Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
KMeans Clustering Assignment
Import the modules
from pandas import Series, DataFrame import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pylab as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn import preprocessing from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
Load the dataset
data = pd.read_csv("C:\Users\guy3404\OneDrive - MDLZ\Documents\Cross Functional Learning\AI COP\Coursera\machine_learning_data_analysis\Datasets\tree_addhealth.csv")
data.head()
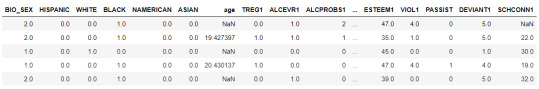
upper-case all DataFrame column names
data.columns = map(str.upper, data.columns)
Data Management
data_clean = data.dropna() data_clean.head()
subset clustering variables
cluster=data_clean[['ALCEVR1','MAREVER1','ALCPROBS1','DEVIANT1','VIOL1', 'DEP1','ESTEEM1','SCHCONN1','PARACTV', 'PARPRES','FAMCONCT']] cluster.describe()

standardize clustering variables to have mean=0 and sd=1
clustervar=cluster.copy() clustervar['ALCEVR1']=preprocessing.scale(clustervar['ALCEVR1'].astype('float64')) clustervar['ALCPROBS1']=preprocessing.scale(clustervar['ALCPROBS1'].astype('float64')) clustervar['MAREVER1']=preprocessing.scale(clustervar['MAREVER1'].astype('float64')) clustervar['DEP1']=preprocessing.scale(clustervar['DEP1'].astype('float64')) clustervar['ESTEEM1']=preprocessing.scale(clustervar['ESTEEM1'].astype('float64')) clustervar['VIOL1']=preprocessing.scale(clustervar['VIOL1'].astype('float64')) clustervar['DEVIANT1']=preprocessing.scale(clustervar['DEVIANT1'].astype('float64')) clustervar['FAMCONCT']=preprocessing.scale(clustervar['FAMCONCT'].astype('float64')) clustervar['SCHCONN1']=preprocessing.scale(clustervar['SCHCONN1'].astype('float64')) clustervar['PARACTV']=preprocessing.scale(clustervar['PARACTV'].astype('float64')) clustervar['PARPRES']=preprocessing.scale(clustervar['PARPRES'].astype('float64'))
split data into train and test sets
clus_train, clus_test = train_test_split(clustervar, test_size=.3, random_state=123)
k-means cluster analysis for 1-9 clusters
from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist clusters=range(1,10) meandist=[]
for k in clusters: model=KMeans(n_clusters=k) model.fit(clus_train) clusassign=model.predict(clus_train) meandist.append(sum(np.min(cdist(clus_train, model.cluster_centers_, 'euclidean'), axis=1)) / clus_train.shape[0])
""" Plot average distance from observations from the cluster centroid to use the Elbow Method to identify number of clusters to choose """ plt.plot(clusters, meandist) plt.xlabel('Number of clusters') plt.ylabel('Average distance') plt.title('Selecting k with the Elbow Method')
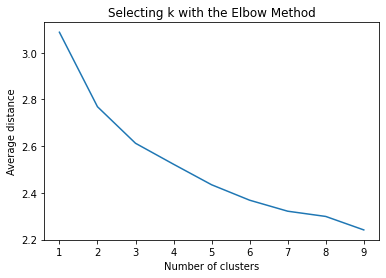
Interpret 3 cluster solution
model3=KMeans(n_clusters=3) model3.fit(clus_train) clusassign=model3.predict(clus_train)
plot clusters
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA pca_2 = PCA(2) plot_columns = pca_2.fit_transform(clus_train) plt.scatter(x=plot_columns[:,0], y=plot_columns[:,1], c=model3.labels_,) plt.xlabel('Canonical variable 1') plt.ylabel('Canonical variable 2') plt.title('Scatterplot of Canonical Variables for 3 Clusters') plt.show()
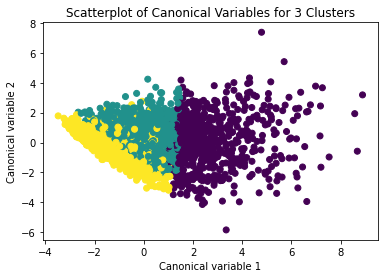
The datapoints of the 2 clusters in the left are less spread out but have more overlaps. The cluster to the right is more distinct but has more spread in the data points
""" BEGIN multiple steps to merge cluster assignment with clustering variables to examine cluster variable means by cluster """
create a unique identifier variable from the index for the
cluster training data to merge with the cluster assignment variable
clus_train.reset_index(level=0, inplace=True)
create a list that has the new index variable
cluslist=list(clus_train['index'])
create a list of cluster assignments
labels=list(model3.labels_)
combine index variable list with cluster assignment list into a dictionary
newlist=dict(zip(cluslist, labels)) newlist
convert newlist dictionary to a dataframe
newclus=DataFrame.from_dict(newlist, orient='index') newclus
rename the cluster assignment column
newclus.columns = ['cluster']
now do the same for the cluster assignment variable
create a unique identifier variable from the index for the
cluster assignment dataframe
to merge with cluster training data
newclus.reset_index(level=0, inplace=True)
merge the cluster assignment dataframe with the cluster training variable dataframe
by the index variable
merged_train=pd.merge(clus_train, newclus, on='index') merged_train.head(n=100)
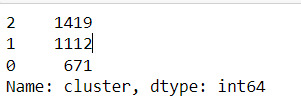
cluster frequencies
merged_train.cluster.value_counts()
""" END multiple steps to merge cluster assignment with clustering variables to examine cluster variable means by cluster """
FINALLY calculate clustering variable means by cluster
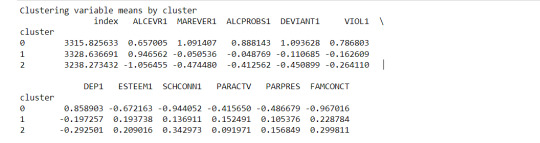
clustergrp = merged_train.groupby('cluster').mean() print ("Clustering variable means by cluster") print(clustergrp)
validate clusters in training data by examining cluster differences in GPA using ANOVA
first have to merge GPA with clustering variables and cluster assignment data
gpa_data=data_clean['GPA1']
split GPA data into train and test sets
gpa_train, gpa_test = train_test_split(gpa_data, test_size=.3, random_state=123) gpa_train1=pd.DataFrame(gpa_train) gpa_train1.reset_index(level=0, inplace=True) merged_train_all=pd.merge(gpa_train1, merged_train, on='index') sub1 = merged_train_all[['GPA1', 'cluster']].dropna()
Print statistical summary by cluster
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf import statsmodels.stats.multicomp as multi
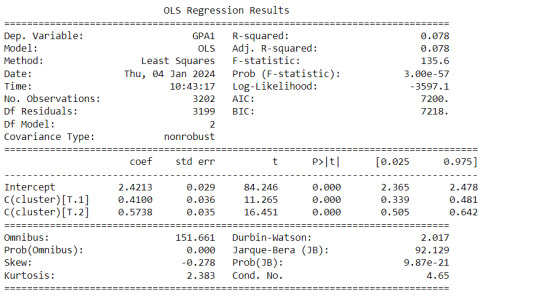
gpamod = smf.ols(formula='GPA1 ~ C(cluster)', data=sub1).fit() print (gpamod.summary())
print ('means for GPA by cluster') m1= sub1.groupby('cluster').mean() print (m1)
print ('standard deviations for GPA by cluster') m2= sub1.groupby('cluster').std() print (m2)

Interpretation
The clustering average summary shows Cluster 0 has higher alcohol and marijuana problems, shows higher deviant and violent behavior, suffers from depression, has low self esteem,school connectedness, paraental and family connectedness. On the contrary, Cluster 2 shows the lowest alcohol and marijuana problems, lowest deviant & violent behavior,depression, and higher self esteem,school connectedness, paraental and family connectedness. Further, when validated against GPA score, we observe Cluster 0 shows the lowest average GPA and CLuster 2 has the highest average GPA which aligns with the summary statistics interpretation.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Running Lasso Regression Analysis
Import Libraries
from pandas import Series, DataFrame import pandas as pd import numpy as np import os import matplotlib.pylab as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.linear_model import LassoLarsCV
Load the dataset
data = pd.read_csv("C:\Users\guy3404\OneDrive - MDLZ\Documents\Cross Functional Learning\AI COP\Coursera\machine_learning_data_analysis\Datasets\tree_addhealth.csv")
Getting information aboubt the dataset
data.info()
upper-case all DataFrame column names
data.columns = map(str.upper, data.columns)
Total size of data
len(data)
We observe some of the columns of the dataset contains null values . We need to drop them
Drop Null values
data_clean = data.dropna()
Data management
recode1 = {1:1, 2:0} data_clean['MALE']= data_clean['BIO_SEX'].map(recode1)
Length of dataset after dropping null values
len(data_clean)
Split into training and testing sets
select predictor variables and target variable as separate data sets
predvar= data_clean[['MALE','HISPANIC','WHITE','BLACK','NAMERICAN','ASIAN', 'AGE','ALCEVR1','ALCPROBS1','MAREVER1','COCEVER1','INHEVER1','CIGAVAIL','DEP1', 'ESTEEM1','VIOL1','PASSIST','DEVIANT1','GPA1','EXPEL1','FAMCONCT','PARACTV', 'PARPRES']]
target = data_clean.SCHCONN1
standardize predictors to have mean=0 and sd=1
predictors=predvar.copy() from sklearn import preprocessing predictors['MALE']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['MALE'].astype('float64')) predictors['HISPANIC']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['HISPANIC'].astype('float64')) predictors['WHITE']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['WHITE'].astype('float64')) predictors['NAMERICAN']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['NAMERICAN'].astype('float64')) predictors['ASIAN']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['ASIAN'].astype('float64')) predictors['AGE']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['AGE'].astype('float64')) predictors['ALCEVR1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['ALCEVR1'].astype('float64')) predictors['ALCPROBS1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['ALCPROBS1'].astype('float64')) predictors['MAREVER1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['MAREVER1'].astype('float64')) predictors['COCEVER1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['COCEVER1'].astype('float64')) predictors['INHEVER1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['INHEVER1'].astype('float64')) predictors['CIGAVAIL']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['CIGAVAIL'].astype('float64')) predictors['DEP1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['DEP1'].astype('float64')) predictors['ESTEEM1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['ESTEEM1'].astype('float64')) predictors['VIOL1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['VIOL1'].astype('float64')) predictors['PASSIST']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['PASSIST'].astype('float64')) predictors['DEVIANT1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['DEVIANT1'].astype('float64')) predictors['GPA1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['GPA1'].astype('float64')) predictors['EXPEL1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['EXPEL1'].astype('float64')) predictors['FAMCONCT']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['FAMCONCT'].astype('float64')) predictors['PARACTV']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['PARACTV'].astype('float64')) predictors['PARPRES']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['PARPRES'].astype('float64'))
split data into train and test sets
pred_train, pred_test, tar_train, tar_test = train_test_split(predictors, target, test_size=.3, random_state=123)
specify the lasso regression model
model=LassoLarsCV(cv=10, precompute=False).fit(pred_train,tar_train)
print variable names and regression coefficients
dict(zip(predictors.columns, model.coef_))

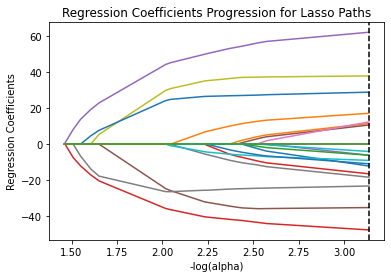
plot coefficient progression
m_log_alphas = -np.log10(model.alphas_) ax = plt.gca() plt.plot(m_log_alphas, model.coef_path_.T) plt.axvline(-np.log10(model.alpha_), linestyle='--', color='k', label='alpha CV') plt.ylabel('Regression Coefficients') plt.xlabel('-log(alpha)') plt.title('Regression Coefficients Progression for Lasso Paths')
MSE from training and test data
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error train_error = mean_squared_error(tar_train, model.predict(pred_train)) test_error = mean_squared_error(tar_test, model.predict(pred_test)) print ('training data MSE') print(train_error) print ('test data MSE') print(test_error)

R-square from training and test data
rsquared_train=model.score(pred_train,tar_train) rsquared_test=model.score(pred_test,tar_test) print ('training data R-square') print(rsquared_train) print ('test data R-square') print(rsquared_test)

Summary
The study used lasso regression to figure out which factors affect how connected adolescents feel to school. They had 23 variables, including things like age, substance use, and family-related factors. The data was split into a training set (70%) and a test set (30%). The model found 18 key variables that together explained 33.4% of the variation in school connectedness. Self-esteem, depression, violent behavior, and GPA were the strongest influencers. Positive factors included older age, Hispanic/Asian ethnicity, family connectedness, and parental involvement. Negative factors included being mal, Black/Native American, substance use, deviant behavior, and expulsion history. The R square and MSE values of both train and test datasets are very close, indicating a lower variance in the model results.
0 notes
Text
Running a Random Forest
from pandas import Series, DataFrame import pandas as pd import numpy as np import os import matplotlib.pylab as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.metrics import classification_report import sklearn.metrics # Feature Importance from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier
Load the dataset
data = pd.read_csv("C:\Users\guy3404\OneDrive - MDLZ\Documents\Cross Functional Learning\AI COP\Coursera\machine_learning_data_analysis\Datasets\tree_addhealth.csv")
data.head()
Getting information aboubt the dataset
data.info()
Total size of data
len(data)
We observe some of the columns of the dataset contains null values . We need to drop them
Drop null values from dataset
data_clean = data.dropna()
data_clean.dtypes
data_clean.describe()
Length of dataset after dropping null values
len(data_clean)
Split into training and testing sets
predictors = data_clean[['BIO_SEX','HISPANIC','WHITE','BLACK','NAMERICAN','ASIAN','age', 'ALCEVR1','ALCPROBS1','marever1','cocever1','inhever1','cigavail','DEP1','ESTEEM1','VIOL1', 'PASSIST','DEVIANT1','SCHCONN1','GPA1','EXPEL1','FAMCONCT','PARACTV','PARPRES']]
targets = data_clean.TREG1
pred_train, pred_test, tar_train, tar_test = train_test_split(predictors, targets, test_size=.4)
pred_train.shape pred_test.shape tar_train.shape tar_test.shape
Build model on training data
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
classifier=RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=25) classifier=classifier.fit(pred_train,tar_train)
predict using random forest classifier on test data
predictions=classifier.predict(pred_test)
Print confusion matrix and accuracy score
sklearn.metrics.confusion_matrix(tar_test,predictions)
sklearn.metrics.accuracy_score(tar_test, predictions)
fit an Extra Trees model to the data
model = ExtraTreesClassifier() model.fit(pred_train,tar_train)
Get feature importances
feature_importances = model.feature_importances_
Create a Series with feature importances and corresponding feature names
feature_importance_series = pd.Series(feature_importances, index=pred_train.columns)
Sort features based on importance
sorted_feature_importance = feature_importance_series.sort_values(ascending=False)
Plot the feature importances
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) sorted_feature_importance.plot(kind='barh') plt.title('Feature Importance') plt.xlabel('Importance Score') plt.show()

#Running different number of trees and see the effect of that on the accuracy of the prediction
trees=range(25) accuracy=np.zeros(25)
for idx in range(len(trees)): classifier=RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=idx + 1) classifier=classifier.fit(pred_train,tar_train) predictions=classifier.predict(pred_test) accuracy[idx]=sklearn.metrics.accuracy_score(tar_test, predictions)
plt.cla() plt.plot(trees, accuracy)

Random forest analysis was performed to evaluate the importance of series of variables in predicting whether a person is a regular smoker or not. We observed that out of all features, marijuana use has the highest feature importance, followed by deviance and GPA. The random model could predict with an accuracy score of 85%.
1 note
·
View note