Text

oh uh. scuse me. just a lil snail crossing your dash
182K notes
·
View notes
Text
i learned about Tim Wong who successfully and singlehandedly repopulated the rare California Pipevine Swallowtail butterfly in San Francisco. In the past few years, he’s cultivated more than 200 pipevine plants (their only food source) and gives thousands of caterpillars to his local Botanical Garden (x)

130K notes
·
View notes
Text
I know! I am screaming!
WOW.
Scientists found an amazingly well-preserved village from 3,000 years ago


Text below, in case article access dries up:
LONDON — A half-eaten bowl of porridge complete with wooden spoon, communal rubbish bins, and a decorative necklace made with amber and glass beads are just a handful of the extraordinarily well-preserved remnants of a late Bronze Age hamlet unearthed in eastern England that’s been dubbed “Britain’s Pompeii” and a “time capsule” into village life almost 3,000 years ago.
The findings from the site, excavated in 2015 to 2016, are now the subject of two reports, complete with previously unseen photos, published this week by University of Cambridge archaeologists, who said they cast light onto the “cosy domesticity” of ancient settlement life.
“It might be the best prehistoric settlement that we’ve found in Britain,” Mark Knight, the excavation director and a co-author of the reports, said in an interviewThursday. “We took the roofs off and inside was pretty much the contents,” he said. “It’s so comprehensive and so coherent.”
The reason for the rare preservation: disaster.
The settlement, thought to have originally consisted of several large roundhouses made of wood and constructed on stilts above a slow-moving river, was engulfed by a fire less than a year after being built.
During the blaze, the buildings and much of their contents collapsed into a muddy river below that “cushioned the scorched remains where they fell,” the university said of the findings. This combination of charring from the fire and waterlogging led to “exceptional preservation,” the researchers found.
“Because of the nature of the settlement, that it was burned down and its abandonment unplanned, everything was captured,” Knight added.
“As we excavated it, there was that feeling that we were picking over someone else’s tragedy,” he said of the eerie site in the swampy fenland of East Anglia. “I don’t think we could smell the fire but the amount of ash around us — it felt close.”
Researchers said they eventually unearthed four large wooden roundhouses and an entranceway structure, but the original settlement was probably “twice as big.”
The site at Must Farm dates to about 850 B.C., eight centuries before Romans came to Britain. Archaeologists have been shocked at “just how clear the picture is” of late Bronze Age life based on the level of detail uncovered, Knight said.
The findings also showed that the communities lived “a way of life that was more sophisticated than we could have imagined,” Duncan Wilson, head of Historic England, the public body responsible for preserving England’s historic environment, said in a statement.
The findings unearthed include a stack of spears, possibly for hunting or defense; a decorative necklace “with beads from as far away as Denmark and Iran”; clothes of fine flax linen; and a female adult skull rendered smooth, “perhaps a memento of a lost loved one,” the research found.
The inhabitants’ diet was also rich and varied, including boar, pike and bream, along with wheat and barley.
A pottery bowl with the finger marks of its maker in the clay was also unearthed, researchers said, still containing its final meal — “a wheat-grain porridge mixed with animal fats” — with a wooden spatula resting inside the bowl.
“It appears the occupants saved their meat juices to use as toppings for porridge,” project archaeologist Chris Wakefield said in the university’s news release. “Chemical analyses of the bowls and jars showed traces of honey along with ruminant meats such as deer, suggesting these ingredients were combined to create a form of prehistoric honey-glazed venison,” he added.
Skulls of dogs — probably kept as pets and to help with hunting — were also uncovered, and the dogs’ fossilized feces showed they fed on scraps from their owners’ meals, the research found.
The buildings, some connected by walkways, may have had up to 60 people living there all together, Knight said, along with animals.
Although no intact sets of human remains were found at the site, indicating that the inhabitants probably fled the fire safely, several sheep bones were found burned indoors. “Skeletal remains showed the lambs were three to six months old, suggesting the settlement was destroyed sometime in late summer or early autumn,” according to the university’s news release.
Ceramic and wooden vessels including tiny cups, bowls and large storage jars were also found. Some pots were even designed to nest, stacked inside one another, Knight said — evidence of an interest in aesthetics as well as practicality.
A lot of similar items were found replicated in each home, Knight added, painting the picture of completely independent homesteads for each family unit rather than distinct buildings for shared tasks — much like we live today.
Household inventories often included metal tools, loom weights, sickles for crop harvesting, axes and even handheld razors for cutting hair.
The roundhouses — one of which had almost 50 square meters (nearly 540 square feet) of floor space — had hearths and insulated straw and clay roofs. Some featured activity zones for cooking, sleeping and working akin to modern-day rooms.
The Must Farm settlement has produced the largest collection of everyday Bronze Age artifacts ever discovered in the United Kingdom, according to Historic England, which partly funded the 1.1 million pound ($1.4 million) excavation project.
The public body labeled the site a “time capsule,” including almost 200 wooden artifacts, over 150 fiber and textile items, 128 pottery vessels and more than 90 pieces of metalwork. Some items will go on display at the nearby Peterborough Museum next month.
Archaeologists never found a “smoking gun” cause for the fire, Knight said. Instead, they suspect it was either an attack from “outside forces,” which may explain why the inhabitants never returned to collect their possessions from the debris, or an accidental blaze that spread rapidly across the tightly nestled homes.
“Probably all that was left was the people and what they were wearing; everything else was left behind,” Knight said of the fire.
But the preservation has left a window for people to look back through in the future. “You could almost see and smell their world,” he said.
“The only thing that was missing was the inhabitants,” Knight added. “And yet … I think they were there — you certainly got glimpses.”
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Although no intact sets of human remains were found at the site, indicating that the inhabitants probably fled the fire safely
This cheered me up.
WOW.
Scientists found an amazingly well-preserved village from 3,000 years ago


Text below, in case article access dries up:
LONDON — A half-eaten bowl of porridge complete with wooden spoon, communal rubbish bins, and a decorative necklace made with amber and glass beads are just a handful of the extraordinarily well-preserved remnants of a late Bronze Age hamlet unearthed in eastern England that’s been dubbed “Britain’s Pompeii” and a “time capsule” into village life almost 3,000 years ago.
The findings from the site, excavated in 2015 to 2016, are now the subject of two reports, complete with previously unseen photos, published this week by University of Cambridge archaeologists, who said they cast light onto the “cosy domesticity” of ancient settlement life.
“It might be the best prehistoric settlement that we’ve found in Britain,” Mark Knight, the excavation director and a co-author of the reports, said in an interviewThursday. “We took the roofs off and inside was pretty much the contents,” he said. “It’s so comprehensive and so coherent.”
The reason for the rare preservation: disaster.
The settlement, thought to have originally consisted of several large roundhouses made of wood and constructed on stilts above a slow-moving river, was engulfed by a fire less than a year after being built.
During the blaze, the buildings and much of their contents collapsed into a muddy river below that “cushioned the scorched remains where they fell,” the university said of the findings. This combination of charring from the fire and waterlogging led to “exceptional preservation,” the researchers found.
“Because of the nature of the settlement, that it was burned down and its abandonment unplanned, everything was captured,” Knight added.
“As we excavated it, there was that feeling that we were picking over someone else’s tragedy,” he said of the eerie site in the swampy fenland of East Anglia. “I don’t think we could smell the fire but the amount of ash around us — it felt close.”
Researchers said they eventually unearthed four large wooden roundhouses and an entranceway structure, but the original settlement was probably “twice as big.”
The site at Must Farm dates to about 850 B.C., eight centuries before Romans came to Britain. Archaeologists have been shocked at “just how clear the picture is” of late Bronze Age life based on the level of detail uncovered, Knight said.
The findings also showed that the communities lived “a way of life that was more sophisticated than we could have imagined,” Duncan Wilson, head of Historic England, the public body responsible for preserving England’s historic environment, said in a statement.
The findings unearthed include a stack of spears, possibly for hunting or defense; a decorative necklace “with beads from as far away as Denmark and Iran”; clothes of fine flax linen; and a female adult skull rendered smooth, “perhaps a memento of a lost loved one,” the research found.
The inhabitants’ diet was also rich and varied, including boar, pike and bream, along with wheat and barley.
A pottery bowl with the finger marks of its maker in the clay was also unearthed, researchers said, still containing its final meal — “a wheat-grain porridge mixed with animal fats” — with a wooden spatula resting inside the bowl.
“It appears the occupants saved their meat juices to use as toppings for porridge,” project archaeologist Chris Wakefield said in the university’s news release. “Chemical analyses of the bowls and jars showed traces of honey along with ruminant meats such as deer, suggesting these ingredients were combined to create a form of prehistoric honey-glazed venison,” he added.
Skulls of dogs — probably kept as pets and to help with hunting — were also uncovered, and the dogs’ fossilized feces showed they fed on scraps from their owners’ meals, the research found.
The buildings, some connected by walkways, may have had up to 60 people living there all together, Knight said, along with animals.
Although no intact sets of human remains were found at the site, indicating that the inhabitants probably fled the fire safely, several sheep bones were found burned indoors. “Skeletal remains showed the lambs were three to six months old, suggesting the settlement was destroyed sometime in late summer or early autumn,” according to the university’s news release.
Ceramic and wooden vessels including tiny cups, bowls and large storage jars were also found. Some pots were even designed to nest, stacked inside one another, Knight said — evidence of an interest in aesthetics as well as practicality.
A lot of similar items were found replicated in each home, Knight added, painting the picture of completely independent homesteads for each family unit rather than distinct buildings for shared tasks — much like we live today.
Household inventories often included metal tools, loom weights, sickles for crop harvesting, axes and even handheld razors for cutting hair.
The roundhouses — one of which had almost 50 square meters (nearly 540 square feet) of floor space — had hearths and insulated straw and clay roofs. Some featured activity zones for cooking, sleeping and working akin to modern-day rooms.
The Must Farm settlement has produced the largest collection of everyday Bronze Age artifacts ever discovered in the United Kingdom, according to Historic England, which partly funded the 1.1 million pound ($1.4 million) excavation project.
The public body labeled the site a “time capsule,” including almost 200 wooden artifacts, over 150 fiber and textile items, 128 pottery vessels and more than 90 pieces of metalwork. Some items will go on display at the nearby Peterborough Museum next month.
Archaeologists never found a “smoking gun” cause for the fire, Knight said. Instead, they suspect it was either an attack from “outside forces,” which may explain why the inhabitants never returned to collect their possessions from the debris, or an accidental blaze that spread rapidly across the tightly nestled homes.
“Probably all that was left was the people and what they were wearing; everything else was left behind,” Knight said of the fire.
But the preservation has left a window for people to look back through in the future. “You could almost see and smell their world,” he said.
“The only thing that was missing was the inhabitants,” Knight added. “And yet … I think they were there — you certainly got glimpses.”
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
now I'm thinking about hospitality rituals in the Odyssey and looking up when the events of the Iliad were supposed to have taken place (14-13th century BCE) and looking at total human population estimates for that time period and it could have been less than a million people and I'm wondering if anyone who passed down the Iliad orally would be horrified and astonished that we aren't madly curious about every single one of the people who die in it when we read it today, wondering about a world where an adult human man who can speak your language washing up on the beach is a matter of national interest and hearing his story is reason enough to give him clothes, and food, and shelter, and wine, and passage to his home. why wouldn't you, when a human being is a sight for sore eyes? how passionately were the rituals of hospitality defended and felt by those who lived at a time when the world had so few people to meet in it? would they find the modern world completely inhospitable to them as human beings? would they mourn it as a loss? would they be proud that we still know Achilles?
541 notes
·
View notes
Text
Casually asks ‘who domesticated grain in your fantasy world?’ but while ripping her shirt off with a WWE stage and a roaring crowd just behind and slightly to the left.
9K notes
·
View notes
Photo



03.26.2021
River Lethe
read from right to left! (also i know theres a typo but i dont have the original file anymore to fix it :’’)
#hades game#i imagine the little blue butterflies all over are more friendly souls#i have no idea if thats canon#i just like the idea of people becoming peaceful butterflies
8K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Count is readying the castle for his esteemed guest! There's much to be done.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Great Mouse Detective version of Dracula happening simultaneously as the events of Dracula, so there’s just five mice in Victorian clothes unnoticed by the human cast desperately trying to kill a bat.
50K notes
·
View notes
Text
Oh my god this is excellent. I've been looking for an explanation of heddles on a warp-weighted loom for ages.
Today I am thinking about weaving.

I can knit and crochet, but those crafts didn't exist in Roman times. Any historically accurate Roman cloth must be woven. So when a little potholder loom jumped into my shopping basket for 50 cents, it felt like a sign I should learn.
One potholder that was 50% yarn and 50% weird gaps later, I looked up a tutorial, and realized why the damn thing was 50 cents. I needed a better, more adaptable loom. And, because I am a cheapskate and slightly loony, I decided to make one instead of buying it.
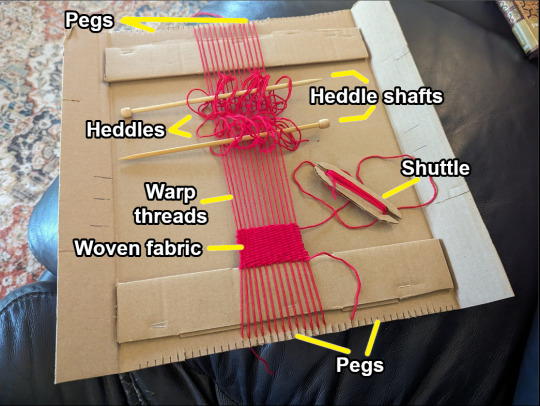
So, how does this thing work?
First, you string the warp threads up and down, around the pegs. Here, I made a zigzag shape. Then, you use a needle or shuttle to weave more yarn over and under the warp, horizontally, back and forth. This produces woven fabric.

Some looms weave from the top, some from the bottom. This Greek urn shows two weavers working from the top. The left weaver uses a rod to compact the woven fabric upward, keeping it even and sturdy. The right weaver is passing an oval-shaped shuttle through the warp threads to form another row.

Most Roman looms would have looked like this, with the finished cloth at the top. Unlike my looms, these are warp-weighted. That means you keep the warp yarns taut by hanging weights at the bottom, rather than through a bottom row of pegs.
Warp-weighted looms also have a big advantage over my little potholder loom: you can easily create multiple sheds.
A "shed" is a temporary gap between lifted strands and non-lifted strands. Instead of having to go over and under each strand individually, you raise the entire shed, then pull the shuttle or needle straight through. This saves lots of time! Then, to weave the next row, you close the shed, lift up a different set of threads to create a new shed, and send the shuttle/needle through the other direction.

On a warp-weighted loom, the sheds are opened by loops called heddles (H), which are attached to a heddle rod (G). When the rod is down, shed (1) is open (middle diagram). When you pull the rod up, shed (1) closes and shed (2) opens instead (right diagram). Most warp-weighted looms also have a pair of forks you can rest the heddle rod on, to free your hands.
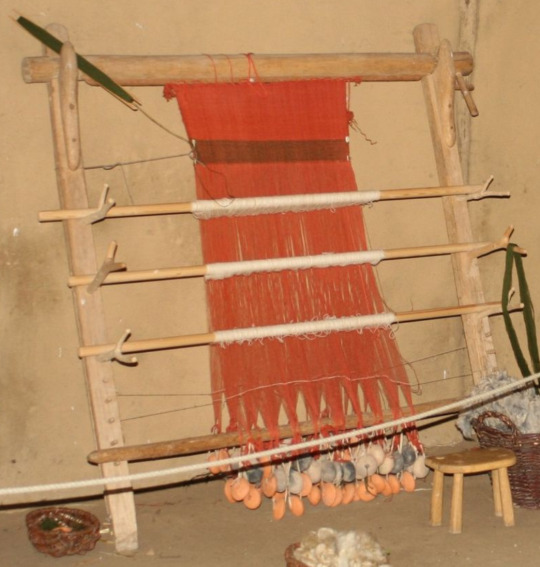

Here, there are three heddle rods and sets of forks, the heddles are white, and the warp thread is red. This gives you four different sheds, and the potential to weave very complex patterns indeed. Not bad for a device invented over 6500 years ago!
I liked the multiple heddle-rod design so much, I tried incorporating it into my DIY loom, too. I've tested both yarn and paperclips as heddles:

I actually got both sheds and heddle-rods working, too. Which is pretty cool for a lap loom - every other lap loom I found only has one shed, so you have to go over-under the individual threads on alternate rows.* More time-consuming. However, the sheds here are narrow, and I'll need a smaller and smoother shuttle to pass through them smoothly. This wouldn't be an issue on a warp-weighted loom, where the warp hangs freely downward, and can move more flexibly with the heddles.
Anyway. I may get a "real" loom at some point, but I wanted to build one first, and I think it gave me more appreciation for just how resourceful ancient weavers were. They created technology, clothing, and artwork out of very basic materials, and civilization depended on these skills.
Now, I need to go finish the...whatever the hell it will be. Big thanks to Wikipedia and to the lovely Youtubers who make this craft easier to learn. I think it'll be a lot of fun.
(*Edit - found out a rotating heddle bar can make two sheds on a lap loom! Exciting!!)
586 notes
·
View notes
Text
It is a beautiful day, and you are a horrible research transport vessel. Things are progressing as normal (i.e. it's boring) when a SecUnit pings you, lies right to your metaphorical face, and then tries to bribe you with human media to give it a ride. This is as unexpected as it is unprecedented, and the sheer nerve of it is really to be admired. There's no protocol to this, so what should you do?
Now, this is against a bunch of rules, and could be dangerous if you weren't so impressive and incredible, and you're technically an employee (and can probably rewrite the Univeristy charter at will (until someone notices and puts it back)) so those rules are for other entities.
So, what you should do is allow the rogue SecUnit with a broken governor module and a sketchy story aboard. If you check the files it dumps and find zero (0) malware (which is confusing), and it doesn't even try to trash the place or lay in wait to ambush a crew member, then you've got a good candidate!
Next, what you're going to want to do is absolutely nothing. Just watch it patrol your halls until it's time to leave. Continue staring at it while you're undergoing embarkment procedures. Maybe analyze it a little (you've got plenty of processing power to spare) when it finally sits down and starts watching media. Allow it to settle in and get comfortable while you stare at it and get further and further from port.
Now that you two are alone (intimacy is key!) and you've determined that watching media is all the SecUnit is going to do, it's time to make contact! Make sure to open by telling it it's only survived due to dumb luck, and letting it know you could melt its brain into putty. This starter will work to develop conversation naturally and smoothly, just like you've seen the humans do, and it will be smooth sailing from there!
This has been Perihelion's guide to making friends/finding life partners/fuck off Holism I had to work hard for this find your own
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo

“What did you say, to make him try to kill you?”
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
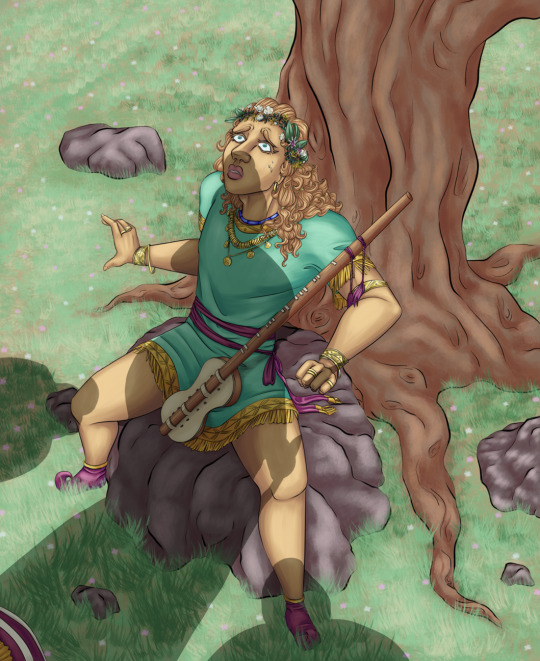

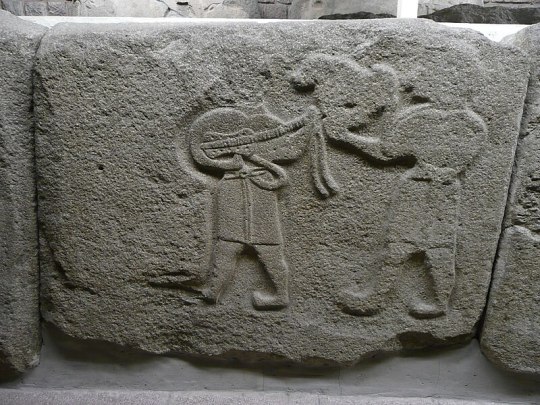
The Judgment, focusing not on Paris' view of the goddesses, but of the reverse. Specifically the initial moment of appearance, because I wanted to focus on something that's there from some of the earliest representations to the latest that we have of the Judgment; Paris' fear.
The earliest surviving pieces that show this is visual (we have no surviving early, full textual version of the Judgment), and among many of these vase paintings you will see Paris running away.
In two of our latest (textual) versions, Ovid's Heroides and Lucian's Dialogue of the Gods, Paris' fear makes appearances as well, and would be our only textual surviving sources for it, too.
Some more notes under the cut!

An example of that type of "Paris fucking booking it out of there when Hermes and the goddesses appear to him" vase painting.
Lucian:
Hermes: `These dames,' good Paris, are Hera, Athene, and Aphrodite; and I am Hermes, with a message from Zeus. Why so pale and tremulous? Compose yourself; there is nothing the matter.
Ovid:
"I was mute, and chill tremors had raised my hair on end, when “Lay aside thy fear!” the winged herald said to me [...]"
Paris' only instrument that you see in visual arts (and the accessory he's shown with most often), is a lyre; some later textual sources have him playing pipes at the Judgment, to lean into the "pastorality" of the scene, and Paris as a shepherd.
I've gone with a Bronze Age Hittite lute, to keep the string instrument angle. It was a two-stringed instrument and would, compared to a lyre, be easier to care for out in the wilderness!

227 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reblogging would be a great help, but don’t feel pressured to
19K notes
·
View notes
Text
He is doing a good job! I am proud of him!
I swear he was much more skilful at this yesterday but this is far more entertaining
To quote the poem by @robotsfromouterspace
Leg so short
Short short leg
Leg so short he roll like eg
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
He is so cute I think I will explode.
Activity that I can finally partake in
696 notes
·
View notes