The United Nations General Assembly designated 4 December as International Day of Banks to recognize of the significant potential of multilateral development banks and other international development banks in financing sustainable development and providing know-how, and also in recognition of the vital role of the banking systems in the United Nations Member States in contributing to the improvement of the standard of living.
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
How to escape the Middle-income Trap?
More than 100 countries—including China, India, Brazil, and South Africa—face serious obstacles that could hinder their efforts to become high-income countries in the next few decades, according to a new World Bank study that provides the first comprehensive roadmap to enable developing countries.... UN Web TV
Watch the World Bank explaining How to escaoe the Middle-income Trap?

#3i strategy#low income#middle income#investment#innovation#global leaders#comprehensive roadmap#high-income countries#low-income contries
0 notes
Text
Monetary Policy and the Evolution of Wealth Disparity - An Assessment Using US Survey of Consumer Finance Data.
This session examines the distributional effects of recent - monetary policies on income and wealth. Using the Federal Reserve Board's Survey of Consumer Finances, the research tracks key subpopulations as monetary policy shifted from conventional interest rates to Quantitative Easing. Employing advanced modeling techniques, the study analyzes volatility and bifurcation in capital gains and incomes among U.S.
Watch the Monetary Policy and the Evolution of Wealth Disparity - An Assessment Using US Survey of Consumer Finance Data!

#Survey of Consumer Finances#income and wealth#monetary policies#Quantitative Easing#interest rates#capital gains#income#united states#wealth disparity#distributional effects#federal reserve bank#consumer finance#monetary policy
0 notes
Text
Strategies and Structures of Financial Institutions.
A financial sector comprises a set of institutions, instruments, and markets established in the context of a legal and regulatory framework. Financial institutions face challenges for gaining competitive advantage in the context of rapid changes in technological, economic, social, demographic, and regulatory environments. The deep transformation of the financial sector is witnessing can be attributed to a number of factors such as technology innovation, deregulation, worldwide consolidation and restructuring, deregulation, and changing demographic profiles. Information technology is the primary force that keeps the financial industry dynamic. The post-economic crisis witnessed a series of policy reforms initiated by regulatory authorities. The global technology trends in the financial industry indicate the relevance of next-generation remote banking solutions, business intelligence, and analytics in transaction monitoring. Financial institutions face much complexity in the types of risks they have to manage. The trends indicate the growing significance of the emerging Asia market, consisting of China, India, and ASEAN countries for growth opportunities in the financial services industry.
Learn more about Strategies and Structures of Financial Institutions related to the publication - Strategies of Banks and Other Financial Institutions: Theories and Cases.
#Financial institutions#remote banking solutions#business intelligence#transaction monitoring#financial services industry#international day of banks#4 december#banks#banking system
0 notes
Text
Regulatory Environment of Financial Institutions.
Financial regulations are laws and rules that govern financial institutions. Regulations of financial institutions focus on providing stability to the financial system, fair competition, consumer protection, and prevention and reduction of financial crimes. By the mid-1970s, the global financial system witnessed market-oriented reforms that led to liberalization in the financial system, such as the reduction of interest rate controls, removal of investment restrictions on financial institutions and a line of business restrictions, and control on international capital movements. The modern trend observed is that financial sector regulation is moving toward a greater cross-sector integration of financial supervision. In 1998, the adoption of the Basel Accord, which required international banks to attain an 8% capital adequacy ratio was a major significant milestone in banking regulations. The collapse of the global financial system that led to the global crisis can be attributed to the systemic failure of financial regulation. Basel I defined bank capital and bank capital ratio based on two-tier systems. The Basel II framework consisted of Part 1, the scope of application and three pillars, the first one being minimum capital requirements, the second one a supervisory review process, and the third pillar is market discipline. The Basel III framework prepared new capital and liquidity requirements for banks.
Learn more about Regulatory Environment of Financial Institutions related to the publication - Strategies of Banks and Other Financial Institutions: Theories and Cases.
#Financial regulations#Regulations of financial institutions#financial security#financial industry#financial markets#financial risk management#bank capital ratio#Basel Accord#interest rate controls#international capital movements#banking system#4 december#sustainable development goals#international day of banks
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Risks Inherent in Financial Institutions.
The major risks faced by banks and related financial institutions include credit risks, interest rate risks, market risk, and operating and liquidity risks. The other risks include residual, dilution, settlement, compliance, concentration, country, foreign exchange, strategic, and reputational risks. The major tools of a risk management system used by banks are stress testing and asset and liability management. The different forms of interest rate risk are gap or mismatch risk, basis risk, embedded-option risk, yield curve risk, price risk reinvestment risk, and others. The instruments for credit risk management consist of estimating expected loan losses, multitiered credit-approving systems, prudential limits, risk ratings, risk pricing, portfolio models, loan review mechanisms, and the like. The instruments for measurement of interest rate risk are maturity gap analysis, duration gap analysis, and simulation analysis. The basic model for measurement of market risk is value at risk. Liquidity risks are measured through various ratios. The risks in major non-banking financial institutions such as insurance includes underwriting and investment risks along with market, credit, and provisioning risks. Pension fund risks consist of firm specific risks, funding risks, investment risks, plan termination risks, and compliance risks. Mutual fund risks consist of market risks, liquidity risks, call risks, and currency risks.
Learn more about Risks Inherent in Financial Institutions related to the publication - Strategies of Banks and Other Financial Institutions: Theories and Cases.
#liquidity risk#credit risk#financial risk management#operational risk#legal risk#non-banking financial institutions#interest rate risk#credit risk management#4 december#international day of banks#currency risk#mutual funds
0 notes
Text
Money Markets, Bond Markets, and Mortgage Markets.
Capital markets consist of money market, bond market, mortgage markets, stock market, spot or cash markets, derivatives markets, foreign exchange and interbank markets. Money market instruments consist of Treasury bills, federal agency notes, certificates of deposit (CD), commercial papers, bankers’ acceptances, repurchase agreements (repos), among others. The securities market consists of primary and secondary markets. The primary market works with new issues whereas the secondary market is meant for trading of existing issues. Capital market instruments include Treasury notes, Treasury bonds, municipal bonds, corporate bonds. Corporate bonds consist of zero coupon bonds, floating rate bonds, and convertible bonds. Bond ratings are assigned by credit rating agencies (e.g., S&P, Moody’s, etc.). The major debt issued in the international market includes euro banknotes, Eurobonds, euro medium-term notes, global and foreign bonds. The three major groups in bond market are issuers, underwriters, and purchasers. Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) are created through the process of securitization. The different types of MBS include pass-through securities and collateralized mortgage obligations.
Learn more about Money Markets, Bond Markets, and Mortgage Markets related to the publication - Strategies of Banks and Other Financial Institutions: Theories and Cases.
#Money Markets#Bond Markets#Mortgage Markets#international day of banks#4 december#capital markets#Money market#Mortgage-backed securities (MBS)
0 notes
Text
Stock Markets, Derivatives Markets, and Foreign Exchange Markets.
The stock market is an important part of the economy of a country. The stock market consists of primary and secondary stock markets. Initial public offerings are issued in the primary market. Seasoned equity offerings are new shares offered by firms that already have stocks outstanding. The secondary stock market where investors trade can further be divided into auction and dealer markets. Derivatives have become an effective tool to reduce business risks. Corporations and financial institutions are the major users of derivatives. Most derivatives are based on one of the four types of assets: foreign exchange, interest rates (debt securities), commodities, and equities. Forwards, futures, options, and swaps are the major derivatives instruments. Mortgage-backed securities, collateralized debt obligations, and collateralized loan obligations are instruments of securitization. The most common forms of credit derivatives are credit default swaps, total return swaps, credit spread options, and credit-linked notes.
International monetary systems refer to the operating systems of the financial environment that consist of financial institutions, multinational corporations, and investors. The forex market is the world’s largest financial market where trillions are traded daily. The foreign exchange market consists of currency spot, forwards, futures, options, and swap markets. Foreign exchange risk consists of economic and translation exposure.
Learn more about Stock Markets, Derivatives Markets, and Foreign Exchange Markets related to the publication - Strategies of Banks and Other Financial Institutions: Theories and Cases.
#Foreign exchange risk#International monetary systems#financial environment#Investors#financial markets#multinational corporations#international day of banks#4 december#stock market#Mortgage-backed securities#collateralized debt obligations#collateralized loan obligations
0 notes
Text
Strategies of Depository Institutions.
Depository institutions are broadly classified into commercial banks and thrift institutions. The commercial banking industry provides commercial, industrial, and consumer loans and accepts deposits from individual and institutional customers. Commercial banking covers services such as cash management, credit services, deposit services, and foreign exchange. The explosive growth of secondary loan and credit markets altered the shape of the corporate banking industry. Commercial banks face challenges with respect to additional revenue generation in the event of economic uncertainty, regulatory issues, high liquidity costs, and low demand for loans. The basic functions of commercial banks are to accept deposits and provide loans. Other functions include providing overdraft facilities, discounting bills of exchange, fund investments, and agency functions. A commercial bank’s performance can be evaluated along the dimensions of deposit mobilization, quality of lending, capital adequacy analysis, liquidity, earnings, and loan growth. The CAMEL rating system is a supervisory tool for evaluating the soundness of a financial institution. Thrift institutions consist of mutual savings banks, savings and loan associations, and credit unions. These financial intermediaries raise funds through time and savings deposits and invest in residential mortgages and loans. Savings institutions face liquidity, credit, and interest rate risk.
Learn more about Strategies of Depository Institutions related to the publication - Strategies of Banks and Other Financial Institutions: Theories and Cases.
#Depository institutions#commercial bank’s performance#mutual savings banks#savings and loan associations#credit unions#CAMEL rating system#Savings institutions
0 notes
Text
Investment Banks and Finance Companies.
Investment banks offer services in equity capital markets, leveraged debt capital markets, commercial real estate, asset finance and leasing, and corporate lending services. The major functions of investment banks are raising funds, asset management, mergers and acquisitions advisory services, brokerage services, and market making. The asset management function of investment banks involves managing the funds of corporations and investing in stocks, fixed-income securities/bonds, derivatives investments, and other types of investments. Investment banks are actively involved in mergers and acquisitions by performing the functions of deal making. Securities underwriting is the process by which investment banks raise investment capital from investors in the form of equity and debt capital on behalf of companies and government authorities. Underwriters offer a set of services for initial public offerings (IPOs) or seasoned equity offerings. The methods used for IPO pricing are the fixed price method and book building process. The debt capital markets services divisions of investment banks solicit structures and execute investment-grade debt and related products, which include new issues of public and private debt. The strategic changes in investment banks has often been cited as a reason for the economic crisis that crippled the global economy.
Finance companies are specialized financial institutions that make loans to individuals and corporations for the purchase of consumer goods and services. The three major types of finance companies are consumer finance, business or commercial finance, and sales finance.
Learn more about Investment Banks and Finance Companies related to the publication - Strategies of Banks and Other Financial Institutions: Theories and Cases.
#initial public offerings (IPOs)#investment capital#investment banks#sales finance#consumer finance#business or commercial finance#and#international day of banks#4 december#asset liability management
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mutual Funds, Insurance, and Pension Fund.
Mutual funds, insurance, and pensions funds are major financial intermediaries. Mutual funds represent the second-largest pool of private capital in the world after the banking industry. Mutual funds are classified into open-ended, closed-end, and unit investment trusts. The main categories of funds are stock or equity funds, bonds or fixed-income funds, money market funds, and hybrid funds.
The insurance industry is basically classified as life and property insurance. The two main types of life insurance are term and permanent life insurance. There are also other life insurance products such as group life insurance, credit life insurance, annuity and pension plans. Property/casualty insurance is insurance on homes, cars, and businesses. The three fundamental risks faced by insurance companies are underwriting, market, and regulatory risks. Value at risk and expected shortfall are two major metrics used to measure and manage financial risks in insurance. Pension funds are classified into different types: public and private pension plans, occupational and personal pension plans, DC and DB plans, protected and unprotected pension plans, funded versus unfunded pension plans, single- and multiple-employer pension funds. Private pension funds consist of 401(k), 403(b), and individual retirement accounts (IRAs).
Learn more on Mutual Funds, Insurance, and Pension Funds.
#Mutual funds#money market funds#bonds or fixed-income funds#credit life insurance#Private pension funds#and individual retirement accounts (IRAs).#Pension funds#international day of banks#4 december#financial risk management#insurance industry
0 notes
Text
Private Equity and Hedge Funds.
Private equity (PE) is a type of equity investment in private companies that are not listed on the stock exchanges. The primary aim of investments by a PE firm is to get involved in the business, increase the value of the business, and sell shares in the business to get the desired payoff. PE strategies involve leveraged buyouts, venture capital, growth capital, distressed investments, and mezzanine capital. The different types of PE funds are categorized as leverage buyout funds, venture capital funds, growth equity funds, and special situation funds. Venture capital is a type of PE investment for promoting new technology, new marketing concepts, and new products. A hedge fund is an alternative investment fund that is available to institutional investors and high net-worth individuals with significant assets. Hedge funds are highly leveraged and invest in high-risk financial derivatives. Popular hedge fund strategies can be categorized as equity-based strategies, arbitrage-based strategies, opportunistic strategies, and multiple strategies. Some of the major investment strategies of hedge funds are equity long strategy, fixed income strategy, convertible arbitrage strategy, funds of fund strategy, global macro, relative value arbitrage, and managed futures.
Learn more on Private Equity and Hedge Funds.
#hedge funds#investment strategies#financial risks#Venture capital#Private equity (PE)#international day of banks#4 december#alternative investment fund
0 notes
Text
Islamic Influence.
Islamic finance is based on Islamic principles and jurisprudence. The payment and receipt of interest (riba) is prohibited under Islamic principles. Contracts that involve speculation (maysir) and uncertainty (gharar) are considered void in Islamic finance. Financing instruments in Islamic finance consist of equity-like and debt-like instruments.
Fixed claim instruments include murabaha, ijarah, salam, and istisna. Sukuk is an asset-backed trust certificate (bond) representing ownership of an asset or its usufruct (earnings) based on the principle of sharia. Equity instruments include mudarabah and musharakah. In mudarabah one partner provides the capital investment (rabb ul maal) to another partner (mudarib) who is responsible for operations and management of the business. Musharakah is a profit-and-loss sharing partnership contract.
Islamic financial institutions face various risks such as credit risk, benchmark risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, legal risk, and fiduciary risk. Takaful is commonly referred to as Islamic insurance. The two basic models of takaful insurance are the Al mudharabah and al wakala model.
#Islamic finance#Islamic financial institutions#credit risk#benchmark risk#liquidity risk#operational risk#legal risk#and fiduciary risk.#Financing instruments#capital investment
0 notes
Text
Consolidations in Financial Institutions and Markets.
The major contributing factors for mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in the finance sector can be attributed to advances in information technology, financial deregulation, and globalization of financial markets. Consolidation has led to a one-stop shopping concept in the finance sector. The trend of insurance firms merging with banking companies is known as bancassurance. During the period 1990-2001, more than 10,000 financial firms were acquired in developed nations. The 1990s saw some of the largest mergers in banking history in the United States. Particularly in United States, financial mergers have been more heavily concentrated in banking during the last few decades. In comparison, Australia, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom witnessed greater M&As activity in insurance, securities, and other segments of the financial industry.
Consolidations in Financial Institutions and Markets
#international day of banks#Financial firms#financial markets#mergers and acquisitions (M&A)#banking system#financial industry
0 notes
Text
How and why do strategic perspectives of financial institutions differ by class and region?
Strategies of Banks and Other Financial Institutions: Theories and Cases is an introduction to global financial institutions that presents both theoretical and actual aspects of markets and institutions. The book encompasses depository and non-depository Institutions; money markets, bond markets, and mortgage markets; stock markets, derivative markets, and foreign exchange markets; mutual funds, insurance, and pension funds; and private equity and hedge funds. It also addresses Islamic financing and consolidation in financial institutions and markets. Featuring up-to-date case studies in its second half, Strategies of Banks and Other Financial Institutions proposes a useful theoretical framework and strategic perspectives about risk, regulation, markets, and challenges driving the financial sectors.
Key Features
Describes theories and practices that define classes of institutions and differentiate one financial institution from another
Presents short, focused treatments of risk and growth strategies by balancing theories and cases
Places Islamic banking and finance into a comprehensive, universal perspective
#Banking models#Banking system regulation#Bank risk management#fund transfer pricing#liquidity risk funding#Asset liability management#market risks#capital markets
0 notes
Text
Banks bolster metals-trading desks after wild year for markets.

The biggest banks are set for a bumper year in commodities, as the war in Ukraine whipsaws raw materials prices. That follows a sluggish decade during which many lenders scaled back or exited metals trading.

0 notes
Text
UNEP FI Toolkit for Impact Management.
youtube
UNEP FI is pleased to launch the Impact Protocol for Banks, along with the latest Module of Version 3 of the Portfolio Impact Analysis Tool for Banks, marking the consolidation of a full toolkit for impact management for banks.
In 2017 UNEP FI’s Principles for Positive Impact Finance put forward a new, holistic, approach to impact management by private financial institutions, involving the systematic consideration of both positive and negative impacts across the three pillars of sustainable development (environmental, social, socio-economic).
In 2019, UNEP FI released the Principles for Responsible Banking (PRB), which requires signatory banks to align their core strategy, decision-making, lending and investment with the Sustainable Development Goals, and international agreements such as the Paris Climate Agreement. To achieve this, Principle 2 requires banks to perform an impact analysis of their portfolios, to identify their most significant impact areas and to set impact targets and action plans accordingly, so as to manage their positive and negative impacts.
The Impact Protocol provides a step-by-step overview of how to analyse and manage bank portfolio impacts as per UNEP FI’s holistic impact approach, and in conformity with the requirements of the Principles for Responsible Banking.
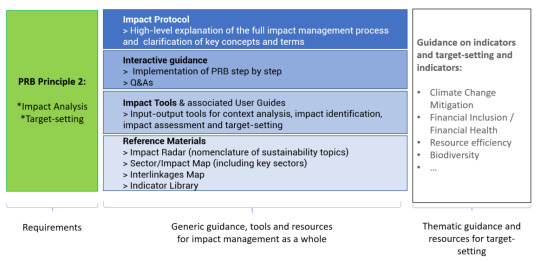
#private financial institutions#public financial institutions#Principles for Responsible Banking#UNEPFI#United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative#Banks#Impact Protocol#Sustainable Development Goals#Paris Climate Agreement#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Transforming Finance, Accelerating Change.
UNEP FI welcomed more than 3000 participants at its 17th Global Roundtable (GRT), held virtually under the theme “Transforming Finance, Accelerating Change”.
#Banking#Climate Change#Investment#Pollution & Circular Economy#SDGs and Impact#Roundtables#United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative#UNEPFI
0 notes