Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Mastering Business Process Modeling: Techniques, Tools, and Implementation
In the dynamic landscape of modern business, efficiency is paramount. Business process modeling emerges as a powerful tool to streamline operations, enhance communication, and drive innovation. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of business process modeling, covering techniques, advantages, tools, implementation steps, case studies, future trends, and the pivotal role of intelligent document processing.

Introduction: Understanding Business Process Modeling
Business process modeling serves as the blueprint for organizational workflows, offering a visual representation of interconnected processes across departments. Its primary goal is to simplify complex workflows, optimize processes, and facilitate informed decision-making.
Exploring Business Process Modeling Techniques
BPMN (Business Process Modeling Notation): Utilizes standardized symbols to represent organizational workflows, fostering effective communication and collaboration.
UML (Unified Modeling Language) Diagrams: Object-oriented charts that depict relationships between actors and systems within a business context.
Flowcharts: Simple yet versatile diagrams that visualize process flows using standardized shapes and symbols.
Gantt Charts: Project management tools that provide a timeline view of tasks, aiding in scheduling and resource allocation.
PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) Diagrams: Project management tools for scheduling and coordinating tasks within a project, particularly beneficial for large-scale projects with uncertain timeframes.
Advantages of Business Process Modeling
Visualization of Complex Processes: Simplifies complex workflows, making them accessible and understandable for all stakeholders.
Enhanced Communication: Improves communication among teams and departments, fostering collaboration and alignment.
Resource Optimization: Identifies inefficiencies in resource utilization, leading to higher productivity and cost savings.
Better Decision-Making: Provides insights for informed decision-making based on real data and facts.
Automation Opportunities: Identifies tasks for automation, enhancing efficiency and competitiveness.
Selecting the Right Business Process Modeling Tool
Considerations include compatibility with business needs, user-friendliness, integration capabilities, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Popular tools include BPMN-based tools like Signavio and Bizagi, UML tools like Lucidchart and Enterprise Architect, flowchart tools like Microsoft Visio, and process automation tools like Hyland IDP and Hyland RPA.
Implementing Business Process Modeling: 7 Steps to Success
Define objectives, select the right technique, train your team, start with a pilot project, collect feedback, roll out across the organization, and regularly review and update.
Case Studies for Successful Implementations
Examples include saving hours of administration work for a fashion company through RPA implementation and improving interdepartmental collaboration for a healthcare organization using business process modeling solutions.
Future Trends in Business Process Modeling
Trends include the integration of AI and ML, increased emphasis on cloud-based solutions, enhanced focus on customer-centric processes, greater adoption of low-code and no-code platforms, and a focus on sustainability and compliance.
youtube
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) and its Role in Business Process Modeling
IDP solutions like Hyland IDP enhance efficiency, speed, data accuracy, integration, scalability, compliance, security, and continuous improvement within the business process modeling framework.
Conclusion: Business Process Modeling as a Cornerstone for Efficiency and Competitiveness
Business process modeling empowers organizations to navigate modern challenges with agility and resilience, driving strategic innovation and sustainable growth.
SITES WE SUPPORT
Business Modeling - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
0 notes
Text
The Power of Business Process Management (BPM)
Are you feeling held back by outdated processes? Business Process Management (BPM) might be the solution you need. In this guide, we'll delve into what BPM is, why it's essential, the different types of BPM, the stages of the BPM lifecycle, best practices, and the benefits it offers.
What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
Business Process Management (BPM) involves analyzing and enhancing business processes to achieve specific organizational goals. These processes, which comprise a series of tasks or activities, may become inefficient or ineffective over time due to changes in team size or technology. BPM helps identify bottlenecks, automate manual work, and optimize processes for efficiency and effectiveness simultaneously.
Why is BPM Important?
BPM synchronizes people, systems, and information to achieve targeted business outcomes. It enhances operational efficiency, productivity, and innovation by streamlining processes and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. For example, a software development team improved project completion rates and collaboration efficiency after adopting BPM systems.
Types of BPM
There are three main types of BPM:
Human-centric BPM: Focuses on processes predominantly carried out by people, integrating notifications, user-friendly interfaces, and effective tracking capabilities.
Document-centric BPM: Centers on processes where documents are the primary output, such as legal documents or blog posts.
Integration-centric BPM: Addresses the challenge of using multiple tools by enabling integrations to create a central source of truth for information.
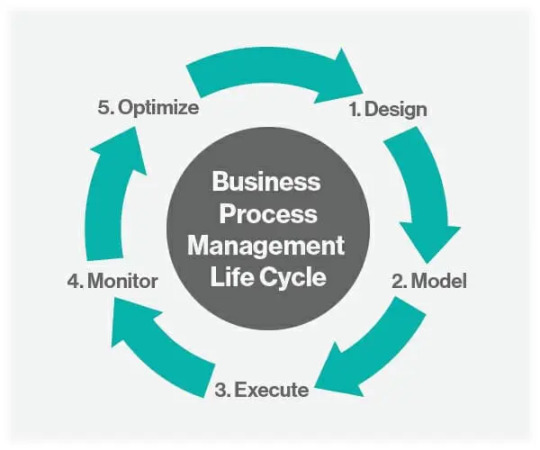
Stages of the BPM Lifecycle
The BPM lifecycle consists of five stages:
Analyze: Understand current processes from start to finish without making changes.
Model: Design the ideal process flow based on analysis findings.
Implement: Put the model into action and establish metrics for success or failure.
Monitor: Continuously assess new processes' performance and address any issues.
Optimize: Tweak and improve processes over time, automating where possible.
BPM Best Practices
Effective BPM implementation requires:
Engaging diverse perspectives
Establishing a BPM Center of Excellence (CoE)
Managing expectations
Integrating performance measurement
Benefits of BPM
BPM offers numerous benefits, including:
Mapping and improving processes
Automating tasks
Reducing waste and errors
Improving efficiency and effectiveness
Generating better products and services
Enhancing customer satisfaction
Business Process Management Software
BPM software helps organizations map, monitor, and streamline processes. It typically includes features for mapping current processes, modeling ideal ones, automating tasks, and tracking ongoing work.
Types of BPM Technologies
BPM technologies include:
Process design tools
Process mining tools
Process performance monitoring tools
Business Process Examples
BPM transforms processes in various departments:
Sales: Streamlines lead generation, tracking, and performance analysis.
Human Resources: Automates recruitment, onboarding, and performance management.
Finance: Optimizes budgeting, invoicing, and financial reporting.
Choosing the Right Process Optimization Approach
When selecting a process optimization approach, consider:
BPM vs. workflow management: BPM focuses on end-to-end processes, while workflow management targets specific workflows.
BPM vs. project management office (PMO): BPM improves processes across the organization, while a PMO focuses on project management best practices.
BPM vs. business process automation (BPA): BPA automates manual processes within BPM.
Robotic process automation (RPA): Specialized automation for repetitive tasks.
youtube
In summary, BPM helps organizations identify and improve inefficient processes, leading to increased efficiency, productivity, and innovation across the board. Whether you're a large enterprise or a small team, BPM can drive meaningful improvements and help achieve strategic objectives. SITES WE SUPPORT
Business Modeling - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
0 notes
Text
7 Types of Pre-Employment Assessment Tests and Screenings
Pre-employment testing has become a crucial step in the hiring process for many employers. These assessments are designed to evaluate various aspects of a candidate's suitability for a particular job role. By understanding the different types of pre-employment tests, you can better prepare yourself for the hiring process and increase your chances of landing your desired job.

What is Pre-Employment Testing?
Pre-employment testing refers to the standardized assessments and screenings that employers use to gather information about candidates during the hiring process. These tests aim to assess a candidate's skills, abilities, personality traits, and other relevant factors to determine their suitability for a specific role.
Why Do Employers Use Pre-Employment Testing?
Employers utilize pre-employment testing for several reasons:
Accelerate the Hiring Process: Pre-employment tests help employers streamline the hiring process by quickly identifying qualified candidates from a large pool of applicants.
Assess Skills: These tests allow employers to evaluate a candidate's skills and competencies related to the job requirements. For example, a writing test may be administered to assess a candidate's writing abilities for a copywriter position.
Improve Interview Quality: By gathering comprehensive data on candidates, employers can conduct more targeted interviews that focus on specific skills and experiences relevant to the job.
Types of Pre-Employment Tests
There are several types of pre-employment tests that candidates may encounter during the hiring process:
Job Knowledge Tests: These tests assess a candidate's knowledge and understanding of the specific job they are applying for. Candidates may be tested on their knowledge of relevant industry practices, tools, and processes.
Integrity Tests: Integrity tests evaluate a candidate's honesty, ethics, and reliability. Employers use these tests to assess a candidate's trustworthiness and suitability for roles that require high levels of integrity.
Cognitive Ability Tests: Cognitive ability tests measure a candidate's mental capacity and problem-solving skills. These tests assess a candidate's ability to think critically, solve problems, and adapt to new situations.
Personality Tests: Personality tests aim to evaluate a candidate's personality traits and characteristics. Employers use these tests to assess whether a candidate's personality aligns with the company culture and the requirements of the job role.
Emotional Intelligence Tests: Emotional intelligence tests assess a candidate's ability to recognize and manage emotions, both in themselves and others. These tests evaluate skills such as teamwork, adaptability, and empathy, which are essential for success in many workplace environments.
Skills Assessment Tests: Skills assessment tests evaluate a candidate's proficiency in specific job-related skills, both soft and hard. These tests may include tasks such as writing samples, presentations, or practical exercises to assess a candidate's abilities.
Physical Ability Tests: Physical ability tests measure a candidate's strength, stamina, and physical capabilities. These tests are often used for roles that require physical labor or specific physical fitness requirements, such as firefighting or law enforcement.
youtube
By understanding the different types of pre-employment tests and screenings, candidates can better prepare themselves for the hiring process and demonstrate their suitability for the desired job role. Preparation may include familiarizing oneself with the format and content of the tests, practicing relevant skills, and showcasing relevant experiences and achievements during interviews.
SITES WE SUPPORT
Business Modeling - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
0 notes
Text
Understanding Business Process Modeling Notation
Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) is a method used to visually represent the steps of a planned business process from start to finish. It serves as a key component of Business Process Management (BPM), providing a detailed depiction of business activities and information flows necessary to complete a process.

History and Evolution
BPMN was initially developed by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI) and has undergone several revisions over time. In 2005, the BPMI merged with the Object Management Group (OMG), which subsequently took over the development of BPMN. In 2011, OMG released BPMN 2.0, introducing a more comprehensive standard for business process modeling. This version, now known as Business Process Model and Notation, expanded the set of symbols and notations available for creating Business Process Diagrams (BPDs). Additionally, BPMN has been complemented by the Decision Model and Notation standard since 2014, addressing decision flows in business processes.
Purpose and Benefits
At its core, BPMN aims to improve efficiency, adaptability, and competitiveness by providing a standardized visual representation of business processes. It serves as a common language for stakeholders involved in process understanding, implementation, and optimization, bridging the gap between business intent and technical execution. BPMN diagrams facilitate easier communication and collaboration among stakeholders, leading to the development of efficient processes that deliver high-quality results. Moreover, BPMN diagrams can aid in the generation of XML documents required for executing various processes, with standards like Business Process Execution Language for Web Services (BPEL).
Diagram Elements and Symbols
BPMN diagrams consist of various elements and symbols, including:
Flow Objects: Representing events, activities, and gateways within a process. Connecting Objects: Including sequence flow, message flow, and association, defining relationships between flow objects. Swimlanes: Dividing the diagram into pools and lanes to represent different participants or organizational units. Artifacts: Providing additional information such as data objects, groups, and annotations to enhance diagram clarity. Key Components of BPMN Diagrams
Events: Triggering actions that start, modify, or complete a process, classified into various types based on their function. Activities: Tasks or actions performed by individuals or systems, often detailed with sub-processes and variations. Gateways: Decision points within a process, directing the flow based on conditions or events. Sequence Flow: Indicating the order in which activities are performed. Message Flow: Depicting messages exchanged between participants across organizational boundaries. Association: Linking artifacts or text to events, activities, or gateways for additional context.
Sub-Models and Diagram Types
BPMN supports the creation of sub-models within diagrams to cater to diverse audiences, including private, abstract, and collaboration processes. Additionally, other diagram types such as choreography, collaboration, and conversation diagrams offer alternative views of process interactions and messaging flows.
Key Tips for Business Process Modeling
Clearly define the scope of the process, identifying its start and end points. Map the current business process to identify inefficiencies before modeling improvements with BPMN. Aim for diagrams that fit on a single page to enhance readability and understanding. Layout sequence flows horizontally and associations vertically for clarity. Customize diagram versions for different stakeholders based on their level of detail requirements. Use BPMN for process modeling, avoiding organizational structures or data flow representations. How to Use Lucidchart for BPMN Modeling
youtube
Lucid chart provides a user-friendly platform for creating BPMN diagrams. Users can access BPMN shapes libraries, drag and drop elements onto the canvas, and customize diagram appearance and layout. The tool enables easy collaboration, sharing, and exporting of BPMN diagrams to facilitate communication and implementation of business processes.
SITES WE SUPPORT
Business Modeling - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
0 notes
Text
Understanding Business Process Management
Business process management (BPM) is a strategic approach aimed at modeling, analyzing, and optimizing end-to-end business processes to align with organizational goals, such as enhancing customer experience frameworks. It involves systematically evaluating and improving repetitive, ongoing, or predictable tasks and processes within a business context.

A business process encompasses a series of activities that collectively contribute to achieving a specific objective. By leveraging BPM, organizations can assess their existing processes to identify opportunities for enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, minimizing errors, and facilitating digital transformation initiatives.
BPM is a continuous endeavor that yields progressive improvements in business outcomes over time. It enables organizations to replace ad hoc workflow management practices with optimized operational strategies, thereby delivering superior products and services to customers.
BPM Methodology
The BPM methodology typically comprises several iterative phases:
Analyze: Evaluate the current state of the process, identifying areas of inefficiency, bottlenecks, or issues, and assess how they impact overall performance and objectives.
Model: Design an optimized version of the process, considering potential improvements and variations, and create a visual representation to illustrate the proposed changes.
Execute: Implement the redesigned process, documenting the modifications made and the rationale behind them to ensure clarity and accountability.
Monitor: Track the performance of the updated process, collecting relevant data to measure its effectiveness against predefined benchmarks and strategic objectives.
Optimize and Automate: Continuously refine the process based on ongoing monitoring and feedback, exploring opportunities for automation to further enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
BPM and Automation
While BPM primarily involves human-driven practices, automation technologies play a crucial role in facilitating process improvements and streamlining operations. BPM software and automation tools, akin to enterprise resource planning (ERP) and data management systems, can be leveraged to implement identified process enhancements.
Automation enhances business efficiency by utilizing software to execute tasks, thereby reducing costs, complexity, and errors associated with manual intervention. While BPM serves as the foundational methodology for understanding end-to-end processes, automation complements these efforts by continuously monitoring and refining process efficiencies.
Why Automate with Red Hat
Red Hat advocates for a paradigm shift in business automation, emphasizing the need to move beyond conventional process streamlining towards innovative strategies for automating core business functions. Rather than focusing solely on internal efficiency and cost control, organizations must prioritize customer engagement and the creation of new business opportunities.
youtube
Red Hat collaborates with the open-source community to develop automation technologies that enhance features, reliability, and security, ensuring robust and stable IT operations. Their solutions, services, and training empower organizations to embrace automation fully, enabling them to reallocate resources towards innovation and future growth initiatives.
SITES WE SUPPORT
Business Modeling - Wix
SOCIAL LINKS Facebook Twitter LinkedIn
1 note
·
View note