Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
A complete analysis of the painting process of shaft couplings: key steps to improve durability and aesthetics
As the core components of mechanical transmission systems, cardan shaft couplings are widely used in metallurgy, mining, shipbuilding and heavy machinery. The painting process is not only related to the appearance, but also directly affects the anti-rust performance and service life. This article will introduce the painting requirements of cardan shaft couplings in detail, including surface treatment, coating selection, spraying process and quality control, to help users optimize the painting process and improve product performance.
1. Surface treatment before painting (key foundation)
(1) Thorough cleaning Remove oil stains: Use industrial cleaning agents (such as acetone or special degreasers) to remove oil stains, dust and rust on the surface of the coupling.
Sandblasting/shot blasting: Sandblast or shot blast the metal surface to ensure that the roughness is controlled within Ra3.2μm~6.3μm to enhance the adhesion of the paint film.
(2) Check surface defects The welding parts need to be polished smooth to remove burrs, welding slag and other protrusions.
If cracks or pores are found, they need to be repaired and re-polished first, otherwise the coating will easily peel off after painting.

2. Coating selection and painting process
Spraying thickness: usually 50-80μm, even coverage is required to avoid missing spraying or excessive thickness causing sagging.
(2) Topcoat spraying Recommended topcoat: polyurethane topcoat (strong weather resistance) or alkyd enamel (economical and practical).
Color standard: usually orange-red (JB/T standard), but can be customized according to customer needs8.
Spraying distance: keep the spray gun 15-20cm away from the workpiece to avoid paint accumulation due to being too close or uneven paint film due to being too far away.
(3) Treatment of special parts Flange end face and spline part: only apply anti-rust grease to avoid spraying affecting assembly accuracy.
Bearing hole and cross shaft contact surface: need to be protected with tape to prevent paint mist from entering and affecting lubrication performance.

3. Paint quality control (1) Paint film thickness detection Use a coating thickness gauge to ensure that the total thickness of the primer + topcoat is between 120-150μm.
(2) Adhesion test Use the cross-cut method (ISO 2409 standard). The paint film should not fall off or peel off in a large area.
(3) Drying and curing Natural drying: more than 24 hours at room temperature.
Bake curing (optional): bake at 60-80℃ for 2-4 hours to accelerate curing and increase the hardness of the paint film.
0 notes
Text
A complete analysis of common problems with crane wheels
Crane wheels are core equipment for industrial transportation and heavy lifting, and wheels, as their key load-bearing and operating components, directly affect the safety and service life of the equipment. However, due to long-term high-load operation, installation errors or improper maintenance, crane wheels often have problems such as rail gnawing, wear, deformation, and even derailment accidents in severe cases. This article will deeply analyze the common failures, causes and solutions of crane wheels to help equipment managers optimize maintenance strategies and extend the life of wheels.
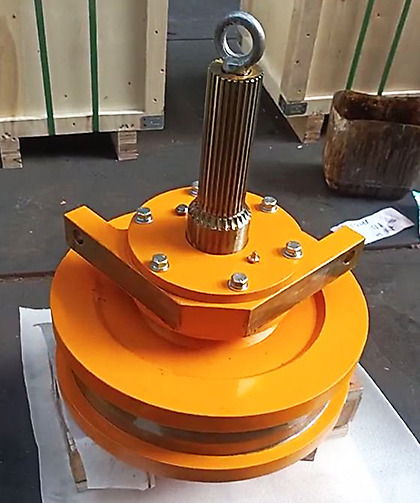

一、Common problems with crane wheels 1、Rail biting Rail biting refers to the friction between the wheel flange and the side of the track when the crane wheels are running on the track, resulting in abnormal wear and noise. Rail biting is extremely harmful, including:
(1)Increased wheel and track wear: Under normal circumstances, the wheels can be used for more than 5 years, but when the rail biting is serious, the life span may be shortened to 1 year.
(2)Increased running resistance: Cause motor overload and even drive shaft deformation.
(3)Cause derailment risk: In severe cases, the wheels may climb onto the track and cause the equipment to overturn.
Main causes of rail biting:
(1)Horizontal/vertical wheel deviation: Installation error or bridge deformation causes the wheel to be non-parallel to the track.
(2)Transmission system asynchrony: For example, the motor speeds on both sides are inconsistent or the brakes are not adjusted evenly.
(3)Rail installation deviation: Track spacing, height or straightness is out of tolerance
2、Wheel wear Crane wheels are subjected to heavy loads for a long time, and the main forms of wear include:
(1)Tread wear: If the original thickness exceeds 15%, it needs to be replaced or repaired.
(2)Rim wear: If the wear reaches 50% or there is a break, it needs to be scrapped.
(3)Crushing of hardened layer: Insufficient depth of quenching layer (should be ≥20mm) leads to surface peeling.
(4)Wheel cracks: If cracks are found, it must be replaced immediately, otherwise it may break and cause an accident.
二、Solutions and maintenance tips (1) Adjust the wheel unit Correction of horizontal deflection: adjust the bearing support or add or remove shims to ensure that the deflection is ≤D/400 (D is the wheel diameter).
Correction of vertical deflection: adopt an "eight" layout (the top of the wheel faces outward) to reduce the impact of deflection.
Span and diagonal adjustment: the span error of the trolley is ≤±7mm, and the trolley is ≤±3mm.
(2) Optimize the transmission system Synchronous drive motor: ensure that the motor model and parameters at both ends are consistent to avoid speed difference.
Braker balance adjustment: the braking torque on both sides must be the same to prevent asynchronous braking.
(3) Track maintenance and wheel replacement Regularly check the track: measure the track gauge and levelness every 6 months, and clean oil and frost.
Replace worn wheels: the diameter deviation of the driving wheel is ≤0.1%, and the driven wheel is ≤0.2%.
0 notes
Text
Speed reducer = gear box? Revealing the "heart" of industrial transmission, how the Gear Box changes the world
In the roaring workshop of the factory, behind the slowly turning blades of the wind turbine, and even on the top of your elevator, there is an underestimated "power magician": the gear box. This seemingly bulky metal box is actually the hidden champion of modern industry. Today, we will use the perspective of an engineer to help you understand this key component that is both familiar and unfamiliar!
1、Why is the reducer called a "gear box"? The essence of a reducer is a precision system that achieves "speed reduction and torque increase" through a gear set. Just like a car's transmission adjusts the speed of the car, the industrial gear box converts the high-speed rotation of the motor into the low-speed, high-torque output required by the equipment through a combination of gears of different sizes.

2、 Three magical abilities of Gear Box
Speed converter
Is the motor speed too fast? For example, a 3000rpm motor only needs 30rpm to drive the conveyor belt. The gearbox is like an "industrial brake" that accurately reduces the speed.
Power amplifier
Through gear meshing, the torque can be amplified a hundred times (formula: torque output = input torque × reduction ratio).
Energy guardian
The transmission efficiency of high-quality Gear Box exceeds 97%, which is more efficient than any other transmission method invented by humans!
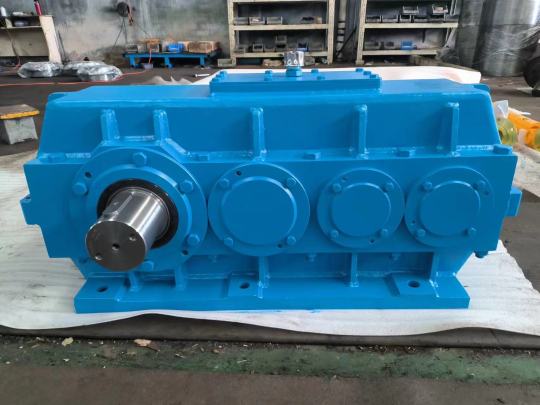

3、Principle of gearbox
The gear box is the core component of the mechanical transmission system, which realizes power transmission, speed regulation and torque conversion through gear meshing. Its basic principle can be summarized as: "the small gear drives the large gear to reduce speed, and the large gear drives the small gear to increase speed"
4、Gearbox structure
The gearbox is mainly composed of an input shaft, a gear set, an output shaft, a housing and a lubrication system. The input shaft is connected to the power source to drive the active gear, and the power transmission is achieved by meshing with the driven gear; the multi-stage gear set can adjust the speed and torque step by step, and the output shaft transmits the adjusted power to the actuator; the housing provides support and sealing, and the internal lubrication system reduces gear wear through oil bath or forced circulation. This compact and efficient structural design enables the gearbox to adapt to various transmission requirements from precision instruments to heavy machinery.
0 notes
Text
Crane drum: analysis of the core components behind efficient operation
In crane equipment, Crane Drum is one of the most important components. It is responsible for the winding and release of wire ropes, which directly affects the load capacity and operating efficiency of the crane. Whether it is port hoisting, construction site or mining operation, the performance of the drum determines the safety and stability of the equipment.
This article will explore the structure, working principle, common types and maintenance points of the crane drum in depth to help you better understand the operating mechanism of this key component.

Basic structure of crane drum Crane drum usually consists of the following core parts:
Drum: The main structure that carries the wire rope, usually made of high-strength steel to ensure wear resistance and deformation resistance.
Flange: Located at both ends of the drum to prevent the wire rope from falling off and enhance safety.
Shaft and bearing: Support the rotation of the drum to ensure smooth operation.
Rope groove (optional): Some drums are designed with spiral rope grooves to make the wire rope more neatly arranged and reduce wear.
Working principle of crane drum The core function of crane drum is to realize the retraction and release of wire rope through the drive of motor or hydraulic system, so as to complete the lifting or horizontal movement of goods. Its working process is as follows:
Power input: The motor or hydraulic motor drives the drum to rotate.
Wire rope winding: When the drum rotates, the wire rope is wound or released in a specific direction.
Load control: The drum speed is adjusted through the braking system to ensure a smooth and safe lifting process.
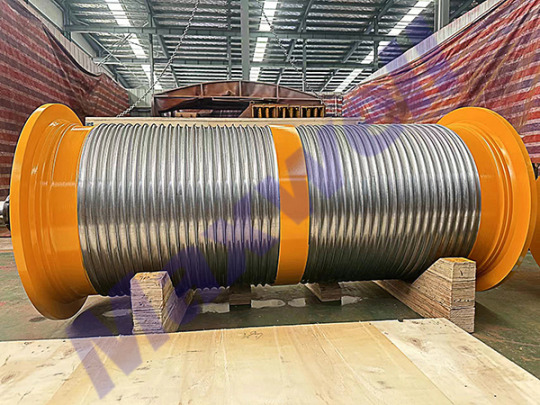

3. Maintenance and optimization of crane drum In order to ensure the long-term stable operation of Crane Drum, the following maintenance points should be noted: ✅ Regular lubrication: reduce the friction between the wire rope and the drum and extend the service life. ✅ Check wear: pay attention to whether there are cracks, deformation and other problems on the rope groove or drum surface. ✅ Wire rope management: avoid tangled ropes and skipping grooves, and ensure neat arrangement. ✅ Braking system inspection: prevent accidental rotation of the drum to ensure operation safety.

Key points for crane drum selection Choosing a suitable crane drum is crucial to the performance and life of the crane. The following are key selection factors:
(1) Load capacity Select the load capacity of the drum according to the maximum lifting weight to ensure that the drum and wire rope match.
(2) Wire rope specifications The drum diameter should be ≥ 20 times the wire rope diameter to reduce bending stress and extend life.
(3) Working environment Wet/corrosive environment: Use stainless steel or galvanized drums to improve rust resistance.
High temperature environment: Choose high temperature resistant materials to avoid deformation.
(4) Operating speed High-speed operation requires a rope groove drum to prevent the wire rope from jumping.
Smooth drums can be used for low speed and light load to reduce costs.
(5) Installation method Select a single-support or double-support drum according to the crane structure to ensure stability.
0 notes
Text
Crane wheels: Choose the right wheels, and the crane will be as stable as Mount Tai!
Crane wheels are key components of the crane's operating mechanism, just like car tires, which directly affect the stability, safety and service life of the equipment. If the wrong wheels are chosen, the wear will accelerate at best, and the crane may derail or even cause a safety accident!
So, how should crane wheels be chosen? What types are there? How to extend the service life? This article will answer all your questions in the simplest and most understandable way!

一、 The function of crane wheels
Crane wheels have three main roles:
✅ Carrying weight - supporting the entire weight of the crane and the load
✅ Smooth operation - ensuring smooth movement of the crane on the track
✅ Preventing derailment - the wheel rim design can prevent the wheel from sliding off the track
二、How to choose the right crane wheel?
Choosing the wrong wheel = wasting money + safety hazard! Remember these 5 key points:
1. Look at the carrying capacity
Rated load of the wheel ≥ Maximum wheel pressure of the crane × 1.2 (safety factor)
For example: The maximum load of a single wheel is 10 tons, and a wheel of more than 12 tons should be selected
2. Look at the track matching
The wheel tread width should be slightly larger than the track top width (usually 5-10mm larger)
The wheel flange height should be able to effectively prevent derailment (generally ≥25mm)
3. Look at the working environmen
High temperature environment (such as steel mills) → Choose heat-resistant alloy steel
Humid/corrosive environment (such as ports) → Choose stainless steel or coating treatment
High dust environment (such as cement plants) → Choose sealed bearing design
4. Look at the running speed
Low-speed crane (≤30m/min) → Ordinary cast steel wheels are sufficient
High-speed crane (>60m/min) → Precision machining + dynamic balancing test required
5. Look at the maintenance cost
Lubrication method: Automatic lubrication wheels can reduce manual maintenance
Convenience of replacement: Modular design can reduce downtime

三、 Common problems and solutions for crane wheels
❌ Problem 1: Wheels wear too fast
Possible causes:
Uneven track
Overloaded operation
Wheel material mismatch
Solutions:
✔ Check track levelness regularly
✔ Replace wheels with higher hardness (such as HRC50+)
❌ Problem 2: Crane deviation
Possible causes:
Wheel diameter inconsistency
Track installation error
Solution:
✔ Use tapered tread wheels (automatic deviation correction)
✔ Check and adjust track parallelism
❌ Problem 3: Wheel rim fracture
Possible causes:
Unqualified material (prone to cast iron wheels)
Excessive impact load
Solution:
✔ Replace forged steel or alloy steel wheels
✔ Install buffer devices
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to choose the right crane drum?
一、When choosing a drum, the following key factors need to be considered:
1. Load capacity (Ton Capacity)
The drum must be able to withstand the maximum working load and leave a safety margin (usually calculated as 1.25~1.5 times).
2. Wire rope diameter and length
The drum diameter should be ≥20 times the wire rope diameter to reduce bending fatigue.
The drum length needs to match the wire rope length to avoid over-winding or under-winding.
3. Working environment
Indoor: ordinary steel drums are sufficient.
Outdoor/corrosive environment: galvanized, stainless steel or special coating is required for rust prevention.
High temperature/low temperature environment: heat-resistant or cold-resistant materials are selected.
4. Operating speed and frequency
High-speed crane: use high-strength, low-friction spiral groove drums.
High-frequency operation: wear-resistant cast drums are preferred.
5. Installation method
End support type (fixed at both ends)
Middle support type (single-side drive)

二、Maintenance and care of crane drum
In order to extend the life of the drum, it is recommended to:
✅ Regular lubrication: reduce the friction and wear between the wire rope and the drum.
✅ Check wear: if the groove is deformed or cracked, it should be replaced in time.
✅ Avoid overloading: prevent the drum from deforming or the wire rope from breaking.
✅ Clean and prevent rust: when used outdoors, water and dust should be cleaned regularly.
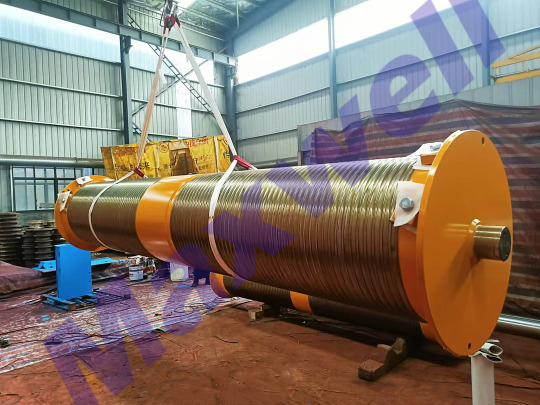

三、Why choose our crane drum?
✔ High-strength material: Made of high-quality cast steel/steel plate to ensure durability.
✔ Precision machining: Optimized spiral groove design to reduce wire rope wear.
✔ Customized service: Support different sizes, materials and coating requirements.
✔ Global certification: Comply with international standards such as ISO, CE, ASME, etc.
Need professional advice? Contact our engineers for free selection support!
0 notes
Text
Wrong buffer selection = short life of equipment?
In equipment such as cranes, elevators, and automated production lines, buffers are like "mechanical airbags" - they can absorb impact energy at the moment of collision and protect the equipment from damage. But did you know? Choosing the wrong buffer may cause equipment vibration to intensify, bearings to fail, and even cause safety accidents!
一、What is a buffer? Why is it so important?
1. Core role
✅ Absorbing impact: converting collision kinetic energy into heat energy to reduce equipment damage.
✅ Protecting the structure: preventing metal parts from directly hitting (such as a crane hitting the end of the track).
✅ Reducing noise: reducing the "bang" impact sound and improving the working environment.
2. The cost of buffer failure
Direct loss: Equipment maintenance costs up to tens of thousands of yuan (such as the end beam of the crane being deformed by collision).
Hidden costs: Damage to guide rails, bearings and other components, and extended maintenance cycles.
Safely risks: Loss of control of elevators or cranes may cause casualties.
Industry data: According to OSHA statistics, 27% of crane accidents are related to buffer failure!


二、Comparison of the three major mainstream buffers
1. Hydraulic buffer (most commonly used)
Principle: The hydraulic oil flows through the small hole to create resistance, which cushions the impact like "drinking honey with a straw".
Advantages:
Strong energy absorption capacity (suitable for medium and high speed impacts of 1-5 m/s).
Reusable and long life (5-8 years).
Disadvantages:
The oil becomes thicker at low temperatures and the cushioning force increases (low temperature hydraulic oil must be selected).
Applicable scenarios: crane trolleys, port gantry cranes, punching machines.
2. Polyurethane buffer (economical type)
Principle: Use elastic deformation to absorb energy, similar to "rubber band".
Advantages:
Low price, maintenance-free.
Corrosion-resistant (suitable for humid environments).
Disadvantages:
Weak energy absorption capacity (suitable for low-speed impacts <1 m/s).
Long-term compression will age (need to be replaced every 3-5 years).
Applicable scenarios: light conveyor belts, storage shelves, small lifts.
3. Spring buffer (traditional type)
Principle: Rely on metal spring compression to store energy and rebound like a "trampoline".
Advantages:
Simple structure and extremely low cost.
Disadvantages:
Easy to rebound (impact energy is not fully absorbed).
Springs are prone to fatigue fracture (frequent inspection is required).
Applicable scenarios: low-speed and light-load equipment (such as trolley limit)


三、 Common Problems and Maintenance
⚠️ Fault Warning:
Oil Leakage → Hydraulic Buffer Seal Failure (Replace Immediately).
Weak Rebound → Polyurethane Aging or Spring Breakage.
Abnormal Sound → Loose Installation or Internal Parts Damage.
🔧 Maintenance Tips:
Check the Buffer Fixing Bolts for Looseness Every Month.
Test the Buffer Stroke Every Year (It Should Return Slowly After Pressing).
Replace the Seal of the Hydraulic Buffer Every 3 Years (or Replace the Entire Buffer).
0 notes
Text
Wrong coupling selection = equipment scrapped? 5 minutes to teach you to avoid 90% of selection pitfalls!
In industrial equipment, couplings are like "joints" in the human body, responsible for connecting motors, reducers and loads, transmitting power and compensating for deviations. But did you know? Choosing the wrong coupling may cause equipment vibration, bearing damage, or even the entire machine to be scrapped! Today, we will use 5 minutes to help you avoid 90% of selection pitfalls and save huge repair costs!

一.、4 disastrous consequences of choosing the wrong coupling
1. Intensified equipment vibration → premature bearing failure
❌ Wrong selection: rigid coupling is used for high deviation conditions.
💥 Consequence: vibration is transmitted to the bearing, shortening the life by 70% (e.g. SKF bearings cost thousands of yuan each!).
2. Insufficient torque → coupling breakage
❌ Wrong selection: light plum coupling is used to carry heavy rolling mill torque.
💥 Consequence: coupling breakage, production line shutdown loss of 100,000 yuan/day!
3. Braking failure → crane hook slipping
❌ Wrong selection: ordinary coupling is used instead of coupling with brake disc.
💥 Consequence: hoisted heavy objects fall out of control, causing major safety accidents.
4. Corrosion perforation → chemical pump leakage
❌ Wrong selection: carbon steel coupling is used in acid and alkali environment.
💥 Consequences: 6 months of rust and perforation, replacement costs + loss of production suspension exceeding 500,000 yuan.
Data warning: According to ISO statistics, 32% of transmission failures are caused by incorrect coupling selection!
二、3 real selection cases
Case 1: Port gantry crane
Wrong choice: ordinary gear coupling.
Problem: Impact during braking causes pitting on the tooth surface.
Correct solution: Use WGP drum gear coupling with brake disc, which increases the service life by 3 times.
Case 2: Chemical plant centrifugal pump
Wrong choice: cast iron plum coupling.
Problem: Corrosion stuck after 3 months.
Correct solution: stainless steel diaphragm coupling, running for 5 years without trouble.
Case 3: CNC machine tool spindle
Wrong choice: rigid coupling.
Problem: Machining accuracy of ±0.1mm cannot meet the standard.
Correct solution: zero backlash diaphragm coupling, with accuracy increased to ±0.01mm.
Need one-on-one selection support?
📞 Free consultation: Submit your equipment parameters
+86+8615936560589
0 notes
Text
From forging to heat treatment: revealing the whole process of crane hook manufacturing
At construction sites, port terminals or factory workshops, crane hooks silently bear hundreds of tons of weight. But do you know? From raw materials to finished products, a qualified hook has to go through multiple processes such as forging, heat treatment, and precision machining. Any mistake in any step may cause a major accident!
Today, we take you into the factory of a crane hook manufacturer to reveal the birth process of the hook - see how these "steel strongmen" are forged!

Step 1: Material selection - A good hook starts with "good steel"
✅ Core materials:
Alloy steel (such as 34CrMo, 42CrMo): high strength, impact resistance, suitable for heavy lifting.
High-quality carbon steel (such as 45 steel): economical and practical, suitable for light and medium cranes.
❌ Risks of inferior materials:
Many impurities → There are pores and cracks inside the hook, which is easy to break.
Insufficient hardness → Deformation during use, causing the hanging object to fall off.
Step 2: Forging - hammering into a "hook"
Heating The billet is sent into a furnace at 1200℃ and burned until it is red hot, becoming as soft as plasticine.
Forging and forming Die forging: Use a 10,000-ton hydraulic press to press the red-hot billet into a die to initially form the shape of a hook (high efficiency, suitable for mass production).
Free forging: Manually controlled hammering, suitable for customized large-tonnage hooks (such as metallurgical hooks).
Why is forging better than casting?
The inside of the forged hook is denser, without bubbles, and the impact resistance is increased by 50%!

Step 3: Heat treatment - make the hook "hard and flexible"
Quenching The hook is heated to 850℃ and then quickly immersed in oil or water to cool, and the surface hardness soars to HRC 45-50 (like "plating a layer of armor" on steel).
Tempering The hook is heated to 400-600℃ again to eliminate the quenching stress, making the hook "hard outside and tough inside" - both wear-resistant and fracture-resistant.
Consequences of poor heat treatment:
Uneven quenching → Local brittleness, cracking during use.
Insufficient tempering → Residual stress leads to deformation.
Step 4: Machining - Precision determines safety
Turning: CNC machine tools process hook thread holes (error ≤ 0.05mm).
Milling: Open pulley mounting grooves and lock positions.
Flaw detection:
Ultrasonic: Check for internal cracks.
Magnetic particle inspection: Detect surface defects.
Step 5: Assembly and testing
Pulley assembly The bearing is hot-fitted (pressed in after heating to 120°C).
Test the rotational flexibility (there should be no jamming when turning manually).
Overload test Hang for 30 minutes at 1.5 times the rated load (for example, a 50-ton hook should be hoisted at 75 tons!).
Check for deformation or cracking after unloading.
Conclusion
From a piece of steel billet to a reliable crane hook, behind it is the perfect combination of materials science, thermodynamics, and mechanical processing. Choosing a regular crane hook manufacturer is not only responsible for the equipment, but also respect for life!
Is your crane using the right hook? Welcome to leave a message to consult technical details, or request a free hook selection guide!
0 notes
Text
Coupling: The "smart joint" of mechanical transmission - how to choose the right model to save millions of repair costs?
In industrial equipment, couplings are like "joints" in the human body, responsible for connecting motors, reducers and loads, transmitting power and compensating for deviations. Choose the wrong coupling? At the very least, the equipment will vibrate and make abnormal noises, and at the worst, it will cause a production stoppage accident! Today, we will reveal the three key coupling types (including Gear Type Coupling and Crane Drum Coupling) to help you avoid 90% of the selection pitfalls!
一、What is a coupling? Why is it so important?
Core function 1、Transmitting power: transmitting the rotational force of the motor to the equipment (such as crane drum, pump, fan) without loss.
2、Compensating deviation: tolerating slight misalignment between shafts (radial/angular deviation).
3、Buffering and shock absorption: absorbing the impact when the equipment starts and stops (protecting bearings and gears).
二、Comparison of the three major industrial couplings (with selection guide)
1、gear coupling Features: Like "two gears meshing", torque is transmitted through internal and external teeth, heavy-load resistant, and can be fine-tuned for deviation.
Advantages: ✅ Ultra-large torque (up to one million N·m) ✅ Large allowable deviation (radial ±1.5mm, angular ±1°)
Disadvantages: ❌ Regular lubrication is required (otherwise the tooth surface will wear) ❌ Loud noise at high speed
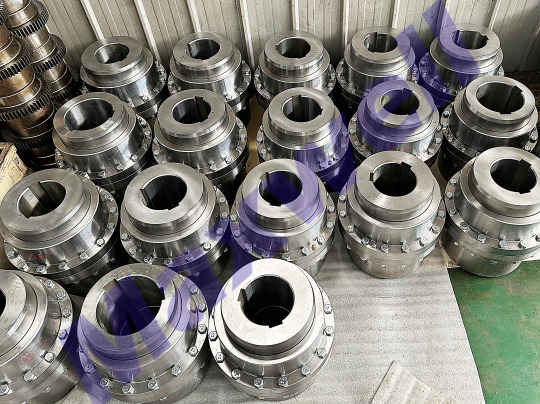

Crane Drum Coupling Features:
Designed specifically for cranes, with strong impact resistance to prevent wire rope vibration from causing shaft breakage.
Advantages: ✅ Integrated with brake wheel (space saving) ✅ Forged steel body, fatigue resistant (100,000 start-stop test)
Disadvantages: ❌ Bulky (20% heavier than ordinary couplings)

Elastic coupling Features:
Rubber/polyurethane elastomer in the middle, shock and noise reduction.
Advantages: ✅ Maintenance-free (no lubrication required) ✅ Suitable for high speed (>5000 rpm)
Disadvantages: ❌ Not resistant to heavy loads (generally <5000 N·m

三、Five golden rules for coupling selection
Torque: Select rated torque > 30% of actual demand (leave a safety margin).
Speed: Select elastic coupling for high speed, Gear Type Coupling for low speed and heavy load.
Deviation: Large angular deviation? Choose universal coupling.
Environment: Select stainless steel for humid environment, heat-resistant alloy for high temperature.
Maintenance: Too lazy to maintain? Choose lubrication-free diaphragm coupling.
四、Need professional support? We provide free coupling selection services, covering:
Torque calculation
Deviation measurement
Failure analysis
📞 Consult now: Send your equipment parameters and get a customized solution!
Tel: +8615936560589
Email:[email protected]
0 notes
Text
Crane Hook Rotation Out of Control? 3 Causes and Emergency Solutions | Crane Hook Safety Guide
During crane operation, the crane hook suddenly spins wildly or becomes uncontrollable, which not only affects work efficiency, but may also cause serious accidents such as wire rope entanglement and cargo falling! Today, we will analyze 3 common causes of failure and provide ready-to-use emergency treatment solutions to ensure your Lifting Safety!
Fault 1: Bearing damage or poor lubrication 🛠️ Fault manifestation The hook makes a "squeaking" sound when rotating
The rotation is stuck, or it suddenly accelerates and spins
The hook temperature rises abnormally
🔧 Emergency treatment Stop the operation immediately to avoid the bearing being completely stuck.
Manual lubrication attempt: If there is high-temperature grease on site, temporarily add it to the bearing part.
Temporary fixation: Use nylon cable ties to limit the rotation of the hook (only for light load emergency).
✅ Preventive measures Clean the bearing and replace the grease every quarter (molybdenum disulfide lithium grease is recommended).
Choose sealed self-aligning bearings to prevent dust and water.

Fault 2: Unbalanced winding of wire rope 🛠️ Fault manifestation Irregular rotation of hook
Spiral twisting of wire rope
Severe shaking of suspended objects in the air
🔧 Emergency treatment Slowly lower the load to avoid sudden loosening of the rope to aggravate the winding.
Unwinding:
If it is a slight winding, the hook can be manually rotated in the opposite direction to reset.
If it is a serious winding, the wire rope needs to be temporarily fixed with an anti-rotation shackle.
✅ Preventive measures Use anti-rotation wire rope
Install a rotation limiter

Fault 3: Locking device failure 🛠️ Fault manifestation Hook rotates freely without resistance Locking nut/pin shaft falls off Bottom thread wear
🔧 Emergency treatment Emergency reinforcement: Temporarily replace the damaged locking parts with high-strength bolts + anti-loosening glue.
Limit operation: Reduce the operating speed to avoid sudden stop and start.
✅ Preventive measures Check the locking nut torque every week (refer to GB/T 3098.1 standard).
Replace with hydraulic anti-loosening nut (such as Nord-Lock washer).
0 notes
Text
From Forging To Heat Treatment: The Entire Process Of Crane Hook Manufacturing
From forging to heat treatment: the whole process of crane hook manufacturing is revealed Crane hooks are the core components of lifting equipment, carrying huge weight, and their manufacturing process directly affects the safety of operations. Today, we take you into the factory to reveal the complete manufacturing process from raw materials to finished products, and understand the precision technology behind the hook suspension system.
1. Raw material selection: high-strength alloy steel Hooks are usually made of alloy steels such as 20CrMnTi and 34CrMo. These materials have high strength, wear resistance and impact resistance, ensuring that they will not deform under heavy loads.
2. Forging: high-temperature shaping to create a prototype The steel billet is heated to more than 1200°C and repeatedly hammered by a forging press to initially form the curved structure of the hook. This process can optimize the internal structure of the metal and improve toughness.

3. Machining: Precision turning and drilling The forged blank is finely processed by CNC machine tools to ensure that the hook size and thread hole position of the hook meet the standards so as to accurately match the Hook Suspension system (such as the pulley block).
4. Heat treatment: Enhance hardness and toughness The hook needs to be quenched + tempered:
Quenching: Rapid cooling to increase surface hardness (HRC 45-50).
Tempering: Eliminate internal stress and enhance fracture resistance.
5. Surface treatment: Rust and wear resistance Galvanized, sprayed or blackened to prevent rust and extend service life.

6. Quality inspection: 100% non-destructive testing Each Crane Hooks must undergo:
Magnetic particle inspection (detect surface cracks).
Ultrasonic inspection (check internal defects).
Load test (1.5 times rated load test).
7. Assembly: Integrated Hook Suspension System Qualified hooks are assembled with pulleys, bearings, locks and other components to form a complete Hook Suspension unit to ensure stable operation.
0 notes
Text
A must-read for crane drivers! 5 daily checks on hooks
As a crane driver, the bottom hook block is one of the parts you come into contact with the most every day, and its safety directly affects the safety of your operations. According to statistics, 30% of crane accidents are related to damage or improper use of the hook. Therefore, daily checks are essential!
Today, we have compiled 7 key actions for daily checks on hooks to help drivers quickly identify hidden dangers and ensure operational safety.

Check the surface cracks of the hook (visually + touch) ✅ Correct operation:
Observe whether there are cracks, deformation or rust on the surface of the hook.
Focus on checking the bending part of the hook (stress concentration area).
Touch it with your hand to feel whether there are abnormal bumps or cracks.
❌ Danger signal:
If cracks or severe deformation are found → Stop using and replace immediately!
Severe rust (affecting strength) → Need to remove rust and evaluate whether to scrap
Test the flexibility of the hook rotation ✅ Correct operation:
Turn the hook gently by hand to check whether it is smooth.
Observe whether the bearing or pulley (if any) is stuck.
❌ Danger signal:
Difficult rotation → Possible lack of oil or bearing damage.
Abnormal noise → Internal parts are worn and need to be disassembled for inspection.
Maintenance advice: Add grease regularly to keep the hook flexible.

Check if the safety latch is normal ✅ Correct operation:
Open and close the latch manually to confirm that the spring rebounds strongly.
Check the wear of the latch to ensure that it can close automatically.
❌ Danger signal:
The latch cannot close automatically → Do not use!
The latch is deformed or worn beyond the limit → Replacement is required.
Failure of the safety latch of the Bottom Hook Block may cause the hanging object to fall off, so it must be strictly checked!

Check the connection between the wire rope and the hook ✅ Correct operation:
Confirm that the shackle or pressure plate is not loose or cracked.
Check whether the wire rope is broken or worn (especially near the hook).
❌ Danger signal:
The shackle bolt is loose → tighten immediately.
The wire rope has excessive broken wires → replace with a new rope.
Maintenance tips: The connection of the Bottom Hook Block should be fully inspected once a month.
Observe the wear mark of the hook ✅ Correct operation:
Check the wear limit mark on the hook (if any).
Measure the thickness of the hook tip, and it is safe if the wear is ≤5%.
❌ Danger signal:
The hook tip is worn thin → the load-bearing capacity is reduced and needs to be replaced.
No wear mark → It is recommended to contact the manufacturer to confirm the standard.
Keyword optimization: Bottom Hook Block Excessive wear will reduce the safety factor and needs to be evaluated regularly.
0 notes
Text
Let's learn about the crane C-hook
The C-hook is a lifting tool specially used for lifting cylindrical or ring-shaped cargoes. It looks like the letter "C" and is usually made of high-strength alloy steel. It is used to carry steel coils, pipes, tires, large coils, etc.
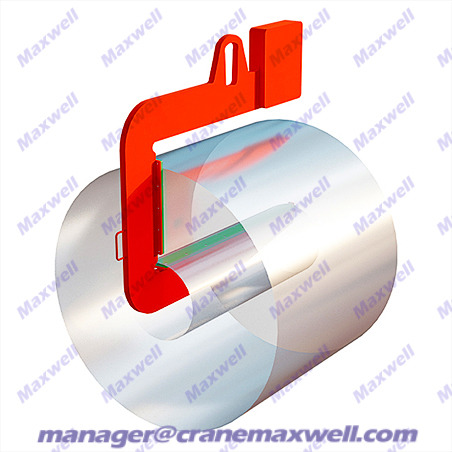

Main features of C-type hook
Special shape: the opening faces downward or sideways, which is convenient for "hooking" the cargo instead of hooking it like ordinary hooks.
Self-locking function: rely on the dead weight of the cargo to press the inner arc surface to prevent slipping (some models also have spring locks or safety pins).
Strong specialization: mainly optimized for annular/cylindrical cargo such as steel coils and pipes, safer and more efficient than ordinary hooks.
How does the C-hook work?
It looks like the letter "C": It is like a huge steel clamp, with the opening facing downward or sideways, and is specially used to hook circular/cylindrical goods such as steel coils and pipes.
Use gravity to self-lock:
When the C-hook lifts the goods, the weight of the goods will press on the inner arc surface of the hook, and the hook will naturally "clamp" the goods.
The inside of the hook usually has anti-slip grooves or rubber pads to increase friction and prevent sliding.
Use with crane: Connect the crane hook through the top ring or lifting lug, and lift/move the crane to move the goods.
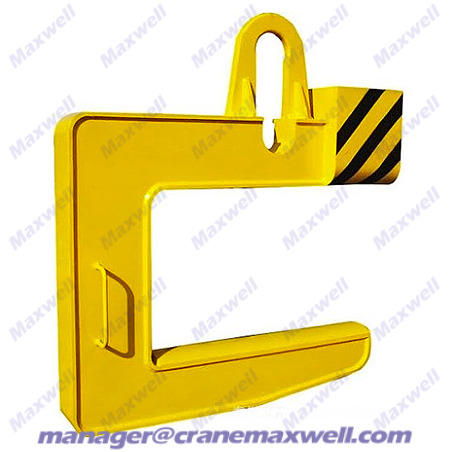

How to choose?
Weight: The rated load of the hook must be greater than the maximum weight of the cargo (for example, if the cargo is 1 ton, choose a hook of more than 1.5 tons).
Shape and size: The width of the hook opening must be greater than the diameter/thickness of the cargo, and the inner arc shape must fit the cargo (for example, a deep arc hook should be used to hang steel coils, and a shallow arc hook should be used to hang pipes).
Look at the working environment:
Temperature: High temperature resistant steel should be selected for high temperature environments (such as steel mills).
Corrosiveness: Select stainless steel or galvanized hooks for humid or chemical environments.
Frequency of use: For frequent use, choose a thickened design or a hook with a bearing (to reduce wear).
Safety function:
Anti-slip design: A hook with a spring lock and a safety pin (to prevent the cargo from falling off when shaking).
Double hook configuration: Overweight or overlong cargo can be lifted and transported in a balanced manner with two C-type hooks.
0 notes
Text
Do you know the wheels of a crane?
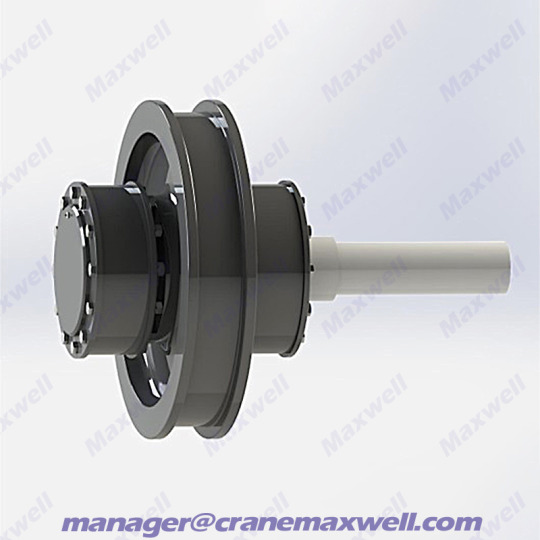
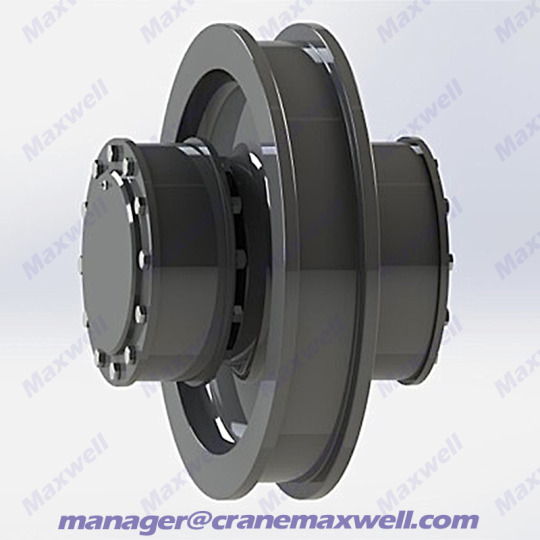
Introduction to Crane Wheels
Idler wheel unit are load-bearing and guiding components installed on the crane's traveling mechanism. They are cast/forged from high-strength alloy steel and achieve directional movement through the engagement of the wheel flange with the track. They have anti-fatigue, wear-resistant and anti-derailment properties under rated load.

Product Introduction
一,What does it look like?
Appearance: A heavy metal wheel (usually made of cast steel or alloy steel) with a raised rim (to prevent derailment).
Size: Depending on the tonnage of the crane, the diameter ranges from 200mm to more than 1 meter (the larger the tonnage, the wider and thicker the wheel).

���, How does it work?
Motor drive: After the crane is powered on, the motor drives the wheels to rotate through the reducer, allowing the entire device to move forward/backward along the track.
Load-bearing: The Idler wheel unit must bear the weight of the crane itself + the weight of the lifted cargo (for example, for a 100-ton crane, each wheel may bear 25 tons).
Derailment prevention: The wheel flange is stuck on the inside of the track to prevent the wheel from deviating (just like the wheels of a train will not fall off the rails).
三,Why is it so strong?
Hard material: Generally made of high-strength alloy steel , which is more wear-resistant than ordinary steel.
Stable design: The wheels of large-tonnage cranes are made into double rims (with bulges on both sides) to double the insurance against derailment.
Good heat dissipation: Some wheels have heat dissipation grooves to prevent overheating due to long-term friction.
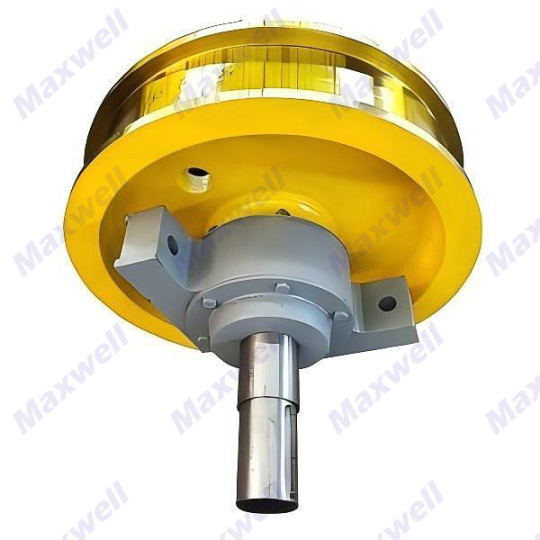

四, The "partner" of the crane wheel
Track: It is equivalent to its "runway" and must be flat otherwise the wheels will wear unevenly.
Bearing: It allows the wheels to turn more smoothly and reduce friction.
Drive motor: It provides power and controls speed.
五, Common Problems Wheel wear: uneven tracks or overloads can cause pits on the wheel surface .
Abnormal noise: when the bearing is short of oil, it will make a "squeaking" sound, and it must be refueled in time.
Derailment: It may occur when the wheel flange is severely worn or the track is offset, which is very dangerous!
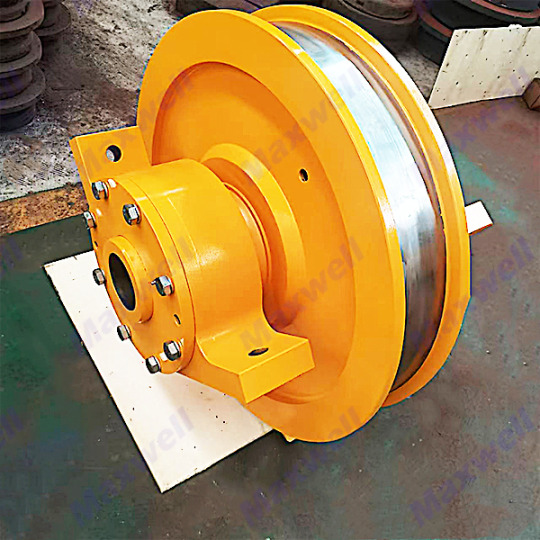

六, How to maintain? Monthly inspection:
Wheeler surface cracks or severe wear.
Rim thickness wear should not exceed 10% of original size.
Quarterly refueling: Add high temperature grease to the bearings .
Track maintenance: Regularly clean the track of gravel and rust.
0 notes
Text

What is a sheave?
Crane hot rolled sheave is the core component of the crane lifting mechanism. Its function can be simply understood as "a deflector and labor-saving helper for the wire rope".
Appearance: A round wheel with grooves (like the pulleys on fitness equipment) with a steel wire rope in the middle.
Material: Usually cast steel or alloy steel, wear-resistant and pressure-resistant.
What is sheave used for?
(1) Change the direction of the wire rope Just like the guide ring of a fishing rod guides the fishing line, the pulley changes the direction of the wire rope from "pulling upward" to "pulling horizontally" or diagonally.
Example: The hook of a tower crane can move left and right, which is to change the direction of the rope by the top pulley.
(2) Save effort and amplify the pulling force The pulley group (a combination of multiple pulleys) can reduce the required pulling force by multiples.
Physics principle: For each additional movable pulley, the pulling force is halved (the "movable pulley saving effort" principle of junior high school physics).
Example: With a pulling force of 1 ton, 4 tons of cargo can be lifted through 4 pulley groups.

Common Problems And Solutions
Problem 1: Wire rope jumps Phenomenon: The rope is out of the pulley groove or drum groove.
Cause: The pulley is skewed and the rope arrangement on the drum is uneven.
Solution: Adjust the pulley position and install a rope arrangement device.
Problem 2: The pulley bearing is stuck Phenomenon: The pulley does not rotate, and the wire rope is hard and smokes.
Cause: Long-term lack of lubrication or rust caused by water ingress.
Solution: Add high-temperature grease (such as lithium-based grease) every month.
Problem 3: Drum presses the rope Phenomenon: The new rope presses the old rope, resulting in local extrusion and deformation.
Cause: The drum has too many layers of winding (generally no more than 3 layers).
Solution: Use a longer drum or thicker wire rope.
Why does the pulley break?
Common faults:
The groove is worn out deep (wire rope wear is accelerated).
The bearing is stuck (the pulley does not turn, the rope is hard).
Prevention method:
Add lubricating oil once a month.
Replace the rope groove if it is found to be worn more than 3mm.
0 notes
Text
The core component of the elastic coupling
The elastic coupling is simply a shaft connector with a "buffer pad" that allows the machine to transmit force more smoothly, last longer, and make less noise! It is specially used to solve the "hard-on-hard" problem when connecting two rotating shafts.

1. The role of the spider pad The spider pad is the core buffer element of the elastic coupling, usually made of polyurethane (PU), rubber or nylon. Its main functions include:
(1)Shock absorption and buffering: Absorbing the impact and vibration when the motor or equipment starts and stops.
(2)Compensating deviation: Allowing certain axial, radial and angular deviations (such as installation errors or thermal expansion and contraction).
(3)Electrical insulation: Preventing current conduction between the two shafts (suitable for anti-static or insulation requirements).
(4)Noise reduction: Reduces friction noise caused by direct contact between metal parts.

2. Installation steps of plum blossom pad (1)Check the coupling: make sure the two halves of the coupling are not damaged and the shaft hole matches the shaft. (2)Align the axis: try to align the two shafts (you can use a dial indicator to calibrate to reduce subsequent wear). (3)Installing the plum blossom pad: Put the plum blossom pad into the claw groove of one half of the coupling. Gently press the other half of the coupling to fully embed the plum blossom pad (avoid hard knocking to prevent deformation). (4)Tighten the bolts: tighten the coupling bolts evenly in diagonal order to ensure uniform force. (5)Manual turning test: rotate the coupling to check for jamming or abnormal friction.

3. Maintenance points of plum blossom pads (1)Regular inspection (every 3 to 6 months):
Observe whether there are cracks, aging, and compression deformation.
Check the alignment of the coupling to avoid premature damage to the plum blossom pad due to excessive deviation.
(2)Lubrication (optional):
Rubber/polyurethane plum blossom pads generally do not require lubrication, and nylon materials can be coated with a small amount of silicone grease to reduce friction.
(3)Replacement standard:
If tearing, permanent deformation, and obvious decrease in elasticity are found, they need to be replaced immediately.
It is recommended to replace in pairs when replacing to avoid vibration caused by uneven hardness of the new and old gaskets.
4. Plum blossom coupling plum blossom pad size measurement method (1)The size of the plum blossom pad is usually determined by the following parameters (unit: mm):
Outer diameter (OD): the maximum outer diameter of the plum blossom pad.
Inner diameter (ID): the diameter of the center hole (the part that matches the coupling claw).
Thickness (T): the axial thickness of the plum blossom pad.
Number of claws (N): common 4 claws, 6 claws, 8 claws, etc. (need to match the coupling).
(2)Measurement steps:
Method 1 (direct measurement): Use a caliper to measure the outer diameter, inner diameter, and thickness of the old plum blossom pad, and count the number of claws.
Method 2 (coupling parameter matching): Find the coupling model nameplate and select the corresponding plum blossom pad according to the specification table provided by the manufacturer.
0 notes