Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Controlling Informative Features for Improved Accuracy and Faster Predictions in Omentum Cancer Models
Abstract
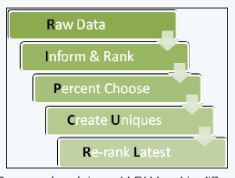
Identification of suitable biomarkers for accurate prediction of phenotypic outcomes is a goal for personalized medicine. However, current machine learning approaches are either too complex or perform poorly. Here, a novel feature detection and engineering machine-learning framework is presented to address this need. First, the Rip Curl process is applied which generates a set of 10 additional features. Second, we rank all features including the Rip Curl features from which the top-ranked will most likely contain the most informative features for prediction of the underlying biological classes. The top-ranked features are used in model building. This process creates for more expressive features which are captured in models with an eye towards the model learning from increasing sample amount and the accuracy/time results. The performance of the proposed Rip Curl classification framework was tested on omentum cancer data. Rip Curl outperformed other more sophisticated classification methods in terms of prediction accuracy, minimum number of classification markers, and computational time.
Read More About This Article: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/CTBEB.MS.ID.555559.php
Read More Juniper Publishers Google Scholar Articles: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=nWCnyqYAAAAJ&citation_for_view=nWCnyqYAAAAJ:YsMSGLbcyi4C
1 note
·
View note
Text
Application of (bio) chemical engineering principles and lumping analysis in modelling the living systems
Abstract
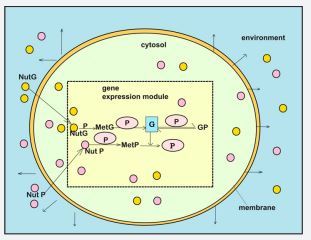
The ”whole-cell” simulation of cell metabolic processes under considering a variable-volume modelling framework has been reviewed to prove their advantages when building-up modular model structures of simplified form that can reproduce complex protein syntheses inside cells. The more realistic “whole-cell-variable-volume” (VVWC) approach is reviewed when developing modular kinetic representations of the homeostatic gene expression regulatory modules (GERM) that control the protein synthesis and homeostasis of metabolic processes. The paper review the general concepts of the VVWC modelling, while the cited literature includes past and current experience with GERM linking rules in order to point-out how optimized globally efficient kinetic models for the genetic regulatory circuits (GRC) can be obtained to reproduce experimental observations. Based on quantitative regulatory indices evaluated vs. simulated dynamic and stationary environmental perturbations, the reviewed literature exemplifies with GERM -s from E. coil, at a generic level, how this methodology can be extended:
i) To characterize the module efficiency, species connectivity, and system stability;
ii) To build-up modular regulatory chains of various complexity;
iii) To prove feasibility of the cooperative vs. concurrent construction that ensures an efficient gene expression, system homeostasis, proteic functions, and a balanced cell growth during the cell cycle;
iv) To prove the effect of the whole-cell content ballast in smoothing the effect of internal/external perturbations on the system homeostasis.
Read More About This Article: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/CTBEB.MS.ID.555566.php
Read More Juniper Publishers Google Scholar Articles: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=nWCnyqYAAAAJ&citation_for_view=nWCnyqYAAAAJ:Se3iqnhoufwC
#biomedical engineering#Juniper Publishers#juniper publisher reviews#biomedical science#Linking GERM-s
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Assessment of Different Sunflower Genotypes under Agro-Climatic Conditions of District Malakand Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa
Authored by Saif Ullah*
Abstract
The present study was conducted with the aim to evaluate sunflower hybrids under agro climatic conditions of district Malakand. A set of 8 sunflower hybrids was evaluated in randomized complete block design having two replications in spring 2014. Each sunflower genotype was sown in five meter long two rows 75cm apart with P-P distance 25cm. Data were recorded on yield and associated traits such as days to flower initiation, days to flower completion, days to maturity, plant height, head diameter, grain yield and 100 grain weight. Significant differences were observed among the genotypes for all the studied traits. The minimum days (80) to flower initiation were observed in Hybrid-14013 while maximum days (85) to flower initiation were observed in Hybrid-14009. Data regarding flower completion showed that Hybrid-14021 took maximum days (95) in flower completion while minimum days (86) was recorded for Hybrid-14013. Data pertaining to plant maturity compiled that Hybrid 14021 took maximum days (120) followed by one day (119) interval rest of all. A maximum plant height (132cm) was observed in Hybrid-14035 while minimum of 109cm in Hybrid-14013. Data related to head diameter showed that a maximum diameter of 17.80cm was recorded for Hybrid-14021 and minimum of 14.20 cm for Hybrid-14048. Maximum 100 seed weight 5g recorded in Hybrid-14041 while maximum (1666kg ha-1) grain yield were noticed in Hybrid 14021 and minimum yield of (661 kg ha-1) in Hybrid-14048. It is concluded that Hybrid- 14021 performed better in agro-climatic condition of Malakand valley and produced maximum yield.
Keywords: Genotypes; Hybrids; Traits
Introduction
Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) is an annual plant native to the Americas. Early settlers grew sunflower for food and garden decoration. European brought sunflower along trade routes to Spain, Italy, Egypt, Afghanistan, China, Russia [1]. It possesses a large flowering head, which is inflorescence of sunflower. The sunflower is named for its huge, fiery blooms, whose shape and image are often used to depict the sun. It has a rough, hairy stem, broad, coarsely toothed, rough leaves and circular heads of flowers. The heads consist of many individual flowers which mature into seeds, often in the hundreds, on a receptacle base.
In Pakistan although it was introduced as an oilseed crop 40 years back but its expansion in acreage and production is fluctuating due to various production and socio-economic constraints. Its seed contains 35-55% oil contents. Research work on this crop has shown that there is great potential of growing it under all the soil and climatic conditions in rain-fed as well as irrigated farming system in different agro-ecological zones (PARC).
The total cultivated area of Pakistan is 20.69 million ha. Out of this cultivated area, 16.48 million ha or 79.65% of the total cultivated area are irrigated. In 1970-71, oilseeds occupied nearly 3% of the total cultivated area, which decreased to 2.5% by 2002-03 [2]. Major share in domestic production of edible oil comes from cottonseed and canola, 67 and 19.6%, respectively. The remaining 13.4% are contributed mainly by sunflower [3]. Edible oil is basic need of every country. In country like Pakistan, About 80% of the total needs are met through imports while only 30% come from local production. Major growing areas of sunflower in Pakistan includes, Multan, Bahawalpur, Sargodha, Faisalabad in Punjab, Peshawar, Malakand in Khyber Pakhtoonkhwa, Khairpur and districts of Hyderabad division in Sindh [4]. During the year 2011-12, the total availability of edible oil was 2.748 million tons. Local production of edible oil remained 0.636 million tons while imports were 2.148 mill tons. The import bill during 2011-12 stood at Rs.216.4 billion (US$ 2.426 billion). During the year 2012-13 (July-March), 1.738 million tons of edible oil valued at PRs. 153.3 billion (US$ 1.595 billion) has been imported. The local production during 2012-13 (July-March) was 0.612 million tons. Total availability of edible oil from all sources is provisionally estimated at 2.35 million tons during 2012-13 (July-March). (Economic survey of Pakistan 2012-13)
Uses of sunflower
I. Sunflower oil is used as edible oil in many parts of the world.
II. Sunflower oil could be used as fuel for cars or trucks.
III. Sunflower oil is an ingredient in salad dressings and cooking.
IV. Sunflowers are used to prepare some special paints.
V. Sunflower oil is used to prepare certain kinds of glue.
VI. Soaps made with sunflower oil.
VII. It has been used in certain paints, varnishes and plastics because of good semidrying properties without color modification associated with oils high in linoleic acid.
VIII. The use of sunflower oil (and other vegetable oils) as a pesticide carrier, and in the production of agrichemicals, surfactants, adhesives, plastics, fabric softeners, lubricants and coatings has been explored
IX. Also use as bird feed.
X. In human diet it is used as snacks and this trend is increased since 15years.
XI. It can be used as a double crop after early harvested small grains or vegetables, an emergency crop, or in areas with a season too short to produce mature corn for silage.
XII. Non-dehulled or partly dehulled sunflower meal has been substituted successfully for soybean meal in isonitrogenous (equal protein) diets for ruminant animals.
XIII. The growing herb is extremely useful for drying damp soils, because of its remarkable ability to absorb quantities of water.
XIV. The Sunflower is a good bee plant, as it furnishes hive bees with large quantities of wax and nectar.
XV. The unexpanded buds boiled and served like Artichokes form a pleasant dish.
XVI. Sunflowers, when the stalks are dry, are as hard as wood and make an excellent fire.
XVII. Of the ash obtained from burning the Sunflower stems and heads (apart from seeds) 62 per cent consists of potash.
XVIII. Being so rich in oil, they are too stimulating to use alone and should only be used in combination with other feeding stuffs.
XIX. The Chinese grow this plant extensively, and it is believed that a large portion of its fiber is mixed with their silks.
Botany of sunflower
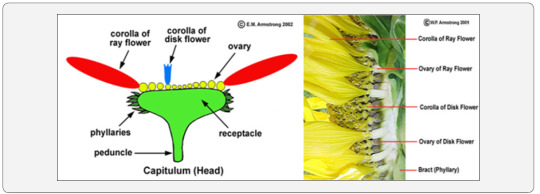
The sunflower is a member of the plant family Asteraceae, or Compositae. Asters are remarkable for their type of inflorescence, which is a head of florets. The head is also called capitulum. The “flower” of the sunflower is actually made up of lots and lots of little flowers, called florets. The center, darker florets are disc florets; while the outer, petal-like ones are ray florets. Sunflower seeds are indehiscent achenes. The genus Helianthus, to which the Sunflower belongs, contains about fifty species. It is an annual herb, with a rough, hairy stem, 3 to 12 feet high, broad, coarsely toothed, rough leaves, 3 to 12 inches long and circular heads of flowers, 3 to 6 inches wide in wild specimens and often a foot or more in cultivation. Chromosome number of sunflower is 34. Sunflower is highly cross pollinated crop. For instance, the sunflower genome 3.5 billion bases long [5], slightly longer than the human genome [6].
Flower
Sunflower is a member of the aster family. A capitulum or head, the characteristic inflorescence of the sunflower family (Asteraceae). The inflorescence consists of ray flowers, disk flowers, or both ray and disk flowers. The ovary of each flower is situated below the attachment of the corolla and stamens, a condition referred to as epigenous or inferior. The disc florets are located in the centre of the composite flower, and the ray florets bear the outer ring of petal-like structures. Ray florets are sterile, and disc florets have both male and female structures, including a single ovary that develops into a sunflower seed. A single flower head may have up to two thousand disc florets, each with the potential to develop into a seed (Figure 1).
Roots system
Sunflowers (Helianthus spp.) have a single taproot and smaller, hairy secondary roots. Sunflower roots usually grow 1 to 3 feet deep, and more than 5 feet long roots are also measured (USDA).
Stem
A sunflower stem sample has many vascular bundles along the edge of its sample. Unlike other plants, fibers are visible next to the vascular bundles. The center part of the sample is called pith, in which most cells are found. Stem have leaves and a terminal head (Figure 2).
Leaves
The leaf of a sunflower is considered a simple leaf, which consists of a single blade. The plumule gives rise to the first leaves of the plant that will go on to grow into organs for transpiration, with the opening and closing of the stomata found within the cell structure of leaves; for photosynthesis, and for other metabolic activities.
Yield contributing traits in sunflower
Seed yield is a quantitative character, which is influenced more from climate and environmental factors in sunflower because of being controlled by large number of genes. To increase seed yield, the study of direct and indirect effects of yield components provides the basis for successful breeding program [7]. Head diameter, 1000 seed weight, plant height are other valuable yield parameters that determine yield improvement in the sunflower [8].
Objective of the study
Present study was carried out to;
I. Check performance of eight sunflower hybrids, obtained from National Agricultural Research Centre Islamabad (NARC) under field conditions of district Malakand.
II. Record data on various quantitative traits.
III. Find out the best sunflower hybrid for the area.
Materials and Methods
A total of 8 sunflower hybrids obtained from NARC oilseed section were sown in the field of district Malakand during February 2014 for yield and associated traits. Plant material was sown in randomized complete block (RCB) design having three replications. Each entry was assigned a two row plot having row to row and plant to plant distance of 75 and 25cm, respectively.
Location
The Research field is located at 34.56 ˚N, 71.96 ˚E, at an altitude of 454m above sea level in the Malakand valley. Malakand is located about 1437 km north of the Indian Ocean, 156km from river Kabul, 96km from river Swat and has semiarid climate. The research farm is irrigated by the Dargai canal from the river Swat. Soil texture is clay loam, low in organic matter (0.87%), extractable phosphorus (6.57mg kg-1), exchangeable potassium (121 mg kg-1), and alkaline (pH 7-8.5) and is calcareous in nature. The climate of the area is semiarid where the mean annual rainfall ranges (400 to 500mm), 60-80% rainfall occurs in summer, while the remaining 30-40% rainfall occurs in winter (Table 1).
A. Parameters studied: Data were recorded on the following parameters.
B. Days to flowering initiation (DFI): Days to flowering initiation was recorded from date of sowing till about five percent of the buds opened flowers in each plot.
C. Days to flower completion (DFC): Flower completion data was recorded when about 90% of the buds opened flower in each plot. This was also calculated from date of planting.
D. Days to Maturity: Data for days to maturity was recorded when back of the heads turned yellow and bracts started turning brownish in color.
E. Plant height (cm): A total of five plants randomly selected in each plot were measured from ground level to attachment of head with stem to record data on plant height. Plant height was recorded at the time of maturity.
F. Head diameter (cm): Head diameter was calculated as it is yield contributing trait in sunflower. Five plants from each line were selected at random and data for head diameter was recorded. Head diameter was measured from one edge of the disk to other.
G. 100-seed weight (g): 100 seed weight was also calculated for each hybrid. An average of three samples of 100-seeds for each hybrid, were taken to record data on 100- seed weight. Seed was weighed in grams with the help of an electronic balance up to two decimal points.
H. Grain Yield (kg ha-1): Total produce after threshing was sun dried for 2-3 days and then seed was weighed with the help of an electronic balance for each hybrid.
I. Statistical analysis: Data after compilation was statistically analysed using STATISTICA 8.1 software and means were separated by LSD test.
Results and Discussion
Days to flower initiation
Analysis of variance revealed highly significant (P=0.01) differences among all the Genotypes (Table 2). Days to flower initiation ranged from 80-85 days. Hybrid-14001 took minimum days (80) to flower initiation whereas Hybrid-14009 took maximum days (85) for flower initiation (Table 3). These results are partially in line with those of Shah [9]. The differences in results may be due to differences in Genotypes or due to environmental effects.
Days to flower completion
Analysis of variance revealed that days to flower completion showed significant (P<0.05) differences among all the Genotypes (Table 2). Days to flower completion ranged from 80-92 days. Hybrid-14023 took minimum days (86) for their flower completion while Hybrid-14035 took maximum days (92) to complete their flowers (Table 3). Furrkh [4] also found significant variation for days to flower completion.
***Significant at 5 and 1% level of probability respectively, whereas NS= Non-significant.
Days to maturity
Analysis of variance revealed that days to maturity showed non-significant (P>0.05) differences among all the Genotypes (Table 2). Days to maturity ranged from 119-120. Hybrid-14005 took minimum days (119) to be matured whereas Hybrid-14021 took maximum days (120) to be matured (Table 3). Khalid [8] also found non-significant differences for days to maturity.
Plant height (cm)
Analysis of variance revealed that plant height showed nonsignificant (P>0.05) differences among all the genotypes (Table 2). Plant height ranged from 110-135cm. Hybrid-14013 had minimum (110cm) plant height whereas Hybrid-14021 had maximum (135cm) plant height (Table 3). Khalid [8] found the plant height to be non-significant.
Head diameter (cm)
Analysis of variance revealed that head diameter showed significant (P<0.05) differences among all the Genotypes. Head diameter ranged from 14-18cm. Hybrid-14048 had minimum (14cm) head diameter while Hybrid-14021 had maximum (18cm) head diameter. These results confirmed the earlier findings of Arshad [1] also found significant variation for head diameter.
Grain yield (kg ha -1)
Analysis of variance showed non-significant (P>0.05) differences for grain yield among all the genotypes (Table 2). Grain yield ranged from 817-1666kg ha-1. Hybrid-14041 had minimum grain yield (817 kg ha-1) whereas Hybrid-14021 had maximum grain yield (1666 kg ha-1) (Table 3) Khalid [8] also found Non-significant relation for Grain Yield kg ha-1.
100-grain weight (g)
Analysis of variance revealed that 100-grain weight showed non-significant (P>0.05) differences among all the genotypes (Table 2). 100-grain weight ranged from 04-05g. Hybrid-14013 had minimum 100-grain weight (04g) whereas Hybrid-14041 had maximum 100-grain weight (05g) (Table 2). Anjum [1] also got non-significant difference for 100 grain weight.
Conclusion and Recommendations
There is sufficient genetic variability in the tested sunflower hybrids which is useful tool for grouping of different hybrids according to their adaptation through the environmental condition, Hybrid 14021 produced highest grain yield (1666kg ha-1) followed by hybrid 14009 (1517kg ha-1) and thus are considered best among all hybrids evaluated during this study. From the above study and data obtained from results it is recommended that Hybrid 14021 and 14009 fits well in the agroclimatic conditions of Malakand valley and produce maximum yield [10-12].
To Know More About Current Trends in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Publishers Please Click on: Juniper Publishers
1 note
·
View note
Text
Ozone Technology: An Emerging Technique in Food Processing Industry

Authored by Nighat Mushtaq*
Nowadays, an increasing attention is focused on the safety of foods and in particular on the intervention methods to reduce and eliminate the pathogens from the fresh products. Traditional technology utilizes water for sanitizing foods which has a limited effect in killing bacteria and other pathogens. Thus, an alternative treatment to improve the quality as safety of foods is being sort. The high demand of ozone in the food industry lies in the fact that ozone is much stronger than chlorine. Complementing the effectiveness, unlike other disinfectants, leaves no chemical residual and degrades to molecular oxygen upon reaction or natural degradation. Ozone has relatively short half‐life and can be taken as an asset and a liability to practitioners. This is particularly true in treatment of drinking water where ozonation is done to enhance filtration and provide primary disinfection but requires the addition of chlorine as the terminal disinfectant to maintain a residual in the distribution system. Ozone destroys microorganisms by reacting with oxidizeable cellular components, particularly those containing double bonds, sulfhydryl groups, and phenolic rings. Therefore, membrane phospholipids, intracellular enzymes, and genomic material are targeted by ozone; these reactions result in cell damage and death of microorganisms. Ozone can be applied in an aqueous solution or gaseous phase to decontaminate food-contact surfaces, sanitize equipment, recycle wastewater, and decrease pesticide levels on fresh produce. The microbiological quality and shelf-life of vegetables, fruits, cheeses, eggs, nuts, and meats can be improved when these products are directly treated with ozone or stored in an ozone containing environment. The use of ozone in the gaseous phase helps in controlling mold and bacteria, both in the air and on the surface of the product. Several researches have shown that treatment with ozone appears to have a beneficial effect in extending the store life of fresh non-cut commodities such as broccoli, cucumber, apple, grapes, oranges, pears, raspberries and strawberries by reducing microbial populations and by oxidation of ethylene. There are tremendous ways to justify the fact that ozone technology is a new and emerging technology for the shelf life extension and reduction of post-harvest losses in fruits and vegetables.
To Know More About Current Trends in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Publishers Please Click on: Juniper Publishers
1 note
·
View note
Text
Bioester in Bioscience Discipline-Past, Present and Future Trends

Authored by Mohammad Shahidul Islam*
Abstract
Bioester, as a member of life science discipline has enormous potential to be incorporated in pharmaceutical and personal care product (PPCP) system because of its increased customer demand. Bioester is produced by transesterification between two immiscible edible oil and organic alcohol phases in presence of an alkaline catalyst. The bioester thus produced has diversified area of applications and PPCP industry is one of them. This bioester has reduced viscosity (10% of neat edible oil), improved physio-chemical properties and excellent compatibility for precious applications. Due to this reason past, present and future of bioester, as a member of life science discipline is very impressive and it will develop in course of time.
Keywords: Alkaline catalyst, bioester, edible oil, life science, organic alcohol, pharmaceutical and personal care product, shea butter ethyl ester, transesterification.
Biomaterial Carriers
Bioscience or life science is derived from life or biomass substances. Biomass substance is renewable in the sense that it absorbs same quantity of carbon di oxide from atmosphere that it emits while combusted. Carbon re-fixation life span varies from few months to few years. Bioester is a transesterifying product of life science species, triglyceride. Triglyceride is produced from various energy seeds, i.e., rape, soybean, mustard, sunflower, coconut, peanut etc. seeds.
Back in 1900 century biofuel, neat peanut oil was used in fueling a car in Paris expo by Rudolf Diesel, inventor of diesel engine. At that time, Dr. Diesel quoted, biofuel may seems to be inferior for the time being because of lack of technological development but it would be valuable in powering engine system in course of time. But later on neat edible oil was found un-suitable in fuel engine system because of its high viscosity (around 45mm2/s at 40 ˚C). High viscous edible oil damages piston of fuel engine because of stocking effect.
Glycerin back bone is responsible for high viscosity in edible oil. To reduce its viscosity to engine friendly level, Bioester product is developed. The underlying chemical reaction is called transesterification. In transesterification reaction, an organic alcohol (ethanol/methanol) is used to split glycerol back bone of the triglyceride. An alkaline catalyst is usually used to promote the transesterification reaction in favorable direction. Usually CSTR or plug flow turbulent reactor system is used to induce vigorous mixing between two immiscible oil and alcohol phases. Three step reactions occur to complete catalyzed transesterification reaction (Figure 1).
Before the transesterification reaction, edible oil is preheated to the boiling temperature of the organic alcohol. At the boiling temperature, triglyceride of the edible oil is substituted to diglyceride. During propagation of the reaction, diglyceride is substituted to monoglyceride. In the last step, monoglyceride is substituted to glycerol. In each step of the three step substitution reactions, equivalent mole of bioester/alkyl ester/biodiesel is produced. When the intermediate by products monoglyceride and diglyceride are produced, two phase oil-alcohol fluid systems are reduced to single phase fluid system where lower viscosity (temperature effect) and weak fluid (oil)-fluid (alcohol) phase boundary enhances oil-alcohol mass transfer. Temperature nearly to boiling point of the alcohol also influences transesterification reaction to favorable direction.
Bioester thus produced by transesterification reaction was originated back in 1900 century. But it was not introduced in diversified area of application at that time. Presently bioester is used as biodiesel, ingredient of cosmetic production, pharmaceutical application, solvent application, reagent of chemical reaction etc [1-3].
Generally methanol and ethanol are used as Solvent for bioester production. Methanol is cheap, non-renewable and toxic. Therefore it is not suitable for cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications. But due to availability and cheap alternative, it is extensively used in biodiesel production to fuel engine system. While ethanol is non-toxic, renewable and costly alternative. Therefore, it is used to produce precious bioester for cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications. Presently shea butter and palm oil are used to produce shea butter ethyl ester and palm oil ethyl ester for cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications.
Future of bioester as bioscience/life science product is enormous. Would wide population is increasing day by day at the rate of 1.12% as of 2017. Presently total population of the world is 7.5 billion as of 2017. Demand for pharmaceutical and personal care product (PPCP) for these large numbers of population is very high. Due to this reason, PPCP industry will grow exponentially to meet the increased customer demand. For this, bioester as a raw material in PPCP can play a dominant roll to meet the increased customer demand.
Finally, renewable and eco-friendly product bioester as a member of bioscience discipline opened a frontier of science in the past after its invention. It undergoes development in the present. It has enormous potential to be incorporated in the future also. As a result past, present and future trends of bioester product reveal impressiveness and it will grow exponentially in course of time for the greatest interest of mankind.
To Know More About Current Trends in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Publishers Please Click on: Juniper Publishers
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Cardio Kinesiograph System
Authored by *
Abstract
The Cardio Kinesiograph System (CKinG) is a novel computerized diagnostic system incorporating a computer model of cardiac kinesis. Cardiac Kinesis (CK) is the interpretation of heart movement or electrical activity of specialized cardiac muscle cells in response to biochemical reactions. The mechanical events occurring during the cardiac cycle consist of changes in pressure in the ventricular chamber which cause(s) blood to move in and out of the ventricle [1]. The events of the cardiac cycle start with an electrical signal and proceed through excitation-contraction coupling (which involves chemical and mechanical events) to contraction of the ventricle (pressure generation) and ejection of blood (flow) into the pulmonary and systemic circulations [2]. Thus, we can characterize the cardiac cycle by tracking changes in ventricular volume (LVV), ventricular pressure (LVP), left atrial pressure (LAP) and aortic pressure (AoP) [3]. In the other hand, because electrical events always precede mechanical events in the cardiac cycle, distortions of a part or parts of the electrical signal have been used as diagnostic indicators of both electrical and mechanical dysfunctions of the heart muscle [4]. There are numerous methods and technical systems available for diagnosis or predict heart disease. However, medical errors and undesirable results [5] in these systems are reasons for a need for conventional computer-based diagnosis of heart diseases systems. The purpose of this study is to design and develop a system that can observe and analyze Kinesiographical Cardiac basted on statistical models and identifies some fundamental characteristic of heart motions.
Keywords: Cardiovascular biomechanics; Statistical analysis methods; Medical heart imaging modalities; DNA modelization in biomedical image
Introduction
Since 1950 cardiologists have studied the functions of heart moments to employ them in the diagnostics of ischemic heart disease (IHD). Indeed, changes of the movements have found their diagnostic application in this field. If blood supply to a certain area of ventricular myocardium is insufficient the con-tractions in this area diminish and even ceases. After systolic increase in ventricular pressure this area dilates and forces intercostal tissues out, causing a “bulge” wave on the record.
Cardiokymography was one of several noninvasive techniques able to detect coronary artery disease. It can qualitatively determine abnormal left ventricular motion, and, based on animal models, this can be directly related to abnormalities in the left coronary artery [7]. Nevertheless sensitivity of cardiokymography in detecting patients with ischaemic left ventricular wall motion abnormalities depended on the extent of left ventricular ischaemia [8]. Cardiokymography is no longer valid [9]. Today Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) is one of the trusted methods in the field of medicine [10]. Advances in medical imaging and image processing techniques have greatly enhanced interpretation of medical images. Computer aided diagnosis (CAD) systems based on these techniques play a vital role [11] in the early detection of cardiovascular diseases and hence reduce death rate. CAD is the most preferable method for the initial diagnosis of heart disease. The combination of Digital and Medical Image Pro-cessing, Cardiac Electrophysiology, Ventricular Pressure-Volume Technique and Phonocardiogram etc makes the CAD system more reliable and efficient. One example of the medical applications in computer aided diagnosis is the detection system for heart disease based on Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR). Cardiovascular magnetic resonance of the heart provides a potentially useful way to assess cardiac mechanical function. Besides CMR, positron emission tomography (PET), and cardiac CT are able to illustrate kinesis of cardiac muscles. Perfusion imaging with cardiac PET is used clinically to produce images of myocardial blood flow, aiding the diagnosis of coronary artery disease and the monitoring of condition of coronary circulation in response to treatment [12].
Clinical imaging in positron emission tomography (PET) is often performed using single-time-point estimates of tracer uptake or static imaging that provides a spatial map of regional tracer concentration [13]. However, dynamic cardiac techniques (e.g. PET, Myocardial perfusion imaging and Dynamic cardiac SPECT [14]) are used to estimate rate parameters activity of myocardial blood flow, and there are limited studies evaluating the role of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance and cardiac PET and cardiac CT for the assessment of cardiac kinesis. Therefore, scientific communities in computational cardiovascular science [15] have contributed to developing mathematical models and algorithms to improve efficiency of cardiac safety data management in clinical trials. In this way in 2014 proposed a new method based on a mathematical model, “Fourier Transform” which calculates an amplitude parametric image for the assessment of cardiac kinetics. This image, calculated from the Cine MR images, allows the localization and quantification of abnormalities related to difference in contraction and their extent [16]. In 2015 Zakynthinaki [17] has also presented effective mathematical model of heart rate kinetics in response to movement. She made conclusion that the new model is able not only to provide important information regarding an individual’s cardiovascular condition but to also simulate and predict heart rate kinetics for any given exercise intensities. The existing models of cardiac kinetics focus mainly on amplitude images or are limited to simulation of biological transformation. The present study provides a novel mathematical model of cardiac kinesis based on visual presentation of numerical data (obtained through the cardiac kinesis) in the form of graph, with a particular focus on Human Cardio Kinesiograph Analysis. The purpose of this study was to de-sign, develop and evaluate a novel method for Kinesiograph of Cardiac for the clinical assessment of cardiac and vascular function.
Methods and Materials
The system includes the following steps:
Data collection: In order to obtain an accurate data, the Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance imaging (CMR), Cardiovascular Ultrasound or Cardiac Computed Tomography are produced better performances for detection of cardiac mobility. However, CMR is provided the most comprehensive anatomic picture for patient selection [18]. The system therefore is obtained relevant information from the CMR.
Video quality assessment: Different medical imaging methods may introduce common artifacts include image distortion, signal pileup (bright regions), and image dropout (area without signal) [19], therefore the quality assessment is an important factor at the operational level. The assessment of quality of video depends upon the type of distortion [20]. Numerous video quality assessment methods and metrics have been proposed over the past years with varying computational complexity and accuracy [21]. We utilize different forms of quality assessment methods, however the merit of these methods is often judged by assessing the quality of a set of results through lengthy user studies [22].
Motion estimation and inertial measurements: Motion estimation is the process of determining the movement of blocks between adjacent video frames (MathWorks). Efficient and accurate motion estimation is an essential component in the domains of image sequence analysis [23] and medical video processing. The estimation of motion is also important from the viewpoint of matching metric technique, which is computed the context similarity between two images. There exist several methods for motion estimation image, and video processing (e.g. pixel-based motion estimation, block-based motion estimation, optical flow method). In this study in order to increase the computational accuracy and improve efficiency in solving problem, DNA Modeling (Dawoudi, 2017) method in biomedical image matching has been proposed. The method is based on the linear mapping and the one-to-one correspondences between point features extracted from the frames and on calculating similarities in pixel values. This correspondence is determined by comparing two strings constructed from pixel values of the frames. The method uses a table called the Quarter Code table, which is the set of characters and numbers. In this table every number between 0 and 255 is translated into a unique string of four letter alphabet. Letters A,C,G,T are chosen, since they are the same as used in DNA sequences. In this way it possible to utilize tools originally programmed to DNA sequences analysis. When all pixel values of the frames (images) are converted to virtual DNA sequences, one can show the differences between two virtual DNA sequences.
Visual representation of numerical data in the form of graphs: The E-value gives a measure of the similarity of sequences. From this function we can obtain the correlation coefficient which will give us a single value of similarity. The rate of similarity between sequences (frames) is plotted as a graph and it’s appearing in the Monitor.
Experiment Results
We demonstrate the system by performing experiment 2D cardiac CMR video (Source: HBSNS library). The practical framework consists of four steps:
A. Step 1: Extract frames from cardiac mri video
The information is obtained by extracting frames from CMR imaging video. There are different tools in order to extract frames from cardiac MRI Video (e.g. Free Video to JPG Converter, VLC or Virtual Dud) (Figure 1).
B. Step 2: Adjacent frames comparisons
The difference between two adjacent frames is used to estimate motion direction and magnitude. This process has been implemented within a tool called Image Diff. The Perforce image diff tool enables researchers to compare two adjacent frames. The following represents pixels difference value (Percent Changed; Pixels) and color difference value (Percent Change; Color) between adjacent Frames (Table 1).
C. Step 3: Presenting data in graphic form
In the final step the percentage of change (pixels and color) from one value to another, between frames are plotted as a graph (Figure 2 & 3).
Results
The results show that the proposed design approach works efficiently in the Cardio Kinesis System for clinical applications of cardiovascular assessment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the proposed Cardio Kinesiograph System (CKinG) may become a robust and efficient tool for the clinical assessment of Cardiac and Vascular function. CKinGbased Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) holds the promise of improving the diagnosis accuracy and reducing the cost.
Discussion
The developed system can be used as a prototype in the clinical sectors for the evaluation of cardiovascular diseases. However, a novel method for real time MRI of cardiac kinesis and simultaneously Kinesiographical Cardiac Analysis Based on Statistical Methods are proposed. The proposed methods may become efficient Medical Diagnostic Support tools (DSTs) for Heart Diseases.
Related Work
The publications below are based on Morbid Motion Monitor related topics:.
A. Dawoudi Mohammad Reza (2017) Morbid Motion Monitor. Current Treads in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences. ISSN: 2572-1151.
B. Dawoudi MR (in press) (2017). Nursing and Technology foresight in Futures of a Complex World. European Journal of Futures Research.
To Know More About Current Trends in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Publishers Please Click on: Juniper Publishers
#Cardiovascular biomechanics#Statistical analysis methods#DNA modelization in biomedical image#Biomedical Engineering#biochemistry
0 notes
Text
The Cardio Kinesiograph System

Authored by
Abstract
The main objective of the present work was to investigate the effect of synthesis parameters (temperature, maturation time, pH, Ca/P˩r ratio of reactants and composition of hydrogen peroxide) on chemical composition and physicochemical characteristics of oxygenated calcium phosphate apatite synthesized by precipitation from calcium nitrate Ca(NO3)2 and phosphoric acid H3PO4. The chemical composition of the products has been determined with chemical analysis and physicochemical characterizations of the samples have been carried out by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and infrared spectroscopy (IR).
Keywords: Synthesis parameters; Oxygenated apatite; Chemical composition; Physicochemical characteristics
Introduction
The phosphocalcic oxygenated apatites are used as bone substitutes and as support matrices of antiseptic agents for many decades [1]. After implantation, they undergo a process of degradation and dissolution combined with bone neo-formation and progressive release of oxygenated species (O2, O22-); responsible for antiseptic properties [1]. We have developed, in a previous studies [2,3], an oxygenated apatite based of calcium phosphate by precipitation reaction from calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) and orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4). However, the composition and crystal characteristics of apatites are, however, more difficult to control during the synthesis, mainly because of the ability of the lattice to accept substituent’s and vacancies [4]. The principal objective of this survey was to describe the effect of various parameters (temperature, maturation time, pH, Ca/P˩r ratio of reactants and composition of hydrogen peroxide) on chemical compositions and physicochemical characteristics of synthesized oxygenated apatites.
Experimental
The synthesis method consists in mixing (500rpm) the calcium solution into 1L capacity reactor maintained at definite temperature. The pH was adjusted manually by addition of NH4OH solution (d=0.92). Then the phosphoric acid solution (3.875.10-2M) was poured into the reactor all at once and the reacting medium was kept under agitation at precise pH value. Finally, the suspension was vacuum filtered, washed with distilled water and dried in vacuo at room temperature. The specific parameters of each synthesis are summarized in Table 1.
The obtained products were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, infrared spectroscopy and by chemical analysis. X-ray diffraction analysis was carried out by means of a SEIFERT XRD 3000 P using CuK radiation. For infrared absorption analysis, 1mg of the powered samples was carefully mixed with 300mg of KBr and palletised under vacuum. The pallets were analysed using a Perkin Elmer 1600 FTIR spectrophotometer. Calcium, phosphorus and oxygenated species contents were determined by wet chemical methods: Calcium was titrated by complexometry [5]. The error on the calcium content is around 0.5%. Phosphorus content was analyzed by colorimetry [6]. The accuracy of this dosage was determined with a relative error of 0.5%. Molecular oxygen was determined by measuring the volume displaced during the acid dissolution of powder [1]. Uncertainty in this dosage is about 2%. Peroxide ions were titrated by manganimetry [7]. The relative error on this dosage is approximately 1%.
Results
Figure 1 shows the X ray diffraction data of dried powders, while, Figure 2 illustrates the infrared spectra’s and Table 2 summarizes the chemical analysis. In result, we got the oxygenated apatites based calcium phosphate with different compositions and crystal characteristics and we examine successively the effect of each parameter:
Temperature
As shown by X-ray powder diffraction in Figure 1, the synthesis, conducted at 30 °C, provides an amorphous apatite while, at high temperatures, we got a more crystallized apatites. Chemical analysis (Table 2) showed, on the one hand, a positive correlation between temperature and rate of oxygenated species in obtained apatites, on the other hand, a negative correlation between the deviation from stoichiometry and the Ca/P ratio.
Maturation time
As can be seen in Table 2, the maturation time affect significantly the precipitate chemical composition. At first, the precipitate contains many peroxide groups, a few molecular oxygen and its Ca/P ratio is far from stoichiometry. Then, the peroxide groups quantity decreases and it was substituted by molecular oxygen. In the same way, our apatite approximates to the stoichiometry. This evolution is associated with refinement on X-ray diffraction patterns (Figure 1).
pH value
Chemical analysis of precipitated apatites at different pH value shows a negative correlation between pH value and deviation from stoichiometry (Table 2). So, at basic pH, Ca/P ratio of prepared apatite is near to the stoichiometry. Also, the infrared spectras of these compounds show a clear decrease of the HPO42- ions bands at basic pH (Figure 2). In contrast, oxygenated species composition occurs a significant positive correlation with pH value (Table 2).
Ca/Pr ratio
According to results presented in Table 2, the both ratios Ca/ Pr and Ca/P evolve in the same away, as well as the content of oxygen species.
H2O2 percentage
For different H2O2 concentrations, we noted here also a positive correlation between hydrogen peroxide concentration and oxygenated species content, as well as the Ca/P ratio (Table 2).
Discussion
According to our results, we can synthesize apatites with large specter, from poorly crystallized oxygenated apatites to greatest crystallized oxygenated one, and from deficient oxygenated apatites to like-stoichiometric oxygenated apatites. Similarly results was reported in previous studies [8-11], they indicate a dependency between the Ca/P ratio, % O2 and % O2 2- of synthesized apatites and the synthesis parameters (temperature, maturation time, pH, Ca/Pr and % H2O2). The Ca/P ratio raise was noted with temperature, maturation time, pH, Ca/Pr or % H2O2 increasing. In fact: The first formed precipitates are calcium deficient amorphous phosphates. Chow [12] have observed that in the first precipitation step, an amorphous calcium phosphate forms with Ca/P ratio ranged from 1.30 to 1.60. Boskeyet & Posner [13] have also observed that the formation of an apatitic phase is always preceded by the formation of an amorphous phase. Legeros [14] are prepared the hydroxyapatite, by precipitation reaction at 100 °C and pH ranging from 4 to 11, while at 60 °C and pH ranging from 5 to 6, they have detected the formation of octocalcic phosphate. This phenomenon was explained by Heughebaert [15] which showed that the amorphous phosphate conversion on apatitic phosphate is even faster than the temperature is higher. The pH of the reaction medium determines the concentration and the type of phosphate species acting during the precipitation. Indeed, the phosphoric acid is a tri-acid which the acidity constants for the various acid-base pairs, at 25 °C, are defined below [16]:
In the case of phosphoric acid (H3PO4) use in basic medium, the phosphorus is mainly present as PO4 3- and HPO42- ions. Thus, at basic pH, the formed apatites approximate to the stoichiometry. The higher Ca/Pr ratio means a reaction medium rich on Ca2+ and PO4 3-ions, which promotes calcium phosphates germination once precipitated and their evolution into a solid with higher Ca/P ratio in the expense of Ca2+ and PO4 3- free ions in solution. The evolution of Ca/P ratio, depending on H2O2 concentration, is in the same direction of evolution of oxygenated species content following the law of electronegativity of the apatite unit cell.
As for oxygenated species composition, all studied parameters seem influential: The decomposition of H2O2 was favored by increasing either the temperature or the pH of medium reaction which facilitates the oxygenated species incorporation in the apatitic structure and explains the elevation of oxygen species content in one of these cases. The elevation of the maturation time is, on the one hand, translates by the decomposition of peroxide groups present in the apatitic structure on molecular oxygen, and secondly, by the incorporation of new peroxide groups existing in solution [8]. This process occurs during the first hours of the evolution of precipitates which also correspond to the increase in the Ca/P ratio of solid phases as we have already mentioned. These two phenomena are probably related to a restructuring of deficient precipitated apatitic structure [8], which the mechanism is however not clarified. The increase of the oxygenated species content of solids, caused by the increase of Ca/Pr ratio, is directly related to the increase of Ca/P ratio of solids. Indeed, these two phenomena appear to be related to the charge-balance of the unit cell which must be neutral. The precipitation in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, of high concentration, promotes the increase of the oxygenated species content in the apatitic structure, which can be explained by the oversaturation of oxygenated species in the reaction medium.
Conclusion
The present report highlights the variations in chemical composition of oxygenated apatite based calcium phosphate according to studied synthesis parameters (Temperature, D, pH, Ca/P r and % H2O2). In fact, the Ca/P ratio and the oxygenated species content vary according to one or more of these parameters. Indeed, the Ca/P ratio of solids and oxygenated species insertion are highly favored by temperature, maturation time, pH, Ca/Pr ratio or the % H2O2. In sum, synthesis temperature, pH medium, Ca/Pr ratio and H2O2concentration explain the effect of reaction medium on the oxygenated apatites composition while the maturation time seems to be more specifically related to the evolution of precipitates after their formation.
To Know More About Current Trends in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Publishers Please Click on: Juniper Publishers
#Synthesis parameters#Oxygenated apatite#Chemical composition#Physicochemical characteristics#Biomedical Engineering#biochemistry
0 notes
Text
Formulation of a Multifunctional Flora Composite for the Prevention and Management of Cancer, Diabetes, Blood Pressure and Strokes

Authored by Paul SH*
Abstract
A research entitled “formulation of a multifunctional flora composite and the roles of life style in the prevention and management of Cancer, Diabetes, Blood Pressure and Stroke” was carried out using the leaves, fruits, rhizomes and other parts of five medicinal plants namely: Garcinia cola, Vernonia amygdalina, Ocimum gratissimum, Psidium guajava and moringa oleifera. The research was aimed at developing a multifunctional composite, a bio-activator or a supplement from the above listed plants with its natural content and form unaltered to double as a food and a drug at the same time by performing bioactive functions, playing nutritional roles and balancing the human body chemistry through its nutritional and medicinal applications with a minimum or no alteration to its natural bioactive forms or nutritional contents. At the end of the research, it was revealed that most of the necessary and important bioactive compounds responsible for the prevention, treatment and or management of Cancer, Diabetes, blood pressure and stroke were present in optimum concentrations. These Bioactive compounds or secondary metabolites as determined, responsible for those roles as listed above, base on average are: Alkaloids (1.17mg/100g), saponins (3.39mg/100g), Tannins (3.98mg/100g), phenols (1.58mg/100g), anthocyanin (0.11mg/100g) anthraquinone (2.07mg/100g), Steroids (0.88mg/100g), glycosides (1.43mg/100g), flavonoids (4.73mg/100g), carotenoids (0.31mg/100g), Terpenoids (1.43mg/100g), oxalate (0.96mg/100g) and phylates (2.33mg/100g). These compounds were all present in both the preliminary screening and the quantitative analysis respectively. The primary metabolites or Nutritional compositions like energy value (273.41Kcal.), moisture content (13.14%), carbohydrate (43.88%), proteins, (12.23%) ( total fibre (8.49%), oil (2.43%), vitamins (13.03%) and ash content(7.24%), were determined in addition to the mineral elements such as: calcium (104.56mg/100g), potassium (318.25mg/100g), magnesium (93.06mg/100g), phosphorus (52.03mg/100g), iron (15.76mg/100g), zinc (4.99mg/100g), manganese (1.54mg/100g) sodium (27.31mg/100g), nickel (2.31mg/100g) and copper (1.68mg/100g). Based on the data obtained from this research, the composite material developed from these six medicinal plants has the capacity to prevent, treat and manage cancer, diabetes, blood pressure and stroke. In addition to the primary and secondary metabolites in the composite, life style modification to favor the effective survivals of the man irrespective of age and gender.
Keywords: Plants; Human health; Life style; Phytochemicals, Metabolites; Nutrition; Cancer; Blood pressure; Diabetes; Stroke
Introduction
Industrialization, modernization, and technological advancement have led to modifications in the lifestyle of the world’s populace, giving rise to increase in the indices of several diseases, including chronic degenerative diseases such as insulin resistance diabetes mellitus, blood pressure, Cancer, malaria fever, typhoid fever, kidney diseases, metabolic syndrome and other related cardiovascular diseases which overall effects are capable of reducing the quality of life, increasing the costs of life, hospitalizations or medications and frustrating living [1]. Many studies have shown that green plants and their extracts, either isolated or crudes, are very helpful in the prevention, management or treatment of such diseases as listed above and many more not mention depending on the phytochemical composition of the source plants, methods and time of extraction, solvents used and components of interest and their functions [2]. The bioactive compounds extracted from the source plants in this case, bitter cola, scent leaves, ginger, moringa oleifera, Psidium guajava and bitter leaves [1]. The above mentioned plants contain very important, effective and excellent primary and secondary metabolites that are beneficial to human and plant growth and health [3]. These bioactive compounds are effective and responsible for: heaptoprotection (Heaptoprotection also called antihepatotoxicity is the ability of a substance to prevent damage to the liver and This damage is known as hepatotoxicity), antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, anti-cancer, antimicrobial, anti-hyperglycaemic, analgesic, endothelial progenitor cells, anti-stomach-aches and anti-diarrhea functions in each or most of them and form the constituents and composition of the scholarly developed multifunctional hybrid flora composite newly developed which can be used for the prevention treatment, and management of Cancer, Diabetes, blood pressure and stroke (Paul SH et al. 2017).
The word Cancer is a broad term referring to a class of diseases characterized by abnormal cells growths that invades healthy cells in the body. Breast cancer for instance, starts in the cells of the breast as a group of cancer cells that can then invade surrounding tissues or spread (metastasize) to other areas of the body just like prostate cancer starts at the abdominal region of the body and later metastasize to other parts of the body [4]. What Causes Cancer to Develop is the abnormality in cell development in the body: Cancer begins in the cells which are the basic building blocks that make up tissue. Tissues are found in the breast, prostate and other parts of the body. Sometimes, the process of cell growth goes wrong and new cells form when the body doesn’t need them and old or damaged cells do not die as they should [5]. When this occurs, a buildup of cells often forms a mass of tissue called a lump, growth, or tumour [6]. Breast cancer for instance, occurs when malignant tumours develop in the breast just like prostrates cancer occurs around the abdominal region of the human body by the formation of malignant growth [6]. These cells can spread by breaking away from the original tumour and entering blood vessels or lymph vessels, which branch or spread into tissues throughout the body. When cancer cells travel to other parts of the body and begin damaging other tissues and organs, the process is called metastasis. Cancer as an abnormal health condition remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the entire universe. Cancer is the second leading cause of death amongst the non-communicable diseases after cardiovascular disease being the first [7]. Chemotherapy is routinely used for cancer treatment. Since cancer cells lose many of the regulatory functions present in normal cells, they continue to divide when normal cells do not [7]. This feature makes cancer cells susceptible to chemotherapeutic drugs. Approximately five decades of systemic drug discovery and development have resulted in the establishment of a large collection of useful chemotherapeutic agents. However, chemotherapeutic treatments are not devoid of their own intrinsic problems [8]. Various kinds of toxicities may occur as a result of chemotherapeutic treatments. For example, 5-fluorouracil, a common chemotherapeutic agent, is known to cause myelotoxicity, cardiotoxicity and has even been shown to act as a vasospastic agent in rare but documented cases. Another widely used chemo drug, doxorubicin causes cardiac toxicity, renal toxicity, and myelotoxicity. Similarly, bleomycin a well known chemotherapeutic agent is known for its pulmonary toxicity [6]. In addition, bleomycin shows cutaneous toxicity [9]. Cyclophosphamide, a drug to treat many malignant conditions, has been shown to have bladder toxicity in the form of hemorrhagic cystitis, immunosuppression, alopecia and at high doses cardiotoxicity The toxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs sometimes creates a significant problem in the treatment of cancer using allopathy or established medicine. Various therapies have been propounded for the treatment of cancer, many of which use plant-derived products [7]. There are four classes of plant-derived anticancer agents in the market today, the vinca alkaloids (vinblastine, vincristine and vindesine), the epipodophyllotoxins (etoposide and teniposide), the taxanes (paclitaxel and docetaxel) and the camptothecin derivatives (camptotecin and irinotecan) [9]. Plants still have enormous potential to provide newer drugs and as such are a reservoir of natural chemicals that may provide chemo protective potential against cancer. Recently, Taneja and Qazi have suggested a number of compounds from medicinal plants with potential anticancer activities [7]. Cancer has the following as its major risks factors: Growing older, intake of Tobacco, Sunlight, exposure to Ionizing radiation, ingestion and exposure to Certain chemicals and other substances, Some viruses and bacteria, Certain hormones, Family history of cancer, Alcohol and Poor diet, lack of physical activity, or being overweight. Most cancers start or enhance by the prevailing influences of these factors [8].
Diabetes is defined as an abnormal health condition that is caused by impaired insulin and Leptin sensitivity [10]. In simple terms, diabetes is an abnormality that means having excess glucose or sugar in the blood [11]. Even though your blood actually needs some amount of glucose for energy supply to keep you strong, too much of it could be disastrous to your health [12]. Glucose comes from the food human ingest into their body, from the liver and also from our muscles. The blood then carries the same glucose into all parts (cells) of the body. Insulin is a chemical or hormone secreted or produced by the pancreas into the blood which controls the rate at which glucose gets into the body cells. If the system does not have enough insulin required for controlling this processes, or if the available insulin does not work optimally as expected, then the glucose will not get into the body cells [13]. Instead, it will remain in the blood cells rather accumulating. Eventually, it will becomes high and at this stage it is said “you have high blood sugar” or diabetes [14]. Leptin or satiety hormone is a hormone produced in a person’s fat cells. Amongst its primary roles is to regulate the individual’s appetites and body weight [15]. It is this hormone if it is functioning optimally, that tells your brain when to eat, how much to eat, and when to stop eating, which is why it’s called the “satiety hormone.” It also tells your brain what to do with the available energy in your body [10]. The primary role of insulin is not to lower your blood sugar, but to store the extra energy (glycogen, a starch) for present and future consumption if need be. Its ability to lower your blood sugar is merely a “side effect” of this energy storage process. Diabetes is basically of three types: type 1 Diabetes, type 2 Diabetes and Gestational diabetes [12]. Type 1 diabetes is insulin dependent diabetes and very common among juveniles even thought adults who have their insulin producing cells destroyed by their immune system, are like to suffer type 1 diabetes and those who had it as kids who are now adults. It can be said to be one of the most dangerous form of diabetes because of its incurability. In any case be it adult or infant; to survive type 1 diabetes, one needs to be taking insulin in the best possible way [16]. Type 2 diabetes, is the most common form of diabetes and is common amongst middle aged and old people even though, infants and adult could also be affected [17]. It is also called non-insulin dependent diabetes. Insulin resistance is usually the starting point of type 2 diabetes. This happens whenever fat, muscles and lever cells fails to use insulin to carry glucose into the body’s cells as source of energy supply [11]. Gestational diabetes is common among pregnant women especially at the late stage of their pregnancy [12]. This is caused by shortage of insulin, or by pregnancy hormone [13]. This disappears shortly after the baby is delivered and the child is likely to become diabetes later in his or her life time A.H.A. 2017). The best way to manage your health and avoid the devastating effects of diabetes is to control your blood glucose level, blood pressure, cholesterol level and avoid smoking or anything that resembles it [16].
Hypertension (HTN) is a medical term for high blood pressure [15]. The condition is dangerous because it makes the heart work too hard and contributes to hardening of arteries (atherosclerosis), apart from increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Hypertension can also lead to other conditions to include but not limited to: congestive heart failure, kidney disease, and blindness [16]. Conventional antihypertensive drugs are usually associated with many side effects. About 75 to 80% of the world population use herbal medicines, mainly in developing countries, for primary health care because of their better acceptability with human body and lesser side effects [17]. Hypertension (HTN) or high blood pressure (HBP) is a chronic medical condition in which the BP in the arteries is elevated (ACS 2010). It is classified as either primary (essential) or secondary. About 90 to 95% of cases are termed primary HTN, which refers to high BP for which no medical cause can be found. The remaining 5 to 10% of cases, called secondary HTN, are caused by other conditions that affect the kidneys, arteries, heart, or endocrine system (B.P.A., 2008). Persistent HTN is one of the risk factors for strokes, heart attacks, heart failure, and arterial aneurysm, and a leading cause of chronic kidney failure [N.H.L.B.I., 2010]. Moderate elevation of arterial BP leads to shortened life expectancy. Both dietary and lifestyle changes as well as medicines can improve BP control and decrease the risk of associated health complications. Hypertension is usually classified based on the systolic and diastolic Blood Pressures [15]. While Systolic Blood Pressure is the one in vessels during a heartbeat, Diastolic blood pressure is the pressure between heartbeats [16]. If the systolic or diastolic blood pressure measurement is higher than the accepted normal values for the age of the individual, it is classified as pre-hypertension or hypertension [17]. Although research has not given any direct cause or causes, however there are many risk factors such as sedentary lifestyle, stress, visceral obesity, potassium deficiency (ACS, 2010). Obesity, more than 85 % of cases occur in those with a body mass index greater than 25, salt (sodium) sensitivity, alcohol intake, and vitamin D deficiency. Risk also increases with aging, some inherited genetic mutations, and having a family history of hypertension. An elevation of rennin, an enzyme secreted by the kidney, is another risk factor, as is sympathetic nervous system over activity (HPSP, 2017). Insulin resistance, which is a component of syndrome X, or the metabolic syndrome, is also thought to contribute to hypertension. Consuming foods that contain high fructose corn syrup may increase one’s risk of developing hypertension. The second types of high blood pressure, is called: Secondary hypertension is said to results from an identifiable cause base on definition (A.S.H., 2010). This type is important and easy to recognize and treated by dealing with the root cause or causes (B.P.A., 2008). Most of the mechanisms associated with secondary hypertension are generally fully understood. However, those associated with primary (essential) hypertension are far less understood. The increase in blood volume leads to hypertension (NHLBI, 2010). An overactive sympathetic nervous system, leading to increased stress responses. It is also known that hypertension is highly heritable and polygenic (caused by more than one gene) and a few candidate genes have been postulated in the etiology of this condition [13]. Recently, work related to the association between primary hypertension and sustained endothelial damage has gained popularity among hypertension scientists (WHO, 2017). It remains unclear however whether endothelial changes precede the development of hypertension or whether such changes are mainly due to long-standing elevated blood pressures (HPSP, 2017). Hypertension is a major independent risk factor for coronary artery disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
risk factor for coronary artery disease, stroke, and kidney failure. The term stroke is used to describe an abnormal health condition that occurs when the flow of blood to an area of the brain is cut off due to interference or leakages in the channels responsible for the flow of the blood into the brain [16]. Sometimes, stroke is refers to as a brain attack. Stroke occurs when a blood vessel that supply blood to the brain leaks or is blocked by a clot. Then part of the brain does not get enough oxygen this is because, when brain cells are starved of oxygen, they die [18]. This type of health condition called Stroke is a medical emergency and must be treated as such. It’s important to get treatment as soon as possible otherwise; it may become very disastrous (BPA, 2008). This is because; a delay in treatment increases the risk of permanent brain damage and consequently death. Research has shown that in men, Stroke is the fifth leading cause of death (ASH, 2010). Killing almost the same number of men each year as prostate cancer and Alzheimer’s disease all combined together. Stroke is also the leading cause of longterm disability and deformation among people. This condition can cause brain damage, which may be permanent and life threatening as well (A.C.S., 2010). Many effects from a stroke can be successfully treated (AHA). One of the ways to treat stroke, is by physiotherapy (subject the victims to exercising machine that shake off (melting) some of the buildup blood clots. Lowering blood pressure is one of the sure ways that can help prevent strokes [11]. This means it is important to know your risk of having a stroke and taking action to reduce that risk as soon as you find out. Taking the appropriate decision and at the right time, is very important. There are basically three types of stroke: Ischemic stroke Ischemic stroke is the most common form of stroke, accounting for around 85% of strokes. This type of stroke is caused by blockages or narrowing of the arteries that provide blood to the brain, resulting in ischemia - severely reduced blood flow [15]. Hemorrhagic stroke: this is caused by arteries in the brain either leaking blood or bursting open. The leaked blood puts pressure on brain cells and damages them [16].The ruptures can be caused by conditions such as hypertension, trauma, blood-thinning medications and aneurysms that are weaknesses in blood vessel walls. Intracerebral hemorrhage is the most common type of hemorrhagic stroke and occurs when brain tissue is flooded with blood after an artery in the brain bursts (WHO, 2012). Subarachnoid hemorrhage is the second type of hemorrhagic stroke which is the type of stroke that bleeding occurs in the subarachnoid space - the area between the brain and the thin tissues that cover it [18]. Transient ischemic attack (TIA) (mini stroke) TIAs is different from the aforementioned kinds of stroke because the flow of blood to the brain is only briefly interrupted [10]. TIAs are similar to ischemic strokes in that they are often caused by blood clots or other debris. TIAs should be regarded as medical emergencies just like the other kinds of stroke, even if the blockage of the artery is temporary. There are a number of factors that causes or at least lead to stroke and they include: High blood pressure, Smoking, Obesity or overweight, Diabetes, Alcohol and Lack of exercise [14].
Materials and Methods
Materials
The equipments used for this research were obtained from and used in federal cereal research centre Bidda and department of Chemical Engineering, federal university of technology minna. The materials used for this research, includes moringa oleifera leaves, scent leaves (Ocimum gratissimum), bitter cola (Garcinia cola), guava leaves (Psidium guajava leaves) and bitter leaves (Vernononia amygdalina leaves).
Preparation of samples and pre-treatment
Pre-treatment and processing of Vernonia amygdalina: The fleshly harvested young and matured leaves of Vernonia amygdalina also called bitter leaves were collected from the farm and washed thoroughly with distilled water to remove impurity. The washed freshly harvested leaves were then dried indoor for 168 hrs (seven days) after which, they were crushed into smaller sizes and grinded to obtained finely divided particles called Vernonia powder.
Pre-treatment and processing of bitter cola (Garcinia cola): The fresh bitter cola were collected and washed thoroughly with distilled water to remove impurities. The washed flesh bitter cola was then sliced and dried under ambient temperature for 240hrs (ten days). The dried sliced bitter cola was then crushed and grinded into a very finely divided powdered.
Pre-treatment and processing of ginger rhizomes (Zingiber officinale): Freshly harvest Ginger rhizomes were collected and washed thoroughly to remove unwanted materials. Then the thoroughly washed rhizomes were then sliced to aid drying, and dried for 240hrs (ten days). The dried mesocarp was then crushed and further grinded into very fine powder.
Pre-Treatment and Processing of Guava: Freshly harvested guava leaves, matured fruits and pills were collected. The collected young and old leaves were washed thoroughly in order to remove unwanted materials from it. The washed leaves were then dried for 168hrs indoor. The dried leaves were crushed. The matured Guava fruits were sliced and dried for 240hrs indoor. The pills were crushed and dried for 240hrs also under the same condition as the two components. The three crushed components (leaves fruits and pills) were blended and grinded to form a very fine powder called guava powder.
Pre-treatment and processing of Moringa olfeira: The freshly harvest leaves of moringa olfera and the matured fruits were collected. The matured dried fruits were piled up using a mortar to get the hard seeds the hard seeds were also pitted to remove the dried harsh dried cover from it. The seeds were then crushed. The young harvested leaves were also washed and dried for 168hrs (seven days). The dried leaves were crushed and blended with the crushed seeds and grinded together to form one component called moringa powder.
Pre-treatment/processing of scent leaves: The fleshly harvested scent leaves was collected from the farm and washed thoroughly with distilled water to remove any impurity from it. The washed fresh scent leaves was then dried under normal atmospheric condition (away from sunlight or room temperature) for 168hrs (seven days). The dried scent leaves was then crushed and grinded to obtained very finely divided powder called scent leaves powder.
Samples preparation and development of multifunctional flora composite
Preparation of samples: The grinded powder of Chanca piedra obtained from pre-treatment and processing of raw materials was sieved using a very fine mesh size of micromillimeters to obtain a finely divided granulated powder. The powder was then divided into different portions 1.0kg each. The same procedures were followed for the remaining eight plants were processed and grinded into powders. One each of the different plants sample materials that that were divided into 1.0kg, were pick to form samples as shown below
1. Zingiber officinale powder: sample “A”
2. Garcinia cola powder sample “B”
3. Vernonia amygdalina powder: sample “C”
4. Scent leaves power sample “D”
5. Moringa oleifera powder: sample “E”
6. Guajava powder: sample “F”
Formulation of a multi-functional flora composite
The five samples of plants’ powders were blended together after weighing 1.0kg of each of each. The resultant composite material was then hydrolyzed with distilled water and stirred for 48hrs using an improvised stirrer in the tank to maintain constant agitation and also aid speedy extraction of both the soluble and extractable components in the composite material. The composite material was then filtered and the filtrate evaporated under 40.2 ⁰C. The solid extract was further dried, and crushed into a fine powder and packaged which can be taken as tea using honey as a sweetener and a preservative.
Phytochemical analysis
Phytochemical analyses: The Phytochemical analyses for the above listed constituents were carried out based of the methods spelt out by Association of Analytical chemists (AOAC, 2012).
Results and Discussion
Discussion of results
The results as presented above shows that both individual plants and their composite material have multi-dimensional compositions. The present of essential secondary metabolites like: alkaloids, Terpenoids, phenols, saponins, tannins, and flavonoids from diverse plant’s origins with enormous individual’s multi functional properties, which include but not limited to; anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, anti-hypertensive, antiinflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-virus and anti-fungi , is worthy of note. The present of primary metabolites such as: minerals elements; calcium (Ca) magnesium (Mg) potassium (K), sodium (Na), iron (Fe) and zinc (Zn) and carbohydrate, proteins, fibre, vitamins, essential oils and huge energy values of which, each plays very crucial roles in the day today functioning and survivals of not only man as animal, but also plants themselves from which they are extracted, have demonstrated the diverse applications of these green medicines to human nutritional and overall health especially in the prevention and management of the above diseases. Phytochemicals or secondary metabolites as they are popularly called; are defined as biologically active compounds found in many green plants in small quantities that do not have established nutrient functions neither in plants nor animals but make effective and significant contributions to protecting their body against degenerative diseases Affor C.E., 2015). Ginger for example, is made up of over 400 different compounds [19] but the major ones as indicated by this result, include: flavonoids (2.54mg/100g) on the average, phenols (2.23mg/100g), Terpenoids/terpene (1.10mg/100g), carbohydrate (28.20mg/100g), amino acids, raw fibre (2.04 %), ash (4.04 %), protein (3.32 %), phytosterols, vitamins, and minerals elements. Terpene components of ginger include zingiberene, β-bisabolene, α-farnesene, β-sesquiphellandrene, and α-curcumene, while phenolic compounds include Gingerol (6-gingerol, 8-gingerol and 10-gingerol), paradols, and shogaol (Table 1).
The word Cancer is a broad term referring to a class of diseases characterized by abnormal cells growths that invade healthy cells in the body [10]. Flavonoids (4.73mg/100g), is composite material with great potent, efficient and effective water-soluble super antioxidants and free radical scavengers that prevent oxidative cell damage in the body. Flavonoids have strong anti-cancer activity when in contact with the human cells and protect the body against all stages of carcinogenesis or cancer cells growth. According to [20] flavonoids in this case with average value of 4.73mg/100g have protective effects including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral and anticarcinogenic. Hence, it is these secondary metabolites that actively help in protecting the body from viral infections and cancer cells formations and consequence growth. Phenols with average value of 3.67mg/100g are also very special secondary metabolites used as antiseptic drugs for the treatment of bacterial infections and fungi inversions. Hence, this composite material can be used for the prevention of typhoid and malaria fever also. Experimental studies also showed that ginger and its bioactive components including 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol which are micro-components of flavonoids; exert anticancer activities against cancer cells especially gastrointestinal cancers [21] (Table 2). The anticancer activity of ginger phytochemical components; flavonoids, Terpenoids and phenols are attributed to their ability to modulate several signaling molecules like cell growth regulatory proteins and caspaces [22]. Caspaces are a family of protease enzymes playing essential roles in programmed cell death (including apoptosis, pyroptosis and necroptosis) and inflammation). Gastrointestinal (GI) cancer for example is a cancer of different organs of the digestive and respiratory system [18]. GI cancer is defined as the cancer of organs of the digestive system including the esophagus, gallbladder, liver, pancreas, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus [23]. The risk factors commonly associated with gastrointestinal cancer include: infection, smoking, drinking alcohol, high fat diet, age, race, gender, family history, and geographical location [20]. The occurrence of gastrointestinal cancer is very high in developed countries because of industrialization and feeding habits. It is one of the most common cancers around the world. Even though a variety of chemotherapeutic drugs have been introduced many decades ago to fight gastrointestinal cancer, most of them are either too expensive and or have higher side effects or a combination of both. Ginger (Zingiber officinale) extracted flavonoids (3.98mg/100g), is a natural agent and with no sight effects hence, considered save for consumption and cost effective. Terpenoid/Terpene (3.82mg/100g) components of ginger include zingiberene, β-bisabolene, α-farnesene, β-sesquiphellandrene, and α-curcumene, while phenolic compounds include gingerol, paradols, and shogaol. 6-gingerol and 6-shogaol components of the phenols (3.67mg/100g) in ginger and others in the composite material, reduced the viability of gastrointestinal cancer cells by damaging microtubules these active ingredients in the composite material, targets several cellular molecules that contribute to tumour-genesis, cell survival, cell proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis.
Phytochemicals and diabetes prevention: Diabetes mellitus is the most common endocrine disorder, which results to too many other complications such as micro- and macrocardiovascular diseases [19]. Preventing diabetes will mean preventing those other cardiovascular complications and diseases. Ginger, bitter leaves scent leaves and guava leaves have great Anti-diabetic, hypolipidemic and anti-oxidative properties. These properties, has been attributed to the presence of different minor biochemical components in their phenols like Gingerol and shogaol, a components of phenols in Ginger (Table 3). Ginger flavonoids, terpene and its polyphenols have been shown to target multiple signaling molecules that provide a basis for its use against multifactorial human diseases like cancer, diabetes, blood pressure and stroke. According to the research carried out by, People with type 2 diabetic were giving Ginger supplementation especially the tea, to examine blood sugar fasting level in their blood after been given a 2g/day of ginger supplements for 12 days [21]. At the end of the exercise, they were examined and noticed significant reduction in the levels of fasting blood sugar hemoglobin A1c, apolipoprotein B, apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A-I and malondialdehyde in ginger group when compared to baseline, as well as control group, while it increased the level of apolipoprotein A-I. Hence, oral administration of ginger powder supplement improves fasting blood sugar, hemoglobin A1c, apolipoprotein B, apolipoprotein A-I, apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A-I and malondialdehyde in type 2 diabetic patients [21]. Diabetes mellitus is a complex metabolic disorder resulting from either insulin Insufficiency or insulin dysfunction [15]. The treatment of diabetes with synthetic drugs is costly and chances of side effects are high. Phytomedicine or green medicines have been used since ancient time in many parts of the world where access to modern medicine is limited. Using a well characterized natural product with known positive effects on the body system is not just a welcome development, but a course that must be encourage by all. Low-fat vegan diet has improved glycemic control in type II diabetic patients (Paul SH et al. 2017). Phytochemicals identified from medicinal plants such as phenols, Terpenoids, flavonoids and tannins, as it is in the case of this very one, presents an exciting opportunity for the development of new types of natural treatments for diabetes mellitus and its accompanied complications like blood pressure and stroke. Most prevalent of phytochemical groups are the alkaloids, terpene/terpenoids, and phenols. Several formulations like herbal teas, extracts, decoctions, infusions and tinctures are prepared from individual medicinal plants or their combinations for superior quality. Essential plants such as ginger, bitter cola, bitter leaves, scent leaves and guajava plants are not only a testimony of great survival agents for man, but the needed natural composites for the modern man overcome the complications that are caused by climate change, the consequent attacks of new breeds of disease causal organisms and emergence of catastrophic infections, disorder and negative influence of mutation (Paul SH et al. 2017). Despite considerable progress in the development of synthetic drugs, the search for the invention of Phytomedicine as alternative therapy for Glycemic control is very important. Glycemic control is a medical term referring to the typical levels of blood sugar (glucose) in a person with diabetes mellitus. “Perfect glycemic control” would mean that glucose levels were always normal (70-130 mg/dl, or 3.9-7.2 mmol/L) and is distinguishable from a person without diabetes. Control and outcomes of both types I and II diabetes may be improved by patients. Home glucose meters can be used to regularly measure their glucose levels [15]. The American Diabetes Association in 1994 recommended that 60- 70% of caloric intake should be in the form of carbohydrates. Even though, some researchers have claimed that 40 % is better, while others have claimed benefits for a high-fibre, 75 % carbohydrate diet .Plant based drug are considered to be less toxic and free from side effects than synthetic ones. The many side effects of insulin therapy and other oral hypoglycemic agents necessitate the use of more effective and safer anti-diabetic drugs [10]. For example, long-term use of Metformin causes diarrhea, nausea, gas, weakness, indigestion, abdominal discomfort and headache. Hence, they play an important role as alternative medicine. Phytomedicine are mainly whole, fragmented or cut, plants parts of plants, algae, fungi, lichen in an unprocessed state, usually in a dried form, but sometimes fresh. Herbal drugs are defined by their botanical (scientific) binomial. The active principles present in medicinal plants have been reported to possess pancreatic beta cells regenerating, insulin releasing and fighting the problem of insulin resistance [24]. Anti diabetic plants also possess strong antioxidant/free-radical scavenging properties. Progressing evidences from in vitro, animal, and epidemiological studies suggest that ginger and its active constituents suppress the growth and induce apoptosis of variety of cancer types including skin, ovarian, colon, breast, cervical, oral, renal, prostate, gastric, pancreatic, liver, and brain cancer. These roles of ginger and its constituents are associated with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-mutagenic properties as well as other biological activities [23].
Caffeine (component of bitter cola originated alkaloids (2.29mg/100g) is a central nervous system natural stimulant. Its chemotherapeutic form is the world’s most widely consumed psychoactive drug. Unlike many other psychoactive substances, it is legal and unregulated in nearly all parts of the world. There are several known mechanisms of action to explain the effects of caffeine. The most prominent is that it reversibly blocks the action of adenosine on its receptor and consequently prevents the onset of drowsiness induced by adenosine. Caffeine (1.17mg/100g) also stimulates certain portions of the autonomic nervous system. Optimum use of caffeine containing alkaloids improves heart functions, reduced or eliminates blood pressure [18]. Caffeine containing alkaloids also reduced body weight, fats, and decreased or eliminates insulin resistance eliminating type 2 diabetes and stroke. At the same time caffeine also enhances glucose-stimulated first- and second-phase insulin secretion and beta-cell hyperplasia. Terpenoids (3.82mg/100g), the largest group of phytochemicals, traditionally used for medicinal purposes in India and China, are currently being explored as anticancer agents in clinical trials. Terpenoids (also called “isoprenoids”) are secondary metabolites occurring in most plants. More than 40 000 individual terpenoids are known to exist in nature with new compounds being discovered every year. A large number of terpenoids exhibit cytotoxicity against a variety of tumour cells and cancer preventive as well as anticancer efficacy in preclinical animal models [25].
Carbohydrate (18.32%): Carbohydrates or polysaccharides are the most abundant biological molecules known. They are said to be chemically simpler nucleotides or amino acid because in there pure form, they contain just three elements namely Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen. They play very important roles in the body as sources of energy or fuel and as well as structural materials. Carbohydrates also provide readily accessible fuel for physical performance and regulate nerve tissue. deducing from the results obtained from phytochemical and mineral screening, reviews from literatures, clinical findings and invitro animals test, it shows that this flora composite made from six medicinal plants including ginger, bitter leaves, scent leaves, guava leaves and fruits, bitter cola and moringa olefera leaves has the capacity to prevent cancer cells formations and their consequence growth when taken for 12 days 600 mg/day. People who took their blood pressure after taken it for 12 days, 200mg each tree times a day. The tea of the six medicinal plants was also given to 12 people with blood pressure and partial stroke, and after 21 days, they regain their sensation and the blood pressure dropped [26]. After running their blood pressure diabetes patients with high sugar level, were also given both the tea and the composite extract and the sugar level droped in their blood after testing and the above results is as a result of the present of this secondary metabolites like alkaloids, terpenoids, flavonoids` (gingerol shogaols composite in the ginger) in the alkaloids.
Triterpenes as α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitors: The therapeutic approach to treating type 2 DM is to decrease postprandial glucose levels. It can be achieved through the inhibition of α-glucosidase and α-amylases which delay the absorbance of carbohydrates in the intestine, leading to a decrease in the postprandial insulin level. There are many in vitro investigations indicating the ability of various plant-derived triterpenes to inhibit α-glucosidase and α-amylase activity. They are responsible for de phosphorylation process of the receptor β-subunit. Inhibitors of PTP 1B can potentially ameliorate insulin resistance and normalize plasma glucose and insulin levels without inducing hypoglycemia Type 2 diabetes mellitus is an important preventable disease and a growing public health problem. Epidemiologic and interventional studies suggest that weight loss is the main driving force to reduce diabetes risk. Landmark clinical trials of lifestyle changes in subjects with pre diabetes have shown that diet and exercise leading to weight loss consistently reduce the incidence of diabetes [27]. However, from these studies it cannot be established whether dietary changes alone play a significant role in preventing diabetes. Here we review epidemiologic and clinical trial evidence relating nutrients, foods and dietary patterns to diabetes risk and the possible mechanisms involved. The differential effects of carbohydrate and fat quantity and quality, and those of specific foods and whole diets are discussed. Importantly, most dietary components influencing diabetes risk have similar effects on biomarkers of cardiovascular risk and inflammation.
Flavonoids: have protective effects including antiinflammatory, anti-oxidant, antiviral, and ant carcinogenic properties. They are generally found in a variety of foods. Garcinia kola can be a good dietary source of flavonoids.
Alkaloids: are heterogeneous group of naturally occurring compounds found in the leaves, bark, roots or seeds of plants. Some alkaloids stimulate the nervous systems like those that contain caffeine and the related constituents. How too much of it is capable of causing paralysis, elevate blood pressure or lower it below minimum. Certain alkaloids act as pain relievers, others act as tranquilizers. Others have also been noted to contain antimicrobial properties. Alkaloids from Garcinia kola Vernonia amygdalina, Psidium guajava, Ocimum gratissimum and moringa olefera, are relevant in the manufacture of vaccines to prevent diseases.
Phenols: is a crystalline aromatic organic compound. Dilute solutions of phenol are useful antiseptics, but strong solutions of phenols are caustic and scarring to tissues. Concentrated phenols are widely used in the manufacture of resins, plastics, insecticides, explosives, dyes and detergents and as raw materials for the productions of medicinal drugs such as aspirin.
Minerals and their functions: Dieticians may recommend that minerals are best supplied by ingesting specific foods rich with the chemical element(s) of interest. The elements may be naturally present in the food (e.g., calcium in dairy milk) or added to the food (e.g., orange juice fortified with calcium; iodized salt fortified with iodine). Dietary supplements can be formulated to contain several different chemical elements (as compounds), a combination of vitamins and/or other chemical compounds, or a single element (as a compound or mixture of compounds), such as calcium (as calcium carbonate, calcium citrate and so on) or magnesium (as magnesium oxide, and so on.), or iron (as ferrous sulfate, iron bis-glycinate, and so on). The dietary focus on chemical elements derives from an interest in supporting the biochemical reactions of metabolism with the required elemental components. Appropriate intake levels of certain chemical elements have been demonstrated to be required to maintain optimal health [28]. Diet can meet all the body’s chemical element requirements, although supplements can be used when some requirements (e.g., calcium, which is found mainly in dairy products) are not adequately met by the diet, or when chronic or acute deficiencies arise from pathology, injury and other forms of complications. Research has supported that altering inorganic mineral compounds (carbonates, oxides and other related compounds) by reacting them with organic ligands (like: amino acids and organic acids.) improves the bioavailability of the supplemented mineral.
A mineral is a chemical element required as an essential nutrient by organisms to perform functions necessary for life. Minerals are of the earth’s origin and cannot be made by living organisms. Plants get minerals elements from the soil. Most of the minerals in a human diet come from eating plants and animals or from drinking water. As a group, minerals are one of the four groups of essential nutrients, the others of which are vitamins, essential fatty acids, and essential amino acids. The five major minerals in the human body are calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, and magnesium. All of the remaining elements in a human body are called “trace elements”. The trace elements that have a specific biochemical function in the human body are sulphur, iron, chlorine, cobalt, copper, zinc, manganese, molybdenum, iodine and selenium. Minerals are inorganic nutrients, usually required in small amounts from less than 1 to 2500mg per day, depending on the mineral element in question. As with vitamins and other essential food nutrients, mineral requirements vary with animal species, ages and heath condition. For example, humans and other vertebrates need large amounts of calcium for construction and maintenance of bones and normal nerves and muscles functions. Phosphorus is an important constituent of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and nucleic acid and is also essential for acid-base balance, bone and tooth formation. Red blood cells cannot function properly without iron in haemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying pigment of red blood cells. Iron is also an important component of the cytochromes that function in cellular respiration. Magnesium, copper, selenium, zinc, iron, manganese and molybdenum are important co-factors found in the structure of certain enzymes and are indispensable in numerous biochemical pathways. Vertebrates need iodine to make thyroid hormones. Sodium, potassium and chlorine are important in the maintenance of osmotic balance between cells and the interstitial fluid. Magnesium is an important component of chlorophyll in plants. The interactions between nutrition and diseases, nutrition and drug metabolism have been reported. Excessive intake of some minerals can upset homeostatic balance and cause toxic side effects. For example, excess sodium intake is associated with high blood pressure and excess iron can cause liver damage. Also, severe shortages or self-prescribed minerals can alter the delicate balance in body functions that promotes health most chemical elements that are ingested by organisms are in the form of simple compounds. Plants absorb dissolved elements in soils, which are subsequently ingested by the herbivores and omnivores that eat them, and the elements move up the food chain. Larger organisms may also consume soil (geophagia) or use mineral resources, such as salt licks, to obtain limited minerals unavailable through other dietary sources.
Calcium makes up 920 to 1200mg of adult body weight, with 99% of its contained in bones and teeth. Phosphorus makes up about 1% of a person’s body weight. The other major minerals potassium, sodium, chlorine, sulphur and magnesium) make up only about 0.85% of the weight of the body. Together these eleven chemical elements (H, C, N, O, Ca, P, K, Na, Cl, S and Mg) make up 99.85% of the body. There is not scientific consensus on whether all of the elements in light green in periodic table are essential or not. Zinc (Zn) is one of the essential trace elements and has numerous physiological functions. Zn acts as an antioxidant and also as a part of other antioxidant related proteins, such as metallothionein (MT) and Zn-copper superoxide dismutase. Zn deficiency often occurs in patients with diabetes. Therefore, the effect of Zn deficiency or Zn supplementation on diabetes-induced cardiac and renal pathogeneses has been explored by researchers. Zn deficiency was induced by chronic treatment of diabetic mice with Zn chelator N, N, N, N-Tetrakis (2-pyridylmethyl)-1,2-ethylenediamine (TPEN) for 4 months. For Zn supplementation study, diabetic mice or rats were treated with Zn for 3 months. Inflammation, fibrosis, and histopathological changes in the heart and kidney of these diabetic mice and rats were examined by western blotting assay, immunohistochemical and fluorescent staining. Results showed that diabetes induced cardiac and renal oxidative damage, inflammation and fibrosis, which were reversed by Zn supplementation that also induced cardiac and renal MT synthesis. Furthermore, Zn deficiency was found to significantly enhance the renal damage induced by diabetes. Several clinical observations also support the preventive effect of Zn in the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy and nephropathy. Therefore, Zn plays an important role in the protection of the heart and kidney against diabetes-induced oxidative damage, inflammation, and fibrosis. These studies suggested that diabetic patients should be monitored and treated for Zn deficiency to avoid the acceleration of diabetes-induced cardiac and renal injury.
Conclusion
Deducing from the result obtained; green medicines especially the multifunctional flora composite developed from ginger, scent leaves, bitter leaves moringa, guava and bitter cola or their combination, is a very important composite material for the prevention of cancer, diabetes, blood pressure and stroke and also for their optimum management, in case they have already occurs. This is because; the compounds are composed of multidimensional bioactive compounds needed for both the nutritional and phytochemical functioning of the human body. The minerals elements such as calcium, are needed for bones and teeth formation, sodium and potassium is needed for acidbase balance in the body, zinc and iron for blood formations and coloration of blood, phosphorus and others for body building, Carbohydrates at optimum level is needed for energy supply, proteins for body build up, vitamins for maintenance of our body, fibres for effective digestions and body balance and fluid or moisture needed for food and blood circulation. Taking a balance supplement prepared using a very simple formulation method such as this, will give you the optimum result in terms of health and nutritional needs. Taking this green medicines and observing simple healthy life styles and tips, will helps prevent the occurrence of cancer, diabetes or it cardiovascular consequences like blood pressure, liver or kidney failure and stroke in the first instance and help in the management of secondary cases. That is, taking the bio-activator along side with the maintenance of ideal body weight, the promotion of the so-called prudent diet (characterized by a higher intake of food groups that are generally recommended for health promotion, particularly plant-based foods as envisaged by this research) and a lower or total abstinences from the intake of red meat its products, sweets, high-fat dietary and refined grains or food) or a Mediterranean dietary pattern rich in olive oil, fruits and vegetables, including whole grains, pulses and nuts, low-fat dairy, and avoidance of alcohol consumption (mainly red wine) appears as the best strategy to decrease diabetes risk, especially if dietary recommendations take into account individual preferences, thus enabling long-time adherence. The adherence to these basic and fundamental health tips as prescribed by these research findings will help rid Nigeria of unnecessary cancer, diabetes, blood pressure and stroke cases. In summary, using a multi-functional flora composite developed from selected medicinal plants either as combined effects or consumed individually along sides with life style modification to favor the disappearance of this diseases, is the best way to avoid the occurrence of the diseases in the first place. When green medicine well characterized is consumed, active exercise, avoidances of alcohols, maintenance of a good body weight (body mass index between 18.5-23.5kg/m2), abstinence from smoking, avoiding exposure to harsh radiation, living in a highly healthy and sanitized environment; obeying the rules of life and natural orders will give human the best health condition no matter the age or gender.
To Know More About Current Trends in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Publishers Please Click on: Juniper Publishers
0 notes
Text
Computational Modeling Studies of the Beta-Amyloid Protein Binding to Develop Drugs for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
Authored by Jerry A Darsey*
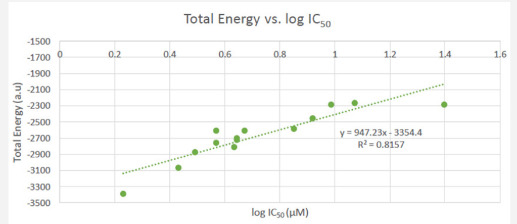
Abstract
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects memory and other mental functions due to the accumulation of Amyloid-Beta (Aβ) plaques. The functions carried out by the Aβ protein leads to abnormalities in the suffering patient. If a molecule binds to the Aβ protein, it could lead to potential treatment. To propose new treatments for AD, novel molecules were identified that bind to the active site of Aβ. First, a correlation between reported IC50 values of fourteen chemicals and their energy gap, dipole moment, and total energy were analyzed. The best correlation was discovered between 1/IC50 values and total energy (R2=0.9279). Then, each identified molecule was virtually modified and its new IC50 value was determined utilizing Gaussian 09, a molecular modeling program, which was used to predict total energies. Some of the most useful modifications included the addition of oxygen (-O), chlorine (-Cl), and fluorine (-F) atoms. The results of this study can be used as a tool to finding novel, medically relevant new molecules for other neurodegenerative diseases and assist researchers in developing new drugs to treat AD
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Beta-Amyloid protein; Drug design; Protein misfolding; amyloid-β aggregation; Oxidative stress; Neuroinflammatory processes; Parkinson’s disease; Huntington’s disease; Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), IC50; Computational molecular modelling; Density functional theory
Introduction
Nearly six million people suffer from Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in the United States, and the number of patients with this multifaceted neurodegenerative disorder could rise to include as many as 16 million people by 2050 [1]. Moreover, in 2017, this disease is estimated to cost $259 billion in global health care expenditures [1]. Alzheimer’s disease is an irreversible neurological disorder that is characterized by memory loss, personality changes, and decline in thinking abilities. Though memory loss is the most widely recognized symptom of Alzheimer’s disease, many other complications, such as a range of behavioral and cognitive deteriorations, are also common. The cognitive symptoms include memory loss, confusion, and disorientation while the behavioral symptoms include depression, insomnia, and hallucinations [2]. Due to the often-intense nature of the symptoms, AD patients can suffer in a multitude of ways and eventually become bedridden and dependent on custodial care. On average, death occurs nine years after diagnosis [3].
AD is characterized at a molecular level by factors such as protein misfolding and aggregation, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammatory processes. The complex pathogenesis has provided for only a limited development of effective therapeutic solutions to combat disease progression [3,4]. Currently, there are several symptomatic medications and treatments for AD. Some of these registered treatments include cholinesterase inhibitors, donepezil, galantamine, and rivastigmine [2,4,5]. Although these drugs are beneficial to some degree, they only provide temporary improvements in cognition and function of the diagnosed patient. Because there is still no efficient medication to prevent the deterioration of the neurodegenerative processes in AD patients, there remains an urgent need for novel drugs that may slow the neurodegenerative disease and potentially reverse its effects. Overall, no treatment with a strong disease modifying effect is currently available.
The primary suspects that are thought to cause Alzheimer’s disease are amyloid-beta (Aβ) and hyper-phosphorylated tau proteins. Agents inhibiting one or both forms of aggregation are promising drug candidates for AD [6]. Amyloid-β peptide chains consist of 40 to 42 amino acids and are suspected to contribute to the degenerative condition of AD. The amyloidbeta precursor protein (APP) is found in many types of cell membranes. The actions of the β-secretase and γ-secretase release the Aβ proteins at an elevated rate into the cytoplasm. These proteins accumulate at high levels in neural cells; they are internalized and folded into a β-pleated shape which results in stacking that forms long aggregates known as senile plaques [2]. Acting as monomers, dimers, or multimers in cell membranes, the Aβ proteins interfere with neurotransmission and memory formation. As the protein aggregates continue to increase in size, they become insoluble in the bloodstream. Scientists have begun to study this problem and suggest treatment strategies, which include inhibitors of the β-secretase and γ-secretase activities, as drugs and physiological compounds to prevent amyloid-β aggregation in the brain [7].
Much research in pursuit of novel compounds that have efficient inhibitory properties of AD still needs to be completed. For example, innovative techniques are needed to offset the financial expenditures related to the traditional tissue culture and model organism experiments. Though several vaccines are in the process of being developed, a breakthrough discoveries are needed to speed up this slow process. A successful drug discovery process would not only revolutionize the treatment of AD and improve the lives of countless people all over the world, but it could also act as an example of how beneficial drugs for other diseases could be discovered in the future. In conjunction with previous research, drug candidates that bind to Aβ proteins could be designed based on specific properties known to enhance this binding. For example, chemical compounds that have a low IC50 value (a measurement of the effectiveness of a drug or inhibitorof binding to a biological molecule by IC50 % and expressed in micromolar concentration, M) could be identified and evaluated to better treat AD. As part of the described study, it was proposed that there exists a correlation between the IC50value and other notable parameters of a chemical compound and its interaction with Aβ proteins. Using computational molecular modeling and virtual simulations, molecules best suited to bind and therefore inhibit Aβ proteins were identified and tested.
As shown in previous studies, determining a molecule to bind to Aβ would result in a major step towards creating a drug to help treat Alzheimer’s disease [8,9]. By determining specific molecules that bind to the Aβ active site, a correlation can be found between its binding affinities and energies. To achieve this goal, computational molecular modeling was used in this research. The goal of this study was to create a molecule that would bind efficiently to the Aβ protein by finding correlations between chemical properties when creating the modified molecule. The plan of this research was to alter molecules that have been previously identified as inhibitors of Aβ and then determine by how much these modified molecules change the IC50 values of the “parent” molecule. By collecting data such as the dipole moment (the product of the separation of two ends of a dipole molecule and the magnitude of the charges), highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO), lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO), energy gap (value found by subtracting the HOMO value from the LUMO value), and plotted vs. the IC50 value, a correlation was determined and analyzed after the modifications were incorporated. New, IC50 values were then predicted using the line of best fit. The newly designed compounds with a lower predicted IC50 values would be a potential new drug to treat Alzheimer’s disease.
Materials and Methods
The research was initiated by locating and analyzing the native structure of the Beta-Amyloid (Aβ) protein. After a detailed study of their properties and relevance to Alzheimer’s disease, 21 compounds were identified in publications and patents that had been tested as potential inhibitors of the Aβ protein [10]. However, the molecules mentioned in various sources were not always described using the IUPAC naming system. Thus, the correct name of these molecules had to be determined.
To accomplish this task, PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi. nlm.nih.gov/) was utilized as the database to find important information about the molecules and their activities with respect to Aβ protein. PubChem, a free public tool is maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Center at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and provides the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) name, InChIKey (International Chemical Identifier), and chemical structures of more than 92.1 million compounds. To enable the extraction of this information from the PubChem database, the OPSIN tool (Open Parser for Systematic IUPAC nomenclature), freely available from the University of Cambridge, was used. The InChIKey was identified for each chemical and was then used to search for chemical properties on the PubChem website. In ChIKey is a textual chemical identifier for compounds that encodes chemical information and can be used to search online databases. To extract all InChIKeys for the 22 identified compounds, a Google Sheet was created with the first column showing the original name of each chemical as cited in each publication. Table 1 shows the compounds identified by thoroughly searching the literature and their respective IC50 values [10].
Compound Alterations
Using the computational molecular modeling program (Gaussian 09), each chemical was altered by adding specific functional groups and thus resulted in the generation of a new group of compounds. Elements, bond types/sizes, and chemical groups were altered using tools accessible to the user. Each molecule was analyzed using the optimization method, which was applied to clean the molecular bonds and structures utilizing the DFT (Density Functional Theory) 6-31G* basis set (defined for atoms H to Zn and is a double-zeta polarized basis set). The total energy (a.u.), dipole moment (Debye), and HOMOLUMO (Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital-Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital) energy gap (Hartrees), were established and recorded for each molecule.
Statistical correlations
Once the data from all the trials was recorded, binding affinities, measured by the experimentally determined IC50 values of each of the 22 molecules. These values would serve as a tool to later produce modified compounds and their IC50 values to be compared to the original unmodified molecule. The data was entered into an Excel 2016 spread sheet and graphed using the scatter plot tool. Plots included IC50 , log IC50 , and 1/ IC50 values vs. the various calculated parameters (the total energy, dipole moment (Debye), and HOMO-LUMO energy gap). From these plots, the strength of correlations were determined. It should be noted that some data points were outliers and were therefore removed from the data set since they were more than two standard deviations away from the linear trendline. Plots were included with and without the outliers (Figures 1-4).
Results
Data points from the plots of the various Amyloid-Beta (Aβ) inhibitors were used to identify characteristics that would show the best correlations with IC50 values. The values of the total energy, dipole moment, and energy gap of the promising compounds were calculated using the Gaussian 09 software. Numerous correlations were looked at including total energy vs. log IC50 , total energy vs. 1/ IC50 , total energy vs. IC50 , dipole moment vs. log IC50, dipole moment vs. 1/IC50, dipole moment vs. IC50 , energy gap vs. log IC50 , energy gap vs. 1/ IC50 , and energy gap vs. IC50 values. The analysis revealed that the most highly correlated properties were total energy vs. 1/ IC50 values and total energy with log IC50 values (Figures 1-4). This information was then used to find novel, modified molecules and more efficient Aβ compounds that could become new drugs to potentially reduce the negative physiological effects of Alzheimer’s Disease.
The log IC50 values of all the literature derived compounds were used to determine a relationship between total energy and IC50 values. The plot reveals that the log IC50 values for all. The log IC50 values were used to determine a relationship between total energy and IC50values. The plot reveals that the log IC50 values are proportional to the total energy; this statement is supported by the linear equation and R2 =0.8157 value of the trendline.
The 1/ IC50 values of all the literature derived compounds were used to determine a relationship between total energy and IC50 values and are plotted with respect to total energy that was determined using the Gaussian 09 program (see Figure 3). The plot depicts a correlation between the 1/ IC50 values and total energy, with an R2=0.5076 value.
The data points in Figure 4, show the I IC50 values that were obtained from previous experimental research after the removal of the outliers; while the total energy associated with each was obtained using the Gaussian 09 software. The 1/I C50 values were used to determine a relationship between the two parameters. The graph depicts how the 1/ IC50 values are inversely proportional to the total energy, according to the equation and R =0.9279 value of the trendline.
Modifications
Another set of trials was conducted after the highest correlation was determined i.e. total energy vs. 1/IC50 values). To find novel molecules with lower IC50 values than those mentioned in the literature, simple modifications had to be made to accomplish this task. Therefore, the fourteen compounds were modified by an addition of chemical groups/elements to the existing structure and a new IC50value was calculated after the total energy value was outputted from the Gaussian 09 program. For this round of testing, each molecule was run first under the optimization method, and then using the DFT (Density Functional Theory) with the 6-31G* basis set. Table 2 shows the results of the new IC50 values after modifications had been completed.
After running the DFT with the 6-31G* basis set on all the compounds, 3 compounds identified as C02, C13, C22 yield the lowest IC50(largest binding affinities) values in the sets tested. Their chemical structures are show in order in Figure 5a-5c.
Discussion
The accumulation of the Beta-Amyloid (Aβ) proteins, which are derived from the Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP), can form plaques within the human brain [6,11-15]. This ability to form plaque can cause numerous health problems to the patient, which culminate in Alzheimer’s disease. It was therefore beneficial to identify molecules that could bind to these plaque molecules marking them for excretion from the body. The purpose of the current study was to investigate not only whether such potential drug molecules exist, but also to design modifications that would improve their binding capacity. To accomplish this goal, first, it was important to establish if there is a correlation between the literature-derived IC50 values of various chemicals and notable properties including total energy, energy gap, and/or the dipole moment. The property that correlated best with was the 1/IC50 values vs. total energy with an R2=0.9279. Therefore, total energy was calculated for the proposed modifications to the original compounds and the IC50 values for these were determined using total energies and the linear regression equation in Figure 4. The chemical modifications with lower determined IC50 values were selected for further consideration. Any chemical that exhibited lower IC50 values than its original parent molecule should be tested experimentally for efficacy of binding Aβ plaques and its ability to treat Alzheimer’s disease.
In the computational molecular modeling field of research, having a reference chemical is a vital aspect of future research. Based on the procedures of this current study, novel compounds could be identified for various other diseases such as Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). In addition to the distinguishing aspect of this research that allows for modeling treatment for various notable diseases, it also allows for far less time consuming laboratory work since so much of the process is done computationally. Because synthesizing novel chemicals and measuring their IC50 values is both laborious and expensive, the computational research reported here is invaluable to the future expansion of pharmacology. Because scientists do not have to spend large amounts of time synthesizing chemicals and testing them, the computer-aided approach offers a much faster and efficient way to obtain data critical to improving treatment of many deadly diseases. Using this procedure, hundreds of molecules can be analyzed and a far greater number of novel compounds can be identified as promising medications. Ultimately, identifying compounds with high binding affinities for the Aβ protein (with lower IC50 values) that can act as inhibitors, can be applied to Alzheimer’s disease research to develop new drugs to treat patients.
Conclusion
The set of experiments described here reveal an opportunity to design new molecular Amyloid Beta (Aβ) inhibitors using computational molecular modeling techniques. The hypothesis that new IC50 values of virtually altered chemicals could be predicted by first finding a linear correlation between reported IC50 values and a specific, calculable property of these molecules was supported when a strong correlation identified between Total Energy and 1/ IC50 values led to the discovery of lower IC50 values of the modified molecules. More specifically, the linear regression equation generated after graphing 1/ IC50 values vs. Total Energy was used to predict how modifying the previously reported chemicals could lower their predicted IC50 values and so increase their binding capacities to Aβ. The data that allowed for these predictions was generated using the quantum mechanical Gaussian 09 software program. The significance of this novel work is that it suggests new drug candidates to treat Alzheimer’s disease (AD). One of the main causes of the mental symptoms of AD are a buildup of Aβ plaques in the brain. By proposing modifications to various chemicals that improve binding and therefore inhibit Aβ, the experiments described here allow for a set of novel chemicals to be tested in tissue culture and animal models with Aβ buildup. The benefit of doing the preliminary experiments virtually using a computer-aided approach is that it is cheaper, faster and more efficient than biological synthesis and testing. Finding leading drug candidates for the treatment of AD, is critical for future researchers to be able to develop effective medications to combat this debilitating and deadly disease.
The presented research could also lead to investigations of other protein misfolding diseases including Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and various Prion diseases. The computational molecular modeling techniques described in this manuscript could be used to identify molecules that bind proteins associated with specific diseases, and then promote the discovery of novel drugs by proposing modifications that could make these molecules more efficient inhibitors, thus producing better treatments for these neurodegenerative diseases. These computationally driven findings could allow for quicker discoveries of treatments that could improve and even save millions of lives.
Competing Interests
The authors have declared that there exist no known competing interests.
Author Contributions
Sanidhya Tripathi (ST) carried out all the procedures. ST and Jerry Darsey (JD) conceived of the study and performed the statistical analysis. ST drafted the manuscript with the help of PK and JD. JD and PK read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgement
The authors would also like to thank the University of Arkansas at Little Rock Center for Molecular Design and Development and the Arkansas School for Mathematics, Sciences, and the Arts for facilitating my research and providing the venue to share these research findings.
Furthermore, the authors would like to thank Ms. Sumreen Gul, a Ph.D. student, for help with running the Gaussian 09 software and giving one of the authors (ST) consistent feedback and tips throughout the process. Finally, the author (ST) would like to thank the parents Sanjay and Arati Tripathi for all the encouragement and support.
To Know More About Current Trends in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Publishers Please Click on: Juniper Publishers
#Juniper Publishers#open access journals#biomedical engineering#biochemistry#Beta-Amyloid Protein#Alzheimer’s Disease
0 notes
Text
The Ameliorating Effect of Uncooked beans Diet in Cd-1 Mice
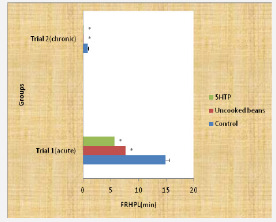
Authored by Aduema W*
Abstract
Beans contain serotonin and its precursor, 5-Hydroxytryptophan which have neurobehavioral actions on memory, anxiety, mood and pain. This study was therefore, designed to investigate the ameliorating effect of uncooked beans on pain sensation using three groups of Swiss white mice (control and test) weighing 18g-35g (n=10 each).The control group received normal rodent chow, while the test group received 50g of uncooked beans in 50g of rodent chow per day and serotonin precursor (5HTP) (0.2mg/50g w/w) diet. Water was given adlibitum while daily food and water intake, as well as body weight changes, were monitored during the 30-day study. The formalin tests were used to assess pain sensation. The results showed that in the formalin test, the frequency and duration of paw attention in both phases of the test was significantly lower (P<0.05) compared to the control group. The duration and frequency of paw licks (P<0.05) was also significantly lower in the uncooked beans diet and serotonin precursor group compared to the control. Therefore, consumption of uncooked beans diet may decrease pain sensation.
Keywords: Beans; Pain sensation; Formalin; Mice
Introduction
Pain can simply be referred as an emotional feeling which is associated with tissue damage. It is therefore a protective mechanism in the body. Beans are considered as good source of protein content, complex carbohydrates, dietary fibers and some minerals and vitamins [1]. In addition to these nutritional components, common beans are rich in a variety of several phytochemicals with potential health benefits, such as polyphenolic compounds, flavonoids, saponins, alkaloids, glycosides, tannin, lectin, trypsin inhibitor, and phytic acids, among others [2,3]. It has also been reported that beans contain serotonin and its precursor 5-Hydroxytrytophan (5-HTP) [4]. Since beans contain neurotransmitters and chemicals that can potentially affect behavioural patterns, it may be worthwhile to find out whether long term consumption of uncooked beans diet can affect behaviour, such as pain sensation.
Materials and Methods
Experimental animals/grouping
Thirty Swiss white mice weighing between (18-35g) and bred at the animal room of the Department of Human Physiology, University of Abia State University. The animals were acclimatized under standard laboratory conditions and given free access to normal feed and clean drinking tap water. The animals were randomly assigned into two groups, control and a test group. The animals in the control group received normal feed (rodent chow) only; while the test group received mixed feed of 50g powdered uncooked beans per every 50g of rodent chow (50% of the uncooked beans diet) and (0.2mg/50g) serotonin precursor diet for 30 days.
Experimental design
The formalin test was used to test for pain sensation as developed by [5]. Mice were carried into the room in their home cages. Each mouse was picked by the base of its tail and 0.2ml of 2.5% formalin was injected into the right hind paw of the mouse using a needle and syringe. The animal was placed in the observation box and observed for 5 minutes. The animal was then returned to its cages and allowed for 30 minutes before it was taken back to the observation box to be re-observed for another 5 minutes. This procedure was repeated for each animal.
Behaviour scored during the pain test included the following;
a) Frequency of Right hind lick/scratch
b) Frequency of Right hind paw attention
c) Duration of attention.
Statistical analysis
Data Obtained from the experiments was statistically analyzed using Microsoft excel, with factorial ANOVA/T-test in the statistics programme start view version for windows or Mac. Post-hoc comparison was also done using the student ±Newmankeuls design. Values were represented as Mean ± SEM and a “P” value less than 0.05, was considered as significant.
Results
Figure 1 shows the frequency of right hind paw licks for mice fed normal, uncooked beans and serotonin precursor diets as 14.90±1.59; 7.71±0.75 and 5.71±0.42/5mins respectively in the first trial after 5 minutes of formalin administration denoting acute pain. The frequency of paw lick for the mice fed uncooked beans and serotonin precursor diet was significantly shorter (p<0.05) than that of the control fed mice. In the second trial after 30 minutes of formalin administration denoting chronic pain, the frequency of paw licks was 0.87±0.22; 0.14±0.14 and 0.14±0.14/5mins for mice fed normal, uncooked beans and serotonin precursor diet respectively. The frequency of right hind paw lick in the uncooked beans and serotonin precursor diet fed mice was significantly shorter (p<0.05) than those of the control fed mice.
The values for duration of hind paw lick following administration of normal, uncooked beans and serotonin precursor diets were 26.79±2.56; 17.75±2.32 and 8.67±2.08 seconds respectively in the first 5 minutes. The duration of hind paw lick in the uncooked beans and serotonin precursor fed mice was significantly lower (p<0.05) compared to control. In the second trial, after 30 minutes of formalin administration, the hind paw lick duration in the group of mice fed normal, uncooked beans and serotonin precursor diets were 1.30±0.52; 0.16±0.16 and 0.16±0.16 seconds respectively. The duration of hind paw lick was significantly lower in the uncooked bean and serotonin precursor fed mice compared to the control group (p<0.05) see Figure 2.
The values for the frequency of hind paw attention following administration of normal, uncooked beans and serotonin precursor diet were 24.00±2.07; 8.14±1.18 and 6.00±0.82/5mins respectively in the first trial after 5 minutes of formalin administration. The frequency of hind paw attention was significantly lower in the uncooked beans and serotonin precursor fed mice compared to control (p<0.05).In the second trial, after 30 minutes of formalin administration, the values were 1.20±0.47; 0.43±0.30 and 0.43±0.30. The frequency of hind paw attention was significantly lower in the serotonin precursor and uncooked beans group compared to control (p<0.05) See Figure 3.
The values for the duration of hind paw attention following administration of normal, uncooked beans and serotonin precursor diet were 89.38±11.33; 53.59±4.14 and 39.03±5.51 seconds respectively. The duration of hind paw attention fed with uncooked beans and serotonin precursor was statistically shorter than those fed with control diet (p<0.05). In the second trial, after 30 minutes of administration of formalin, the duration of paw attention was 2.60±0.60; 0.37±0.24 and 0.55±0.39 seconds respectively. The duration of hind paw attention was significantly lower in the uncooked beans and serotonin precursor fed mice compared to control (P<0.05) (Figure 4).
Discussion
The response of formalin-induced behaviour reflects activation of C fibre primary afferent nociceptors [6]. This test was in two phases. The response within the first 30 seconds following formalin injection is the perception of acute pain, while the later period shows chronic pain perception. Frequency of hind paw attention and hind paw-licking following injection with formalin was defined as the number of times the mice lick or shake their hind paw after injection with formalin. Lower frequencies of hind paw attention and hind paw licking indicate analgesic effect while higher frequencies indicate hyperalgesia. Our finding showed that during acute and chronic phases of pain, the beans diet- fed mice and that of the serotonin precursor fed mice had significantly less pain perception compared to control, since the frequencies and durations of hind paw lick and hind paw attention following formalin injection was significantly lower in the beans and serotonin precursor diet- fed mice than the control.
Pain reduction was observed on the first and second phases of pain following chronic consumption of beans diet. It is therefore interesting to note that beans diet can be beneficial in the reduction of chronic pain if the results in mice can be extrapolated to man. The Serotonin circuitry is a well-established pathway involved in brain’s analgesia system during transmission of pain in the central nervous system. It is known that the analgesic fibers of this system release neurotransmitters that inhibit pain transmission to the brain, and the neurotransmitters released by the fibers of analgesic pathway are serotonin and encephalin [7,8]. Our findings suggest that uncooked beans and serotonin precursor diet mice showed less sensitive to pain, when compared to those fed with the control diet. Beans diet may decrease pain sensitivity which may also be due to the presence of flavonoids and phlobatannins in the beans which has been reported to reduce pain perception due to their anti-inflammatory properties [9,10]. Finally, uncooked beans diet reduces pain sensation in mice. This may be so because beans contain 5-HTP (serotonin precursor) and 5-HT (serotonin) that plays a positive role in the brain analgesia system. A second set of experiments implicated the serotonergic pathway, as the threshold for pain perception was increased in the mice that consumed the serotonin precursor diet [11,12].
Acknowledgement
We acknowledged Pa and Mrs. BA Aduema, Mr. Iwasam Joshua, Prof EE Osim and Associate Prof AA Nwankwo for their support.
Author(S) Contribution
All authors have contributed one way or the other to the success of this paper and there is no conflict in relation to funding or whatsoever that may prevent the publication of this piece.
To Know More About Current Trends in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Publishers Please Click on: Juniper Publishers
0 notes
Text
Uridine Triacetate: the First Ever Chemoprotectant for 5-Fluorouacil Toxicity
Authored by Krishnan V*

Abstract
Antimetabolites 5-Fluorouracil and capecitabine are used in many cancers including breast, colon, anal canal, etc. Toxicity of these agents is mild to severe and may be fatal, toxicity more common in high dose chemotherapy and patients with dihydropyromidine deficiency patients. Uridine triacetate approved as first ever chemoprotectant molecule to prevent 5-Fluorouracil and capecitabine toxicity.
Keywords: Flurouracil overdose; capecitabine adverse effects; chemoprotectant; uridine triacetate
Introduction
5 -Flurouracil (5-FU) is one the common anticancer drug belonging to antimetabolite category. Its Anatomical Therapeutic Calcification code is L01BC02 and its chemical formula is C4H3FN2O2. It is S phase specific agent, affects DNA synthesis and replication. It inhibits thymidylate synthesis enzyme and thereby conversion of deoxyuridine monophosphate to thymidine triphosphate.
Since its introduction in cancer chemotherapy, 5-FU used in various cancers. Currently it's a part of gastric cancer, breast cancer, colon cancer (FOLFOX regimen-Flurouracil, leukovorin, oxaliplatin) and (FOLIRNOX regimen-flurouracil, leukovorin, irinotecan, oxaliplatin) etc . Its congeners, floxuridine used intra-arterially in hepatic metastasis and capecitabine used in recurrent breast colon and breast cancer. 5-FU as a neoadjuvant therapy along with irradiation used in anal cancer, premalignant skin conditions and basal cell carcinoma, Adverse effects of 5-FU are considerable; they are severe gastric ulceration and fatal mucosal bleeding, severe leukopenia, hand foot syndrome, acute myocardial damage and acute cerebellar toxicity. 5-FU is one the low therapeutic index agent and requires careful precise intravenous administration. Toxic effects can be seen in normal individuals and more severe in patients with dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency with more than eight percent mortality [1].
Uridine triacetate; clinical trials and FDA approval
This drug was granted approval by United states-Food and drug administration (US-FDA) as an orphan drug for patients with documented 5-FU toxicity or those who are exposed to high dose of 5-FU. It should be administered within 96 hours of signs and symptoms for optimum benefits. This molecule was evaluated in two trials comprising adult and pediatric patients of 135 sample sizes who were exposed to 5-FU or capecitabine and developed signs of toxicity. Success rate was more than ninety percent than the historical control where 5-FU toxicity mortality was severe and mortality rate was about 80 -85 percent [2] (Figure 1).
Uridine Triacetate; Pharmacodynamics
5-FU is converted in the body as as triphosphate derivative (FUTP). This derivative combines with ribonucleic acid (RNA) and form toxic intermediates which cause cell cycle arrest. Uridine from urdine triacetate is competitive to FUTP incorporation and thereby prevents the formation of toxic intermediates [3].
Uridine Triacetate; Clinical Pharmacokinetics
Its chemical formula is C15H18N2O9. It triacetate can be administered orally and available as oral granules in a sachet. It is s prodrug converted into active form by deacetylation and concentration maximum is attained is within two to three hours and it is also excreted faster from the body with a half of 4.5-5 hours. Dose for adults is 10g every 6 hours, can be given fifteen to twenty doses and pediatric dose must be calculated based on standard formula 6g/m2. It does not cause renal and hepatic impairment and can be used safely in renal or hepatic insufficiency patients; however there no evidence available till date to support its use in pregnancy and lactating mother [3].
UridineTriacetate; Post Marketing Status
Post marketing surveillance did not receive any serious adverse effects uridine triacetate. The common side effects are vomiting diarrhea and mild rashes. Wa, et al. [4] a leading gastrointestinal oncologist recently said on GI cancers and drug development program at San Francisco, Uritidine triactetae is expected to reduce more than ninety five percent of deaths from 5-Fu or capecitabine grade 3 to grade 5 toxicity. Few other reports are also encouraging the use of uridine triacetate [4-6]
Conclusion
Uridine triacetate discovery tends to ameliorate all theadverse effects of 5-FU without compromising its efficacyenables more efficient use of 5-FU with good patient compliance.
To Know More About Journal of Biomedical Engineering Please Click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Publishers Please Click on: Juniper Publishers
0 notes
Text
Biological Samples as a Tool for Analysis of Metals in Serum of Cataract Patients

Authored by Aima Iram Batool*
There is much evidence suggesting that metallic elements may play a role in the formation or cure of human cataract, a disease that is on the increase due to the growing percentage of elderly persons in the world population.We have evaluated the levels of nickel, copper, cadmium, calcium, magnesium, lead and zinc in hairs and nail samples of cataractic subjects and compared these findings to the levels of healthy controls.A group of patients diagnosed with cataract and a group of healthy controls were chosen as subjects. Serum and hair samples were analyzed by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Results were statistically evaluated by SPSS/PC software and student t-test.A significant difference was found in mean concentrations of metallic elements in comparison of patient group to control group (p < 0.05). Mean concentrations of nickel, copper, cadmium and calcium were found significantly higher among cataractous patients at (p<0.05) matched to healthy ones while concentrations of magnesium, zinc and lead were significantly lower among group suffering from cecity. Significant difference was observed among two groups under study regarding zinc, nickel, copper, calcium, magnesium, and lead while for cadmium difference was statistically non-significant. In spite of the fact that this study was carried out on a relatively small sample population, the findings suggest some thought-provoking questions, considering that there has been a good amount of controversy regarding the status of these trace elements and their possible role in cataractogenesis suggesting the need for further studies.
For Read More... Fulltext click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/CTBEB.MS.ID.555562.php
For More Articles in Current Trends in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/index.php
For More Open Access Journals In Juniper Publishers Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php
0 notes
Text
Current and Future Applications for DNA Sequence for Forensics, Biosurveillance, Clinical Health and Detection-Juniper Publishers
Current and Future Applications for DNA Sequence for Forensics, Biosurveillance, Clinical Health and Detection by John P Jakupciak in Juniper Publishers in Journal of Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences

Many DNA/RNA/protein analytical methods are currently available, ranging from the standard culturing methods, which are tedious, slow, and dependent on achieving culture of the agent, to simplistic single biomarker genomic based tests, to high resolution DNA sequencing, which for a few unique techniques, provide identification of metagenomics samples at the strain level. The latter are faster than culture but perform in a near real-time response window. Real-time PCR limited detection methods are restricted to multiplex identification of few bioagents and test results contain the potential of error due to innate amplification errors, coupled with the requirement to know in advance what the agent is in the sample prior to design primers (probes) for detection. Rapid direct sequencing, coupled with data base matching, offers the most reliable, effective, reproducible, and cost effective approach to biological detection at strain level with details to measure major and minor population content. The evidence is now convincing, although a steep education curve is daunting to decision-maker acceptance, that strain to strain variation in genomic sequence renders probabilistic identification from direct sequence the method of choice for forensics, biosurveillance, clinical health and detection. Herein, the application of NGSbioinformatics tools for forensic analyses of bacterial samples was examined against specially prepared samples. These results were used to elucidate benefits, caveats, and potential pitfalls of direct-sequence analysis; revealed subtle errors in sequence information that are overlooked by the community and demonstrated utility of sequencing to match evolved populations back to its source.
https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/CTBEB.MS.ID.555561.php
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Human Facing the Dangerous Day for Multidrug Resistant Organisms or Antibiotic Resistant At Present and Future
Ikram Hasan

Authored By Ikram Hasan
Multi-drug resistance organism are very clever and gradually resistant the most antibiotic. Now a days maximum antibiotic such as penicillin, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, macrolides etc. group resisted by microorganism. Esch. coli resistant the antibiotic such as amoxicillin, cotrimoxazole, cephalexin, cepharadine, ceftriaxone, ceftrazidime, ciprofloxacin, nalidixic acid and Coliform bacteria resistant the antibiotic such as azithroycin, ceftrioxane, cefepime, doxycycline, gentamycin, nitrofurantion and Acinetobacter species resistant the antibiotic such as amoxicillin, amoxicillin/clav, cephadine, cefuroxime, ceftriaxone, cefixime, ceftazidime, aztreonam, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, amikacin, netilmicin, imipenem, meropenem, mecillinam, nitrofurantoin, cotrimoxazole. Many infectious diseases could not relief by single antibiotic and many people have died due to antibiotic resistance and need the double or triple types antibiotic drug for relief the diseases. Antibiotic resistance are very dangerous for surgical patients. If the patients affected by microorganism during operation or after operation of the patients then the life of the patients may be critical even death. At this time the doctor cannot permission the patients for operation or the doctor are afraid for permission of the patients for operation. If the new antibiotic do not discovery or invention then the human life become dangerous even death. After 20-40 years later 90-95% antibiotic will be resist by microorganism all around the world.
For Read More... Fulltext click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/CTBEB.MS.ID.555560.php
For More Articles in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/index.php
For More Open Access Journals In Juniper Publishers Please Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php
0 notes
Text
Controlling Informative Features for Improved Accuracy and Faster Predictions in Omentum Cancer Models

Authored by Damian R Mingle Identification of suitable biomarkers for accurate prediction of phenotypic outcomes is a goal for personalized medicine. However, current machine learning approaches are either too complex or perform poorly. Here, a novel feature detection and engineering machine-learning framework is presented to address this need. First, the Rip Curl process is applied which generates a set of 10 additional features. Second, we rank all features including the Rip Curl features from which the top-ranked will most likely contain the most informative features for prediction of the underlying biological classes. The top-ranked features are used in model building. This process creates for more expressive features which are captured in models with an eye towards the model learning from increasing sample amount and the accuracy/time results. The performance of the proposed Rip Curl classification framework was tested on omentum cancer data. Rip Curloutperformed other more sophisticated classification methods in terms of prediction accuracy, minimum number of classification markers, and computational time.
For More open access journals in juniper publishers please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/
For Moreo articles in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/
To read more... Full Text in Current Trends in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences in Juniper publishers
0 notes
Text
JuniperPublishers|Controlling Informative Features for Improved Accuracy and Faster Predictions in Omentum Cancer Models
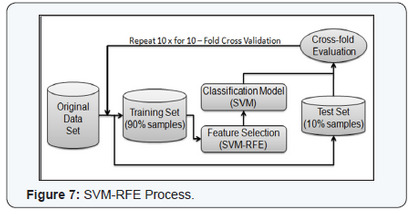
Authored by Damian R Mingle
Identification of suitable biomarkers for accurate prediction of phenotypic outcomes is a goal for personalized medicine. However, current machine learning approaches are either too complex or perform poorly. Here, a novel feature detection and engineering machine-learning framework is presented to address this need. First, the Rip Curl process is applied which generates a set of 10 additional features. Second, we rank all features including the Rip Curl features from which the top-ranked will most likely contain the most informative features for prediction of the underlying biological classes. The top-ranked features are used in model building. This process creates for more expressive features which are captured in models with an eye towards the model learning from increasing sample amount and the accuracy/time results. The performance of the proposed Rip Curl classification framework was tested on omentum cancer data. Rip Curloutperformed other more sophisticated classification methods in terms of prediction accuracy, minimum number of classification markers, and computational time.
For More Open Access Journals in Juniper Publishers Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/journals.php
For More Articles in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/
To Read More...Full Text in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences in Juniper Publishers
1 note
·
View note