to gain end-to-end visibility across their digital infrastructure. But what exactly makes Splunk service the go-to platform for enterprise security and observability? Let’s break it down.
1. Unified Data Platform for Security and IT Operations
Splunk provides a unified platform that bridges the gap between IT security, and business operations. Unlike siloed tools that provide fragmented views, Splunk consolidates data from across your network, applications, endpoints, and cloud services to deliver a single source of truth.
Whether you’re monitoring for performance issues, detecting security breaches, or ensuring compliance, Splunk enables stakeholders to work from a common, real-time data set. This holistic approach empowers faster, more accurate decisions and fosters collaboration across departments.
2. Powerful Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Capabilities
One of the strongest use cases for Splunk is in enterprise security. Splunk Enterprise Security (ES) acts as a powerful SIEM platform, enabling security teams to detect, investigate, and respond to threats efficiently. It offers advanced analytics, prebuilt dashboards, threat intelligence integration, and real-time alerting.
With features like risk-based alerting, behavioral analytics, and threat detection rules, Splunk helps security teams cut through the noise and focus on high-priority incidents. It empowers analysts to conduct rapid incident response and forensic investigations using historical data.
3. Unmatched Observability Tools for Modern Applications
Observability is more than just monitoring—it’s about understanding system behavior across distributed environments. Splunk Observability Cloud offers a full-stack observability solution that includes infrastructure monitoring, application performance monitoring (APM), log analysis, and synthetic transaction testing.
By leveraging OpenTelemetry and AI-driven insights, Splunk provides real-time visibility into system health, user experiences, and performance bottlenecks. This enables DevOps and SRE teams to troubleshoot faster, optimize application performance, and deliver consistent uptime.
4. Scalability for Enterprise Workloads
Enterprise environments are complex, and the volume of machine data they produce can be staggering. Splunk is designed to scale with your business, whether you're analyzing gigabytes or petabytes of data daily. Its distributed architecture supports horizontal scaling and high availability, ensuring consistent performance even under heavy loads.
This scalability is critical for large enterprises that require long-term retention, high-speed analytics, and support for thousands of users accessing data concurrently.
5. Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning
Splunk's analytics capabilities go beyond simple search and dashboards. With built-in machine learning (ML) and support for custom models, Splunk enables predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and behavior profiling. Security and IT teams can use ML to identify suspicious patterns, forecast system failures, or automate threat detection.
The Splunk Machine Learning Toolkit (MLTK) empowers users to apply, train, and tune models using their existing data—no data science degree is required. This intelligent layer of automation enhances situational awareness and drives proactive responses.
6. Robust Ecosystem and Integrations
Splunk integrates seamlessly with a wide range of tools, platforms, and services, including AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Kubernetes, ServiceNow, Palo Alto Networks, and more. These integrations extend Splunk’s capabilities and ensure it fits naturally into your existing technology stack.
The Splunkbase app marketplace features thousands of apps and add-ons for specialized data sources, dashboards, and utilities—making it easier for teams to customize the platform to suit their needs.
7. Enhanced Compliance and Audit Readiness
For industries like finance, healthcare, and government, regulatory compliance is a top priority. Splunk simplifies compliance management by offering prebuilt dashboards and reports aligned with standards like HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR, and ISO 27001.
Automated data collection, alerting, and audit trails make it easier to demonstrate compliance and pass audits with confidence. Splunk also provides role-based access controls and data masking to protect sensitive information.
8. Flexible Deployment Options: On-Prem, Cloud, or Hybrid
Not all enterprises are at the same stage of cloud adoption. Splunk’s flexible deployment options allow organizations to deploy the platform on-premises, in the cloud, or a hybrid environment.
Splunk Cloud Platform offers the same functionality as on-prem with the added benefits of scalability, automatic updates, and reduced infrastructure management. It’s ideal for businesses that want to accelerate time to value and reduce operational overhead.
9. Real-Time Dashboards and Visualizations
Splunk’s intuitive dashboards and data visualizations help users transform raw machine data into actionable insights. From real-time alerts on security threats to performance metrics for executive reports, Splunk offers customizable dashboards that can be tailored to user roles and use cases.
Interactive charts, graphs, and maps help bring data stories to life, making it easier for decision-makers to act on insights without technical barriers.
Final Thoughts: Why Splunk Stands Out
In a world where data is both a powerful asset and a potential liability, having the right tools to manage, secure, and understand your data is critical. Splunk delivers on all fronts—offering real-time analytics, enterprise-grade security, and unparalleled observability.
By unifying IT operations, DevOps, and security teams around a single data platform, Splunk breaks down silos, accelerates response times, and drives digital resilience. Its flexibility, intelligence, and scalability make it the ideal choice for enterprises navigating the complexities of modern IT environments.
If your organization is ready to move beyond reactive monitoring and embrace intelligent, proactive operations, Splunk is not just an option—it’s the answer.
#splunk services#microsoft azure sentinel#Splunk solutions#splunk enterprise#splunk security#Splunk consultant#microsoft sentinel#SIEM solutions#Sentinel
0 notes
Text
This month, Andrew Bernier, a US Army Corps of Engineers researcher and a union leader, says that he has received a barrage of menacing messages from the same anonymous email account. Unfolding like short chapters in a dystopian novel, they have spoken of the genius of Elon Musk, referenced the power of the billionaire’s so-called Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), and foretold the downfall of “corrupt” union bosses.
But the most eerie thing about the emails, which Bernier says began arriving after he filed an official charge accusing the Trump administration of violating his union’s collective bargaining agreement, is that they included personal details about his life—some of which he believes might have come from surveillance of his work laptop. The author referenced Bernier’s union activities, nickname, job, travel details, and even the green notebook he regularly uses. The most recent email implied that his computer was loaded with spyware. “Andy's crusade, like so many before it, had been doomed from the start,” one email stated. “The real tragedy wasn't his failure—it was his belief that the fight had ever been real.”
The unsettling messages, which were reviewed by WIRED, are an extreme example of the kinds of encounters that workers across the US government say they have had with technology since President Donald Trump took office. WIRED spoke to current employees at 13 federal agencies for this story who expressed fears about potentially being monitored by software programs, some of which they described as unfamiliar. Others said that routine software updates and notifications, perhaps once readily glossed over, have taken on ominous new meanings. Several reported feeling anxious and hyperaware of the devices and technology around them.
At the General Services Administration (GSA), one worker cited a Chrome browser extension called Dynatrace, an existing program for monitoring app performance. Inside the Social Security Administration (SSA), another employee pointed to Splunk, a longstanding tool that’s used to alert IT staff to security anomalies like when an unauthorized USB drive is plugged into a laptop. At the US Agency for International Development (USAID), one worker was caught off guard by Google’s Gemini AI chatbot, installations of which kicked off days before Trump took office.
“Everyone has been talking about whether our laptops are now able to listen to our conversations and track what we do,” says a current GSA employee, who like other workers in this story, was granted anonymity because they didn’t have authorization to speak and feared retaliation.
Dynatrace and Splunk did not respond to requests for comment from WIRED.
The workers’ accounts come as Musk’s DOGE organization is rapidly burrowing into various government agencies and departments, often gaining access to personnel records, logs of financial transactions, and other sensitive information in the process. The efforts are part of the Trump administration’s broader plan to terminate thousands of government employees and remake the face of federal agencies.
Like many private companies, US federal agencies disclose to staff that they have tools to monitor what workers do on their computers and networks. The US government’s capabilities in this area have also expanded over the past decade.
It couldn’t be learned whether the Trump administration has begun using existing tools to monitor employees in new ways; multiple agencies, including the Social Security Administration and the General Services Administration, denied that they have. The White House did not respond to requests for comment. Public evidence has not emerged of new government purchases of user-monitoring software, which is generally needed for detailed surveillance such as tracking which files a worker has copied onto a thumb drive. Some of the updates and changes that have been noticed by federal workers date back to software purchases and plans enacted long before Trump was in power, WIRED reporting shows.
“I will say my concerns are primarily based in general fear as opposed to specific knowledge,” says a worker at the Department of Homeland Security, who adds: “I’d love to be told I’m wrong.”
But activity that some workers perceive as signs of increased surveillance has prompted them to take precautions. Bernier, who works as a civil engineer for the Army Corps based in Hanover, New Hampshire, says the messages he received spooked him enough that he asked local police to keep an eye on his home, removed the battery from his work-issued laptop, and kept his work phone on airplane mode while traveling to a non-work conference last week. “There are things I don’t control but actions I can take to protect myself and my family,” he says.
Bernier’s anonymous emailer and the Army Corps did not respond to requests for comment.
A person inside the Environmental Protection Agency told WIRED last week that they’ve witnessed coworkers back out of Microsoft Teams meetings, which can be easily recorded and automatically transcribed, when they are related to topics they believe could get them fired. “Definite chilling effect,” the person says. The EPA did not respond to a request for comment.
An employee at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), whose work with international partners is being audited by DOGE operatives, says they and their colleagues began avoiding messaging one another and have “really cut down on putting things in writing” in recent weeks. They report that correspondence from their supervisors has also significantly dropped off. NOAA declined to comment.
At the Federal Bureau of Investigation, anxiety around officials possibly targeting officers and activities perceived as being disloyal to the president has cratered morale, a federal law enforcement source with knowledge of the agents' concerns tells WIRED. The FBI declined to comment.
Aryani Ong, a civil rights activist and cofounder of Asian American Federal Employees for Nondiscrimination, a group that advocates for government workers, says those she’s been in contact with are in a heightened state of alert. In response, some federal employees have turned to encrypted communications apps to connect with colleagues and taken steps to anonymize their social media accounts, Ong says. (Federal workers are granted an allowance to use non-official communication tools only “in exceptional circumstances.”)
Insider Threat
Long before Trump’s inauguration, user activity monitoring was already mandated for federal agencies and networks that handle classified information—the result of an executive order signed by then-president Barack Obama in the wake of a massive breach of classified diplomatic cables and information about the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan in 2010. The capability is part of government-wide insider threat (InTh) programs that greatly expanded after Edward Snowden’s leak of classified surveillance documents in 2013, and again after an Army specialist murdered four colleagues and injured 16 others at Fort Hood in 2014.
The US government’s current approach to digitally monitoring federal workers has largely been guided by a directive issued by the Committee on National Security Systems in 2014, which orders relevant agencies to tie user activity to “specific users.” The public portions of the document call for “every executive branch department and agency” handling classified information to have capabilities to take screenshots, capture keystrokes, and intercept chats and email on employee devices. They are also instructed to deploy “file shadowing,” meaning secretly producing facsimiles of every file a user edits or opens.
The insider threat programs at departments such as Health and Human Services, Transportation, and Veterans Affairs, also have policies that protect unclassified government information, which enable them to monitor employees’ clicks and communications, according to notices in the Federal Register, an official source of rulemaking documents. Policies for the Department of the Interior, the Internal Revenue Service, and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporate (FDIC), also allow collecting and assessing employees’ social media content.
These internal agency programs, overseen by a national task force led by the attorney general and director of national intelligence, aim to identify behaviors that may indicate the heightened risk of not only leaks and workplace violence, but also the “loss” or "degradation" of a federal agency’s “resources or capabilities.” Over 60 percent of insider threat incidents in the federal sector involve fraud, such as stealing money or taking someone's personal information, and are non-espionage related, according to analysis by Carnegie Mellon researchers.
“Fraud,” “disgruntlement,” “ideological challenges,” “moral outrage,” or discussion of moral concerns deemed “unrelated to work duties” are some of the possible signs that a worker poses a threat, according to US government training literature.
Of the 15 Cabinet-level departments such as energy, labor, and veterans affairs, at least nine had contracts as of late last year with suppliers such as Everfox and Dtex Systems that allowed for digitally monitoring of a portion of employees, according to public spending data. Everfox declined to comment.
Dtex’s Intercept software, which is used by multiple federal agencies, is one example of a newer class of programs that generate individual risk scores by analyzing anonymized metadata, such as which URLs workers are visiting and which files they’re opening and printing out on their work devices, according to the company. When an agency wants to identify and further investigate someone with a high score, two people have to sign off in some versions of its tool, according to the company. Dtex’s software doesn’t have to log keystrokes or scan the content of emails, calls, chats, or social media posts.
But that isn't how things work broadly across the government, where employees are warned explicitly in a recurring message when they boot up their devices that they have "no reasonable expectation of privacy" in their communications or in any data stored or transmitted through government networks. The question remains if and to what extent DOGE’s operatives are relying on existing monitoring programs to carry out Trump’s mission to rapidly eliminate federal workers that his administration views as unaligned with the president’s agenda or disloyal.
Rajan Koo, the chief technology officer of Dtex tells WIRED that he hopes the Trump administration will adjust the government’s approach to monitoring. Events such as widespread layoffs coupled with a reliance on what Koo described as intrusive surveillance tools can stir up an environment in which workers feel disgruntled, he says. “You can create a culture of reciprocal loyalty,” says Koo, or “the perfect breeding ground for insider threats.”
Already Overwhelmed
Sources with knowledge of the US government’s insider threat programs describe them as largely inefficient and labor intensive, requiring overstretched teams of analysts to manually pore through daily barrages of alerts that include many false positives. Multiple sources said that the systems are currently “overwhelmed.” Any effort by the Trump administration to extend the reach of such tools or widen their parameters—to more closely surveil for perceived signs of insubordination or disloyalty to partisan fealties, for instance—likely would result in a significant spike in false positives that would take considerable time to comb through, according to the people familiar with the work.
In an email last month seeking federal employees’ voluntary resignations, the Trump administration wrote that it wanted a “reliable, loyal, trustworthy” workforce. Attempts to use insider threat programs to enforce that vision could be met by a number of legal challenges.
US intelligence community analysts are required by law and directive to provide unbiased and objective work. That means avoiding cherry-picking information to deliberately alter judgements or falling prey to outside pressure, including from personal or political biases. These standards, even when not officially codified, are core to the professional ethics of any intelligence practitioner or law enforcement analyst conducting assessments of insider threats.
A 2018 national insider threat task force framework notes that federal programs should comply with “all applicable legal, privacy and civil liberties rights, and whistleblower protections.” Bradley Moss, an attorney representing US intelligence and law enforcement personnel, says that "disloyalty" to the Trump administration is “too vague” an excuse to terminate employees with civil service protections, adding that if "they're going to go through the statutory process, they need to demonstrate actual cause for termination."
A federal law enforcement source warns that monitoring could theoretically be used to gather political intelligence on federal employees, while the administration looks for more palatable reasons to terminate them later; similar to how law enforcement may obtain evidence that's inadmissible in the course of a criminal investigation, but then search for another evidentiary basis to file charges.
Joe Spielberger, senior legal counsel at the Project On Government Oversight, a nonpartisan group fighting alleged corruption, says that if Musk were serious about cutting government waste, he would be strengthening protections for people who report corruption and mismanagement. Any warrantless or mass surveillance of federal workers without transparent guidelines, he says, would represent a major concern.
“When you create this culture of fear and intimidation and have that chilling effect of making people even more fearful about calling out wrongdoing, it ensures that corruption goes unnoticed and unaddressed,” Spielberger says.
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
TURISIAN.com - Pemerintah bergerak cepat menyambut revolusi kecerdasan buatan. Melalui Kementerian Komunikasi dan Digital, negara meresmikan AI Center of Excellence pada Jumat, 11 Juli 2025, di Jakarta. Pusat pengembangan AI itu bukan sekadar simbol transformasi digital, tapi juga panggung kolaborasi lintas sektor. Menggandeng Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison, Cisco, dan Nvidia. Langkah ini merupakan bagian dari upaya besar merumuskan kedaulatan teknologi. Di atas fondasi jaringan seluler Indosat, infrastruktur cerdas Cisco, dan mesin komputasi mutakhir Nvidia, Indonesia menegaskan ambisinya. Indonesia tak ingin sekadar menjadi pengguna AI, tapi juga pemain utama di dalamnya. “Ini adalah gotong royong digital. Kita membuka satu akses bersama demi manfaat AI yang inklusif dan merata,” ujar Wakil Menteri Komunikasi dan Digital, Nezar Patria. Nezar menekankan bahwa AI Center of Excellence ini bukan hanya rumah riset dan infrastruktur, tapi juga simpul inklusivitas teknologi. Ia menyebut kolaborasi dengan industri, universitas, dan komunitas sebagai fondasi percepatan adopsi AI di Tanah Air. Visi Digital 2025 “Visi besar kita adalah Indonesia Digital 2045. Dan itu tidak bisa dikerjakan sendiri,” katanya. Vikram Sinha, Presiden Direktur dan CEO Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison, menimpali dengan pandangan serupa. Menurutnya, AI bukan semata soal teknologi, melainkan juga soal keadilan akses dan peluang. “Kami ingin masyarakat Indonesia bukan hanya jadi pengguna AI, tapi juga pencipta dan penggeraknya,” ujarnya. Pusat AI ini akan bertumpu pada empat pilar strategis: Infrastruktur Berdaulat Indosat dan Nvidia memimpin pembangunan infrastruktur AI berskala besar pertama di Indonesia. Mengandalkan teknologi NVIDIA GB200 NVL72, fasilitas ini menjanjikan performa tinggi dan kemandirian digital. Lintasarta, anak usaha Indosat, menjadi AI Factory pertama di Asia Tenggara yang mengadopsi teknologi ini. BACA JUGA: Raksasa Teknologi Apple Sedang Mencari Regional Regulatory Compliance Engineer Menyematkan Splunk Keamanan Data yang Cerdas Cisco mengambil peran dalam perisai digital. Melalui Sovereign Security Operations Center berbasis cloud, mereka menyematkan Splunk dan layanan keamanan terkelola. Hal ini demi melindungi aset strategis nasional. Sistem ini didesain untuk mendeteksi ancaman berbasis AI dan menjamin pengelolaan data sesuai regulasi. AI untuk Semua Dengan memanfaatkan jangkauan jaringan Indosat, pusat ini menargetkan akses AI bagi ratusan juta warga Indonesia pada 2027. AI tak lagi hanya milik korporasi dan kota besar, tapi juga hadir untuk desa-desa dan pelaku usaha mikro. Mencetak Talenta Digital Satu juta orang akan dibekali keterampilan digital di bidang jaringan, keamanan, dan kecerdasan buatan. Nvidia berkontribusi lewat program Inception untuk startup dan pelatihan Deep Learning Institute, sementara Cisco menyokong lewat Networking Academy. Targetnya yakni 500 ribu orang terlatih hingga 2030. Pusat AI ini menjadi batu loncatan ambisi digital nasional. Tapi, sebagaimana lazimnya proyek besar, tantangan utama bukan pada teknologi. Melainkan pada keberanian untuk melibatkan sebanyak mungkin masyarakat. Tujuannya, agar tak sekadar jadi penonton revolusi kecerdasan ini. ***
0 notes
Text
Top 3 AI Security Mistakes New Developers Make and How to Avoid Them
Have you ever built an AI model only to realize it’s vulnerable to attacks? As AI powers everything from apps to smart devices, new developers often overlook critical security steps. These mistakes can lead to data breaches or system failures. This article highlights the top three AI security mistakes new developers make and how to fix them.
Mistake 1: Ignoring Data Privacy
Many new developers focus on building AI models but forget to secure the data used for training. Unprotected datasets can expose sensitive user information, like names or credit card details. For example, a healthcare AI trained on patient records could leak data if not encrypted. Always prioritize data privacy to build trust and avoid legal issues.
How to Fix It
Use encryption tools like AES to protect sensitive data. Anonymize datasets by removing personal identifiers before training. Regularly audit data access to ensure only authorized team members handle it. These steps keep your AI system compliant with regulations like GDPR.
Mistake 2: Underestimating Adversarial Attacks
New developers often assume their AI models are foolproof, but adversarial attacks can trick them. For instance, slight changes to an image can mislead a facial recognition system. These attacks exploit weaknesses in how AI processes data. Ignoring this risk leaves systems open to manipulation.
How to Avoid It
Test your AI models with tools like the Adversarial Robustness Toolbox (ART). These platforms simulate attacks to reveal vulnerabilities. A Certified AI Security Expert can guide you in strengthening models against such threats. Regular testing ensures your AI can handle real-world challenges.
Mistake 3: Skipping Regular Model Updates
AI models aren’t “set it and forget it.” New developers often neglect updating models to address new threats. For example, an outdated chatbot might not detect phishing attempts. This oversight can weaken your system’s defenses over time.
How to Stay Updated
Schedule regular model retraining to adapt to emerging threats. Use monitoring tools like Splunk to track performance and flag issues. Stay informed about new attack methods through blogs or webinars. Consistent updates keep your AI secure and reliable.
Tips to Build Secure AI Systems
Start with a security-first mindset. Learn the basics of cybersecurity, like encryption and access control, alongside AI development. Experiment in safe environments, like virtual labs, to test your models. Joining online communities, such as Reddit’s r/cybersecurity, can also provide valuable insights.
Conclusion: Build Safer AI Today
Avoiding these common AI security mistakes—ignoring data privacy, underestimating adversarial attacks, and skipping updates—sets you up for success. By prioritizing encryption, testing for vulnerabilities, and staying current, you can build robust AI systems. Start implementing these tips today to create secure, trustworthy AI that stands the test of time.
#AI Security#AI#Artificial Intelligence#Cyber Security#Cyber Security Training#Cyber Security Course
1 note
·
View note
Text
What are the latest technologies in IT industry?

The Information Technology (IT) industry continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, driven by rapid advancements in innovation and a global demand for smarter digital solutions. Today, businesses and professionals alike are looking to keep up with the latest tech trends, making Emerging Technology Courses more relevant than ever.
Whether you're a student, tech enthusiast, or a seasoned IT professional, understanding these trends can help you future-proof your career. Here’s a look at some of the hottest trends dominating the IT landscape in 2025 and the courses that can help you stay ahead of the curve.
1. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning is the engine behind everything from recommendation engines to self-driving cars. As businesses rely more on data-driven decisions, ML skills are in high demand. Emerging Technology Courses in Machine Learning teach predictive analytics, neural networks, and real-time data processing—skills essential in today's AI-driven world.
2. Data Science
The importance of making sense of data cannot be overstated. Data Science combines statistics, programming, and domain expertise to extract insights from structured and unstructured data. Learning platforms are flooded with Emerging Technology Courses in Data Science that cover Python, R, SQL, data visualization, and big data tools like Hadoop and Spark.
3. Data Fabric
A relatively newer concept, Data Fabric provides a unified architecture that simplifies data access across cloud and on-premise systems. It enhances data visibility and management. Courses in this domain are emerging to support professionals in mastering hybrid cloud architecture and intelligent data integration.
4. Blockchain
Blockchain is revolutionizing sectors like finance, healthcare, and supply chain with its decentralized and secure structure. It’s no longer just about cryptocurrency. Emerging Technology Courses in Blockchain now focus on smart contracts, dApps (decentralized applications), and enterprise blockchain solutions.
5. Internet of Things (IoT)
From smart homes to industrial automation, IoT is expanding rapidly. IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, requiring robust infrastructure and security. Courses on IoT cover topics like embedded systems, wireless communication, sensors, and edge computing.
6. Web 3
Web 3 is the next generation of the internet, emphasizing decentralization, blockchain integration, and user ownership of data. Developers are enrolling in Emerging Technology Courses on Web 3 to learn Solidity, Ethereum, DAOs, and other decentralized technologies shaping the future of the web.
7. Hyper Automation
Hyper Automation uses AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA) to automate complex business processes. It’s gaining traction for its ability to reduce costs and increase efficiency. Courses in this field teach tools like UiPath, Blue Prism, and Python scripting for automation.
8. Cloud Computing
Cloud technology continues to be a cornerstone of digital transformation. From AWS and Azure to Google Cloud, cloud platforms are vital for scalability, remote access, and cost-effectiveness. Emerging Technology Courses in Cloud Computing cover architecture, DevOps, containerization with Kubernetes, and serverless computing.
9. Cyber Security
With increasing cyber threats, cybersecurity is more critical than ever. From ethical hacking to network security and compliance, professionals are upskilling through cybersecurity courses that include tools like Kali Linux, Wireshark, and Splunk.
Final Thoughts
The IT industry is constantly reshaping the way we live and work. Staying updated with these trends not only enhances your career prospects but also helps businesses innovate responsibly and securely. Investing in Emerging Technology Courses in fields like Machine Learning, Data Science, Blockchain, IoT, and Cyber Security is a smart move for anyone looking to thrive in today’s tech ecosystem.
Are you ready to upskill and lead the change?
0 notes
Text
Splunk issues a series of security advisories highlighting multiple critical vulnerabilities.
Splunk has released a series of vulnerability advisories for July 2025. These advisories, identified as SVD-2025-0712 through SVD-2025-0701, highlight important security updates and address several vulnerabilities across Splunk’s product suite. Below, we provide a comprehensive overview of these advisories, their impact, and recommended actions for Splunk administrators and security…
0 notes
Text
AWS Kinesis: Guides, Pricing, Cost Optimization

AWS Kinesis isn't just one service; it's a family of services, each tailored for different streaming data needs:
Amazon Kinesis Data Streams (KDS):
What it is: The foundational service. KDS allows you to capture, store, and process large streams of data records in real-time. It provides durable storage for up to 365 days (default 24 hours), enabling multiple applications to process the same data concurrently and independently.
Use Cases: Real-time analytics, log and event data collection, IoT data ingestion, real-time dashboards, application monitoring, and streaming ETL.
Key Concept: Shards. KDS capacity is measured in shards. Each shard provides a fixed unit of capacity (1 MB/s ingress, 1,000 records/s ingress, 2 MB/s egress per shard, shared among consumers).
Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose:
What it is: A fully managed service for delivering real-time streaming data to destinations like Amazon S3, Amazon Redshift, Amazon OpenSearch Service, Splunk, and generic HTTP endpoints. It automatically scales to match your data throughput and requires no administration.
Use Cases: Loading streaming data into data lakes (S3), data warehouses (Redshift), and analytics tools with minimal effort. It handles batching, compression, and encryption.
Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics:
What it is: The easiest way to process and analyze streaming data in real-time with Apache Flink or standard SQL. It allows you to build sophisticated streaming applications to transform and enrich data, perform real-time aggregations, and derive insights as data arrives.
Use Cases: Real-time anomaly detection, interactive analytics, streaming ETL, and building real-time dashboards.
Amazon Kinesis Video Streams:
What it is: A service that makes it easy to securely stream video from connected devices to AWS for analytics, machine learning (ML), and other processing. It automatically provisions and scales all the necessary infrastructure.
Use Cases: IoT video streaming, smart home security, drone video analytics, and integrating with ML services like Amazon Rekognition.
Understanding Kinesis Pricing Models
Kinesis pricing is "pay-as-you-go," meaning you only pay for what you use, with no upfront costs or minimum fees. However, the billing components vary significantly per service:
1. Kinesis Data Streams (KDS) Pricing:
KDS pricing revolves around shards and data throughput. There are two capacity modes:
Provisioned Capacity Mode:
Shard Hours: You pay for each shard-hour. This is the base cost.
PUT Payload Units: You are charged per million "PUT payload units." Each record ingested is rounded up to the nearest 25 KB. So, a 1 KB record and a 20 KB record both consume one 25 KB payload unit.
Data Retrieval: Standard data retrieval is included in shard hours up to 2MB/s per shard shared among consumers.
Extended Data Retention: Extra cost per shard-hour for retaining data beyond 24 hours, up to 7 days. Beyond 7 days (up to 365 days), it's priced per GB-month.
Enhanced Fan-Out (EFO): An additional cost per consumer-shard-hour for dedicated read throughput (2 MB/s per shard per consumer) and per GB of data retrieved via EFO. This is ideal for multiple, high-throughput consumers.
On-Demand Capacity Mode:
Per GB of Data Written: Simpler billing based on the volume of data ingested (rounded up to the nearest 1 KB per record).
Per GB of Data Read: Charged for the volume of data retrieved (no rounding).
Per Stream Hour: A fixed hourly charge for each stream operating in on-demand mode.
Optional Features: Extended data retention and Enhanced Fan-Out incur additional charges, similar to provisioned mode but with different rates.
Automatic Scaling: KDS automatically scales capacity based on your traffic, doubling the peak write throughput of the previous 30 days.
2. Kinesis Data Firehose Pricing:
Data Ingestion: Charged per GB of data ingested into the delivery stream. Records are rounded up to the nearest 5 KB.
Format Conversion: Optional charge per GB if you convert data (e.g., JSON to Parquet/ORC).
VPC Delivery: Additional cost per GB if delivering data to a private VPC endpoint.
No charges for delivery to destinations, but standard charges for S3 storage, Redshift compute, etc., apply at the destination.
3. Kinesis Data Analytics Pricing:
Kinesis Processing Units (KPUs): Billed hourly per KPU. A KPU is a combination of compute (vCPU), memory, and runtime environment (e.g., Apache Flink).
Running Application Storage: Charged per GB-month for stateful processing features.
Developer/Interactive Mode: Additional KPUs may be charged for interactive development.
4. Kinesis Video Streams Pricing:
Data Ingestion: Charged per GB of video data ingested.
Data Storage: Charged per GB-month for stored video data.
Data Retrieval & Playback: Charged per GB for data retrieved, and additional costs for specific features like HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) or WebRTC streaming minutes.
Cost Optimization Strategies for AWS Kinesis
Optimizing your Kinesis costs requires a deep understanding of your workload and the various pricing components. Here are key strategies:
Choose the Right Kinesis Service:
Firehose for simplicity & delivery: If your primary goal is to load streaming data into a data lake or warehouse without complex real-time processing, Firehose is often the most cost-effective and easiest solution.
KDS for complex processing & multiple consumers: Use Data Streams if you need multiple applications to consume the same data independently, require precise record ordering, or need custom real-time processing logic with Kinesis Data Analytics or custom consumers.
Data Analytics for real-time insights: Use Kinesis Data Analytics when you need to perform real-time aggregations, transformations, or anomaly detection on your streams.
Optimize Kinesis Data Streams (KDS) Capacity Mode:
On-Demand for unpredictable/new workloads: Start with On-Demand if your traffic patterns are unknown, highly spiky, or if you prefer a fully managed, hands-off approach to capacity. It's generally more expensive for predictable, sustained workloads but eliminates throttling risks.
Provisioned for predictable workloads: Once your traffic patterns are stable and predictable, switch to Provisioned mode. It is often significantly cheaper for consistent, high-utilization streams.
Dynamic Switching: For very variable workloads, you can technically switch between Provisioned and On-Demand modes (up to twice every 24 hours) using automation (e.g., Lambda functions) to align with known peak and off-peak periods, maximizing cost savings.
Right-Size Your Shards (Provisioned KDS):
Monitor relentlessly: Use Amazon CloudWatch metrics (IncomingBytes, IncomingRecords, GetRecords.Bytes) to understand your stream's actual throughput.
Reshard dynamically: Continuously evaluate if your current shard count matches your data volume. Scale up (split shards) when throughput needs increase and scale down (merge shards) during low periods to avoid over-provisioning. Automate this with Lambda functions and CloudWatch alarms.
Beware of "Hot Shards": Ensure your partition keys distribute data evenly across shards. If a single key (or a few keys) sends too much data to one shard, that "hot shard" can become a bottleneck and impact performance, potentially requiring more shards than technically necessary for the overall throughput.
Optimize Data Ingestion:
Batching & Aggregation: For KDS, aggregate smaller records into larger batches (up to 1 MB per PutRecord call) before sending them. For Provisioned mode, records are billed in 25KB increments, so aim for record sizes that are multiples of 25KB to avoid wasted capacity. For Firehose, ingestion is billed in 5KB increments.
Pre-process Data: Use AWS Lambda or other processing before ingesting into Kinesis to filter out unnecessary data, reduce record size, or transform data to a more efficient format.
Manage Data Retention:
Default 24 Hours: KDS retains data for 24 hours by default, which is free. Only extend retention (up to 7 days or 365 days) if your downstream applications truly need to re-process historical data or have compliance requirements. Extended retention incurs additional costs.
Long-Term Storage: For archival or long-term analytics, deliver data to cost-effective storage like Amazon S3 via Firehose or a custom KDS consumer, rather than relying on KDS's extended retention.
Smart Consumer Design (KDS):
Enhanced Fan-Out (EFO): Use EFO judiciously. While it provides dedicated throughput and low latency per consumer, it incurs additional per-consumer-shard-hour and data retrieval costs. If you have fewer than three consumers or latency isn't critical, standard (shared) throughput might be sufficient.
Kinesis Client Library (KCL): For custom consumers, use the latest KCL versions (e.g., KCL 3.0) which offer improved load balancing across workers, potentially allowing you to process the same data with fewer compute resources (e.g., EC2 instances or Lambda concurrency).
Leverage Firehose Features:
Compression: Enable data compression (e.g., GZIP, Snappy, ZIP) within Firehose before delivery to S3 or other destinations to save on storage and transfer costs.
Format Conversion: Convert data to columnar formats like Apache Parquet or ORC using Firehose's built-in conversion. This can significantly reduce storage costs in S3 and improve query performance for analytics services like Athena or Redshift Spectrum.
Buffering: Adjust buffer size and buffer interval settings in Firehose to optimize for delivery costs and destination performance, balancing real-time needs with batching efficiency.
Conclusion
AWS Kinesis is an indispensable suite of services for building robust, real-time data streaming architectures. However, its power comes with complexity, especially in pricing. By understanding the unique billing models of each Kinesis service and implementing thoughtful optimization strategies – from choosing the right capacity mode and right-sizing shards to optimizing data ingestion and consumer patterns – you can harness the full potential of real-time data processing on AWS while keeping your cloud costs in check. Continuous monitoring and a proactive approach to resource management will be your best guides on this journey.
0 notes
Text
Cisco Launches Secure Intelligent Network for the AI Era
Cisco launched a new AI-ready secure network architecture with unified management, next-gen low-latency devices, and quantum security, powered by AgenticOps, AI Assistant, and AI Canvas to enable resilient and scalable networks across campus, branch, and industrial environments. Key Points: Meraki/Catalyst, ThousandEyes, and Splunk unified management AgenticOps with a specific LLM: Deep Network Model AI-optimized hardware: C9350/C9610 Smart Switches (51.2Tbps) and 8100-8500 series routers... read more: https://www.turtlesai.com/en/pages-2963/cisco-launches-secure-intelligent-network-for-the-ai-era
0 notes
Text

Red Team vs Blue Team in Cybersecurity: How Offense and Defense Shape Real-World Security
Red Teams simulate real-world cyberattacks to find and exploit security weaknesses before attackers do.
Blue Teams defend against these simulated attacks, monitor systems, and respond to threats in real time.
The goal isn't to "win"—it's to find gaps, improve collaboration, and strengthen the entire security posture.
Modern security practices often involve a Purple Team approach: red and blue teams working together.
Introduction: Why Red vs Blue Still Matters in 2025
If you're in cybersecurity, you've heard the phrase: Red Team vs Blue Team. But in 2025, this classic battle between offense and defense is more relevant than ever. With evolving threats, AI-powered attacks, and ever-growing attack surfaces, organizations can’t afford to guess whether their defenses will hold.
This article unpacks what red and blue teams really do, why their dynamic matters, and how blending them into a Purple Team creates stronger, smarter security operations.
What Is a Red Team?
A Red Team is a group of ethical hackers hired to think and act like real-world adversaries. Their mission? Break into your systems using the same tools, tactics, and procedures as nation-state hackers, ransomware gangs, or cybercriminals.
Core Functions of a Red Team:
Adversary Emulation: Mimic real-world attackers (APT29, FIN7, etc.) using frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK.
Social Engineering: Phishing, vishing, baiting, and even physical intrusion.
Custom Exploits: Develop or modify malware, zero-days, or exploits to test security controls.
Post-Exploitation: Once in, move laterally, escalate privileges, and maintain access.
Real-world insight: In one engagement, a red team gained access to an executive’s email by chaining a spear-phishing attack with MFA fatigue. The blue team didn't detect the intrusion for 19 hours.
What Is a Blue Team?
A Blue Team is the defensive side of cybersecurity. These are your security analysts, incident responders, threat hunters, and SOC operators. Their job is to prevent, detect, and respond to threats in real time.
Core Responsibilities of a Blue Team:
Security Monitoring: Use SIEM tools like Splunk or IBM QRadar to analyze logs and detect anomalies.
Threat Hunting: Proactively search for signs of compromise beyond automated alerts.
Incident Response: Contain, investigate, and recover from breaches using playbooks.
System Hardening: Apply patches, configure firewalls, and reduce the attack surface.
Practical example: A blue team spotted abnormal outbound DNS traffic and traced it to a misconfigured server being used as a command-and-control beacon.
Red Team vs Blue Team: Key Differences (No Table Needed)
Goal:
Red Team: Break in, stay undetected, prove risk.
Blue Team: Stop attackers, contain damage, restore operations.
Mindset:
Red: Creative, offensive, lateral thinking.
Blue: Analytical, defensive, investigative.
Tools:
Red: Cobalt Strike, Metasploit, Burp Suite, custom scripts.
Blue: ELK Stack, EDR platforms (CrowdStrike, SentinelOne), IDS/IPS (Snort, Suricata).
Metrics:
Red: Time to breach, depth of access, number of undetected attack paths.
Blue: Time to detect (MTTD), time to respond (MTTR), alert fidelity.
Why Red vs Blue Teaming Is Critical in 2025
Cyberattacks today aren’t just about malware—they’re about multi-stage, stealthy operations that blend in with normal network traffic. That’s why red vs blue exercises are more important than ever:
Simulate Advanced Threats: From supply chain compromises to zero-day exploitation.
Pressure-Test Defenses: Find blind spots in detection, incident response, and people.
Train Teams Under Stress: Red teams force blue teams to sharpen their real-time response skills.
According to IBM’s 2025 X-Force report, red team simulations led to a 34% improvement in blue team incident response times in organizations that ran quarterly exercises.
Enter the Purple Team: Collaboration Over Competition
Rather than running isolated red-vs-blue battles, many orgs now adopt a Purple Team model—where red and blue teams share findings in real-time.
Benefits of Purple Teaming:
Faster Feedback Loops: Blue teams adjust detections mid-exercise.
Stronger Detections: Red team tactics are turned into new SIEM rules.
Cultural Shift: Moves the org away from blame and toward shared learning.
Want a full breakdown? Read our guide on red team vs blue team
How to Run a Red Team vs Blue Team Exercise (Step-by-Step)
Define Objectives: Are you testing email defenses, privilege escalation, or lateral movement?
Set Rules of Engagement: Define scope, duration, and red team boundaries.
Conduct the Exercise: Red team attacks, blue team defends.
Observe and Record: Use observers or a purple team to track tactics and results.
Debrief: Share findings, metrics, and lessons learned.
Update Controls: Tune detections, fix vulnerabilities, and improve playbooks.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Treating It Like a Game: It's not red vs blue "winning"—it’s about improving.
Skipping the Debrief: Without a debrief, you lose all learning value.
Lack of Realism: Make sure the red team uses realistic attack vectors, not just automated scans.
Blue Team Burnout: Don’t surprise them during mission-critical hours without warning.
FAQs
What’s the main difference between red and blue teams?
Red teams attack. Blue teams defend. One simulates threats; the other stops them.
Can one person be both red and blue?
Yes, especially in small teams. This hybrid approach is common in Purple Teaming.
How often should we run red vs blue simulations?
Quarterly exercises are ideal for most mid to large organizations.
What frameworks support red/blue operations?
MITRE ATT&CK for red team tactics; NIST SP 800-61 for blue team incident response.
Do red teams need to use zero-days?
No. Most attacks succeed using known vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
Is red vs blue the same as penetration testing?
Not exactly. Penetration testing is usually shorter, scoped, and compliance-driven. Red teaming is broader and stealthier.
Conclusion
Red team vs blue team isn’t just cybersecurity theater—it’s essential training for modern threat landscapes. By staging real-world attacks and monitoring real-time defenses, organizations close critical gaps, validate controls, and sharpen both offensive and defensive skill sets.
And when red and blue collaborate instead of compete? You get a purple team that turns chaos into clarity.
0 notes
Text
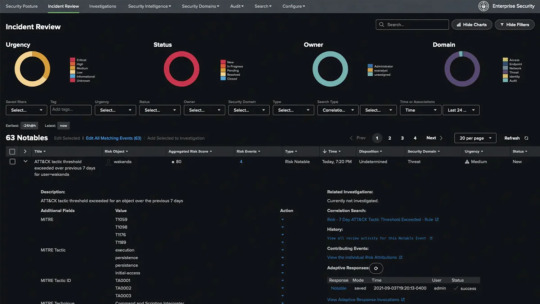
Master Security Operations with Splunk Enterprise Security Training
Are you ready to become a security operations expert? With Splunk Enterprise Security (ES) training, you’ll gain the practical skills and knowledge needed to detect, investigate, and respond to modern cyber threats. At TechshilaMind, our Splunk ES training is designed to launch your career in SOC, threat intelligence, or security analytics roles.
Why Splunk Enterprise Security (ES) Training?
Splunk ES is the industry’s leading SIEM solution, trusted by thousands of organizations for real-time security monitoring and incident response. Whether you’re new to SIEM or already in the security field, Splunk ES training is your gateway to advanced analytics, proactive threat hunting, and streamlined investigations.
Key reasons to enroll in Splunk ES training:
Real-time security skills: Learn how to use dashboards, correlation searches, and risk-based alerting to identify incidents fast.
Hands-on labs: Practice using Splunk ES in a lab environment, mirroring real-world SOC tasks.
Career advancement: Certified professionals are in high demand for security operations, threat detection, and compliance roles.
Certification-focused: Our curriculum prepares you to pass the Splunk Enterprise Security Certified exam on the first try.
What You’ll Learn in Splunk ES Training
Our comprehensive course, based on Splunk’s official syllabus, covers everything you need for success:
Core ES Concepts: Understand features, capabilities, user roles, and how Splunk ES helps security teams prevent, detect, and respond to threats.
Security Monitoring & Incident Investigation: Use security posture dashboards, incident review tools, and workflows to investigate and manage security events.
Risk-Based Alerting: Dive into risk scoring, risk notables, and learn how to leverage Splunk’s risk analysis dashboards for better threat detection.
Assets & Identities: Manage and analyze asset and identity data to enhance context during investigations.
Incident Investigations: Coordinate response with the Investigation Workbench, document analysis, and manage incident timelines.
Security Domain Dashboards: Use domain-specific dashboards to monitor and troubleshoot various security threats in your environment.
User & Web Intelligence: Analyze user activity for insider threats and use web intelligence tools to uncover suspicious network behavior.
Threat & Protocol Intelligence: Leverage Splunk’s threat intelligence framework and protocol analysis dashboards to track, understand, and act on emerging threats.
Who Should Attend?
This training is ideal for:
Security analysts and SOC team members
IT professionals looking to specialize in SIEM or threat intelligence
Anyone preparing for the Splunk Enterprise Security Certified exam
A basic knowledge of Splunk fundamentals (search, dashboards, visualizations) is recommended before joining.
Training Format & Support
Instructor-led sessions (virtual or onsite)
24/7 support and personalized doubt clearing
Career guidance and exam registration assistance
You’ll have access to expert mentors, hands-on labs, and resources tailored to real-world use cases.
Get Started Today
Splunk ES training with TechshilaMind sets you on the fast track to a rewarding cybersecurity career. Ready to level up? Enroll now in Splunk Enterprise Security Certified Training and start mastering the tools top SOC teams trust!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Do I need prior Splunk experience? A: It’s recommended you complete Splunk fundamentals (search, dashboards) before starting ES training.
Q: What kind of support is available? A: You get 24/7 support, live doubt clearing, and ongoing access to learning resources.Q: How is the course delivered? A: Instructor-led (online or onsite) with hands-on labs and real-world case studies.
0 notes
Text
How SIEM Solutions Help You Detect Threats Before They Cause Damage

In an era where cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, frequent, and damaging, the ability to detect and respond to security incidents in real-time is crucial. Traditional security tools alone are no longer sufficient to protect today’s dynamic and distributed IT environments. This is where Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions come into play — acting as the eyes and ears of your cybersecurity infrastructure.
SIEM solutions don't just monitor activity; they intelligently analyze, correlate, and prioritize threats, allowing you to act before they result in severe consequences. Let’s dive into how SIEM solutions help businesses detect threats early — often before they cause any damage — and why they’ve become a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity strategies.
What Is a SIEM Solution?
A SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) system collects and aggregates log data from various sources across an organization’s IT infrastructure — including servers, firewalls, applications, and endpoints. This data is then analyzed in real time using correlation rules and analytics to detect unusual behavior, anomalies, and potential threats.
Unlike standalone antivirus or firewall tools, SIEM solutions provide a centralized and holistic view of your security posture. It’s not just about collecting data — it’s about understanding what the data is telling you and acting on it.
The Growing Importance of Real-Time Threat Detection
Cyber threats don’t wait. From ransomware and insider threats to advanced persistent threats (APTs), bad actors are constantly evolving their tactics. A single undetected intrusion can lead to data breaches, reputational damage, financial losses, and compliance violations.
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, it takes an average of 204 days to detect a breach. That’s more than enough time for attackers to exfiltrate sensitive data or disrupt operations.
SIEM solutions aim to drastically reduce this detection window, enabling organizations to identify and neutralize threats quickly — sometimes within seconds or minutes.
1. Centralized Data Aggregation and Correlation
The first step in early threat detection is visibility. SIEM solutions consolidate logs and events from various systems — including on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments — into one centralized dashboard. This eliminates silos and provides full-spectrum visibility across your entire network.
But visibility alone isn't enough. SIEMs apply correlation rules to connect seemingly unrelated events. For example:
A failed login attempt from a foreign IP followed by a successful login.
Unusual file access outside of business hours.
High volumes of data are being transferred unexpectedly.
These individual events might seem harmless in isolation, but when correlated, they form the footprint of a potential breach — and the SIEM solution will flag it.
2. Real-Time Alerts and Automated Response
SIEM platforms continuously monitor for deviations from normal behavior and trigger real-time alerts when threats are detected. These alerts are not just based on predefined rules but also on behavioral baselines and machine learning models.
For example, if an employee suddenly starts downloading gigabytes of data to a personal device — something they’ve never done before — the SIEM system can immediately flag this as suspicious.
Advanced SIEM systems integrate with SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) platforms to automate incident response — isolating users, blocking IPs, or even initiating password resets without human intervention. This rapid response can contain a threat before it escalates.
3. Behavioral Analytics and Anomaly Detection
One of the most powerful features of modern SIEM solutions is User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA). This uses machine learning to establish normal activity patterns for users, devices, and applications — and then detects anomalies.
For instance:
A user who typically logs in from Dubai between 9 AM and 5 PM is now accessing systems from Russia at 2 AM.
A service account that normally accesses only one server is now connecting to multiple servers unexpectedly.
These anomalies are often early indicators of compromised credentials, insider threats, or lateral movement within your network.
4. Threat Intelligence Integration
SIEMs can be supercharged with threat intelligence feeds that provide real-time information about known malicious IPs, domains, file hashes, and attack signatures. When your SIEM ingests this data, it can:
Instantly recognize known malware signatures.
Detect traffic going to or coming from blacklisted IP addresses.
Identify phishing attempts or command-and-control (C2) communication.
By integrating threat intelligence, SIEMs not only detect what’s happening internally but also connect it with what's happening in the broader threat landscape.
5. Compliance and Forensic Capabilities
Even if a threat doesn’t cause immediate damage, compliance violations can. SIEM solutions help organizations meet regulatory standards like GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and PCI DSS by maintaining detailed logs and audit trails.
In the event of a breach or incident, SIEM logs can be used to:
Conduct forensic investigations.
Pinpoint the source and scope of the attack.
Generate reports for auditors and stakeholders.
Having this documentation readily available can make the difference between a smooth audit and a regulatory fine.
6. Cloud and Hybrid Infrastructure Monitoring
As more organizations move to the cloud, traditional perimeter-based security tools fall short. SIEM solutions offer native integrations with major cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, allowing for complete visibility into:
Cloud-based authentication and user behavior.
API access and misconfigurations.
Unusual traffic patterns across virtual machines.
This ensures that your cloud and hybrid environments are just as protected as your on-premise systems.
7. Scalability and Customization
Whether you're a small business or a large enterprise, modern SIEM platforms offer scalable solutions that can grow with your organization. They can be customized to prioritize alerts based on your business's unique risk profile, industry, or compliance requirements.
For instance, a healthcare company might focus on detecting unauthorized access to patient data, while a fintech firm might prioritize fraud detection and transaction anomalies.
Final Thoughts: Proactive Defense Starts with SIEM
Cybersecurity is no longer just about defending the perimeter — it’s about knowing what’s happening inside your network at all times. SIEM solutions are your early-warning system, continuously scanning, learning, and alerting you to threats before they become full-blown incidents.
For organizations that value uptime, data integrity, customer trust, and compliance, investing in a modern SIEM solution is not just a smart move — it’s an essential one.
#splunk services#microsoft azure sentinel#Splunk solutions#splunk enterprise#splunk security#Splunk consultant#microsoft sentinel#SIEM solutions#Sentinel
0 notes
Text
Top WebApp Security Checklist for Businesses in the USA (2025)

In today’s digital-first world, web applications are the backbone of most business operations—from e-commerce to customer portals, CRMs, and more. However, with increasing cyber threats, securing your web applications is not optional; it's critical. Especially for businesses operating in the USA, where data breaches can lead to legal penalties, loss of customer trust, and significant financial setbacks.
This guide outlines a comprehensive WebApp Security Checklist tailored for businesses in the USA to ensure robust protection and compliance with modern security standards.
1. Use HTTPS with a Valid SSL Certificate
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificates are fundamental. HTTPS encrypts the data exchanged between the user and your application, ensuring it remains private.
Purchase and install a trusted SSL certificate.
Redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS.
Regularly renew and monitor the validity of your SSL certificate.
Fact: Google flags HTTP sites as “Not Secure,” impacting SEO and user trust.
2. Implement Strong Authentication & Access Controls

Weak login systems are a hacker’s playground. Use:
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add extra layers beyond passwords.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Ensure users only access what’s necessary.
Session Management: Set session expiration limits and auto-logout on inactivity.
Bonus Tip: Use OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect for secure federated authentication.
3. Sanitize and Validate All User Inputs
Most web attacks like SQL Injection and XSS stem from unsanitized user inputs. To prevent this:
Sanitize inputs on both client and server sides.
Use prepared statements and parameterized queries.
Escape special characters in output to prevent script injections.
Best Practice: Never trust user inputs — even from authenticated users.
4. Regularly Update Dependencies and Frameworks
Outdated plugins, libraries, or frameworks can be exploited easily.
Use dependency management tools like npm audit, pip-audit, or OWASP Dependency-Check.
Enable automatic updates where possible.
Avoid deprecated plugins or unsupported software.
Real Example: The infamous Log4j vulnerability in 2021 exposed millions of apps worldwide.
5. Conduct Regular Vulnerability Scans and Penetration Testing
Security is not a one-time fix. It's a continuous process.
Schedule monthly or quarterly vulnerability scans.
Hire ethical hackers for real-world pen testing.
Fix discovered issues immediately and re-test.
🔍 Tools to Use: Nessus, Burp Suite, OWASP ZAP.
6. Implement Secure APIs

With APIs powering most modern web apps, they’re a common attack vector.
Authenticate API users with tokens (JWT, OAuth).
Rate-limit API calls to avoid abuse.
Use API gateways for logging and security enforcement.
Extra Tip: Never expose sensitive internal APIs to the public internet.
7. Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit
Whether storing user passwords, payment info, or PII — encryption is essential.
Encrypt sensitive data in the database using AES-256 or better.
Avoid storing passwords in plain text — use hashing algorithms like bcrypt.
Always encrypt data transfers via HTTPS or secure VPN tunnels.
Compliance: Required under data protection laws like HIPAA, CCPA, and PCI-DSS.
8. Monitor Logs & Set Up Intrusion Detection
Monitoring can alert you to threats in real-time.
Use centralized logging systems like ELK Stack or Splunk.
Implement intrusion detection systems (IDS) like Snort or OSSEC.
Set up alerts for unusual activities like multiple failed logins.
Tip: Review logs weekly and set up daily summaries for admins.
9. Backup Regularly & Prepare a Disaster Recovery Plan
Cyberattacks like ransomware can lock you out of your app.
Schedule automatic daily backups.
Store backups offsite or in the cloud (with encryption).
Test your disaster recovery plan quarterly.
Pro Tip: Use versioned backups to roll back only the infected data.
10. Comply with Data Privacy Regulations
For businesses in the USA, compliance isn't just good practice — it's the law.
If you handle health data → HIPAA compliance is mandatory.
Selling to California residents → comply with CCPA.
Accepting payments? → follow PCI-DSS requirements.
Reminder: Non-compliance can lead to heavy penalties and lawsuits.
11. Educate Your Team
The weakest link is often human error.
Train employees on phishing and social engineering attacks.
Enforce strong password policies.
Run annual cybersecurity awareness programs.
Result: A well-trained team is your first line of defense.
12. Use Web Application Firewalls (WAFs)

WAFs provide an extra layer of protection.
Block malicious traffic before it reaches your server.
Protect against DDoS, brute force, and zero-day attacks.
Use cloud-based WAFs like Cloudflare, AWS WAF, or Imperva.
Bonus: Easily deployable and scalable with your infrastructure.
Conclusion
For U.S.-based businesses, web application security should be a strategic priority — not a checkbox. With cyberattacks growing in complexity and volume, following a thorough security checklist is vital to protect your data, users, and brand reputation.
At the end of the day, your web application is only as secure as its weakest link. Make sure there isn’t one.
Ready to Secure Your WebApp?
If you're looking for expert support to secure or build a robust, secure web application, WeeTech Solution is here to help. Get in touch with our development and cybersecurity team today!
0 notes
Text
How the DarkShield IRI Tool Automates Sensitive Data Classification and Masking
Keeping private data safe is a big deal. Today, businesses deal with huge amounts of personal data. This includes names, phone numbers, credit card details, and more. If that data ends up in the wrong hands, it can lead to serious problems. That’s where the IRI DarkShield comes in.
This powerful tool helps teams find and protect personal information across different types of files and databases. You don’t need to be a tech expert to use it, but it helps to have some IT knowledge.
What Makes IRI DarkShield Unique?
The IRI DarkShield tool is designed to work with all kinds of data. Whether the data is structured, like a database, or unstructured, like a PDF file or image, it can still find and protect it. It does this using smart search methods and rules that you can set up in advance.
You can even search and mask data across entire networks, cloud storage, or file systems. This means you don’t have to search files one by one. Everything is centralized and automatic.
Getting Started with IRI Workbench
The tool uses a program called IRI Workbench, which is easy to work with. It looks and feels like many other computer programs, so you won’t feel lost. With IRI Workbench, you can:
Connect to your data
Choose what types of private data you want to find
Pick how you want to hide it (for example, by encrypting it)
This makes the job easier and faster. One feature that stands out is that everything runs on your own system. So you don’t need to worry about uploading sensitive data to outside websites.
Setting Up Data Classes and Rules
Before you start, you tell the tool what kinds of data to look for. These are called “data classes.” For example, you might want to find phone numbers or Social Security numbers. Then, you link each type of data with a way to find it and a way to hide it.
Once you set this up, you don’t need to do it again. The data masking tool will always know how to find and protect those details.
How DarkShield Finds Sensitive Information
The tool is very smart when it comes to searching. It can look for specific patterns (like a phone number format) or use tools like machine learning models to detect personal data. It even works with images and PDFs.
After searching, it saves the results in a log. You can use this log to see what was found or send it to another program to take action, like hiding the data right away.
Masking Data in Files
With just a few clicks, you can search and hide sensitive data in all sorts of files. This includes text, Word, Excel, JSON, XML, and even medical and image files. The best part? It works both on your computer and in the cloud.
This is where IRI DarkShield really shines. You pick the files, and the tool uses your earlier rules to search and mask sensitive information. You can even set filters so it only checks certain files, which saves time.
Working with NoSQL and Relational Databases
DarkShield isn’t just for files. It also works with many types of databases. These include NoSQL databases like MongoDB and Elasticsearch, as well as regular databases like Oracle and MySQL.
In both cases, the tool uses the same steps. You choose what to look for and how to hide it. Then, you let the program do the work. Everything is automatic once your job is set up.
Command Line and API Use
Even though the Workbench makes things easy, the tool also works behind the scenes. Developers can use the command line or API to run jobs without opening the software. This is perfect for teams that want to schedule tasks or connect the tool with other systems.
These options give your team more power and flexibility to protect data without slowing down other work.
Keeping Track with Audit Logs
Every time the tool runs a job, it creates reports and logs. These logs show what was found, what was masked, who did it, and when. They can also be viewed on dashboards or sent to other tools like Splunk.
This helps companies stay on top of their data protection efforts and show that they are meeting privacy rules.
FAQs
Q1: What is IRI DarkShield used for? IRI DarkShield is used to find and protect private data, like names and credit card numbers, in files and databases.
Q2: Can I use it even if I don’t know how to code? Yes. If you have some IT knowledge, you can use the IRI Workbench to set up and manage everything without writing code.
Q3: Does it work with images and PDFs? Yes. It can search and mask data in many types of files, including images and documents.
Q4: Can I use it with cloud storage? Yes. You can connect it to cloud folders like OneDrive, SharePoint, Google Cloud, and more.
Q5: Is IRI DarkShield a web app? No. Everything runs on your own system, so your data stays safe within your control.
Final Thoughts
IRI DarkShield is a smart and powerful way to protect sensitive information. It helps companies meet data privacy rules without slowing down their work. With easy setup, flexible options, and strong security, it’s a great choice for any business that takes data protection seriously.

0 notes
Text
Cybersecurity training for entry-level roles
Kickstart Your Cybersecurity Career with SoftLucid
Introduction In today’s digitally driven world, organizations of every size face constant threats from cyberattacks. For aspiring IT professionals, building a solid foundation in cybersecurity opens the door to high-demand, well-paid roles. At SoftLucid, our Cybersecurity Training for Entry-Level Roles is designed to equip you with the practical skills, industry best practices, and hands-on experience you need to stand out from day one.
Why Choose Entry-Level Cybersecurity Training?
Rapidly Growing Job Market
The global cybersecurity workforce shortage means organizations are actively hiring junior analysts, incident responders, and security auditors.
Entry-level roles often come with strong starting salaries and clear pathways to advancement.
Practical, Project-Based Learning
Theory only gets you so far. Our labs let you practice vulnerability assessments, internal network scans, and simulated incident response in a safe, virtual environment.
You’ll complete real-world projects—like securing a demo web application or conducting a phishing-awareness campaign—that showcase your skills to employers.
Industry-Recognized Tools & Techniques
Learn to configure and use essential tools such as Wireshark, Nmap, Metasploit, and Splunk.
Understand frameworks and standards like NIST, ISO 27001, and the CIS Controls, so you can align your work with corporate and regulatory requirements.
Course Highlights
Fundamentals of Network Security: TCP/IP basics, firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection/prevention systems.
Risk Management & Compliance: Identifying threats, performing risk assessments, and mapping to compliance standards.
Endpoint & Cloud Security: Securing workstations, servers, and cloud-hosted environments against malware and unauthorized access.
Ethical Hacking Essentials: Penetration testing methodologies, reporting, and remediation strategies.
Incident Response & Forensics: Establishing response plans, collecting evidence, and preserving chain-of-custody.
Your SoftLucid Advantage
Live Virtual Classes: Interactive sessions with expert instructors—ask questions in real time and learn from their industry insights.
1:1 Career Coaching: Resume reviews, mock interviews, and personalized job-search strategies to help you land your first cybersecurity role.
Community & Peer Networking: Join fellow learners in group projects, discussion forums, and alumni events to build your professional network.
Lifetime Access: Revisit course materials anytime you need a refresher or to prepare for advanced certifications.
0 notes
Text
How Can Cybersecurity Training Secure Your Career Path?
Learn how to protect digital systems with expert cybersecurity skills and hands-on training. As our world grows more digital, cyber threats are becoming more common and dangerous. Every day, businesses face risks like hacking, data breaches, and online fraud. To protect digital information, companies need skilled professionals with the right knowledge. That’s where Cybersecurity Training plays a vital role.
Cybersecurity is no longer just an IT concern—it’s a top business priority. Trained professionals are essential to keeping sensitive data and systems safe. Whether you’re a student, IT professional, or career switcher, cybersecurity skills can open the door to exciting job opportunities.
Why Cybersecurity Training Is Crucial Today
With increasing digital threats, organizations are prioritizing strong security systems and trained staff. Hackers use advanced tools and techniques to attack, making prevention a challenge. Without proper security, businesses can lose money, data, and trust.
Cybersecurity Training teaches you how to identify threats, protect systems, and respond to incidents. These skills are in demand across many industries, including healthcare, banking, retail, and education.
What You Learn in Cybersecurity Training
Training usually begins with basic concepts like internet security, firewalls, and network protection. You’ll learn about malware, phishing, and ransomware attacks—and how to stop them.
Advanced modules cover encryption, ethical hacking, and incident response. You’ll also learn about security policies and how to apply legal compliance standards. Most courses include hands-on practice and real-world scenarios.
Common Tools and Techniques Covered
In training, you will use industry tools like Wireshark, Splunk, and Metasploit. These help you detect threats and perform security analysis. You’ll also learn how to set up firewalls, monitor traffic, and run vulnerability scans.
By mastering these tools, you’ll be ready to work in real security environments.
Who Can Benefit from Cybersecurity Training?
Cybersecurity skills are valuable to both beginners and experienced professionals. Students, IT workers, and job seekers can use this training to launch or grow their careers.
Even business owners and non-tech professionals benefit by learning how to protect their data. The demand for skilled cybersecurity talent makes this training a smart investment for your future.
Training Options Available
Cybersecurity courses are available online, offline, and in hybrid formats. Online training offers flexibility, while classroom programs give more interaction. You can choose full-time, part-time, or weekend options based on your schedule.
Look for programs that offer certifications like CompTIA Security+ or CEH to boost your resume.
Conclusion
The rise of cybercrime makes cybersecurity one of the most important skills today. By enrolling in Cybersecurity Training, you gain the tools to fight digital threats and secure valuable information.
This training helps you build a meaningful and future-ready career in tech. Don’t wait—start your cybersecurity journey now and step into a secure, high-demand field.
0 notes
Text
The Big Data Security Market Size, Share | CAGR 17.3% during 2025-2032

The global big data security market size was valued at USD 23.68 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 83.95 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 17.3% during the forecast period (2025–2032). The increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, growing regulatory compliance requirements, and rapid digital transformation across sectors are driving significant investment in big data protection.
Key Market Highlights
2024 Global Market Size: USD 23.68 billion
2025 Forecast Start Point: USD 27.40 billion
2032 Global Market Size: USD 83.95 billion
CAGR (2025–2032): 17.3%
Market Outlook: Rising demand for security solutions that protect structured and unstructured big data across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Key Players in the Global Big Data Security Market:
IBM Corporation
Oracle Corporation
McAfee LLC
Microsoft Corporation
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Symantec (Broadcom Inc.)
Cloudera Inc.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
Check Point Software Technologies
Imperva
Palo Alto Networks
Talend
Splunk Inc.
Request for Free Sample Reports:
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers
Explosion in data volumes across enterprises, cloud platforms, and edge devices
Stringent compliance mandates (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA)
Increased adoption of cloud and hybrid cloud models needing secure data movement and storage
Surge in cyberattacks targeting high-value data sets like PII and financial records
Growing implementation of AI/ML for security analytics and anomaly detection
Key Opportunities:
Development of AI-powered big data threat detection platforms
Integration of big data security with DevSecOps and data governance models
Expansion of managed security services (MSS) in data-heavy verticals
Customized solutions for healthcare, BFSI, retail, and energy sectors
Opportunities in edge and IoT security, especially for real-time big data use cases
Emerging Trends:
Adoption of AI and deep learning for automated data threat mitigation
Rise of unified data governance frameworks integrating security and compliance
Shift toward Zero Trust architectures for granular access control
Demand for real-time risk scoring and behavioral analytics
Cloud-native security solutions for containerized and serverless environments
Technology & Application Scope:
Core Solutions: Encryption, tokenization, firewall, antivirus/antimalware, SIEM, IAM, and data loss prevention
Deployment Models: On-premise, cloud-based, and hybrid
Data Types Secured: Personal Identifiable Information (PII), financial transactions, operational data, sensor data, unstructured business records
Industries Served: BFSI, government, healthcare, retail, telecom, manufacturing, and energy
Applications: Real-time risk analytics, compliance auditing, insider threat detection, and secure cloud analytics
Speak to analysts: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/enquiry/speak-to-analyst/big-data-security-market-109528
Recent Developments:
March 2024 – IBM launched an updated Guardium Data Protection for Big Data, optimized for hybrid multicloud environments, offering AI-based anomaly detection and advanced auditing features.
September 2023 – Palo Alto Networks integrated advanced threat intelligence with big data processing platforms to deliver improved data security visibility and predictive breach detection.
December 2023 – Cloudera announced strategic collaboration with AWS to deliver secure big data analytics-as-a-service tailored for heavily regulated industries.
Conclusion:
The global big data security market is poised for substantial growth as organizations face mounting pressure to secure exponentially growing data ecosystems. Investments are accelerating across technologies that not only protect data but also ensure visibility, regulatory compliance, and resiliency in digital-first environments.
Vendors that offer scalable, cloud-native, and AI-enhanced big data security platforms will be best positioned to lead the market in the coming decade.
#Big Data Security Market Share#Big Data Security Market Size#Big Data Security Market Industry#Big Data Security Market Analysis#Big Data Security Market Driver#Big Data Security Market Research#Big Data Security Market Growth
0 notes