Text
Something I figured out when writing Mandatory Family Reunion is that you can hit a roadblock because you can’t figure out how a character would react, and sometimes the answer is the character doesn’t know either. People are complicated as hell and get confused and contradictory. One character I couldn’t untangle how he’d respond to a situation, and it was because he’d accomplished his life goal only for it to not be the happy ending he expect. He had extremely contradictory feelings about his results and no plan for what happened after he succeeded. I didn’t know what to write because the character himself had no idea what to do. So his character arc became trying to figure out what he wanted and find a new purpose in life.
After a chapter that was somewhere between an emotional rollercoaster and train wreck, I couldn’t figure out the emotions of a different character. I kept trying to force different reactions, and I hated all of them because it didn’t feel right. For some reason I couldn’t figure out how he was feeling. Simple answer: he wasn’t. I realized the character was despondent, shutting down as a coping mechanism after the emotional whirlwind of the chapter. When I allowed him that reaction, the emotional flow of the piece made more sense and the chapter I struggled with for months became much easier to finish.
There can be a lot of reasons why it’s hard to figure out a character’s response/feelings. Might be there’s too much whiplash between starkly different emotions, or there isn’t enough context on their perspective/backstory/etc for the response to make sense, could clash with the tone, on and on etc etc. But it might also be because the character doesn’t know either, and that can also be really interesting to write. Good luck out there!
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
What No One Tells you about Writing #3
Opening this up to writing as a whole, because it turns out I have a lot more to say!
Part 1
Part 2
1. You don’t fall in love with your characters immediately
But when you do, it’s a hit of serotonin like no other. I’d been writing a tight cast of characters for my sci-fi series since 2016 and switched over in a bout of writer’s block this year to my new fantasy book. I made it about ⅓ through writing the book going through the motions, unable to visualize what these new characters look like, sound like, or would behave like without a ‘camera’ on them.
Then, all of a sudden, I opened my document to keep on chugging with the first draft, and it clicked. They were no longer faceless elements of my plot, they were my characters and I was excited to see what they could accomplish, rooting for them to succeed. Sometimes, it takes a while, but it does come.
2. Sometimes a smaller edit is better than a massive rewrite
Unless you’re changing the trajectory of your entire plot, or a character’s arc really is unrecoverable, sometimes even a single line of dialogue, a single paragraph of introspection, or a quick exchange between two characters can change everything. If something isn’t working, or your beta readers consistently aren’t jiving with a character you yourself love, try taking a step back, looking at who they are as a person, and boil down what your feedback is telling you and it might demand a simpler fix than you expect.
Tiny details inserted at the right moment can move mountains. Fan theories stand on the backs of these minutiae. One sentence can turn a platonic relationship romantic. One sentence can unravel a fair and just argument. One sentence can fill or open a massive plot hole.
3. Outline? What outline?
Not every book demands weeks upon weeks of prep and worldbuilding. I would argue that jumping right in with only a vague direction in mind gives you a massive advantage: You can’t infodump research you haven’t done. Exposition is forced to come as the plot demands it, because you haven’t designed it yet.
Not every story is simple and straightforward, but even penning the first draft with your vague plan, *then* going back and adding in deeper worldbuilding elements, more thematic details, richer character development, can get you over the writer’s block hurdle and make it far less intimidating to just shut up and write the book.
4. It’s okay to let your characters take the wheel
I’ve seen writing advice that chastises authors who let their characters run wild, off the plan the story has for them. Yeah, doing this can harm your pacing and muddy a strong and consistent arc, but refusing to leave the box of your outline greatly limits your creativity. I do this particularly when writing romantic relationships (and end up like Captain Crunch going Oops! All Gays!).
Did I plan for these two to get together? No, it just happened organically as I wrote them talking, getting closer, getting to know each other better in the circumstances they find themselves in. Was this character meant to be gay? Well, he wasn’t meant to be straight, but you know what, he’d work really well with this other boy over here. None of that would have happened if I was bound and determined to follow my original plan, because my original plan didn’t account for how the story that I want to tell evolves. You aren’t clairvoyant—it’s okay if it didn’t end up where you thought it would.
5. Fight. Scenes. Suck.
Which is crazy because I love fantasy and sci-fi, the actiony-est genres. Some authors love battle scenes and fistfights. It comes naturally to them and I will forever be jealous. I hate fight scenes. I hate blocking and choreographing them. I hate how it doesn’t read like I’m watching a movie. I hate how it could take me hours to write a scene I can read in 5 minutes. I hate that there’s no way around it except to just not write them, or put in the elbow grease and practice.
Whatever your writing kryptonite is, don’t be too hard on yourself. It won’t ever replicate the movie in your head, but our audience isn’t privy to that movie and will be none the wiser of how this didn’t fit your expectations, because it’s probably awesome on its own. It could be a fight scene, sex scene, epic battle, cavalry charge, courtroom argument, car chase—whatever. Be patient, and kind to yourself and it will all come together.
6. Write the scenes you want to write first
And then be prepared to never use them. It can be mighty difficult working backwards from a climax and figuring out how to write the story around it, but if you’re sitting at your laptop staring at your cursor and watching it blink, stuck on a tedious moment that’s necessary but frustrating, go write something exciting. Even if that amazing scene ends up no longer working in the book your story becomes, you still get practice by writing it. Particularly if you hate beginnings or the pressure of a perfect first page is too high, you’re allowed to write any other moment in the book first.
And with that, be prepared to kill your darlings. Not your characters, I mean that one badass line of dialogue living rent free in your head. That epic monologue. That whump scenario for your favorite character. Sometimes it just doesn’t work out anymore, but even if it ends up in the trash, you can always salvage something from it, even if that’s only the knowledge of what not to do in the future.
7. “This is clearly an author insert.” … Yes. It is. Point?
No one likes Mary Sues, because a character who doesn’t struggle or learn to get everything they want in life is uncompelling. The most flagrant author inserts I see aren’t Mary Sues, they’re nerdy, awkward, boring white guys whose world changes to fit their perspective, instead of the other way around—they don’t have anything to say. I’m not the intended audience to relate to these characters and I accept that, but I don’t empathize with the so-called “strong female character” who also doesn’t have flaws or an arc either.
A good author insert? When the author gives their characters pieces of themselves. When the “author insert” struggles and learns and grows and it’s a therapeutic experience just writing these characters thrown into such horrible situations. They feel human when they’re given pieces of a human’s soul. They have real human flaws and idiosyncrasies. I don’t care if the author wrote themselves as the protagonist. I care that this protagonist is entertaining. So if you want to make yourself the hero of your book, go for it! But make sure you look in the mirror and write in your flaws, as much as your strengths.
537 notes
·
View notes
Text
how to write creepy stories
over describe things
under describe things
short sentences in rapid succession build tension
single sentence paragraphs build dread
uncanny valley = things that aren't normal almost getting it right
third person limited view
limited expressions
rot, mold, damage, age, static, flickering, espsecially in places it shouldn't be
limited sights for your mc - blindness, darkness, fog
being alone - the more people there are, the less scary it is
intimate knowledge, but only on one side
your reader's imagination will scare them more than anything you could ever write. you don't have to offer a perfectly concrete explanation for everything at the end. in fact, doing so may detract from your story.
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
im putting my entire soul and bussy behind the following writing advice:
learn about a bunch of different ways that stories are traditionally structured (optional but i'll always encourage it)
eventually have it strike you like lightning from the heavens that traditional plot structures all follow the character development of the protagonist, which means that
it is absolutely possible to pace your plot in a way that strays from traditional storytelling but still feels like a natural and satisfying progression for your readers, as long as you structure it roughly along the path of whatever the fuck is happening with your protagonist
sounds like a small obvious thing but this can save you from a lot of headaches if you've been struggling to cram your plot into a traditional model where it might not even belong in the first place. try to isolate the character development of your protagonist, and make that your primary guide instead
#writeblr#writing advice#story planning#plot structure#kinda goes unsaid that you also need good character development but thats another beast lol#idk. this has made the whole plotting thing a lot easier on me so
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
"A story doesn't need a theme in order to be good" I'm only saying this once but a theme isn't some secret coded message an author weaves into a piece so that your English teacher can talk about Death or Family. A theme is a summary of an idea in the work. If the story is "Susan went grocery shopping and saw a weird bird" then it might have themes like 'birds don't belong in grocery stores' or 'nature is interesting and worth paying attention to' or 'small things can be worth hearing about.' Those could be the themes of the work. It doesn't matter if the author intended them or not, because reading is collaborative and the text gets its meaning from the reader (this is what "death of the author" means).
Every work has themes in it, and not just the ones your teachers made you read in high school. Stories that are bad or clearly not intended to have deep messages still have themes. It is inherent in being a story. All stories have themes, even if those themes are shallow, because stories are sentences connected together for the purpose of expressing ideas, and ideas are all that themes are.
29K notes
·
View notes
Text
Questions I Ask My Beta Readers
"Did you like it?" just doesn't cut it when you're trying to get useful feedback, so here's some questions that get your reader really thinking about your work:
What are your general impressions after reading? How did you feel when the book ended?
(For fantasy/sci-fi) What did you find most confusing about the world? What did you find the most interesting? What do you want to know more about?
Were there any scenes that broke your suspension of disbelief? Which ones? Why?
Which chapters were the hardest to get through? Did you find yourself skimming the text at any point in the story?
Which character was your favorite? Which was your least favorite? Why? (Note that this question is best when asking multiple readers. If one person really dislikes a character, it could be personal preference. If multiple people can't stand a character for the same reason.... well, that's a problem you need to fix. Unless, of course, you want your readers to hate that character. Just make sure that their hatred enhances the reading experience instead of ruining it).
Did you get any characters confused or mixed up? If so, did this make the story hard to follow?
What was the most suspenseful moment in the book? What was your favorite moment of the story? What was your least favorite moment in the story? Why?
Which setting in the book was clearest to you as you were reading it? Which setting was the most difficult to envision?
Did you feel there was a lot of info dumping at any point? If so, where?
How do you feel about the plot? Were there any parts that confused you or seemed nonsensical/ illogical?
Did you feel any part of the story was predictable? Do you have any predictions for the next book(s)? If so, what are they? (Again, another question that's best when asking multiple readers. Be aware of your audience here. Some people, especially those who read a lot, are really good at predicting where stories are going to go. If those people are able to guess what happens next, that might actually be a good thing, because it could indicate that your story is progressing logically. Too much predictability is a problem, but a little isn't bad. This question is just to make sure the plot twists/progression aren't painfully obvious to most readers).
What plot holes did you find in the story so far?
Were you invested in the story? If so, at what point did you become invested? Did you lose this interest at any point? (The second point here is really good for determining whether you have a slow beginning. Sometimes readers might really like your story overall, but would not have gotten past the first few chapters if they were reading it for fun instead of as a favor for you. This happened to me last time I asked someone to read my work, and it made it clear how much of the beginning I needed to rewrite entirely).
Any other questions or comments?
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Literally cannot emphasize enough that my #1 writing advice is to stop being afraid. Stop being afraid of sounding too cringe, or too stupid, or too horrifying, or too horny, or too weird, or too much, or too little, or too you. You need to put your entire pussy into your art. Sure, it won't be to everyone's tastes, but if you keep yourself to the blandest tamest safest roads possible you will be of no one's tastes, not even yours.
64K notes
·
View notes
Text
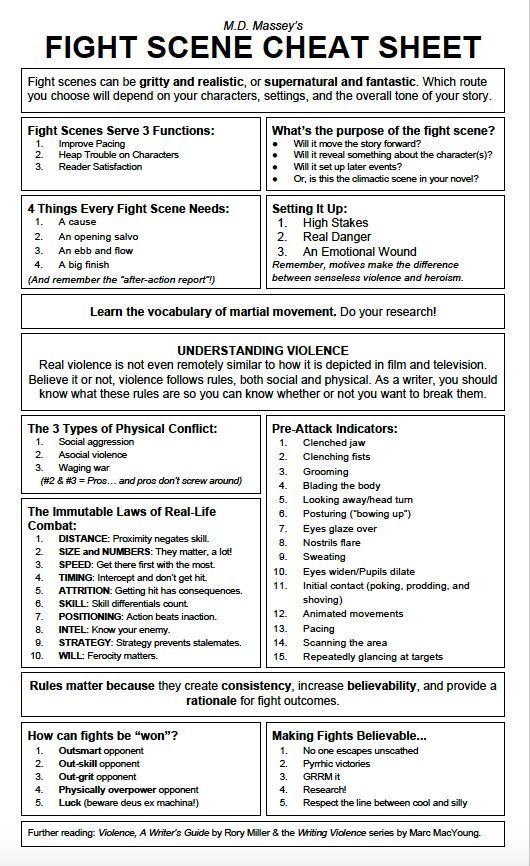
Some basic things to consider when writing the aftermath of a (sudden) fight.
Your character over the next few hours or days will find new marks, wounds, etc they didn't know they had due to adrenaline blocking out the actual moment. They may not realize/remember where they've been struck.
Your character may struggle to recall the fight or what they did during the fight due to adrenaline, again.
The emotional turmoil is usually much more prevalent/important right after the fight and the hours afterward than the actual physical aspect of what happened. Is your character feeling scared, enraged, betrayed, satisfied, bloodthirsty, vindicated? Adrenaline can bring out some pretty raw and intense displays of emotion, even in someone who doesn't often show emotion. It can make someone's mask break and their bottled frustrations spill over.
The extent of the pain and injuries may not settle/become apparent until the next day. The second and third day post-fight is often the worst for aching and pain. They'll have difficulty moving and be incredibly slowed down/limited. Of course, this depends on the severity of the fight and the injuries received. Someone who was punched twice in the head and once in the arm will feel differently from someone who was slammed into the floor.
Continuing off the last point, how does your character feel about their injuries now that the adrenaline has worn off and they can think about them/feel them clearly? Do they hate looking at them or are they constantly prodding at the injuries and looking them over? How do they feel about the fight in general and what is their perspective about it since the intense, immediate emotion has tapered off?
Do not underestimate how long injuries can/will last. A lump/bruise can last for over a month, and physical pain from said bruise can last for over a week. Keep in mind that the type of physical pain even for the same injury will change over time. Of course this can vary if your character has a naturally quicker or slower healing process.
Of course, with all writing advice, take your story/scene and characters into consideration before/when using it! The fight between a character who is a professional boxer and fighting another professional will differ from somebody who got into a petty fist-fight with their friend or a stranger. This advice was made with spontaneous fights in mind like the latter example.
611 notes
·
View notes
Text
I hate to say this, and like, rain on everyone’s parade, but after scrolling past three posts about it on a writing tag …
If you are looking up synonyms to exchange words out in your story with the purpose of sounding smarter, more sophisticated, or complicated to your reader, you are probably abusing the thesaurus.
Now, if you *want* to do this, I mean, you can write whatever or however you want! But I just want you to know that this is frowned upon if you are trying to write at a professional level.
I have an old article on this somewhere …



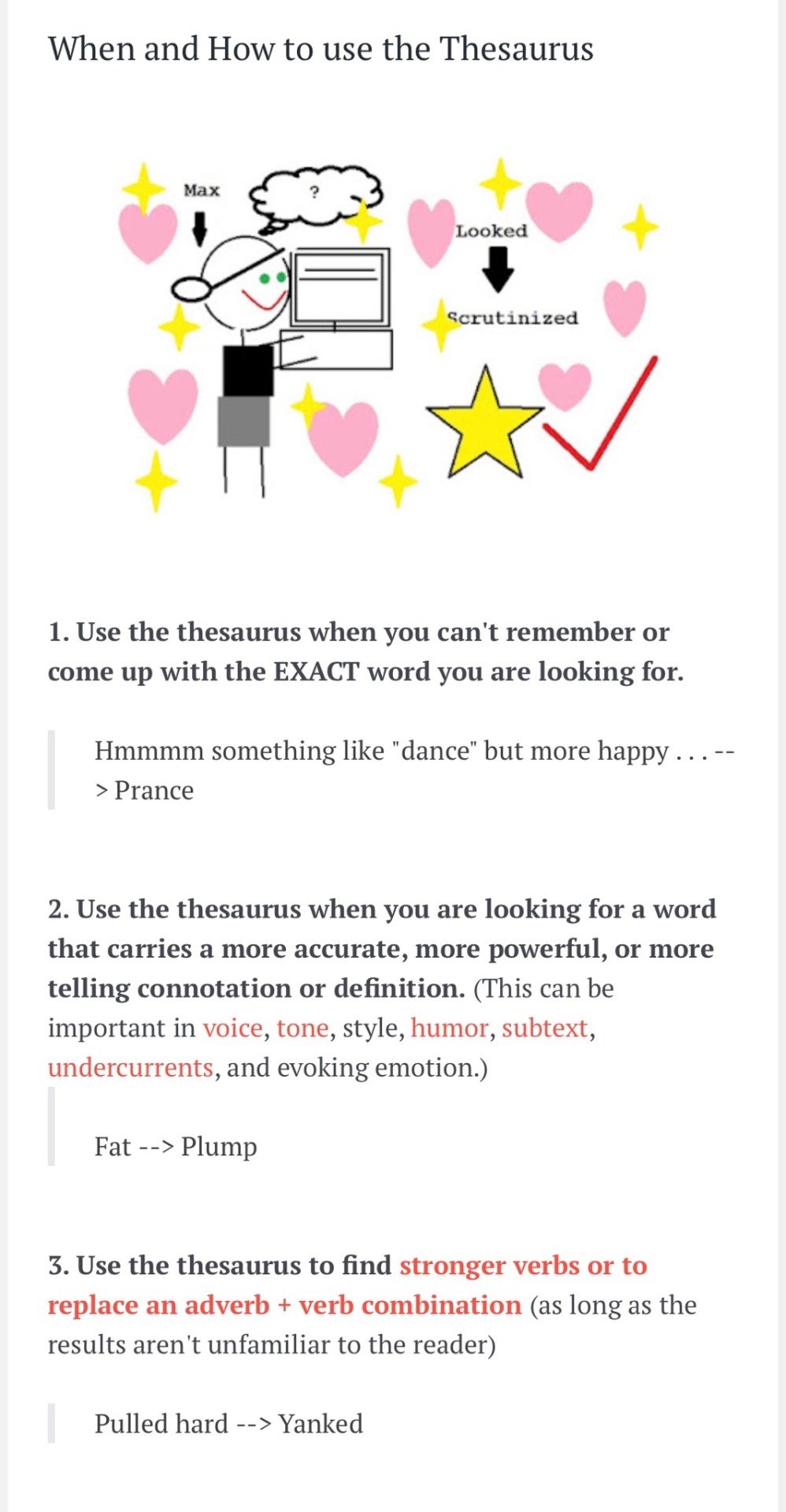
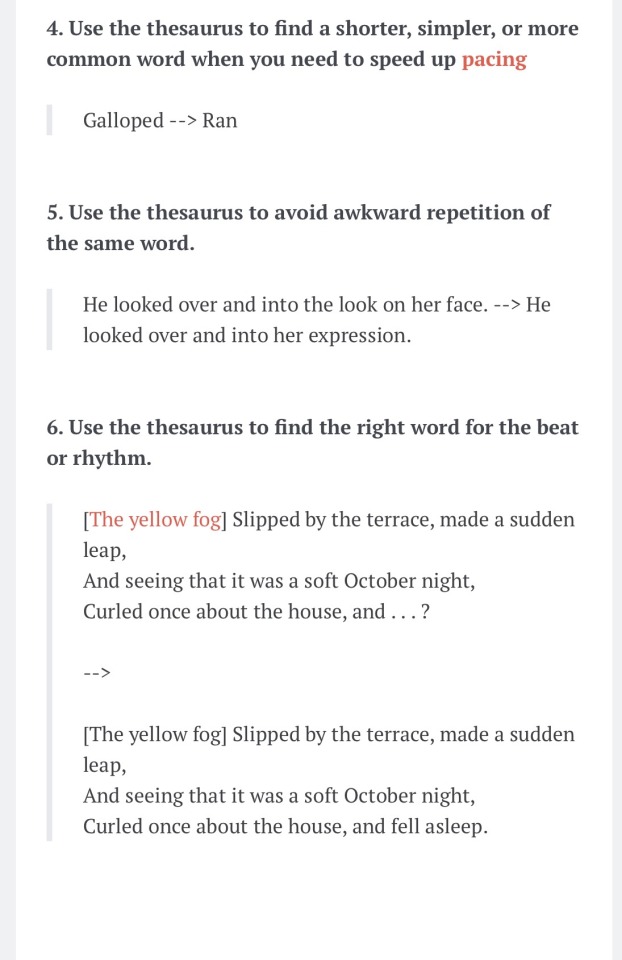

If you want to look at the original article…
https://www.septembercfawkes.com/2018/08/how-to-use-thesaurus-properly.html
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Crafting Compelling Villains
1. The "Evil for the Sake of Being Evil" Villain:
This type of villain lacks depth and clear motivations. They simply exist to be wicked and cause chaos without any believable reason or backstory.
2. The One-Dimensional Bully:
This villain is characterized solely by their physical strength or intimidating presence. They lack complexity, depth, and fail to challenge the protagonist on an intellectual or emotional level.
3. The Overpowered and Unbeatable Villain:
This villain is excessively powerful with no apparent weaknesses or vulnerabilities. They pose no real threat to the protagonist, as their defeat seems implausible or impossible.
4. The Expository Villain:
This villain constantly explains their evil plans and motivations without any subtlety or nuance. Their dialogues become monotonous and predictable, diminishing the impact of their character.
5. T The Forgettable Villain:
This villain lacks distinct traits, memorable characteristics, or a unique presence. They fail to leave a lasting impression on readers and are easily overshadowed by other elements of the story
6. The Plot Device Villain:
This villain exists solely to advance the plot without any independent goals or desires. They lack agency and depth, merely serving as a convenient obstacle for the protagonist to overcome.
7. The Unrelatable Monster:
This villain is completely devoid of humanity or relatable qualities. They are monstrous in every sense, lacking any redeeming or understandable characteristics that could engage the audience emotionally.
8. The Placeholder Villain:
This villain is introduced briefly and abruptly, without any significant development or impact on the story. They serve as a mere distraction or temporary obstacle, leaving readers feeling unsatisfied.
9. The Inconsistent Motivations:
This villain's motivations and actions are erratic and inconsistent, making it difficult for readers to understand their choices. Their lack of clear direction undermines the credibility and coherence of their character.
2K notes
·
View notes
Note
How do I make internal conflict subtle, without being so subtle the readers miss it?
Internal conflict is a vital component of any compelling story. It’s the central axis of any good character arc and drives the narrative forward. However, writing internal struggles effectively without resorting to heavy-handed exposition can be challenging. Here are some quick tips on writing subtle internal conflict.
Show, don’t tell
Reveal a character’s emotions through actions, thoughts, and dialogue.
Use body language and gestures to convey inner turmoil, like fidgeting, clenched fists, or avoiding eye contact.
Write sensory details to immerse readers in the character's emotional experience, like describing the taste of bitterness or the prickling of anxiety.
Incorporate changes in a character's routine or habits that hint at inner changes, like a punctual character being late, or changing taste in music.
Use the character's reactions to their environment as a reflection of their emotions. The same setting might appear grey and dark to one, but bright and vibrant to another.
Use subtext
Write subtext into dialogue, where characters say one thing but mean another.
Drop subtle hints at emotions that readers can infer rather than spelling everything out.
Experiment with non-verbal communication like meaningful glances, pauses, or hesitations.
Invoke subtext through characters' internal thoughts and uncertainties, without the character fully acknowledging their deeper feelings.
Use dramatic irony, where the reader knows more than the character does about their own feelings or situation.
Develop complex characters
Give your characters conflicting desires, values, and goals to naturally generate internal conflict.
Create backstories that reveal past traumas or experiences that continue to haunt and influence their decisions.
Consider using character flaws and contradictions to highlight internal struggles.
Use relationships to create conflicting desires and expectations.
Give your characters both internal and external conflicts to build tension between dealing with personal struggles and outside problems.
Employ inner monologues
Incorporate introspective moments where characters wrestle with their inner demons, doubts, and fears.
Use first-person or close third-person perspectives to allow readers direct access to the character's thoughts.
Balance inner monologues with external action to maintain pacing and engagement.
Use an unreliable narrator so readers try to distinguish between what is a misperception and what is the truth.
Create inner thoughts that highlight the difference between a character's public persona and their private world.
Create moral dilemmas
Force characters to make difficult decisions that represent turning points in their arcs.
Explore the consequences of a character’s choices on their sense of self and their relationships.
Have your character confront a personal sacrifice where they must question their own motives and values.
Have a character balance loyalty and personal integrity, having to decide where their personal morality lies.
Force a choice between self-preservation and the greater good where their choice not only has personal stakes, but story-wide ones as well.
884 notes
·
View notes
Text
Expanding a thought from a conversation this morning:
In general, I think "Is X out-of-character?" is not a terribly useful question for a writer. It shuts down possibility, and interesting directions you could take a character.
A better question, I believe, is "What would it take for Character to do X?" What extremity would she find herself in, where X starts to look like a good idea? What loyalties or fears leave him with X as his only option? THAT'S where a potentially interesting story lies.
In practice, I find that you can often justify much more from a character than you initially dreamed you could: some of my best stories come from "What might drive Character to do [thing he would never do]?" As long as you make it clear to the reader what the hell pushed your character to this point, you've got the seed of a compelling story on your hands.
49K notes
·
View notes
Text
Cheat Sheet for Writing Emotion
Anger:
Grinding teeth
Narrowing eyes
Yelling
A burning feeling in the chest
Heavy breathing
Unjustified or justified accusations towards other characters
Jerky movements
Glaring
Violence
Stomping
Face reddening
Snapping at people
Sadness:
Lack of motivation
Messy appearance
Quiet
Slow movements
Crying
Inability to sleep
Frowning
Red eyes
Isolating oneself
Fatigue
Not concentrating
Keep reading
46K notes
·
View notes
Text
Concepts to use in horror
• Being watched/followed. Can be used with plots like a home invasion or someone watching another person through a webcam.
• Losing control. Can be used with plots like possession, being forced to kill/hurt people to save oneself or a loved one, being blackmailed, etc.
• The nature of humanity. This can work when the “monster” is a human, and can call into question the concept of good and evil. Works well with the above in my opinion, as a human being doing monstrous things can sometimes lead to questions about humanity and whether humankind is good.
• The end of humanity. Can be cheesy (like in a lot of zombie plots), but is innately scary to a lot of people to think about. Things that seem more plausible, such as an apocalypse related to pandemics or environmental pollution, can come across in a more serious way when done subtly.
• Isolation. In some cases this can seem a little too convenient to the plot, but when done right isolation can up the terror of the plot, or even serve as the plot itself. Being trapped somewhere, like in the woods or in a small space, could work for this.
• One’s own insignificance. Most cases I’ve seen where this works well show the character’s smallness in relation to something else. The ocean, space, cosmic gods, etc.
• The unknown. Often works well with the above in my opinion. The ocean and space, for example, would be good settings for this.
• Instinctive responses. The human brain tends to naturally react to things like violence, disease and contamination, and other things that threaten survival. Using these things too gratuitously can easily become campy or even voyeuristic and insensitive, but they can be used well.
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
This is a friendly reminder to never, ever publish your book with a publishing company that charges you to publish with them. That is a vanity press, which makes money by preying on authors. They charge you for editing, formatting, cover art, and more. With most of these companies, you will never seen a cent of any royalties made from sale of your book. A legitimate publishing company only makes money when you make money, they will never charge you to publish with them. If a company approaches you and says "Hey, we'll publish your book, just pay us X amount of money," tell them to go fuck themself and block them.
49K notes
·
View notes