Just a writer that loves fantasy, dragons, reading, and writing. Wishes that dragons were real and I can be a dragon rider princess or queen. : D Did I mention I like dragons? My first book in a series, Lyndom Tales I: Pirates & Princesses By: S.C.Cardenas!
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text

Writing with Color: Description Guide - Words for Skin Tone
We discussed the issues describing People of Color by means of food in Part I of this guide, which brought rise to even more questions, mostly along the lines of “So, if food’s not an option, what can I use?” Well, I was just getting to that!
This final portion focuses on describing skin tone, with photo and passage examples provided throughout. I hope to cover everything from the use of straight-forward description to the more creatively-inclined, keeping in mind the questions we’ve received on this topic.
So let’s get to it.
S T A N D A R D D E S C R I P T I O N
B a s i c C o l o r s

Pictured above: Black, Brown, Beige, White, Pink.
“She had brown skin.”
This is a perfectly fine description that, while not providing the most detail, works well and will never become cliché.
Describing characters’ skin as simply brown or beige works on its own, though it’s not particularly telling just from the range in brown alone.
C o m p l e x C o l o r s
These are more rarely used words that actually “mean” their color. Some of these have multiple meanings, so you’ll want to look into those to determine what other associations a word might have.

Pictured above: Umber, Sepia, Ochre, Russet, Terra-cotta, Gold, Tawny, Taupe, Khaki, Fawn.
Complex colors work well alone, though often pair well with a basic color in regards to narrowing down shade/tone.
For example: Golden brown, russet brown, tawny beige…
As some of these are on the “rare” side, sliding in a definition of the word within the sentence itself may help readers who are unfamiliar with the term visualize the color without seeking a dictionary.
“He was tall and slim, his skin a russet, reddish-brown.”
Comparisons to familiar colors or visuals are also helpful:
“His skin was an ochre color, much like the mellow-brown light that bathed the forest.”
M o d i f i e r s
Modifiers, often adjectives, make partial changes to a word.The following words are descriptors in reference to skin tone.
D a r k - D e e p - R i c h - C o o l
W a r m - M e d i u m - T a n
F a i r - L i g h t - P a l e
Rich Black, Dark brown, Warm beige, Pale pink…
If you’re looking to get more specific than “brown,” modifiers narrow down shade further.
Keep in mind that these modifiers are not exactly colors.
As an already brown-skinned person, I get tan from a lot of sun and resultingly become a darker, deeper brown. I turn a pale, more yellow-brown in the winter.
While best used in combination with a color, I suppose words like “tan” “fair” and “light” do work alone; just note that tan is less likely to be taken for “naturally tan” and much more likely a tanned White person.
Calling someone “dark” as description on its own is offensive to some and also ambiguous. (See: Describing Skin as Dark)
U n d e r t o n e s
Undertones are the colors beneath the skin, seeing as skin isn’t just one even color but has more subdued tones within the dominating palette.

Mentioning the undertones within a character’s skin is an even more precise way to denote skin tone.
As shown, there’s a difference between say, brown skin with warm orange-red undertones (Kelly Rowland) and brown skin with cool, jewel undertones (Rutina Wesley).
“A dazzling smile revealed the bronze glow at her cheeks.”
“He always looked as if he’d ran a mile, a constant tinge of pink under his tawny skin.”
Standard Description Passage
“Farah’s skin, always fawn, had burned and freckled under the summer’s sun. Even at the cusp of autumn, an uneven tan clung to her skin like burrs. So unlike the smooth, red-brown ochre of her mother, which the sun had richened to a blessing.”
-From my story “Where Summer Ends” featured in Strange Little Girls
Here the state of skin also gives insight on character.
Note my use of “fawn” in regards to multiple meaning and association. While fawn is a color, it’s also a small, timid deer, which describes this very traumatized character of mine perfectly.
Though I use standard descriptions of skin tone more in my writing, at the same time I’m no stranger to creative descriptions, and do enjoy the occasional artsy detail of a character.
C R E A T I V E D E S C R I P T I O N
Whether compared to night-cast rivers or day’s first light…I actually enjoy seeing Characters of Colors dressed in artful detail.
I’ve read loads of descriptions in my day of white characters and their “smooth rose-tinged ivory skin”, while the PoC, if there, are reduced to something from a candy bowl or a Starbucks drink, so to actually read of PoC described in lavish detail can be somewhat of a treat.
Still, be mindful when you get creative with your character descriptions. Too many frills can become purple-prose-like, so do what feels right for your writing when and where. Not every character or scene warrants a creative description, either. Especially if they’re not even a secondary character.
Using a combination of color descriptions from standard to creative is probably a better method than straight creative. But again, do what’s good for your tale.
N A T U R AL S E T T I N G S - S K Y

Pictured above: Harvest Moon -Twilight, Fall/Autumn Leaves, Clay, Desert/Sahara, Sunlight - Sunrise - Sunset - Afterglow - Dawn- Day- Daybreak, Field - Prairie - Wheat, Mountain/Cliff, Beach/Sand/Straw/Hay.
Now before you run off to compare your heroine’s skin to the harvest moon or a cliff side, think about the associations to your words.
When I think cliff, I think of jagged, perilous, rough. I hear sand and picture grainy, yet smooth. Calm. mellow.
So consider your character and what you see fit to compare them to.
Also consider whose perspective you’re describing them from. Someone describing a person they revere or admire may have a more pleasant, loftier description than someone who can’t stand the person.
“Her face was like the fire-gold glow of dawn, lifting my gaze, drawing me in.”
“She had a sandy complexion, smooth and tawny.”
Even creative descriptions tend to draw help from your standard words.
F L O W E R S

Pictured above: Calla lilies, Western Coneflower, Hazel Fay, Hibiscus, Freesia, Rose
It was a bit difficult to find flowers to my liking that didn’t have a 20 character name or wasn’t called something like “chocolate silk” so these are the finalists.
You’ll definitely want to avoid purple-prose here.
Also be aware of flowers that most might’ve never heard of. Roses are easy, as most know the look and coloring(s) of this plant. But Western coneflowers? Calla lilies? Maybe not so much.
“He entered the cottage in a huff, cheeks a blushing brown like the flowers Nana planted right under my window. Hazel Fay she called them, was it?”
A S S O R T E D P L A N T S & N A T U R E

Pictured above: Cattails, Seashell, Driftwood, Pinecone, Acorn, Amber
These ones are kinda odd. Perhaps because I’ve never seen these in comparison to skin tone, With the exception of amber.
At least they’re common enough that most may have an idea what you’re talking about at the mention of “pinecone.“
I suggest reading out your sentences aloud to get a better feel of how it’ll sounds.
"Auburn hair swept past pointed ears, set around a face like an acorn both in shape and shade.”
I pictured some tree-dwelling being or person from a fantasy world in this example, which makes the comparison more appropriate.
I don’t suggest using a comparison just “cuz you can” but actually being thoughtful about what you’re comparing your character to and how it applies to your character and/or setting.
W O O D

Pictured above: Mahogany, Walnut, Chestnut, Golden Oak, Ash
Wood can be an iffy description for skin tone. Not only due to several of them having “foody” terminology within their names, but again, associations.
Some people would prefer not to compare/be compared to wood at all, so get opinions, try it aloud, and make sure it’s appropriate to the character if you do use it.
“The old warlock’s skin was a deep shade of mahogany, his stare serious and firm as it held mine.”
M E T A L S

Pictured above: Platinum, Copper, Brass, Gold, Bronze
Copper skin, brass-colored skin, golden skin…
I’ve even heard variations of these used before by comparison to an object of the same properties/coloring, such as penny for copper.
These also work well with modifiers.
“The dress of fine white silks popped against the deep bronze of her skin.”
G E M S T O N E S - M I N E R A LS

Pictured above: Onyx, Obsidian, Sard, Topaz, Carnelian, Smoky Quartz, Rutile, Pyrite, Citrine, Gypsum
These are trickier to use. As with some complex colors, the writer will have to get us to understand what most of these look like.
If you use these, or any more rare description, consider if it actually “fits” the book or scene.
Even if you’re able to get us to picture what “rutile” looks like, why are you using this description as opposed to something else? Have that answer for yourself.
“His skin reminded her of the topaz ring her father wore at his finger, a gleaming stone of brown, mellow facades.”
P H Y S I C A L D E S C R I P T I ON
Physical character description can be more than skin tone.
Show us hair, eyes, noses, mouth, hands…body posture, body shape, skin texture… though not necessarily all of those nor at once.
Describing features also helps indicate race, especially if your character has some traits common within the race they are, such as afro hair to a Black character.
How comprehensive you decide to get is up to you. I wouldn’t overdo it and get specific to every mole and birthmark. Noting defining characteristics is good, though, like slightly spaced front teeth, curls that stay flopping in their face, hands freckled with sunspots…
G E N E R A L T I P S
Indicate Race Early: I suggest indicators of race be made at the earliest convenience within the writing, with more hints threaded throughout here and there.
Get Creative On Your Own: Obviously, I couldn’t cover every proper color or comparison in which has been “approved” to use for your characters’ skin color, so it’s up to you to use discretion when seeking other ways and shades to describe skin tone.
Skin Color May Not Be Enough: Describing skin tone isn’t always enough to indicate someone’s ethnicity. As timeless cases with readers equating brown to “dark white” or something, more indicators of race may be needed.
Describe White characters and PoC Alike: You should describe the race and/or skin tone of your white characters just as you do your Characters of Color. If you don’t, you risk implying that White is the default human being and PoC are the “Other”).
PSA: Don’t use “Colored.” Based on some asks we’ve received using this word, I’d like to say that unless you or your character is a racist grandmama from the 1960s, do not call People of Color “colored” please.
Not Sure Where to Start? You really can’t go wrong using basic colors for your skin descriptions. It’s actually what many people prefer and works best for most writing. Personally, I tend to describe my characters using a combo of basic colors + modifiers, with mentions of undertones at times. I do like to veer into more creative descriptions on occasion.
Want some alternatives to “skin” or “skin color”? Try: Appearance, blend, blush, cast, coloring, complexion, flush, glow, hue, overtone, palette, pigmentation, rinse, shade, sheen, spectrum, tinge, tint, tone, undertone, value, wash.
Skin Tone Resources
List of Color Names
The Color Thesaurus
Things that are Brown (blog)
Skin Undertone & Color Matching
Tips and Words on Describing Skin
Photos: Undertones Described (Modifiers included)
Online Thesaurus (try colors, such as “red” & “brown”)
Don’t Call me Pastries: Creative Skin Tones w/ pics 3 2 1
Writing & Description Guides
WWC Featured Description Posts
WWC Guide: Words to Describe Hair
Writing with Color: Description & Skin Color Tags
7 Offensive Mistakes Well-intentioned Writers Make
I tried to be as comprehensive as possible with this guide, but if you have a question regarding describing skin color that hasn’t been answered within part I or II of this guide, or have more questions after reading this post, feel free to ask!
~ Mod Colette
170K notes
·
View notes
Text
Surnames are just as important as given names. So, I compiled a list of the websites I use to find my surnames.
English Surnames
Dutch Surnames
Spanish Surnames
Scottish Surnames
German Surnames
Italian Surnames
Irish Surnames
French Surnames
Scandinavian Surnames
Welsh Surnames
Jewish Surnames
Surnames By Ethnicity
Most Common Surnames in the USA
Most Common Surnames in Great Britan
Most Common Surnames in Asia
269K notes
·
View notes
Text
IT’S NOT ‘PEEKED’ MY INTEREST
OR ‘PEAKED’
BUT PIQUED
‘PIQUED MY INTEREST’
THIS HAS BEEN A CAPSLOCK PSA
701K notes
·
View notes
Text
Fantasy Guide: Horses, Steeds and Mounts

Horses are a staple of fantasy. Instead of writing them as emotionless vehicles lets give them life.
Horse Terminology

Mare: female horse
Gelding: castrated male horse, big boned and gentle
Stallion: male horse, more agressive
Foal: baby horse
Filly: girl baby horse
Colt : boy baby horse
Yearling: a horse a year old, too young to ride
Pony: small, smart and sturdy,
Colour

When writing horses, we like to colour them in. Make sure to have a look at my colours post for some symbolic choices.
Appaloosa: white hair and dark patches
Bay: red-brown, dark, mahogany bay, red bay, sandy are all common shades but bay must always have a hint of black.
Black: black but keep in mind that pure black is very rare.
Chestnut/Sorrel: reddish coat, may have brown/rws
Dun: yellowish commonly but can be reddish yellow horse
Paint/Pinto – white patches
Palomino: golden coat, white mane
Piebald – dark-skinned, with large splotches of black and white
Roan: blue or strawberry; mixed colored and white hairs. A blue roan has black and white manes, red roans have white manes.
Physical signs

These all tell you what the horse is telling you. Listen to your horse.
Blow: exhaling through the nose. This indicates curiousness and often followed by nuzzling.
Breathing: Yes, check if the horse is breathing first. Always a good point. But yes, horses have a resting breath that is relaxed. Changes to this could mean anxiety or fear.
Ears are up and pointed forward: alert and interested
Ears are pointed out to the side: Sleepy, tired, unwell or submissive.
Ears are pointed up: unwell or bored
Ears are back and pinned flat against the head: angry and aggressive. Fuck off right now or you’ll catch these hooves.
Neigh/Whinny: a sound made to look for company in people or horses.
Nicker: usually means “hello” in either a friendly context or a mating context. Mama horse will nicker to their kids.
Scream: usually while fighting some other horses.
Snort: exhaling through the nose sharply which is code for where’s the danger.
Feeding time

Horses need to be fed and it’s expensive. Horses are the most costly thing for a castle or army to have. It takes money to field a large calvary so make sure you have some food on board.
Apples and fruit.
Barley
Bran
Grass
Hays
Oats
Root vegetables – beetroot, carrots, parsnips, and turnips
Tack
Corn
Tack

This is the term for your horses kit. This will be a basic list.
Saddle: Your seat on the horse
Stirrups: supports that hang from either side of the saddle to support the feet.
Girth: A belt that fastens the saddle to the horse.
Bridle: The bit that goes over the horse’s face
Reins: connected to the bridle and ensures you have a grip
Bit: this is what the horse has between its teeth.
Horn: a raised portion of the saddle that sits at the point where the saddle is close to the neck.
Blanket: a drape of fabric used to warm a horse or stop rubbing from the saddle.
Things you ought to know about horses

Riding bareback (i hear you laughing, pervert) is actually quite hard and dangerous
Horses have limits and most can gallop all night without a break
Horses often break legs and sometimes must be put down (honestly fuck you Veronica, #cobalt deserved better)
Horses die in battle, not all horses make it out (you go, Joey)
Common horses mentioned in fantasy

Destrier: The most popular war horse of the medieval era. These horses are only ever really used by knights in battles, tournaments, and jousts. It was not the most common horse but it was considered the desired of horses even being called “the great”. Usually male, these horses were renowned for their agility able to turn quickly making it suitable for battle. Destriers are expensive. When one looks in the histories you seen them going for almost ten times the price of another breed. The breed has since died out but scientists and equestrians have since been trying to reproduce them.
Courser: This was the more commonly used and available war horse. It is fast and strong horse ridden by knights and men-at-arms. They were not expensive than the destrier but still would cost a pretty penny.
Rouncey: A commonly used horse used anything and everything. Mostly used for riding, the horse could be trained for battle.
Palfrey: Would be an expensive horse for riding. It was a slender horse with an ambling gait so it was prized for traveling over distance.
Hunters: Or more commonly called Thoroughbred. The Thoroughbred is a fast horse and an agile one. Though vest for racing, the thoroughbred was mostly used when the nobility went riding in hunting excursions.
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
I am a(n):
⚪ Male
⚪ Female
🔘 Writer
Looking for
⚪ Boyfriend
⚪ Girlfriend
🔘 An incredibly specific word that I can't remember
411K notes
·
View notes
Text
know the difference
It has come to my attention that many people mistake wyverns for dragons, so here’s a post to help you remember
Dragon: 4 legs, 2 wings

Wyvern: 2 legs, 2 wings
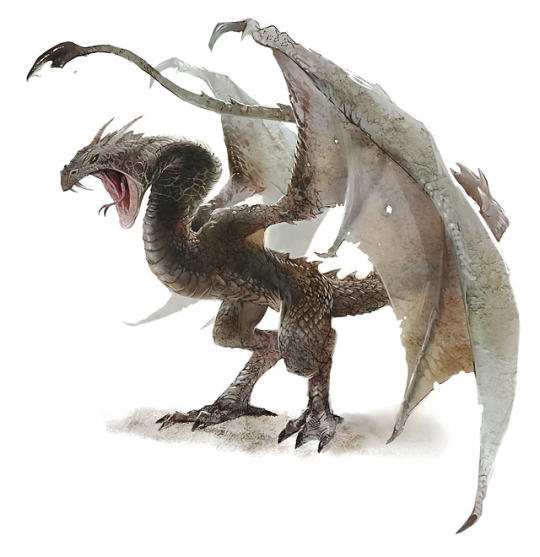

Drake: 4 legs, flightless

Wyrms: long snake like body with no appendages, can also appear as a traditional Chinese dragon with 4. Legs and no wings yet can fly

Amphithere: 0 legs 2 wings, can be feathered
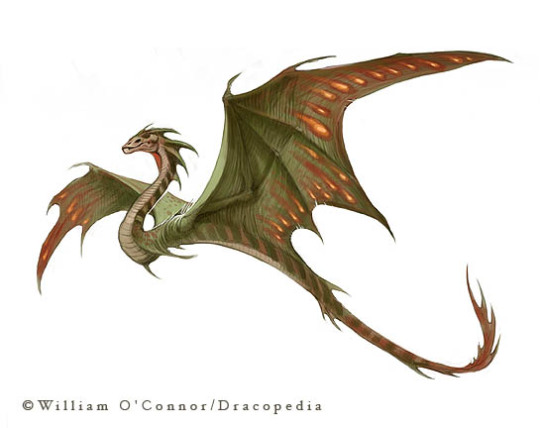

Lindwurms: 2 legs, 0 wings, long body

Luck dragon: 4 legs, no wings, can fly, long body, furry with dog like face

Komodo dragon: 4 legs, no wings, real

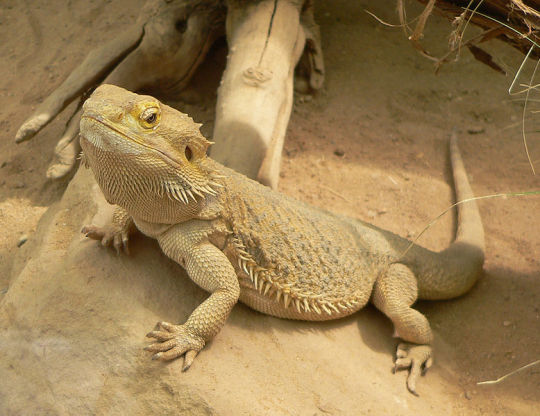
Bearded dragon: 4 legs, 0 wings, often kept as pets

322K notes
·
View notes
Text
Cheat Sheet for Writing Emotion
Anger:
Grinding teeth
Narrowing eyes
Yelling
A burning feeling in the chest
Heavy breathing
Unjustified or justified accusations towards other characters
Jerky movements
Glaring
Violence
Stomping
Face reddening
Snapping at people
Sadness:
Lack of motivation
Messy appearance
Quiet
Slow movements
Crying
Inability to sleep
Frowning
Red eyes
Isolating oneself
Fatigue
Not concentrating
Love:
Thinking about someone
Good communication
Not forcing a friend/lover into something
Smiling randomly
Making eye contact with loved one
Nervous behaviors (fiddling hands, biting lip)
Cuddling
Flirting
Inside jokes
Holding hands
Kissing
Offering gifts
Fluttering stomach
Racing heart
Losing track of time while with loved one
Daydreaming
Denial:
Disagreement with someone
Shaking head frantically
Backing away
Putting hand on one’s chest
Rapid speaking
Rationalization or justifying something
Dismissing someone or something
Embarrassment:
Blushing
Avoiding eye contact
Grimacing
Looking down
Changing the conversation
Rubbing back of neck
Shoulders slumping
A weak voice
Tightening chest
Panicked thoughts
Running away
Getting quiet
Concentrating on something else
Happiness
Smiling
Laughing
Squealing
Bouncing on toes
Warmth in chest
Fast pulse
A sense of contentment
Relaxed posture
Quick movements
Breathlessness
Desire to help
Fear:
Face going pale
Panicked thoughts
Jerky movements
Mind racing for a solution
Running
Freezing
Fighting
Fawning (doing what people tell you to do)
Side note: flight, fight, freeze, and fawn are all reactions to adrenaline. Aka the fight or flight response
Thinking of survival
Rapid breathing
A panicked feeling
Guilt:
Feeling horrible about oneself
Lying
Grimacing
Trying to redeem themselves
Asking for forgiveness
Anxious thoughts
46K notes
·
View notes
Text
Roles on a Pirate Ship
[by Mark Cookman / Tribality 1, 2, 3] @we-are-pirate, @we-are-scarlet-corsair

Officer Roles on a Pirate Ship
If you are running a game with pirates in it, then you should know what the job entails. It’s not all boarding ships, counting booty, and drinking rum like you might think. A great deal of hard work is required to run a sailing ship with a law-abiding crew, let alone one populated by pirates. In this essay we are going to examine the five principle officers on board a pirate ship, their duties, and their responsibilities. This is part one of a three part lesson. In the next lesson we will examine the duties and responsibilities of other officers and crew members with special duties. In the final lesson, we will look at one very special group of crew members that are almost always overlooked. Read on to learn what pirates expected of their primary officers.
The principal officers of a pirate ship were the captain, the quartermaster, the pilot, the boatswain, and the master gunner. On some ships these positions were all elected by an equal vote of the crew and on others the captain picked the crew members he wanted to serve in the positions. The captain on a pirate vessel was almost always elected by an equal vote of the crew. On a privateer vessel this was not very often the case. Privateer captains were often the owners of the ship or were given commission by their monarch to take a vessel to sea. So it follows with the other officers. If the captain was elected, then generally all of the officers were elected. If the captain was appointed or held his position by means of ownership, then generally he picked the officers. In either case, an officer on a pirate ship served at the whim of the crew. Even a man picked by the captain would be booted down to a simple crewman if he could not do his job. For the most part though, a person elevated to serve as one of the principle officers did so for life. The title of this article refers to the fact that most often the authorities that captured, tried, and hung pirates concentrated on the five principle officers of the ship. These officers were generally the most intelligent and skilled crewmen on board the pirate vessel. They were people that everyone else on board the ship admired for their ability to do their job. Diligent action is the mother of respect on board a ship.
Captain
The captain, however he came to his position, was chosen for his leadership, bravery, and cunning. The captain was responsible for the ship and everything aboard her; every item and every man. He was responsible for the overall decisions affecting the ship and her crew. The captain decided where to sail and what to attack. He was the voice of his crew to all beyond the ship. He often led his crew in battle. In terms of daily duties, the captain kept a log of the voyage, managed the affairs of the ship through the officers, and generally served a four to six hour shift at the helm. The captain stayed in power by being successful. As long as there are prizes to plunder, rum to drink, and food to eat, the captain will not be voted out or mutinied against. It is when things get lean that the captain must worry about crew voting him unfit for command.
Quartermaster
The quartermaster (or first mate on a privateer vessel) was the number two man on the ship. He was responsible for enforcing the ship’s articles and administering punishment when necessary. The quartermaster was the trustee of the ship and her crew. He directly represented the crew to the captain. It was his responsibility to serve as a counterbalance to the captain in decisions that might be hazardous to the ship or the crew. A wise captain made no decisions that his first mate didn’t support. The quartermaster took responsibility for prize vessels and picked the treasure that the crew would take from a prize. He was also responsible for counting the booty and splitting the shares. Each day would find him working with his subordinate officers the boatswain, the master gunner, and the master at arms to effectively run the ship. The first mate also served a turn at the helm, generally a four to six hour shift.
Pilot
The pilot was the number three man on the ship and often the most educated. He served as the ship’s navigator and was generally the best all around sailor aboard the ship. He was responsible for plotting the ship’s course and maintaining that course. The pilot maintained all of the ship’s charts and maps as well as the tools of navigation. He was charged with keeping a daily log of every event relating to the sailing of the ship. He recorded the depth, the currents, the wind patterns, the ship’s location, the locations of reefs and sandbars, and the state of the rigging. He reported directly to the captain. The pilot oversaw the work of the sail-master and almost always had at least one assistant (a pilot’s mate) to help him with his duties. The pilot and his mate both served separate shifts at the helm in addition to taking readings from the moon and stars to plot and maintain the course.
Boatswain
The boatswain was the number four man on the ship and often the most feared by the crew. He was in charge of the provisions for the ship. He maintained the stores of food, water, rum, gunpowder, shot, sails, rope, wood, and tar required to keep the ship and crew fit for action. The boatswain also directed the loading of cargo into the hold to maintain the proper ballast to ensure level sailing. He was in charge of keeping the watches on the ship and maintaining discipline among the deck crew. He was responsible for the ship’s longboats and for picking a crew to man the sweeps when the longboats were used. The boatswain was charged with maintaining the ship’s seaworthy status. He oversaw the duties of both the carpenter and the cook. The boatswain generally had a mate to help him with his responsibilities. In general, his duties were to make certain that all the work of running the ship was done. He reported to the quartermaster. The Boatswain was often the most feared man on the ship because his obligations often made him uncompromising. It was his responsibility to keep everything “ship-shape”. Leniency was something the quartermaster might give to the crew, but it was not something the boatswain was in the position to give. Day and night, the boatswain would drive the crew to do whatever work was required. He maintained the watch log and reported any problems to the quartermaster.
Master Gunner
The master gunner was the number five man on the ship. He was responsible for the care and cleaning of all firearms, culverin (deck guns), and cannons on board the ship. He was also responsible for training the crew in the use of both firearms and ship’s weaponry. The master gunner picked and ran the gunnery crew. He reported to the quartermaster, but was responsible to the entire ship to make certain that the cannons hit the declared target. He was also responsible for maintaining the inventory of powder and shot for all of the guns on the ship. The master gunner was the only crew member besides the captain and the quartermaster entrusted to carry a key to the ship’s powder magazine. Additionally, the master gunner often led or picked hunting parties when they were called for. His day to day duties mainly consisted of drilling the gunnery crew and maintaining the guns.

The Next in Line to Hang – More Roles on a Pirate Ship
In this second part of a three part lesson dealing with the crew positions aboard a pirate vessel, we are going to look at the responsibilities of the Sail-master, the Carpenter, the Cook, the Surgeon, and the Master at Arms. These were all lower officer positions and were either voted upon or assigned by the captain as discussed in the first part of this lesson. The sailors who served in these positions were skilled laborers and, as such, their skills were always very much in demand on a ship. They were almost always offered a greater share of the treasure because of their skills. These were definitely crew members that a pirate ship could not function without.
Sail-master
The Sail-master was the most experienced crewman in the rigging and usually one of the best sailors on the ship. He was responsible for maintaining the sails and the rigging. The Sail-master knew every knot, line, rope, block and tackle in the rigging as well as how to repair them all. He was also responsible for training and running the sail crew as well as overseeing the making and patching of sails. The Sail-master took orders from and reported to the pilot.
Carpenter
The Carpenter was a skilled wood worker, often with some shipwright experience, who did all of the woodworking required by the crew. He was primarily responsible for repairing damage to the wooden portions of the ship and for plugging leaks that got too bad. (Ye should understand right now, before ye go to sea, that all ships leak, mates. It’s just when they really leak badly that you have to worry about it.) The Carpenter was also responsible for the construction of barrels and crates, as needed, to store cargo, as well as maintaining the tools of his trade. He took orders from and reported to the Boatswain.
Cook
The Cook was one of the most important of the lower officers. He was in charge of all matters relating to food on the ship. He made certain there was enough food, water, and rum on board for the planned cruise. He cooked the meals and suggested rationing when it was necessary. The Cook butchered the meat brought back by hunting parties and was the only man trusted to light a fire below decks. He maintained the necessary tools for both cooking and butchering. The Cook took orders from and reported to the Boatswain.
Surgeon
The Surgeon was likely one of the toughest men on the ship. He served as the barber/doctor/emergency surgeon for the entire crew. He was equally capable of shaving your beard and cutting off your damaged leg. The Surgeon dealt with not only the sick and the wounded, but also the dead. He, like the other lower officers, was responsible for maintaining the necessary tools of his trade. The Surgeon took his orders from and reported to the Quartermaster. It was rare for a ship to have a real doctor and it was common for the carpenter or the cook to fill this role as needed.
Master at Arms
The Master at Arms was often the most skilled warrior on the crew. He was responsible for training the crew in hand to hand combat. He also led the ship’s boarding parties and hunting parties when they were necessary. The Master at Arms position was not a separate position on every vessel and often these responsibilities fell to the Quartermaster. When the Master at Arms position was filled on a ship, he took orders from and reported to the Quartermaster.
These 5 core positions represent the Non-Commissioned Officers of a pirate or privateer ship. These men all commanded other men on work details and so their words carried great sway with the crew. It was often from among these men that the next captain was chosen when a captain lost his position through a vote of no confidence. Thus, these were the men that the captain had to keep loyal to him to stay in command of the ship.
And Hang the Musikers, Too – Even More Roles on a Pirate Ship
In this article, we will be looking at the makeup of the crew itself. Remember that the only rule with pirates is that there are no rules; no two crews of any two pirate ships were exactly the same. Even so, we can narrow down some roles common to pirate/privateer crews based upon the jobs that must be done aboard ship. Most simply put, pirate crews are a mixture of brutes, gunners, swabbies, and musikers. Let’s examine each category in turn.
Brutes
A great deal of hard work and heavy hauling is involved in just sailing a tall-masted ship. In strong winds the canvas sails must be man-handled by a deck crew that is stronger. Loading and unloading supplies, most especially cannons or chests of gold, requires a number of strong backs. This is why every ship has its share of brutes – big, strong men capable of handling themselves no matter the work or the fight. In addition to the tasks already mentioned, brutes would be key men in hunting parties, ship boarding, and raiding groups as well. Keep in mind that not all brutes need to be hulking bruisers. A wiry-tough and dexterous hunter, skilled with both blades and long rifle, could be a brute as well. Brutes, no matter their size, do not shrink from a hard task. Men of this sort make up perhaps as much as ½ of a pirate crew, but they will be mixed among the gunners and swabbies, not a stand alone corp. Most of the men on a pirate or privateer ship were probably gunners.
Gunners
Depending upon the size of their shot, each cannon required a crew of either 3 or 4 men to load and fire it. So a sloop carrying 4 small guns per side would require a minimum of 24 men to fully maintain them and that does not include the officers directing the cannon fire. On a large ship, like Blackbeard’s Queen Anne’s Revenge, a full gun crew would be 160 men dedicated only to firing the cannons. (It is important to note here that Blackbeard had a total crew compliment of 125 on board the Queen Anne’s Revenge.) These crewmen would have to be available 24/7 to do their job whenever required, but otherwise might have no duties on the ship. There was double-duty in most crews though. Most pirate ships didn’t keep a full compliment of gunners like warships of the time did because fewer crew members meant fewer shares and that meant more money for everyone when the treasure was split. Gunners could make up between 1/3 to 2/3 of a crew.
Swabbies
Swabbies, or actual trained sailors, are the crew members responsible for handling the rigging and the sails to keep the ship moving. These are the guys and gals who climb the ratlines into the rigging and walk the spars that jut from the masts. Swabbies sometimes fight from the highest position that they can get to on their own ship and then leap into the rigging of the enemy vessel when boarding. Often dexterous fighters, swabbies are known for leaping into the fray, but sometimes they hide in the rigging as deadly snipers. It might be surprising to discover that skilled sailors usually comprised less than 1/3 of the total crew compliment of the ship.
Musikers
It is difficult to prove that “musikers”, or musicians as we call them, were ever a stand-alone part of a pirate crew. However, two excellent examples from the pirate period demonstrate that they have been a common part of most ships of war, pirate and privateer ships included. The first example is from the early Seventeenth century. In Captain John Smith’s advice concerning how to conduct a one-on-one naval engagement he remarks when preparing to board one should, “… sound Drums and Trumpets, and Saint George for England.” The second example comes from the early Eighteenth century. In the articles of Captain Bartholomew Roberts it is stated: “The Musikers to have Rest on the Sabbath Day, but the other six Days and Nights, none without special Favour.” When thinking about the musicians on board a ship in the 16th to 18th centuries, one must not think of a band. That would be far too organized a concept. There is no way to know how many crew members may have been musicians, but one assumes that the number is not large.
It is likely that ships of this period had crew members who owned musical instruments as varied as brass horns, mouth harps, fiddles, bag pipes and accordions. Furthermore, sailors could gather numerous instruments from the various ports of call their ship made. Examples here are numerous: cowhide and goatskin drums from Africa, dried gourd maracas from Cuba, bamboo drums and flutes from Hispaniola, and even tambourines from Morocco. Pause a moment and consider the combined sounds of all of the instruments mentioned here. Now you know why a band is not the idea you want to have. The musicians were popular with the crew, as they were entertainment as well as a valuable battle element. The musicians played during meal times and during work breaks allowing the crew some entertainment to break the monotony of long hours of tiring work. This boost in moral was welcome at anytime, but was perhaps the most effective when used in battle.
From stories of Bartholomew Roberts crew and others, we know that when a ship with musicians approached another ship with the intention to fight, the effects of the music could be terrifying to the enemy. The musicians would play marches and other martial music. There were drum rolls, trumpet and bugle calls, and perhaps even a piper given the nationality of the crew. Add to this the noise of the ship’s cook beating upon his pots and pans and the crew stamping their feet or beating their weapons against the ship. Finally top this off with the sounds of shouting, screaming, and shooting, both pistols and rifles as well as cannons and deck guns. Your imagination can supply you with the details of the scene. The intended result is achieved: the morale aboard the pirate vessel is raised to a fevered pitch while the morale of their intended prize is shaken. So do not forget that pirates and privateers know the value of bardic inspiration when you run those encounters.
19K notes
·
View notes
Text
CHARACTER FACIAL EXPRESSIONS (WRITING REFERENCE)
EYES/BROWS
his eyes widened
her eyes went round
her eyelids drooped
his eyes narrowed
his eyes lit up
his eyes darted
he squinted
she blinked
her eyes twinkled
his eyes gleamed
her eyes sparkled
his eyes flashed
his eyes glinted
his eyes burned with…
her eyes blazed with…
her eyes sparked with…
her eyes flickered with…
_____ glowed in his eyes
the corners of his eyes crinkled
she rolled her eyes
he looked heavenward
she glanced up to the ceiling
she winked
tears filled her eyes
his eyes welled up
her eyes swam with tears
his eyes flooded with tears
her eyes were wet
his eyes glistened
tears shimmered in her eyes
tears shone in his eyes
her eyes were glossy
he was fighting back tears
tears ran down her cheeks
his eyes closed
she squeezed her eyes shut
he shut his eyes
his lashes fluttered
she batted her lashes
his brows knitted
her forehead creased
his forehead furrowed
her forehead puckered
a line appeared between her brows
his brows drew together
her brows snapped together
his eyebrows rose
she raised a brow
he lifted an eyebrow
his eyebrows waggled
she gave him a once-over
he sized her up
her eyes bored into him
she took in the sight of…
he glared
she peered
he gazed
she glanced
he stared
she scrutinized
he studied
she gaped
he observed
she surveyed
he gawked
he leered
his pupils (were) dilated
her pupils were huge
his pupils flared
NOSE
her nose crinkled
his nose wrinkled
she sneered
his nostrils flared
she stuck her nose in the air
he sniffed
she sniffled
MOUTH
she smiled
he smirked
she grinned
he simpered
she beamed
her mouth curved into a smile
the corners of his mouth turned up
the corner of her mouth quirked up
a corner of his mouth lifted
his mouth twitched
he gave a half-smile
she gave a lopsided grin
his mouth twisted
he plastered a smile on his face
she forced a smile
he faked a smile
her smile faded
his smile slipped
he pursed his lips
she pouted
his mouth snapped shut
her mouth set in a hard line
he pressed his lips together
she bit her lip
he drew his lower lip between his teeth
she nibbled on her bottom lip
he chewed on his bottom lip
his jaw set
her jaw clenched
his jaw tightened
a muscle in her jaw twitched
he ground his jaw
he snarled/his lips drew back in a snarl
her mouth fell open
his jaw dropped
her jaw went slack
he gritted his teeth
she gnashed her teeth
her lower lip trembled
his lower lip quivered
SKIN
she paled
he blanched
she went white
the color drained out of his face
his face reddened
her cheeks turned pink
his face flushed
she blushed
he turned red
she turned scarlet
he turned crimson
a flush crept up her face
WHOLE FACE, ETC.
he screwed up his face
she scrunched up her face
he grimaced
she winced
she gave him a dirty look
he frowned
she scowled
he glowered
her whole face lit up
she brightened
his face went blank
her face contorted
his face twisted
her expression closed up
his expression dulled
her expression hardened
she went poker-faced
a vein popped out in his neck
awe transformed his face
fear crossed her face
sadness clouded his features
terror overtook his face
recognition dawned on her face
SOURCE
82K notes
·
View notes
Text
HEY, Romance Writers!
A few followers have asked for tips on writing romance into their stories or as the basis of their stories. Here’s a masterlist of sources that may help [UPDATED].
Romance:
What Defines Romantic Love?
How to Plot a Romance Novel
How to Build a Romance Thread in Your Story
How to Write a YA Romance Without Cliché
Writing Healthy Couples in Fiction
9 Romance Writing Mistakes to Avoid
An Antidote to “Love at First Sight”
How Attractive Should Your Characters Be?
6 Ways to Get Your Readers Shipping Like Crazy
3 Great Ways to Show That Your Character Is In Love
Seven Great Sources of Conflict for Romances
20 Tips for Writing Lovable Romance Novel Heroes
Six Steps to Stronger Character Arcs in Romances
How to Write a Kissing Scene in a Romance Novel
List of Ideas to Keep Romantic Tension High
100 Questions for Character Couples
Romantic Development/Compatibility (ask)
Pinterest Board “Writing: Romance Arcs and Plots”
Bad Romance:
Removing the Creeps From Romance
+ Why The Surprise Kiss Must Go
Possessiveness 101
10 Signs You May Be in an Emotionally Abusive Relationship
Edward & Bella Are In An Abusive Relationship
Red Flags, Verbal Abuse, Stalking… | Script Shrink
5 Huge Mistakes Ruining the Romantic Relationships in Your Book
General Tips for Writing Characters Love Interests:
How to Write from a Guy’s POV
Writing Awesome Male Characters: What You’re Doing Wrong
7 Point-of-View Basics Every Writer Should Know
How Do You Describe a Character?
4 Ways to Make Readers Instantly Loathe Your Character Descriptions
3 Signs Your Story’s Characters Are Too Perfect
Is a Quirk Just What Your Character Needs?
Six Types of Character Flaws
Is Your Character Optimistic Or Pessimistic?
5 Ways to Keep Characters Consistent
9 Simple and Powerful Ways to Write Body Language
10 Body Language Tricks for Deeper Characterization
Describing People Part Three: Gestures, Expressions, and Mannerisms
33 Ways To Write Stronger Characters
Conveying Character Emotion
Distinguishing Characters in Dialogue
How to Make Readers Love an Unlikable Character…
Characters: Likability Is Overrated
Relationships in General:
How to Create Powerful Character Combos
8 Secrets To Writing Strong Character Relationships
Character Relationships: 6 Tips for Crafting Real Connections
Stereotypes, Archetypes, & Tropes:
Five Signs Your Story Is Sexist: Part 1, Part 2
Five Signs Your Story Is Sexist – Against Men
AlwaysFemale vs Always Male
Born Sexy Yesterday & Manic Pixie Dream Girl
7 (Overused) Female Love Interests
When Friends Fall for Each Other (ask)
Intercultural Romance:
How do I write an interracial couple accurately? (ask)
15 Common Stereotypes About Intercultural Relationships
Cross Cultural Relationships
[Ideas for] Your [Fictional] Cross-Cultural Relationship
Things to Avoid When Writing Interracial Romance
— — —
Ko-Fi // Wattpad // Goodreads // Pinterest
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
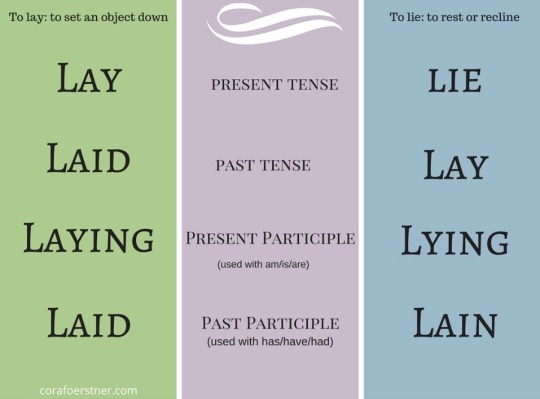
I dream of the day when I won’t have to look at this fucking chart….

48K notes
·
View notes
Text
When your brain finally has some good creative ideas but it’s 3 AM and you need to sleep

310K notes
·
View notes
Photo


“The seat of House Clegane, which is located southeast of Lannisport in the Westerlands. The keep was given to the first Clegane knight, the kennelmaster at Casterly Rock, who saved Lord Tytos Lannister from a lion and lost a leg in the effort.” (x)
386 notes
·
View notes
Text
I just read an article by a male author where he is trying to give advice to romance authors on how to write believable men. Basically his advice is to make them dumber and hornier. Like bruh…I don’t think you understand the point of romance novels.
We know what standard, low effort, uninteresting men are like in real life (trust me. We knooooow)
Sorry if being held to a higher standard makes you feel bad :(
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
what y’all thinking about fellas
155K notes
·
View notes











